Anatomy + Physiology - Bones of the Skull, Bone Structure, and Types of Bones
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
foramen magnum
big hole for spinal cord to exit skull
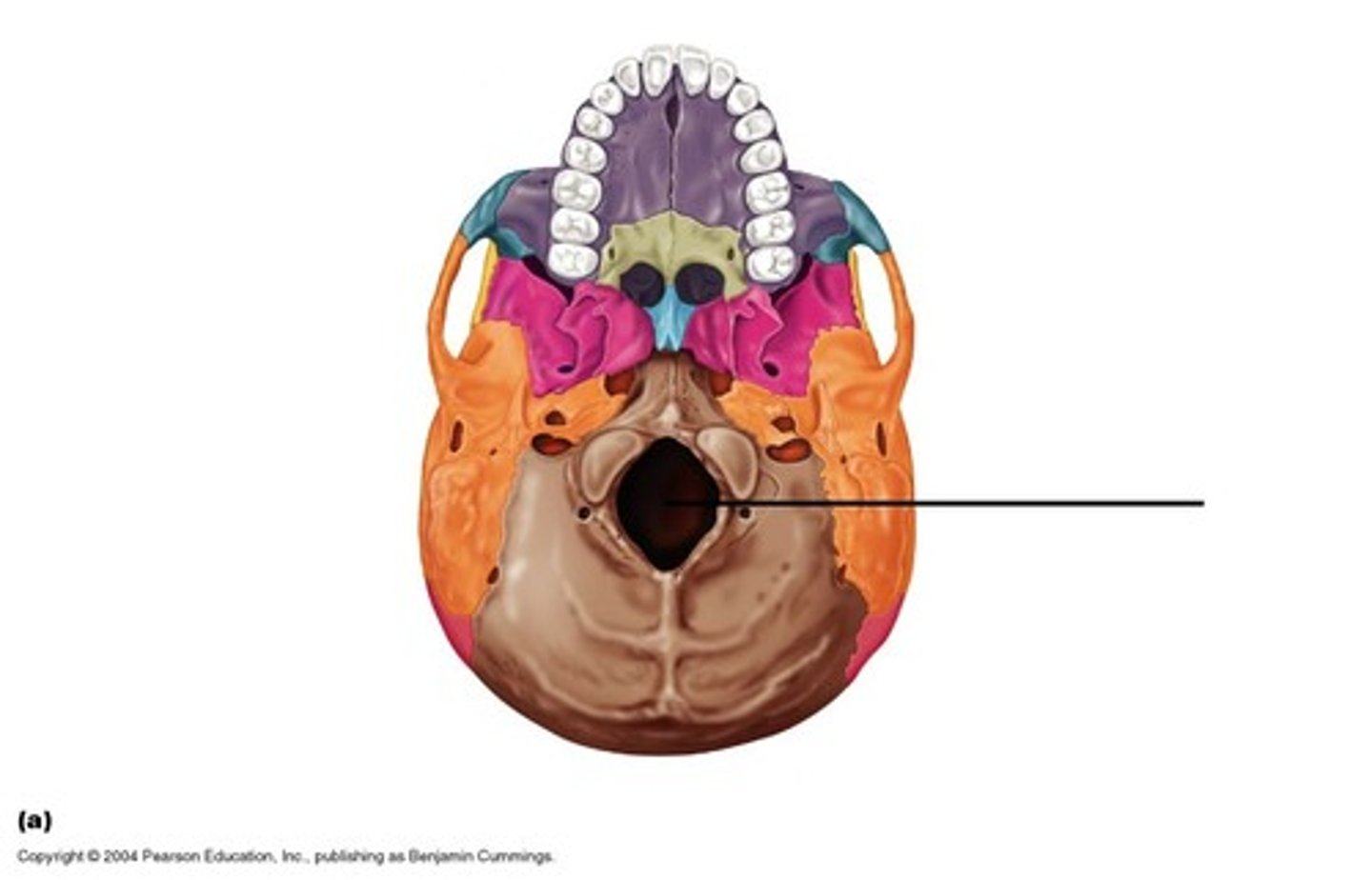
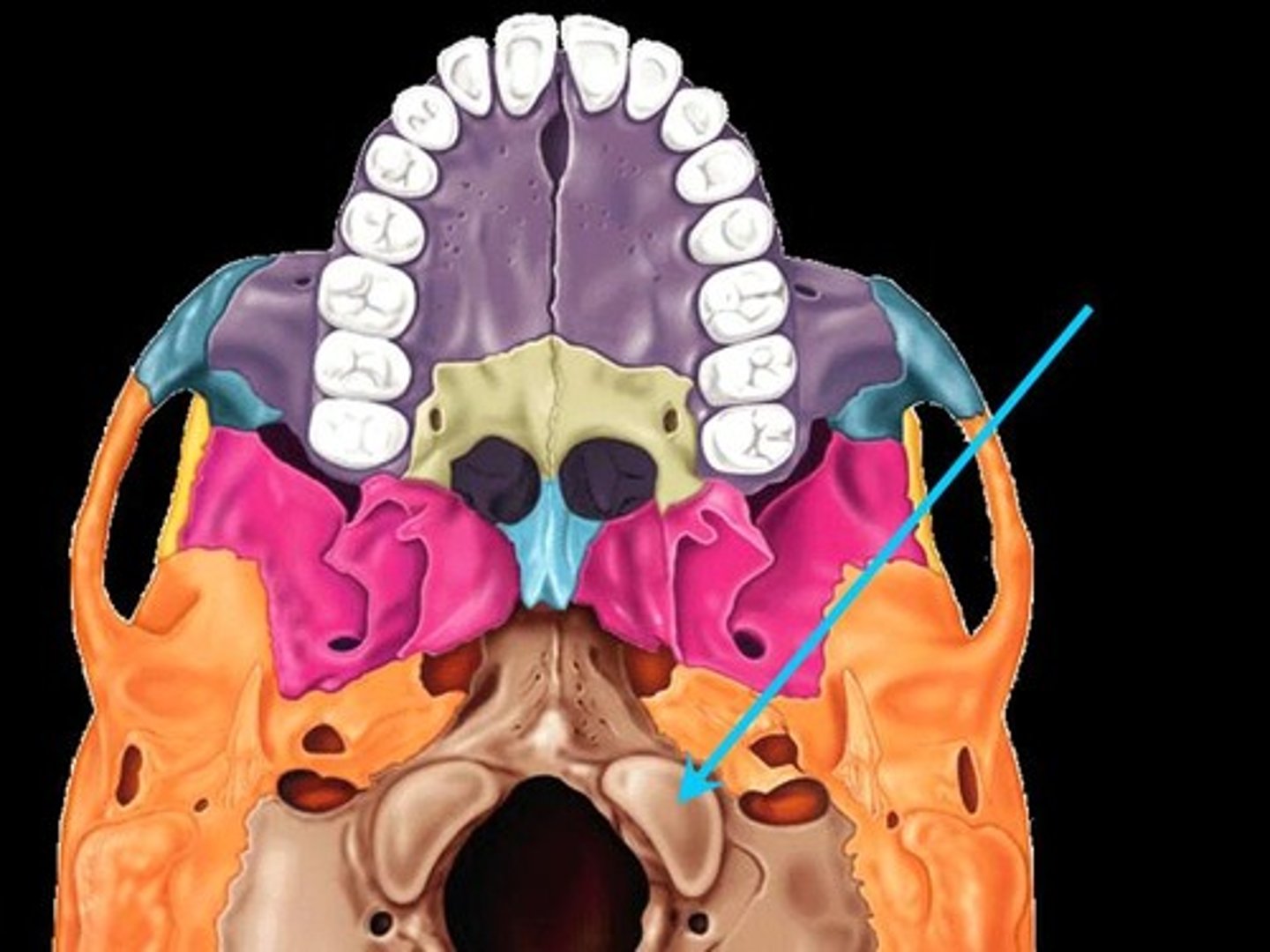
occipital condyles
where occipital bone attaches to atlas (C1 vertebrae, top of spine)
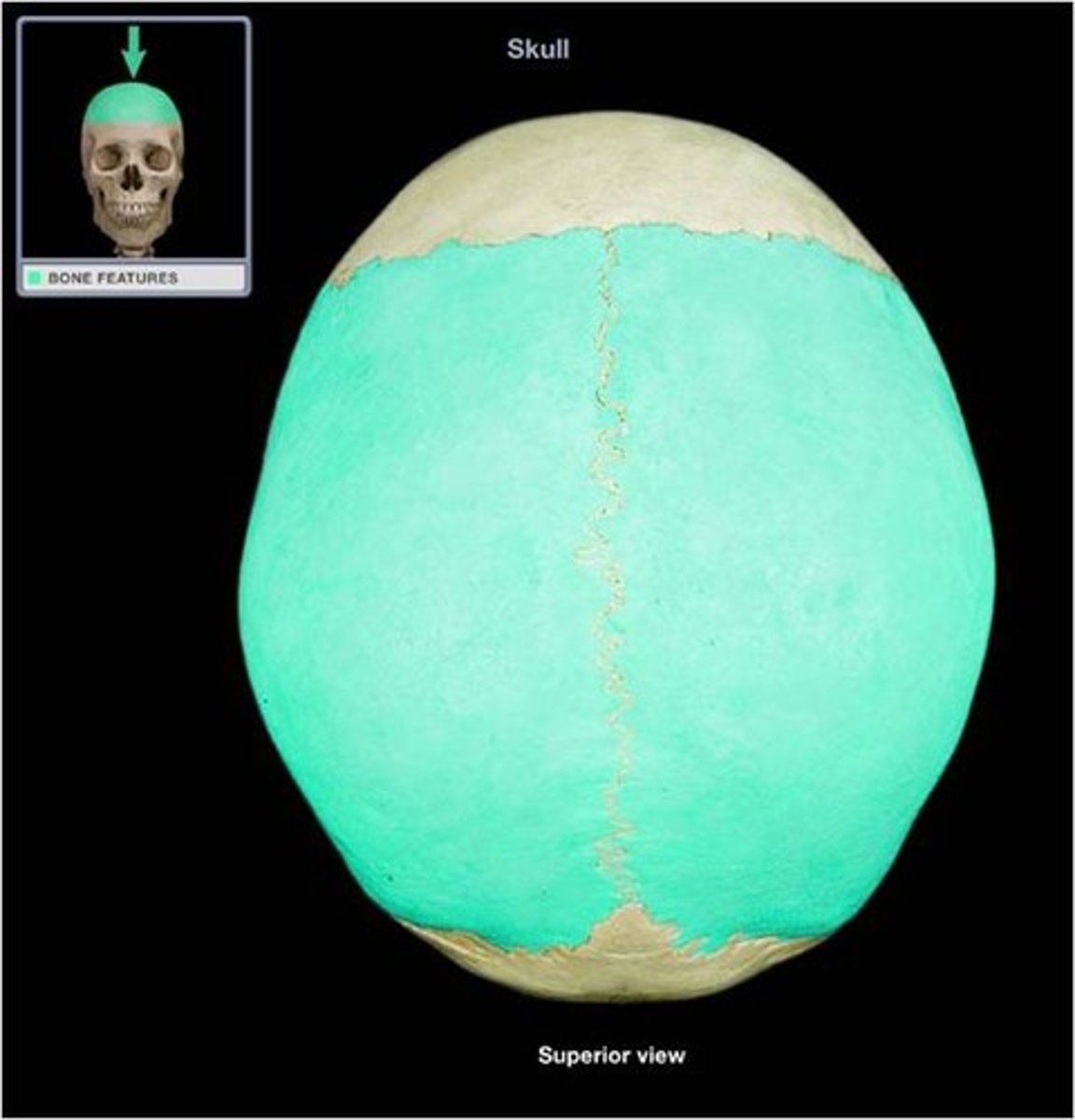
parietal
walls of the cranium
frontal
forehead bone, contains the glabella and the frontal sinus
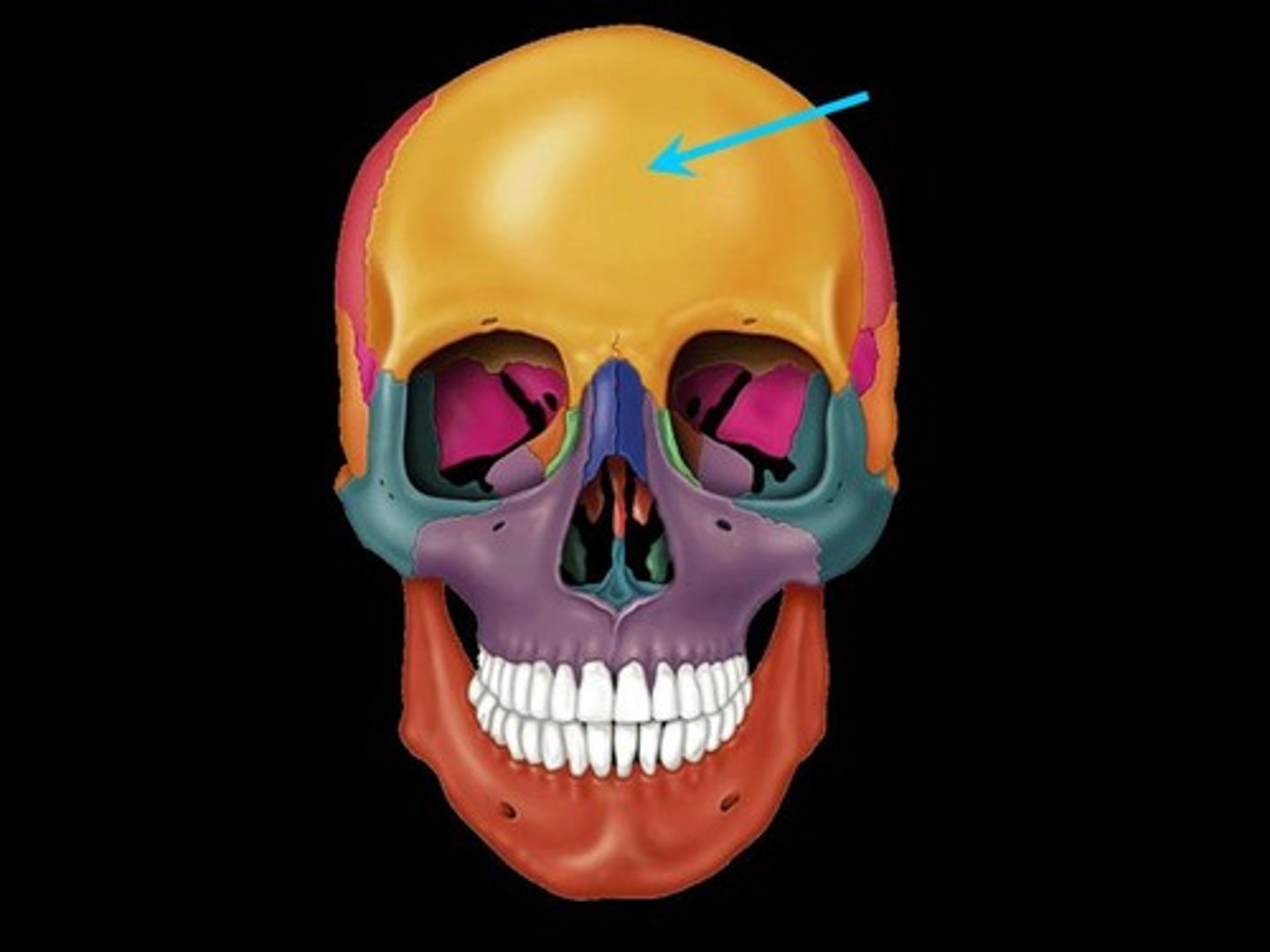
glabella
part medial to the eyes and superior to the nose
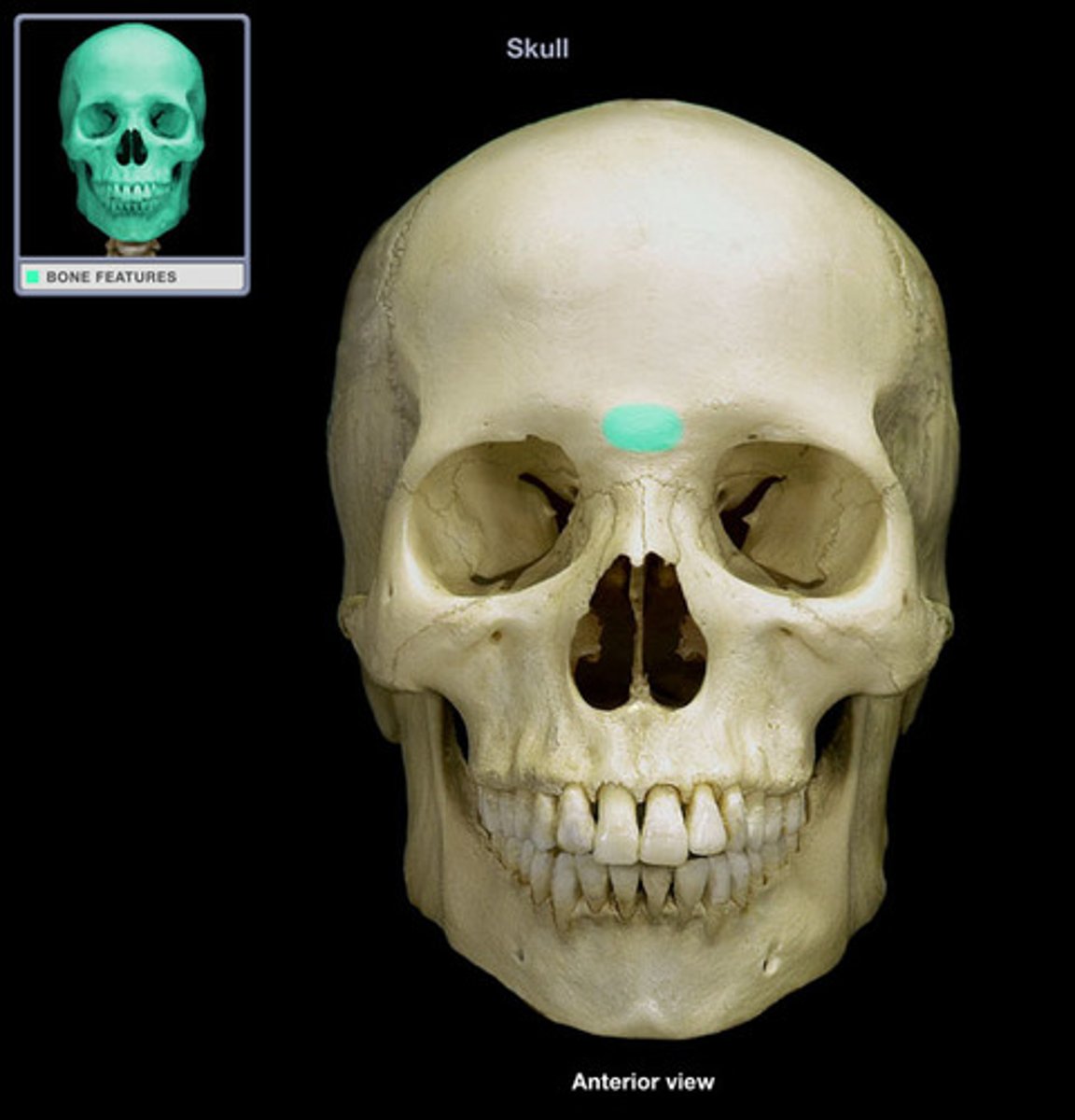
frontal sinus
part of nasal passages, completely inside the bone
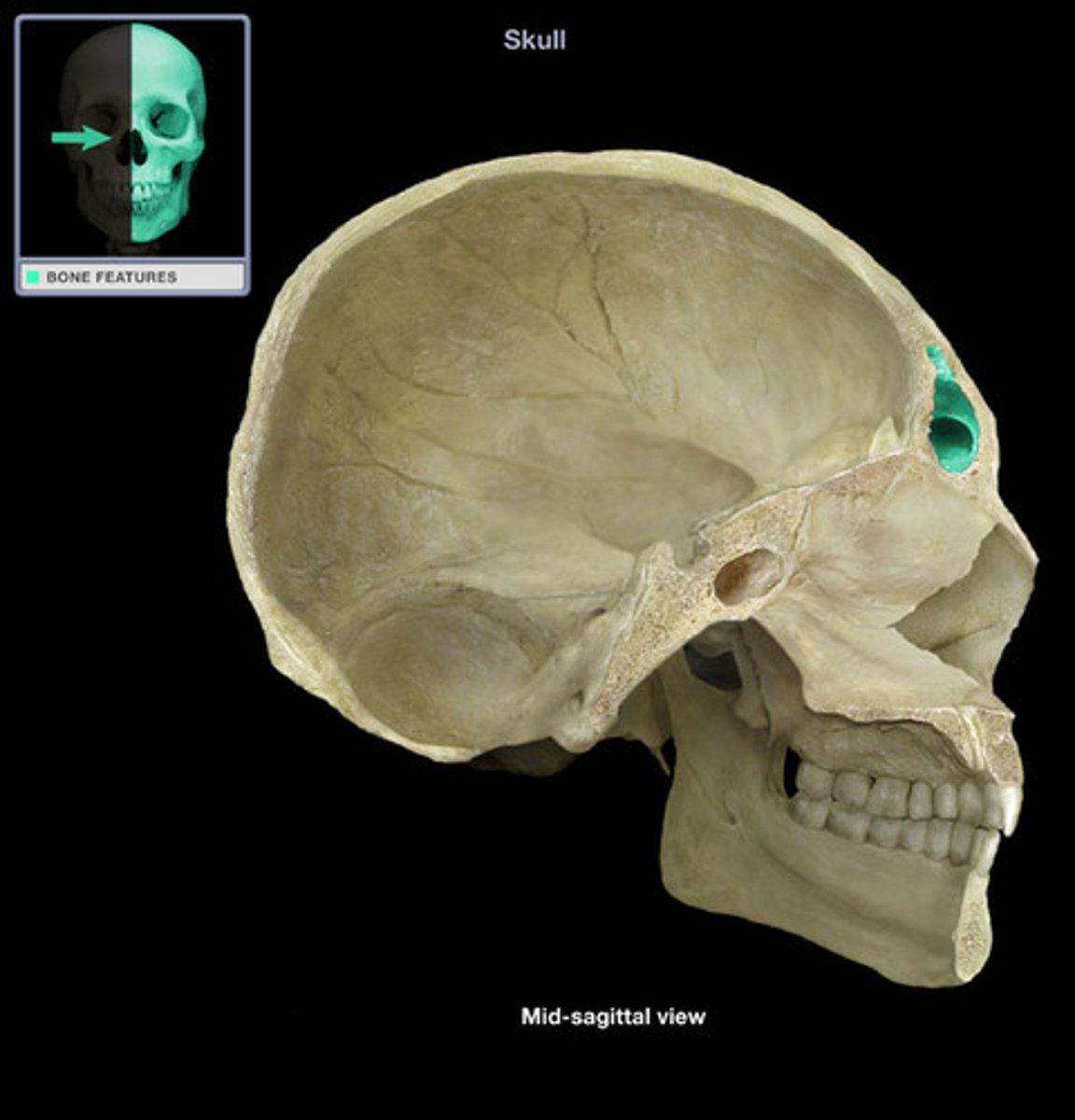
temporal
side of your head (along temple), contains mastoid process, styloid process, and external auditory meatus
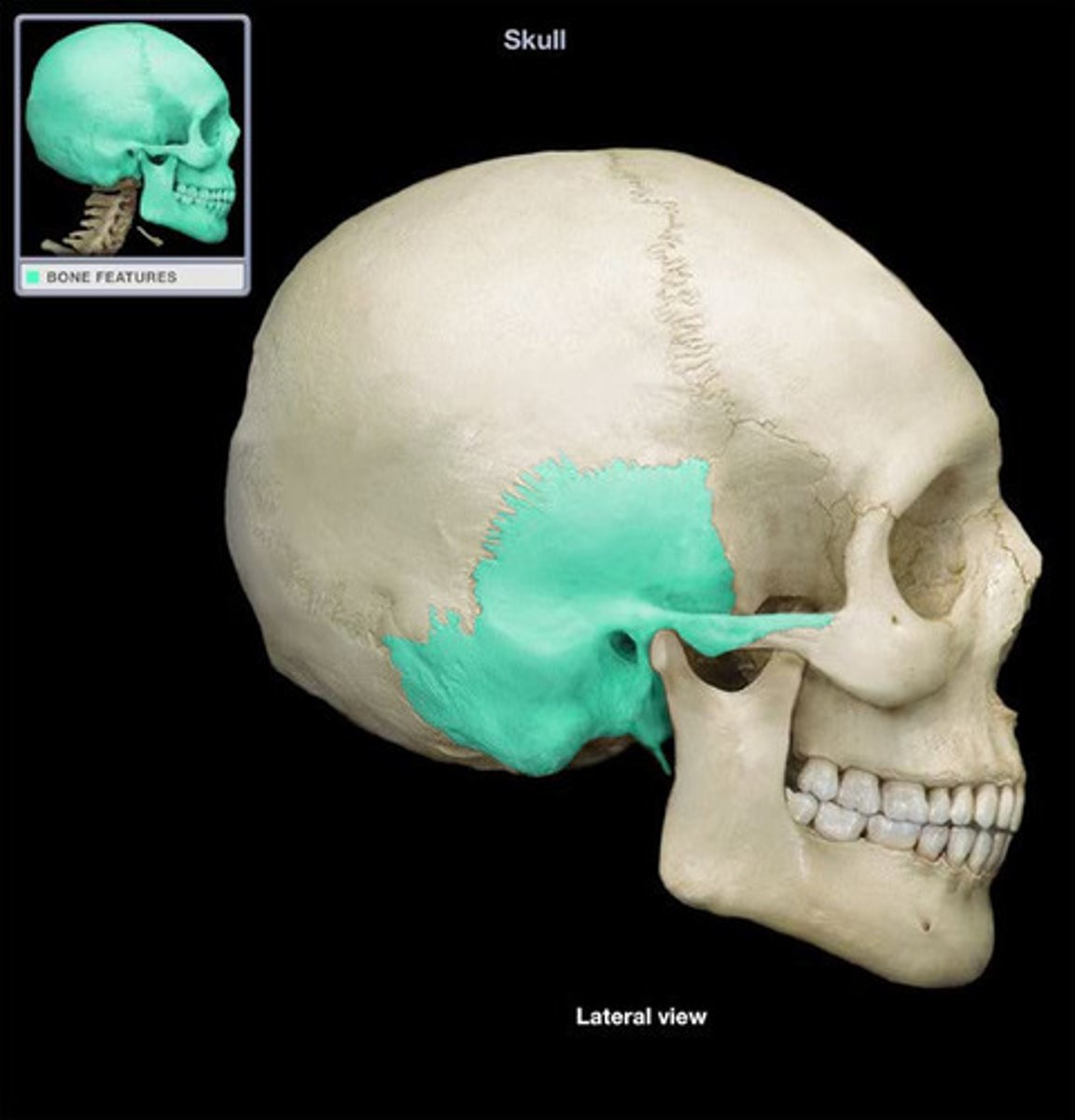
mastoid process
attachment for sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM - rotates + flexes head)
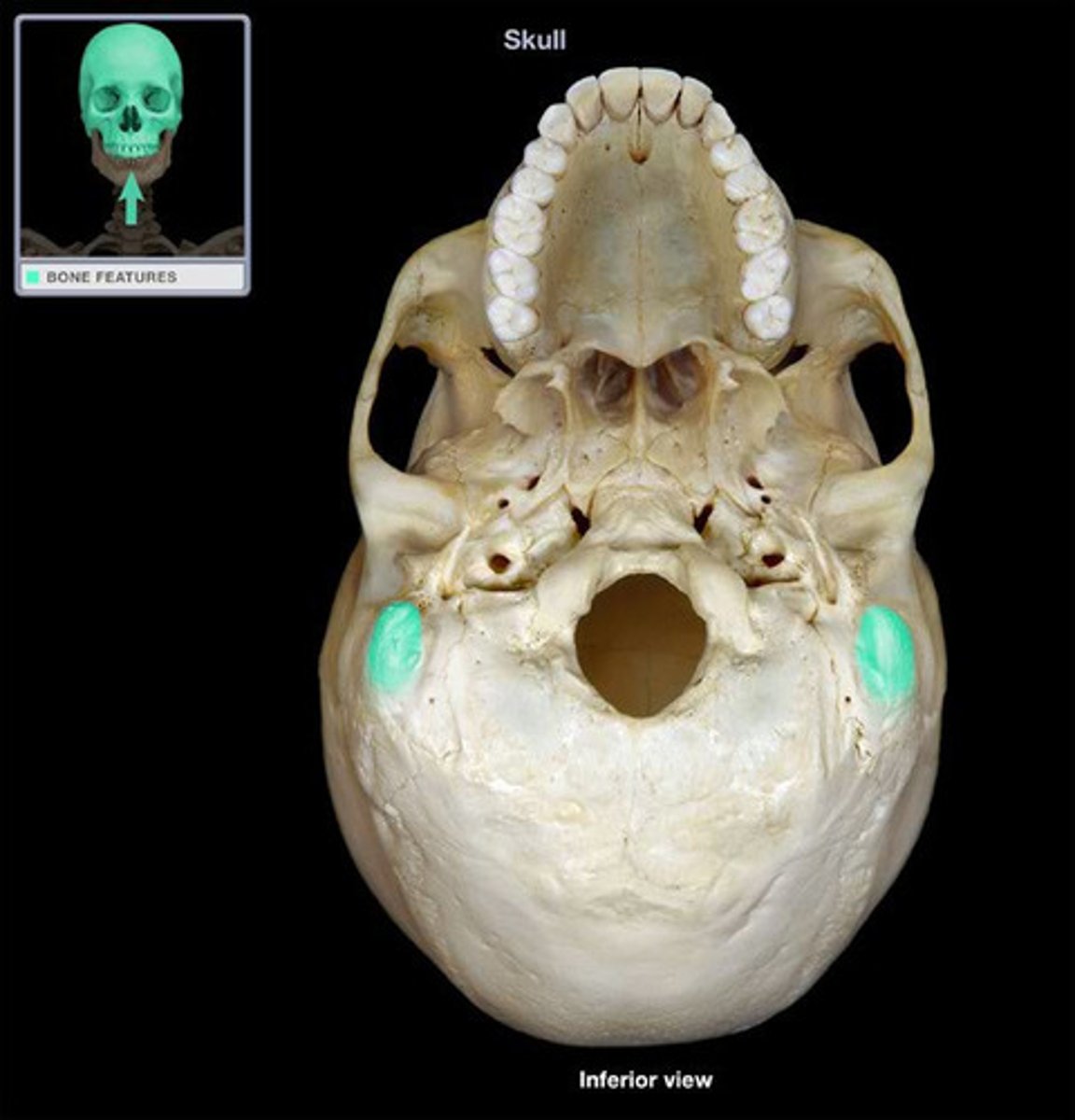
styloid process
attachment for muscles of the tongue/throat
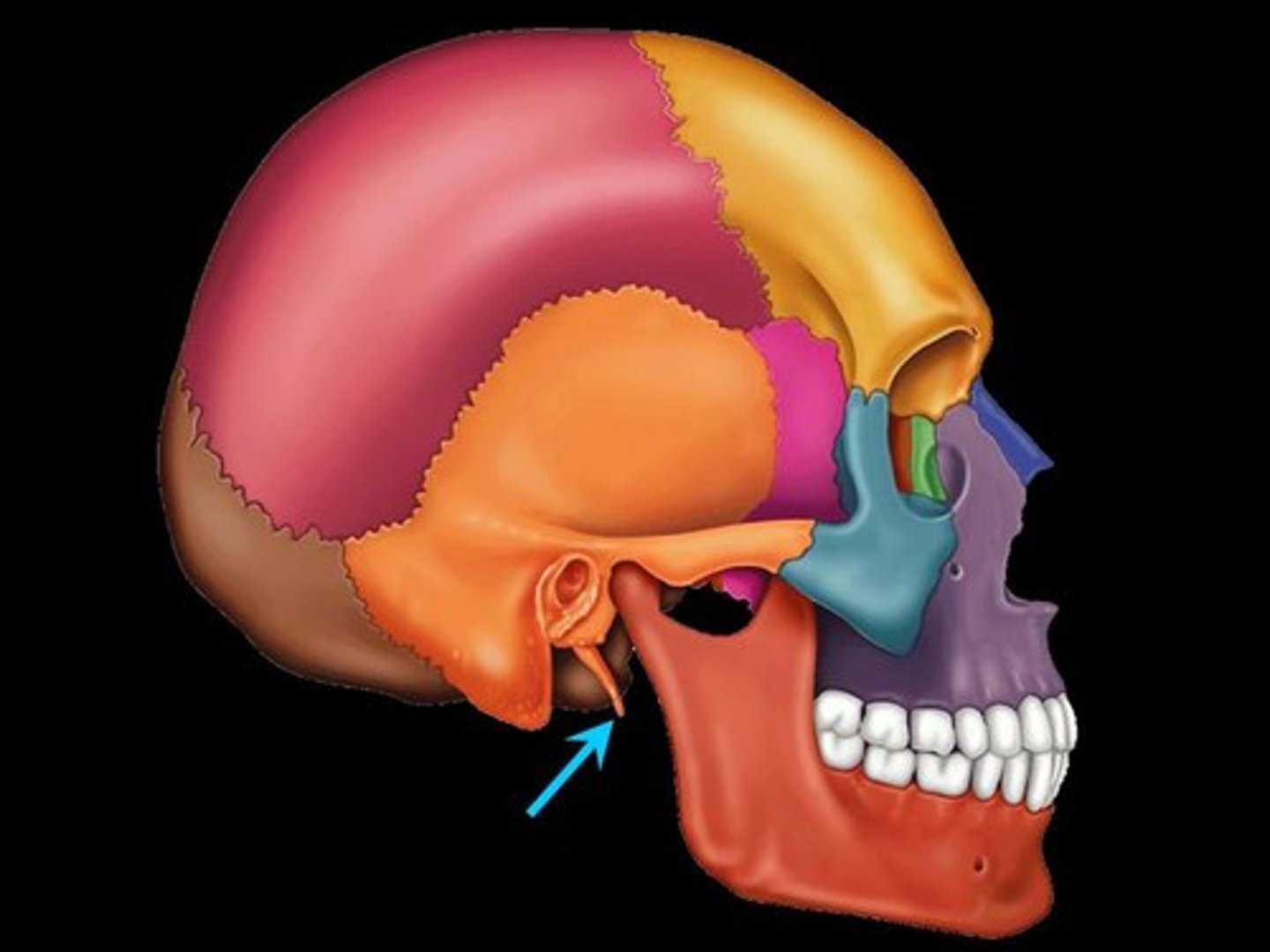
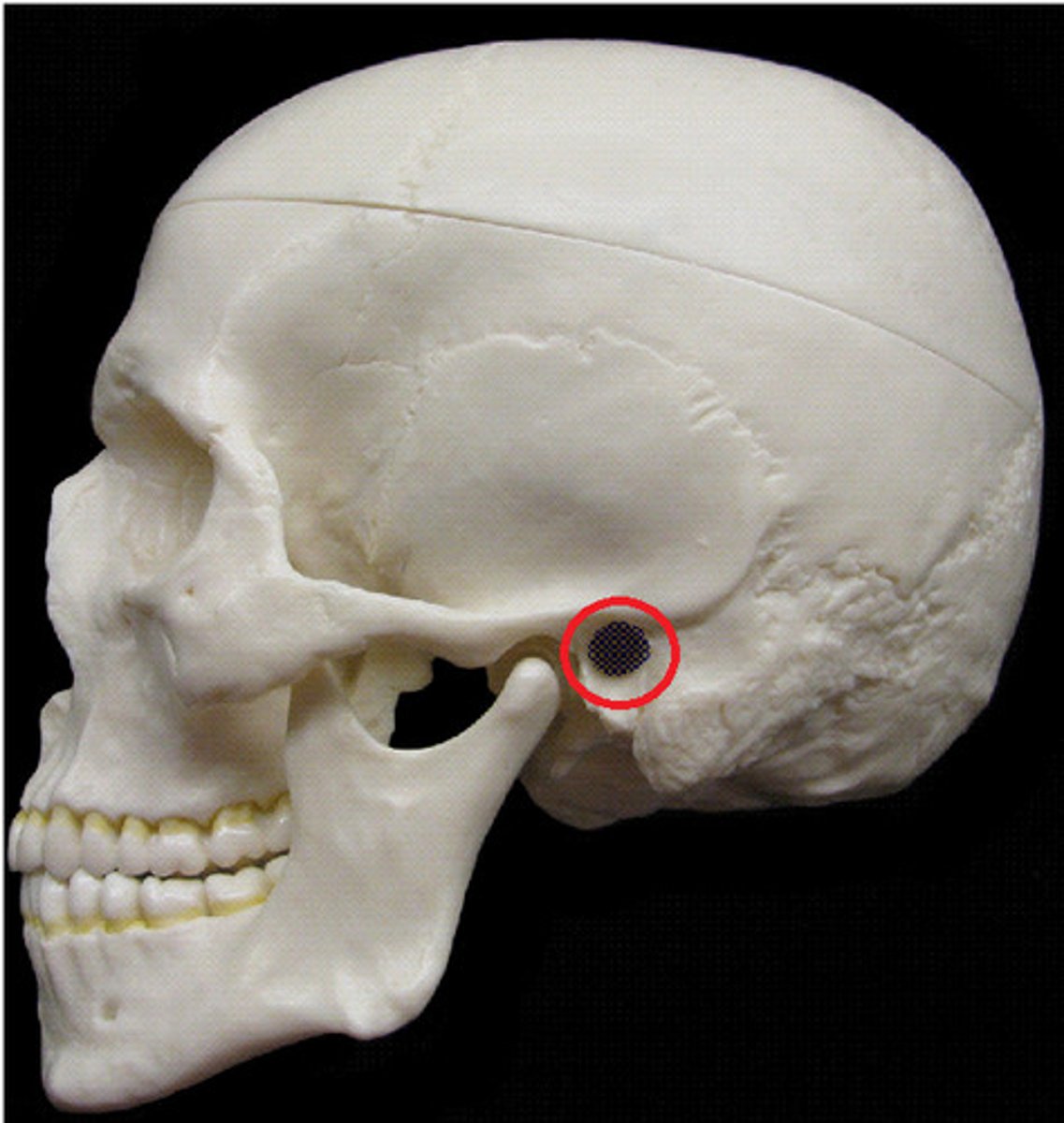
external auditory meatus
hole-like depression, channel for external ear canal
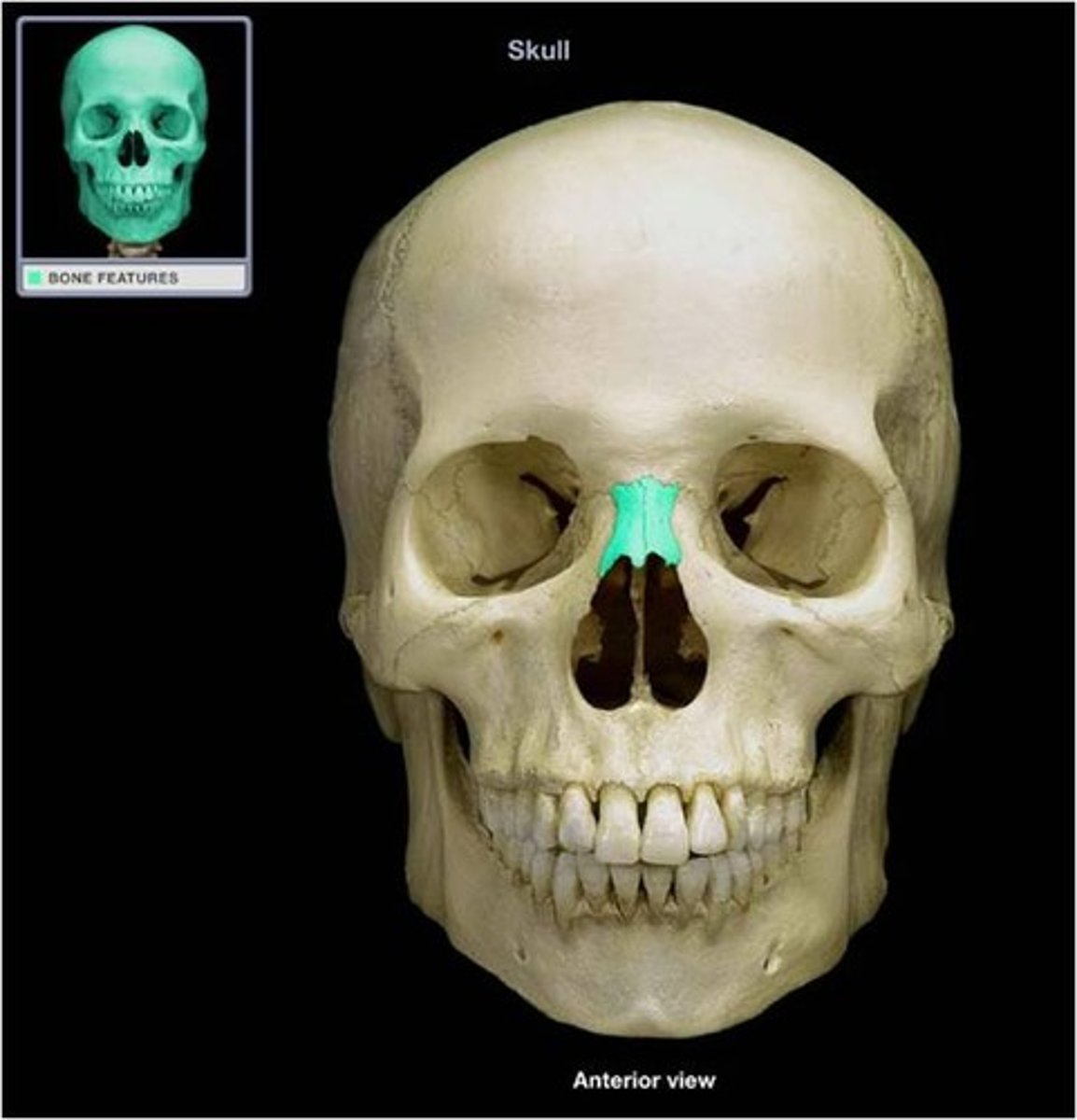
nasal
the hard bridge of the nose
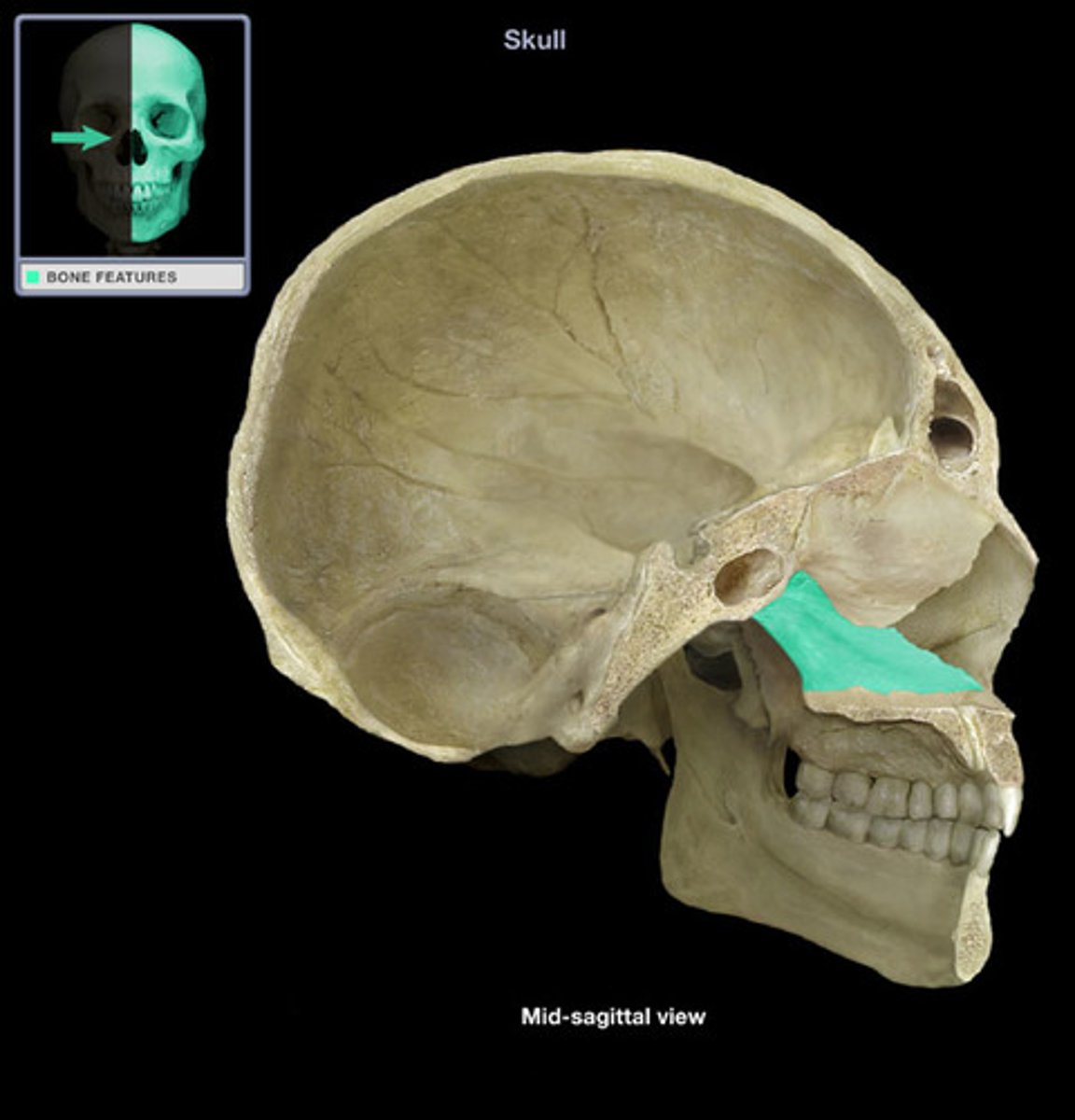
vomer
bottom part of bony nasal septum, V-shaped bone
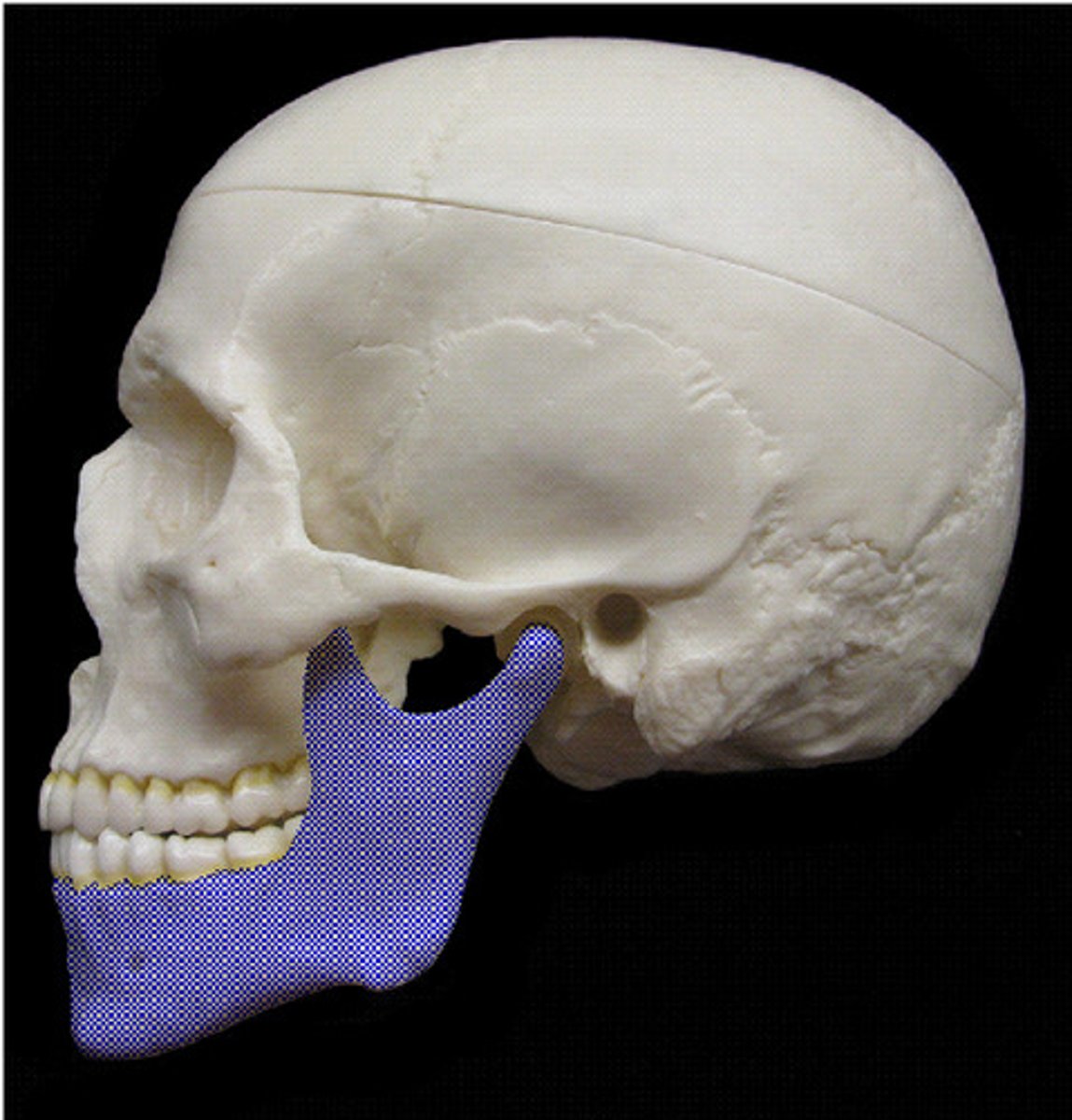
mandible
only moving bone of skull, lower jaw
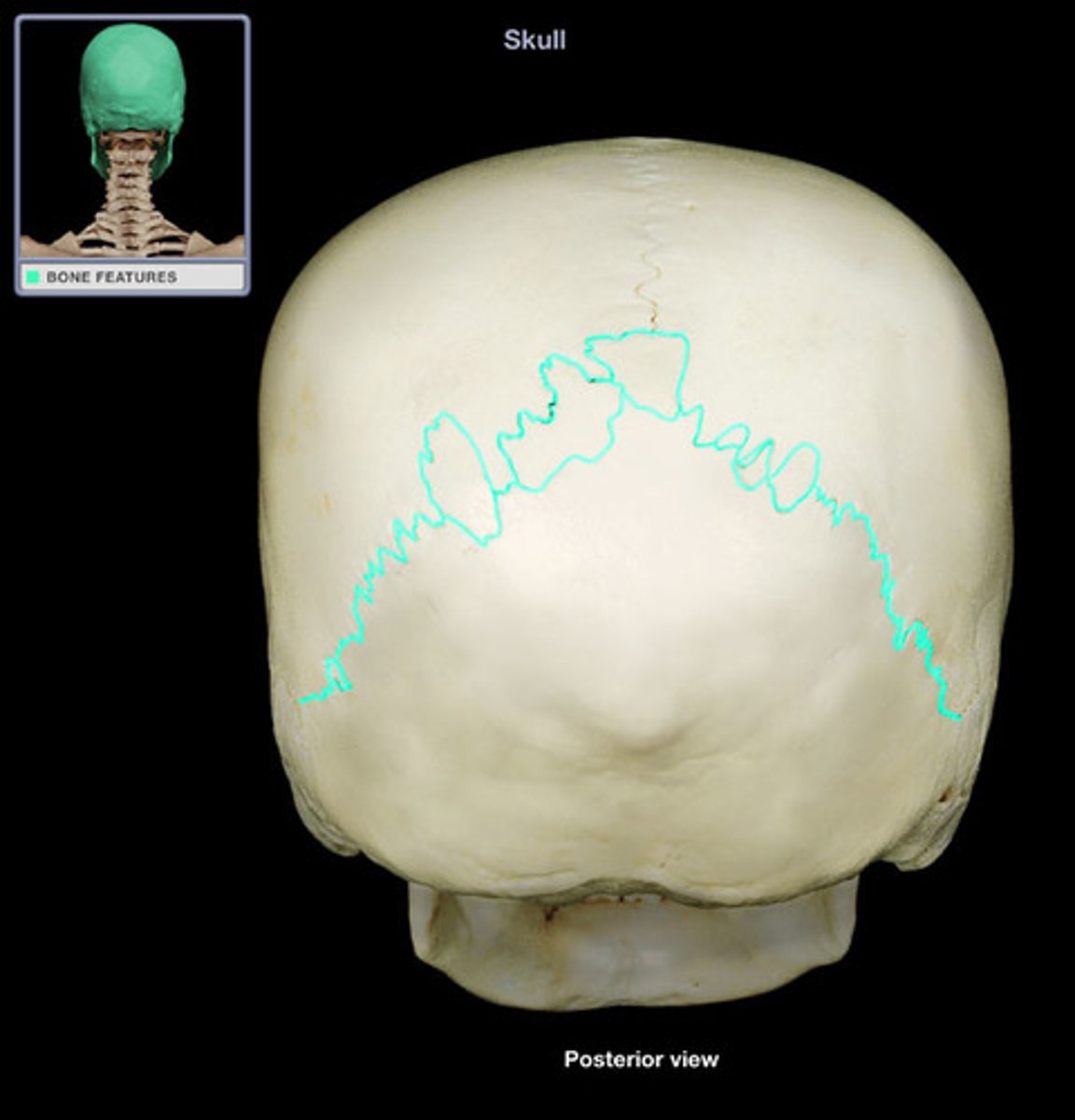
lambdoidal suture
the suture between the parietal + occipital bones
hydroxyapatite and collagen protein
two main things a bone is made of
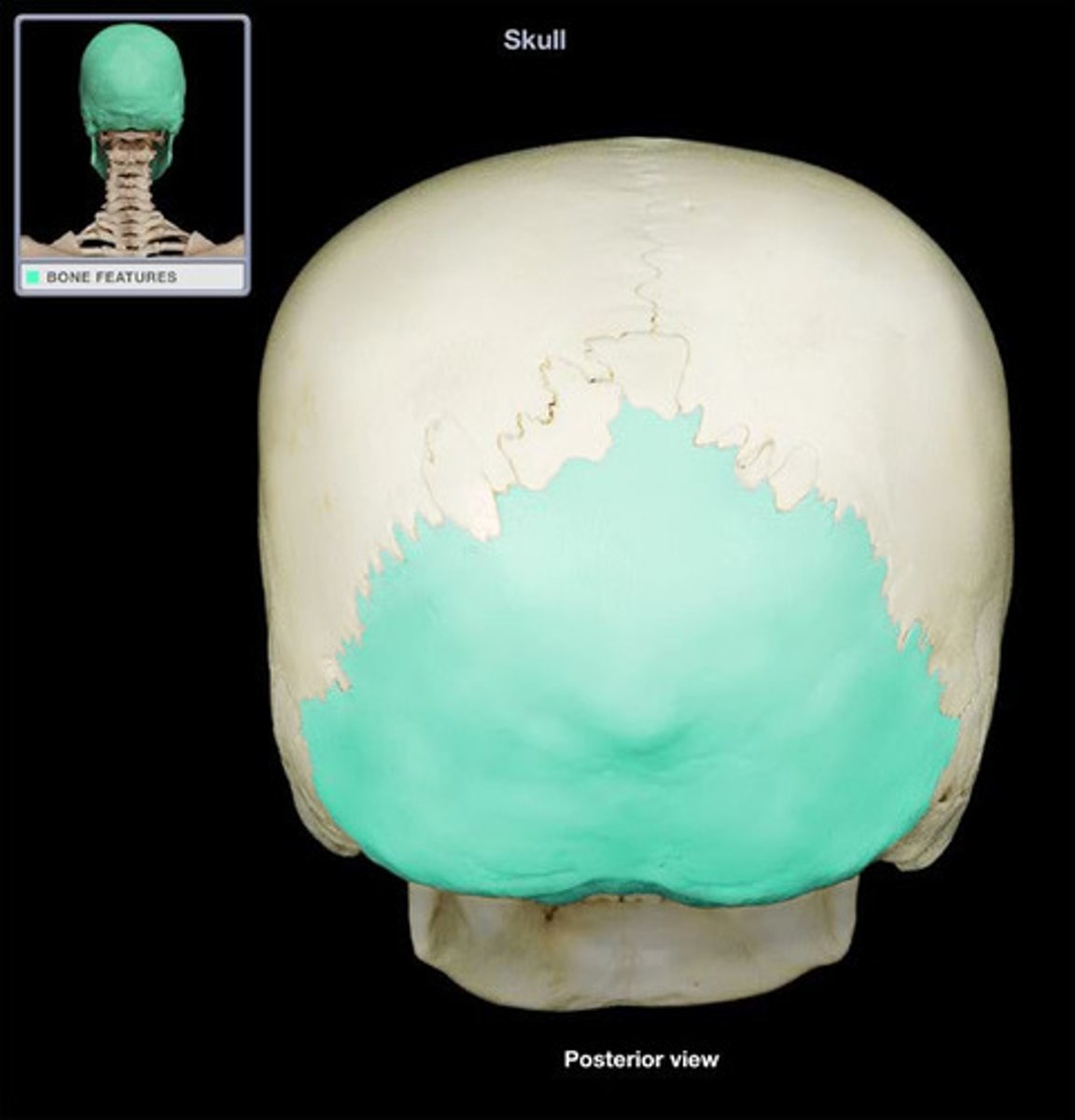
occipital
back of the head, contains foramen magnum and occipital condyles
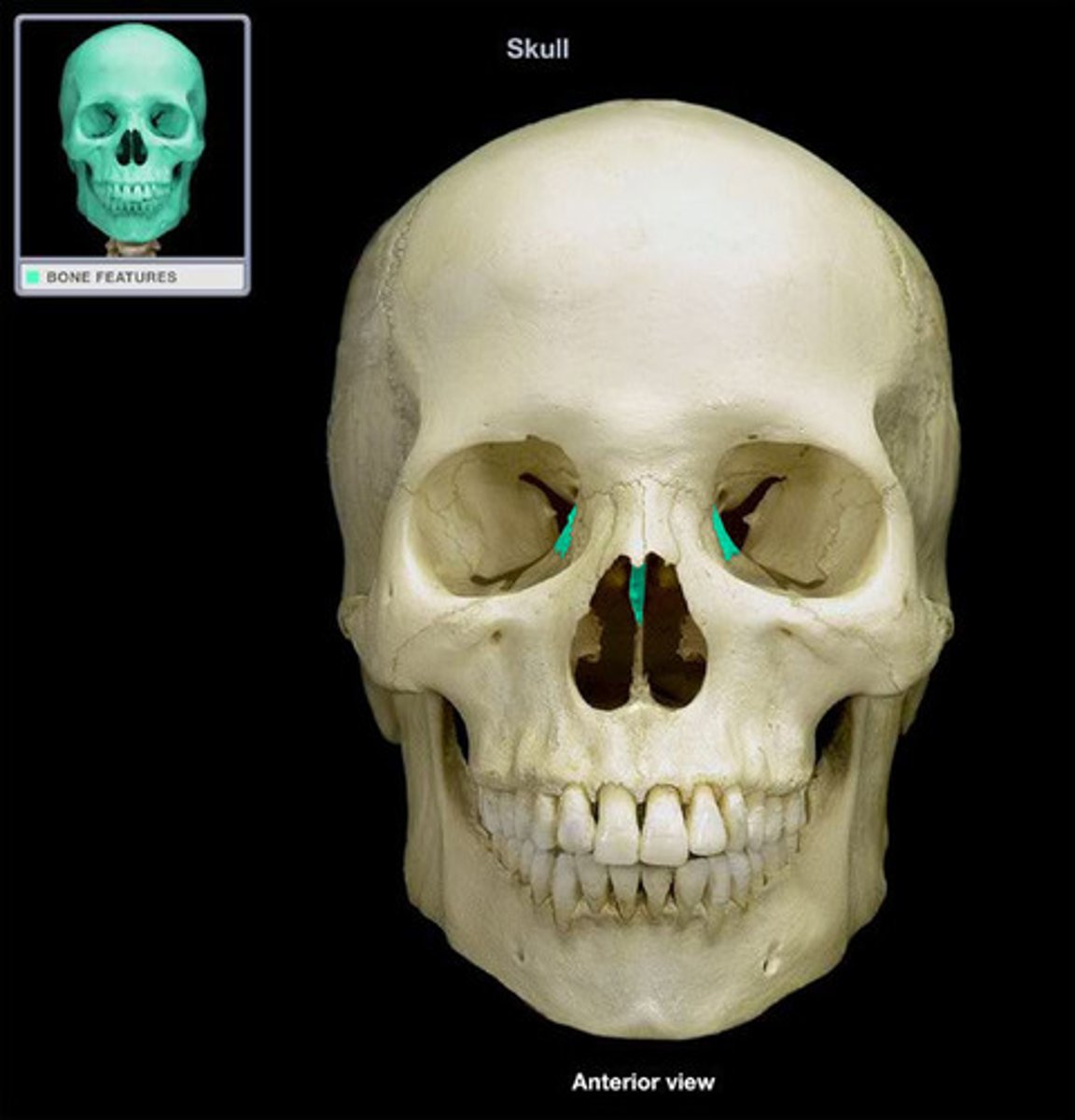
ethmoid
back of the nose, contains ethmoid sinus, cribriform plate, and perpendicular plate
ethmoid sinus
inside of ethmoid bone
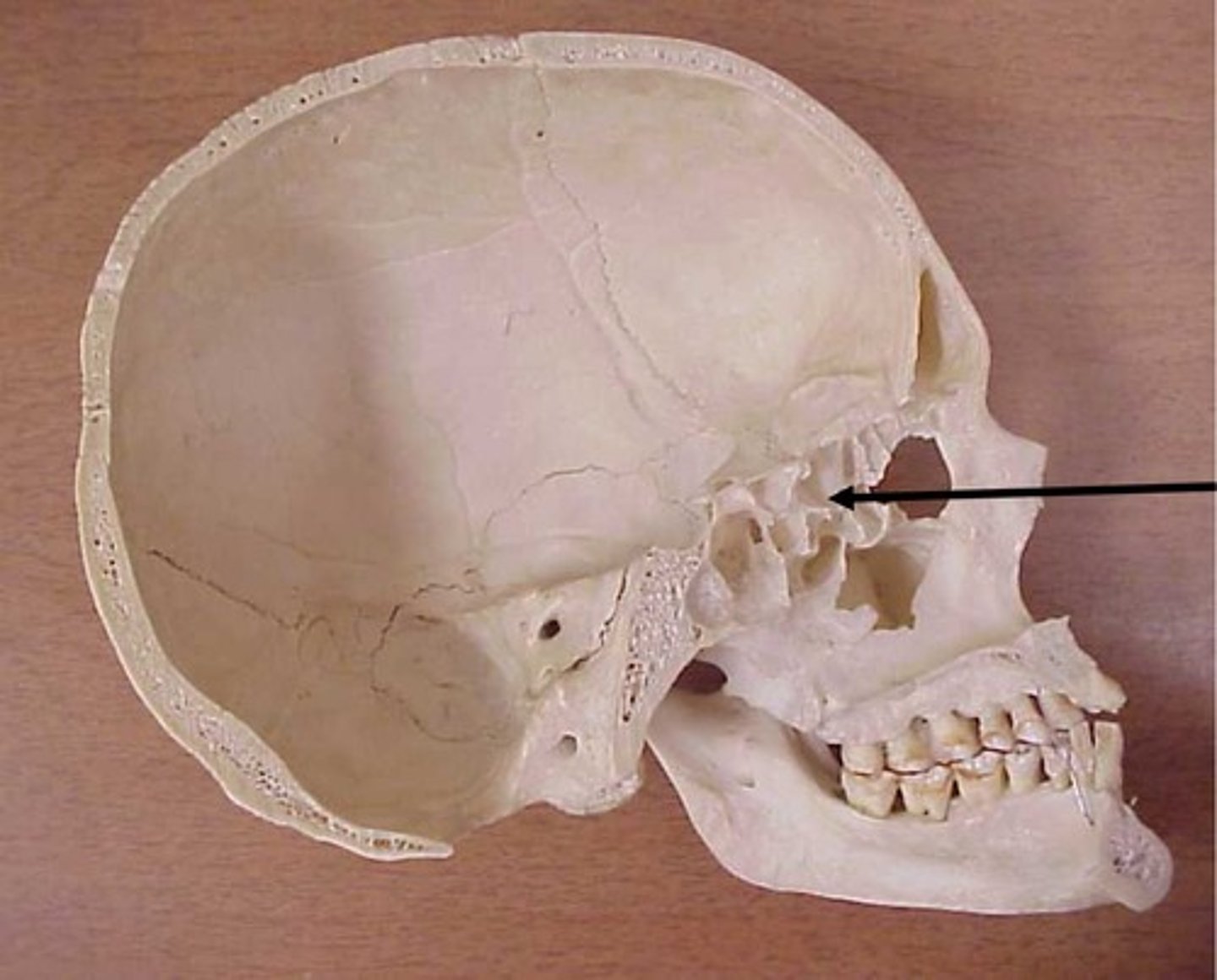
cribriform plate
olfactory (smell) nerves pass through here
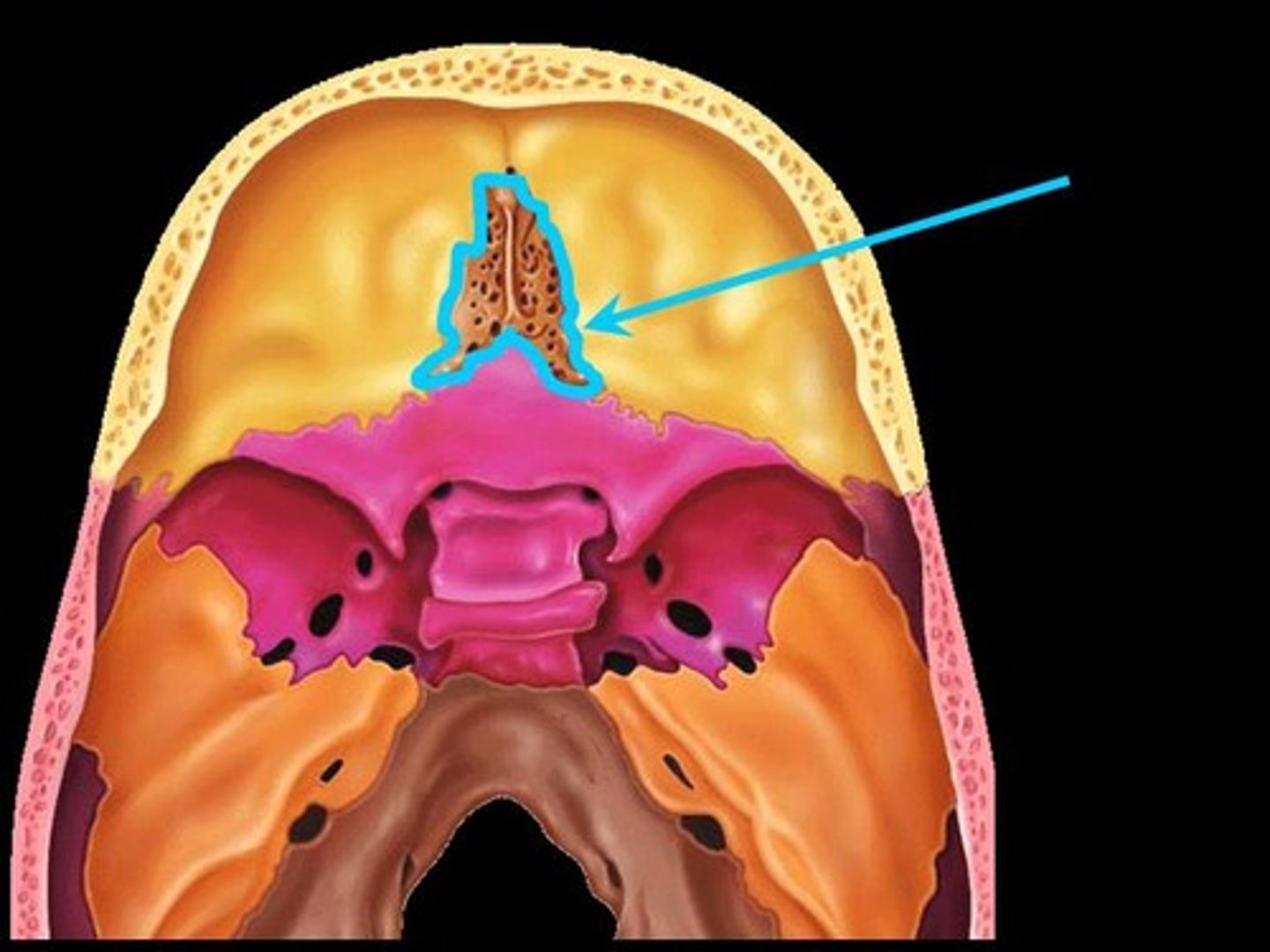
perpendicular plate
forms bony nasal septum
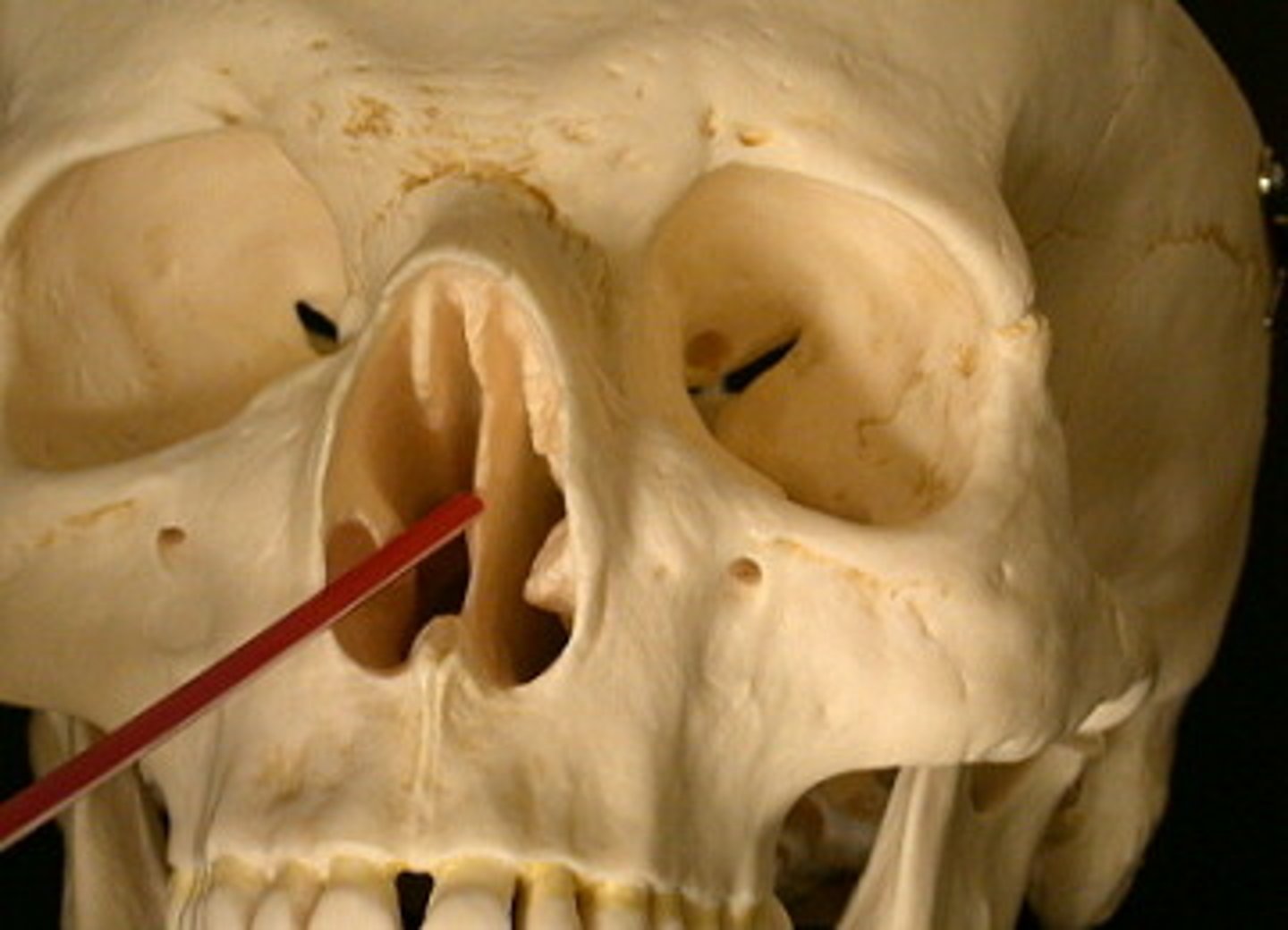
sphenoid
bat shaped bone, back wall of eye sockets, contains the sphenoid sinus
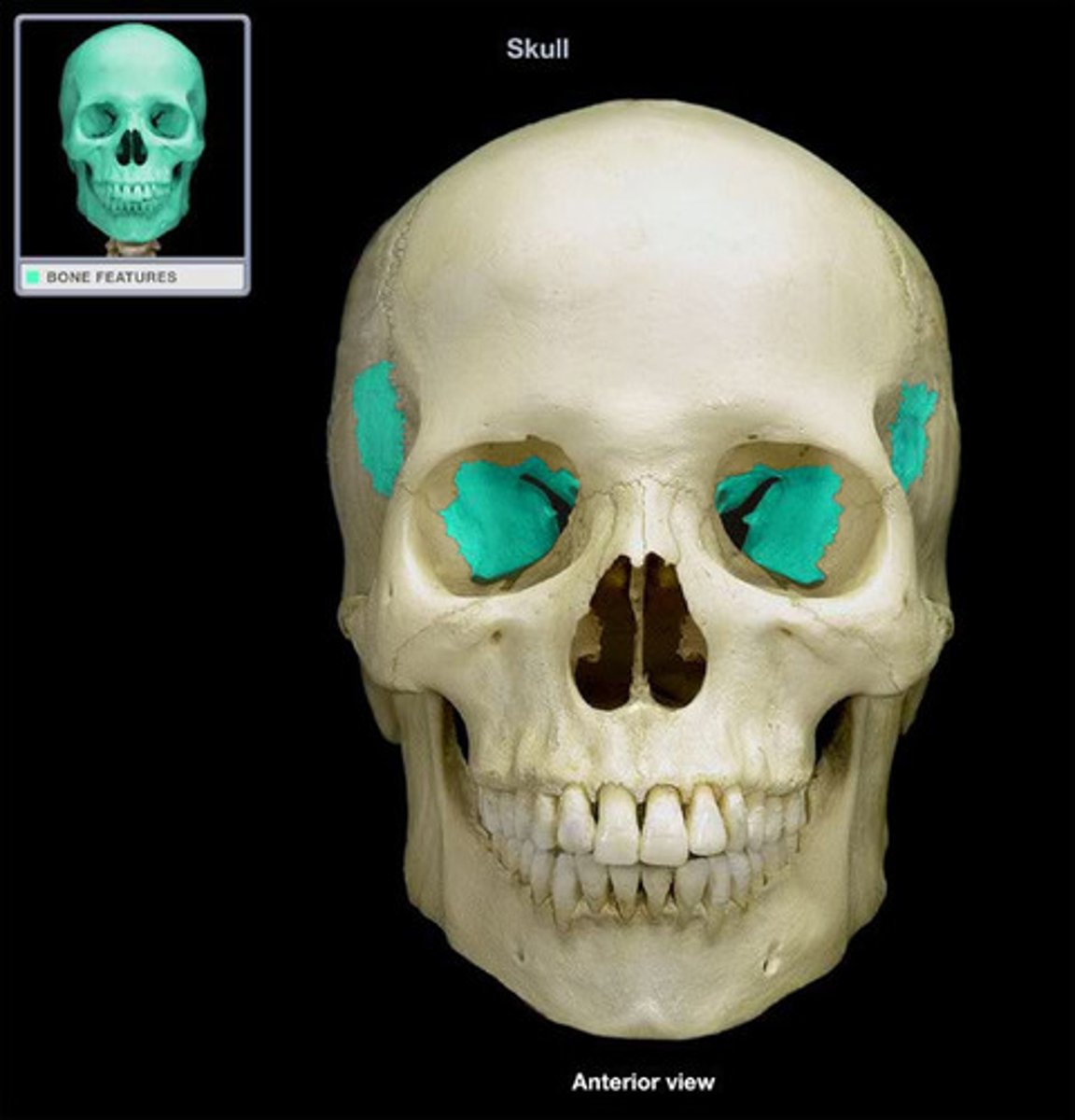
sphenoid sinus
middle body of sphenoid bone
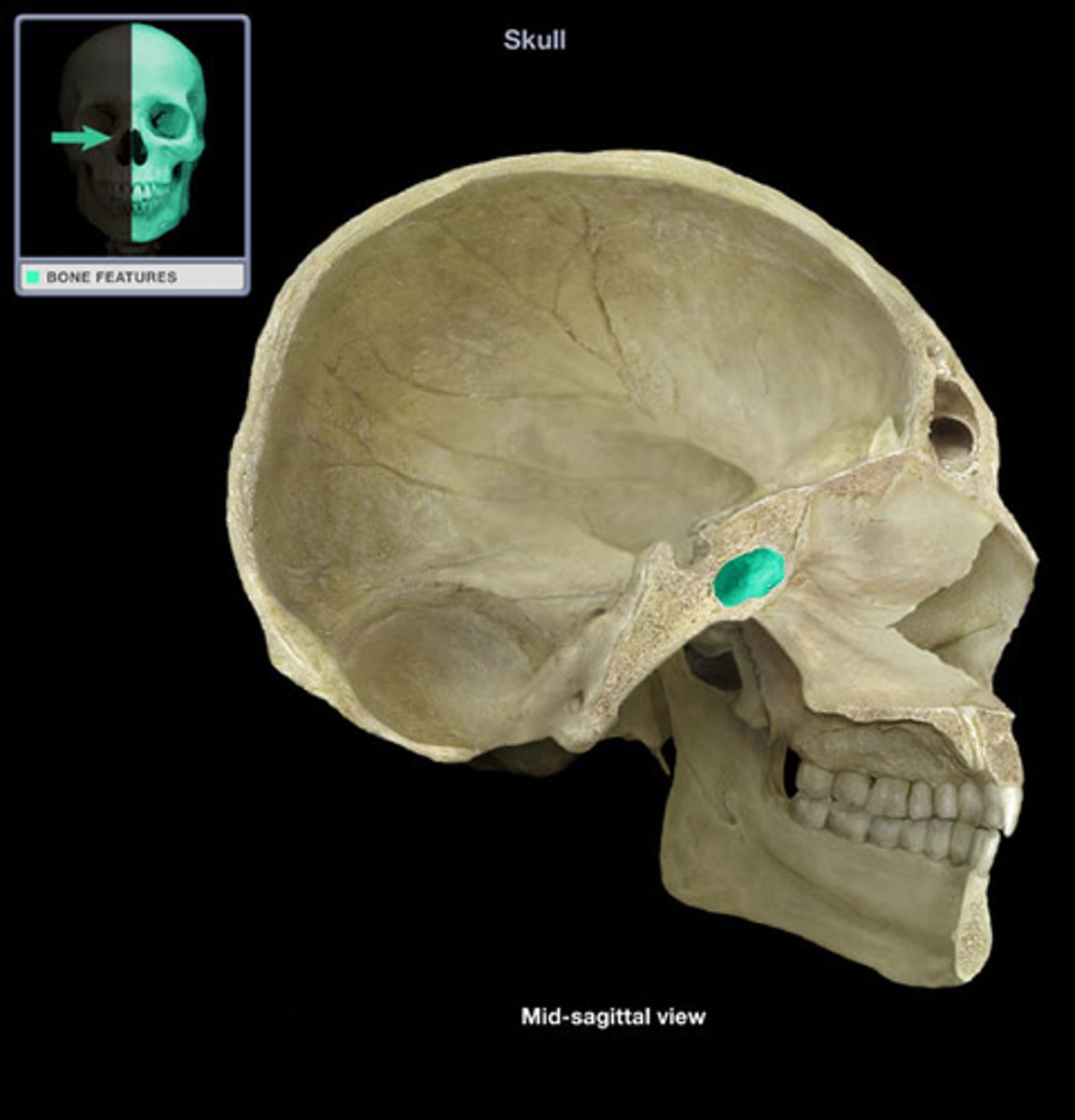
zygomatic
cheek bones, forms part of orbital cavities (eye sockets), can transfer impact of cheek to orbital cavity and break bones that form orbital cavity
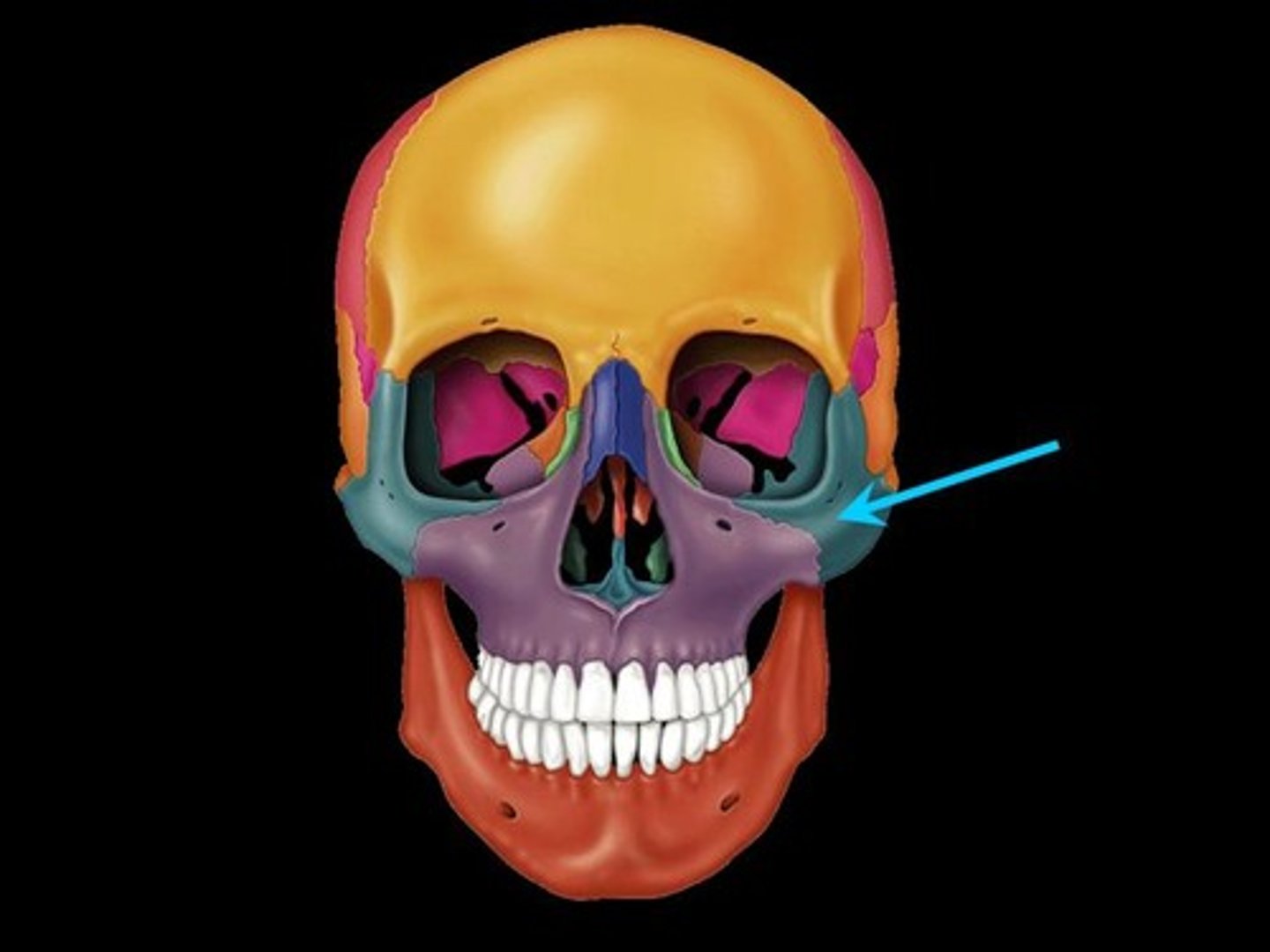
palatine
back 1/3 of the hard palate
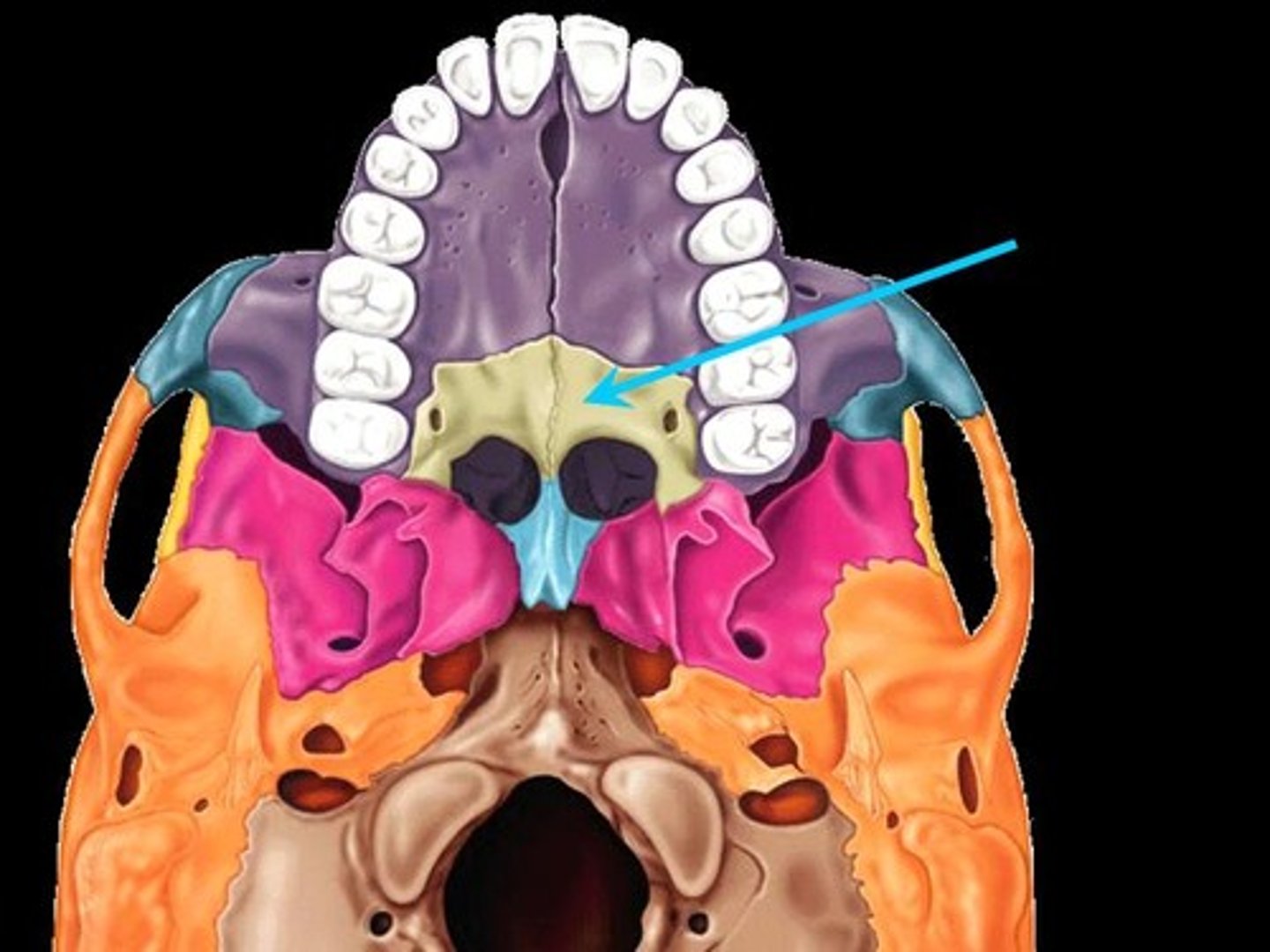
maxilla
front 2/3 of the hard palate
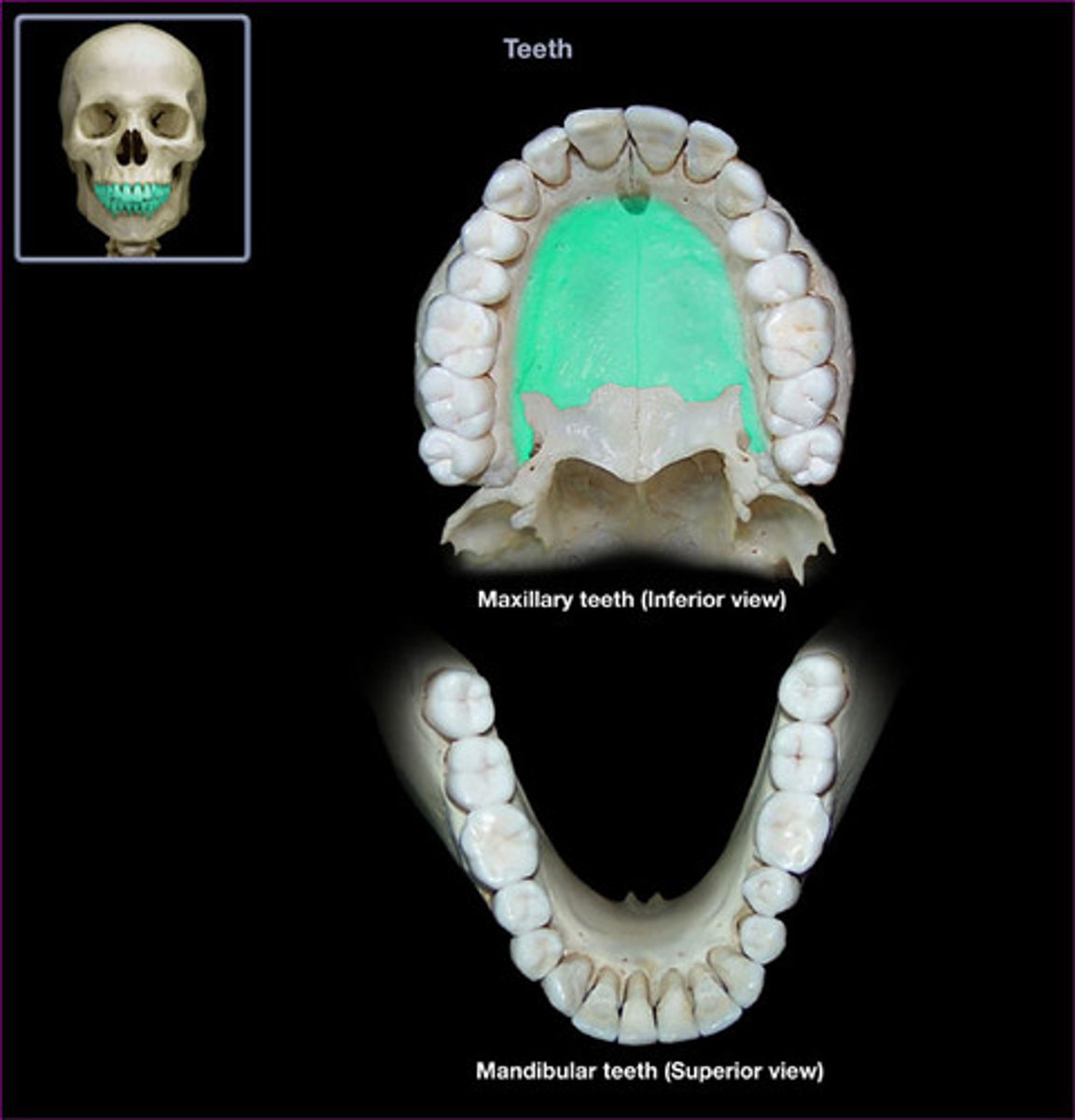
inferior nasal concha
conchae form "bumps" on the inside walls of nasal passage, causes swirling air flow to warm + humidify air
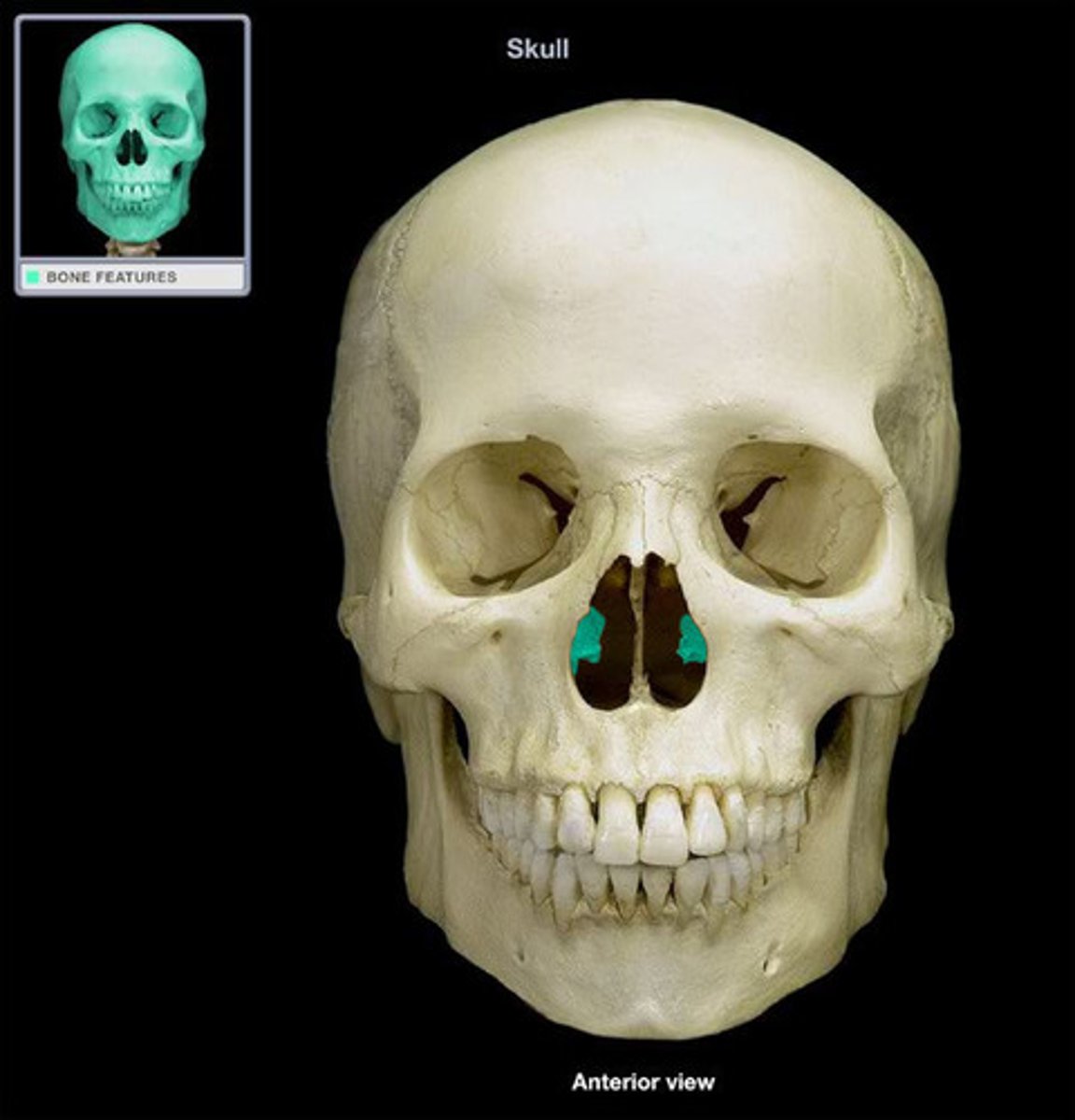
sutures
inflexible joint between bones
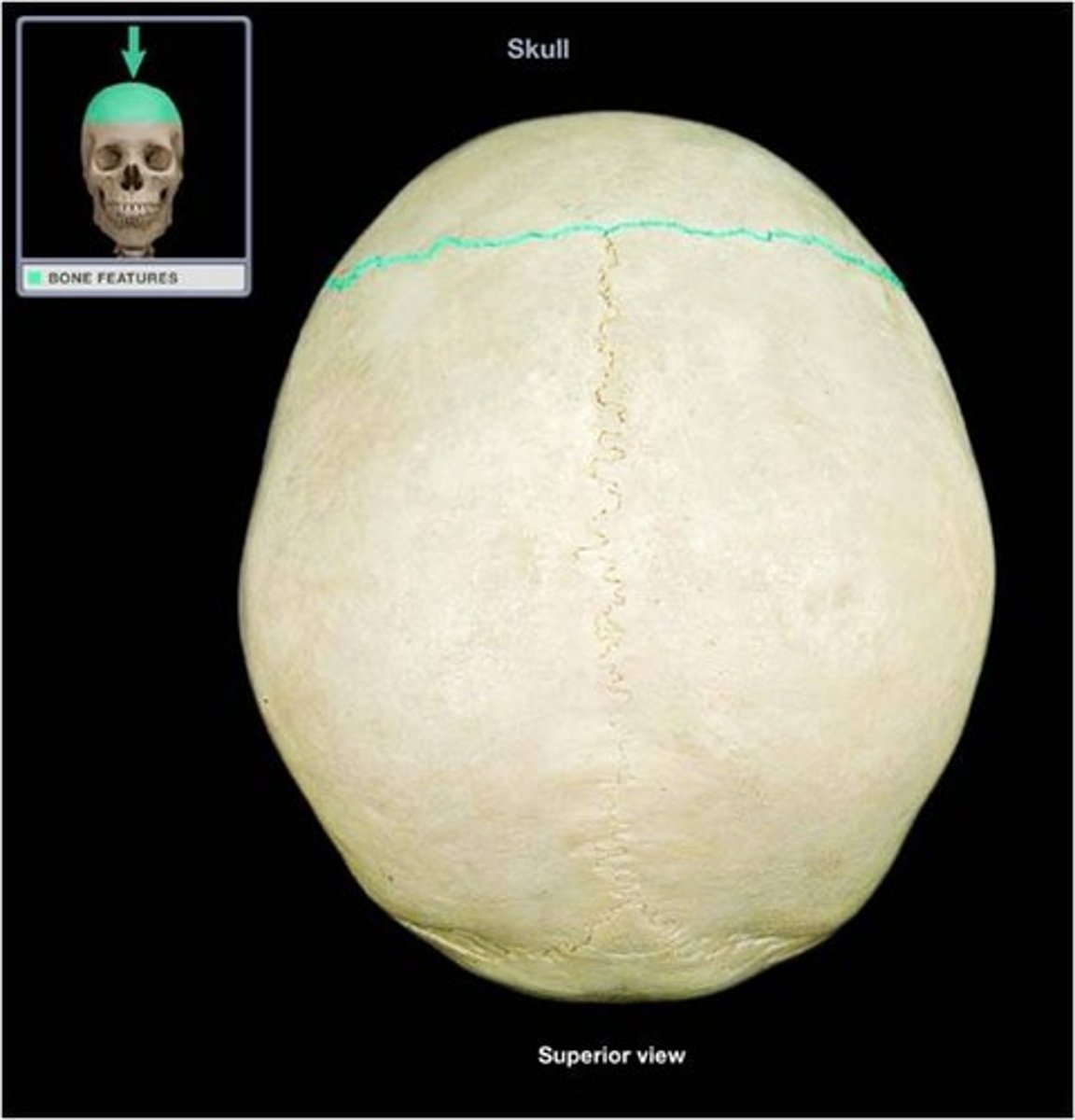
coronal suture
the suture between the frontal + parietal bones
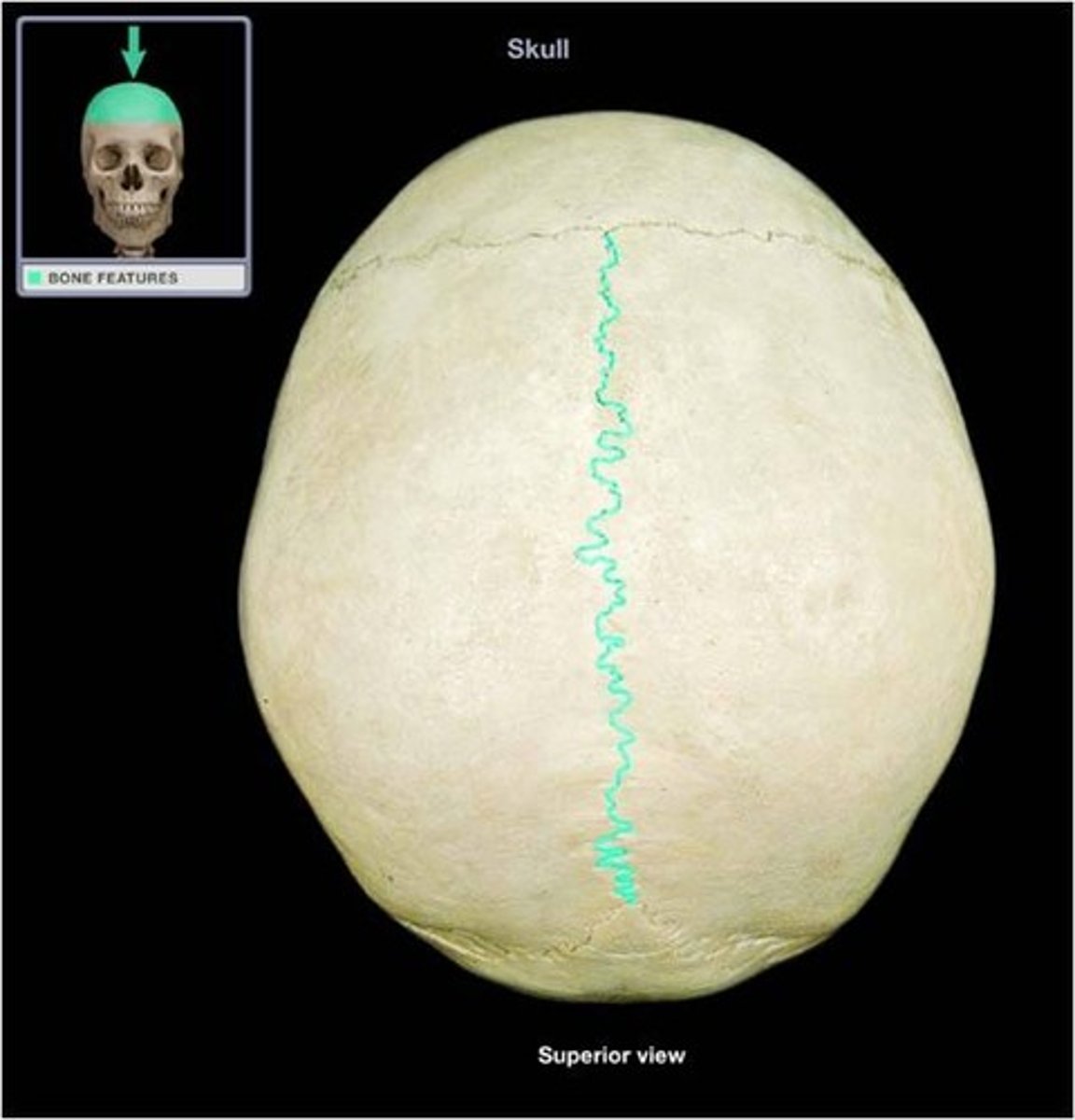
sagittal suture
the suture between the parietal bones
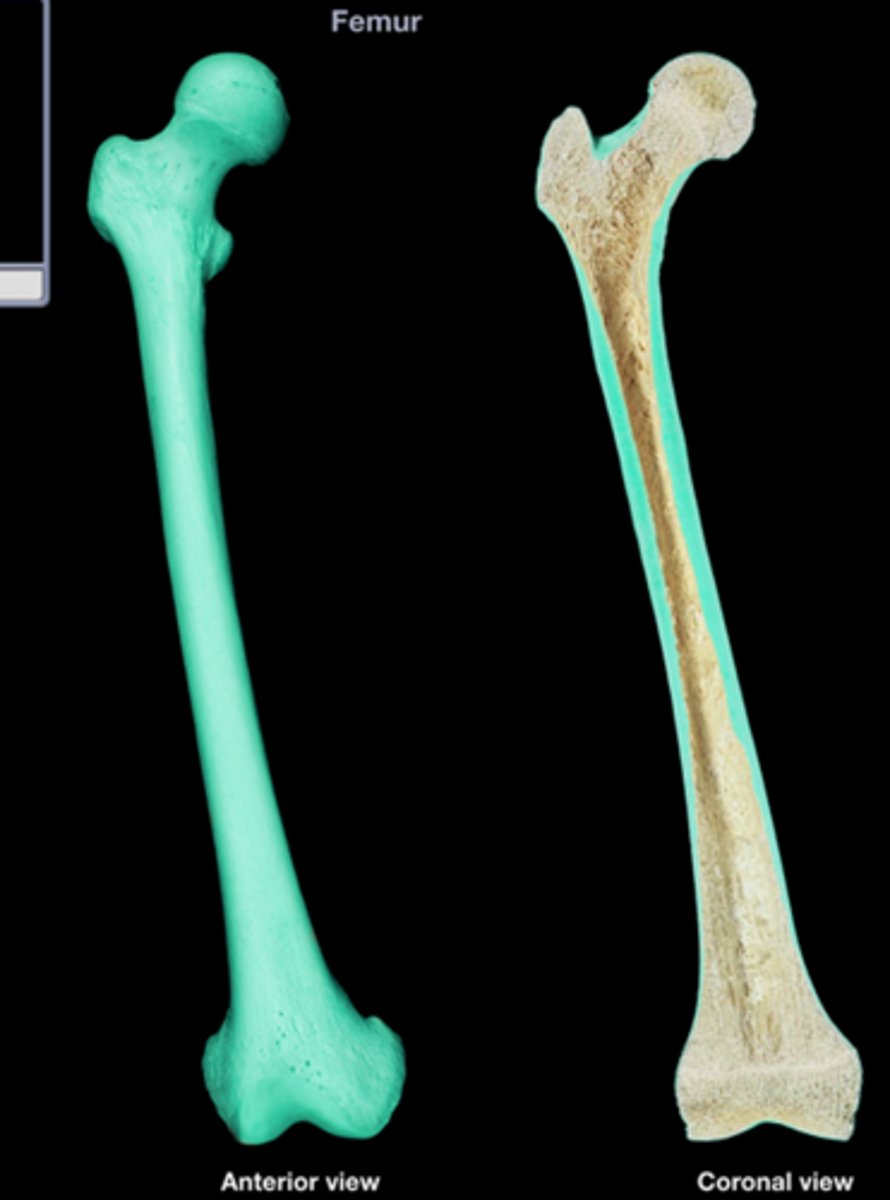
long bones
bones that are longer than they are wide (ex: phalanges, ulna, humerus)
short bones
carpal and tarsal bones (ex: trapezoid, talus, scaphoid)
flat bones
bones thin, flattened, and usually curved (ex: sternum, ribs, parietal bone)
irregular bones
bones that aren't long, short, or flat (ex: pelvis, coccyx, vertebrae)
hydroxyapatite
inorganic, non-living, made of salts, contains calcium and phosphorus, is brittle like chalk, is 2/3 the weight of the bone, is resposible for compressive strength
collagen protein
organic (carbon + hydrogen), living, made of amino acids, contains carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, is bendy and strong like steel, is 1/3 the weight of the bone, is responsible for tensile strength and resilience
epiphysis
end of long bone
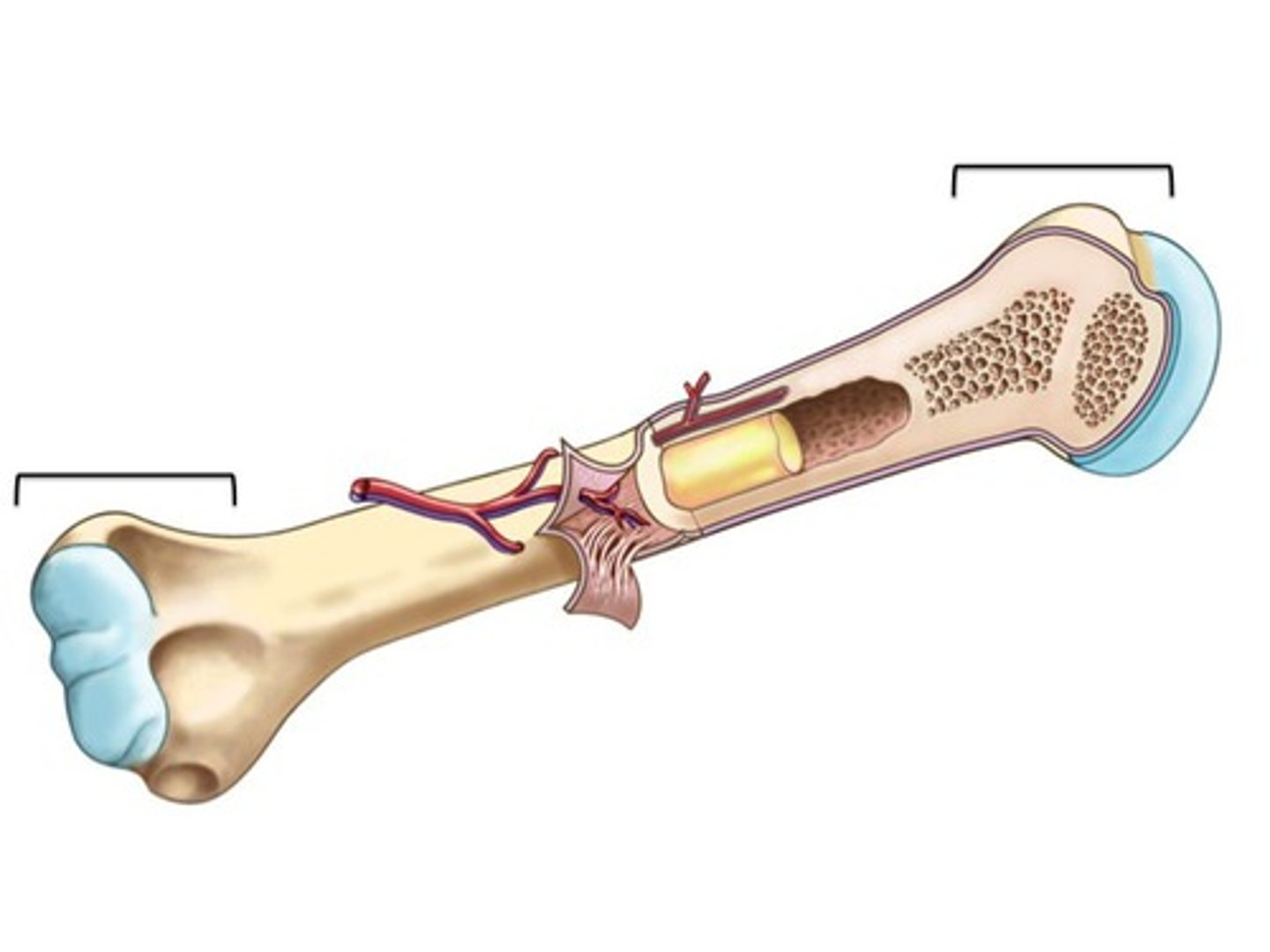
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
marrow
the soft connective tissue that fills the internal spaces in bone
spongy bone
layer of bone tissue having many small spaces and found just inside the layer of compact bone
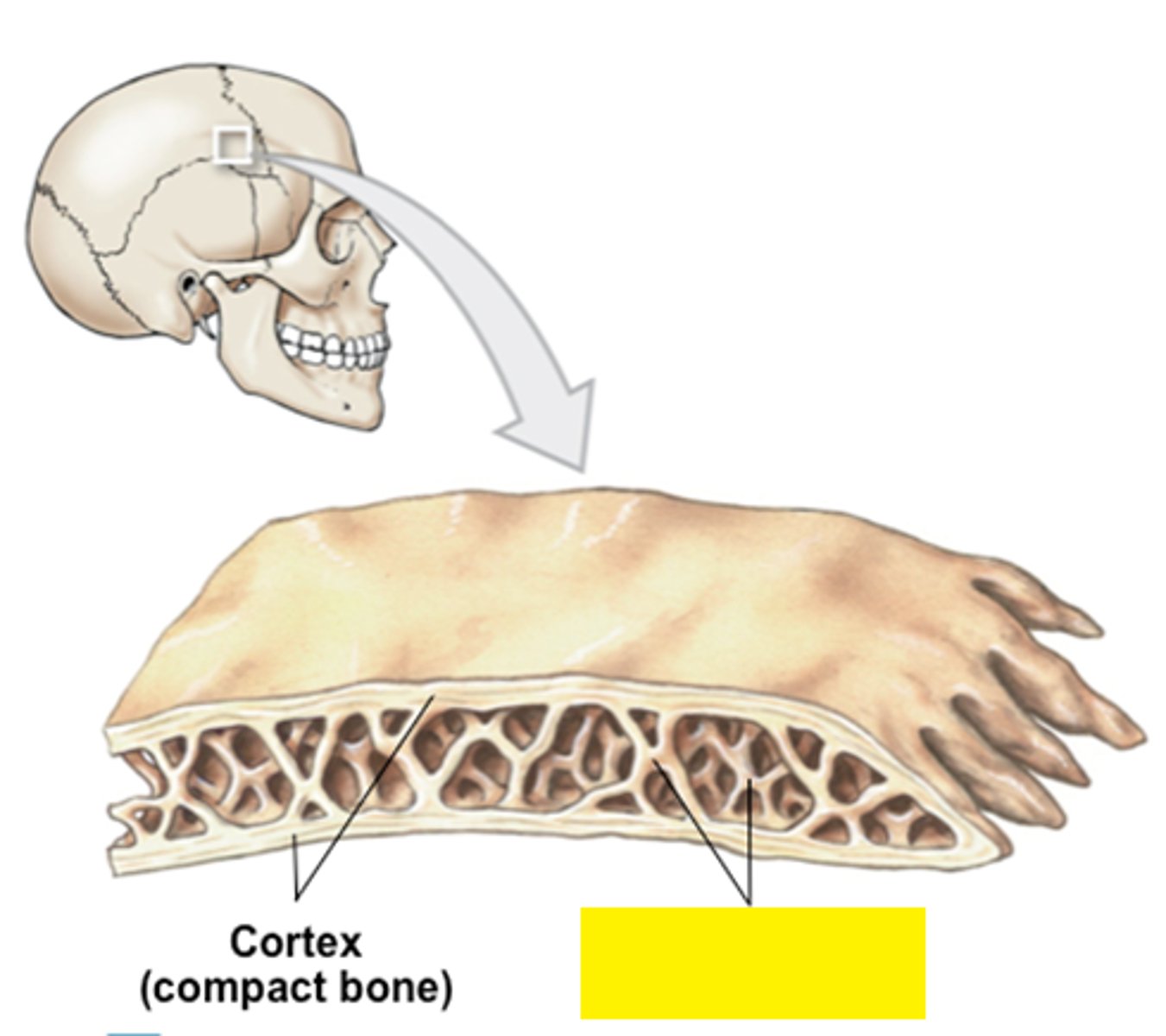
compact bone
hard, dense bone tissue that is beneath the outer membrane of a bone
adipose
fat, yellow bone marrow
Still learning (15)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!