Transplantation & HLA Perfect Exam-Ready Flashcards (16)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
MHC vs HLA
What is the difference between MHC and HLA?
MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex): General term used across species
HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen): The human version of MHC
Function: Present antigens to T cells and distinguish self from non-self
HLA Class 1 Expression
Where are HLA Class I molecules expressed?
HLA Class 1 molecules are expressed on all nucleated cells and include HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C, where they present endogenous antigens to CD8⁺ cytotoxic T cells.
HLA Class II Expression
Where are HLA Class II molecules expressed?
HLA Class II molecules are expressed only on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and include HLA-DR, HLA-DQ, and HLA-DP, where they present exogenous antigens to CD4⁺ helper T cells.
HLA Polymorphism
What does it mean that HLA genes are highly polymorphic?
HLA genes are described as highly polymorphic because thousands of different alleles exist within the population, which enhances overall immune defence but also makes finding a perfect transplant match difficult.
HLA Haplotype Inheritance
Front: What is HLA haplotype inheritance?
HLA genes are inherited together as a haplotype on chromosome 6, with one haplotype passed down from each parent, which means siblings have a 25% chance of being a complete HLA match.
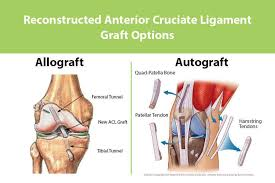
Autograft vs Allograft
What is the difference between an autograft and an allograft?
Autograft: Tissue transplanted within the same individual → no rejection
Allograft: Tissue transplanted between genetically different individuals → risk of rejection
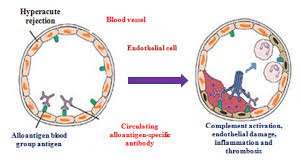
Hyperacute Rejection
What is hyperacute rejection?
Occurs minutes to hours after transplantation
Caused by pre-existing antibodies (anti-HLA or anti-ABO)
Leads to immediate graft thrombosis and failure
Transplant must be stopped
Acute Rejection
Front: What is acute rejection?
Occurs days to weeks post-transplant
Mainly T-cell mediated
Recipient T cells recognise donor HLA as foreign
Often reversible with immunosuppression
Chronic Rejection
Front: What is chronic rejection?
Chronic rejection occurs months to years after transplantation and is caused by long-term immune-mediated injury, leading to progressive fibrosis and vascular narrowing that results in gradual graft failure.
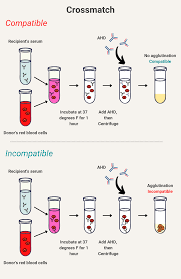
Crossmatch Test
Front: What is the crossmatch test?
Final compatibility test before transplant
Recipient serum mixed with donor lymphocytes
Cell death = positive crossmatch = incompatible transplant
Why is HLA typing performed?
to Identifies donor and recipient HLA alleles
to Improves graft survival
to Reduces rejection risk
to Minimises immunosuppression requirements
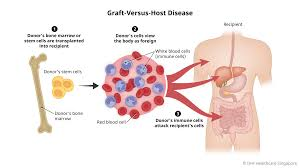
Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD)
Front: What is graft-versus-host disease?
Donor T cells attack recipient tissues, Occurs mainly in bone marrow / HSCT, Potentially fatal complication
Requirements for GVHD
Front: What three conditions are required for GVHD?
Graft contains immunocompetent T cells
The donor and the recipient are HLA-incompatible
The recipient is immunocompromised
Target Organs in Acute GVHD
Front: What organs are primarily affected in acute GVHD?
Skin: Rash, Liver: Jaundice, GI tract: Severe diarrhoea
Transfusion-Associated GVHD (TA-GVHD)
Front: How is transfusion-associated GVHD prevented?
By irradiating blood products
Destroys donor T-cell DNA
Prevents T-cell proliferation in the recipient
What is Panel Reactive Antibody (PRA)?
The measure of the percentage of HLA antibodies in a patient
High PRA = highly sensitised patient
Makes finding a compatible donor difficult