Physiology- Vision & Auditory Unit
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
Sclera Functions (2)
Provide strengths & flexibility
Covers majority of eye’s exterior
Sclera Important Details (3)
Contains collagen (strength) fibers
Contains elastic (flexibility) fibers
Is white
Choroid Functions (2)
Intermediate layer
Provides oxygen & nutrients to retina
Choroid Important Details
Blood vessels
Vascular
Retina Functions (2)
Innermost layer of eye
Focused image lands here
Retina has ____&____
cones & rods
Cones
Color vision (sensory neurons)
Rods
Vision in low lighting (sensory neurons)
Fovea Function
Provides highly detailed vision
Fovea Contains _____ _____
ONLY Cones
Optic Disc Functions (2)
Blind Spot
Location where optic nerve connects to retina.
Optic Disc is area where
No photoreceptors are found.
Cornea Functions (2)
Covers anterior of eye
Lets light enter through pupil.
Cornea Important Detail
Transparent
Iris Functions (2)
Regulates amount of light entering eye.
Provides color to eye.
Iris important detail
Smooth muscle
Pupil Function
Opening through which light enters.
Pupil Important details (2)
Bright Light: Smaller opening (constrict)
Dim Light: Larger opening (dilating)
Lens Function
Bends light to focus the image
Bend means
Refract
Accomodation
lens ability to change shape
Lens Important Details (2)
Near by objects: Thicker
Far away objects: Thinner
Internal components (2)
Aqueous humor
Vitreous humor
Aqueous humor function
Provides nutrients to avascular structures & removes waste.
Vitreous humor Function
Maintains shape of eye
Aqueous humor important detail
Watery
Vitreous humor important detail
jelly like
External components (2)
Optic nerve
Optic muscles
Optic nerve function
Carries info to brain
Optic muscles
Moves the eye voluntarily
Optic nerve important detail
Sensory neuron
Optic muscles important detail
Skeletal muscle
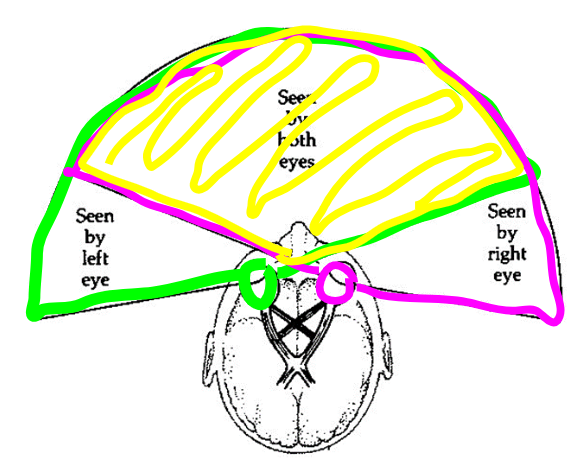
Binocular Vision (3)
Overlapping fields of vision of two eyes.
Each eye sees slightly diff, image & brain processes this into one image.
Gives depth perception to our image.
Depth Perception (2)
3 Dimensional imaging
Allows individual to better understand spatial awareness ( near & far objects)
Vision Sensory Neurons: Rods (4)
More neurons
Only one type
Used in darkness or low lighting
Detect light
Vision Sensory Neurons: Cones (4)
Fewer cones that rods
3 types: red, green, blue
Used during day or well lit environments.
Detect color (based on combination of which cones are activated
Snellen Chart (3)
Test visual acuity of a person
Test for myopia
Reading chart
Visual acuity
Amount of detail a person can see.
Myopia
Nearsightedness (can see near objects but not far)
Reading chart top #
Distance person is from chart
Reading chart bottom #
Distance a “normal” eye can see at top #.
Bind spot (2)
Where light rays converge (land) on optic disc.
No photoreceptors present: no stimulation of neurons, no electrical impulse, no image seen.
Astigmatism Chart
Cornea or lens have IRREGULAR shape: makes light rays spread out, causes blurry vision
Peripheral Vision (3)
Side vision when a person is looking straight
Exam results: Distinguish black/white vision is better than red/blue.
Exam reasonings: More rods on that part of retina than cones. Light rays converge (meet) at side of retina, not fovea.
Accomodation (Vision lab) (3)
Movement of lens with help of smooth muscle.
Near objects: objects get rounder, light rays converge (meet) on retina.
Far objects: lens get flatter.
Iris Photo
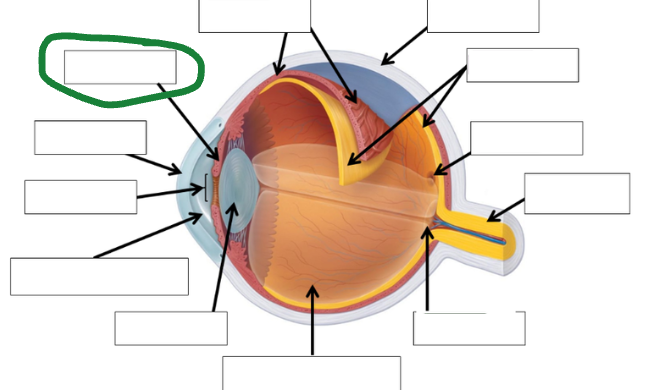
Cornea Photo
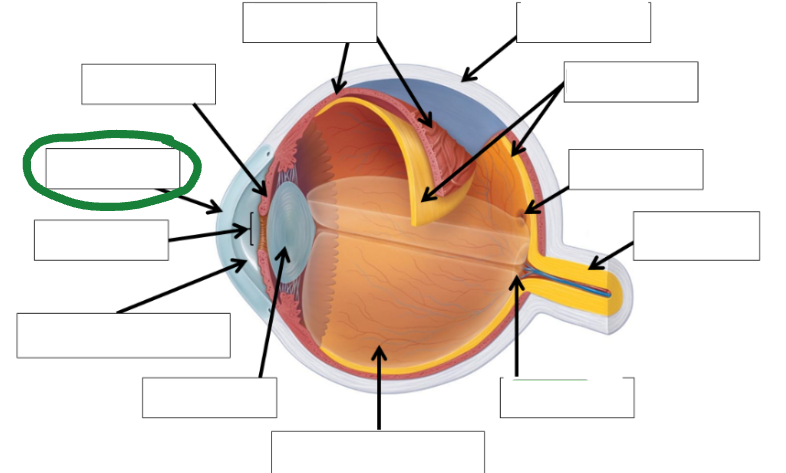
Pupil Photo
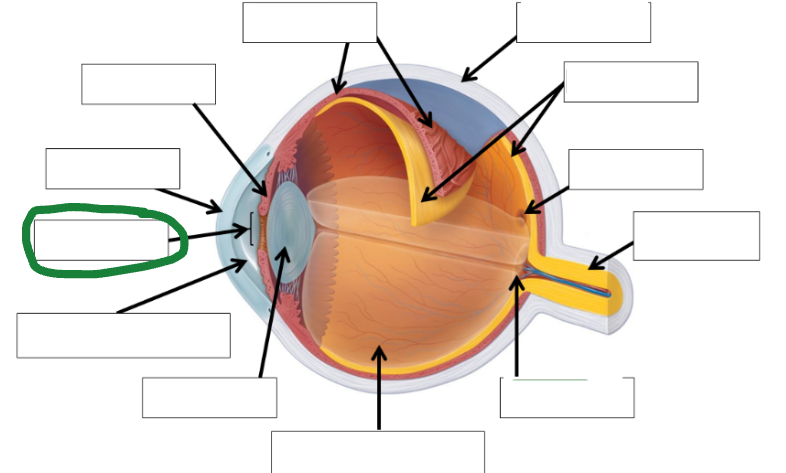
Aqueous Humor Photo
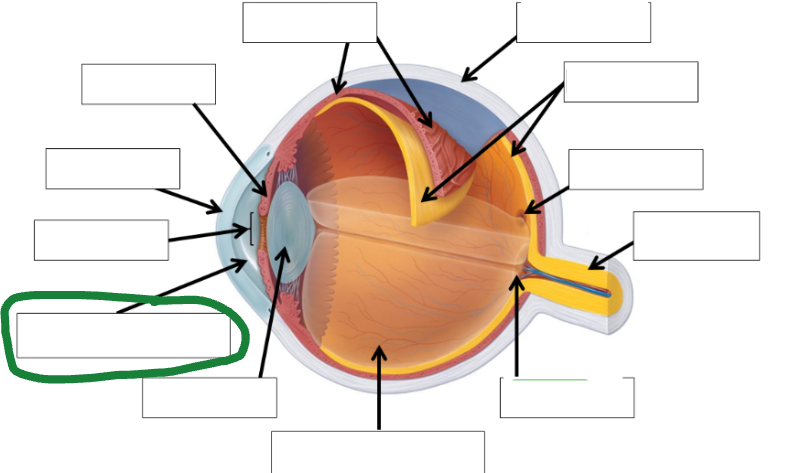
Lens photo
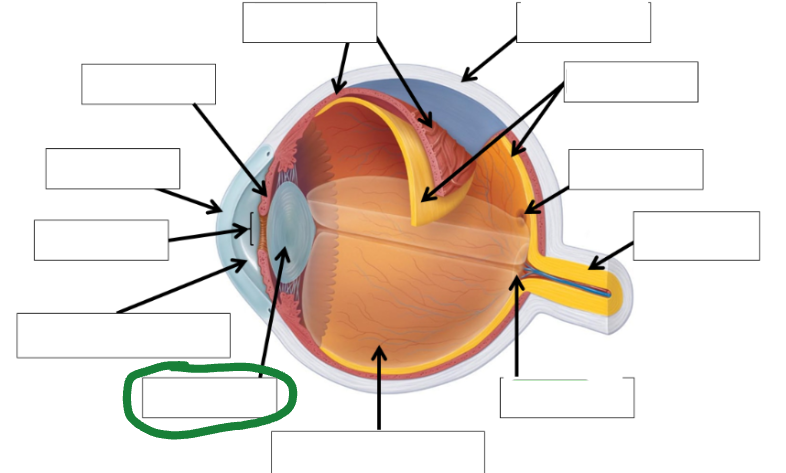
Vitreous humor photo
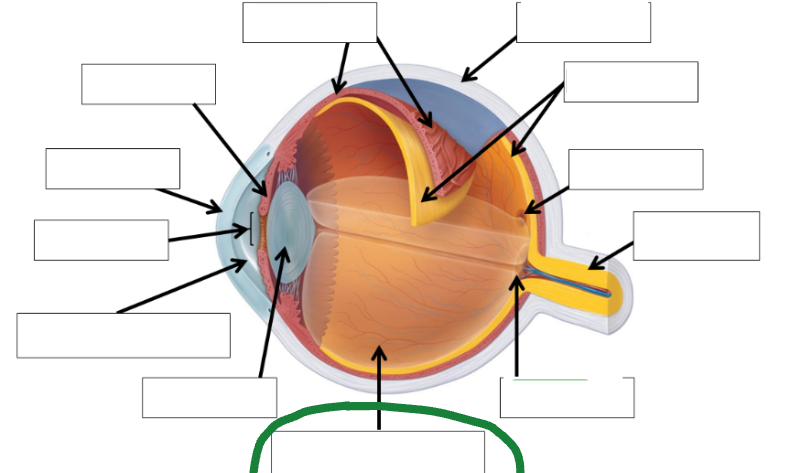
Optic disc photo
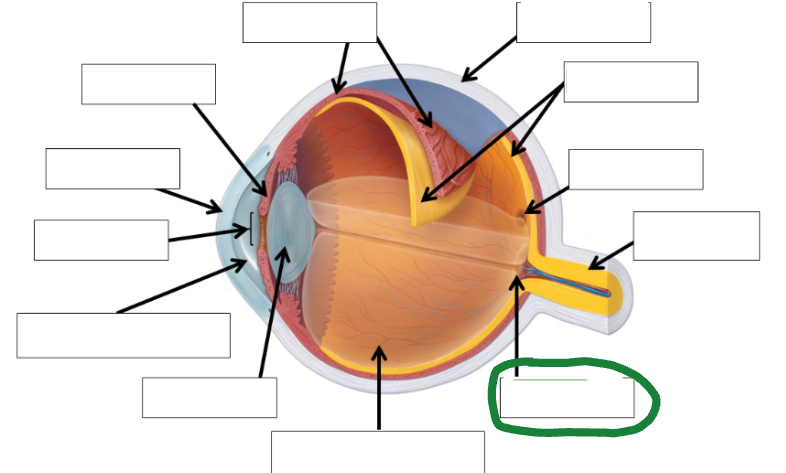
Optic nerve photo
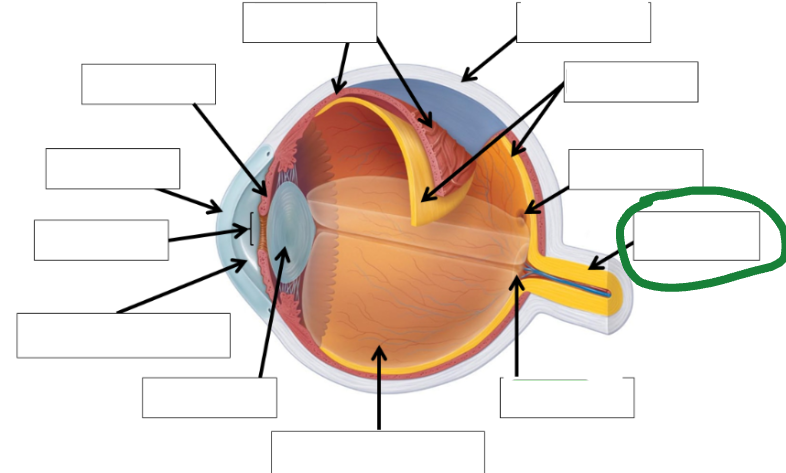
Fovea photo
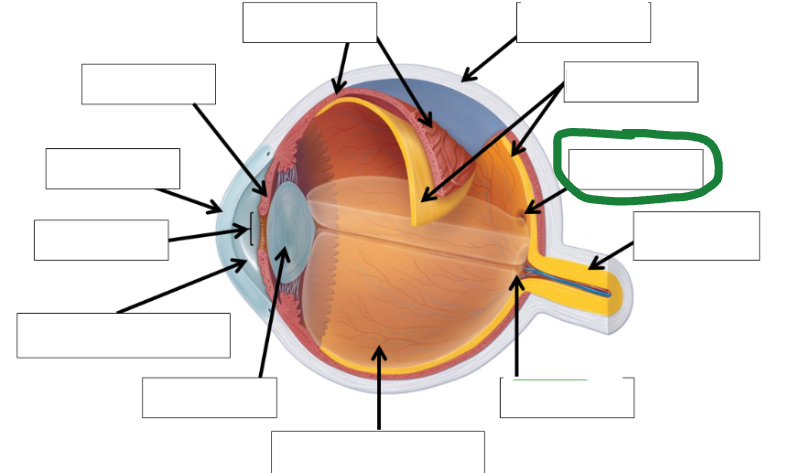
Retina photo
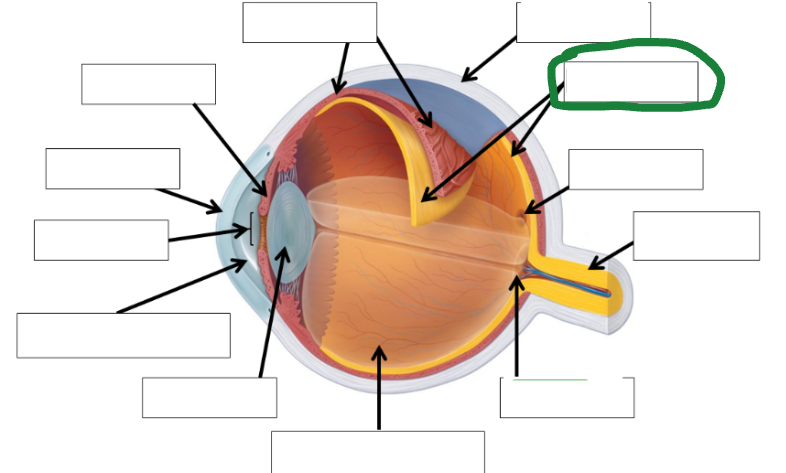
Sclera photo
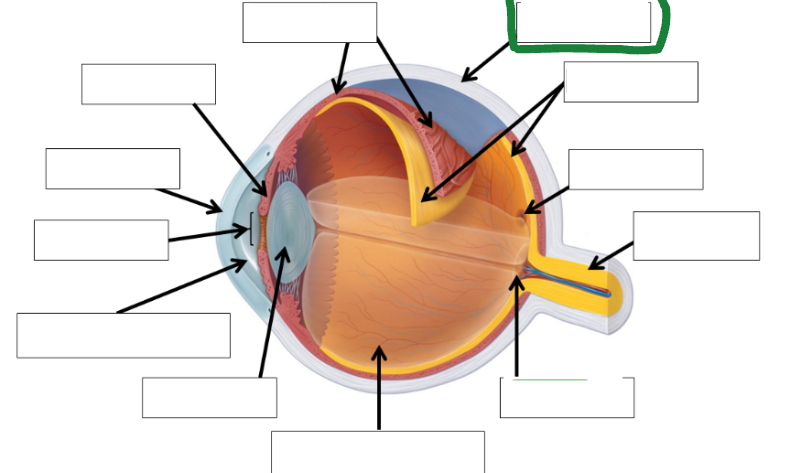
Choroid photo
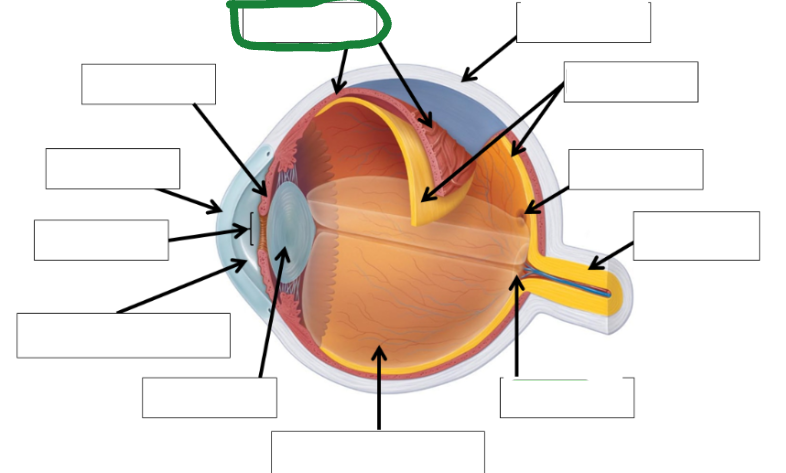
Fields of view
Optic Tract image
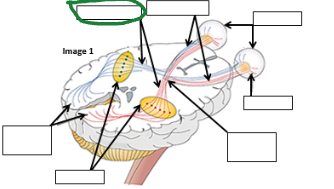
Optic nerve image
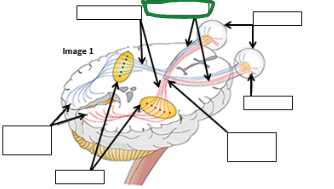
Eyes image
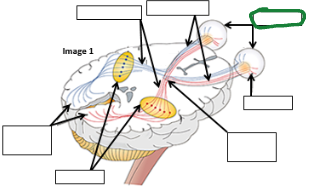
Retina image (vision pathway)
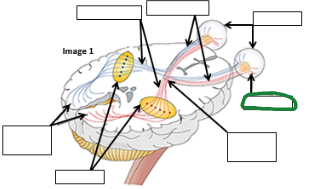
Optic chiasm image
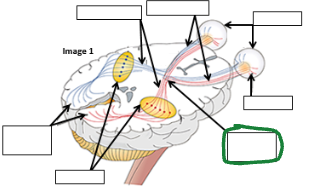
Thalamus image
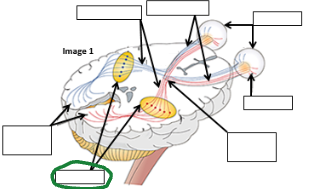
Occipital lobe image
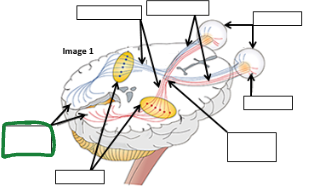
Refracted light image comes to retina _____ an then is processed in occipital lobe as ________.
Upside down
Right side up
Conjunctiva function
Lubricates the eye
Emmetropia aka
Normal Vision
Emmetropia: Distant images: ______, Nearby Images:_____
In focus
In focus
Emmetropia image focuses ____ retina
on retina
Emmetropia eye shape
Normal eye shape
Emmetropia Corrective Lens Type
None
Hyperopia aka
Farsightedness
Hyperopia: Distant images: ____, Nearby Images: ____
Focused
Blurry
Hyperopia Image focuses where
Behind retina
Hyperopia eye shape
Too short eye shape
Hyperopia Corrective Lens type
Converging concave
Myopia aka
Nearsightedness
Myopia: Distant images: ____, Nearby images:____
Blurry
In focus
Myopia image focuses where
In front of retina
Myopia eye shape
Eye shape = too long
Myopia corrective lens type
Diverging concave
Visual Acuity
Amount of detail a person can see.
Astigmatism Issue
Irregular curvature of cornea or lens
Astigmatism & Cataracts vision are both
BLURRY
Cataracts issue
A cloudy lens
Conjunctivitis aka
Pink eye
Conjunctivitis Issue
Inflammation of the conjunctiva due to an infection.
Conjunctivitis Vision
N/A (Not affected)
Glaucoma issue
Posterior eye pressure from fluids which causes damage to the optic nerve
Glaucoma vision
Blurry, loss of peripheral
Macular Degeneration issue
Center of retina deteriorates or blood vessels leak under retina.
Macular Degeneration Vision
Loss of center vision
Retinal Detachment Issue
Innermost layer (retina) pulls away from the intermediate (choroid) layer.
Retinal Detachment Vision (4)
Major dark floaters
Flashing lights
Corner of vision starts to disappear
Blindness
Glaucoma image

Macular Degeneration image

Retinal detachment image

Cows have _________ which allows for night vision while humans do NOT
Tapetum lucidium
Cow Layers (4)
Retina
Tapetum Lucidium
Choroid
Sclera