Organic Chemistry Fundamentals
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is Ms. Giovannone's first lesson for Structure 3.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Organic Chemistry
field of chemistry where carbon-based compounds are studied
since carbons have 4 valence electrons, they can form 4 covalent bonds allowing for catenation
makes it a big field of study
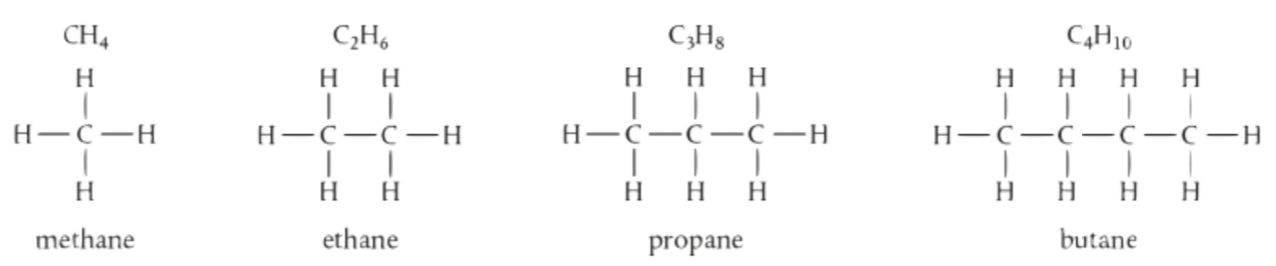
Homologous Series
a family of compounds with similar structures and reactivities due to sharing the same functional groups
they have the same general formula except for one -CH₂ group
Members of a homologous series have a graduation in physical properties
Members have similar chemical properties
Example of Homologous Series
Functional Groups
an atom, or group of atoms, that give compounds their unique physical or chemical properties
site of reactivity
all organic compounds are divided into classes dependent on the functional group present
Ways to Describe an Organic Molecule
Chemical Formula
Nomenclature

How Nomenclature is determined
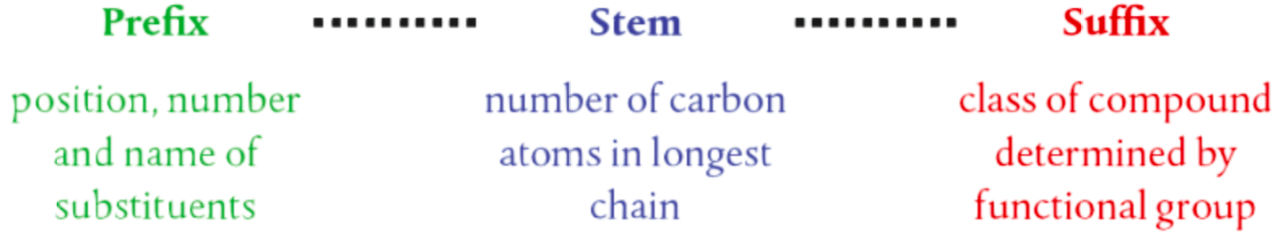
Types of Formulas
Empirical Formula
simplest ratio of atoms in a molecule eg. C2H6 —> CH3
Molecular Formula
Molecular formula - actual number of atoms in a molecule
Problem:
no structure can be deduced from this information
What are Structural Formulas and what are their names?
Full/Graphic/Displayed
Condensed
Skeletal/Line
Stereochemical
What are Full/Graphic/Displayed Structural Formulas?
2D representations of compounds with all carbons, bonds, and positions relative to one another
What are Condensed Structural Formulas?
all atoms and their relative positions present with some or all bonds not displayed (if bonds can be assumed)
some atoms may be grouped together (e.g. CH₃)
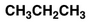
What are Condensed Structural Formulas?
simplest form
each vertex or end of line is a C
What are Stereochemical Structural Formulas?
Shows relative positions of atoms or groups in 3D
How can Covalent Bonds be represented?
