electrolytes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
normal Na range
135-145
hypernatremia causes
usually due to loss of water or hypertonic IV solution, rarely caused by excessive oral intake
hypernatremia pathophys
hypothalamus senses osmolarity → triggers thirst reflec adn secretes ADH to save water
all conditions are hypertonic (over 295 mOsm/kg), must determine if pt is oliguric (under 0.5mL/min) or non-oliguric (over 0.5mL/min)
hypernatremia sx
acute sx due to cell death from shrinkage but chronic Na shifts present w less sx
severe hypernatremia (over 160) = orthostatic hypotension, lethargy, irritability, weakness, hyperthermia, deliruim, seizures, coma, oliguria, rarely osmotic cerebral myelation
oliguric hypernatremia =
urine osmolality over 300
oliguric hypernatremia causes
reduced water = lack access to water, body fluid loss, heat injuries
nonrenal losses = Gi, lungs, sweat
water shift into cells (rare)
osmotic diuresis (mannitol, urea)
non-oliguric hypernatremia=
urine osmolality under 250
non-oliguric hypernatremia causes
central DI = no ADH so kidneys peeing a lot
nephrogenic DI = ADH being produced but renal receptors not accepting it
(both kinds of DI make dilute urine, dx via ADH challenge)
give ADH and they stop peeing = central DI
hypovolemic hypernatremia tx
fluid replacement: if mild give hypotonic fluids (water orally/enterally OR 5% dextrose in water). if severe give NS 0.9% until stable, then give 5%dextrose to fix imbalance
if salt ingestion was the cause give diuretic
how much water do we give to pt w acute hypernatremia (rare)
give 5%dextrose fast until Na drop stop 145, then more slowly to 140
w central DI give DDVAP
extreme cases need dialysis
how much water do we give to pt w chronic hypernatremia
5% dextrose w rate based on weight and Na level, goal is under 140, limit correction of chronic hypernatremia to 12mEq/L in 24hrs
most common intracellular electrolyte, with normal serum levels of 3.5-5
potassium
hypokalemia levels
mild = 3-3.5, moderate = 2.5-3 severe = under 2.5
how are intracellular and extracellular K levels balanced
intracellular = balance w Na/K pump
extracellular = balanced w dietary intake
external eti for hypokalemia (from Gi or kidneys)
hypokadiarrhea (most common in developing countries), meds (diuretics), adrenal tumors (aldosterone secreting), sweat, low magnesium, (no magnesium = no K absorption), inadequate intake
internal eti for hypokalemia (shift from extracellular to intracellular)
from metabolic alkalosis, hyperglycemia/insulin use, beta-2 adrenergic agonists, hypothermia
hypokalemia sx (K is like a spark plug, so when low cell membranes are less reactive to stimulation)
short term = polyuria and polydipsia
long term = tubulointerstitial nephritis
cardiac arrhythmias and arrest, constipation (smooth muscles), weakness/cramps/flaccid paralysis of LE/hyporeflexia (skeletal muscles), respiratory depression, fatigue, hallucinations, delerium, psychosis
hypokalemia dx
EKG is biggest one!!!!! = T wave flattening → ST depressions and T wave inversions → prolonged QT intervals → u waves → torsades
aldosterone, cortisol, renin, TSH, BMP, ABGs
24hr urine K (if under 25 a day kidneys are normal, if over 40 then the kidneys are the problem)
spot K:creatinine ration = under 13 means non renal cause
imaging to find adrenal adenoma, pit tumor, RAAS
hypokalemia tx
tx underlying cause (if metabolic acidosis treat the low K first, then tx acidosis)
mild-mod = oral K
severe (under 3) = IV K
cardiac monitoring
if needed start K sparing diuretic, check magnesium
hyperkalemia levels
over 5.2 = hyper, over 6.5 = severe
hyperkalemia eti caused by release from cells
pseudo-hyperkalemia = articifically inc serum K, seen w clenching fists, tourniquet use, small bore needes (MOST COMMON CAUSE) (seen w drawing blood)
tissue breakdown = rhabdo, tumor lysis syndrome, severe hemolysis,
hyperglycemia (glucose makes K leave cells)
metabolic acidosis = cellular exchange of K for H
hyperkalemia eti from impaired renal excretion
AKI or CKD, hyporeninemic-hypoaldosteronism (less K excretion)
excessive K intake w renal disease or impaired K secretion
hyperkalemia eti from meds
ACE/ARB, BB, K sparing diuretics, aldosterone antagonists, NSAIDS
hyperkalemia sx
mild =asx if develops slowly
severe= too much “electrical noise” on nerves and muscles ESP HEART, interferes how nerves talk to muscles
cardiac cells depolarize adn become more excitable (inc arrhythmia risk, palpitations, SOB, hyperventilation)
weak muscles → flaccid paralysis
worsening metabolic acidosis
what labs do we get for hyperkalemia
CBC, CMP, ABG, aldosterone, renin, cortisol
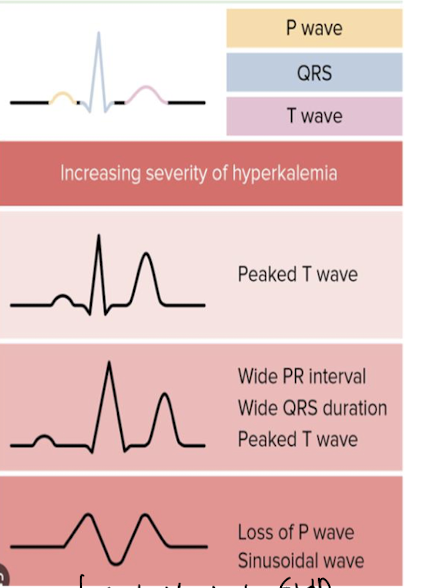
what do we se on an EKG for hyperkalemia (start seeing if K over 5.5, life threatening K is over 7)
PEAKED T WAVES (heart recharging)
progresses to prolonged PR interval and QRS duration (electrical signal slowing)
loss of P waves → QRS merges w T wave (sine wave pattern) → v-fib or asystole
NORMAL EKG DOES NOT = NORMAL K, gotta check both
emergent hyperkalemia tx (over 6.5 w or w/o EKG changes)
protect heart w IV calcium gluconate (stabilizes cardiac cells and prevents arrhythmias, does NOT lower K)
insulin to shift K into cells (or beta agonist salbuterol)
metabolic acidosis = sodium bicarb
loop diuretics → pee off K
hemodialysis if AKI, CKD, life threatening, or refractory
sodium polystyrene only w life threatening K and dialysis not avalibale or failed (risk for colonic necrosis)
non emergent hyperkalemia tx (under 6.4)
repeat blood tests and get EKG
fix underlying problem (acidosis, renal disease), remove source (supplements, salt substitutes), stop meds (ACE/ARB, K sparing diuretics like spironolactone)
pee it out = loop/thiazide diuretics
poop it out = K binders (patiromer, sodium zirconium cyclosilicate)
filter it out = dialysis
SGLT2 inhibitors to prevent chronic high K