RBC
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Erythrocyte
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
WBC
Leukocyte
Platelet
Thrombocyte
Normal hematocrit value for males
40-54%
Normal hematocrit value for females
37-47%
Granulocytes
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes, monocytes
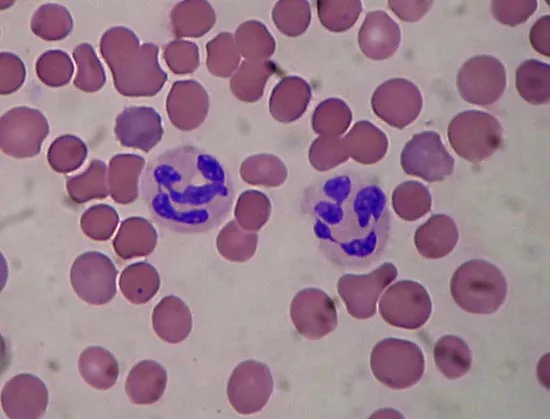
Neutrophil
40-70%
acute bacterial infection
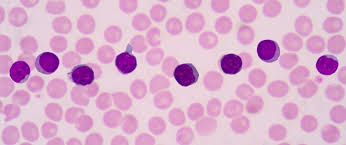
Lymphocyte
20-40%
chronic infections, hypersensitivity reactions, leukemia
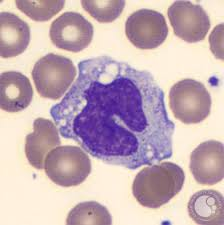
Monocyte
3-8%
bacterial or viral infections, autoimmune disease
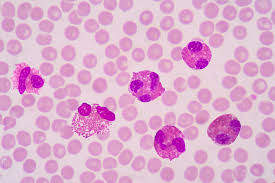
Eosinophil
2-4%
parasite infections, allergies
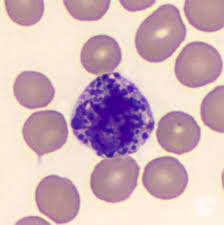
Basophil
<1%
allergies, leukemia
Antigen
found on the surface of cells and trigger immune responses
Antibody
Produced by B-lymphocytes that bind to antigens to mark for destruction
Polycythemia
Too many red blood cells
Sickle Cell
RBC’s are crescent shaped and rigid, improper oxygen supply
Anemia
Too little blood cells
Blood Type A
antibodies: Anti-B
antigens: A
Compatible Donor: A, O
Blood type B
antibodies: anti-A
antigens: B
Compatible Donor: BO
Blood type AB
antibodies: none
antigens: A & B
Compatible Donor: A, B, AB, O
Blood type O
antibodies: Anti-A and Anti-B
antigens: none
Compatible Donor: O
Universal Blood Type RECIPIENT
AB+
Uninversal Blood Type DONOR
O
Agglutination
When incompatible blood is mixed and the antibodies bind to the antigens causing clumping
What does Rh do?
determines whether your blood type is + or -, if you test positive for Rh you are +.