Exam 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Components of a feedback system
receptor, control center, effector
receptor
monitors controlled condition and sends inputs to control center
control center
receives input from receptor & determines appropriate response
effector
provides the means for the control center's response to the stimulus
positive feedback
Feedback tends to reinforce the effects of the stimulus
negative feedback
feedback tends to negate the effects of the stimulus
What kinds of bonds are present within water molecules?
polar covalent
properties of water
solvent, cohesion, adhesion
electrolytes
substances that release ions in water
acids
compounds that form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
bases
Compounds that reduce the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
pH
the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
low pH
acidic
high pH
basic
buffer function
resist changes in pH
buffer
mixture of weak acids or bases and their conjugates
hydroxyl group
-OH
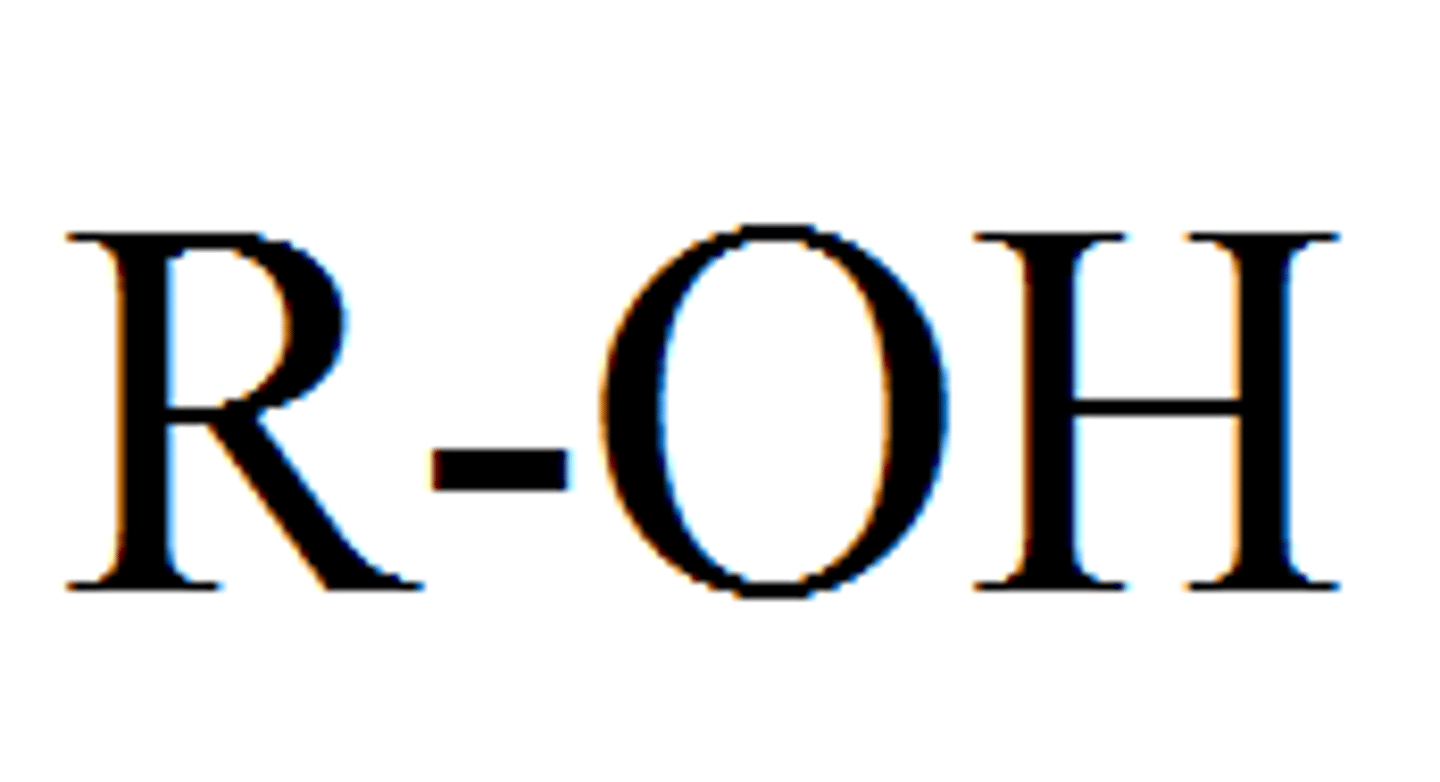
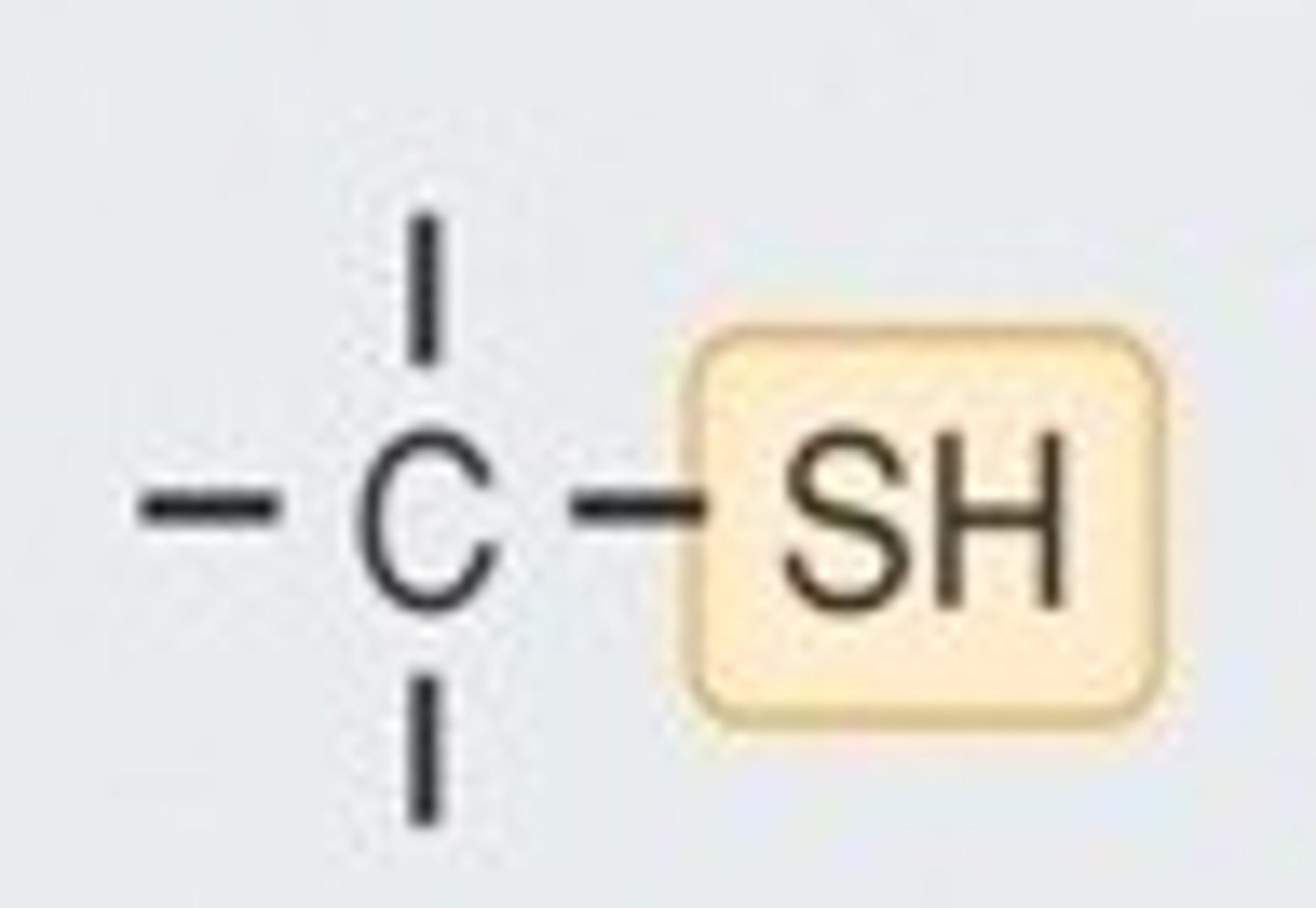
sulfhydryl group
-SH
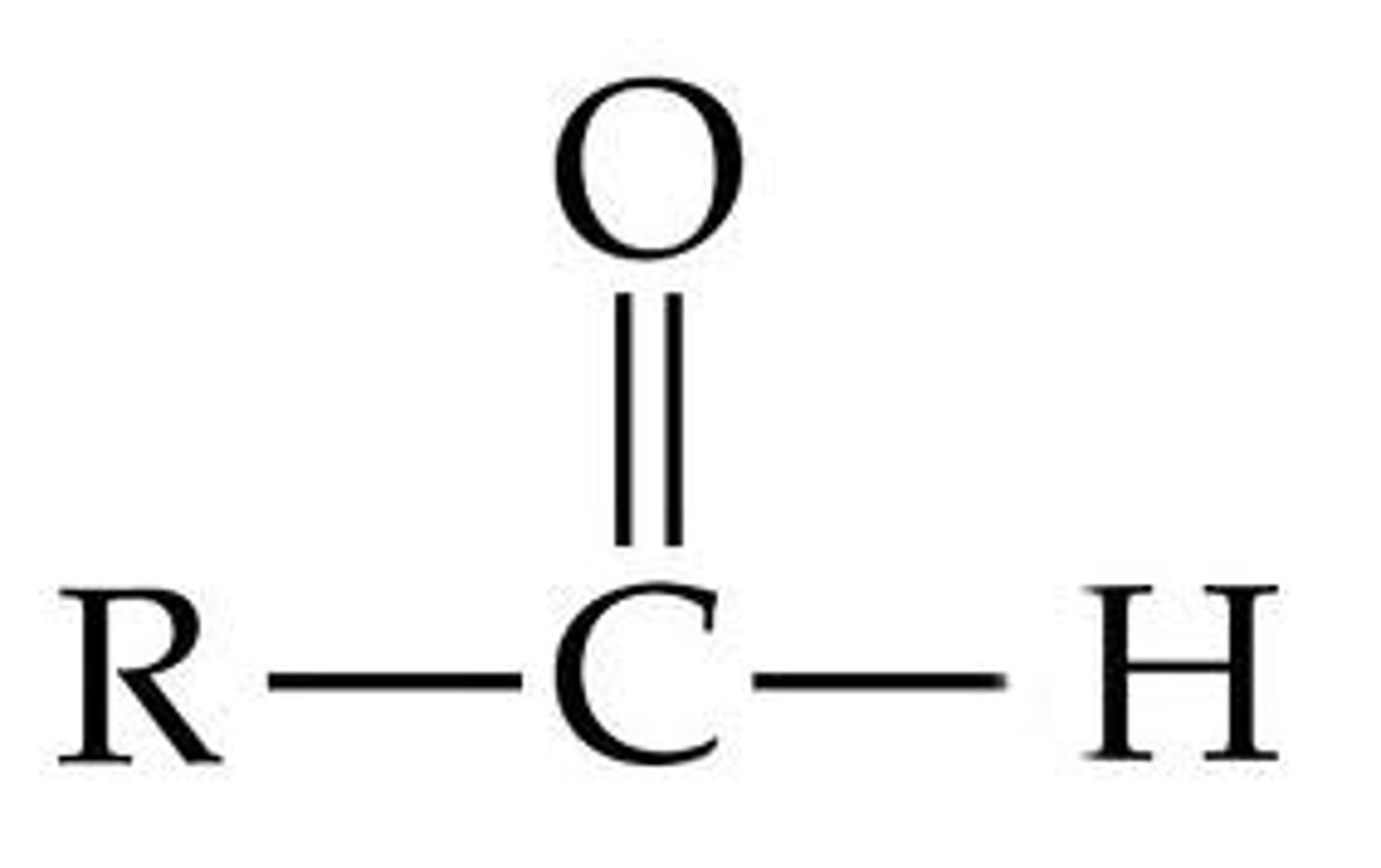
carbonyl group
C=O
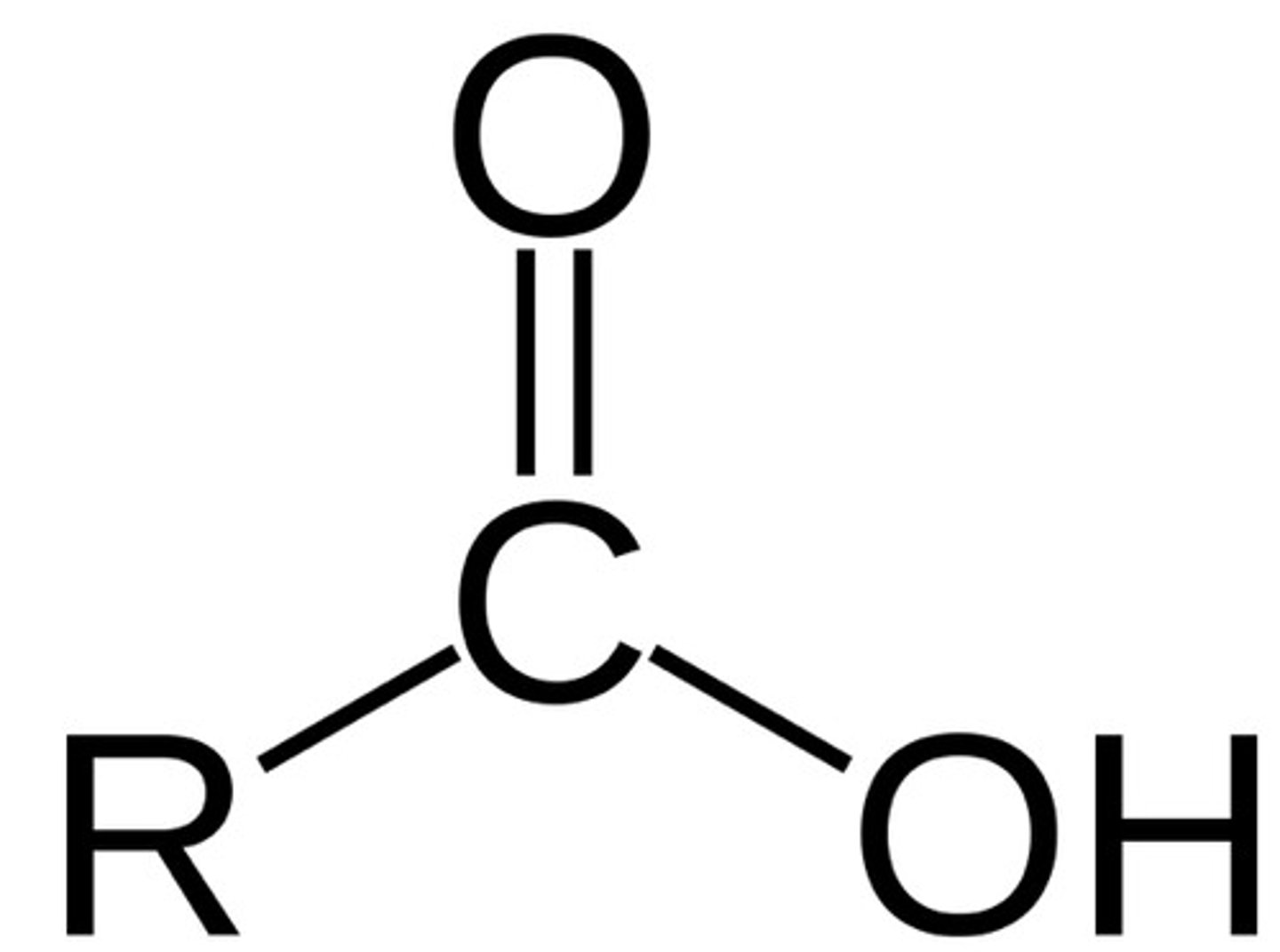
carboxyl group
COOH
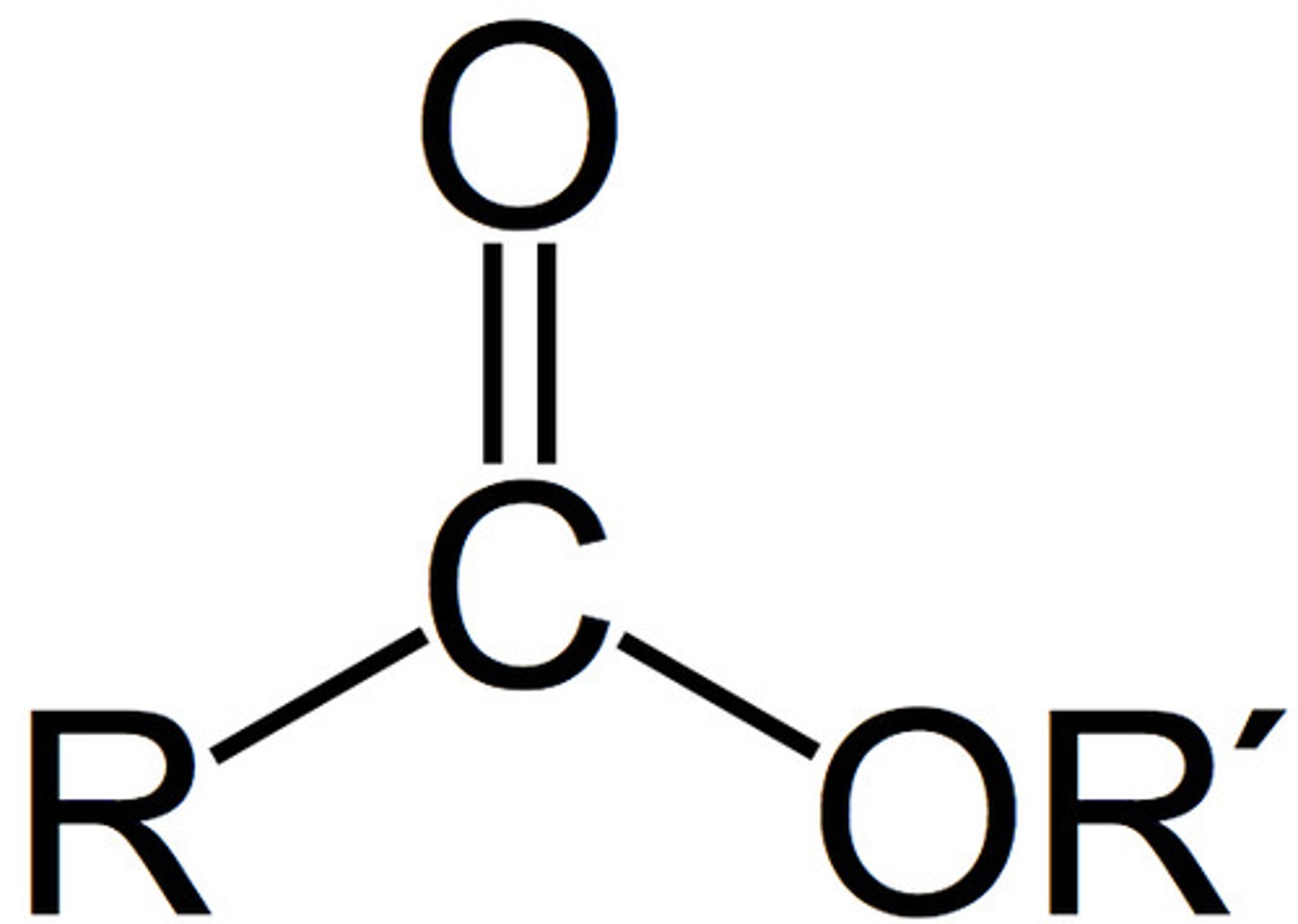
ester group
RCOOR
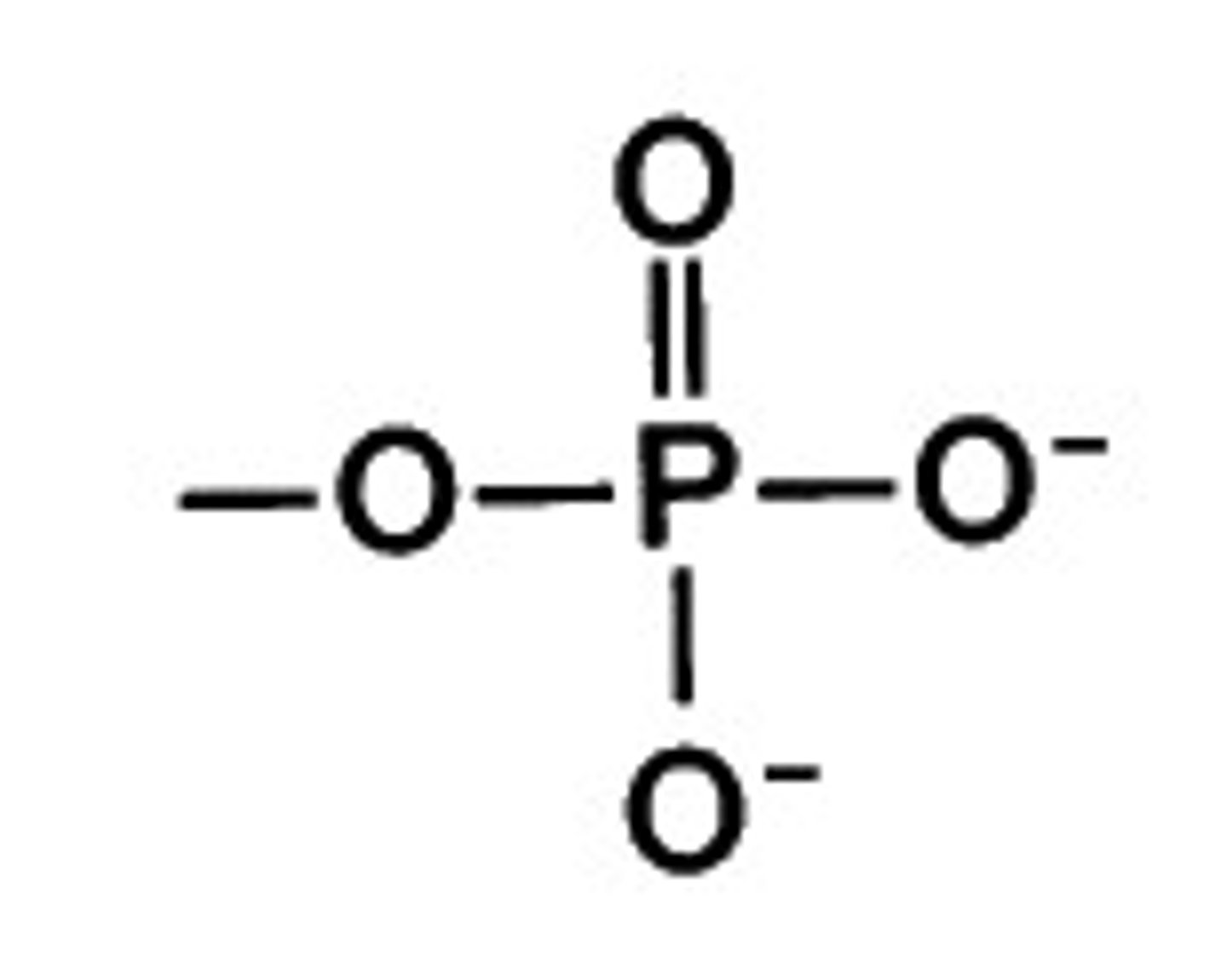
phosphate group
PO4
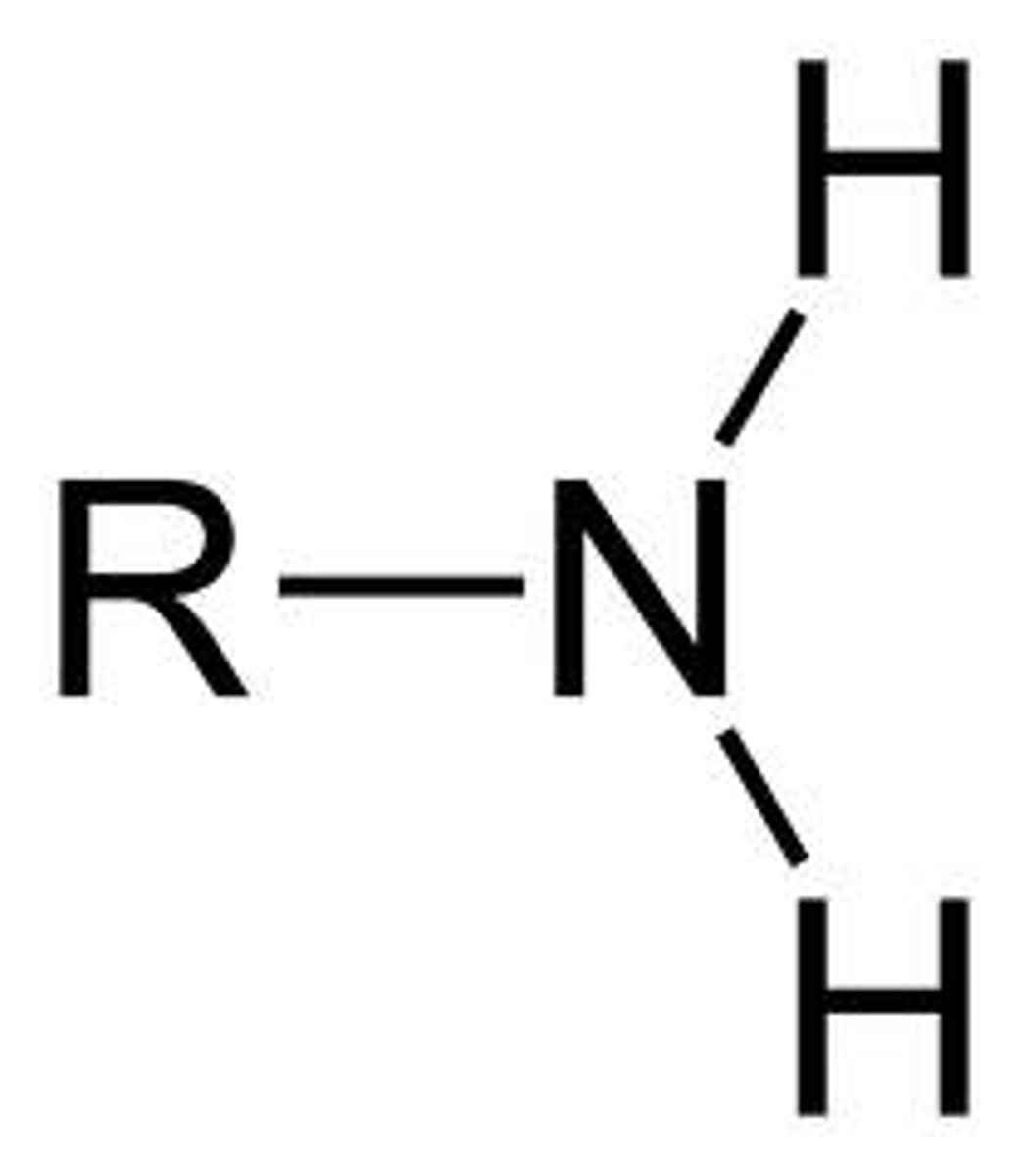
amino group
NH2
carbohydrate functions
primary source of energy
carbohydrate structure
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
lipid functions
energy storage, regulating and signaling, insulating and protecting
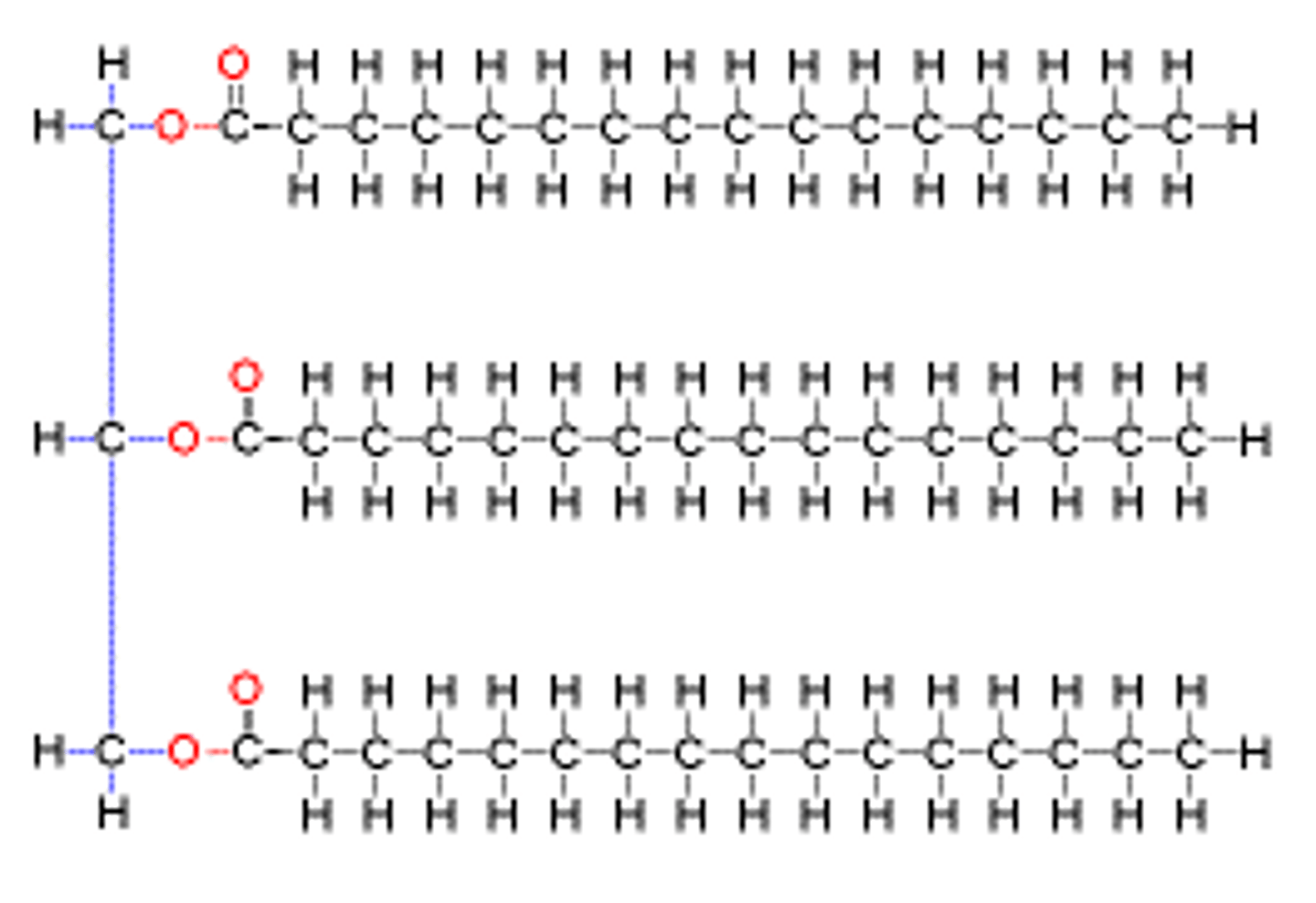
triglyceride structure
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
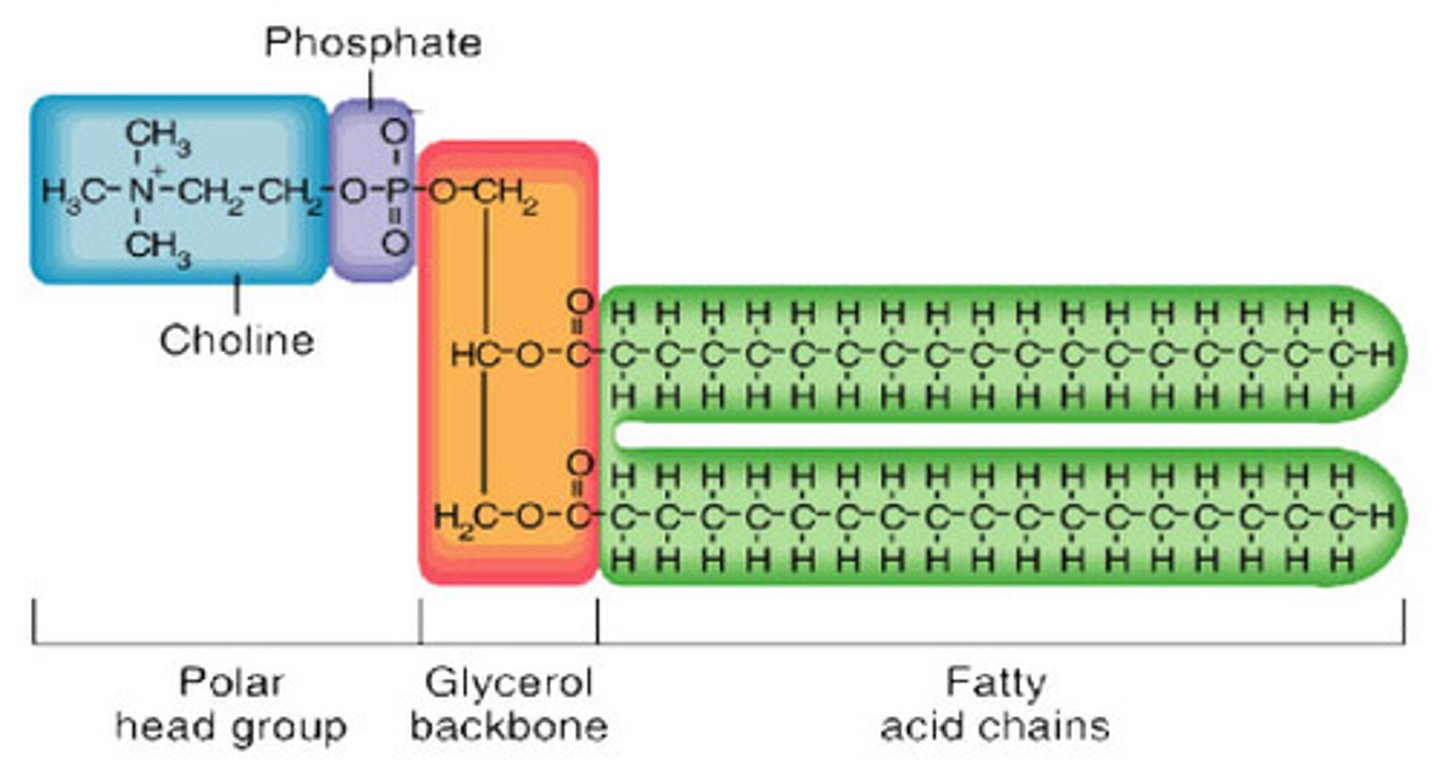
phospholipid structure
2 fatty acids, 1 glycerol, 1 phosphate group
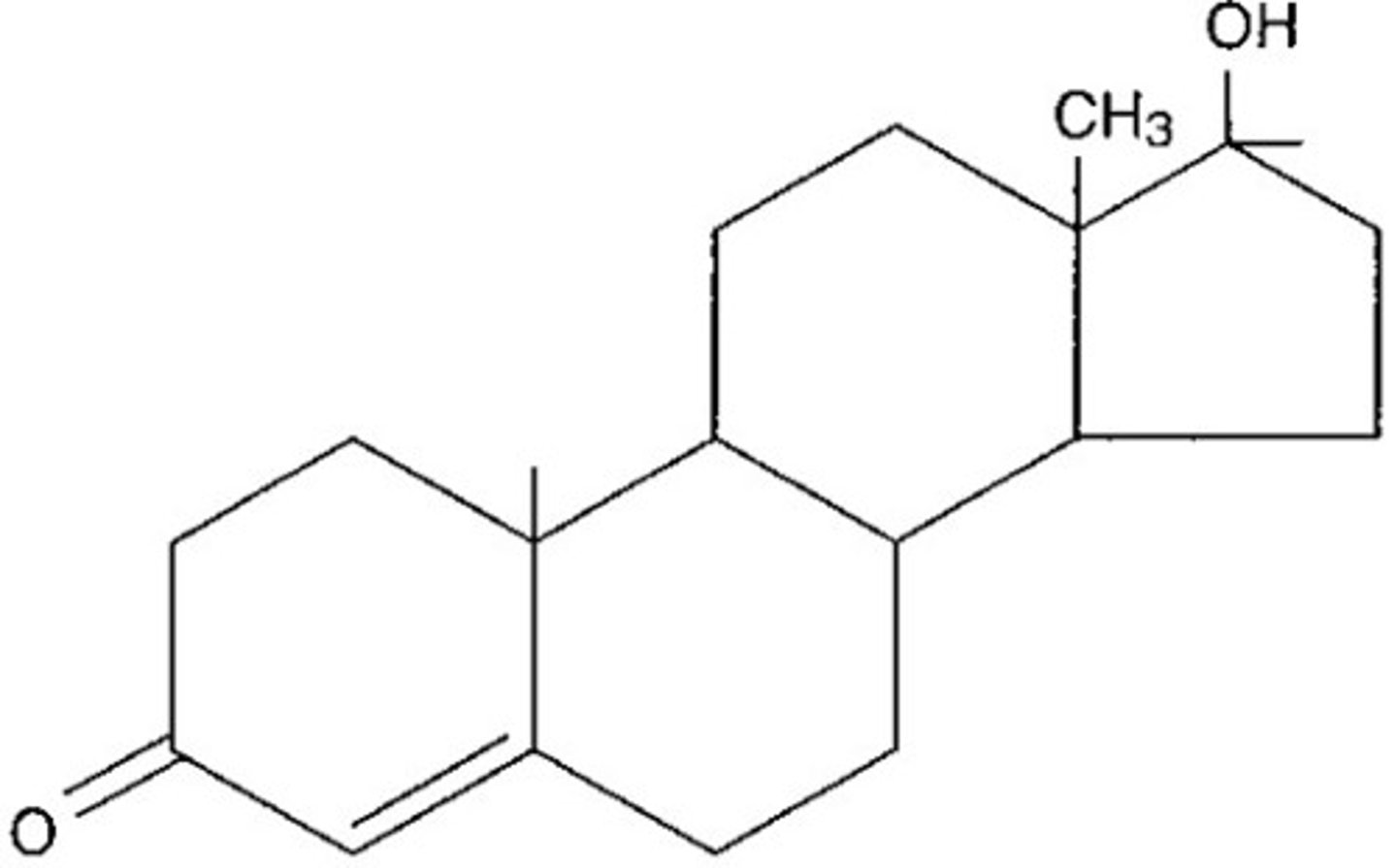
steroid structure
4 fused rings
protein functions
structure, communication, receptors, transporters, enzymes, protection
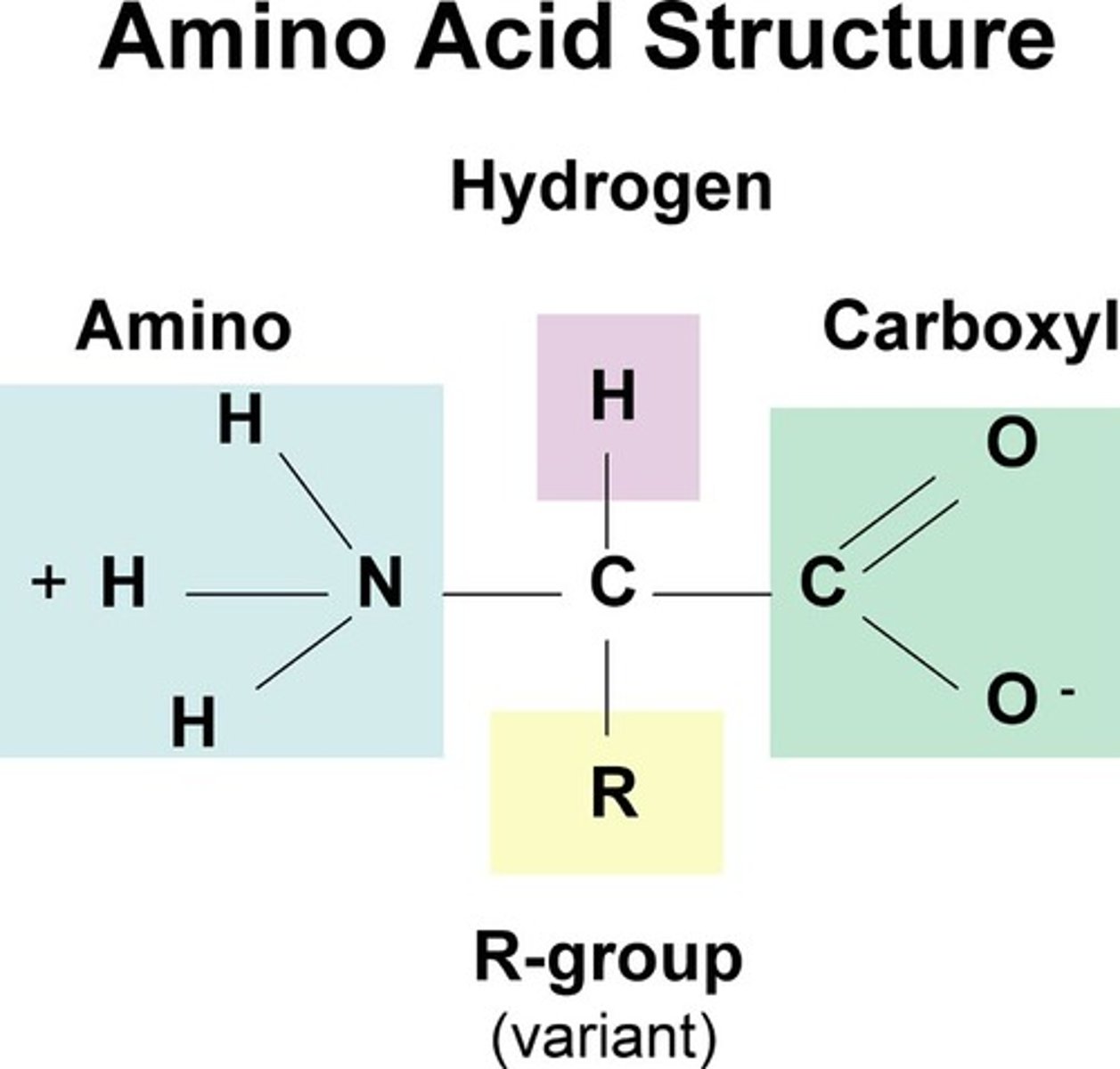
amino acid structure
carboxyl group, amine group, functional group
polypeptide chain
long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
peptide bonds
bonds between amino acids formed by dehydration synthesis
primary structure
sequence of amino acids

secondary structure
alpha helices and beta sheets
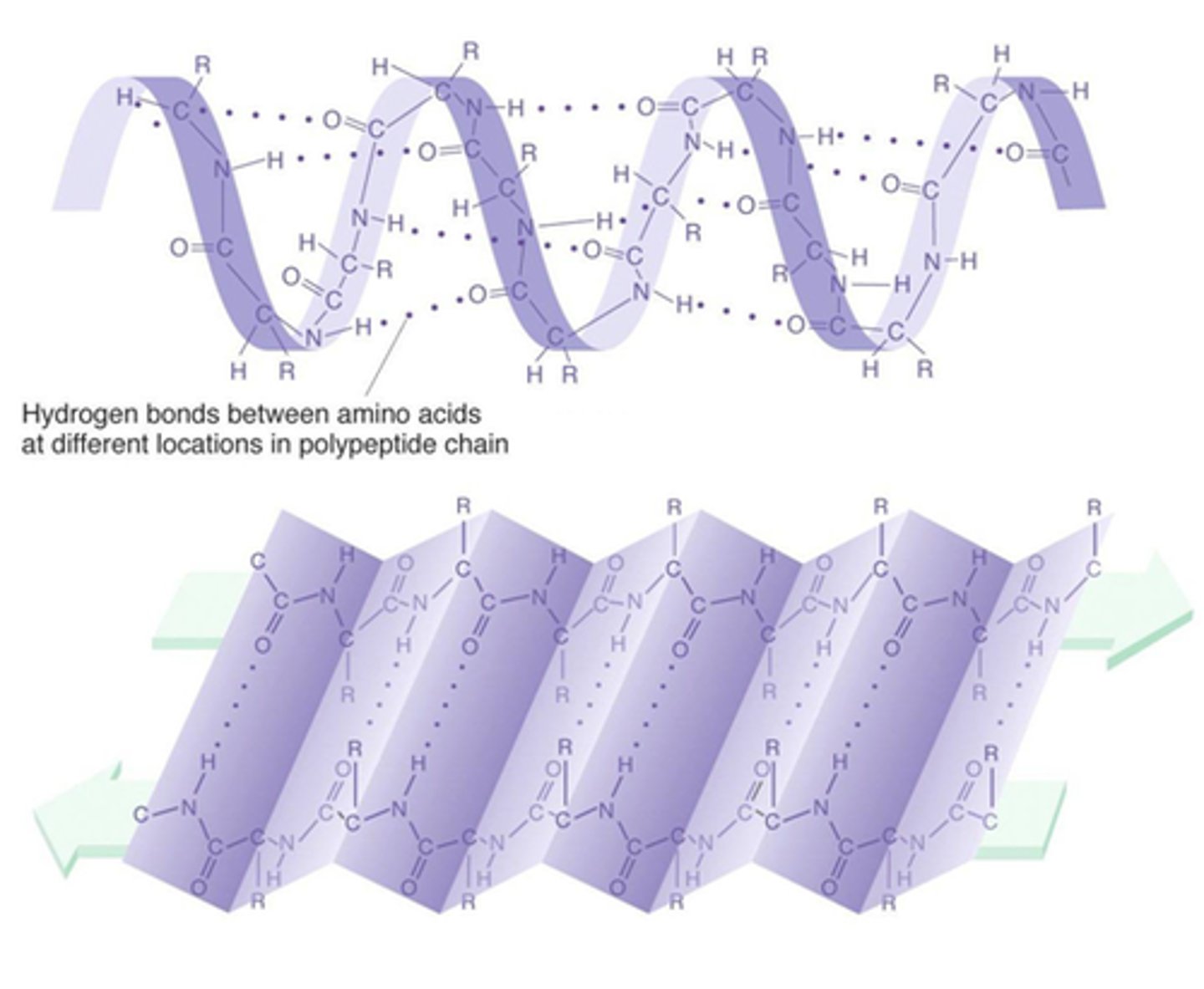
tertiary structure
folding and coiling due to interactions among functional groups
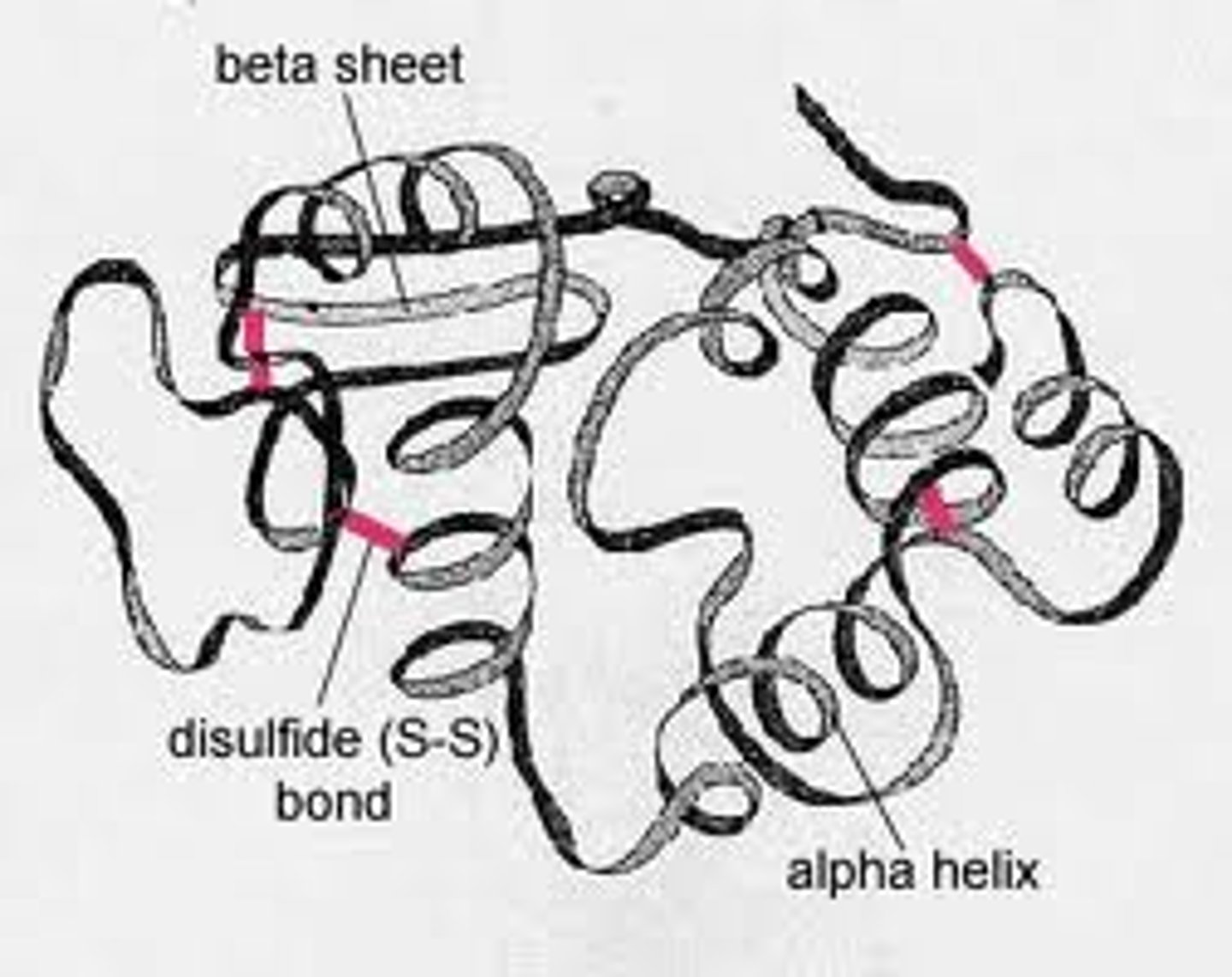
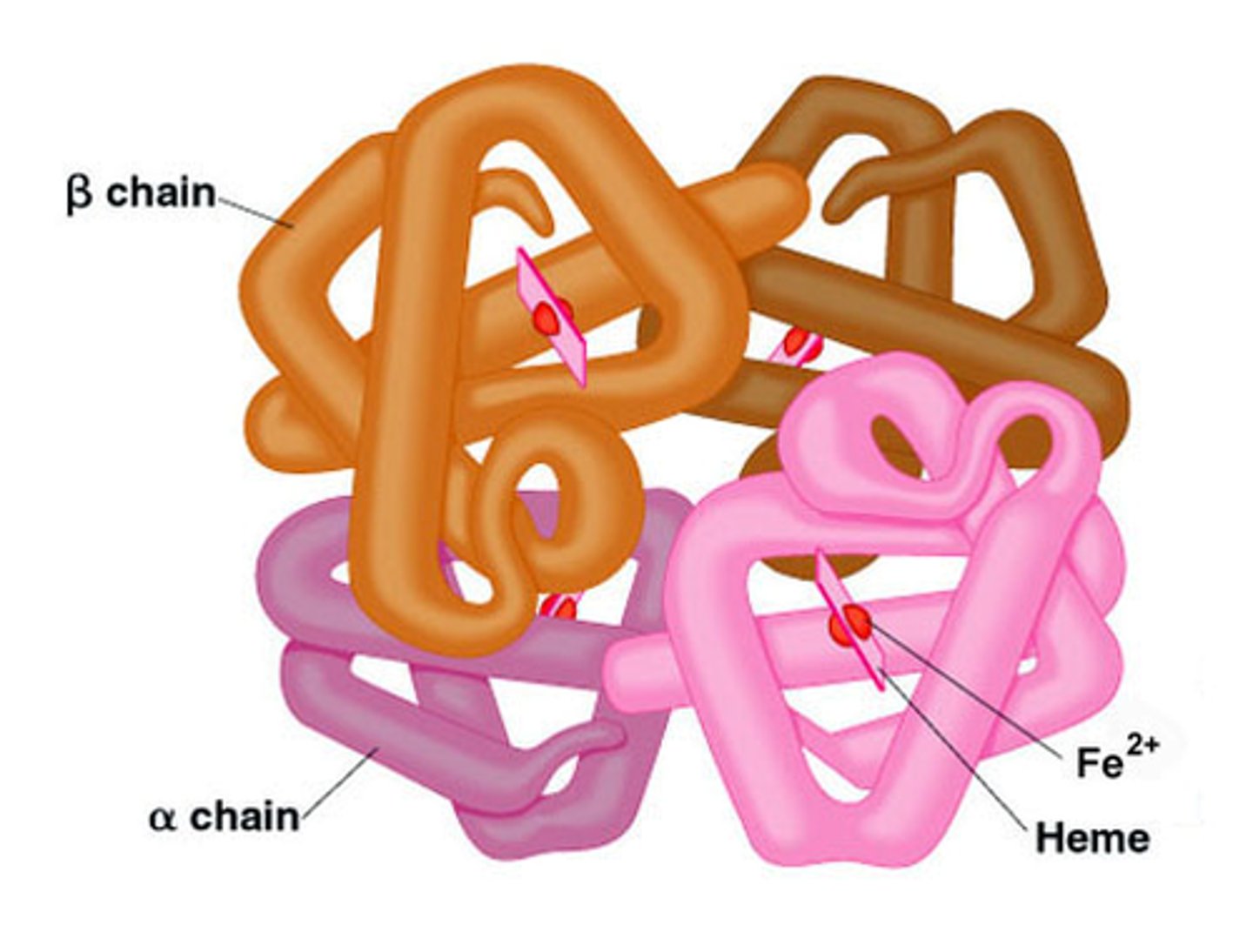
quaternary structure
the association of two or more polypeptide chains
DNA function
stores genetic information
RNA function
protein synthesis
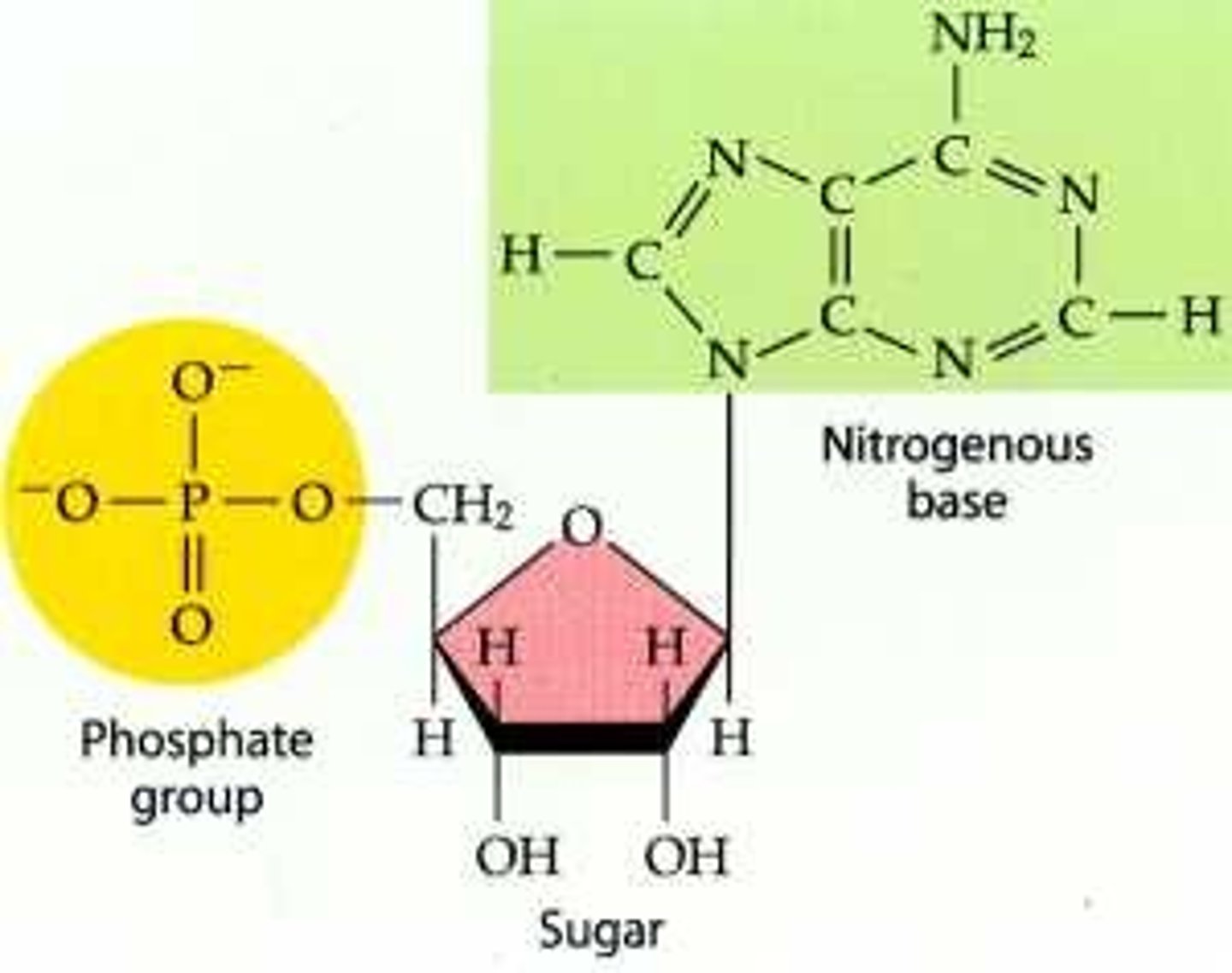
nucleic acid structure
phosphate group, 5-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
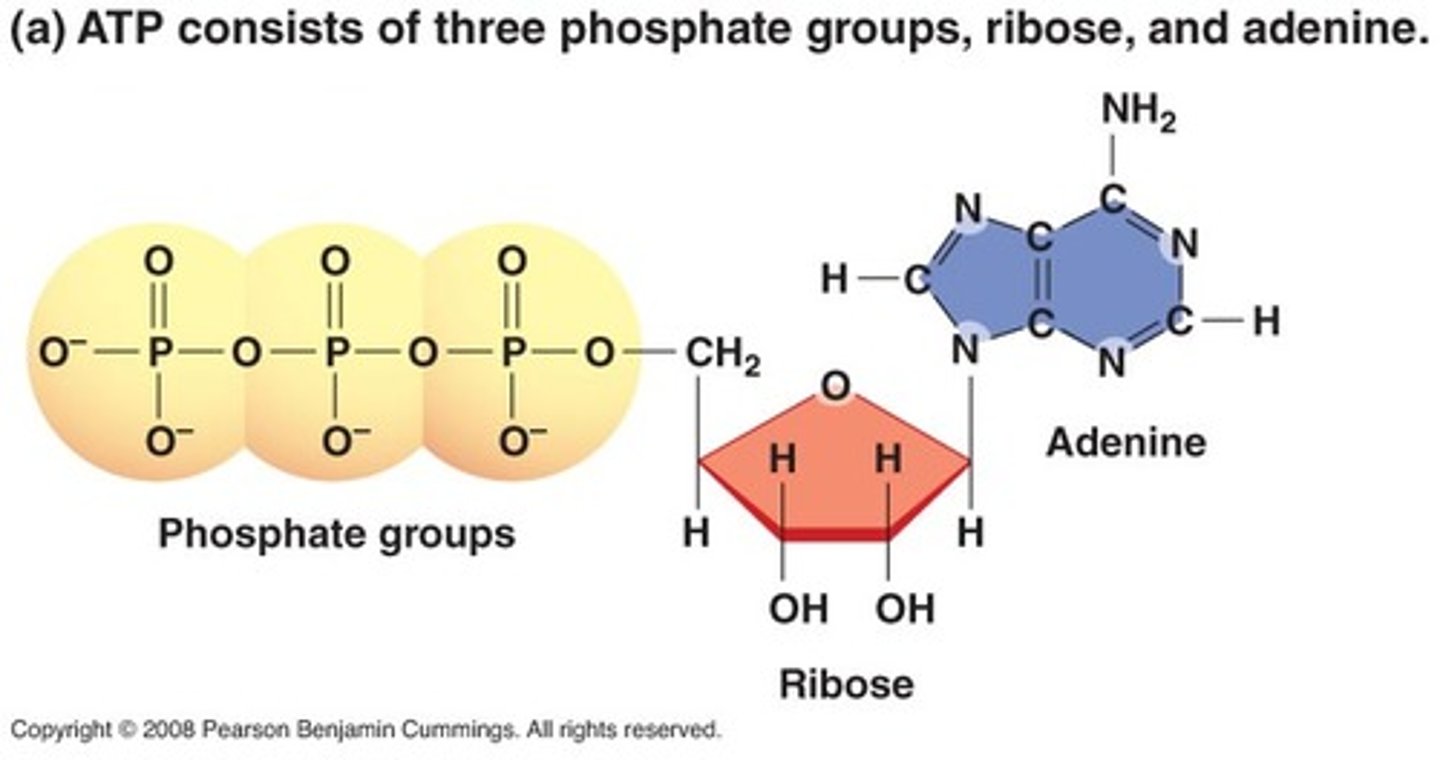
ATP structure
adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups
ATP function
transfer and storage of energy
3 main parts of cells
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus
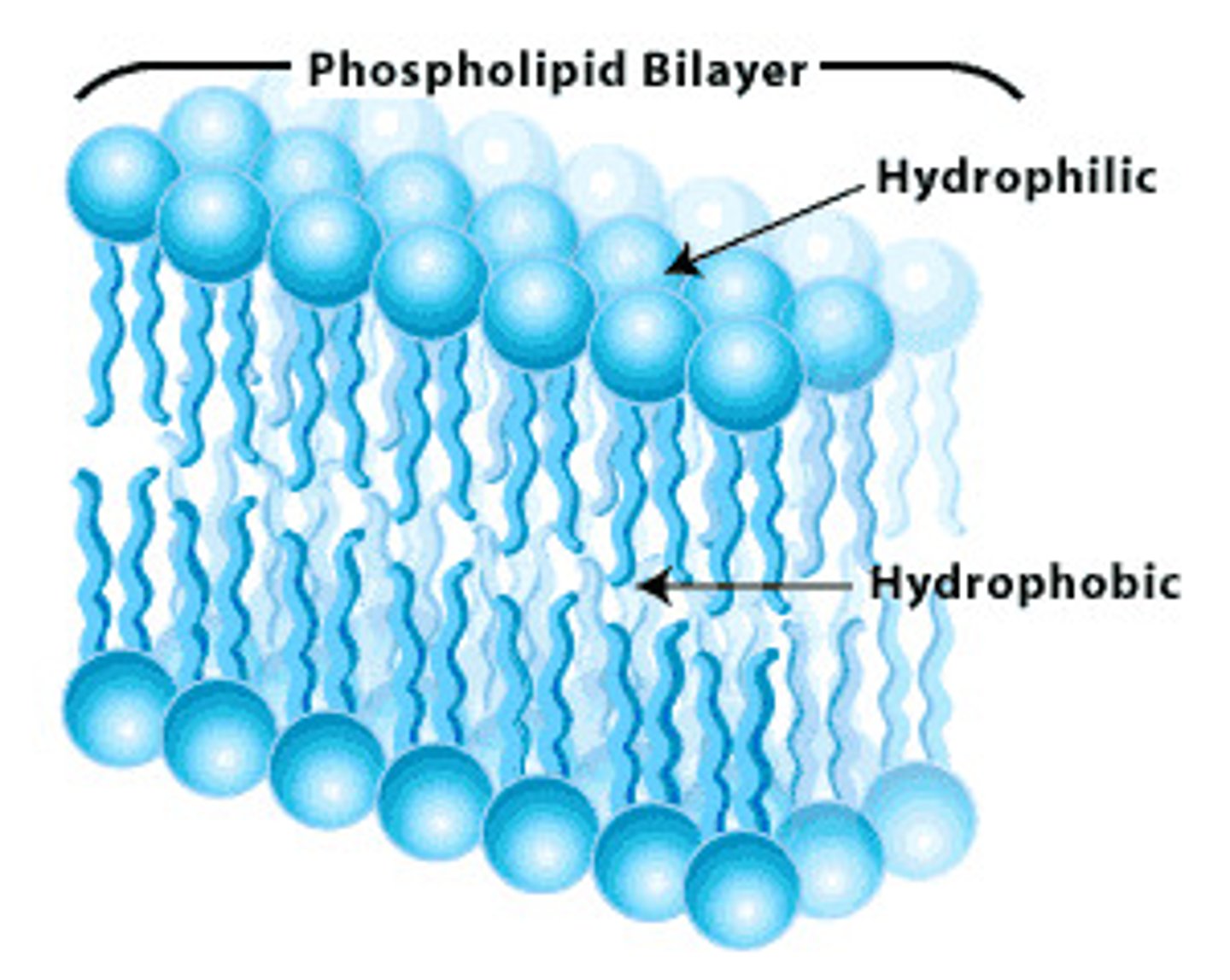
structure of plasma membrane
phospholipid bilayer with hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads
Functions of membrane proteins
transport, enzymes, receptors, join membranes, structure, cell identity markers
selective permeability
A property of a plasma membrane that allows some substances to cross more easily than others.
electrochemical gradient
The combination of forces that acts on membrane potential
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
transport maximum
transport rate when all carriers are occupied
hypotonic
surrounding medium has less solute than the cell interior
hypertonic
surrounding medium has more solute than the cell interior
isotonic
surrounding medium has the same solute as the cell interior
filtration
passive process where liquid flows due to hydrostatic pressure
primary active transport
Active transport that relies directly on the hydrolysis of ATP
secondary active transport
energy is provided indirectly
vesicular transport
Transport of large particles and macromolecules across plasma membranes
cytoskeleton function
strength and support, movement of cellular structures and materials
endoplasmic reticulum function
transports synthesized proteins and lipids to other parts of the cell
lysosome function
intracellular digestion
Mitchondria function
ATP production
Golgi apparatus function
modifies and packages proteins and lipids
nucleus function
Control center of the cell, stores genetic material