Chemistry IAL Uni1 1
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is electronegativity?
It is the ability of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
What is electron affinity?
The energy change when one mole of gaseous atoms gains one mole of electrons t form one more f gaseous 1- ions.
State whether the different stages of electron affinity are positive or negative and explain why.
The first electron affinity is (mostly) negative, hence the process is exothermic. This is because the incoming electron is attracted to the nucleus of the atom.
The second affinity is always positive, hence the process is endothermic. This is because we are adding a negative electron to an already negative in so the strong electrostatic repulsion needs to be overcome (so energy is required).
What are the trends for electron affinity across a period? Why?
Electron affinity becomes more negative (reaction becomes more exothermic) from left to right (of period).
Reason: The nuclear charge increases, the atomic radius decreases and the effective nuclear attraction for the incoming electron increases.
What are the trends for electron affinity down a group? Why?
The electron affinity becomes less negative (exothermic) down the group.
Reason: Atomic radius increases, so electron experiences more shielding so the attraction is weaker.
What is ionization energy?
The amount of minimum energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous positive ion. It is a measure of how strongly a nucleus holds onto it’s electrons.
This process is endothermic.
What happens to the atomic radius across a period?
The atomic radius decreases from left to right because the effective nuclear charge (Zeff) increases.
What happens to the atomic radius down a group?
The atomic radius increases from top to bottom because the number of electron shells (energy levels) increases.
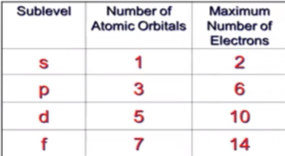
Fill the following table:
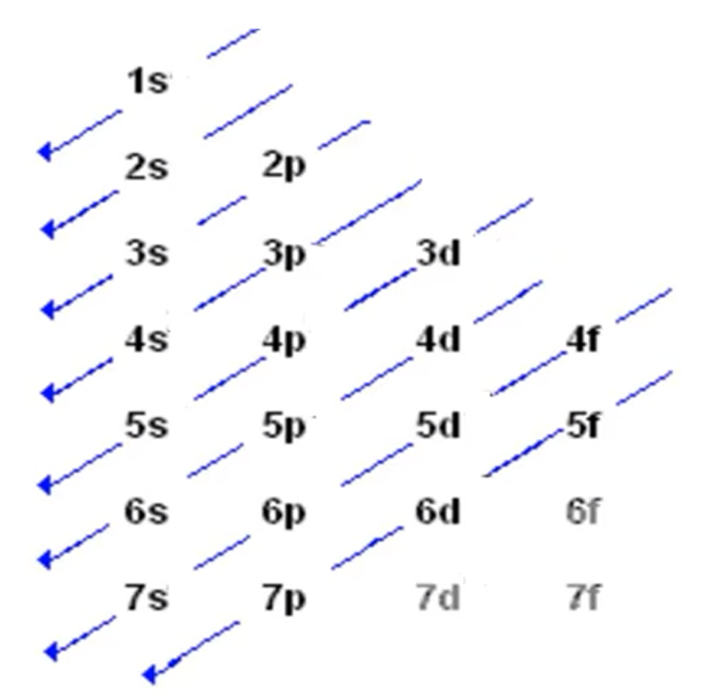
Draw the diagram in terms of increasing energy in s,p,d units
Why must orbitals have opposite spins in an orbital?
To counteract the repulsion between their negative charges.
Describe how fractional distillation separates isooctane from octane?
Isooctane boils first,
and then it condenses and is collected.
Carbon monoxide and nitrogen monoxide are both pollutants produced in car engines. Describe how each pollutant is formed in car engines, including the conditions required.
carbon monoxide is formed by incomplete combustion
due to insufficient oxygen / too much hydrocarbon
nitrogen monoxide is formed by the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen (from the air)
due to high temperature (in the engine) / high pressure (in the engine) / a spark
Isooctane reacts with an excess of chlorine to form a mixture of chlorinated compounds containing the same number of carbon atoms as isooctane.
(i) State the type and mechanism of this reaction
Free radical substitution
One of the chlorinated compounds contains 44.1% carbon and 6.9% hydrogen by mass. Calculate the molecular formula of this compound. (3)
100 ‒ 44.1 ‒ 6.90 = 49.0
C 44.1 ÷ 12 = 3.675
H 6.9 ÷ 1 = 6.9
Cl 49.0 ÷ 35.5 = 1.38
C:H:Cl = 2.66 : 5 : 1 = 8 : 15 : 3
Therefore C8H15Cl3
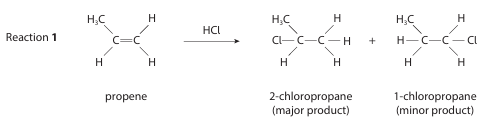
(i) Name the mechanism and type of reaction for Reaction 1. (1)
(ii) Explain why the structures of the intermediates in Reaction 1 mean that 2‑chloropropane is formed in greater yield than 1‑chloropropane. (3)
i) electrophilic addition
ii) (because) the formation of 2-chloropropane / the major product proceeds via a secondary carbocation
(but) the reaction / the formation of 1-chloropropane / the formation of the minor product proceeds via a primary carbocation
(and) secondary carbocations are more stable than primary carbocations
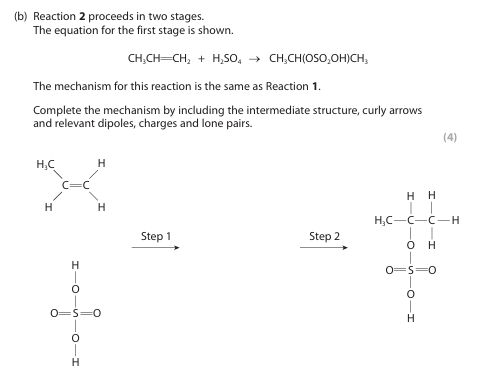
The periods in the Periodic Table show trends in physical properties. (a) (i) Explain the general trend in first ionization energies for the Period 2 elements
4 points award 2 marks
2 or 3 points award 1 mark
• first ionization increases (across the period)
• due to increased nuclear attraction / because there is an increasing attraction between the electrons and the nucleus
• as electrons are added to / removed from the same shell of electrons
• the number of protons / positive charge increases
Explain which one of the elements from lithium to nitrogen deviates from this general trend.
• boron
• the electron (being removed) is from the 2p subshell (not the 2s as for Li and Be)
• which is further from the nucleus than the 2s electrons so is more shielded
Explain why the melting temperature of carbon is high, with reference to its structure and bonding (3)
• Graphite / diamond / carbon are lattices / giant structure with covalent bonds (between the atoms)
• Held together by strong covalent bonds
• (which) require a lot of energy to break
Deduce, using electron‑pair repulsion theory, the expected shape of BCl3 , AlCl3 and TlCl3 . Justify your answer. (3)
• all three will be the same shape (because they have the same number of outer shell electrons to form bonds with chlorine)
• trigonal planar
• because there are three bonding pairs of electrons and no lone pairs of electrons which are at maximum separation / minimum repulsion
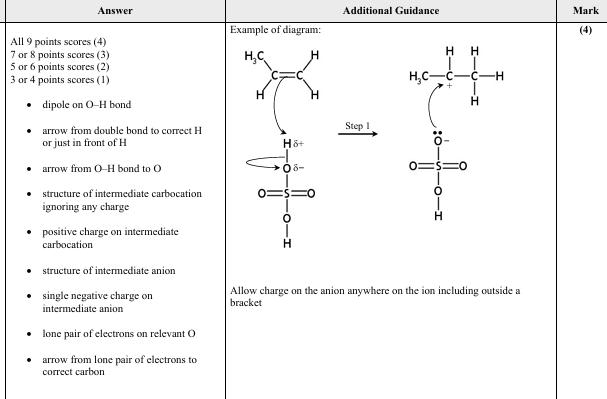
DRAW the dot‑and‑cross diagram for Al2 Cl6 .
Use dots (•) for the electrons of aluminum and crosses (×) for the electrons of chlorine. 24
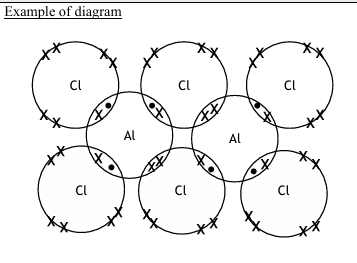
Thallium also forms ions containing chlorine, for example the TlCl4 3– ion.
In this ion, the thallium atom has 10 electrons in its outermost shell.
Phosphorus in phosphorus pentachloride, PCl5 , also has 10 electrons in its outer shell.
Draw the shape of the TlCl4 3– ion and predict the bond angles. Include any lone pairs of electrons that influence the shape
• a diagram of the TlCl4 3‒ ion including one lone pair of electrons on Tl
• an estimated bond angle of ≤ 120º shown between the two equatorial Cls
• at least one estimated bond angle of ≤ 90º shown between two Cl (an axial and an equatorial Cl)
Explain why 1-chloropropene exists as two geometric isomers but chloroethene does not.
There is restricted rotation around the carbon-carbon double bond in both molecules. 1-chloropropene has two different groups on each of the carbons in the double bond. There are two hydrogen atoms on one carbon.
Advantages of PVC instead of metal water pipes?
They’re cheaper, won’t rust, less mass/less dense. And also no metal ions get into the water supply.
Compare and contrast the atomic structure of an atom of germanium-76 with an atom of selenium-76?
They have the same total number of protons and neutrons. Germanium has 2 fewer protons, 2 fewer neutrons and 2 fewer electrons.
Explain what is meant by the term polar and why chlorine is not polar?
One end is slightly positive and one end is slightly negative. Chlorine is symmetrical so no slight positive or slight negative end.
Explain why chlorine reacts with alkenes even though its not polar?
The carbon-carbon double bond in alkenes repels electrons and distorts the electro cloud in the chlorine molecule.
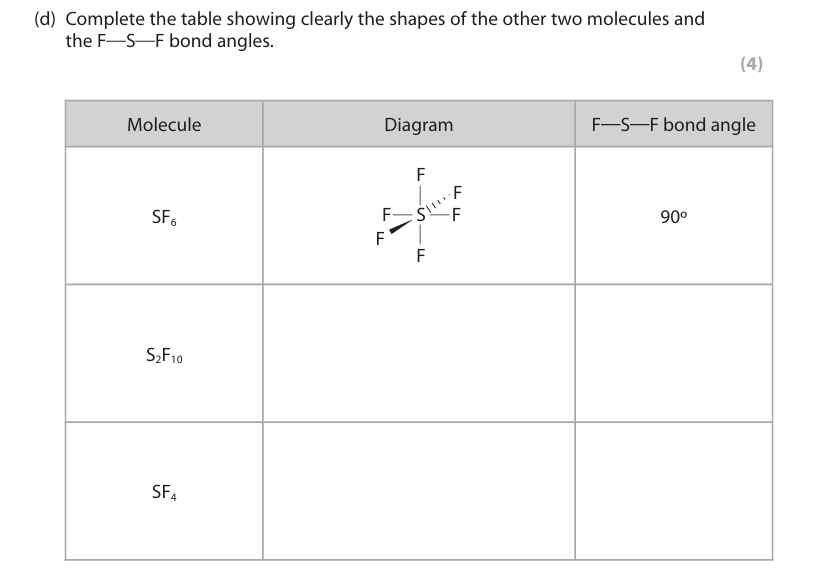
ii) Justify the shape around the sulfur atom in both SF6 and SF4 (3)
ii) Sulfur in SF6 has 6 bonding pairs. Sulfur in SF4 has 4 bonding pairs. The pairs repel to be as far as possible.
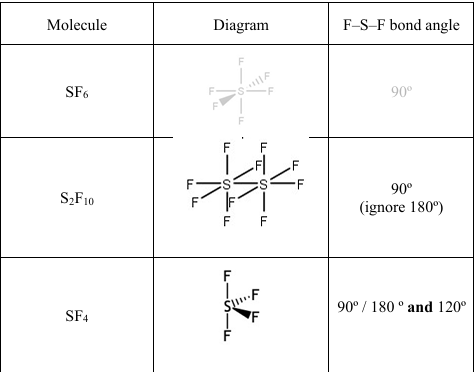
SF4 and S2 F10 are reactive, but SF6 is unreactive. Suggest reasons for this by considering the shape and bonding in each molecule.
• sulfur in SF6 has six bonding pairs (of electrons) (and no lone pairs)
• sulfur in SF4 has four bonding pairs (of electrons) and one lone pair
• the (electron) pairs repel to be as far away as possible / maximum separation