MET 3100 (Applied Physical Metallurgy) - Chapter 2: Crystal Structures
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a Motif?
An atom or a group of atoms associated with each lattice point - WHAT is repeated in the crystal
Crystals have a translationally periodic arrangement of these
What is a Lattice?
The underlying periodicity of the crystal - HOW the crystal repeats
It is a translationally periodic arrangement of points
What is the Basis of a crystal?
The entity associated with each lattice point
3D Lattices
Infinite in three dimensions / distances (a, b, c), and contain angles (alpha, beta, and gamma)
What are the Bravais Lattices?
The 14 distinct lattices possible in 3D space
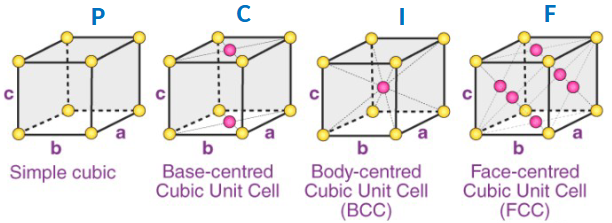
What are the 4 different “center types” of unit cells
Simple cubic, Base-centered Cubic, Body-centered Cubic, Face-centered Cubic
What is the Seven Crystal System? (and what are the seven types?)
Based on symmetry, crystals are classified into seven types;
simple cubic
tetragonal
orthorhombic
hexagonal
rhombohedral
monoclinic
triclinic
What are the parameters of a “Simple Cubic” crystal system?
side a = b = c
angle alpha = beta = gamma = 90 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Tetragonal” crystal system?
side a = b /= (does not equal) c
angle alpha = beta = gamma = 90 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Orthorhombic” crystal system?
side a /= b /= c
angle alpha = beta = gamma = 90 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Hexagonal” crystal system?
side a = b /= (does not equal) c
angle alpha = beta = 90 degrees, and gamma = 120 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Rhombohedral” crystal system?
side a = b = c
angle alpha = beta = gamma /= 90 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Monoclinic” crystal system?
sides a = b /= c
angles alpha = gamma = 90 degrees, beta /= 90 degrees
What are the parameters of a “Triclinic” crystal system?
sides a /= b /= c
angles alpha /= beta /= gamma /= 90 degrees
What is the Coordination Number?
It is defined as the total number of nearest neighboring atoms
What are the Coordination Numbers for the different lattices?
SC = 6
BCC = 8
FCC = 12
HCPS = 12
What is the mathematical definition of the Packing Fraction?
___ = Volume occupied by atoms / Volume of Cell
What are Miller Indices used for in crystallography?
Miller Indices are used to express the orientation of crystal directions and planes in terms of their intercepts on the three axes.
What are the conventions for Miller Indices?
There are NO COMMAS between numbers, Negative values are expressed with a bar over the number
x, y, z are the axes, a, b, c are the lattice parameters, h, k, l are the miller indices for planes ( ) and directions [ ]
What is the significance of knowing crystal directions and planes in materials science?
Understanding crystal directions and planes is essential for predicting modes of failure and how materials deform under loading.
How can properties like electrical and thermal conductivity vary in a crystal?
These properties can vary based on the orientation of the crystal.
What is the relationship between slip direction and crystal structure?
Slip direction is critical for understanding how deformation occurs in specific crystalline planes and directions.
What is the importance of crystal structure in applied physical metallurgy?
Crystal structure is crucial as it influences material properties and behavior under stress.
What type of crystal structure does the letter 'P' represent?
'P' represents a Triclinic structure in crystal systems.
What are crystallographic defects?
Crystallographic defects are imperfections in the crystal structure that can affect material properties.
What is the role of deformation in crystal structures?
Deformation occurs on specific crystalline planes and directions, influencing how materials respond to stress.
What does the term 'unit cells' refer to in crystallography?
Unit cells are the smallest repeating units in a crystal lattice that define the crystal structure.
What are the (four) 0D, or “point,” defects?
vacancy
impurity
Frenkel Defect
Schottky defect
What are the (three) 1D, or “Line,” defects?
dislocation
Disclination
Dispiration
What are the (five) 2D, or “Surface / Interface,” defects?
Surface
Interphase boundary
Grain Boundary
Twin Boundary
Stacking faults
What are the (five) 3D, or “Volume,” Defects?
Twins
Precipitate
Faulted region
Voids / Cracks
Thermal Vibration