exercise 1-3
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
compound microscope
can magnify up to 1000 times
electron microscope
can magnify up to one million times
best light
is obtained from indirect sunlight, reflected from the clouds
natural light
is available, the plane mirror is
used to provide uniform illumination of the field
artificial light
is provided, the concave mirror is employed to converge the light rays on
the object being examined
condenser and diaphragm
are used to regulate the intensity and angle of illumination
16 mm
working distance for low power
4mm
working distance for high power
1.8 mm
working distance for oil immersion
arm
connects base and supports head
base
for support to carry microscope
light switch
to turn on and off
illuminator and iris diaphragm
Adjusting light level to increase contrast
Light/ Brightness Adjustment Knob and Illuminator (light source
To adjust and control the amount and intensity of light passing in the microscope
iris diaphragm
adjust the amount of light shining up through the specimen or regulates the amount of light passing through (squarish platform)
stage
platform where organisms are placed
stage clip
holds the slide in place
stage control
moves and control stage clips
Coarse adjustment knob
focus by raising or lowering stage
fine adjustment knob
sharpens image under all powers
Ocular lenses or Eyepiece
where you look through; can magnify specimen up to 10x
Revolving nosepiece
made of rubber; rotates objective lens
Parfocal lens
objectives can be changed with minimal or no refocusing
Working distance
the distance between the lens and the slide
Field
entire circle when viewing
10x
eyepiece magnification
10x
low power objective
40x
high power objective
100x
oil immersion objective
eyepiece x objective
formula for the size of object in focus
red
color for scanning
yellow
color for LPO
blue
color for HPO
black
color for oil immersion
ocular lens x objective lens
totally magnification formula
Candida albicans (purple)
Normal flora found in the human digestive tract, mouth, vagina, etc.
Opportunistic fungal pathogens. They are fungi specifically the yeast.
Candidiasis (Yeast infection
infection caused by candida albicans
Oval or spherical shaped, formed in clusters, and purple
morphology of candida albicans
(size, shape and color)
coccus, bacillus and spiral
The three basic morphology of bacteria
micrometers
measurement for bacteria
binary fission; cytokinesis
Bacteria multiply through __ an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and then divides into two parts (__), with each new organism receiving one copy of DNA.
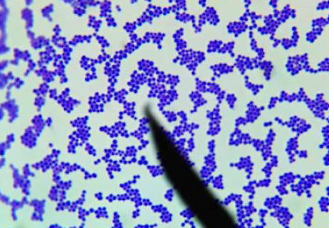
Staphylococcus aureus
representative organism for staphylococci
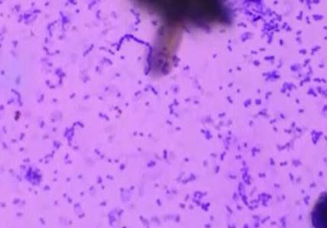
Streptococcus pyogenes
representative organism for streptococci
Streptococcus pneumoniae
representative organism for diplococci
clusters or grape-like masses
morphology of staphylococci
chains
morphology of streptococci
divide to form pairs
morphology of diplococci
chains
Streptobacilli
pairs
Diplobacilli
v-shapes
Snapping
arranged side by side
Slipping
short, thick, oval-shaped bacilli
Coccobacilli
comma-shaped
Vibrio
spiral
Spirillum
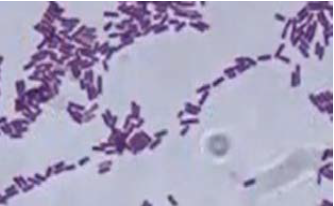
Bacillus subtilis; gram stain (+)
Representative microorganisms and gram stain or acid fast:
Streptobacilli
Mycobacterium tuberculosis; acid fast stain (acid fast)
Representative microorganisms and gram stain or acid fast:
Diplobacilli
Escherichia coli ; gram stain (-)
Representative microorganisms and gram stain or acid fast:
coccobacilli
Vibrio cholerae; gram stain (-)
Representative microorganisms and gram stain or acid fast:
vibrio
Campylobacter jejuni; gram stain (-)
Representative microorganisms and gram stain or acid fast:
sporillum
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae

Bacillus subtilis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis - snapping
Escherichia coli
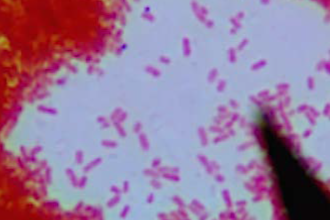
Vibrio cholerae
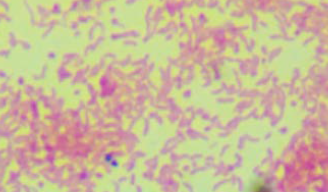
Campylobacter jejuni
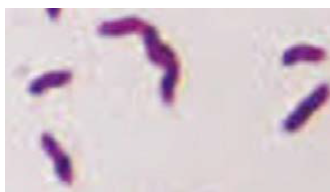
Mycobacterium tuberculosis - slipping
dil. carbon fuchsin
simple staining: positive staining
indian ink method
simple staining: negative staining
hackers method
differential staining: gram staining
Ziehl-Neelsen’s method
differential staining: acid-fast staining
Wirtz-Conklin method
special staining: spore stain
Anthony’s method
special staining: capsule stain
leifson’s method
special staining: flagellar stain
Loeffler’s methylene blue
special staining: Metachromatic granules stain
Crystal violet (Primary Stain)
Gram’s iodine (Mordant)
Acetone alcohol (Decolorize)
Safranin (Counterstain)
order for gram staining
Dilute carbol fuchsin (Primary Stain)
Acid alcohol (Decolorizer)
Methylene blue (Counterstain)
acid-fast staining
Formalinized sputum
source of inoculum: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
stock culture
source of inoculum: Bacillus subtilis
E. coli and s. epidermis
bacteria for gram stain in exercise 3
b. subtillis and m. tuberculosis
bacteria for acid fast stain for exercise 3
negative
in exercise 3, E. coli is gram ?
positive
in exercise 3, S. epidermis is gram ?
positive
in exercise3, m. TB is acid fast ?
negative
in exercise 3, b. subtillis is acid fast ?
rod-shaped, small clumps, non acid fast
B. Subtilis morphology:
size, shape, arrangement and stain reaction
spherical, grape like clusters, gram positive
s. epidermis morphology:
size, shape, arrangement and stain reaction
rod shaped, heaps of small rods, acid-fast +
M. TB morphology:
size, shape, arrangement and stain reaction
rod shaped, singly or in pairs, gram negative
E. coli morphology:
shape, arrangement and stain reaction
Neisseria spp.
Branhamella spp.
Moraxella spp.
Veillonella spp.
cocci: ALL are Gram positive (+), except for:
ACID FAST ORGANISMS
(Mycobacterium, Nocardia)
SPOREFORMERS (Bacillus,
Clostridium)
Corynebacterium spp
bacilli: ALL are Gram negative (-), except for:
-
spiral: ALL SPIRILLUM are Gram ?
spirochete
are difficult to stain due to thin cell wells (unstainable)