Section 2 Questions
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
You are refilling a nondisposable nebulizer supplying O2 to a postoperative patient via aerosol face mask. The capillary tube dislodges and falls on the floor. The most appropriate action would be to
switch the patient to a humidifier
wipe the capillary tube with alcohol and reconnect
reinsert the capillary tube
replace the entire nebulizer with a clean unit
replace the entire nebulizer with a clean unit
Which of the following nondisposable items must be sterilized between use on different patients?
bronchoscope forceps
endoscope
ventilator tubing
face mask
bronchoscope forceps
Any reusable item posing a critical infection risk must be sterilized between use on different patients. Critical items are those introduced into the bloodstream or other parts of the body. These include surgical devices, intravascular catheters, implants, heart-lung bypass components, dialysis components and bronchoscope forceps/brushes. Devices that contact intact mucous membranes such as endoscopes or ventilator circuits are categorized as semi-critical and should be processed using a high-level disinfection method. Items that touch only intact skin or do not contact the patient (such as a face mask) present a a non-critical infection risk and require only detergent washing or low to intermediate level disinfection.
A respiratory therapist is caring for a patient who has a sign posted outside their hospital room door that indicates, "Respiratory Isolation". The therapist should observe all of the following EXCEPT:
Patient should use a mask when visitors are present
Use N95 respirator
Universal precautions
Do not allow visitors to enter the room
Do not allow visitors to enter the room
Which of the following types of equipment processing would you recommend for a reusable external facemask?
soap and water wash
high-level disinfection
low-level disinfection
sterilization
low-level disinfection
Since a face mask only contacts a patient's intact skin, it is considered a noncritical item. Low-level disinfection is the appropriate type of equipment processing for noncritical items.
A patient with a tracheostomy has 40% O2 and aerosol delivered by a tracheostomy mask. If the patient develops an Escherichia coli infection of the stoma and airways, the most likely source is
The patient's own upper airway bacteria
Nebulizer water used past its expiration date.
Inadequate hand washing by the health care workers.
Improper manufacturer sterilization of the mask.
Inadequate hand washing by the health care workers.
This organism is found in the lower intestine. It is often spread from improper hand washing after use of the toilet.
Which type of disinfection inactivates all microorganisms except bacterial spores?
intermediate-level
high-level
surface active
low-level
high-level
By definition, only high-level disinfection inactivates all microorganisms except bacterial spores. Some high-level disinfectants may also destroy spores if the exposure time is sufficient.
Which of the following types of equipment processing would you recommend for reusable PFT mouthpieces/tubing?
high-level disinfection
soap and water wash
sterilization
low-level disinfection
high-level disinfection
Since PFT mouthpieces/tubing may contact a patient's mucous membranes, they are considered semicritical items. High-level disinfection is the appropriate type of equipment processing for semicritical items. Alternatively, one can use disposable HEPA filtration and simply change the mouthpiece and filter between patients.
Which of the following is an acceptable way to dispose of liquid biohazardous/infectious waste, such as blood or body fluids?
pour into sanitary sewer (drain or toilet)
process in hot water cycle (pasteurization)
transport in containers to sanitary landfill
place in a biohazard bag for disposal
pour into sanitary sewer (drain or toilet)
Liquid biohazardous/infectious waste can be disposed of either 1) via the sanitary sewer system (pouring down the drain or toilet) or 2) via steam autoclaving (liquid cycle). If disposing into the sewer, state or local regulations may require pretreatment with a disinfectant like sodium hypochlorite (typically 1 part bleach to 9 parts liquid waste). If autoclaving, be sure to open the collecting vessel before initiating the cycle. After autoclaving the treated liquid can be poured down the drain. Appropriate PPE (e.g., gloves, gown, mask, and protective eyewear) should be worn when handling liquid waste, which must be transported in sealed leak-free containers, not bags. Only treated solid wastes are placed in sanitary landfills.
Which of the following are acceptable for home-care use for the cleaning of non-electric respiratory therapy equipment?
Acetic acid
Sonacide
Cidex
Bleach
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is another name for common household vinegar. Vinegar is a safe and effective cleaning agent for home use. Cidex is not a product that would be appropriate for use in the home. It is not safe to use bleach on respiratory therapy equipment in the home. The use of sonacide is not intended for home use.
You should "double bag" solid or semi-solid infectious waste when:
the waste originates from a reverse isolation area
the waste comes from an immunocompromised patient
the waste originates from a contact isolation area
the waste could easily penetrate the primary bag
the waste could easily penetrate the primary bag
The organisms most commonly associated with contamination of nebulizers are:
fungi
adenoviruses
gram+ bacilli
gram- bacilli
gram- bacilli
The organisms most commonly associated with contamination of aerosol generators are gram- bacilli, particularly Pseudomonas aeruginosa. More recently, disturbing case reports of nosocomial infection by Legionella pneumophila (the cause of the highly virulent Legionnaires' Disease) have been disseminated.
After a 30-minute soak in alkaline gluteraldehyde (Cidex), viable microorganisms are found on the equipment. Which of the following is a possible reason?
high resistance of organism or insufficient soak time
inappropriate sterilization solution type
insufficient aerate
device requires autoclaving
high resistance of organism or insufficient soak time
Alkaline glutaraldehyde, or Cidex, is a liquid that can disinfect and sterilize equipment. There are several factors that dictate its effectiveness. They are: strength of solution, soak time, and resilience or resistance of the organism. Aeration time does not decrease the effectiveness of the solution.
A chemical indicator tape found inside the sealed, packaged disposable mask helps determine which of the following?
if the package has remained closed
if the equipment has been properly sterilized
if the equipment is sterile
if microorganisms remain viable on the equipment
if the equipment has been properly sterilized
A chemical indicator tape inside a sterialized package does not actually indicate the presence or absence of viable spores. It does, however, indicate if the equipment has been through the sterilization process.
A respiratory therapist is working in a 69-bed rural hospital with limited resources. In order to disinfect a re-usable plastic mouthpiece used for pulmonary function testing, the respiratory therapist should
soak in Sonacide for 30 minutes.
send for steam autoclave.
soak in Cidex for 10 hours.
soak in 60% alcohol for 10 hours.
soak in Cidex for 10 hours.
Cidex (alkaline glutaraldehyde), will kill bacteria in 10 min, and everything in 10 hours. It works by using a caustic pH between 7.5 and 8.5. It should be changed every 14 days.
A respiratory therapist is disinfecting reusable mouthpieces in Sonacide. For how long should the equipment soak to achieve disinfection?
6 minutes
10 minutes
2 minutes
8 minutes
10 minutes
Acid glutaraldehyde, like its counterpart glutaraldehyde, has the ability to disinfect and sterilize. However, soak times are different. The acid version can disinfect in 10 min. but can sterilize in only one hour. In this question, we are asked to merely disinfect the reusable mouthpieces.
Which of the following types of equipment processing would you recommend for a reusable device that was introduced into a patient's bloodstream?
sterilization
low-level disinfection
detergent washing
high-level disinfection
sterilization
Your hospital requires all liquid infectious waste be transported and processed centrally before disposal. To transport several full suction collection bottles from ICU for processing you would:
place sealed bottles in a puncture-resistant biohazard bag
seal and label each bottle and transport them one at a time
place sealed bottles into a closable leak-proof biohazard container
transfer all bottle contents into a large secondary carted vessel
place sealed bottles into a closable leak-proof biohazard container
A respiratory therapist is attempting to sterilize a non-disposable IPPB circuit from a patient who has confirmed active tuberculosis. The sterilizing material is acid gluteralderhyde (Sonacide). For how long must the therapist soak the circuit to achieve sterilization?
unable to achieve sterilization with this chemical
10 hours
10 minutes
20 minutes
10 hours
Which of the following types of equipment processing would you recommend for a reusable device that only contacted a patient's intact skin?
high-level disinfection
sterilization
soap and water wash
low-level disinfection
low-level disinfection
Which of the following devices is LEAST LIKELY to transmit pathogenic organisms to the patient?
ultrasonic nebulizer
small volume drug nebulizer
wick-type humidifier
large volume jet nebulizer
wick-type humidifier
A respiratory therapist is working in a 69-bed rural hospital with limited resources. In order to disinfect a re-usable plastic mouthpiece used for pulmonary function testing, the respiratory therapist should
soak in Sonacide for 30 minutes.
send for steam autoclave.
soak in 60% alcohol for 10 hours.
soak in Cidex for 10 hours.
soak in Cidex for 10 hours.
During a procedure in ICU, blood spills onto the outer plastic casing of an in-use ventilator. After cleaning the surface using gloves and disposable gauze pads, how would you decontaminate it?
wash the surface with a detergent and rinse with sterile water
swab the area with a tuberculocidal disinfectant or bleach solution
spray the area with a concentrated isopropyl alcohol solution
take the ventilator out of service and have it sterilized
swab the area with a tuberculocidal disinfectant or bleach solution
A patient has been receiving an aerosolized bronchodilator through a handheld nebulizer over the past day. Which of the following would a respiratory therapist recommend to minimize the risk of her getting a nosocomial infection?
Add a broad-spectrum antibiotic to the nebulizer with each treatment.
Change the handheld nebulizer and mouthpiece every 24 hours.
Discard medications and saline solution 24 hours after opening.
Respiratory therapists should wash their hands before giving a treatment
1 and 2 only
1, 2, 3 and 4
2, 3 and 4 only
3 and 4 only
2, 3, and 4 only
Which of the following are acceptable for home-care use for the cleaning of non-electric respiratory therapy equipment?
Sonacide
Acetic acid
Bleach
Cidex
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is another name for common household vinegar. Vinegar is a safe and effective cleaning agent for home use. Cidex is not a product that would be appropriate for use in the home. It is not safe to use bleach on respiratory therapy equipment in the home. The use of sonacide is not intended for home use.
You need to transport several contaminated nondisposable ventilator circuits from a patient unit to an equipment processing area. You would:
transport the circuits in leak- and puncture-resistant biohazard bags
place circuits in biohazard bags, then transport in a closed, rigid container
wash and disinfect the circuits at point of origin before transporting
bag the circuits, then transport on a cleaned and sanitized cart
place circuits in biohazard bags, then transport in a closed, rigid container
At its point of generation, solid infectious waste should be:
placed in standard garbage bags and sent out for incineration
placed in the unit's utility sink and soaked in disinfectant
placed in a color-coded, puncture-resistant bag or container
broken into small pieces and flush into the sanitary sewer
placed in a color-coded, puncture-resistant bag or container
A bronhoscope has been used on a patient with a staphylococcus infection. To properly sterilize the equipment, perform a
3 minute soak in one-day-old Sonacide
steam autoclave
15 minute soak in 13-day-old Cidex
1 hour soak in 30-day-old Sonacide
15 minute soak in 13-day-old Cidex
Cidex, or alkaline glutaraldehyde, is most commonly used for bronchoscopy sterilization. A 10-hour soak is best, but all bacteria will be destroyed within 10 min. In this example, the primary concern is Staphylococcus, a bacteria. Alkaline glutaraldehyde must be changed no later than every 14 days.
An intubated patient has a size 7.5 mm endotracheal tube in place. Diffuse rhonchi are auscultated. A respiratory therapist is using a 12 Fr suction catheter set to a pressure of -100 cm H2O, attempting to suction for 15 seconds. Only scant secretions are suctioned, and breath sounds do not improve after the procedure. The respiratory therapist should increase the
catheter size to a 14 Fr.
catheter size to an 18 Fr.
suction pressure
suction duration.
suction pressure
While performing a routine ventilator a check on a patient with a balloon-tipped flow-directed pulmonary artery catheter in place, the respiratory therapist notices the inflection points on the waveform indicate the tip of the pulmonary artery catheter is improperly placed in the right ventricle. To correct this problem, the therapist should recommend
removing the catheter and inserting a new one
recording the pulmonary artery pressure as shown on the waveform
inflating the balloon and advancing the catheter
twisting the catheter until pulmonary artery pressures are observed
inflating the balloon and advancing the catheter
The pulmonary catheter should be terminated in the pulmonary artery, which is beyond the right ventricle. Therefore, advancing the catheter is appropriate. The catheter may be advanced by sailing it into position, which is done by inflating the catheter balloon and allowing blood flow to carry the catheter into position and then deflating the balloon once it is in the proper position.
A post-operative patient is receiving positive-pressure ventilation with an IPPB while recovering from anesthesia. The mandatory rate is 10/min. Inspiratory pressure is set to 18 cm H2O. Gradually the rate increases to 16/min while the monometer needle is showing a significant negative deflection before inhalation begins. The pressure monometer no longer rises smoothly during inhalation. What should the respiratory therapist do?
sedate the patient
increase sensitivity
decrease inspiratory flow rate
wean the patient
increase sensitivity
The gradual increase in respiratory rate indicates that the patient is waking up from anesthesia, as expected. The negative deflection before inhalation indicates that the machine sensitivity is too low-requiring the patient to work too hard to trigger inspiration. The manometer not rising smoothly indicates the flow rate is also too low. It is not appropriate to sedate the patient but rather allow him to wake up with more applicable settings.
Which of the following alarms would be most important for a patient receiving positive pressure ventilation by a pressure-cycled ventilator?
high pressure
low FIO2
I:E ratio
low volume
low volume
Adding an aerosol-holding chamber to a metered-dose inhaler
requires more complex patient education regarding technique.
requires greater patient coordination.
minimizes deposition of particles that are too large.
disallows the patient to receive medication by mask
minimizes deposition of particles that are too large.
An aerosol holding chamber, commonly known as a spacer, not only improves medication delivery when added to a metered-dose inhaler, but also reduces the significant amount of coordination required to properly self-administer an MDI and filters out particles that are too large for pulmonary effectiveness.
In working with an electrically powered apparatus, you notice a slight tingling sensation when the metal parts of the equipment are touched. In this case, you should:
use this device only with non-electrically sensitive patients
immediately take the piece of equipment out of service
use an extension cord to increase electrical resistance
use a 'cheater' adapter to bypass the ground connection
immediately take the piece of equipment out of service
A tingling sensation which occurs when the metal parts of a piece of equipment are touched usually indicates improper grounding and the possibility of a serious leakage current. In these cases, you must ensure that the faulty equipment is immediately taken out of service.
A large drop in the humidifier water level in an infant ventilator circuit will result in:
a decrease in the volume lost due to compression
a decrease in the volume received by the infant
an increase in the circuit's mechanical deadspace
an increase in the volume received by the infant
a decrease in the volume received by the infant
Due to the very small tidal volumes delivered to infants, increases in a ventilator circuit's internal volume, as will occur when the humidifier water level drops, cause large increases in compressed volume loss. The larger the compressed volume loss, the lower the actual volume received by the infant.
A patient with CHF requires 5 L/min humidified oxygen by nasal cannula continuously. The patient is being discharged home. Which of the following modalities is not indicated?
molecular sieve device
pulse-dose conservation device
simple mask
portable oxygen tanks
simple mask
A doctors orders continuous heated aerosol for a newborn in an oxyhood. You would recommend a servo-controlled heated membrane humidifier instead for which of the following reasons?
Minimal risk of fluid imbalance
Low and safe noise level
Low likelihood of infection
1 and 3
2 and 3
1 and 2
1, 2 and 3
1, 2, and 3
Newborn infants are at high risk for infection. For this reason, medical gas humidification should always be achieved with an evaporative humidifier that produces only molecular water, not water aerosol (which can spread bacteria and cause overhydration). In order to assure maintenance of a neutral thermal environment, the humidifier selected should allow precise control over gas temperature at the point of delivery. Last, neonatal exposure to high noise levels has been associated with subsequent auditory damage. Thus a 'quiet' device should be used. A servo-controlled heated humidifier meets all three criteria.
An air-entrainment jet nebulizer is set at 50%. The respiratory therapist analyzes the oxygen coming from the end of the tubing and finds it is 60%. Which of the following most likely explains this finding?
poorly calibrated analyzer
leak in the tubing
excess water in the tubing
low flow through the jet orifice
excess water in the tubing
When administering oxygen by any device that has a venturi mechanism, back pressure on the venturi will slow the speed of gas, decrease room air entrainment, and result in an increase in FIO2. Of the options offered, only excess water in the tubing would cause this type of back pressure.
A patient receiving volume-controlled ventilation has a balloon-tipped pulmonary artery catheter in place. The respiratory therapist notices the PA waveform is ascending and descending with inflection points at 25 and 2 mmHg. Based on this information, the therapist should recommend
advancing the catheter
deflating the catheter balloon
rotating the catheter
monitoring the patient closely
advancing the catheter
The pulmonary artery catheter waveform that has a high inflection point of 25 and a low inflection point of 0-2 mmHg is an indication that the tip of the catheter is in the right ventricle of the heart. The proper placement of this catheter is in the pulmonary artery. Therefore, advancing the catheter is indicated. This is done by inflating the balloon and allowing the catheter to sail into a proper position in the pulmonary artery.
A respiratory therapist is initiating mechanical ventilation at the following settings and preferences:
Mode Assist/control
Mandatory rate 20
VT 500 mL
FIO2 0.5
PEEP 5 cm H2O
I:E 1:2
Which of following is the minimum inspiratory flow setting?
80 L/min
40 L/min
65 L/min
28 L/min
40 L/min
To calculate the minimum inspiratory flow rate for a given set of ventilator parameters the I:E ratio can be added together and then multiplied by the minute ventilation. In this case 1+2=3. 3 x 10.0L = 30L/min.
A febrile patient has the following blood gas results: (results are not corrected for temperature)
pH 7.35
PaCO2 44 mmHg
PaO2 28 mmHg
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
BE 0 mEq/L
O2 Sat 90%
Which of the following requires attention?
Clark electrode
Severinghaus electrode
Sanz electrode
spectrophotometer
Clark electrode
In this arterial blood gas a PaO2 of 28 mmHg is reported. That is too low for the patient to still be alive and therefore this data is probably faulty. The question is essentially asking which electrode would you suspect is not working properly. The Clark electrode is another name for the PO2 electrode. The Sanz electrode is another name for the pH electrode and the Severinghaus electrode is called the CO2 electrode.
A patient with diabetes is demonstrating a Kussmaul breathing pattern. The patient is receiving supplemental oxygen at FIO2 1.0 by a single large volume nebulizer device. The inspiratory flow produced by the patient is measured and found to 20 L/min. Pulse oximetry reveals a saturation of 89%. Which of the following would be most helpful in this situation?
Install a tandem large volume nebulizer in the current system
Increase the oxygen flow rate at the flowmeter to 22 L/min
Replace the large volume nebulizer with an ultrasonic nebulizer device
Administer a mild sedative
Install a tandem large volume nebulizer in the current system
When a large-volume nebulizer device is set to 100% oxygen, the maximum achievable flow rate is about 15 L/min. Because this patient has a minute ventilation of 20 L/min, his or her inspiratory demand is not being met. This can be overcome by installing a second, or tandem, large-volume nebulizer. Together, the nebulizers may produce up to 30 L/min, which will exceed the patient's inspiratory demand.
A pressure-volume ventilator graphic fails to return to the point of origin. Which of the following could be the cause?
excessive cuff pressure
leak in the ventilator circuit
pulmonary distension
inadequate PEEP
leak in the ventilator circuit
A pressure volume loop on a ventilator should end in the same place it starts. If a pressure volume loop fails to return to zero, or its point of origin, there is likely a leak in the circuit, reducing return volume.
Excessive bubbling is noted in water seal chamber of a chest tube drainage system. Which of the following could be the cause?
fluid level in the suction control chamber is too low
leak in the tubing between the patient and fluid collection chamber
water seal fluid level is too high
water seal fluid level is too low
leak in the tubing between the patient and fluid collection chamber
Excessive bubbling in the water-seal chamber of a chest tubes drainage system is caused from a leak somewhere between the water-seal compartment and the patient's lung. In this case a leak in the tubing between the patient and fluid collection chamber would cause the excessive bubbling.
Your patient is ordered to start breathing treatments with pentamidine isethionate (NebuPent). To minimize your risk of drug exposure, you should do which of the following?
place an HME between the nebulizer and the mouthpiece
use a metered dose inhaler+valved holding chamber
use a SVN with nonrebreathing circuit+expiratory filter
use a small-particle aerosol generator with a HEPA filter
use a SVN with nonrebreathing circuit+expiratory filter
When administering aerosolized drugs whose toxicity or side effects pose a threat to you or other caregivers or patients, you should make efforts to contain the aerosol by using a nonrebreathing, filtered nebulizer system (such as the RespiGuard) and applying environmental protection strategies, to include use of negative pressure chambers/booths, scavenging system and caregiver wearing of HEPA filtered masks. methods.
When making routine equipment checks you hear the relief valve of a patient's bubble humidifier sounding. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this problem?
excessive oxygen input flow
clogged bubble/diffuser
high wall outlet pressure
decreased patient compliance
excessive oxygen input flow
The relief valve of a humidifier sounds when the pressure in the reservoir container exceeds the valve's threshold pressure (usually between 1-2 psig). The most common reasons for this to occur are 1) excessive oxygen input flow, and 2) downstream obstruction to outflow. In bubble humidifiers that use a diffuser plate to break up the gas stream, clogging of this element would prevent gas from entering and pressurizing the system. Flowmeter restriction prevents high wall outlet pressures (> 50 psig) from affecting pressure in the humidifier. And changes in patient mechanics (e.g., compliance or resistance) would have no effect on pressure in the humidifier.
A large volume jet nebulizer is operating at the 100% O2 setting with an input flow of 12 L/min. What effect will changing the entrainment port setting from 100 to 70% have on the system?
the input liter flow will increase by 30%
the total output liter flow will decrease
the aerosol weight density will increase
the total output liter flow will increase
the total output liter flow will increase
When the air-entrainment port of a large volume jet nebulizer is opened, room air is entrained, and total flow through the system increases (in direct proportion to the size of the opening). This increased output flow increases total aerosol output per minute, but actually lowers aerosol density.
Which of the following are potential complications associated with the use of heated humidification systems with mechanical ventilators?
pulmonary dehydration
thermal injury to the airway
increase of heat and water vapor content of inspired gas
atelectasis
thermal injury to the airway
Overheating of the airway may occur with the use of an electrically powered heater if not properly maintained. Because the device is electrically powered, it also may be associated with electric shock of the patient. These complications are not common, but possible.
An apneic post-op patient is receiving pressure-cycled ventilation with a set expiratory time in the recovery room. Which of the following would occur if the patient's artificial airway were to become partially obstructed?
Decreased delivered volume
Increased respiratory rate
Decreased inspiratory time
1, 2 and 3
2 and 3
1 and 3
1 and 2
1, 2, and 3
When a true pressure-cycled ventilator encounters high resistance (e.g., partial airway obstruction), it will cycle off prematurely. As a result, inspiratory time and delivered volume will decrease. In addition, with a shorter inspiratory time and fixed expiratory time, the respiratory rate will increase.
A respiratory therapist is monitoring a continuous flow CPAP device set at 8 cm H2O. With each inspiration from the patient the monitored pressure drops from 8 cm H2O to 3 cm H2O but then returns to 10 cm H2O during expiration. Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
leak in the mask
gas flow to the patient is insufficient
normal operation
the patient is in need of Bi-level therapy
gas flow to the patient is insufficient
What would occur on a time-cycled ventilator with a fixed rate if the inspiratory flow rate were reduced?
decrease in inspiratory time
increase in tidal volume
decrease in tidal volume
increase in inspiratory time
decrease in tidal volume
A patient receiving volume-controlled ventilation is coughing uncontrollably. The high-pressure alarm is sounding continuously. The respiratory therapist should first
silence the ventilator alarm, calm the patient's anxiety
sedate the patient
provide the patient with manual ventilatory support
suction the patient
provide the patient with manual ventilatory support
The first response to any ventilator alarm is to disconnect the ventilator from the patient and begin manual ventilation. Once ventilation and oxygenation of the patient are assured, troubleshooting for the source of the problem may begin.
Blood pressure obtained by a sphygmomanometer reads higher than the indicated blood pressure from an arterial line on the same patient. To correct problem, the respiratory therapist should FIRST
flush the art line with sodium heparin
discontinue use of the sphygmomanometer
check for air bubbles in the transducer dome
advance the arterial line catheter
check for air bubbles in the transducer dome
When blood pressure by sphygmomanometer (cuff) differs from the blood pressure obtained from an indwelling arterial line, the blood pressure taken by cuff is considered more accurate and reliable. Problems that may occur in the ART line include clots in the line and bubbles in the transducer dome.
A therapist is unable to obtain a reading with a galvanic-type oxygen analyzer when attempting to measure oxygen percentage inside an infant oxygen hood while heated humidity is also applied. The therapist should?
change the electrode
discontinue heated humidity
change the electrolyte solution
change the batteries
change the electrode
When a galvanic-type oxygen analyzer fails to produce a reading, it is likely a problem with the power source. These type of analyzers do not have batteries. The electrode is in essence a battery. So, the solution is to change the electrode. The electrode is also called the fuel cell.
Which of the following are associated with a fenestrated tracheostomy tube?
silver
cap
button
foam cuff
cap
A fenestrated tracheostomy tube has an inner cannula with a hole to facilitate talking and weaning. It also has an inner cannula for resuscitation, or mechanical ventilation. The cuff is like that of an endotracheal tube, low-pressure, high-volume. And finally, a cap is used to close the tube for speech therapy. When the cap is used, the inner cannula should be removed and the cuff should be deflated.
When selecting a suction catheter to be used in an oral endotracheal tube, the respiratory therapist should select a catheter whose diameter should not exceed what fraction of the internal diameter of the endotracheal tube?
1/4
1/2
2/3
3/4
1/2
A 68-kg (150-lb) post-operative female patient is receiving mechanical ventilation in the SIMV mode with a set mechanical rate of 6/min and an actual rate of 10/min. Her set tidal volume is 500 mL with a spontaneous tidal volume of 400 mL. She is comfortable with stable vital signs. What should the respiratory therapist do?
Increase the set tidal volume to 650 mL.
Increase the mechanical rate to 16/min.
Set the low VE alarm to 4.0 L/Min
Start pressure support at 15 cm H2O
Set the low VE alarm to 4.0 L/Min
In this case the patient is comfortable with stable vital signs during weaning. There is no indication that any increase in ventilation is necessary. A respiratory therapist may seek a response that is more aggressive in weaning, but no such choice is offered. Therefore, the best response is to set the alarms and monitor the patient closely to assure that she will continue her spontaneous breaths.
Which of the following oral airways would you select for a newborn infant?
Yankauer
Guedel
Miller
Murphy
Guedel
When using an oral airway in infants, a Guedel type (with a central passageway) is probably the best choice, since the infant tongue may easily occlude the lateral slots of other designs (like the Berman), thereby worsening the obstruction.
You observe that a pressure-cycled ventilator fails to cycle off when the patient exhales. The most likely cause of this problem is:
a improper sensitivity setting
an obstructed endotracheal tube
an airway or patient circuit leak
patient-ventilator dyssynchrony
an airway or patient circuit leak
While providing manual ventilation during a transport of a patient with a standard tracheostomy tube, the therapist notices it is difficult to squeeze the resuscitator bag. The therapist should NEXT
add air to the airway cuff.
palpate the neck and clavicle for subcutaneous emphysema.
deflate the cuff and reattempt manual ventilation.
provide manual ventilation with a bag and mask.
deflate the cuff and reattempt manual ventilation.
When it is difficult to provide manual resuscitation through a tracheostomy tube, the first action should be to check the patency of the tube by inserting a suction catheter. The next step would be to deflate the cuff to ensure that it has not herniated over the end of the tracheostomy tube.
You attach a disposable jet nebulizer to a flowmeter at 12 L/min. If no mist is generated, you should:
increase the pop-off pressure to 5 psi
decrease the FIO2
replace the nebulizer
set the flowmeter to 8 L/min
replace the nebulizer
Which of the following are power sources can be used with most portable O2 concentrators?
Household AC current
12 volt DC car outlet
Portable battery pack
2 and 3
1 and 2
1 and 3
1, 2 and 3
1, 2, and 3
While performing a test discharge of a metered dose inhaler (MDI) prior to administering to a patient, the respiratory therapist is unable to visually confirm the discharge of any particles or aerosol. The therapist should
Shake the canister and administer the dose to the patient
Administer the dose to the patien
Discard the canister, obtain a new MDI
Utilize a chamber and administer the dose to the patient
Discard the canister, obtain a new MDI
Just prior to providing a patient with manual ventilation, following oral intubation, the respiratory therapist assesses the function of a self-inflating resuscitator bag. The therapist notices the bag is easy to squeeze when attached to the patient. It is also evident that there is no chest rise with each squeeze. Which of the following could be the cause of the problem?
insufficient flow
detached reservoir
bag is too small
faulty inlet valve
faulty inlet valve
On a self-inflating resuscitator bag, there is most likely a faulty inlet valve if the bag is easy to squeeze once it is connected to the patient. In normal circumstances, when the bag is connected to the patient, pulmonary resistance should be felt through the resuscitator device. If no resistance is felt, it is likely that the gas is being ejected through a one-way valve that is responsible for allowing gases to enter the bag. This would suggest a faulty inlet valve that is allowing gases to move both directions.
A large volume jet nebulizer is operating on 70% O2 at 12 L/min. You observe that the aerosol being delivered in short rapid puffs and note a gurgling sound in the system. Which of the following actions would be most appropriate?
increase the nebulizer input flow to 15 L/min
switch the nebulizer entrainment port to 40% O2
drain any accumulated water from the delivery tubing
reduce the water volume in the nebulizer reservoir
drain any accumulated water from the delivery tubing
Aerosols produced by large volume jet nebulizers contain a wide range of particle sizes. Many of the larger unstable particles will impact or deposit by sedimentation in the tubing, causing water to accumulate at low points in the circuit, and intermittently blocking flow (as evidence by the gurgling sound). To ensure proper flow and the set FIO2, this water should be regularly drained AWAY from the patient and discarded (never returned to the reservoir).
A patient with CHF requires 5 L/min humidified oxygen by nasal cannula continuously. The patient is being discharged home. Which of the following modalities is not indicated?
molecular sieve device
portable oxygen tanks
simple mask
pulse-dose conservation device
simple mask
A simple mask requires at least 6 L/min flow and is not appropriate for delivery of 5 L/min
Excessive bubbling is noted in the suction control bottle of a chest tube drainage system. All connections are secure. The respiratory therapist should
reduce the wall suction pressure.
advance the tube further into the chamber
increase the wall suction pressure.
discontinue the chest tubes
reduce the wall suction pressure.
Excessive bubbling in the water-seal compartment of a chest tube drainage system is caused by either a leak in the system, a perforation in the patient's lung tissue, or excessive suction pressure. Of the options offered only a reduction in wall suction pressure will most likely remedy the problem.
A patient is receiving heliox therapy with a mixture of 70% / 30% by nonrebreathing mask to reduce airway resistance. The therapist also observes the reservoir bag is not collapsing at all with each inspiration. After ensuring the face mask is sealed around the face properly, the therapist should
Obtain a partial rebreathing mask
Reduce the total flow of gas mixture to the patient
Obtain an arterial blood gas
Discard the valve between the mask and the reservoir
Reduce the total flow of gas mixture to the patient
When a reservoir bag on and on nonrebreathing mask does not collapse at all with each breath, the cause may be one of two problems: It may be due to an improper seal between the mask and the patient's face. It may also be due to excessive total gas flow going to the reservoir bag.
Immediately after insertion of a #4 laryngeal mask airway (LMA) in a 70 kg adult, you should inflate the cuff to:
60 mL volume
60 cm H2O pressure
10 mL volume
30 cm H2O pressure
60 cm H2O pressure
In general, regardless of the size of the LMA, you should inflate the cuff to 60 cm H2O, while at the same time keeping the maximum inflation volume within that specified by the manufacturer. For a #4 LMA, the maximum recommended cuff inflation volume is 30 mL.
A 40-week gestational age infant is to receive oxygen therapy via a blender set at 35% and humidification through a jet nebulizer. The respiratory therapist should properly set the nebulizer by setting it to
21%
anything over 35%
the same FIO2 as the blender
100%
100%
When using an air-oxygen blender, oxygen percentage is predetermined prior to entering the large volume nebulizer device. When this happens, the large volume nebulizer should be set at 100% in order to avoid entraining additional room air and lowering FIO2.
During a disaster, an H-cylinder with 1000 psi is being used to power a Bird Mark 7 pressure ventilator that is set to deliver 100% oxygen at a tidal volume of 500 mL, respiratory rate of 12/min. How many hours will the tank last?
8
4
6
10
8
To determine the answer to this question, the liter flow per minute must be determined. At a rate of 12 per minute and a tidal volume of 500 mL, the minute ventilation is 6.0 L. Tank duration = 3.14 x 1000 psi = 3,140 L. 3,140 L / 6 L/min = 523 minutes. 523 min / 60 = 8.7 hours. The closest answer is eight hours.
A patient is receiving volume ventilation through a tracheostomy tube. In response to a high pressure alarm, the respiratory therapist attempts suctioning but notices the suction catheter will not pass beyond the end of the tracheostomy tube. Which of the following would be the first action the therapist should take?
Resume volume ventilation
Bronchoscopy
Deflate the cuff
Increase catheter size and suction pressure
Deflate the cuff
Because the catheter will not pass beyond the end of the tracheostomy tube, the most obvious suspicion is a herniated tracheostomy tube cuff. To quickly determine if this is the cause of the high-pressure and the inability to pass the catheter, the cuff should be deflated and the catheter should be inserted again to determine if the blockage remains. If the cather is able to pass, then a herniated cuff is present, and the tube should be replaced
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the FIO2 provided by an IPPB device that uses air-entrainment to enhance flow?
the shorter the inspiratory time, the higher the FIO2
the entrainment ratio is fixed at about 3:1 or 40% O2
the higher the inspiratory pressure, the higher the FIO2
air entrainment increases as inspiratory pressure increases
the higher the inspiratory pressure, the higher the FIO2
You are using a portable pressure-cycled ventilator with a heated humidifier and IPPB circuit to temporarily ventilate an intubated patient who is regaining consciousness in the recovery room. When you check the patient and ventilator, you notice that the inspiratory time is prolonged and the machine does not cycle off without active patient effort. How should you correct the problem?
decrease the sensitivity setting
increase the control pressure
switch the unit to 100% source gas
check/adjust ET tube cuff pressure
check/adjust ET tube cuff pressure
A prolonged inspiratory time and delay in off-cycling with a pressure-cycled ventilator indicate a leak. Leakage may be occurring around the ET tube cuff, which can be rectified by adjusting cuff pressure. Alternatively, leakage may be occurring in the delivery circuit. The two most common sources of circuit leakage would be loose connections at the humidifier or (for IPPB circuits) at the nebulizer manifold.
A respiratory therapist working in a 250-bed medical center has a mechanically ventilated patient who has been receiving volume-controlled ventilation for several days due to ARDS. The patient's compliance has improved significantly in the past 12 hours. Which high alarm parameter should be adjusted?
pressure
respiratory rate
volume
minute ventilation
pressure
With improved lung compliance, peak pressures will diminish with constant tidal volumes. Therefore, the therapist should adjust the peak pressures downward in order to remain 10-15 cm H20 above the basline peak pressures.
Which of the following would cause the FIO2 delivered by an air entrainment mask to be different than that specified by the manufacturer?
an increase in resistance downstream from the jet
a decrease in the patient's peak inspiratory flow
an increase in the flow of oxygen into the jet
obstruction of the patient's nasal passages
an increase in resistance downstream from the jet
An increase in flow resistance downstream from the jet (such as would occur were bedding to cover the mask's outlet ports) decreases the amount of air entrained, thereby decreasing total output flow. A similar effect is produced by obstruction of the air entrainment ports. Under these conditions, the delivered O2 concentration rises, but the actual FIO2 may decrease as room air is inhaled around the mask parts. Changes in O2 input flow do not affect the delivered O2 concentration because for a given size jet and entrainment ports, the mixing ratio is fixed. Patient changes also do not affect the O2 concentration delivered by these devices, but (as described above) may alter the actual FIO2. This occurs most commonly when the patient's peak inspiratory flow exceeds that provided by the device, a problem often seen with systems delivering over 35 to 40% O2. Mouth vs. nose breathing has no impact on full face mask systems.
A venturi or air-entrainment mask will deliver more oxygen than intended if:
the flow is set 5 L/min too high
aerosol is being added through the air-entrainment ports
the holes in the mask are too large
the air-entrainment ports have been blocked
the air-entrainment ports have been blocked
A volume ventilator is providing ventilation to a 32-year-old patient with head trauma and possible neurological impairment. The patient is manually ventilated while the respiratory therapist prepares to transfer the ventilator from ER to ICU. With the ventilator running, the therapist disconnects the compressed air supply hose and hears a sudden new thumping type sound emanating from the ventilator. The therapist should
transfer and set up the ventilator as ordered
inform the receiving nurse and therapist that the ventilator may be faulty
exchange the ventilator for a new one during the transfer
change the air inlet filter prior to use in the ICU
transfer and set up the ventilator as ordered
Most ventilators come equipped with a built-in air compressor. If the ventilator detects a lack of 50 PSI pressure from the air hose, there is an automatic trigger to turn on the internal compressor to provide the appropriate air supply so that gases may be mixed and appropriate oxygen provided. When the compressor activates, it often causes a loud thumping sound that can be heard. Without being familiar with the sound, the practitioner may suspect something is wrong. In fact, it is evidence that the machine is operating properly.
How does CO2 measured from expired gas compare to that from arterial CO2?
up to 10 mm Hg lower
higher immediately following CPR associated with cardiac arrest
about the same
up to 10 mm Hg higher
up to 10 mm Hg lower
At the higher end of its flow range, a high flow nasal cannula provides performance comparable to what other O2 delivery device?
simple mask
nonrebreathing mask
28% air-entrainment mask
transtracheal catheter
nonrebreathing mask
Which of the following is used by the ultrasonic nebulizer to produce droplets from the water reservoir?
heat
steam
baffling
vibration
vibration
In preparation for a helium dilution study, a respiratory therapist is calibrating the helium analyzer. While exposing the analyzer to ambient room air, what will the analyzer read for helium concentration?
2%
79%
0%
21%
0%
To calibrate a helium analyzer, sometimes called a Wheatstone Bridge, the device must be calibrated to room air for the low calibration and to a known level of helium for the high calibration. Because room air has no significant level of helium, helium analyzers should read 0% when exposed to ambient room air conditions.
Which of the following is most accurately descriptive of VC ventilation?
flow is constant until a preset volume is delivered
pressure is constant for a specified period of inspiratory time
inspiration ends when a preset pressure setting is reached
the inspiratory phase terminates after delivery of a preset volume
the inspiratory phase terminates after delivery of a preset volume
A pressure-volume ventilator graphic fails to return to the point of origin. Which of the following could be the cause?
excessive cuff pressure
pulmonary distension
inadequate PEEP
leak in the ventilator circuit
leak in the ventilator circuit
A pressure volume loop on a ventilator should end in the same place it starts. If a pressure volume loop fails to return to zero, or its point of origin, there is likely a leak in the circuit, reducing return volume.
Which of the following factors effect the oxygen concentration delivered by an air entrainment system?
Oxygen input to the jet
Device air to oxygen ratio
Downstream flow resistance
1 and 3
1 and 2
1, 2 and 3
2 and 3
2 and 3
The O2 concentration delivered by an air entrainment system is primarily a function of the air:O2 ratio of the device. The delivered O2 concentration will however rise if resistance to flow increases downstream from the jet (which will also lower the total output flow). Total output flow also varies with both the air:O2 ratio and the O2 input flow to the jet. Changes in O2 input flow to the jet do not affect O2 concentrations because for a given jet and entrainment port size the air:O2 mixing ratio is constant.
You know that an O2 concentrator is working properly if:
it provides 100% O2 at maximum flow
the inlet filter is clean and dry
the flow meter reads 5 L/min when wide open
it provides at least 85-90% O2 at maximum flow
it provides at least 85-90% O2 at maximum flow
Oxygen concentrator FIO2s should be checked and confirmed as part of a routine monthly maintenance visit. Routine maintenance of these devices should include cleaning and replacing filters, checking the alarm system, and confirming the FIO2s using either the unit's oxygen sensor or a separate calibrated O2 analyzer. In general, a properly functioning concentrator should be able to provide at least 85 to 90% O2 at its maximum flow setting.
A pressure cycled ventilator with a heated humidifier and modified IPPB circuit is being used to deliver an aerosolized medication and ventilate a patient in the Recovery Room. When the respiratory therapist checks the patient and ventilator, it is noticed that the inspiratory time is longer than when first charted and the machine does not cycle off until the patient blows out. What should be done to correct the problem?
Tighten the humidifier jar and lid.
Increase the peak pressure.
Tighten the medication nebulizer jar and manifold.
Give the patient 100% oxygen.
1, 2 and 3 only
1 and 2 only
1 and 3 only
2 and 4 only
1 and 3 only
There are clear indications of a leak in the system that would prevent a pressure- cycled IPPB-type machine from cycling off. Tightening the humidifier and medication nebulizer jar should help to seal the leaks. If leaks are not the source of the problem, the machine will likely have to be replaced.
A patient is receiving positive pressure ventilation treatments with Albuterol and normal saline. Before the patient is able to complete exhalation, the machine cycles into inhalation. The respiratory therapist should
decrease flow.
adjust sensitivity.
increase flow.
decrease pressure limit.
adjust sensitivity.
When a ventilator cycles into inspiration prematurely either the rate must be decreased or the sensitivity must be adjusted. Of the options offered adjusting sensitivity is the most appropriate response.
Blood pressure obtained by a sphygmomanometer reads higher than the indicated blood pressure from an arterial line on the same patient. To correct problem, the respiratory therapist should FIRST
advance the arterial line catheter
flush the art line with sodium heparin
check for air bubbles in the transducer dome
discontinue use of the sphygmomanometer
check for air bubbles in the transducer dome
A patient is being paralyzed and intubated in preparation to receive positive pressure ventilation with a volume-cycled ventilator in the control mode. Which of the following alarm settings is most important?
low return-volume alarm
low minute ventilation alarm
low PEEP alarm
high-pressure alarm
low PEEP alarm
This is a difficult question. When a patient is intubated after being paralyzed, they do not have the ability to signal or perform any kind of physical manifestation should they accidentally become disconnected from the ventilator. Thus, a ventilator alarm is paramount. The most sensitive alarm that would signify an accidental disconnection is the low PEEP alarm. On some ventilators this is called the disconnect alarm. Keep in mind, this alarm is more sensitive than the low pressure or low-volume alarms. In other words, the low PEEP alarm responds faster than any other alarm when a disconnection has occured.
A 6-year-old patient has been intubated in the emergency room for respiratory failure at a small rural hospital. The hospital has a volume-cycled ventilator with pediatric mode, but has no pediatric ventilator circuits. What should the respiratory therapist do?
Use an uncuffed endotracheal tube
Use an adult circuit following a pre-operational test
Use an infant designed time-cycled, pressure-limited ventilator
Provide IPPB with normal saline QID
Use an adult circuit following a pre-operational test
A pre-operational test on most microprocessor ventilators will result in a correction to the delivered tidal volume after measuring tubing compliance of the circuit. Even without this correction, the compliance factor differences between adult and pediatric circuits is not considered significant enough to matter. Therefore, adult circuits may be used with pediatric patients if necessary.
Increasing the amount of tubing between the "wye" connector of a dual limb ventilator breathing circuit and the patient's airway will have which of the following effects?
decrease in circuit compliance
increase in inspired PCO2
increase in delivered volume
decrease in rebreathed volume
increase in inspired PCO2
Any extra tubing between the "wye" connector of a dual limb ventilator breathing circuit and the patient's airway will increase mechanical deadspace and rebreathed volume, thereby increasing the inspired PCO2, and potentially raising the PaCO2 (the purpose of adding deadspace).The extra tubing will also increase the overall volume of the circuit. The larger the circuit volume, the greater the circuit compliance and volume lost to gas compression/tubing expansion. The greater this volume loss to the circuit, the less the actual volume delivered into the lungs.
In a dual-limb or 'Y' circuit, you will increase mechanical deadspace if you place any additional tubing between:
the heated humidifier and the 'Y' connector
the 'Y' connector and expiratory valve
the ventilator outlet and expiratory valve
the 'Y' connector and the patient's airway
the 'Y' connector and the patient's airway
A patient is in the intensive care unit receiving volume-controlled ventilation and is hemodynamically unstable. A new balloon-tipped, flow-directed, pulmonary artery catheter has been placed. Immediately following insertion, a chest radiograph shows the tip of the catheter is positioned over the right mid lung near the hilum. Which of the following can the respiratory therapist conclude concerning the catheter?
it should be withdrawn several centimeters
it has punctured the pericardial wall
it should be rotated away from the hilum
the balloon should be inflated and the catheter advanced
the balloon should be inflated and the catheter advanced
The chest radiograph reveals improper placement of the pulmonary artery catheter. To advance the catheter, the balloon should be inflated and the catheter should be sailed into place.
An intubated adult patient with severe expiratory airway obstruction requires ventilatory support. Which of the following capabilities would be most important in selecting a ventilator for this patient?
ability to compensate for airway interface leaks
ability to run on 12 volt DC (battery) power
certification for use during MRI procedures
variable flow control and adjustable I:E ratios
variable flow control and adjustable I:E ratios
Of the functions listed, the most important capability when selecting a ventilator for an intubated adult patient with severe expiratory airway obstruction would be variable flow control and adjustable I:E ratios. This will allow clinicians to make sure the expiratory time is sufficiently long to prevent air-trapping/auto-PEEP
A 10-year-old child does not seem to be performing incentive spirometry well with a flow-oriented device. The patient says the device is boring and difficult to get all three balls floating. The respiratory therapist should
obtain a new incentive spirometer with lighter balls
replace the device with a volume-oriented incentive spirometer
provide encouragement and instruct the patient to continue efforts
test the incentive spirometer with a clean mouthpiece
replace the device with a volume-oriented incentive spirometer
A respiratory therapist is preparing to measure SVC on a patient in the emergency department. Which of the following equipment is required?
respirometer
Collins water-seal spirometer
Geissler tube
Wheatstone bridge
respirometer
While monitoring a newborn, the respiratory therapist notices the TcO2 tracing on the monitor suddenly rises sharply. Which of the following is the mostly likely explanation for this rise?
the transcutaneous electrode is below required temperature
the patient's arterial oxygenation has improved
the transcutaneous electrode requires calibration
transcutaneous electrode has become detached from the skin
transcutaneous electrode has become detached from the skin
A patient is receiving NPPV on the general floor to mobilize secretions by portable CPAP connected to medical wall gas. The threshold resistor is not maintaining consistent positive airway pressure when the patient attempts to sigh. What should the respiratory therapist do?
Increase CPAP level
Instruct the patient to avoid sighing
Increase the flowrate
Replace the CPAP unit
Replace the CPAP unit
In this example we have improperly functioning equipment. If given an option to replace such equipment, the respiratory therapist should always choose to do so. One might be tempted to increase the flow rate in this scenario, however, it will not make a difference with this type of resistor.
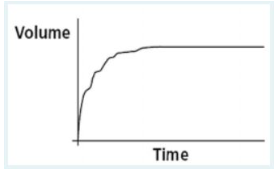
After a patient performs a forced vital capacity (FVC) maneuver, you observe the following volume vs. time plot on the screen of a portable spirometer. What validity error does this plot indicate?
coughing during the maneuver
too slow a start to forced exhalation
breathing during the maneuver
premature end to expiration
coughing during the maneuver
This FVC graph indicates coughing during the maneuver. An abrupt pause occurs about a third of the way through the effort, followed by a short inspiratory effort preceding the cough and then an irregular pattern of exhalation. A normal FVC trace would be smooth throughout.
The package insert quality-control material for a blood gas analyzer defines expected values and upper and lower tolerance levels as follows:
Value Tolerance
pH 7.40 0.5%
PCO2 40 mm Hg 5.0%
PO2 80 mm Hg 3%
Which of the following runs should be closely reviewed?
pH 7.36 PCO2 42 mmHg PO2 79 mmHg
pH 7.44 PCO2 38 mmHg PO2 82 mmHg
pH 7.40 PCO2 40 mmHg PO2 78 mmHg
pH 7.45 PCO2 37 mmHg PO2 81 mmHg
pH 7.45 PCO2 37 mmHg PO2 81 mmHg
The answer that shows a pH of 7.45 and a CO2 of 37 should be examined closely as these values appear to be outside the range of tolerance. If these results are accurate the arterial blood gas machine requires calibration and should not be used to report patient results until maintenance has occurred.