Visceral Anatomy - The Abdomen
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
right upper quadrant
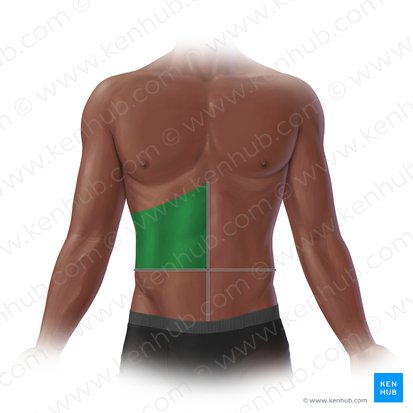
left upper quadrant
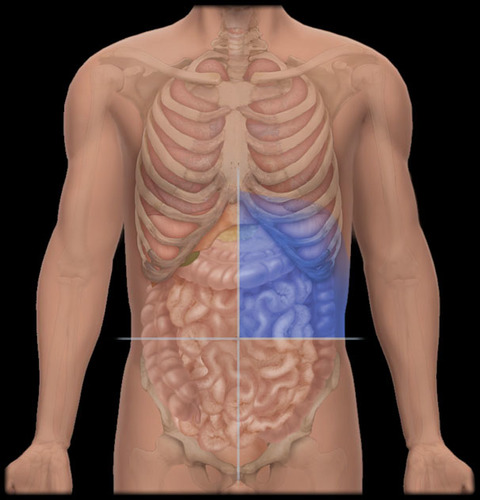
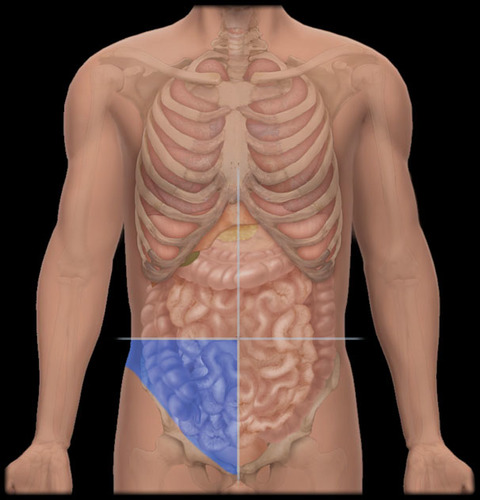
left lower quadrant
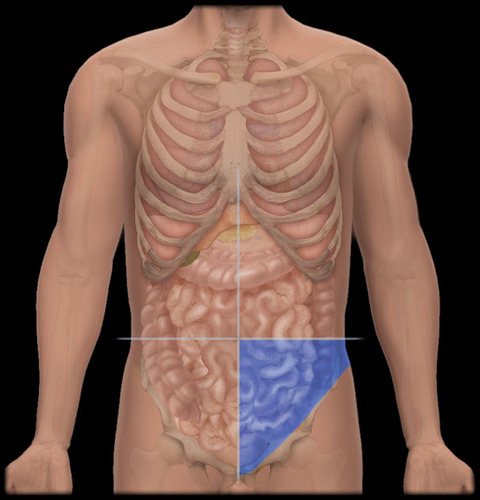
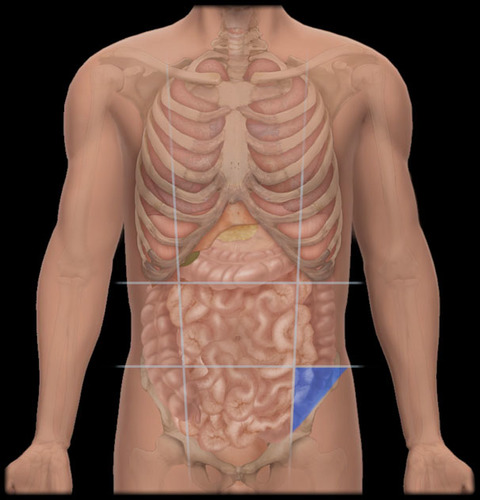
right lower quadrant
epigastric region
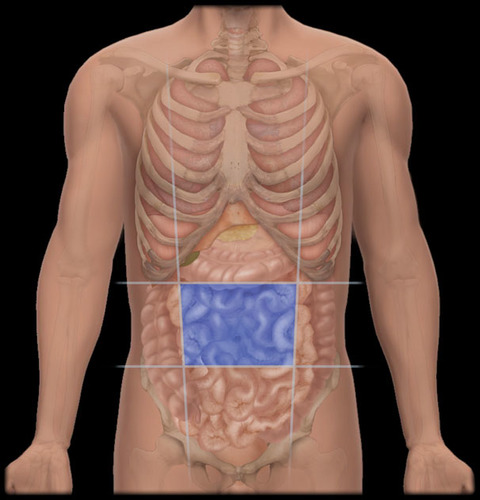
umbilical region
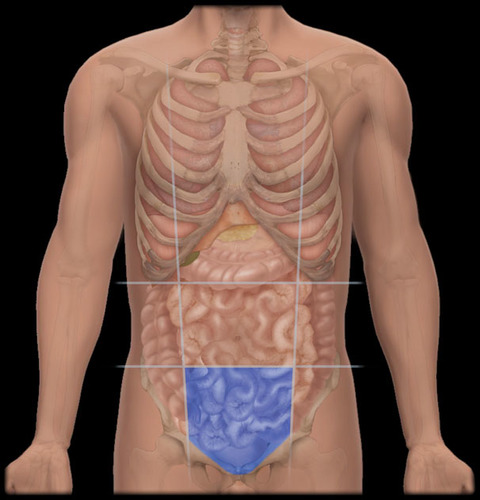
hypogastric region
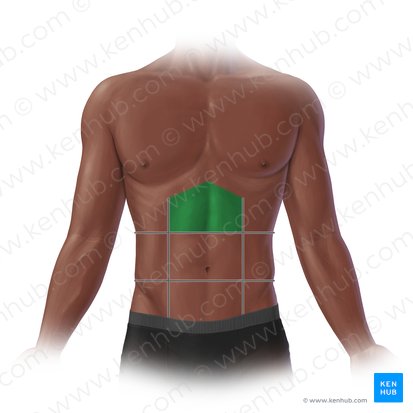
right hypochondriac region
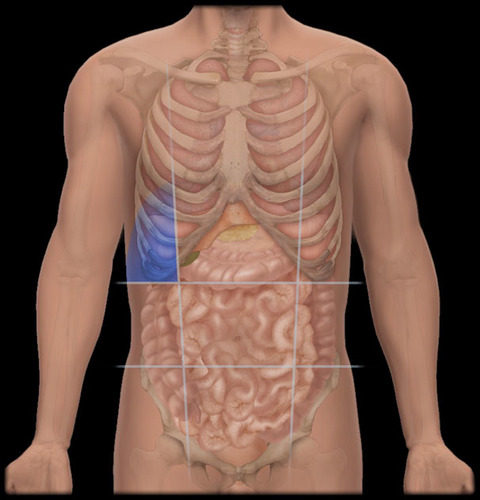
left hypochondriac region
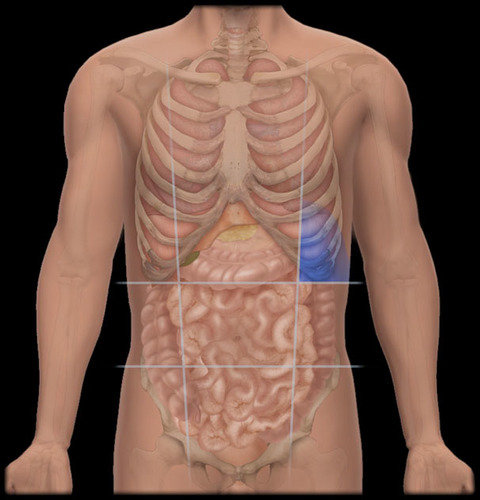
right lumbar region
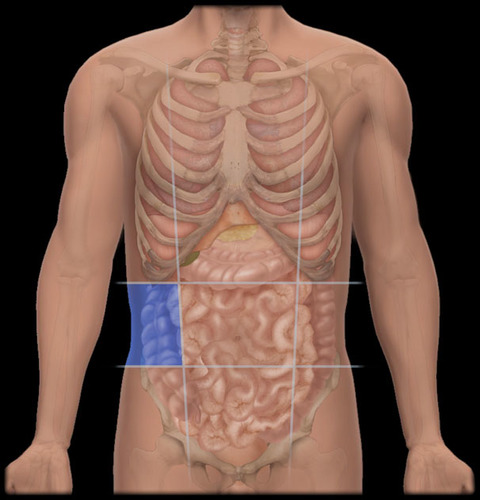
left lumbar region
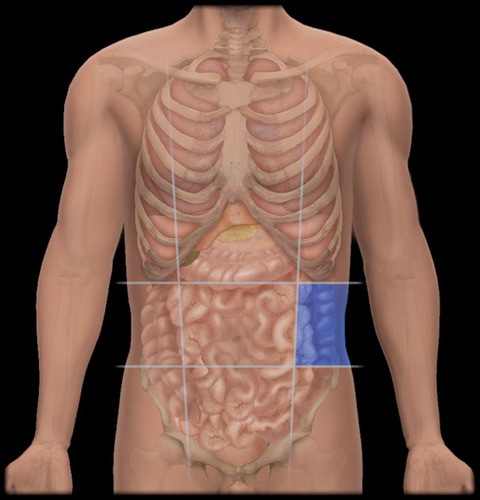
right inguinal region
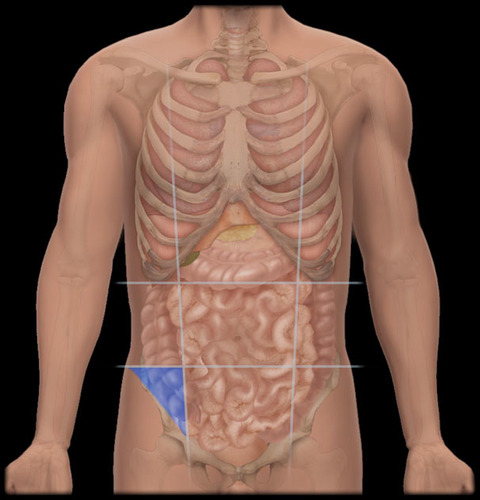
left inguinal region
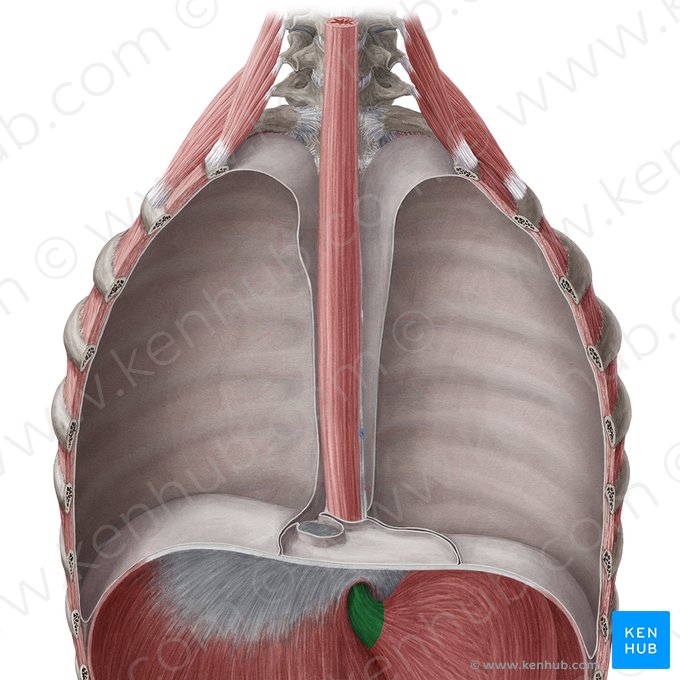
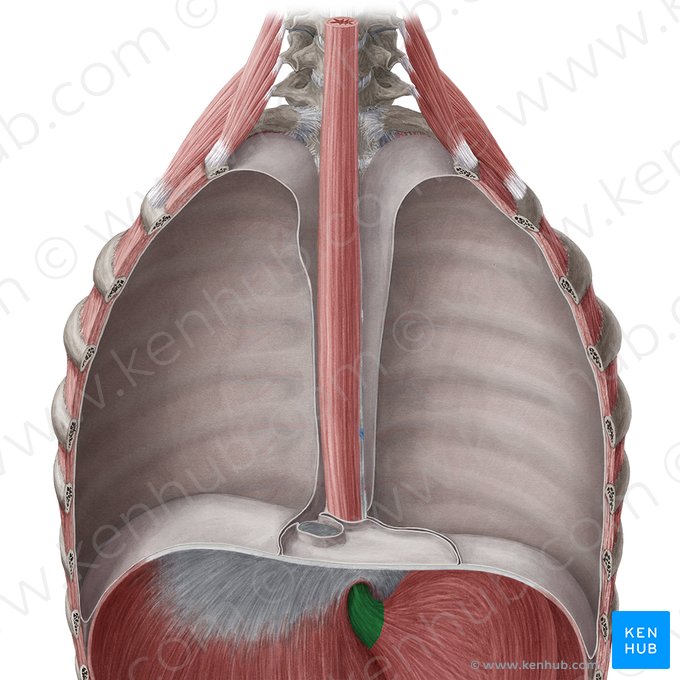
abdominal esophagus
passes through esophageal hiatus in diaphragm at the T10 level
1.5 to 2.5 cm long
connects to stomach (terminates) at cardiac orifice of the stomach (posterior to the 7th costal cartilage on the left)
lies on the horizontal plane that passes approximately through tip of the xyphoid process
fits into a groove on the visceral or posterior surface of the liver
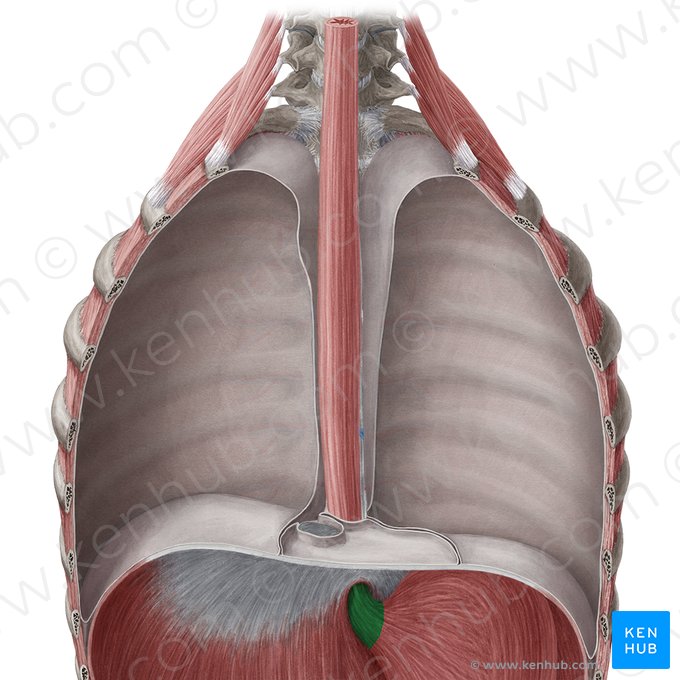
region
retroperitoneal
Is the abdominal esophagus intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal?
foregut
Is the abdominal esophagus a part of the foregut, midgut, or hindgut?
celiac trunk
arterial supply of the abdominal esophagus
swallowing
function of the abdominal esophagus
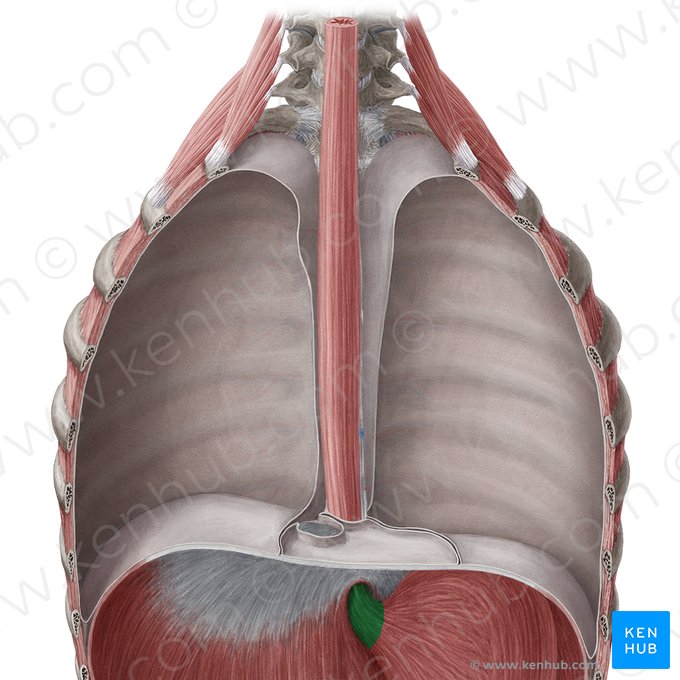
deglutition
What is another term for swallowing?
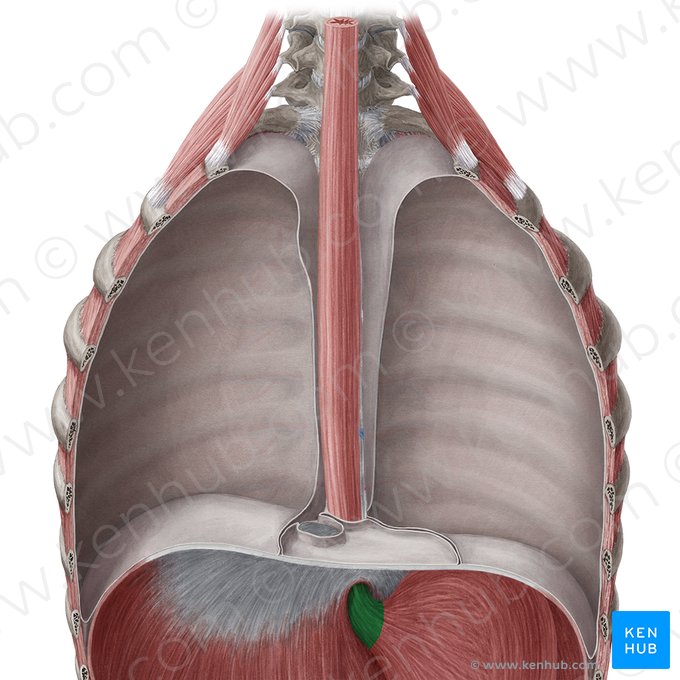
hiatal hernia
pathology of abdominal esophagus
stomach
a muscular, J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen
right and left upper quadrants
Which quadrants can the stomach be found in?
greater curvature of stomach
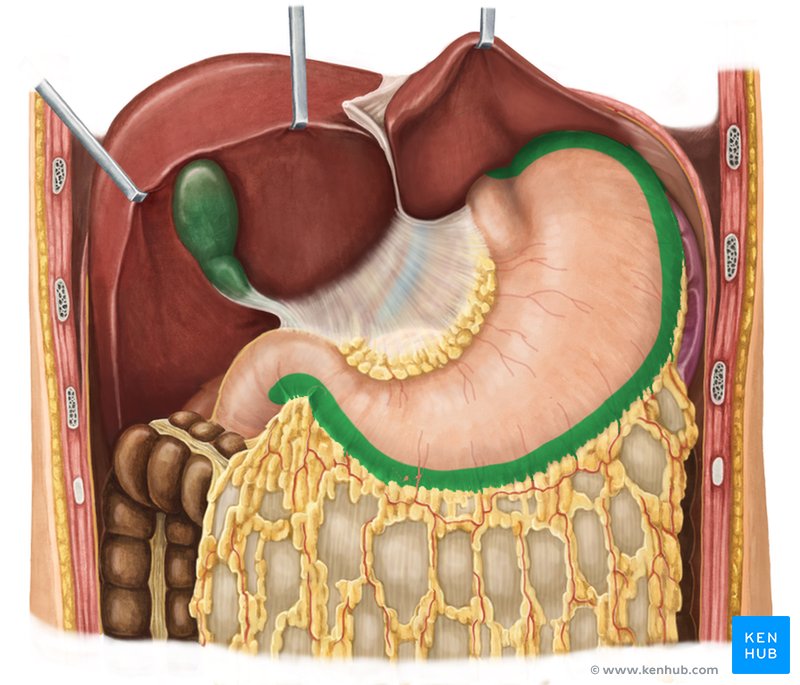
lesser curvature of stomach
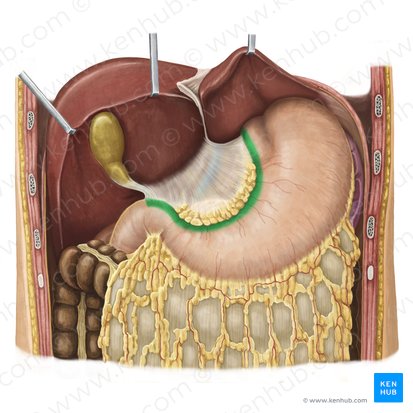
pylorus
aka “gatekeeper”
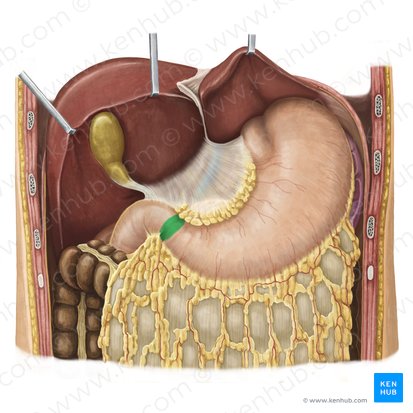
pyloric canal
What is another name for the pylorus?
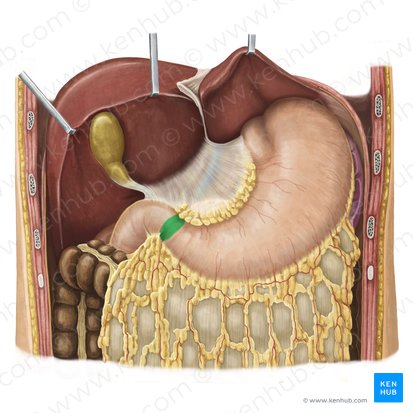
celiac trunk
arterial supply of stomach
stomach
Which organ has the following function:
stores food, mixes it with gastric secretions to form “chyme”
hiatal hernia
pathology of stomach
duodenum
the 1st part of the small intestine
right and left upper quadrants
Which quadrants can the duodenum be found in?
celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery
arterial supply of duodenum
small intestine
Which organ has the following function:
primary site for absorption of nutrients from ingested materials
celiac disease
pathology of duodenum
liver
accessory organ of the GI tract
largest and most vascular organ in the body
accounts for approximately 2.5% of adult body weight
falciform ligament
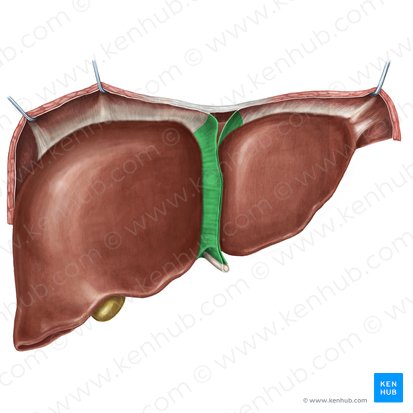
round ligament
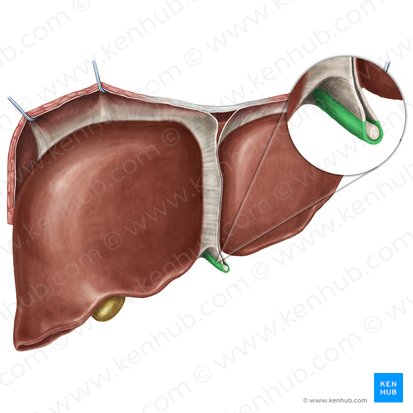
right and left upper quadrants
Which quadrants can the liver be found in?
celiac trunk
arterial supply of liver
liver
Which organ has over 500 functions, including the following:
storehouse for glycogen
forms and secretes bile (aids in emulsification of fat)
removes toxins from the body’s blood supply
hepatomegaly
pathology of liver
gallbladder
a sac located under the liver
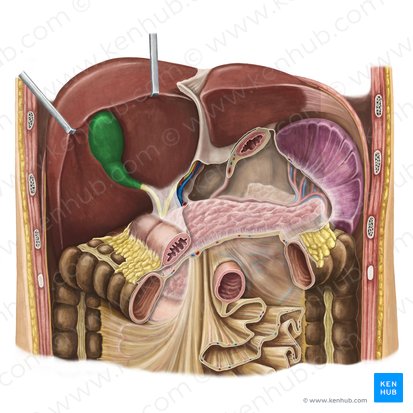
celiac trunk
arterial supply of gallbladder
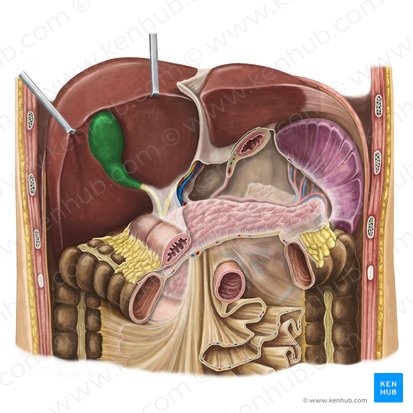
gallbladder
Which organ has the following function:
stores and concentrates bile by absorption of water
pathology of gall bladder
pancreas
a long, flat gland that lies in the abdomen behind the stomach
lies anterior to the L1-L3 vertebrae
tail - “tickles” the spleen
accessory digestive gland
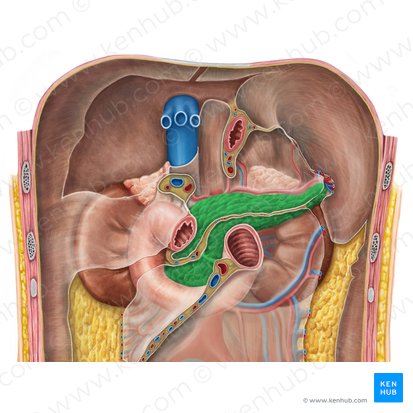
celiac trunk and superior mesenteric artery
arterial supply of pancreas
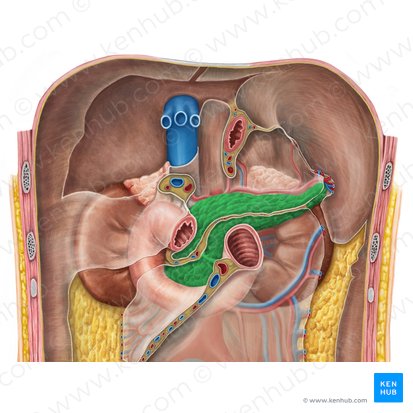
spleen
one of the most commonly injured organs in the abdomen (motor vehicle accidents, athletics, falls from heights, physical abuse)
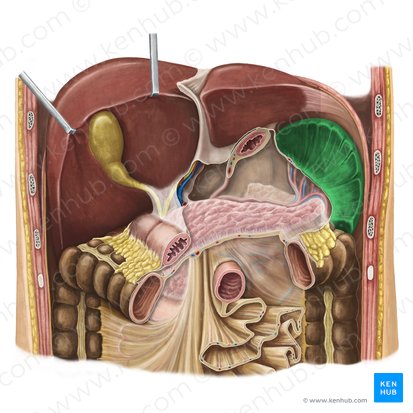
celiac trunk
arterial supply of spleen
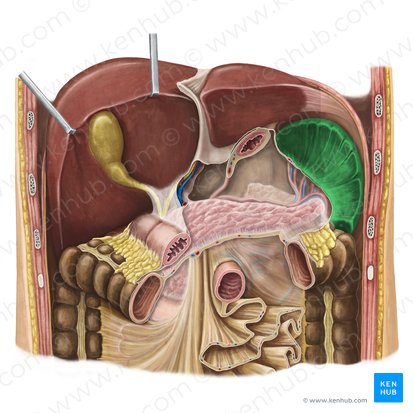
superior mesenteric artery
arterial supply of ileum and jejunum
celiac disease
pathology of ileum and jejunum
large intestine
cecum
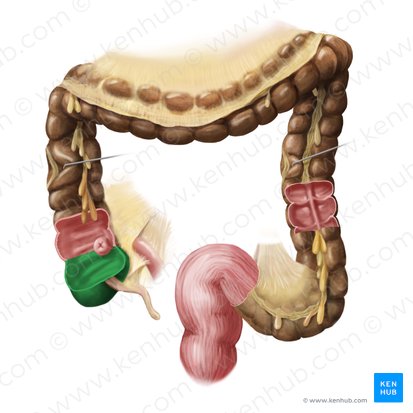
appendix
ascending colon
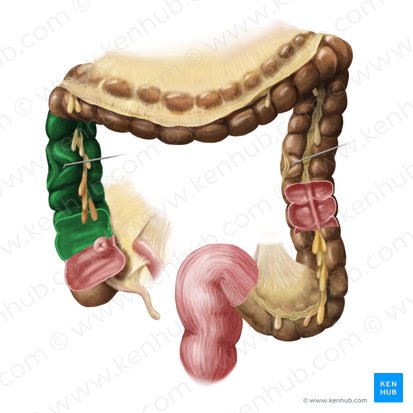
transverse colon
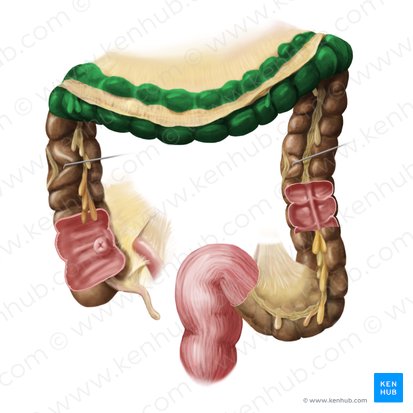
descending colon
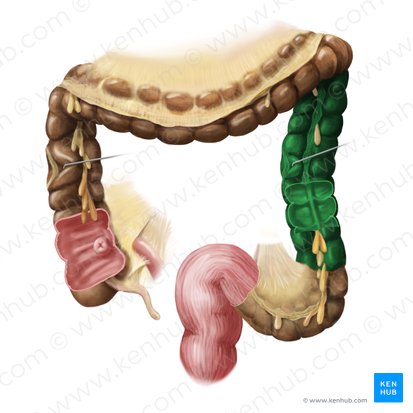
sigmoid colon
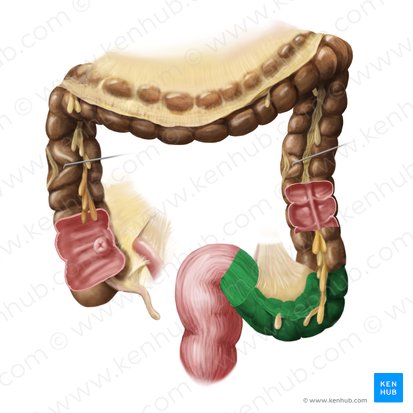
rectum
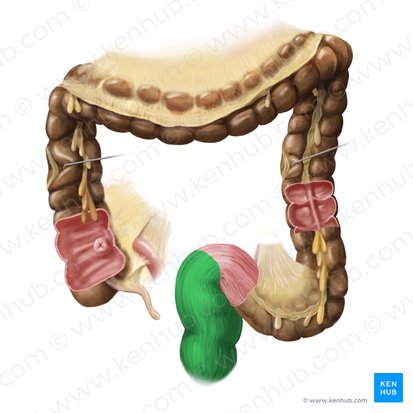
anal canal
superior mesenteric artery and inferior mesenteric artery
arterial supply of large intestine
appendicitis
pathology of large intestine
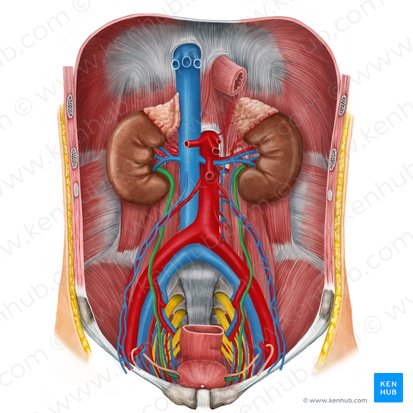
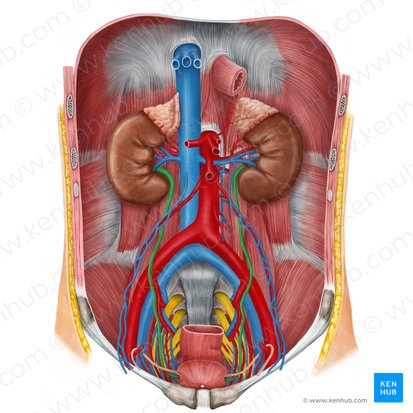
kidneys
protected by thoracic cage - 11th and 12th floating ribs
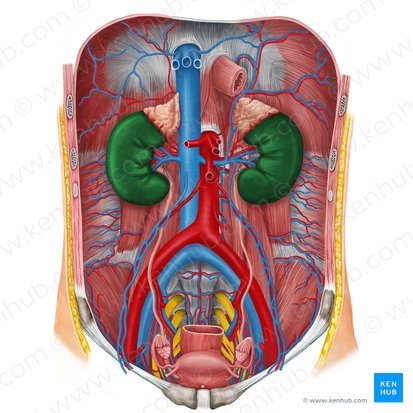
renal arteries
arterial supply of kidneys
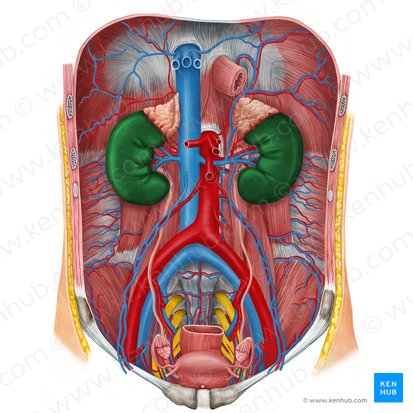
adrenal glands
lie on superomedial aspect of corresponding kidney at level of celiac trunk
suprarenal glands
What is another name for the adrenal glands?
renal arteries
arterial supply of adrenal glands
Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease
pathology of adrenal glands
ureters
two thick tubes which act to transport urine from the kidney to the bladder
abdominal portion: above pelvic brim; lies on psoas, courses anterior to genitofemoral nerve
pelvic portion: inferior to pelvic brim; cross common iliac or external iliac vessels
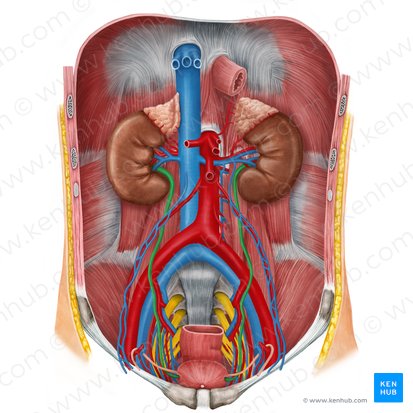
arterial supply of ureters
ureteral obstruction
pathology of ureters