MCAT Biology - The Immune System
1/101
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
immune system
contain and eliminate infections
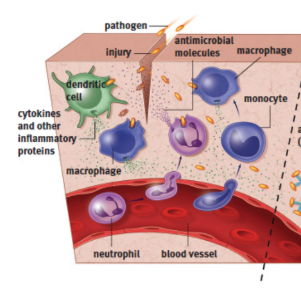
Innate/nonspecific immunity
defenses that are always active against infection, but lack the ability to target specific invaders; acts near entry points into the body
Adaptive/specific immunity
defenses that target a specific pathogen; slower to act, but can maintain immunological memory of an infection to mount a faster attack in subsequent infections
bone marrow
produces leukocytes through the process of hematopoiesis
leukocytes (white blood cells)
participate in the immune system
spleen
location of blood storage and activation of B-cells
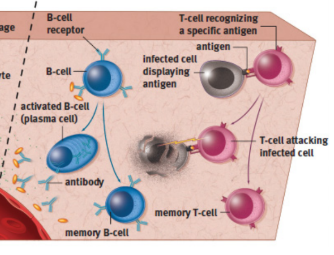
B-cells
turn into plasma cells to produce antibodies as part of adaptive immunity; binding of antigen causes activation
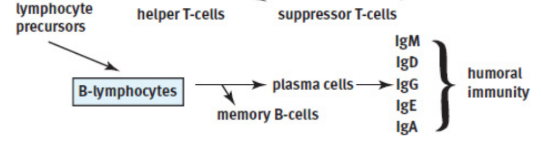
plasma cells
produce antibodies
humoral immunity
antibodies dissolve and act in the blood rather than within cells; driven by B-cells and antibodies
T-cells
coordinate the immune system and directly kill virally infected cells
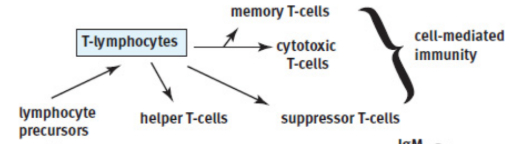
cell-mediated immunity
T-cells
thymus
a small gland just in front of the pericardium, the sac that protects the heart; matures T-cells
lymph nodes
major component of the lymphatic system; provide a place for immune cells to communicate and mount an attack; can activate B-cells
gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
Other immune tissue found in close proximity to the digestive system, which is a site of potential invasion by pathogens
tonsils
gut-associated lymphoid tissue in the throat
adenoids
gut-associated lymphoid tissue in the sinus
Peyer’s patches
gut-associated lymphoid tissue in the small intestine
appendix
contains lymphoid aggregates; attached to cecum
hematopoiesis
development and differentiation of blood cells
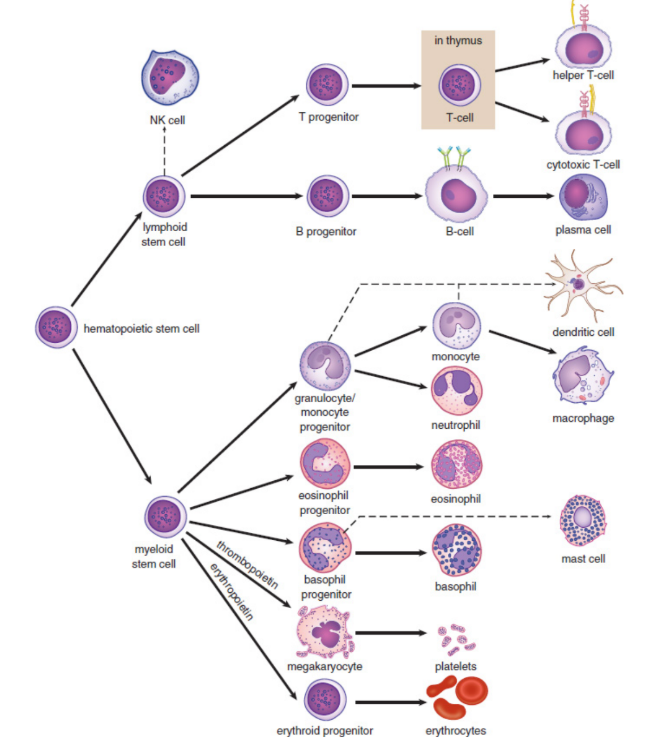
hematopoietic stem cells
make leukocytes and other blood cells
granulocytes
leukocytes containing granules
agranulocytes
leukocytes not containing granules
granules
contain toxic enzymes and chemicals, which can be released by exocytosis, and are particularly effective against bacterial, fungal, and parasitic pathogens
neutrophils
type of phagocytic white blood cell; part of innate immunity; form the most abundant type of granulocytes; very short lived (~5 days); target bacteria via chemotaxis/opsonisation; stained by neutral dyes
eosinophils
type of white blood cell; part of innate immunity; bright red-orange granules; combat parasites and infections; release large amounts of histamine; associated with allergies; stained by acidic dyes
basophils
type of white blood cell; part of innate immunity; large purple granules; responsible for inflammatory responses; the least populous leukocyte; associated with allergies; stained by basic dyes
lymphocytes
responsible for antibody production, immune system modulation, and targeted killing of infected cells
Monocytes
phagocytic cells in the bloodstream
macrophages
monocytes in tissues; phagocytizes the invader through endocytosis, digests the invader using enzymes, presents little pieces of the invader (mostly peptides) to other cells using MHC; release cytokines
microglia
macrophages in nervous system
Langerhans cells
macrophages in skin
osteoclasts
macrophages in bone
skin (integument)
provides a physical barrier between the outside world and our internal organs, preventing most bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites from entering the body
defensins
antibacterial enzymes found on the skin
Sweat
antimicrobial properties
mucous membranes
lined with cilia to trap particulate matter; prevent bacteria and viruses from gaining access to sensitive tissues; respiratory system - push it up toward the oropharynx, where it can be swallowed or expelled
lysozyme
nonspecific bacterial enzyme secreted in tears and saliva
stomach
secretes acid, resulting in the elimination of most pathogens
gut/GI tract
colonized by bacteria that lack the necessary characteristics to cause infection; potential invaders are not able to compete with large population and are thus kept at bay
complement sytem
consists of a number of proteins in the blood that act as a nonspecific defense against bacteria; punch holes in the cell walls of bacteria, making them osmotically unstable
classical pathway
requires the binding of an antibody to a pathogen to activate complements
alternative pathway
does not require antibodies to activate complements
interferons
proteins that prevent viral replication and dispersion produced by cells that have been infected with viruses; cause nearby cells to decrease production of both viral and cellular proteins; decrease the permeability of these cells; upregulate MHC class I and class II molecules, resulting in increased antigen presentation and better detection of the infected cells by the immune system; responsible for many “flu-like” symptoms that occur during viral infection, including malaise, tiredness, muscle soreness, and fever
resident population
permanent, rather than transient, cell group of macrophages in the tissue
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
binds to antigen and carries it to the cell surface, where it can be recognized by cells of the adaptive immune system;
antigen
a substance (usually a pathogenic protein) that can be targeted by an antibody
cytokines
chemical substances that stimulate inflammation and recruit additional immune cells to the area
MHC class I
All nucleated cells in the body; Any protein produced within a cell can be loaded and presented on the surface; allows the immune system to monitor the health of these cells and to detect if the cells have been infected with a virus or another intracellular pathogen; infected cells can then be killed by cytotoxic T-cells to prevent infection
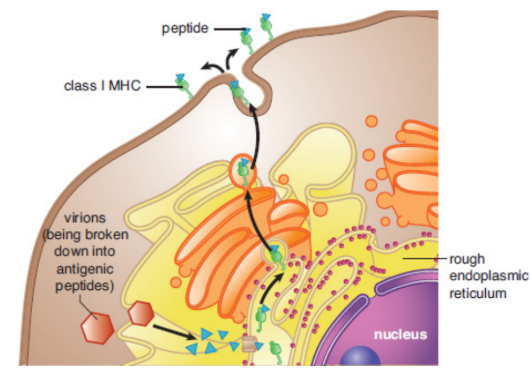
endogenous pathway
MHC-I pathway; binds antigens that come from inside the cell
MHC class II
mainly displayed by professional antigen-presenting cells; presentation may result in the activation of both the innate and adaptive immune systems
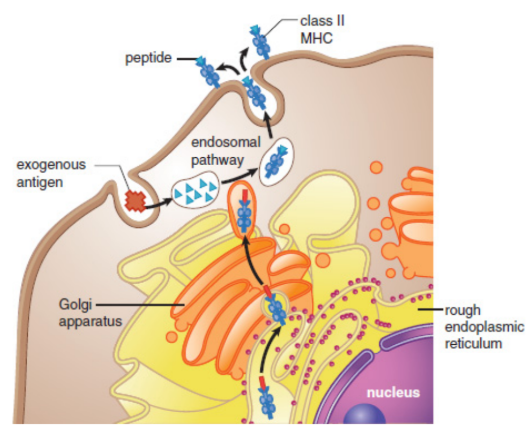
professional antigen-presenting cells
phagocytic cells pick up pathogens from the environment, process them, and then present them
macrophages, dendritic cells in the skin, some B-cells, and certain activated epithelial cells
exogenous pathway
MHC-II pathway; antigens originated outside the cell
pattern recognition receptors (PRR),
special receptors on macrophages and dendritic cells that recognize the category of the invader (bacterium, virus, fungus, or parasite); allows for the production of appropriate cytokines to recruit the right type of immune cells
toll-like receptors (TLR)
class of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes, commonly known as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
Natural killer (NK) cells
nonspecific lymphocyte able to detect the downregulation of MHC and induce apoptosis in these virally infected cells; also target cancer cells that can also downregulate MHC production
opsonized
marked with an antibody from a B-cell
pus
dead neutrophil collections as result of infection
histamine
inflammatory mediator leading to inflammation
inflammation
vasodilation and increased leakiness of the blood vessels, allowing additional immune cells (especially macrophages and neutrophils) to move out of the bloodstream and into the tissue; particularly useful against extracellular pathogens
mast cells
closely related to basophils, but have smaller granules and exist in the tissues, mucosa, and epithelium; release large amounts of histamine in response to allergens, leading to inflammatory responses
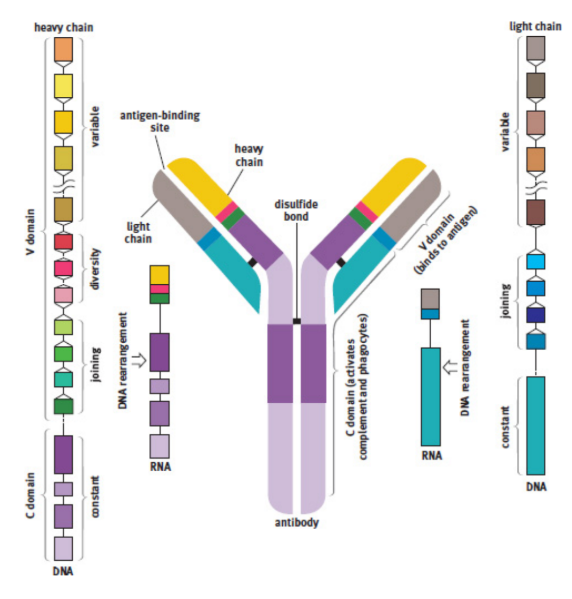
antibodies / immunoglobulins [Ig]
produced by B-cells; present on the surface of a cell or secreted into body fluids; binds to antigens; Y-shaped molecules; five different isotypes (IgM, IgD, IgG, IgE, and IgA)
agglutinate
cause pathogens to clump together; forming large insoluble complexes that can be phagocytized
degranulation
exocytosis of granule contents; antigen binds to antibodies on the surface of a mast cell; releasing histamine and causing an inflammatory allergic reaction
heavy chains
inner part of antibody linked to C domain
light chains
outer part of antibody bonded by disulfide linkages and noncovalent interactions to the larger part
antigen-binding region
specific polypeptide sequences that will bind one, and only one, specific antigenic sequence at the tips of the Y
variable region (domain)
part of the antibody that changes in each type of antibody
variable region (domain)
each B-cell changes its antigen-binding region, trying to find the best match for the antigen
clonal selection
mechanism for generating antibody specificity
constant region (domain)
region that cells such as natural killer cells, macrophages, monocytes, and eosinophils have receptors for, and that can initiate the complement cascade
isotype switching
Cells can change which isotype of antibody they produce when stimulated by specific cytokines
naïve B-cells
have not yet been exposed to an antigen
Plasma cells
daughter B-cell; produce large amounts of antibodies; eventually die
memory B-cells
daughter B-cell; stay in the lymph node, awaiting reexposure to the same antigen; may last the lifetime of the organism
primary response
initial activation of B-cells takes approximately seven to ten days
secondary response
if same microbe is ever encountered again, the memory cells rapidly proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells to produce antibodies specific to that pathogen
vaccination
biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease; prophylactic (pre-infection) or therapeutic (post-infection)
Positive selection
allowing only the maturation of cells that can respond to the presentation of antigen on MHC
Negative selection
causing apoptosis in cells that are self-reactive
thymosin
a peptide hormone secreted by thymic cells that fosters maturation of T-cells
Helper (Th)/CD4+ T-cells
coordinate the immune response by secreting chemicals known as lymphokines; respond to antigens presented on MHC-II molecules; most effective against bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections
lymphokines
capable of recruiting other immune cells (such as plasma cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and macrophages) and increasing their activity
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
causes loss of helper T-cells; prevents the immune system from mounting an adequate response to infection
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
advanced HIV infection; even weak pathogens can cause devastating consequences as opportunistic infections
Cytotoxic T-cells (Tc) / CD8+ T-cells (CTL)
capable of directly killing virally infected cells by injecting toxic chemicals that promote apoptosis into the infected cell; respond to antigens presented on MHC-I molecules; most effective against viral (and intracellular bacterial or fungal) infections
Suppressor / regulatory T-cells (Treg)
express CD4 and Foxp3; help to tone down the immune response once infection has been adequately contained
self-tolerance
turn off self-reactive lymphocytes to prevent autoimmune diseases
memory T-cells
lie in wait until the next exposure to the same antigen until they carry out a more robust and rapid response
Self-antigens
proteins and carbohydrates present on the surface of every cell of the body; signal to immune cells that the cell is not foreign and should not be attacked
autoimmunity
immune system attacks cells expressing particular self-antigens
hypersensitivity reactions
immune systems are hypersensitive to antigens that are not inherently threating and become overactivated when these antigens are encountered; allergies and autoimmunity
glucocorticoids
modified versions of cortisol; potent immunosuppressive qualities
active immunity
immune system is stimulated to produce antibodies against a specific pathogen
ex. infection, prophylactic vaccine
Passive immunity
transfer of antibodies to an individual
ex. fetal immunity, infant immunity
lymphatic system
type of circulatory system; equalizes of Fluid Distribution; transports biomolecules; immunity
lymph / lymphatic fluid
fluid leaked from blood vessels that is picked up and circulated by lymphatic system
thoracic duct
connection of lymphatic and cardiovascular system; delivers the fluid into the left subclavian vein near the heart in the posterior chest
Lymph nodes
small, bean-shaped structures along the lymphatic vessels; contain a lymphatic channel, as well as an artery and a vein; provide a space for the cells of the immune system to be exposed to possible pathogens
edema
swelling due to fluid collecting in tissue; when lymphatics are overwhelmed
Lacteals
small lymphatic vessels; located at the center of each villus in the small intestine; fats, packaged into chylomicrons by intestinal mucosal cells travel through