Bootcamp.com - Circulatory System
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
what is a circulatory system?
how organisms deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues
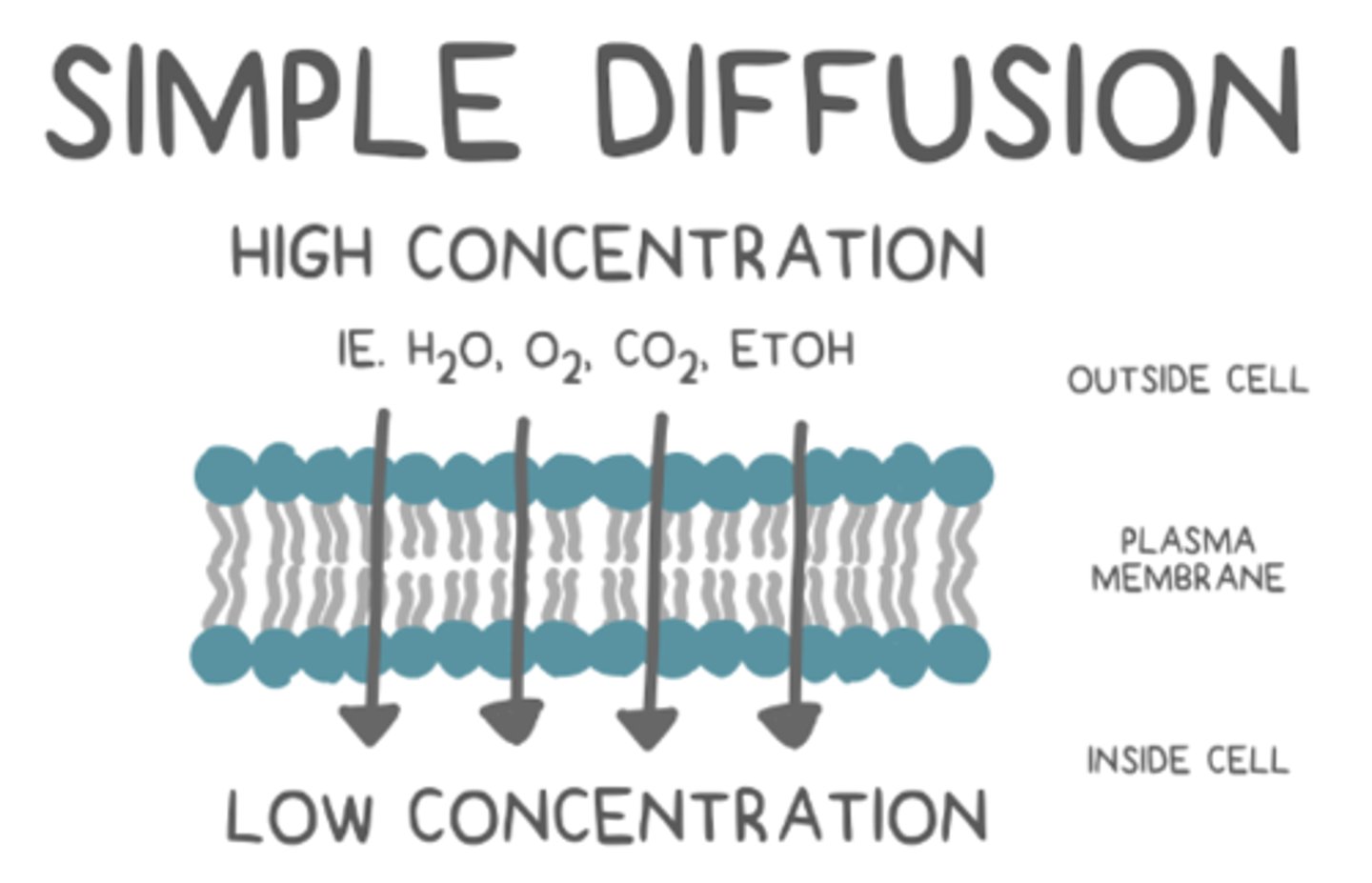
what is simple diffusion?
passive movement of dissolved substances due to concentration gradient
list the organisms that do not have circulatory systems:
- kingdom archaea
- kingdom eubacteria
- kingdom protista
- kingdom fungi
- kingdom animalia
1) porifera
2) cnidaria
3) platyhelminthes
4) nematoda
5) rotifera
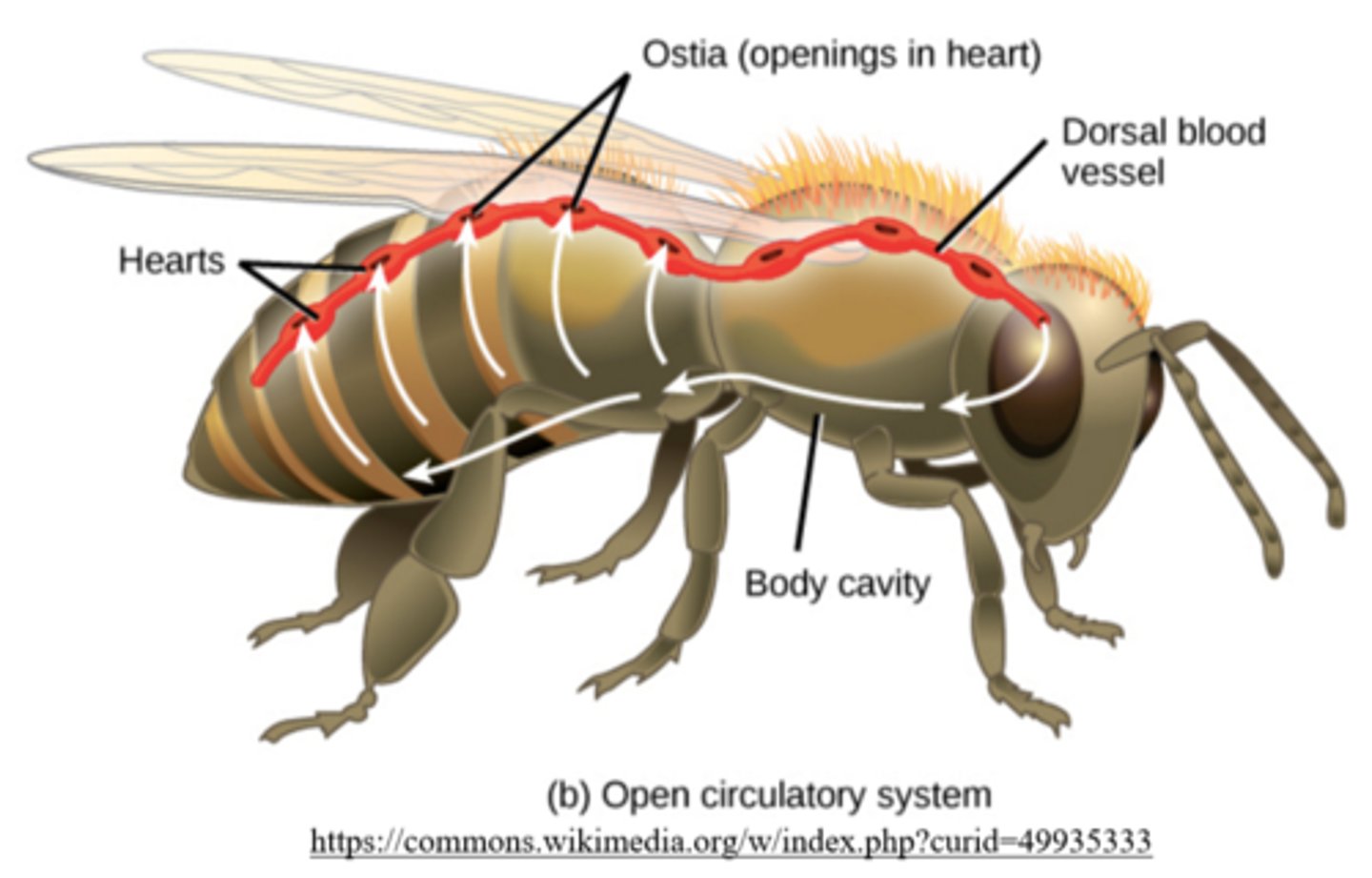
how is hemolymph pumped in an insects body?
tubular hearts pump fluid through a single dorsal vessel --> sinuses --> hemocoel
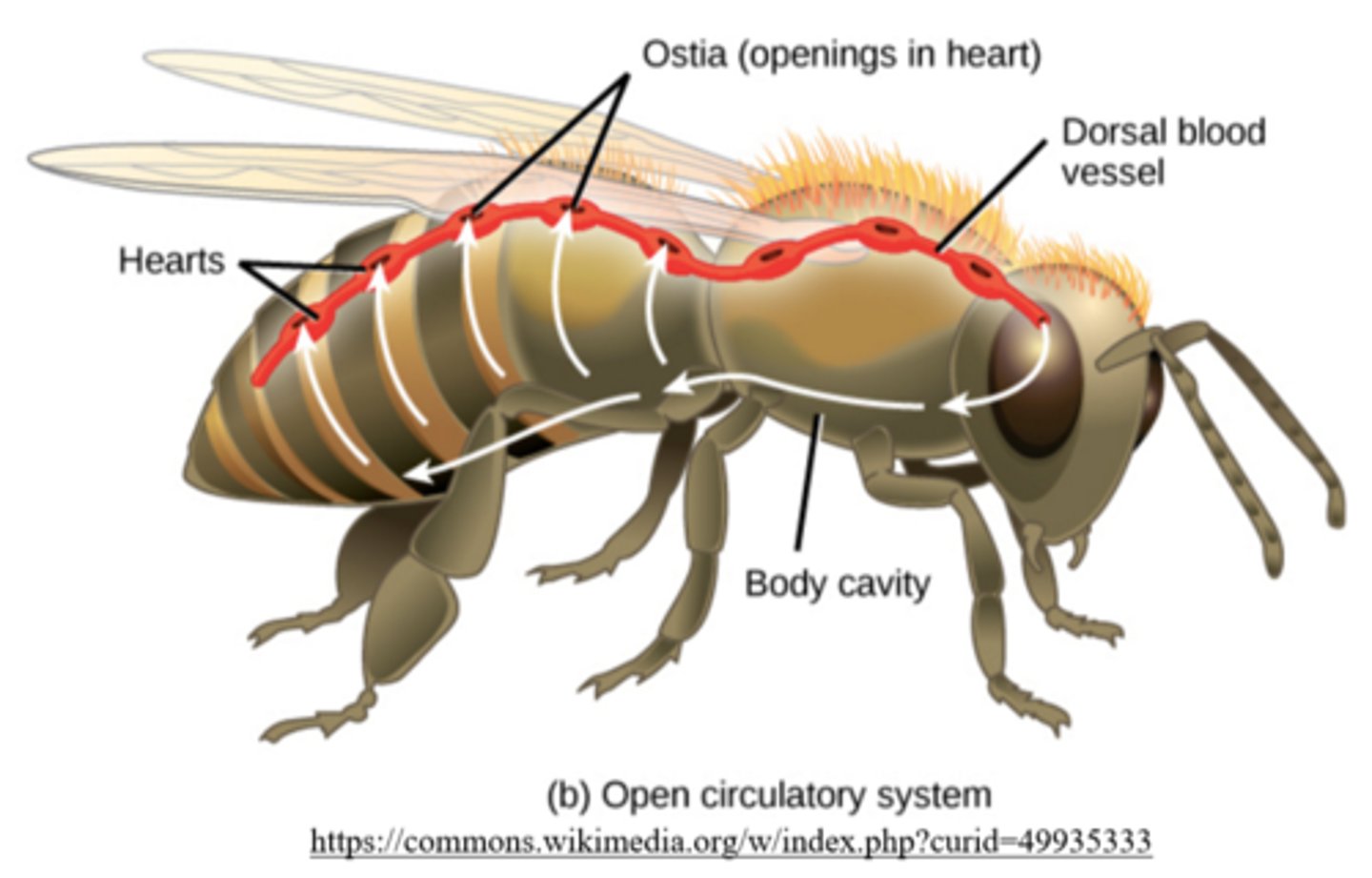
what causes hemolymph to be moved around within the hemocoel?
locomotion and muscular contractions
how does hemolymph re-enter a relaxed insect heart?
ostia
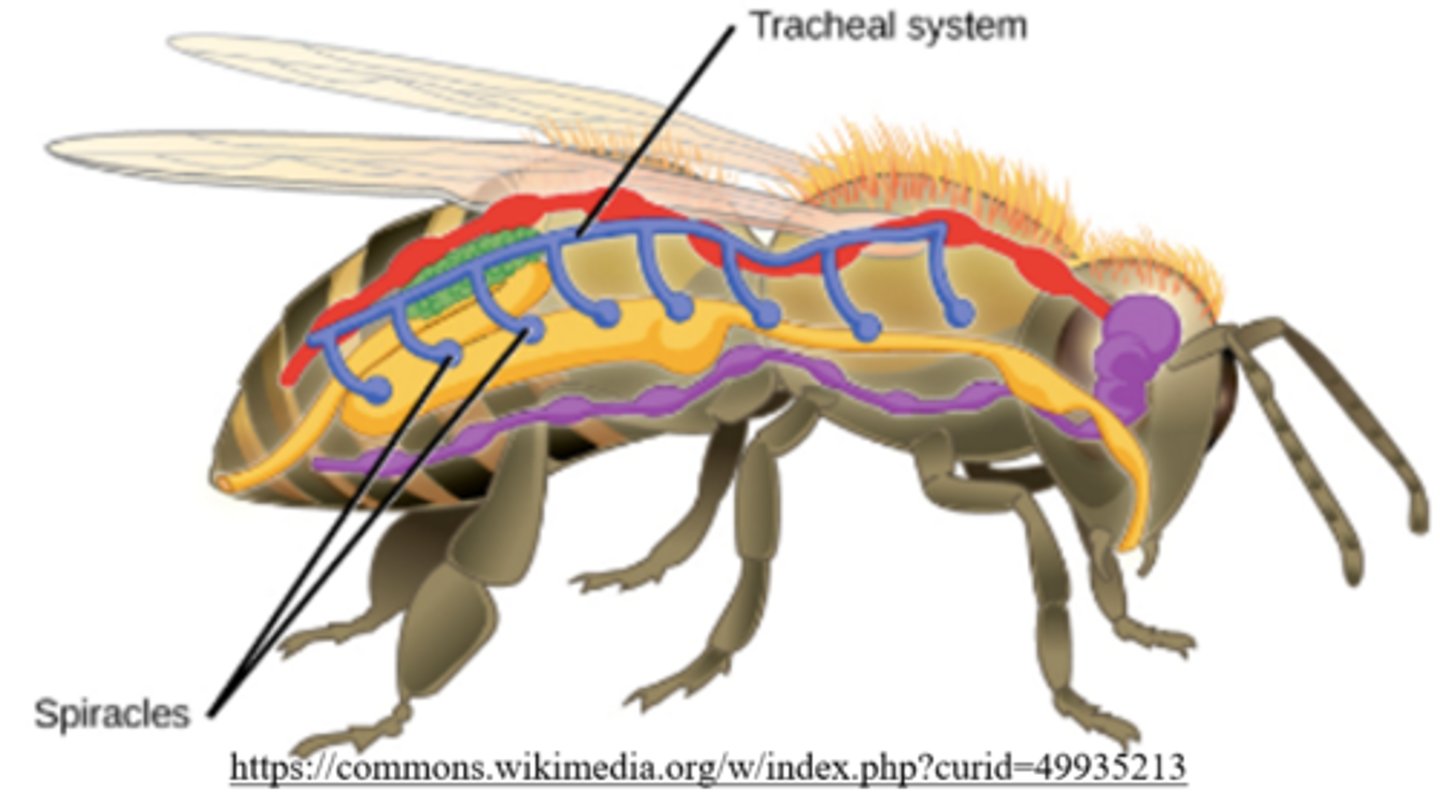
_____ allow air to pass into the tracheal system of insects
spiracles
list the invertebrate animals with an open circulatory system:
kingdom animalia
1) mollusca
2) arthropoda
3) echinodermata
_____ is fluid that allows gas exchange in closed circulatory systems
blood
list the invertebrates with a closed circulatory system:
annelida (segmented worms)
segmented worms (aka annelids) have multiple hearts called _____, which pump blood in a circuit
aortic arches
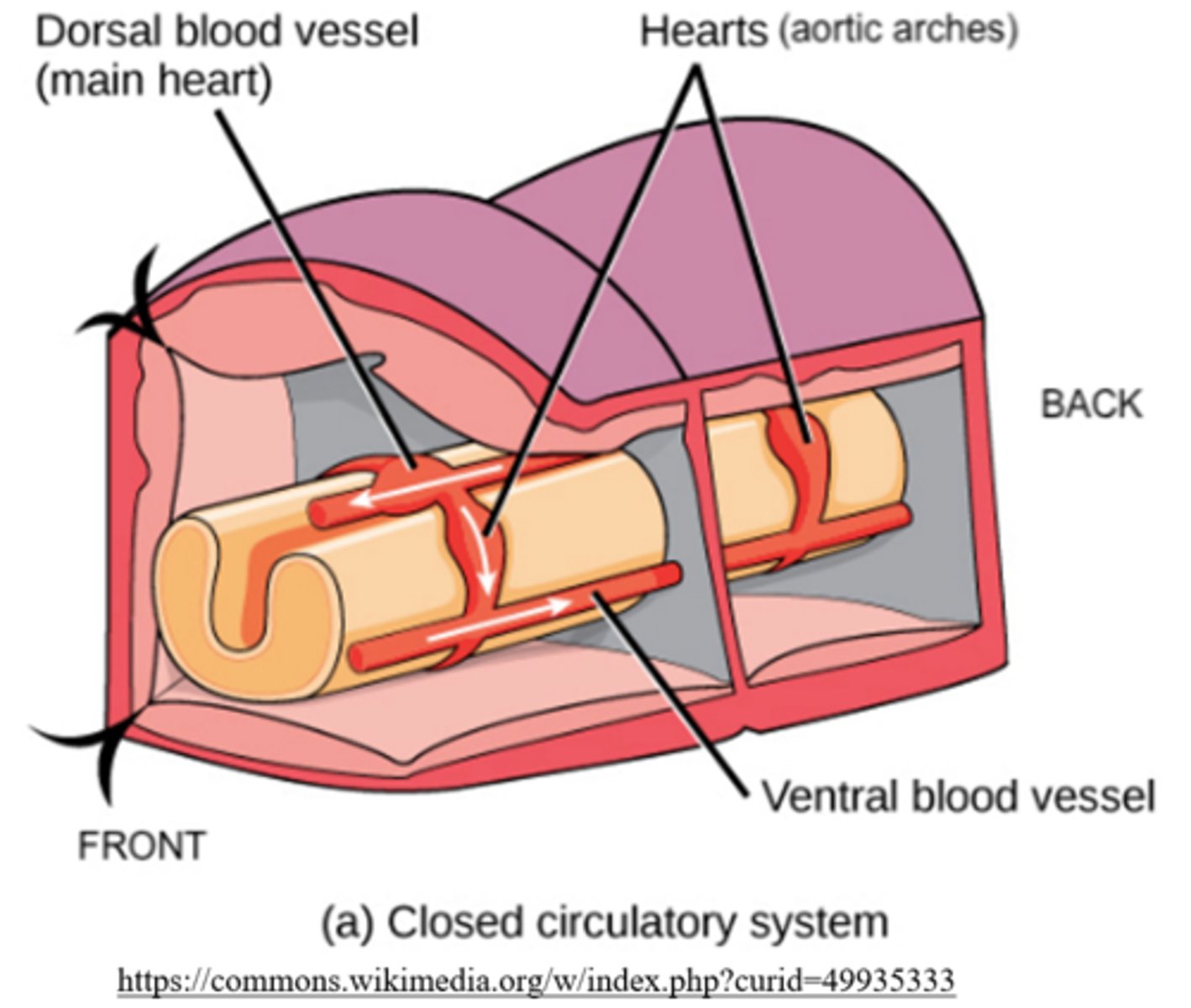
what are the primary/true heart chambers?
atria and ventricles
what are the two primary chambers of two-chambered hearts?
one atrium and one ventricle
two-chambered hearts only pump _____ blood
deoxygenated
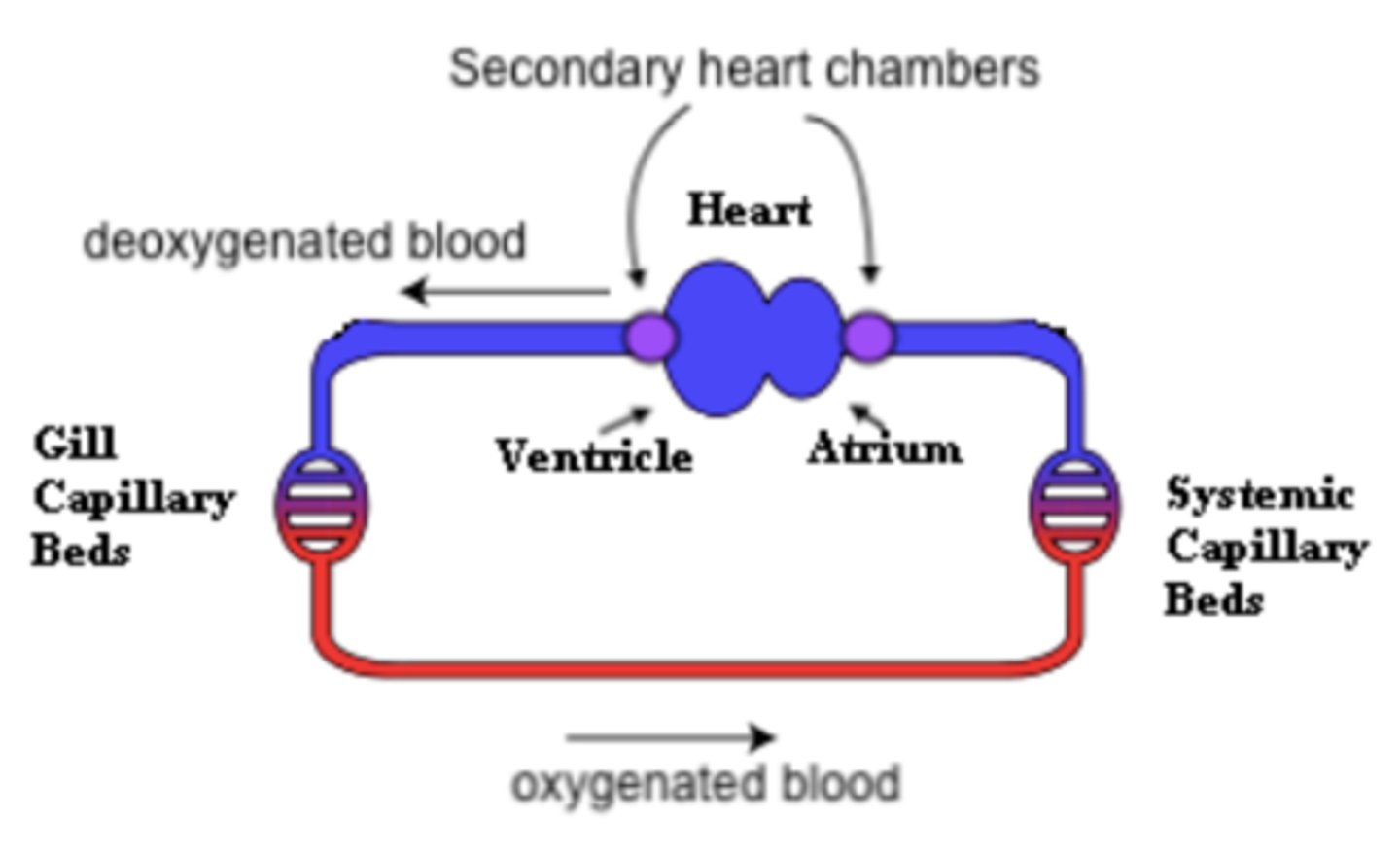
two-chambered hearts are _____ (single/double) circulation hearts
single
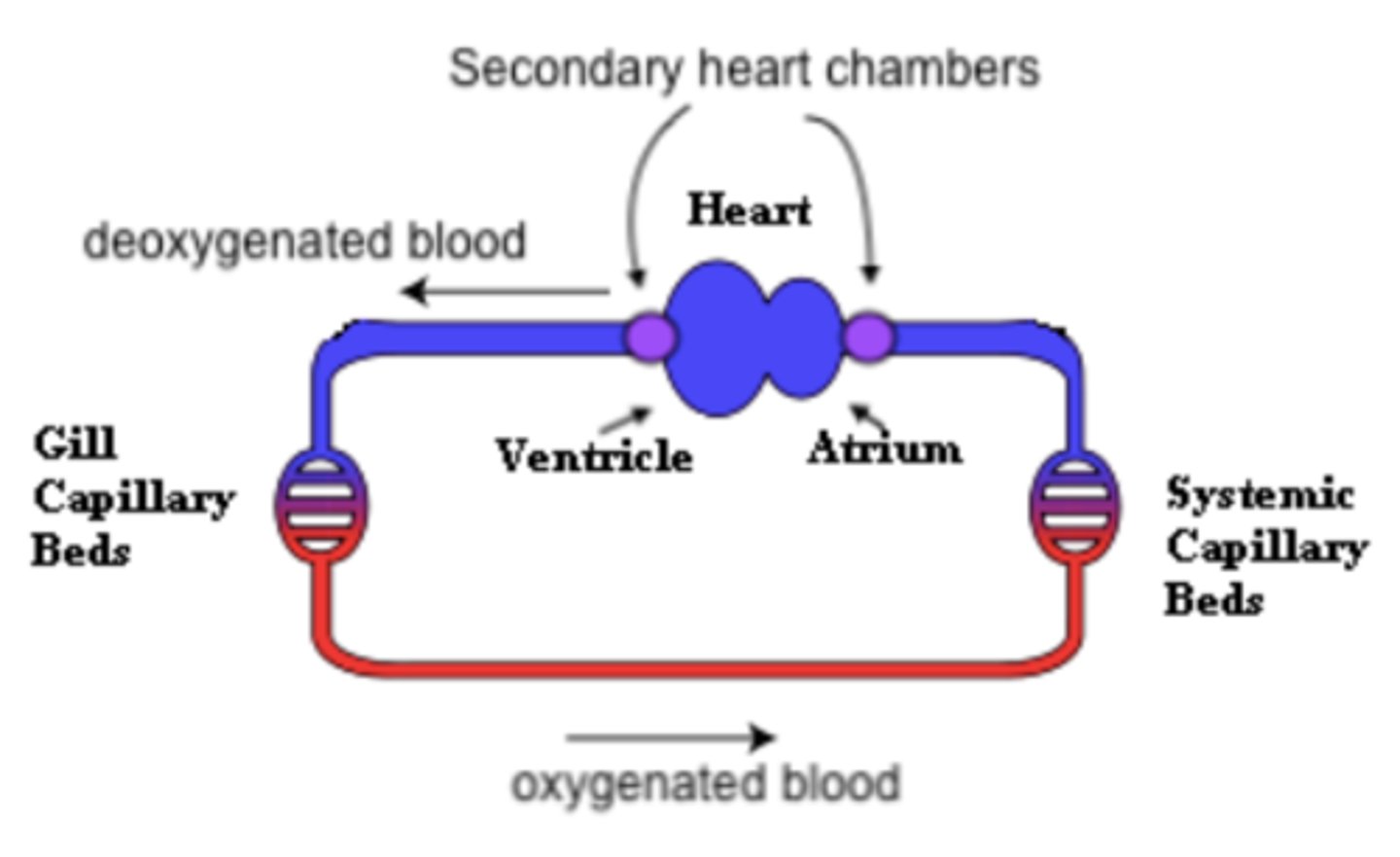
what is a common example of an organism that has a two-chambered heart?
fish
ventricles are (stronger/weaker) than atria - why?
stronger; ventricles pump blood out to the body, while atria only pump blood into the ventricle directly attached to it
what are the three primary chambers of three-chambered hearts?
right and left atrium; single ventricle
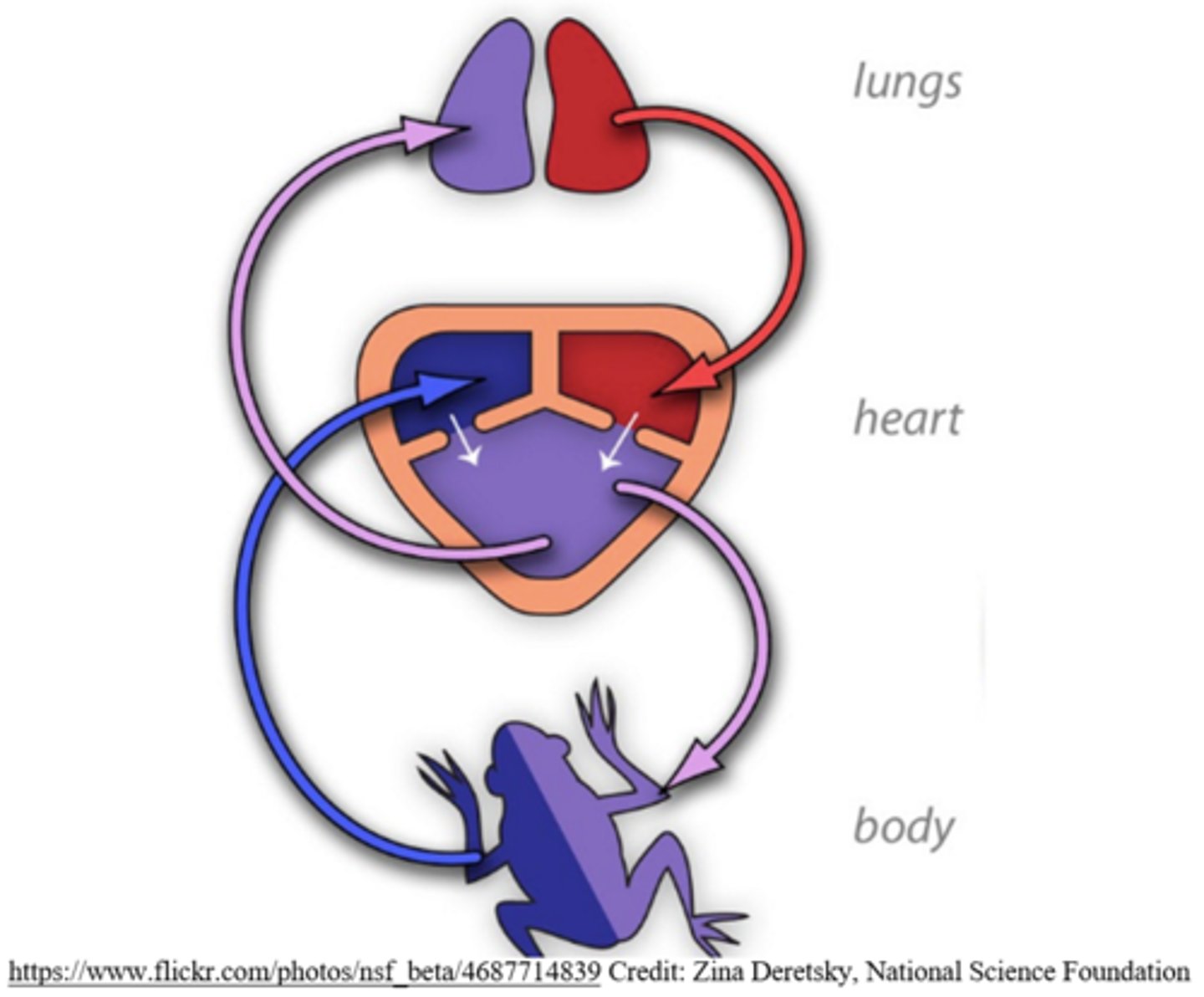
three-chambered hearts mix deoxygenated and oxygenated blood in the _____
ventricle
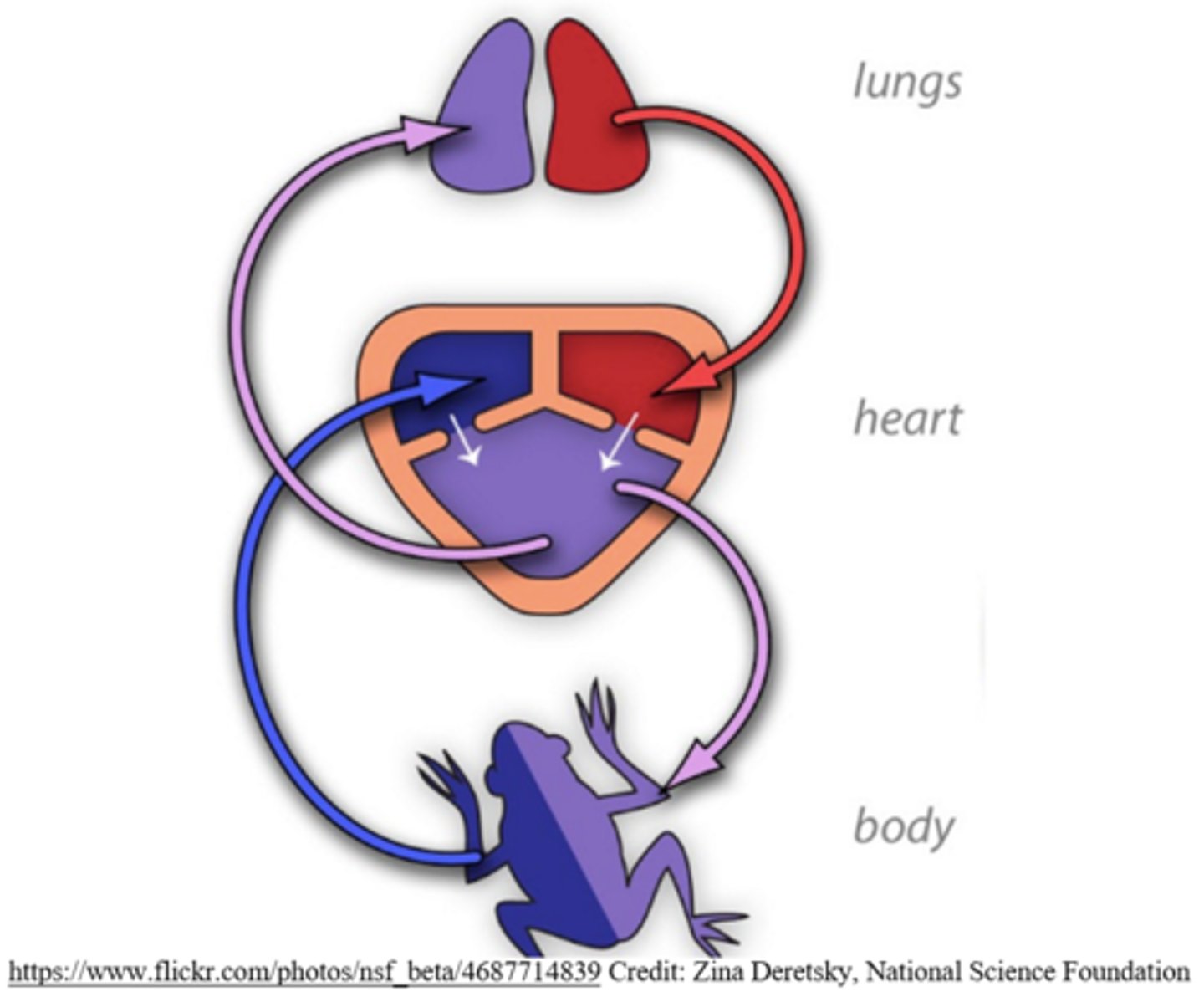
three-chambered hearts are _____ circulation hearts
double
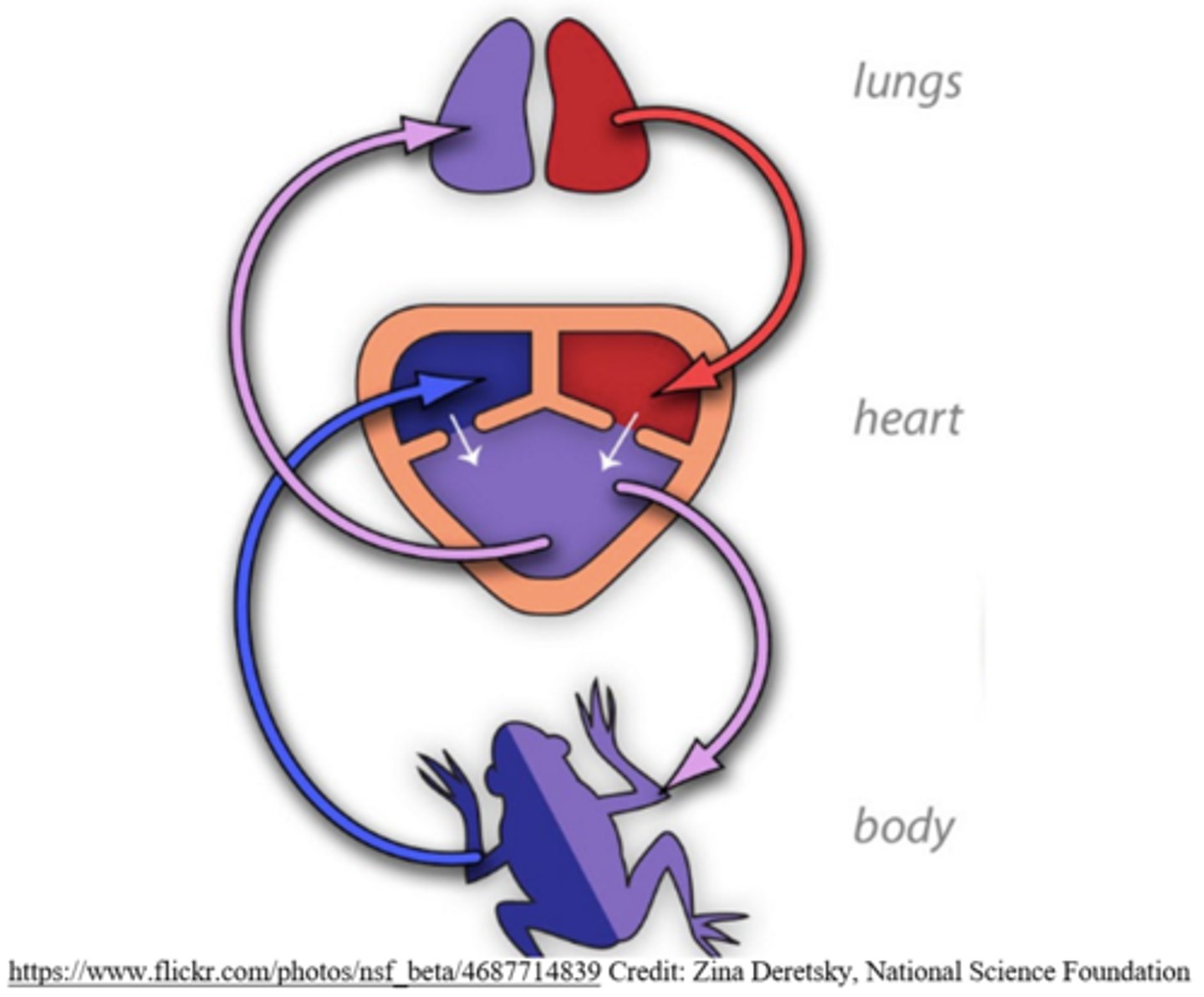
what types of animals have three-chambered hearts?
poikilothermic amphibians and reptiles
what are the four primary chambers of four-chambered hearts?
left and right atrium; left and right ventricle

why does the blood not mix in four-chambered hearts?
because there are two separate ventricles for the deoxygenated and oxygenated blood

four-chambered hearts are _____ circulation hearts
double

what type of animals have four-chambered hearts?
birds and mammals (homeothermic chordates)
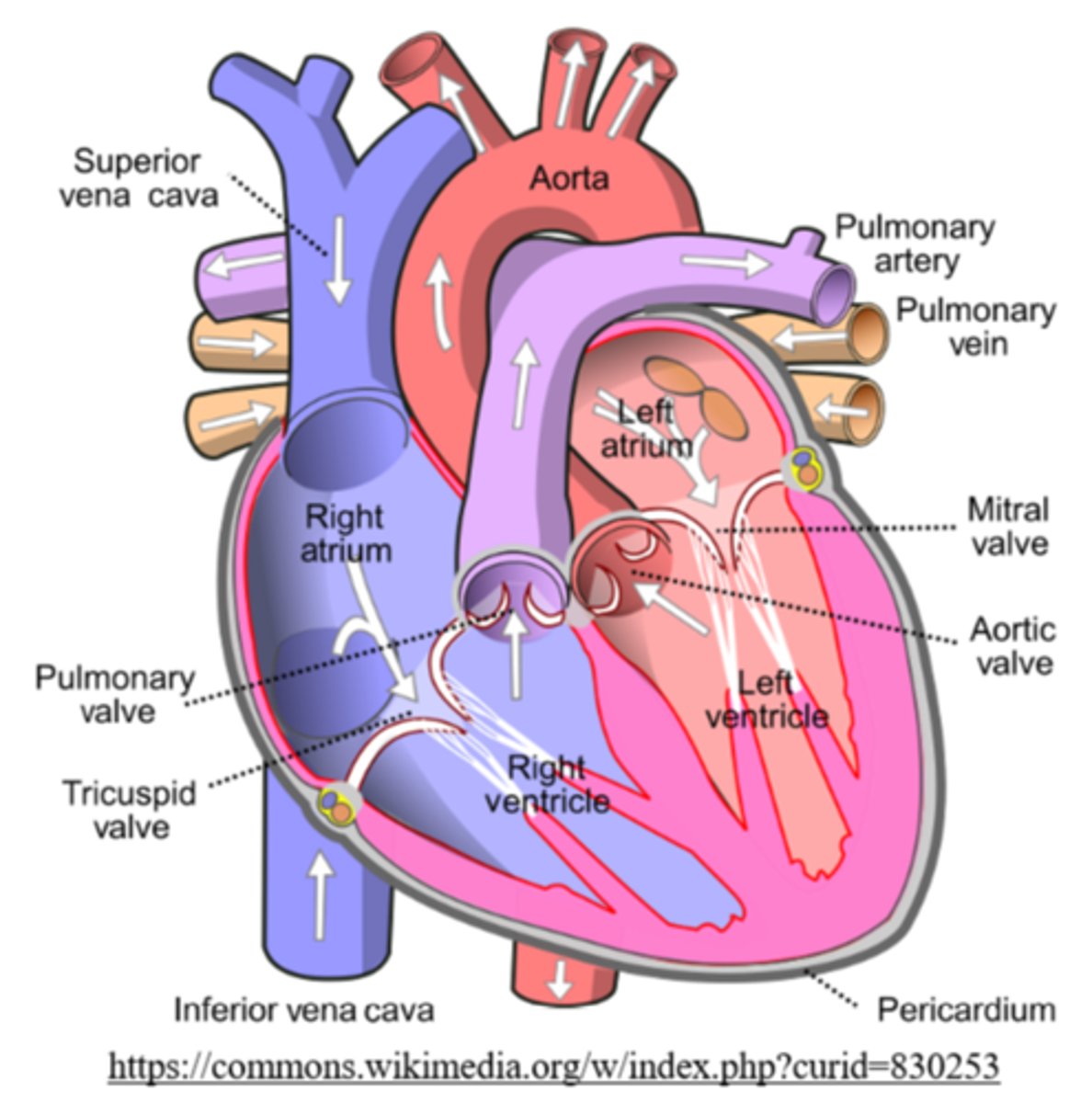
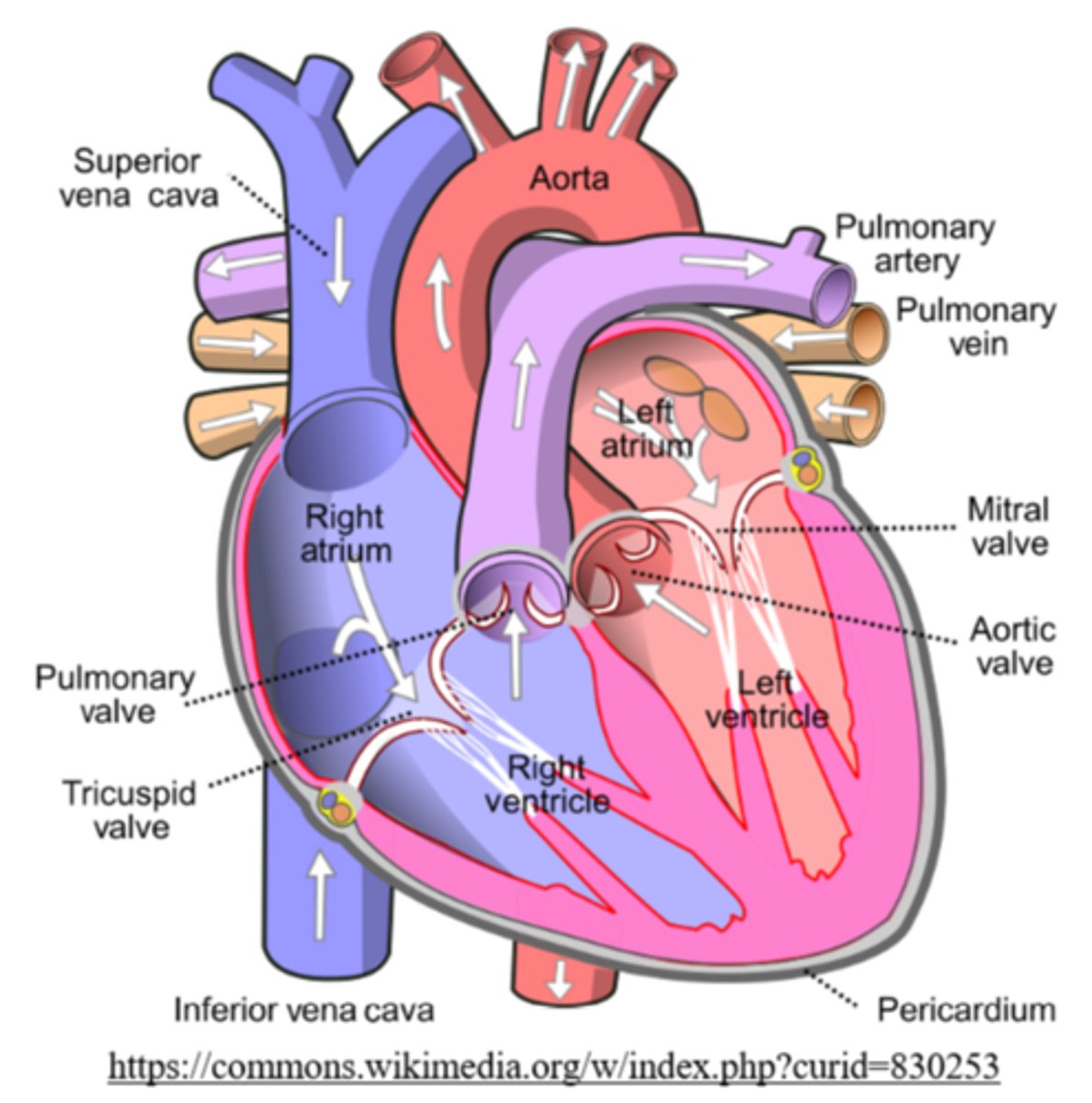
the right atrium accepts _____ (oxygenated/deoxygenated) blood from the vena cava
deoxygenated
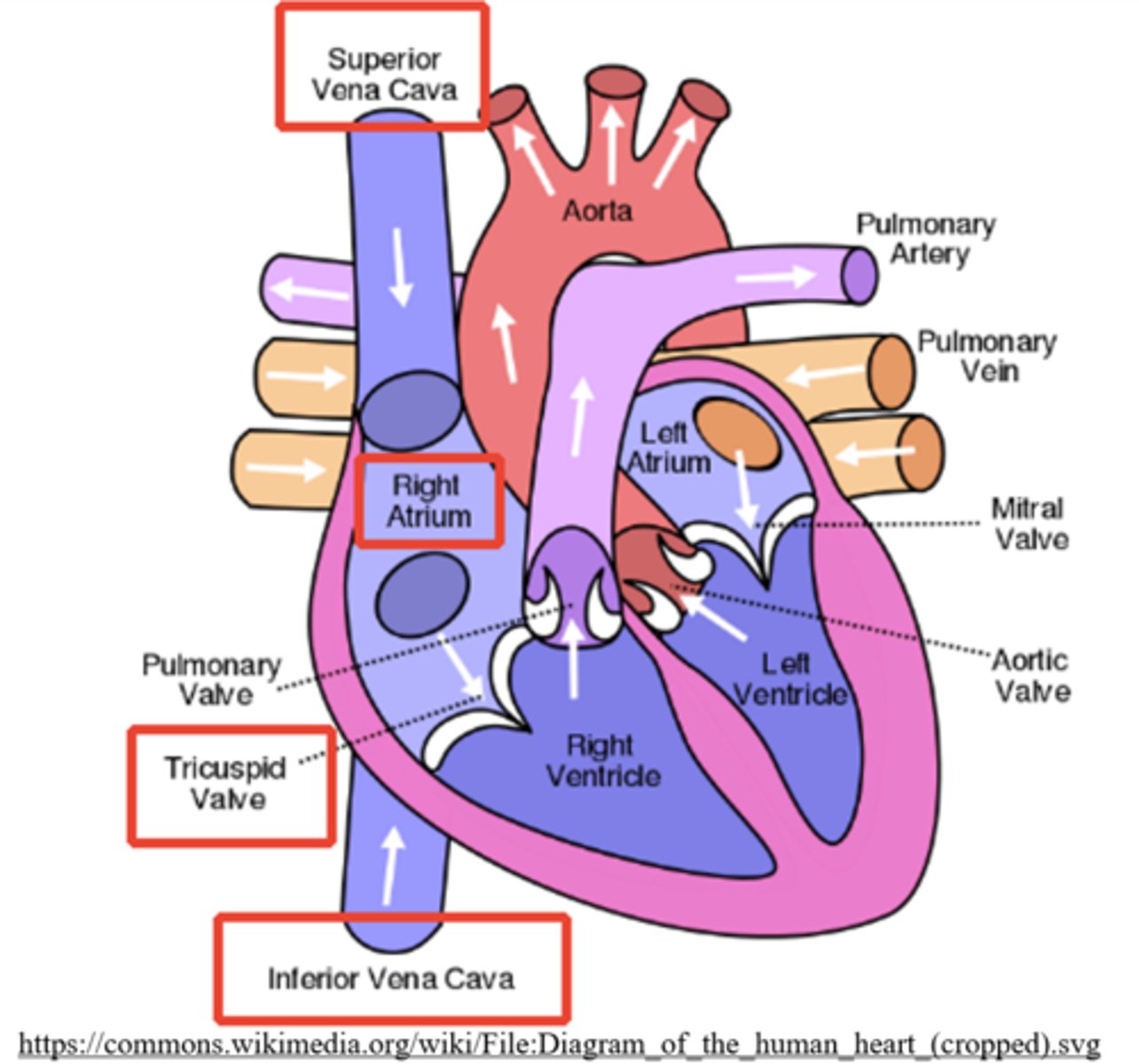
blood pumps from the right atrium to the _____ through the _____
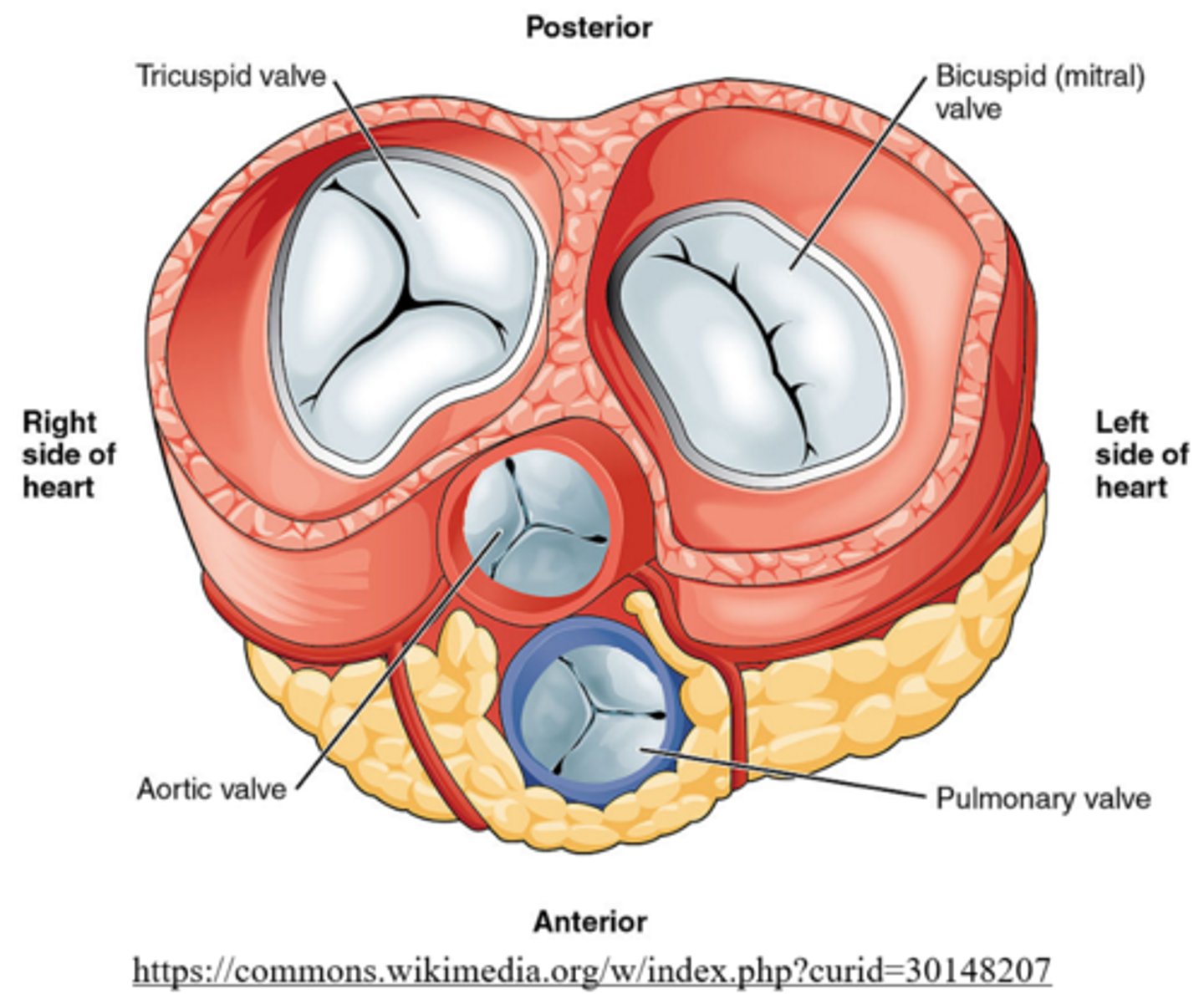
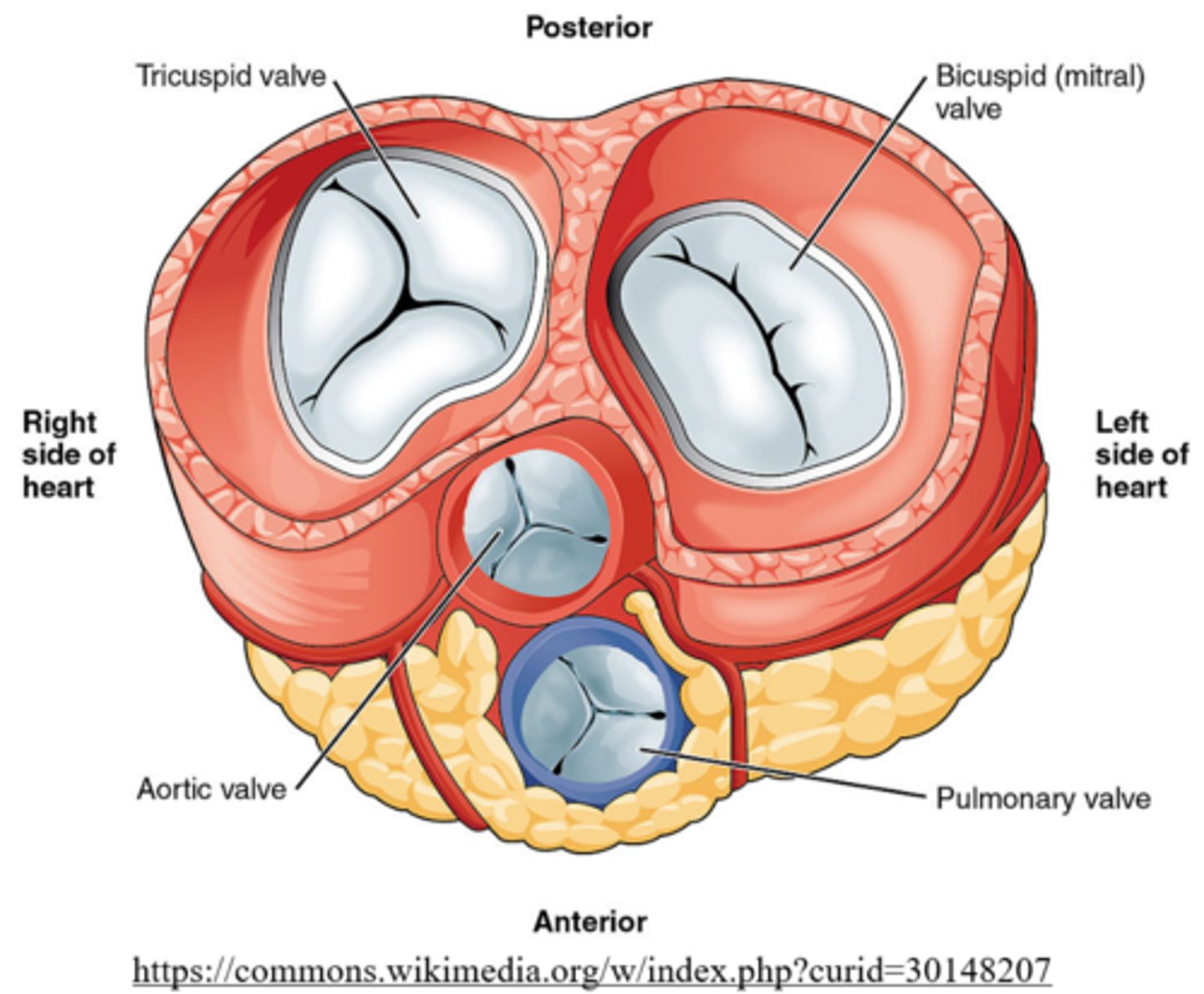
right ventricle; tricuspid (atrioventricular) valve
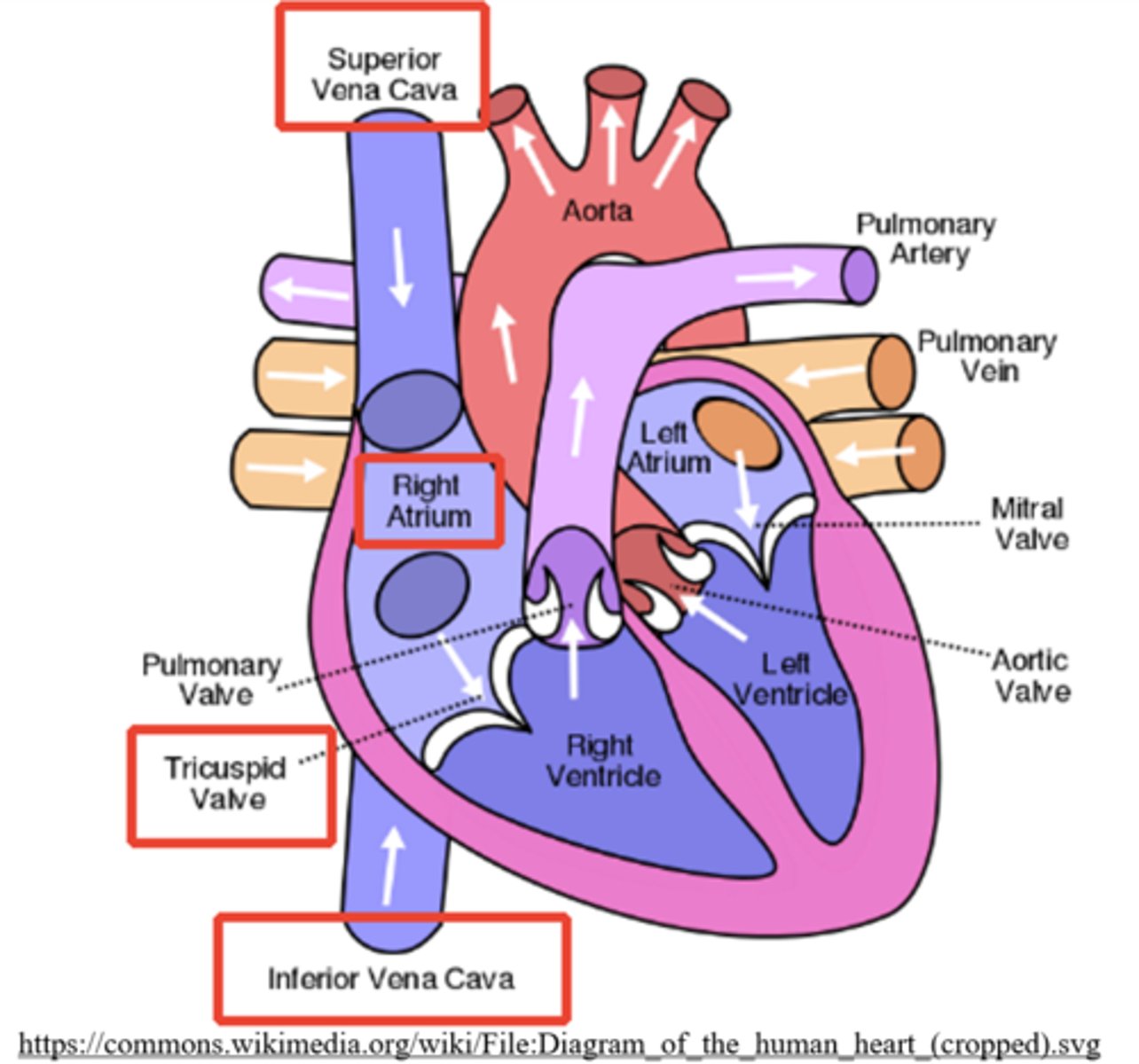
what is the right atrioventricular valve also known as and why?
tricuspid valve; it has three cusps (flaps)
Mnemonic: The Right AV valve = TRicuspid valve
what are the largest veins in the human body and to what do they connect?
vena cava; the right atrium
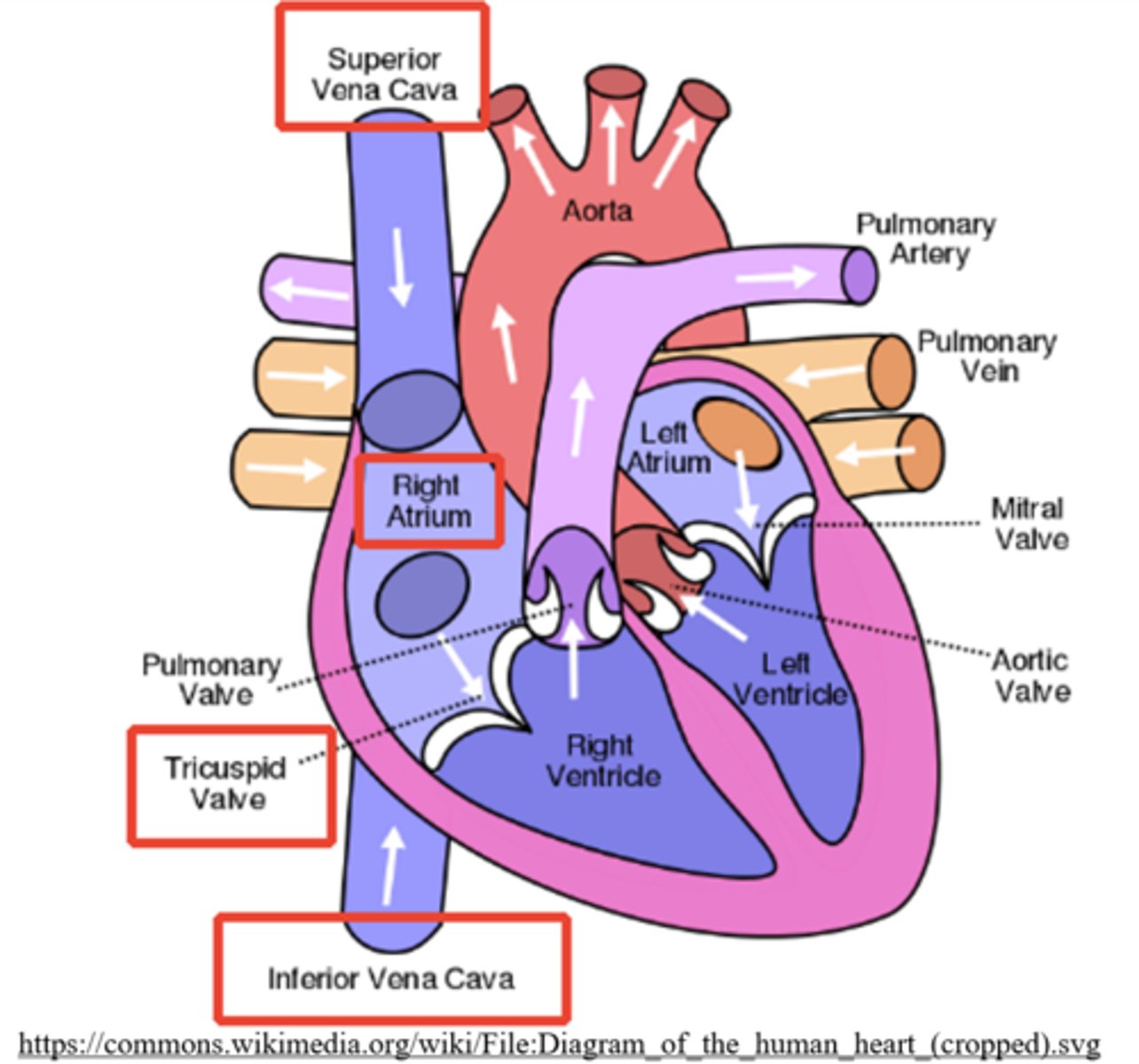
what returns deoxygenated blood from above the heart?
superior vena cava
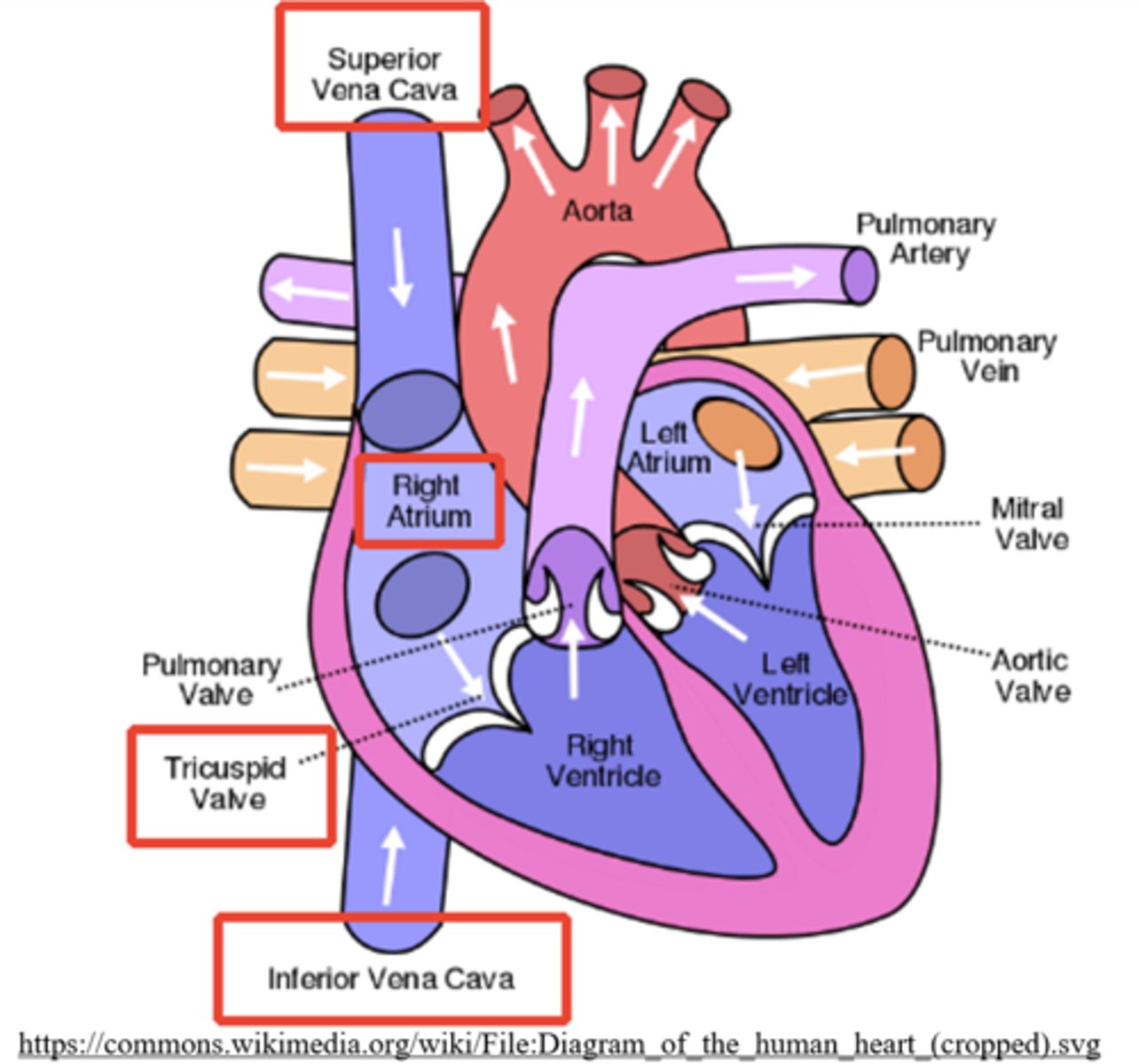
what returns deoxygenated blood from below the heart?
inferior vena cava
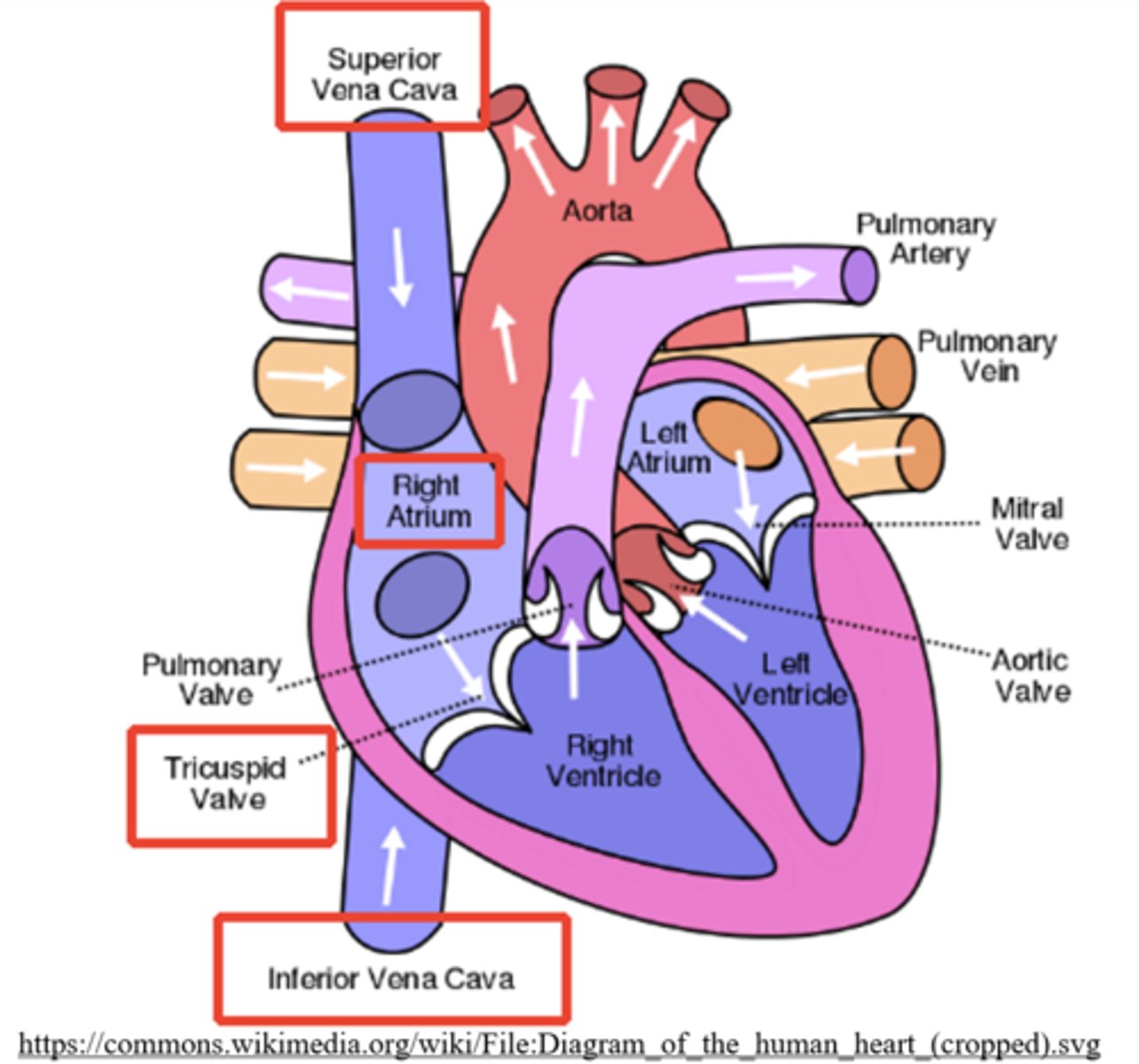
what prevents backflow from the ventricles to the atria?
atrioventricular valves (AV valves)
AV valves close when which muscles contract?
papillary muscles
what are the stringy tendons that attach papillary muscles to AV valves?
chordae tendineae
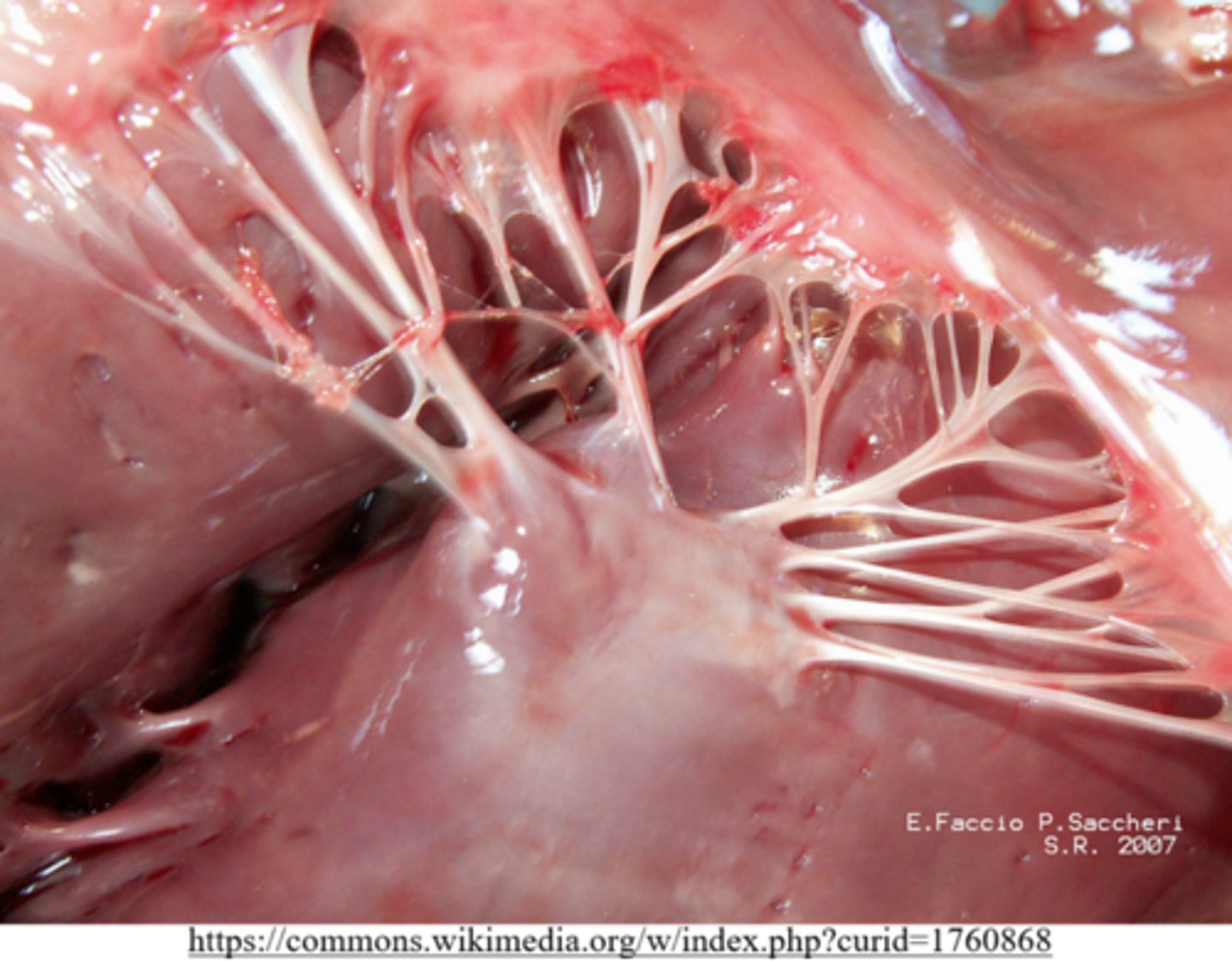
the right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to pulmonary arteries through which valve?
pulmonary semilunar valve
semilunar valves have _____ cusps
3
_____ valves ensure one-way flow of blood from ventricles to arteries
semilunar
the _____ take deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for gas exchange
pulmonary arteries
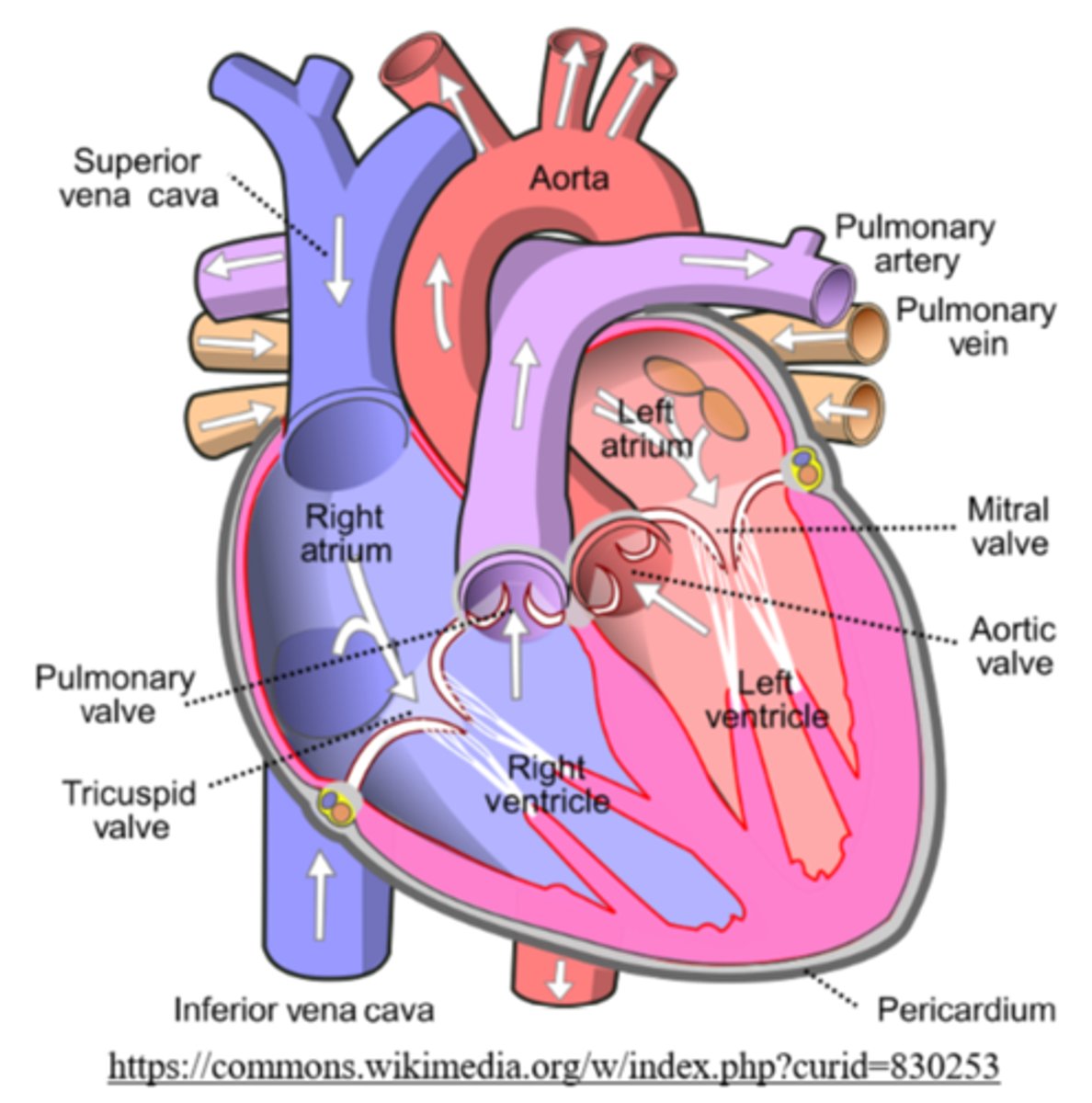
what are the vessels moving away from the heart?
arteries
_____ return oxygenated blood to the left atrium after gas exchange at the lungs
pulmonary veins
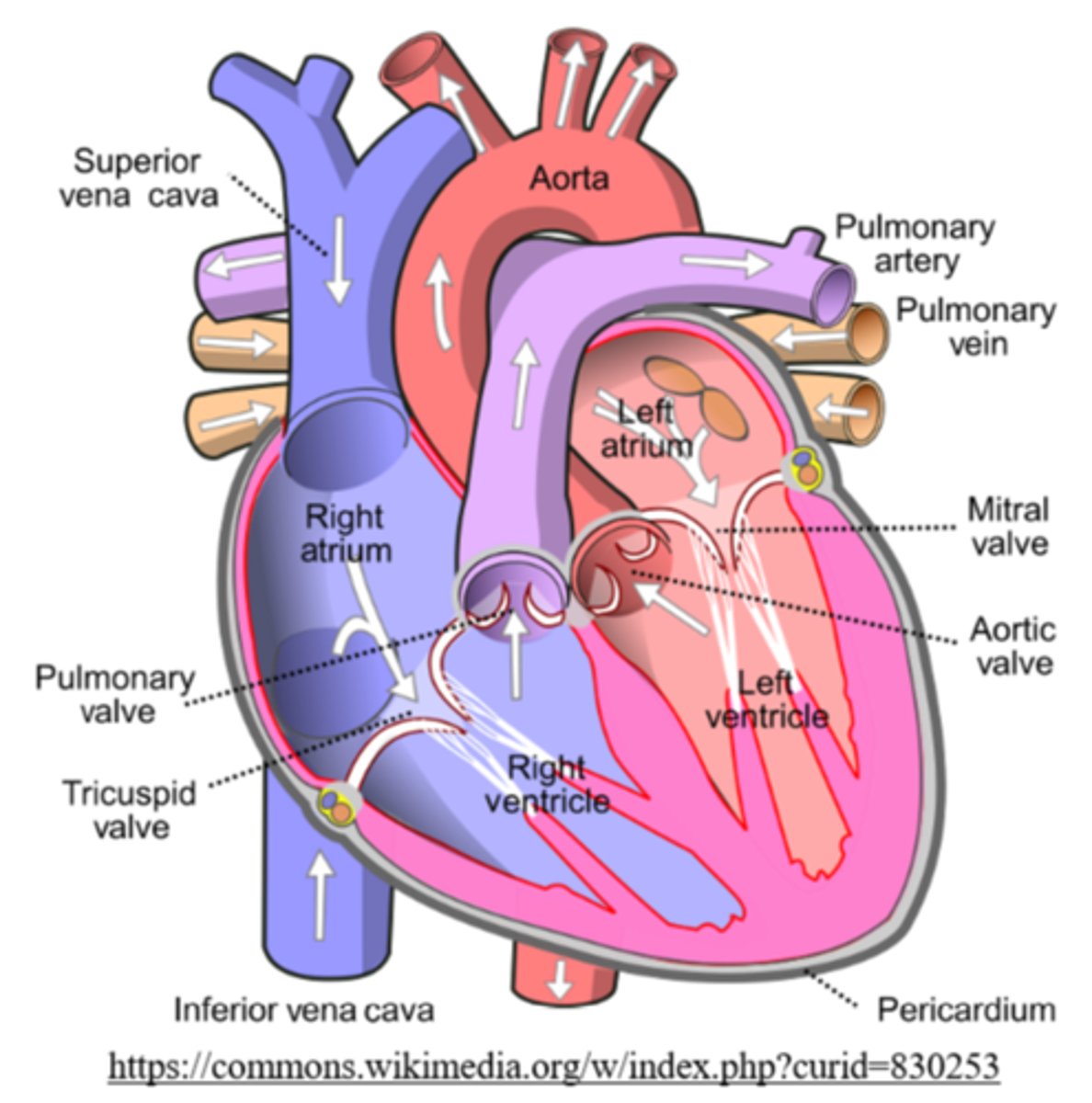
what are the vessels that carry blood toward the heart?
veins
oxygenated blood flows from the left atrium to the left ventricle, through the _____
bicuspid/mitral valve
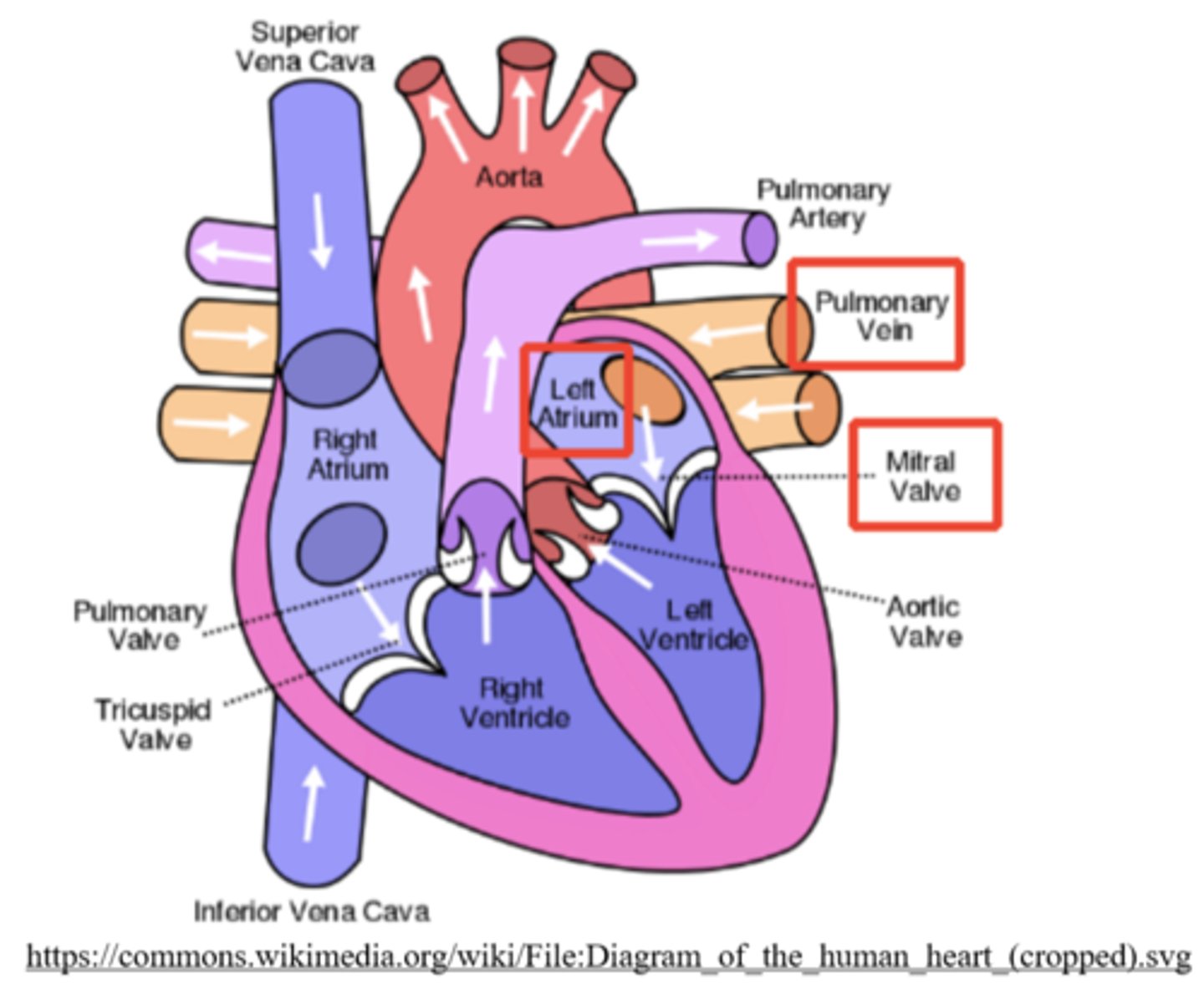
the bicuspid/mitral (AV) valve has _____ to ensure unidirectional blood flow from the left atrium to left ventricle
two cusps/flaps
the _____ is the most muscular chamber of the heart
left ventricle
the left ventricle forcefully ejects oxygenated blood through the _____ valve into the _____
aortic semilunar; aorta
the _____ is the largest artery
aorta
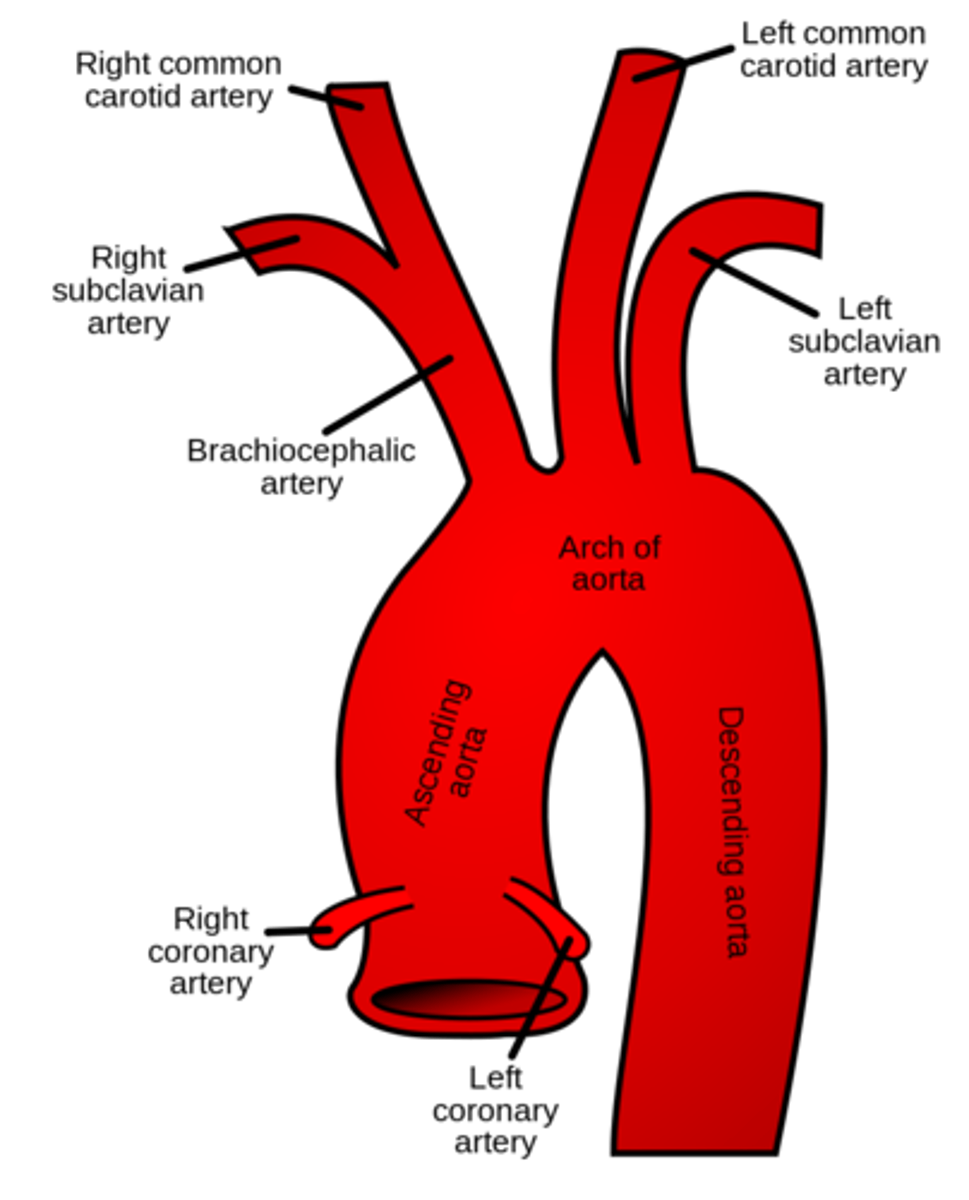
from where does the aorta leave the heart?
left ventricle
the aorta has the highest _____ of any vessel
blood pressure
what are the two circulations of the human cardiac system?
pulmonary; systemic
_____ circulation moves deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation
pulmonary
what is the pathway for pulmonary circulation?
vena cava --> right atrium --> tricuspid valve --> right ventricle --> pulmonary semilunar valve --> pulmonary arteries --> lung --> pulmonary veins --> left atrium
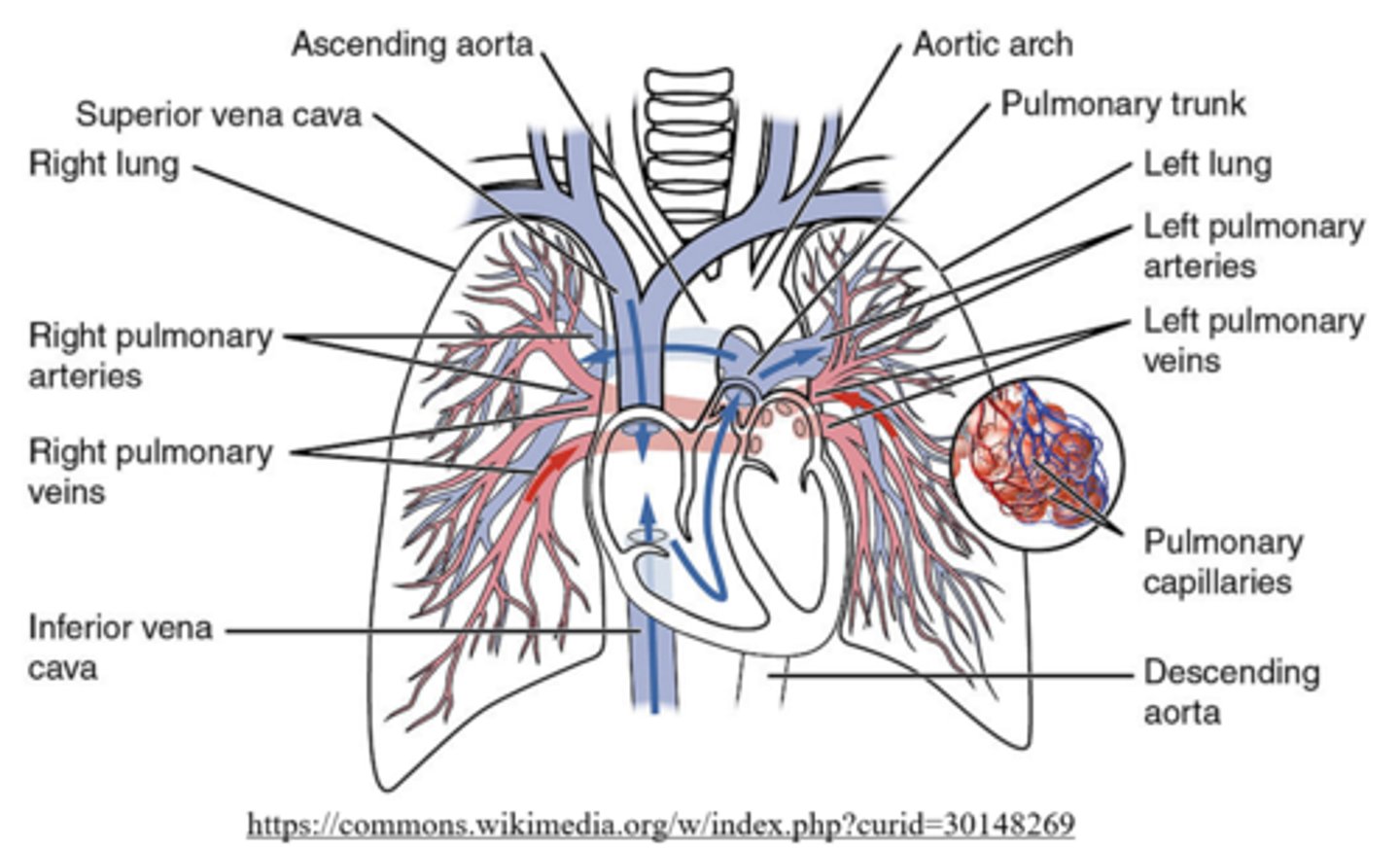
_____ circulation moves oxygenated blood to the body tissues
systemic
what is the pathway for systemic circulation?
left atrium --> bicuspid/mitral valve --> left ventricle --> aortic semilunar valve --> aorta --> body tissues --> vena cava --> right atrium
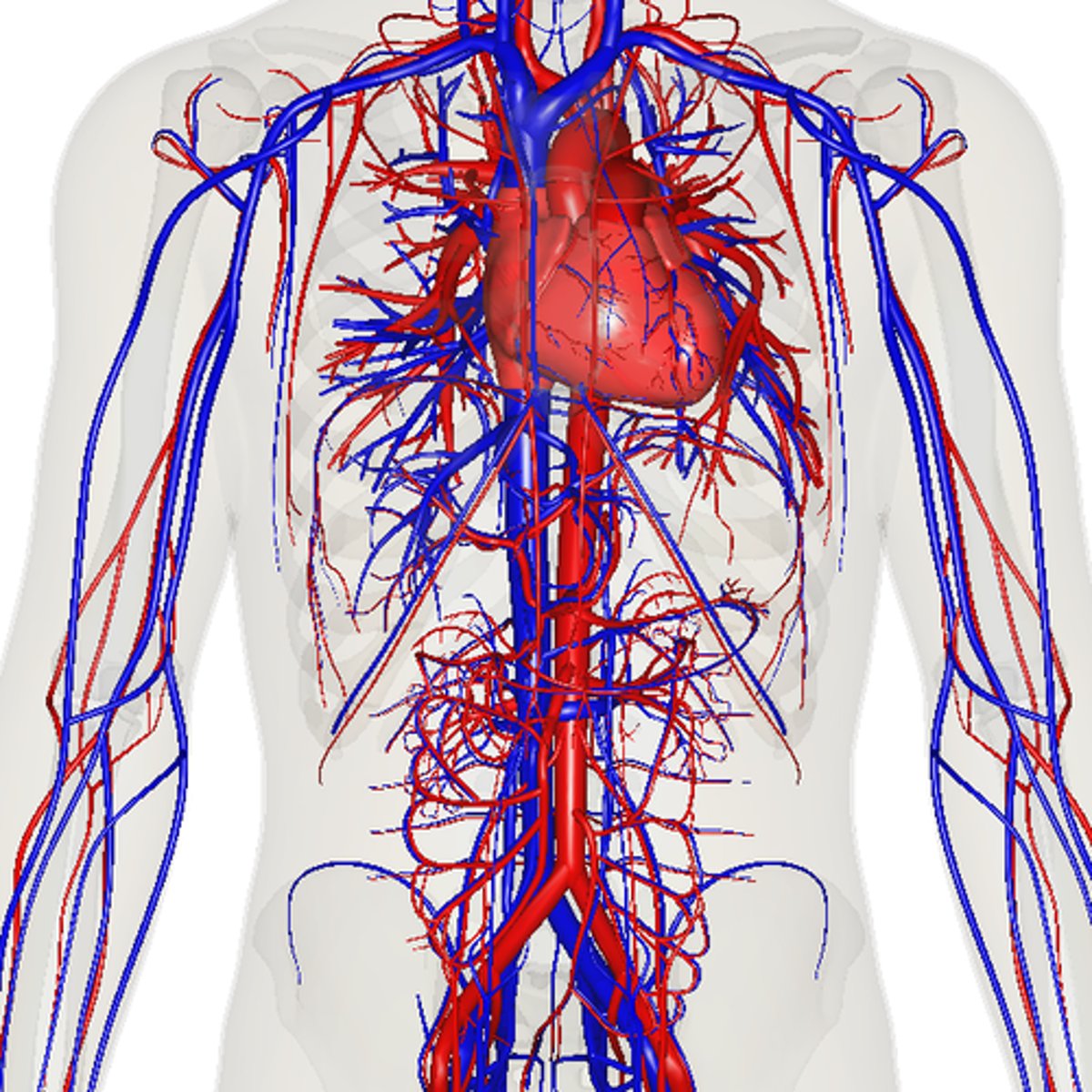
does systemic or pulmonary circulation have a higher resistance to blood flow?
systemic
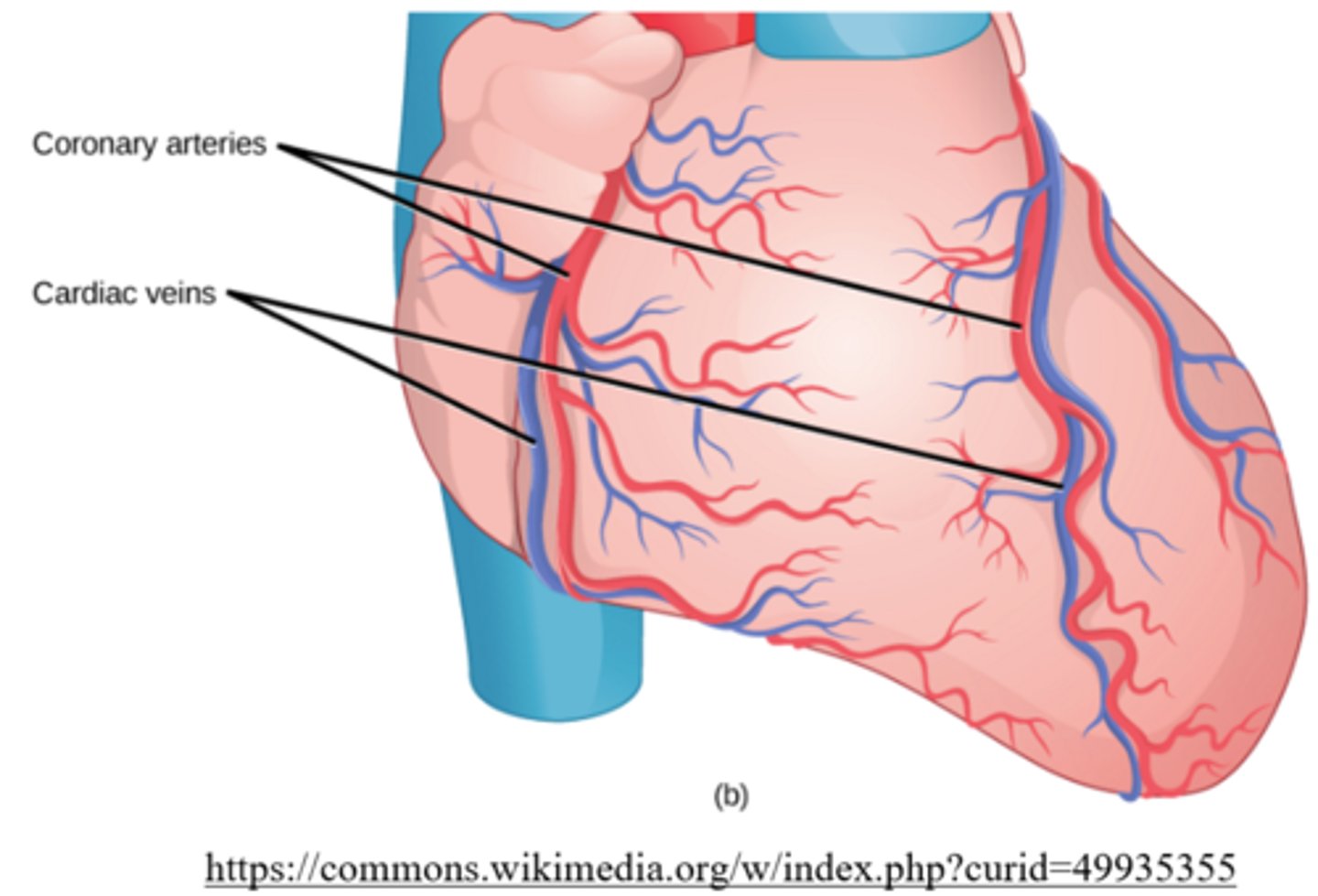
how does the heart pump blood to itself?
coronary circulation
what is the muscular layer of the heart
myocardium
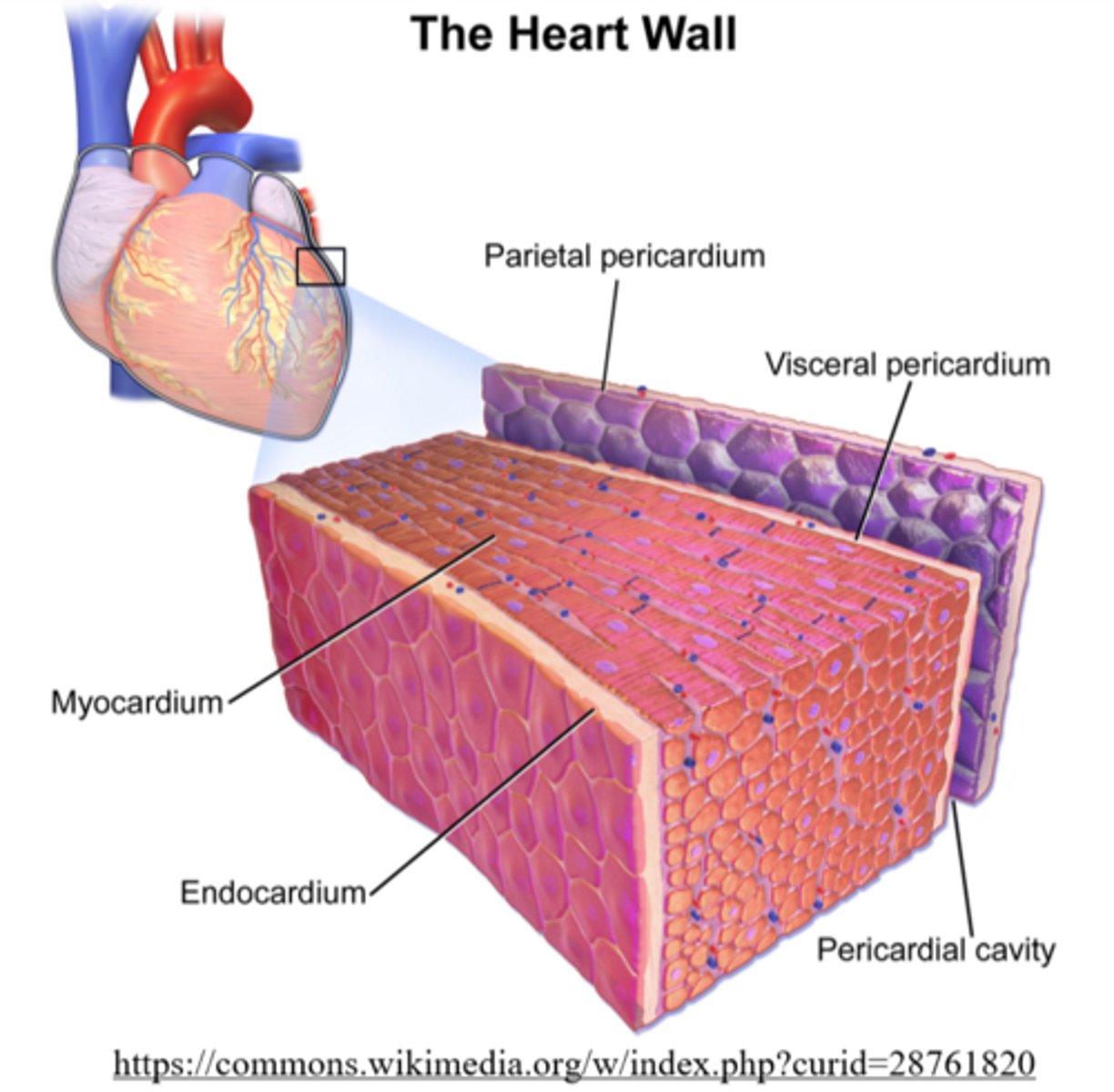
what are the cells contained in the myocardium?
cardiomyocytes
what type of cells line the inside of the heart?
endothelial
the _____ lies beneath the myocardium
endocardium
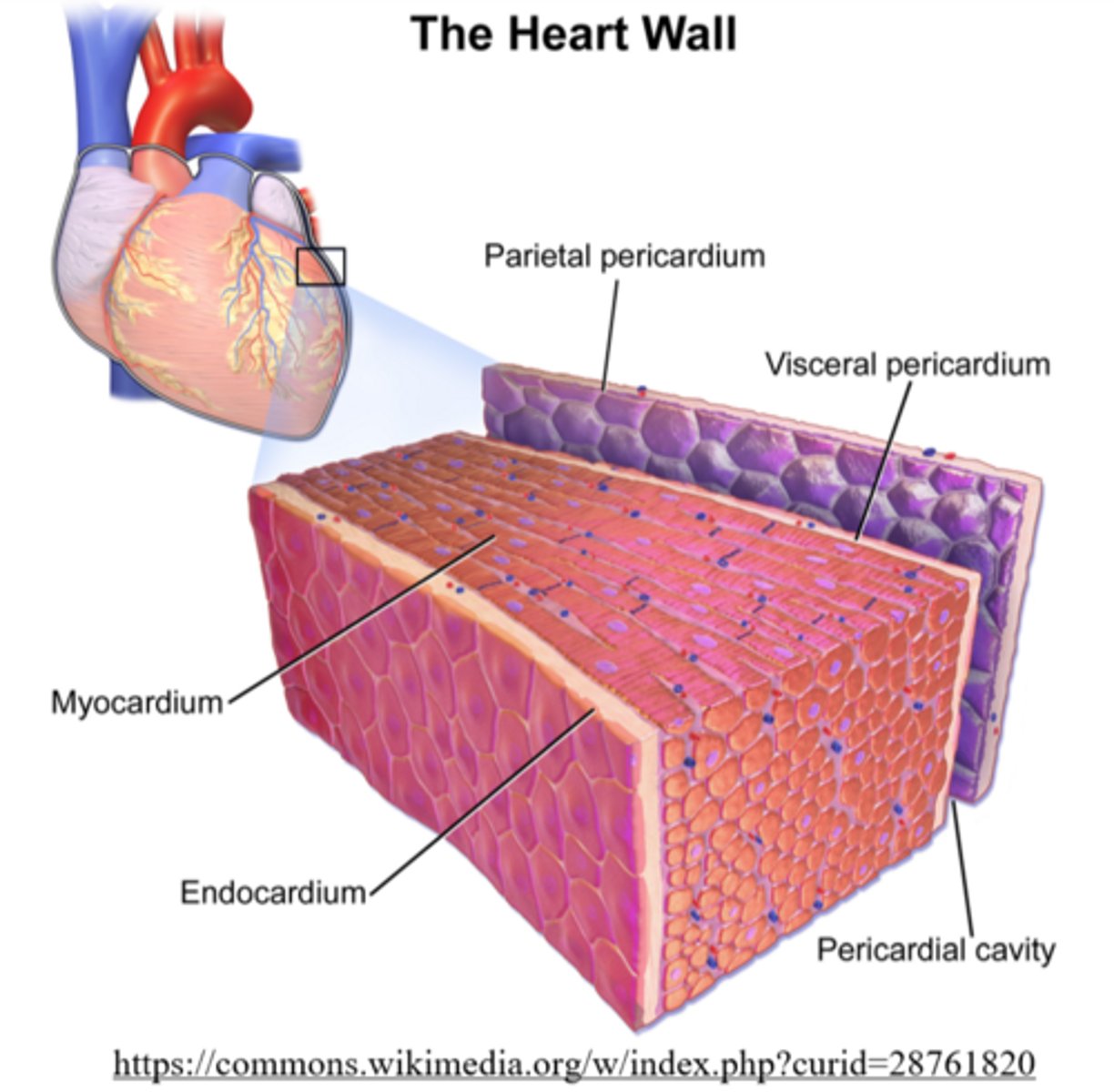
_____ drain deoxygenated blood from the myocardium to the right atrium via the coronary sinus
cardiac veins
what is the small opening in the right atrium that cardiac veins empty into?
coronary sinus
the _____ is a protective sack of fluid surrounding the heart
pericardium
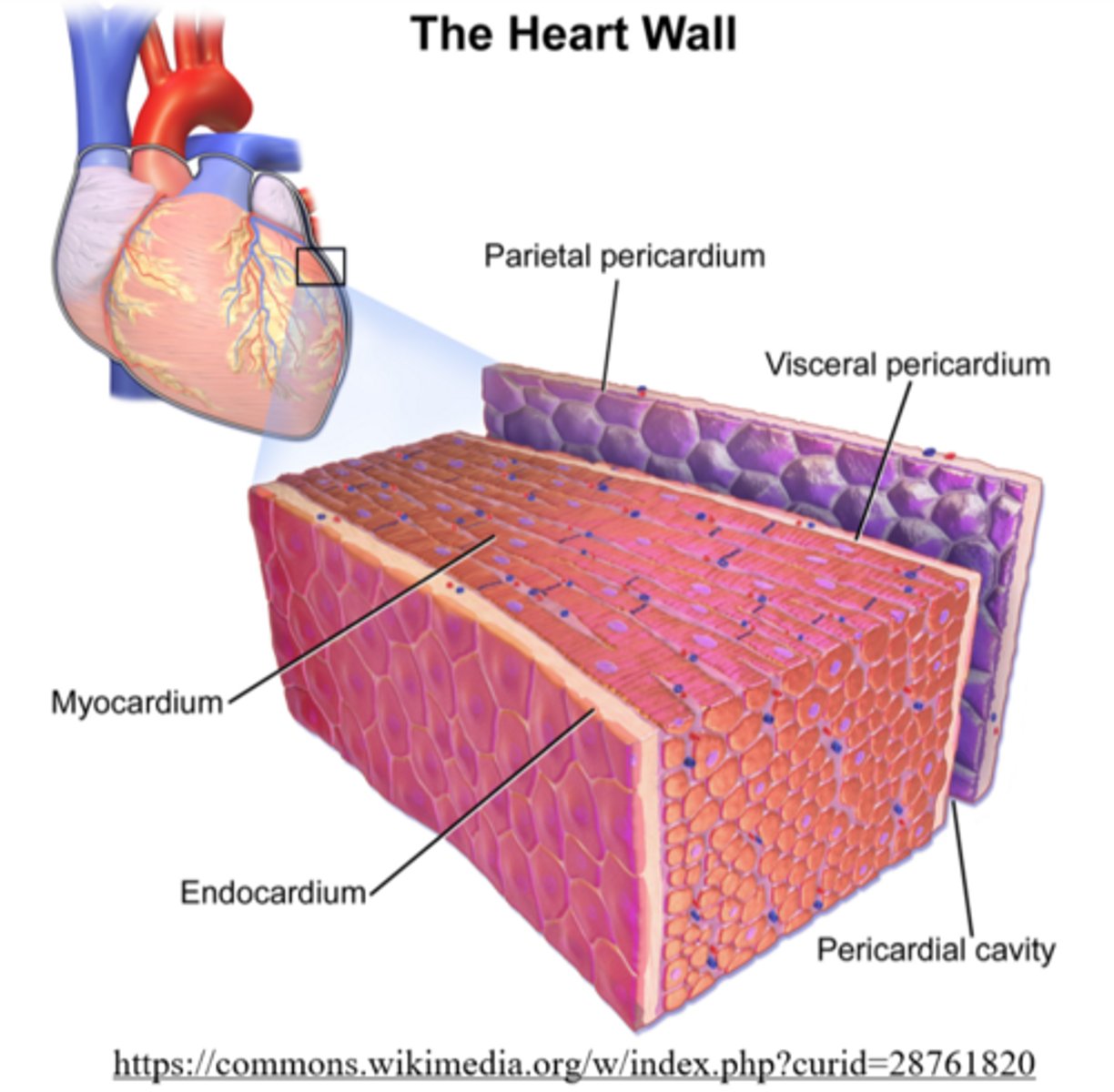
what is the fluid in the pericardium?
serous fluid
cardiomyocytes have automaticity - what does that mean?
action potentials will generate without external nerves having to initiate the action potential
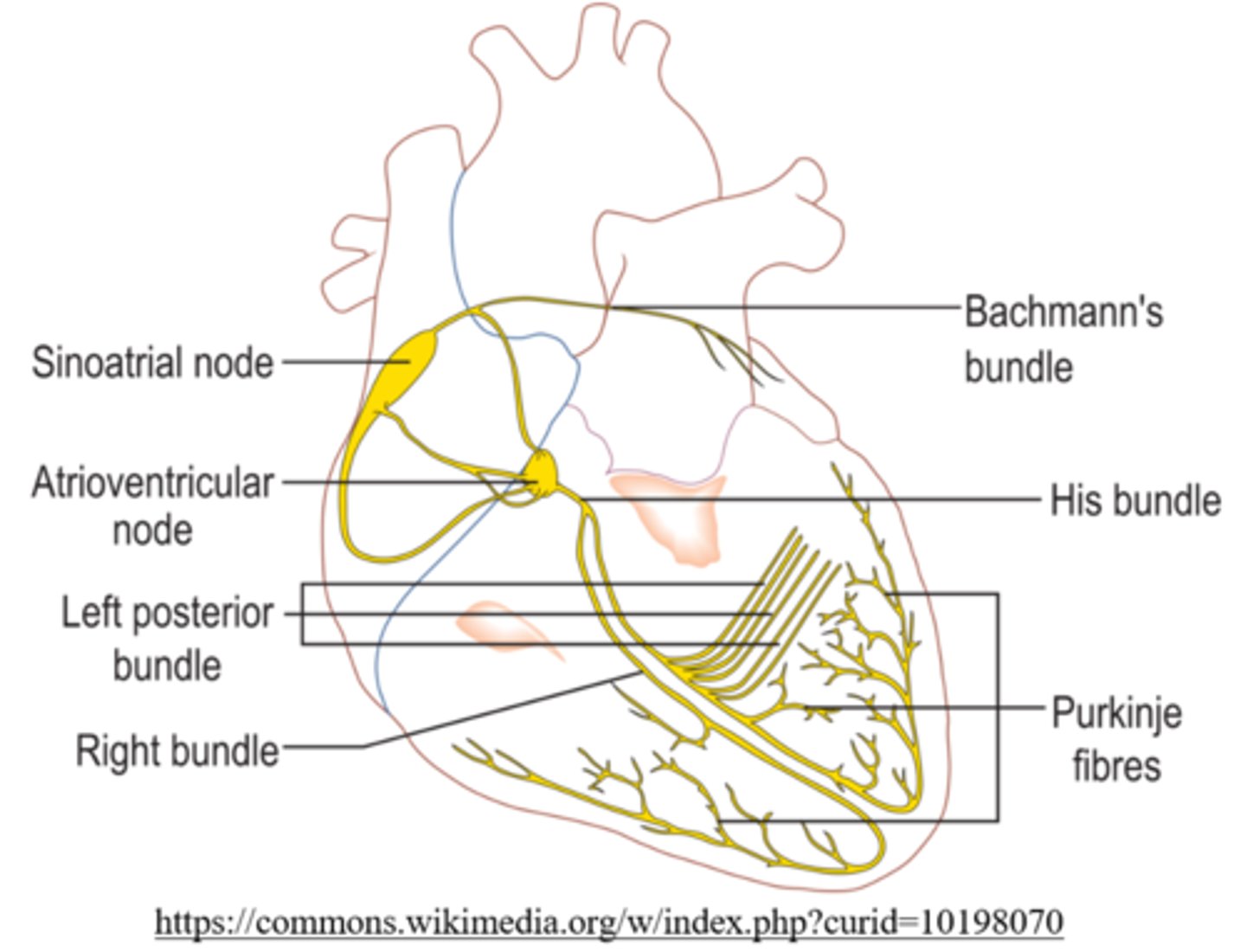
the _____ is the pacemaker of the heart
sinoatrial node (SA node)
which part of the heart has the greatest automaticity?
the SA node
where is the SA node located?
right atrium
which nervous system causes the heart's beating pace to increase and which causes it to decrease?
sympathetic; parasympathetic
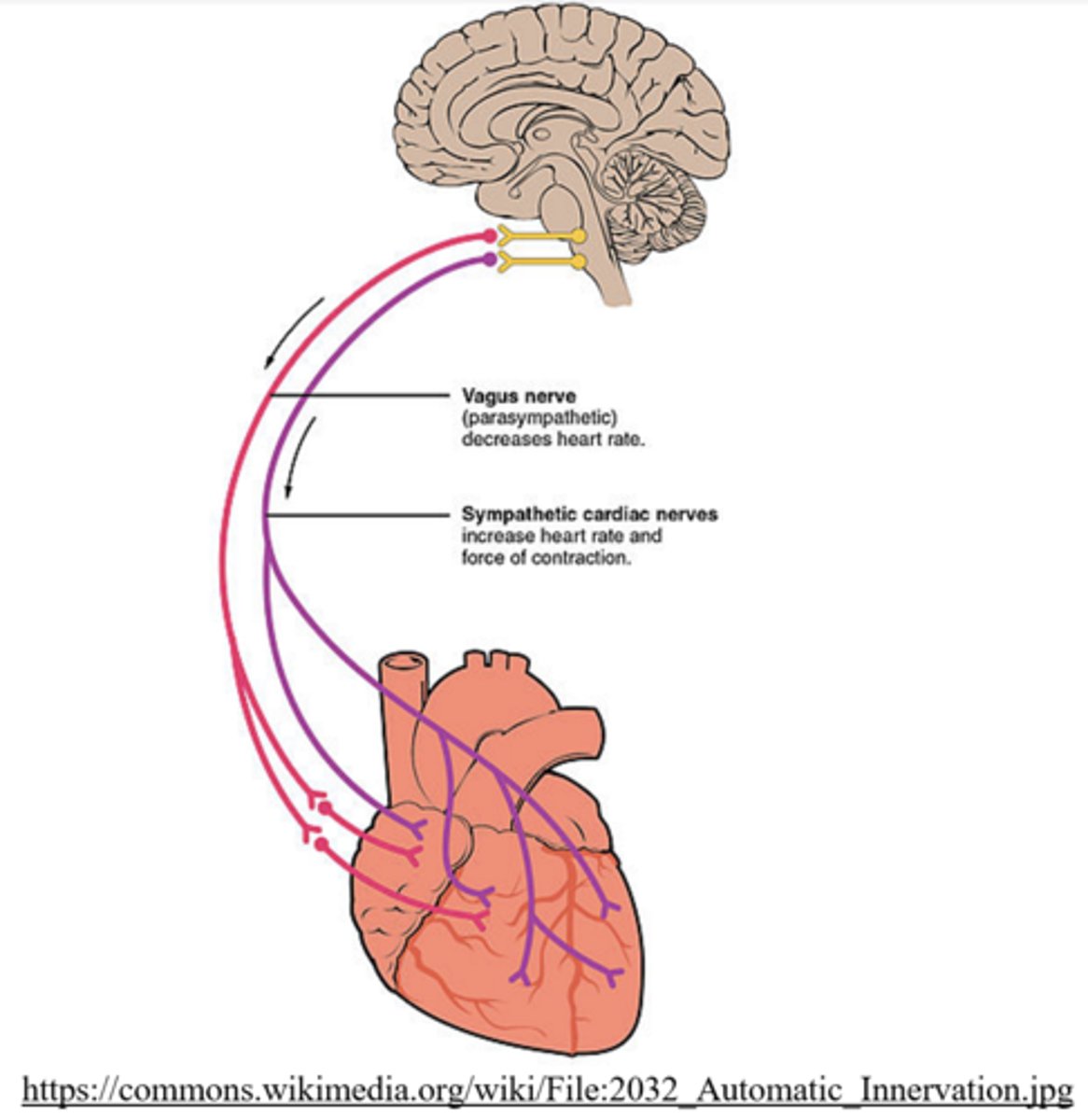
the _____ extends from the medulla oblongata and innervates the SA node
parasympathetic vagus nerve
the parasympathetic vagus nerve sends a default signal to _____ (slow down/speed up) the SA node automaticity to _____
slow down; 60-90 BPM
what is a tachycardic heart rate?
> 100 BPM
what is a bradycardic heart rate?
< 60 BPM
what is the function of the AV node?
add a brief delay between atrial and ventricular contractions
where does the AV node conduct to?
bundle of His
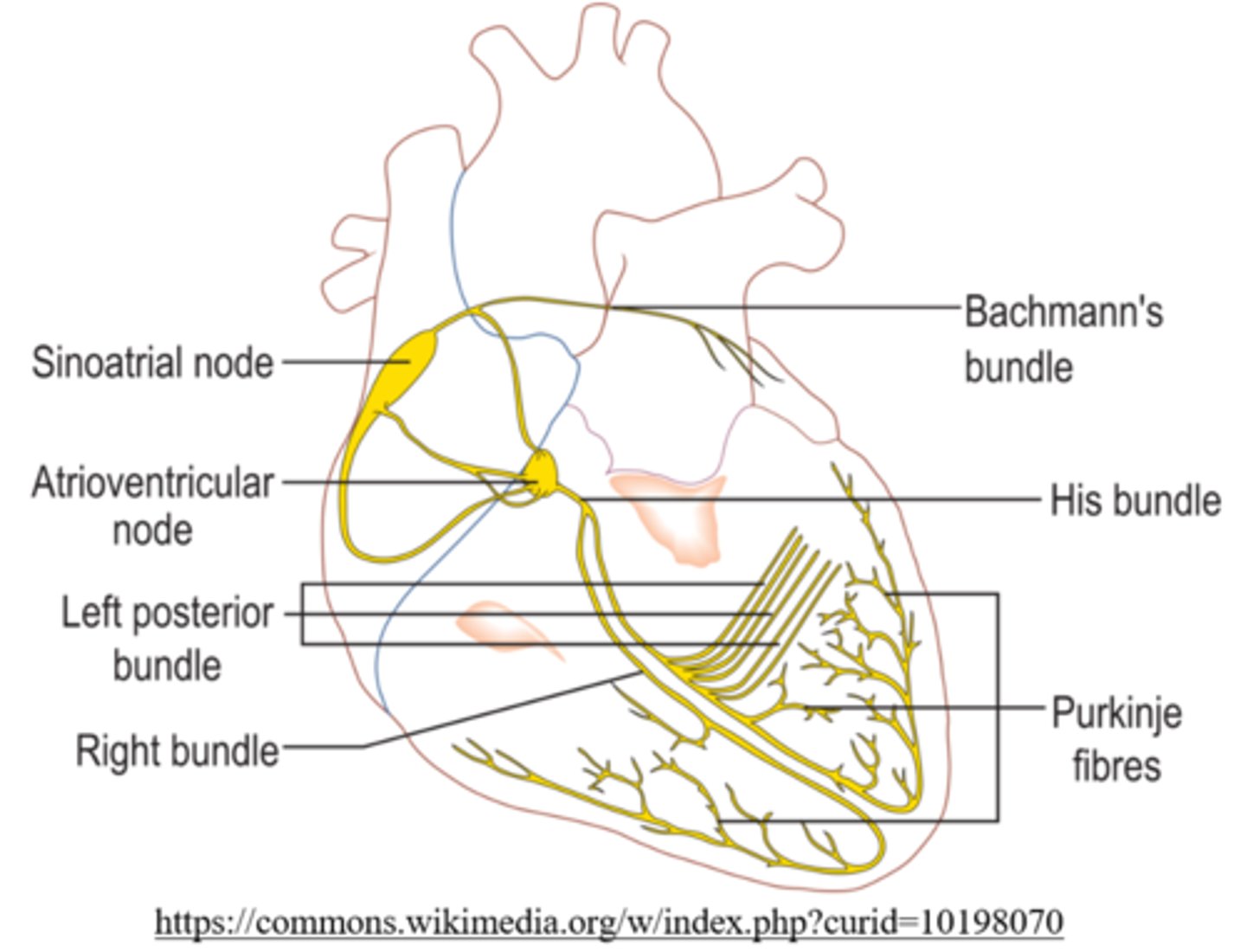
where is the bundle of His located?
interventricular septum
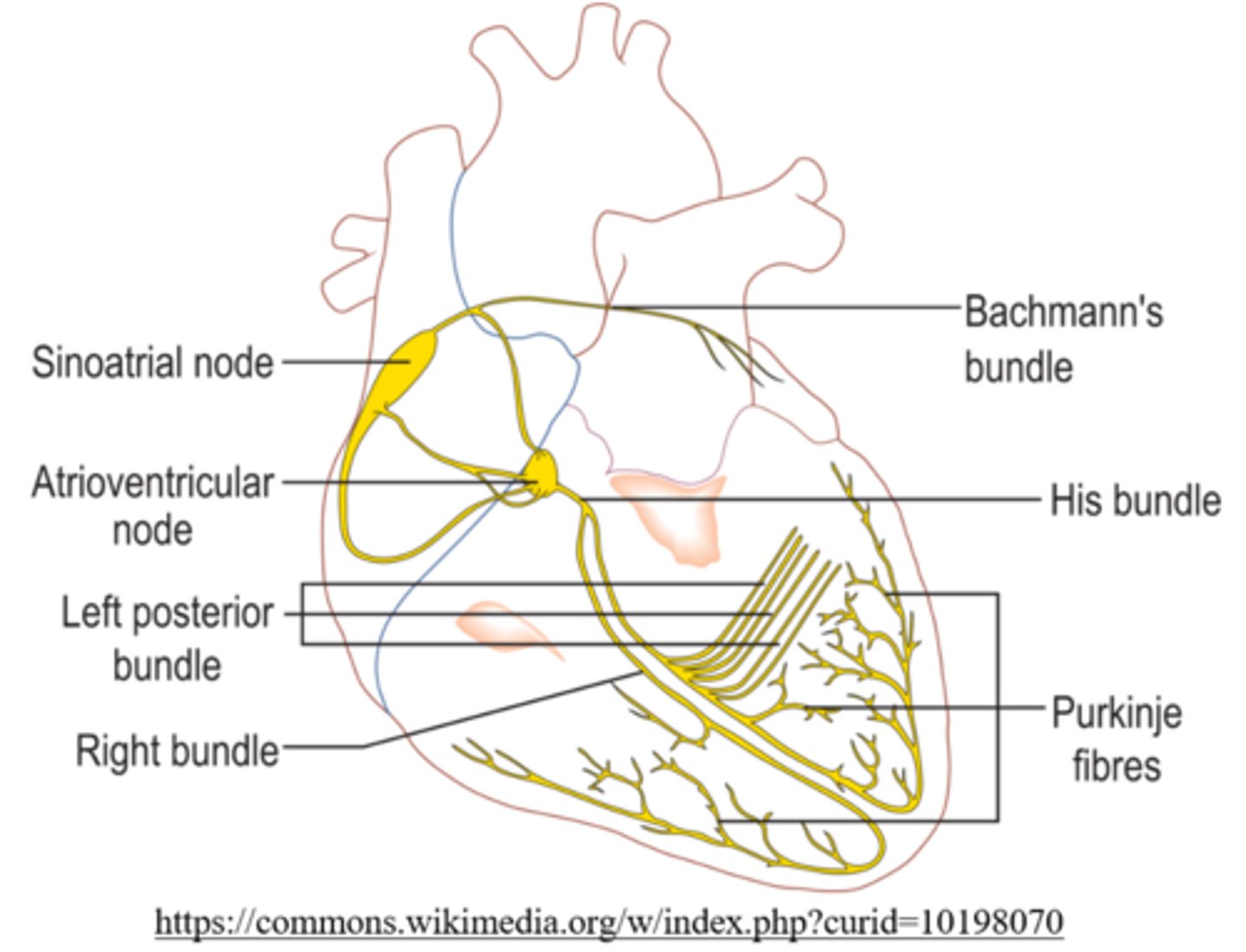
what does the bundle of His do?
carries the signal to the base of the heart
purkinje fibers are located in the walls of the _____
ventricles
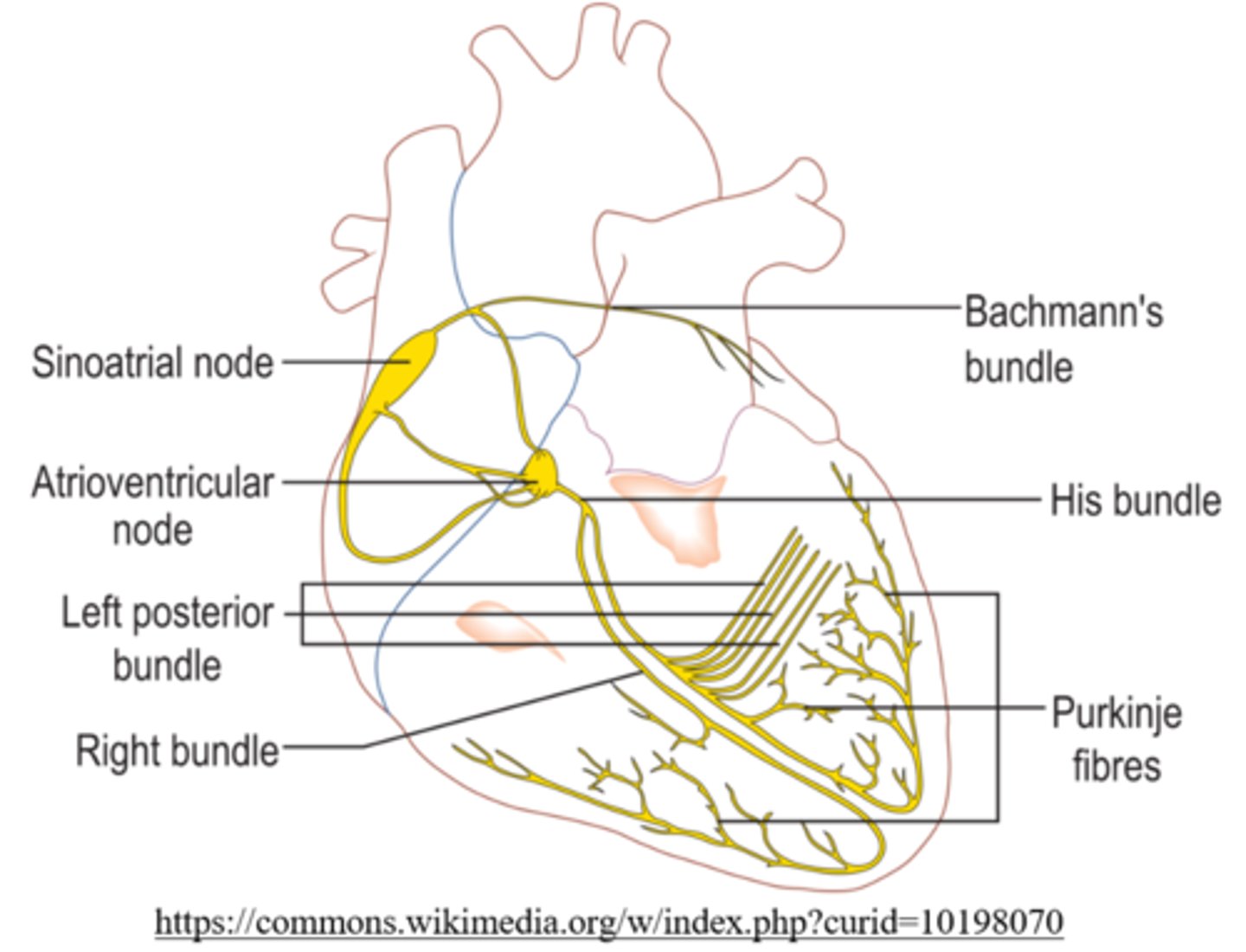
what is the function of the Purkinje fibers?
they ensure a coordinated contraction of both ventricles
_____ receive conduction from the bundle of His
purkinje fibers
what is the name for the period of time right after the ventricles eject their blood?
systole
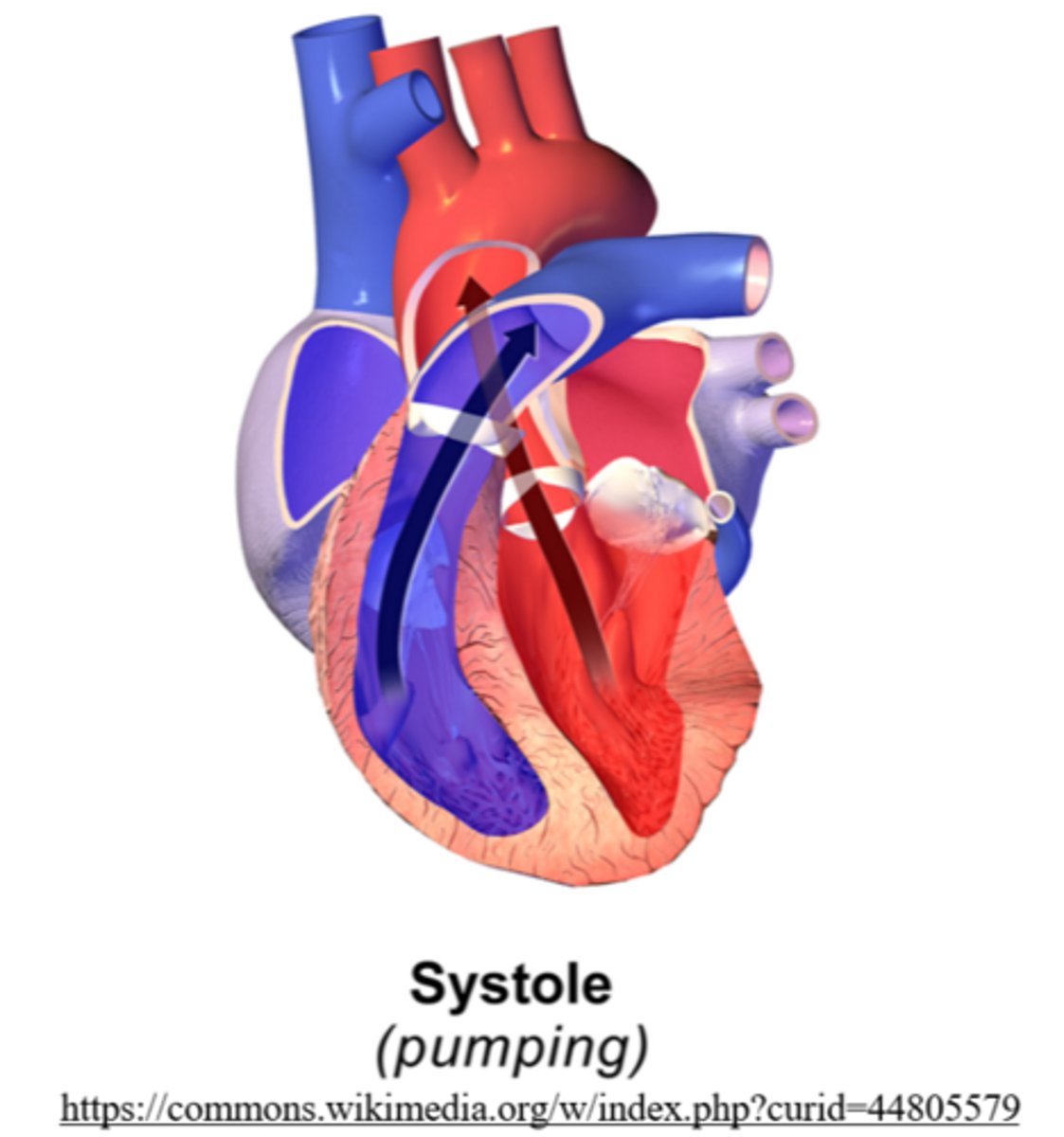
systole is the phase where blood pressure is _____ (highest/lowest)
the highest
what is the period of time right after the atria contract to fill the ventricles?
diastole
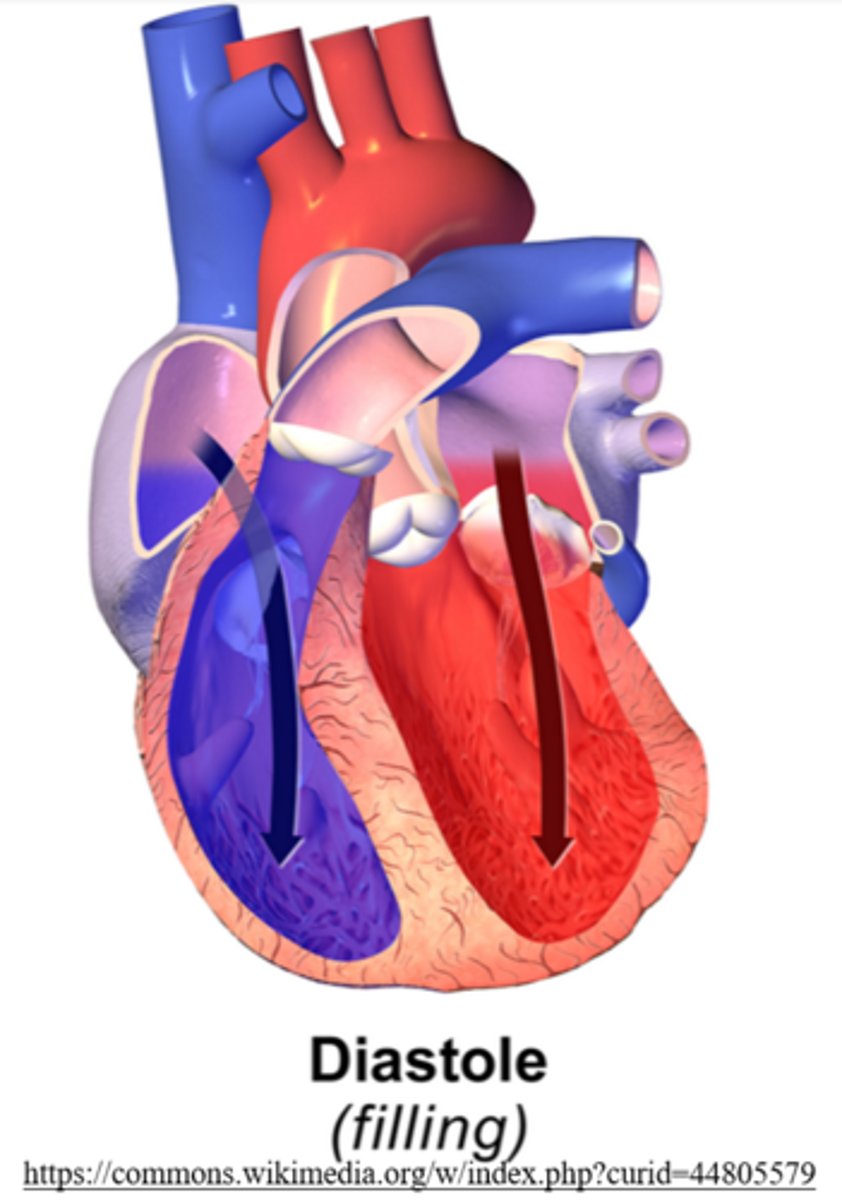
the myocardium is _____ (relaxed/contracted) during diastole
relaxed
diastole is the phase where blood pressure is the _____ (highest/lowest)
lowest
atria are relaxed during the _____ (lub/dub) heart sound
"lub"
_____ are contracting during the "lub" heart sound
ventricles
_____ are contracting during the "dub" heart sound
atria
ventricles are relaxed during the _____ (lub/dub) heart sound
"dub"
when does systole occur (sounds)?
between lub and dub
when does diastole occur (sounds)?
after dub (before next lub)
which side of the heart is stronger - left or right?
left
why is the left side of the heart stronger than the right side?
systemic circulation and greater vascular resistance
_____ are contact points between adjacent cardiomyocytes
intercalated discs
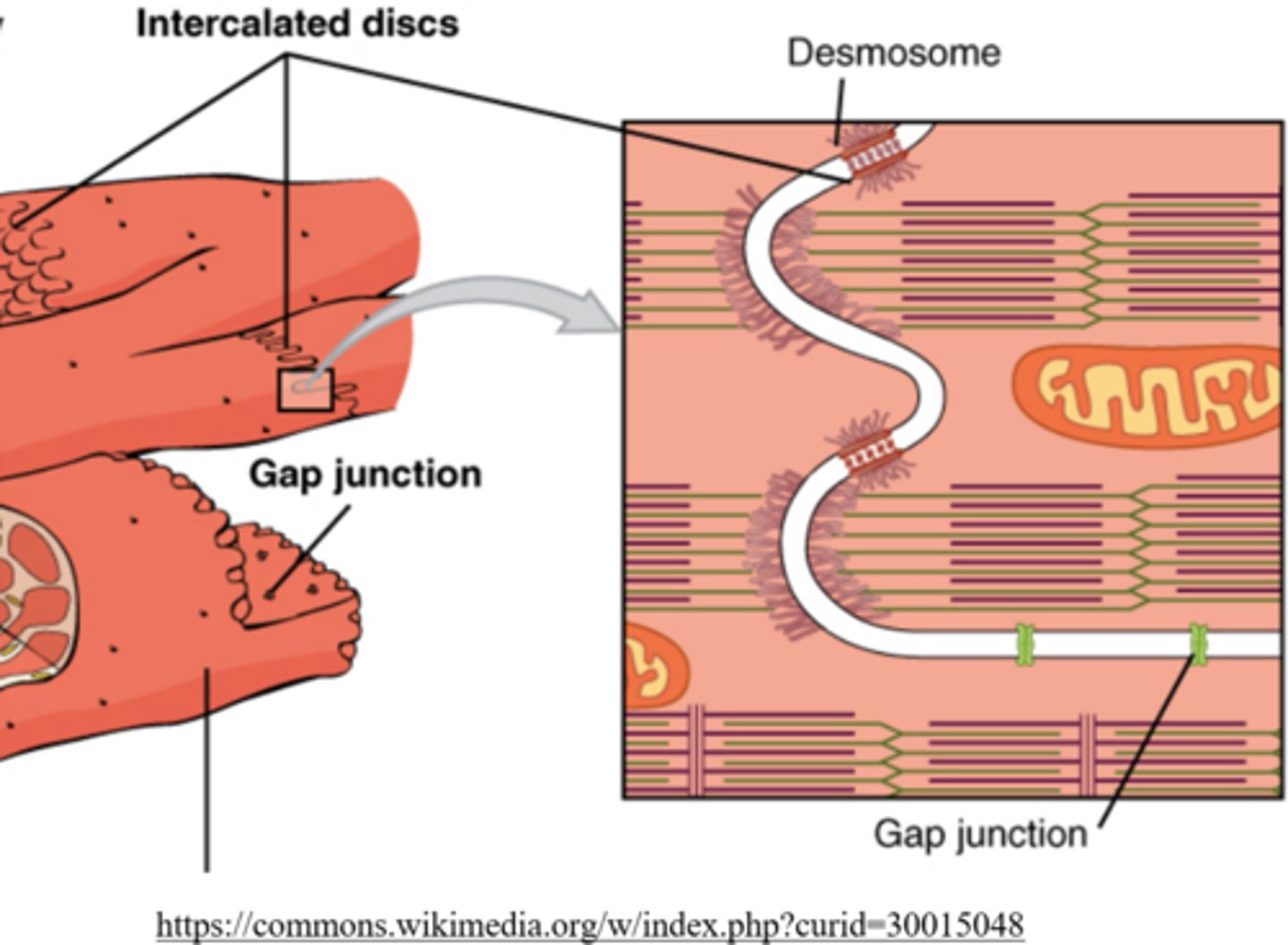
_____ 'stitch' cardiomyocytes together at intercalated disks
desmosomes
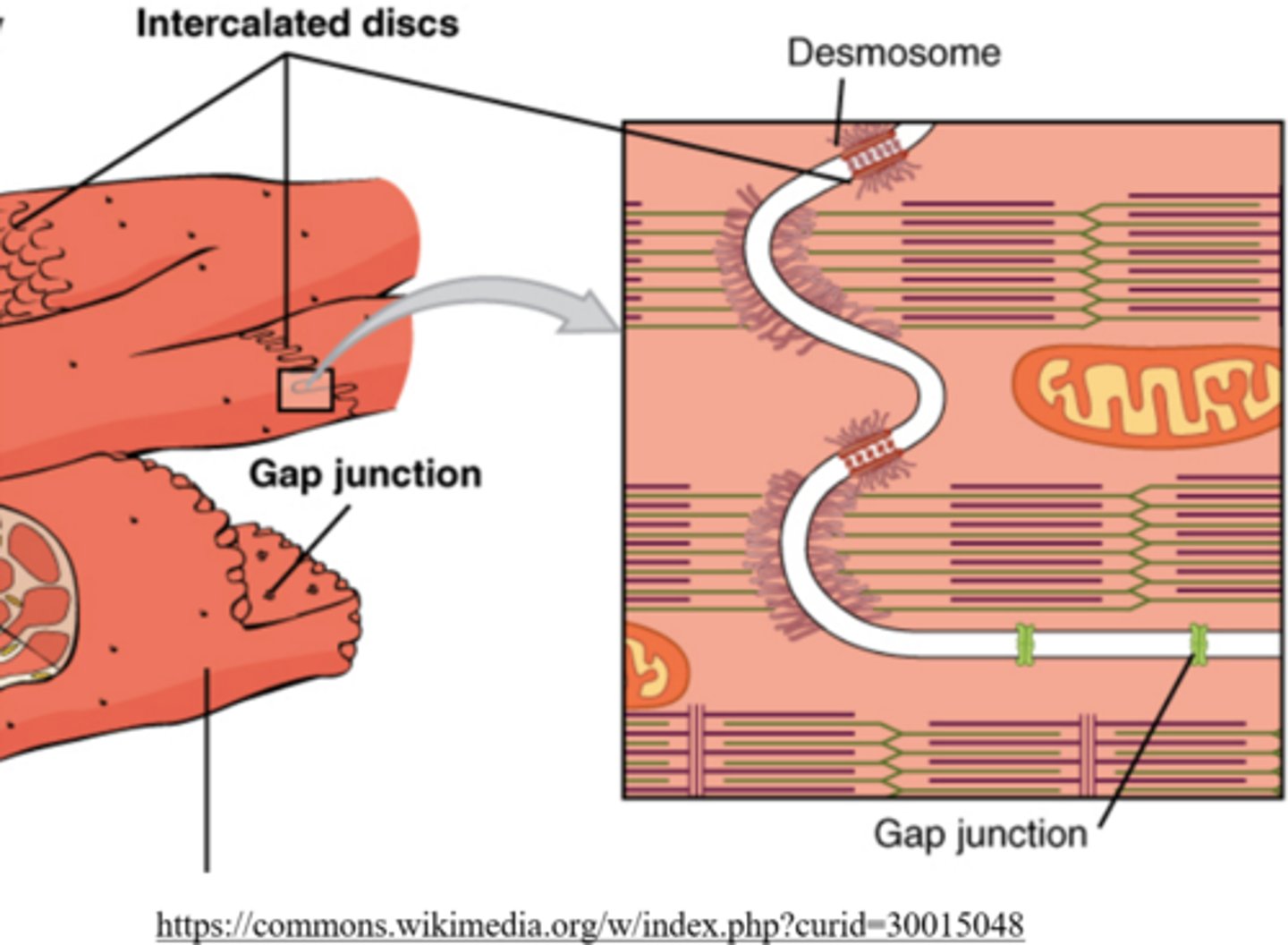
_____ are protein tunnels that connect adjacent cardiomyocytes
gap junctions
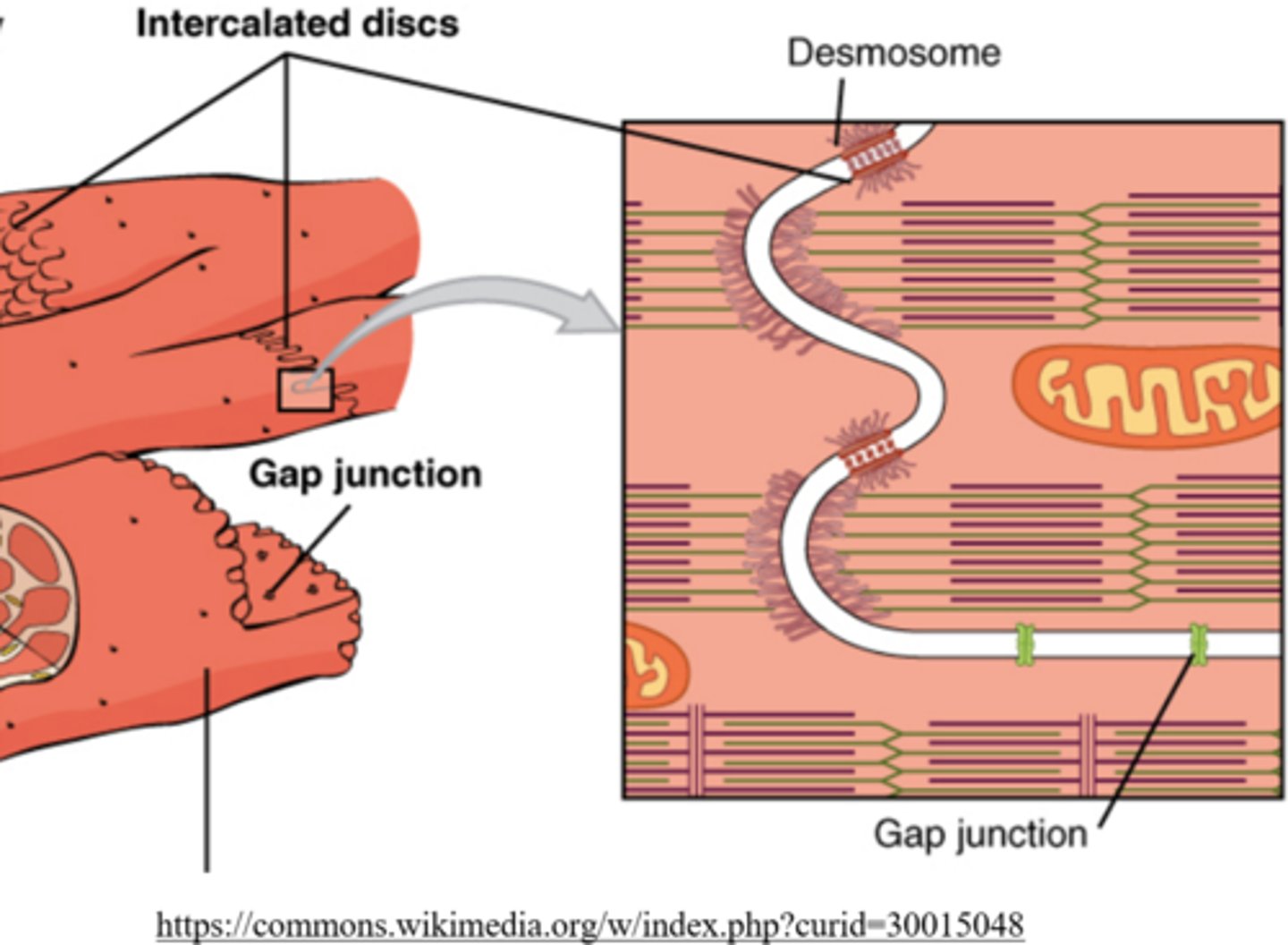
gap junctions are involved with _____ transport
molecule/ion
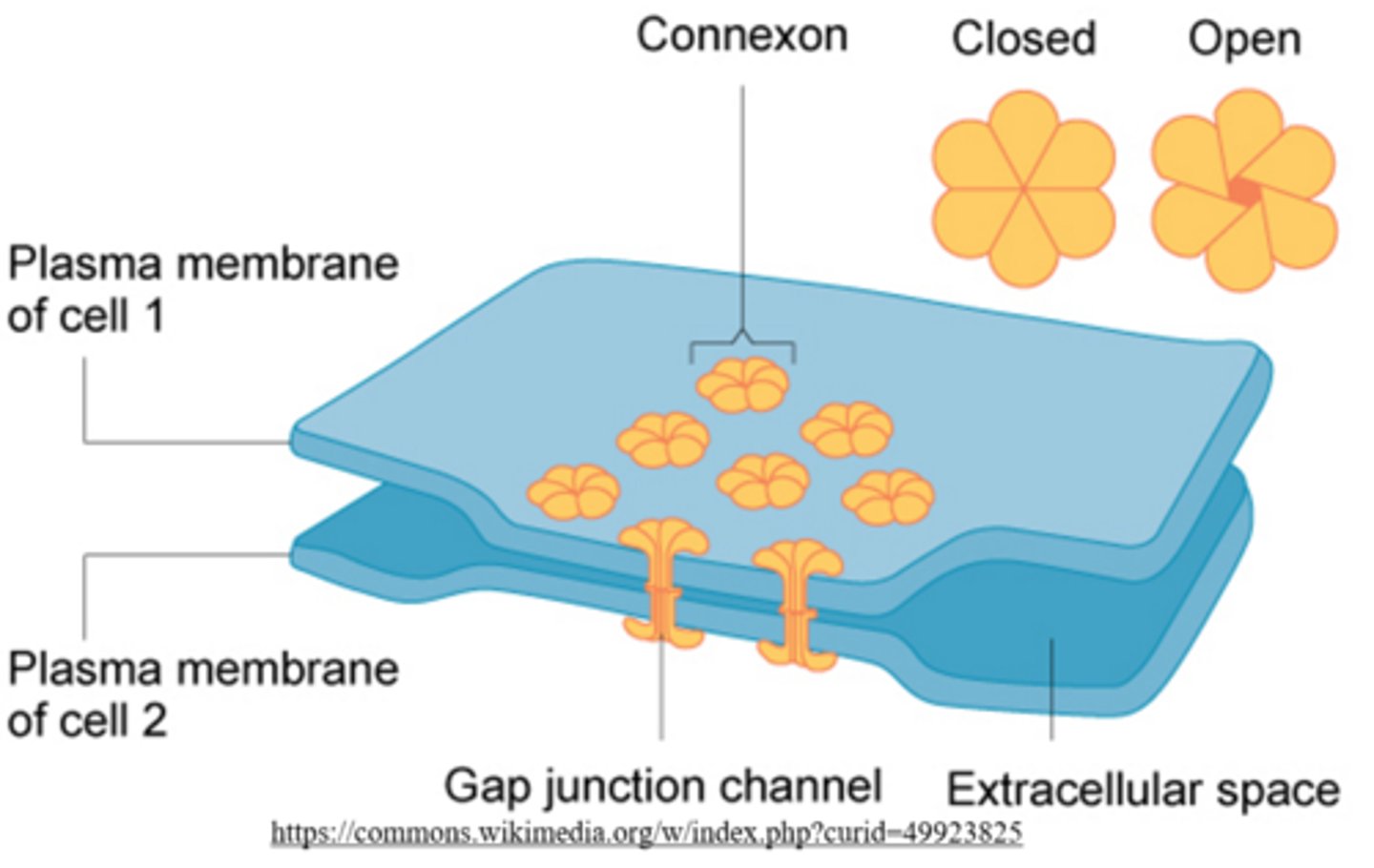
_____ allows the heart to function in unity
cardiac syncytium
what is the wave that represents both atria depolarizing?
p wave
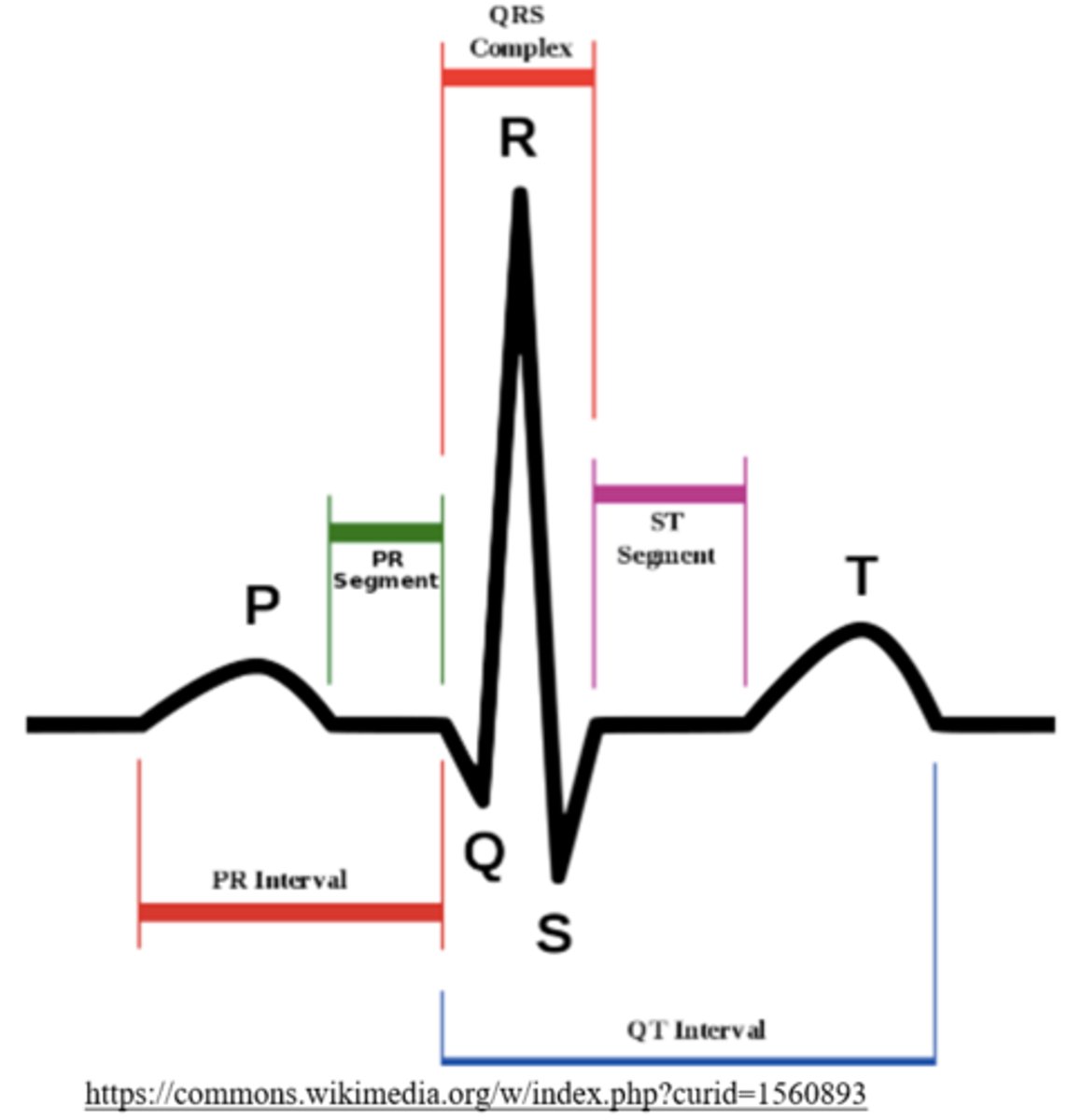
what is the wave that depicts depolarization through the interventricular septum
q wave
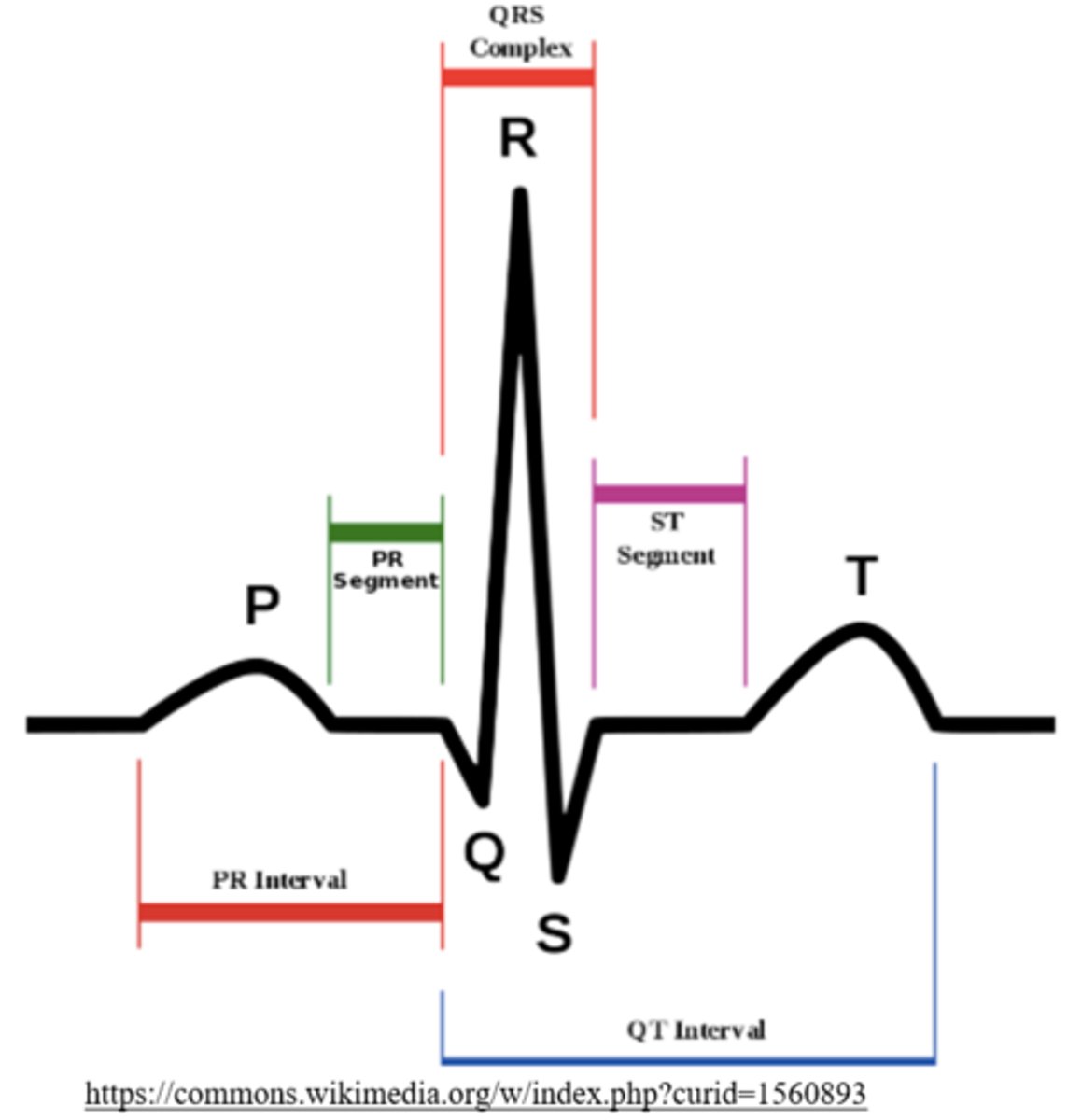
the q wave initiates _____
ventricular depolarization