11- Magnetic field and moving charges
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is the Lorentz Force?
The force exerted on a moving charge by a magnetic field,
q is the charge
v⃗ is velocity
B⃗ is the magnetic field.
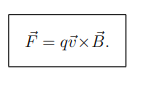
How is the direction of the Lorentz force determined?
By the right-hand rule:
Thumb points in direction of v⃗ × B⃗
If q is positive, F⃗ is in the same direction as v⃗ × B⃗
If q is negative, F⃗ is in the opposite direction
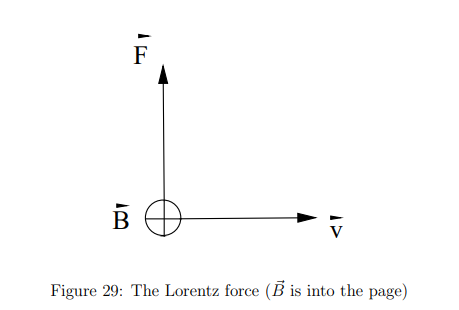
Why can't the Lorentz force change a particle’s speed?
Because it is always perpendicular to velocity v⃗, meaning it cannot do work or change kinetic energy—only the direction of motion.
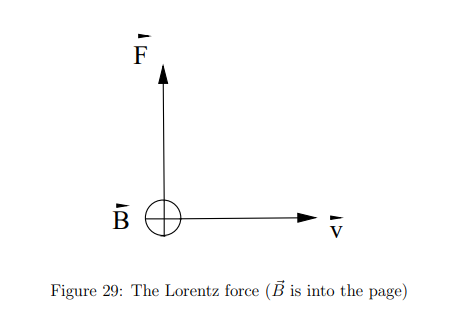
What is a Hall Probe?
A device that measures magnetic fields using the Hall effect
A voltage difference (Hall voltage, VH) is generated due to charge deflection by a magnetic field.
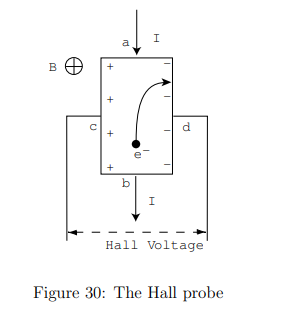
How does a Hall Probe work?
A current I flows through a semiconductor slab placed perpendicular to B⃗.
The Lorentz force deflects charge carriers, creating a charge separation and an internal electric field E⃗H that balances the force.
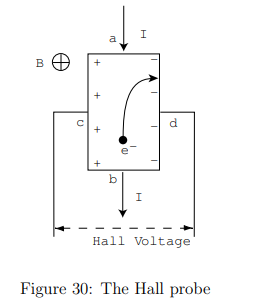
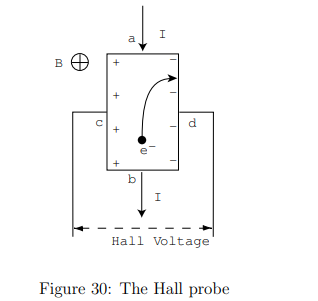
What is the Hall voltage equation?
kH = Hall coefficient (material-dependent)
I = Current through the sample
B = Magnetic field strength
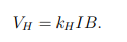
What is the force on a charge in simultaneous electric and magnetic fields?
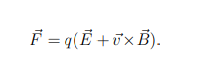
How can the net force on a charge be zero in combined E⃗ and B⃗ fields?
If E⃗ and B⃗ are perpendicular, the charge moves at a velocity v where electric and magnetic forces cancel, leading to F⃗ = 0.
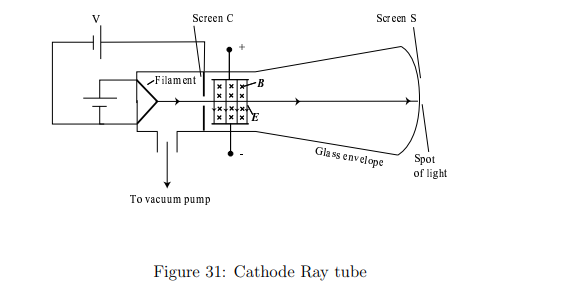
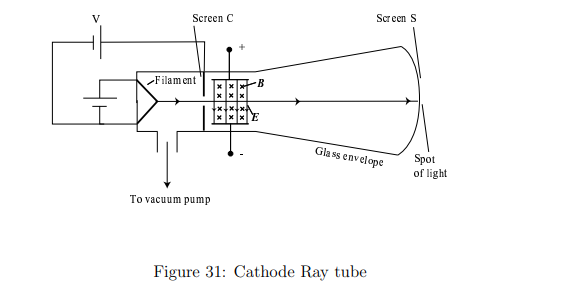
What experimental setup did J.J. Thomson use to discover the electron?
A cathode ray tube with a beam of charged particles passing through crossed electric (E⃗) and magnetic (B⃗) fields
This allowed him to control and measure their deflection.
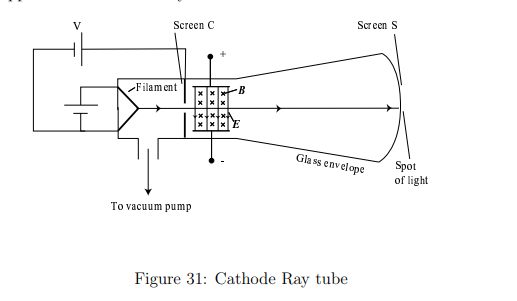
What were the key steps in Thomson’s experiment to discover and electron?
1. Set E = 0 and B = 0 and note the position of the spot on screen S due to undeflected beam.
2. Turn on E⃗ and measure the resulting beam deflection.
3. Maintaining E⃗ , now turn on B⃗ and adjust its value until the beam returns to the undeflected position ⇒ with the forces in opposition, they can be made to cancel