Unit 6: Urban Land Use ALL
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Urban
City
Urbanization
Movement of people from rural areas to cities
Suburbs
Residential areas surrounding cities
Suburbanization
Movement to communities around the central city/urban area
GI Bill
Provided low cost home loans for veterans, contributed to suburbanization
Mass Produced Housing
"cookie cutter houses", caused housing prices to fall and suburbanization to increase
Interstate Highway System
Network of US highways connecting all states, contributed to car ownership and suburbanization
World City
Dominant city in terms of its role in the global politics and economy
Megacity
a city with over 10 million people
Megalopolis
a very large, heavily populated city or urban complex with multiple connected cities
BosWash
the name given to a line of large northeastern cities running south from Boston to Washington D.C.; a megalopolis
Primate City
The largest settlement in a country AND has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement
Primate City Rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the largest settlement has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking settlement.
Rank Size Rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
Central Place Theory (Christaller)
A theory that explains the distribution of services, based on the fact that settlements serve as centers of market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther.
Shape of Christaller's market areas (Central Place Theory)
Hexagons
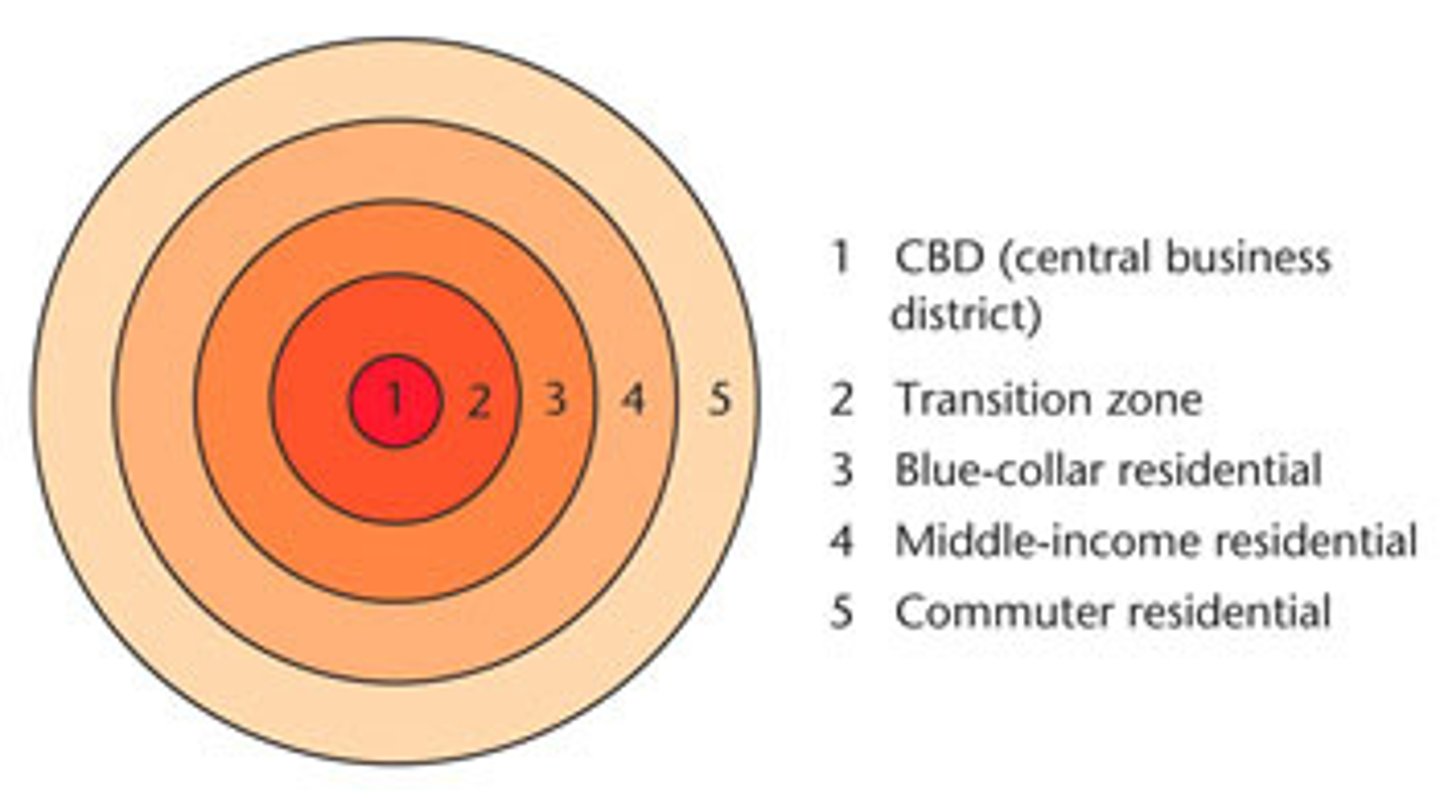
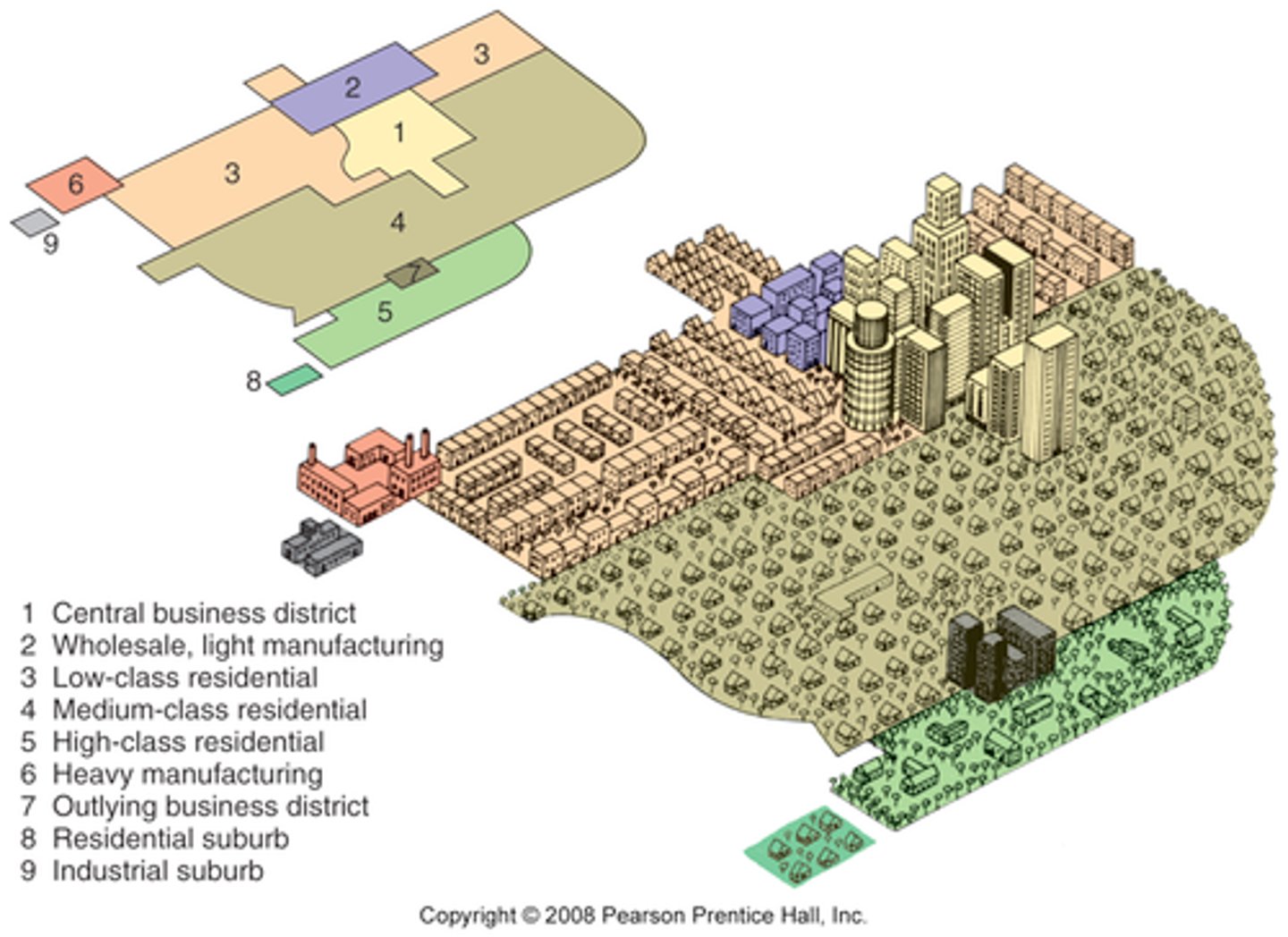
Concentric Zone Model
A structural model of the American central city that suggests the existence of five concentric land-use rings arranged around a common center.
Disparity
inequality; difference
Edge Cities
A term introduced by Joel Garreau in order to describe the shifting focus of urbanization in the United States away from the CBD toward new loci of economic activity at the urban fringe. These cities are characterized by extensive amounts of office and retail space, few residential areas, and modern buildings
Favela
a slum community in a Brazilian city often made of squatter settlements with inadequate housing and infrstructure
Food Desert
An area characterized by a lack of affordable, fresh and nutritious food.
Food Insecurity
the state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
Infrastructure
the basic physical and organizational structures and facilities (e.g., buildings, roads, and power supplies) needed for the operation of a society or enterprise.
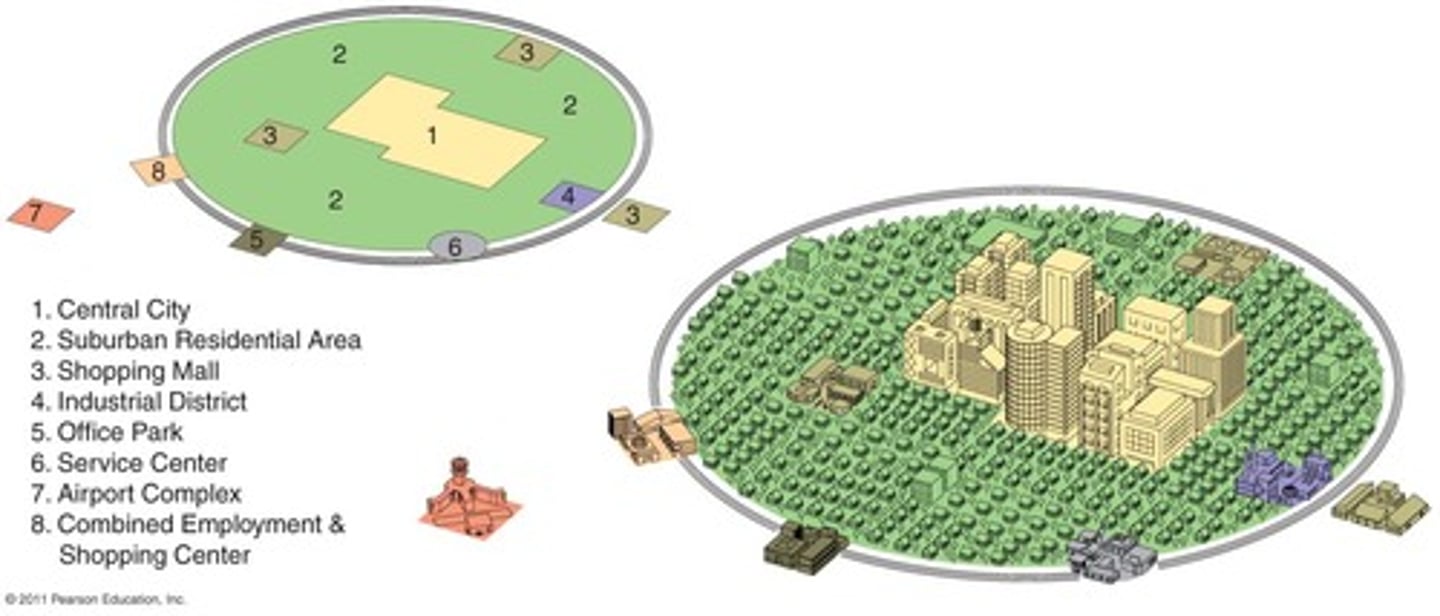
Galactic City Model
Urban Model created in the last half of the twentieth century, represents the post-industrial city, many suburban CBDs have become specialized toward a particular sector
Gentrification
the restoration of run-down urban areas by the middle class (resulting in the displacement of lower-income people)
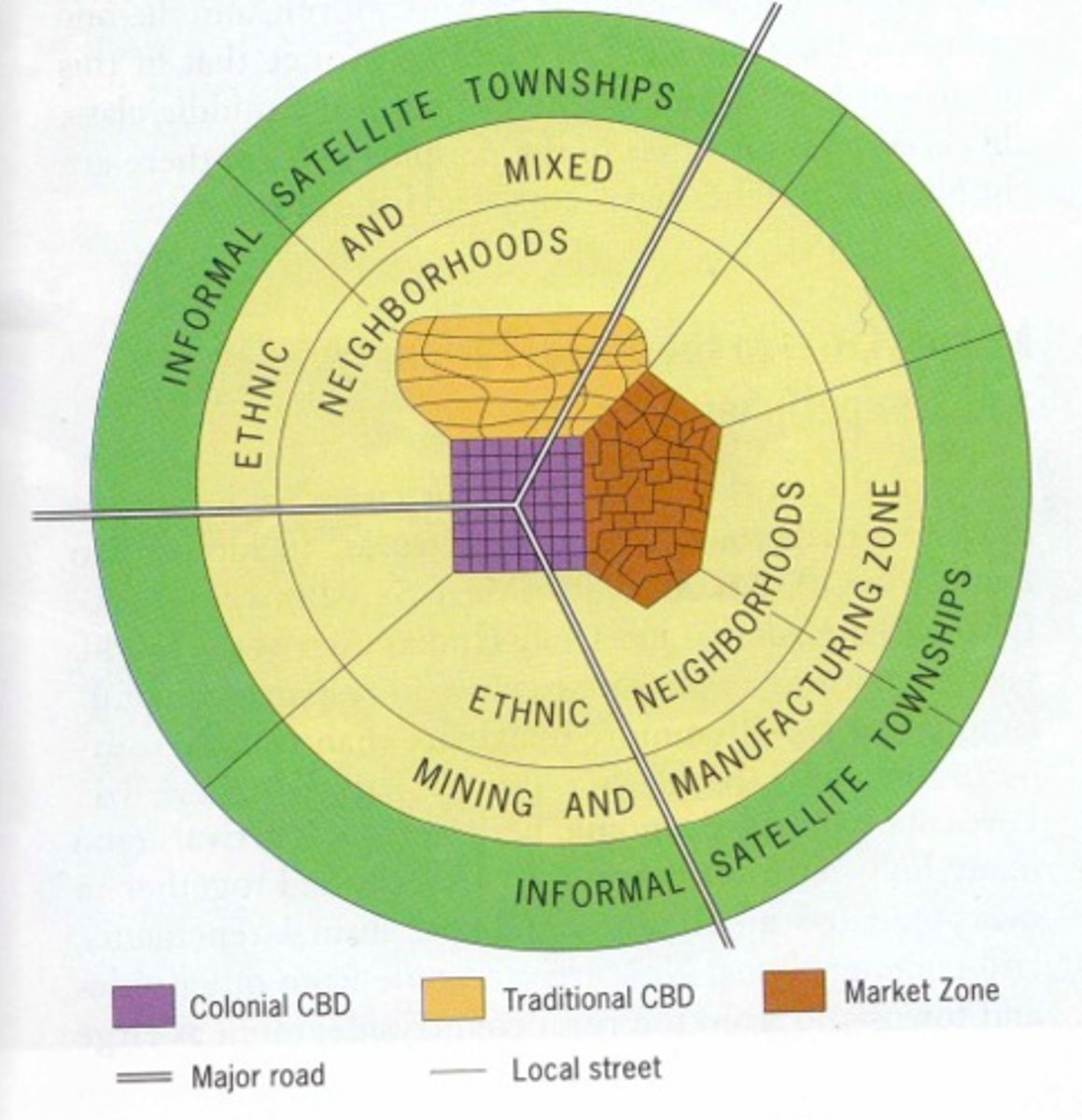
Sub-Saharan African City Model
a spatial city model that is difficult to formulate due to the imprint of European colonialism, but often consists of a colonial CBD as well as a traditional CBD, and a market zone that is surrounded by squatter settlements (informal satellite townships)
Range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
Threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service
Redlining
A process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within the boundaries.
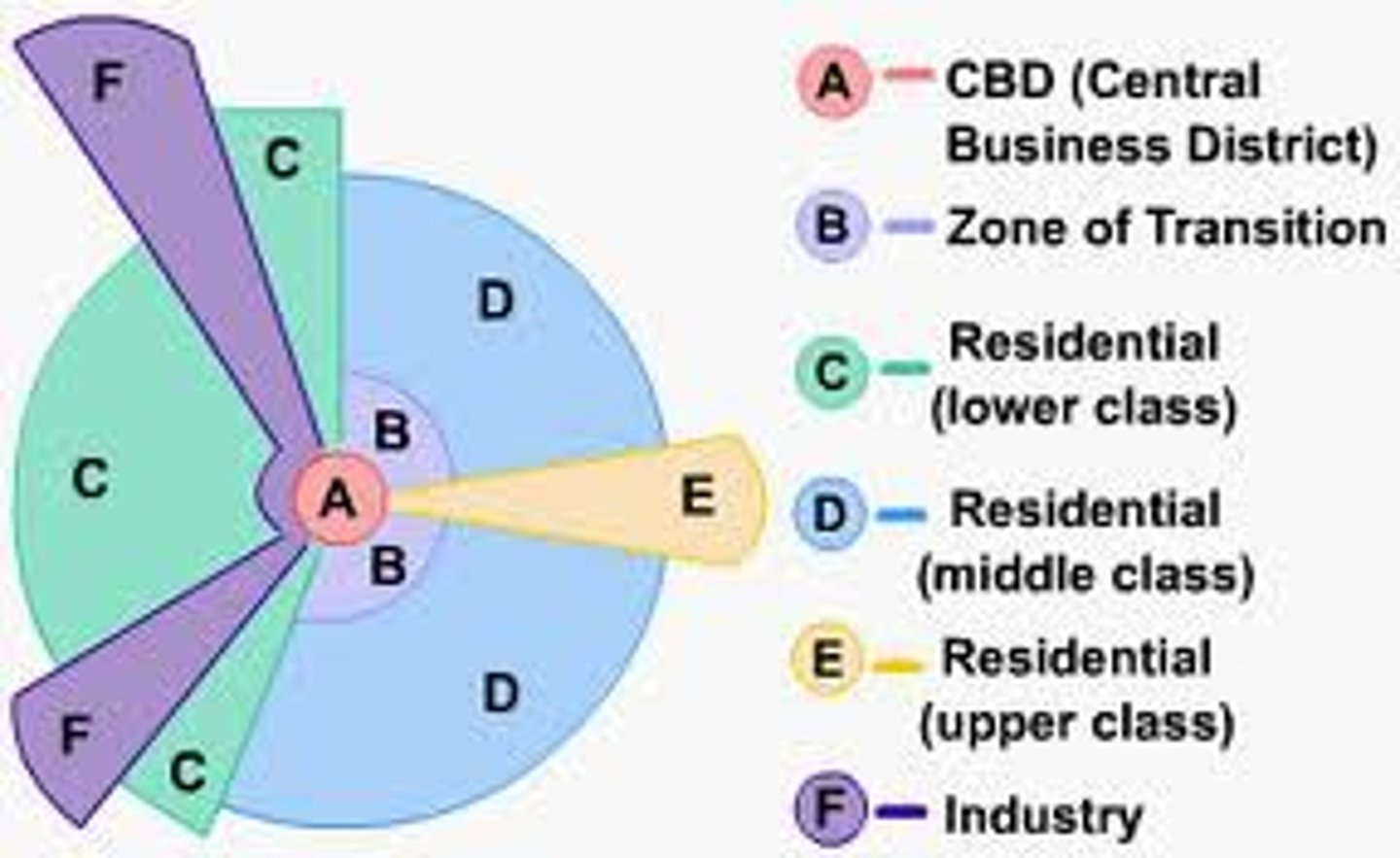
Sector Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors, or wedges, radiating out from the central business district (CBD).
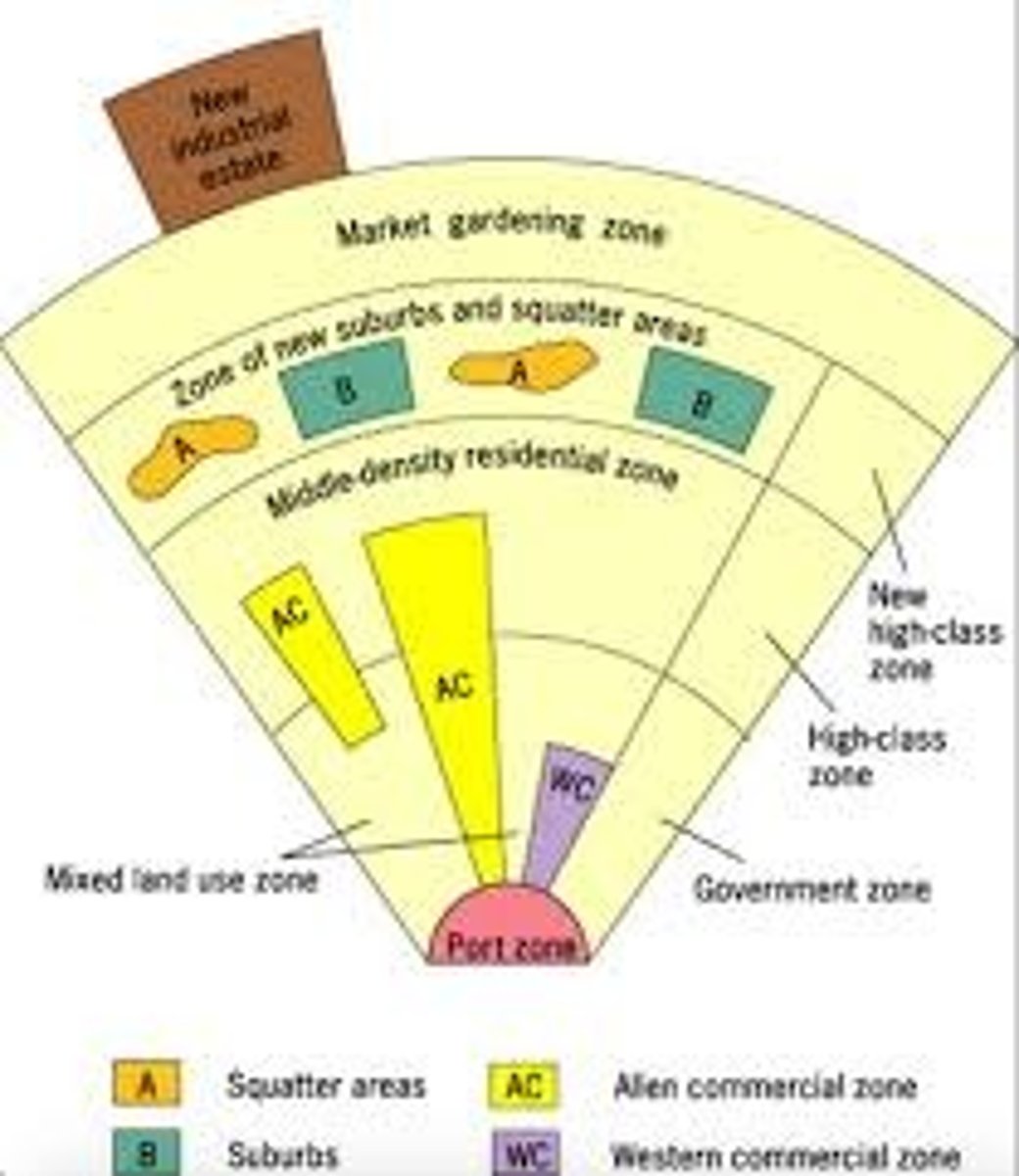
Southeast Asian City Model
a spatial city model that includes an old colonial port zone that is the focal point of the city reflecting a city oriented around exports, and radiating outward from the port zone are the Western commercial zone and Alien commercial zone
Suburban sprawl
unplanned development by many different entities, often as part of urban outgrowth
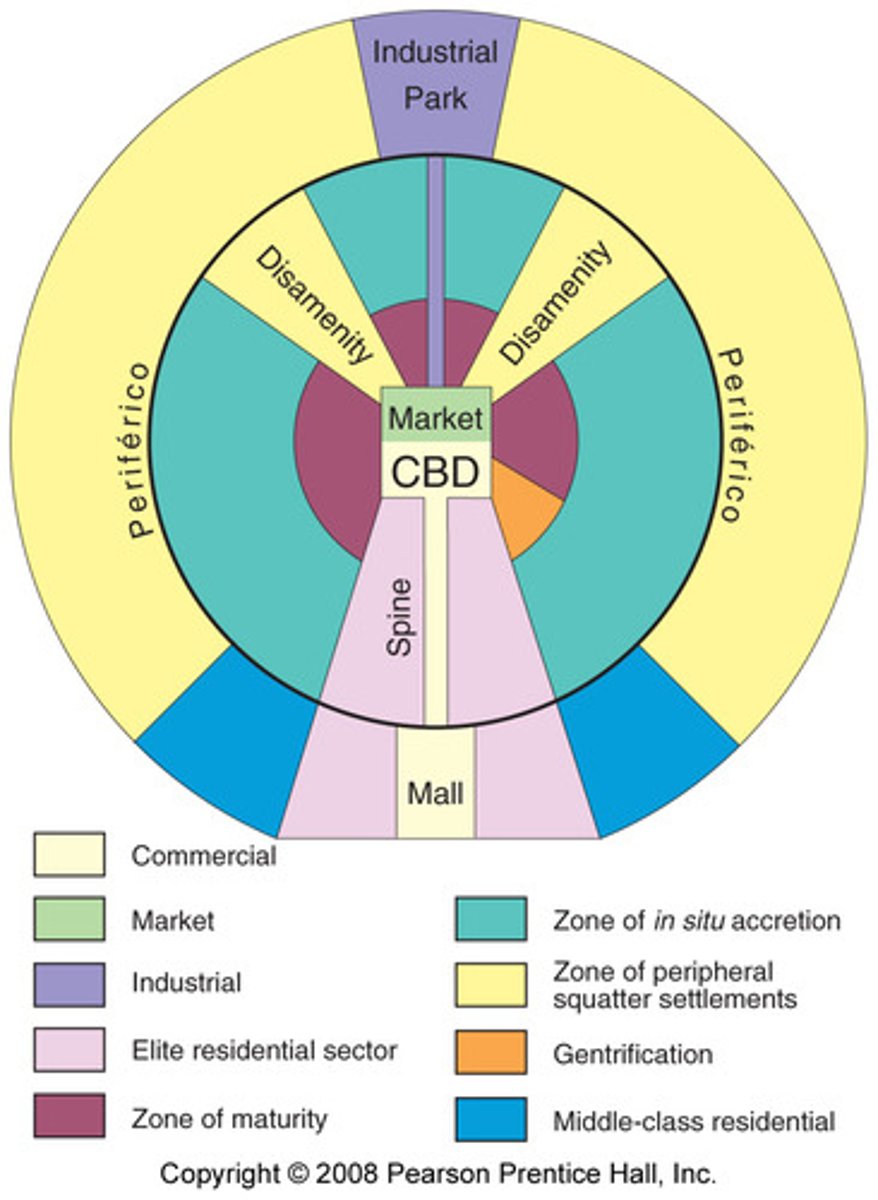
Latin American City Model
Combines elements of Latin American Culture and globalization by combining radial sectors and concentric zones. Includes a thriving CBD with a commercial spine. The quality of houses decreases as one moves outward away from the CBD, and the areas of worse housing occurs in the Disamenity sectors, along the outskirts of the city
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
Mixed Use Development
An approach to urban design that combines different types of land use within a particular neighborhood or district (commercial and residential together)
Multiple Nuclei Model
developed by Chauncy Harris and Edward Ullman, describes urban areas as developing around multiple, independent centers of activity rather than a single central business district.
New Urbanism
A movement in urban planning to promote mixed use commercial and residential development and pedestrian friendly, community orientated cities as a reaction to the sprawling, automobile centered cities of the mid twentieth century.