Radiology ch 9
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Ionization
Gain or loss of an electron
Can cause biological effects
Sources of ionizing radiation
Natural (earth/sun/stars)
Manmade (humans)
Largest portion of human made radiation exposure
Medical and dental X-ray examinations
X-ray production requirements
-source of electrons
-method to accelerate electrons to great speed
-method to stop electrons
- X-ray tube with vacuum inside
X-ray beam is…
Heterogeneous (different energies produced)
Characteristic X-rays
Incoming electron ejects inner shell electron, outer shell fills vacancy, creating X-ray photon
Occurs in X-ray tube 80% of time
Happens bc of ionization
Bremsstrahlung Radiation
“breaking radiation”
produced when high-speed electrons are decelerated upon striking tungsten target
occurs in the X-ray tube 20%
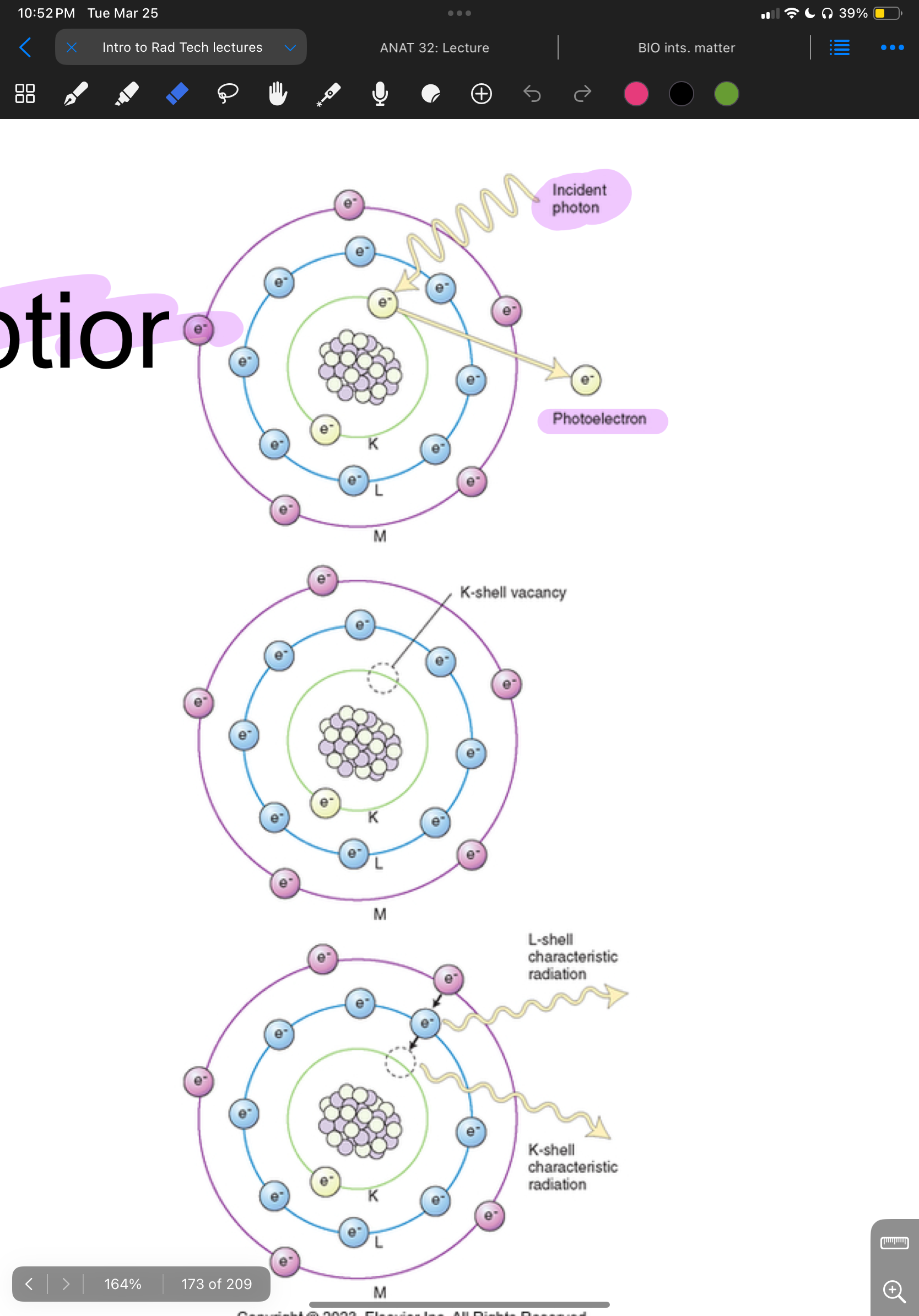
Photoelectric Absorption
process where incoming X-ray photon is absorbed by inner-shell electron, outer shell electrons fill vacancies creating an ion pair. Excess energy will hit body creating “characteristics radiation”
Largest contributor to patient exposure
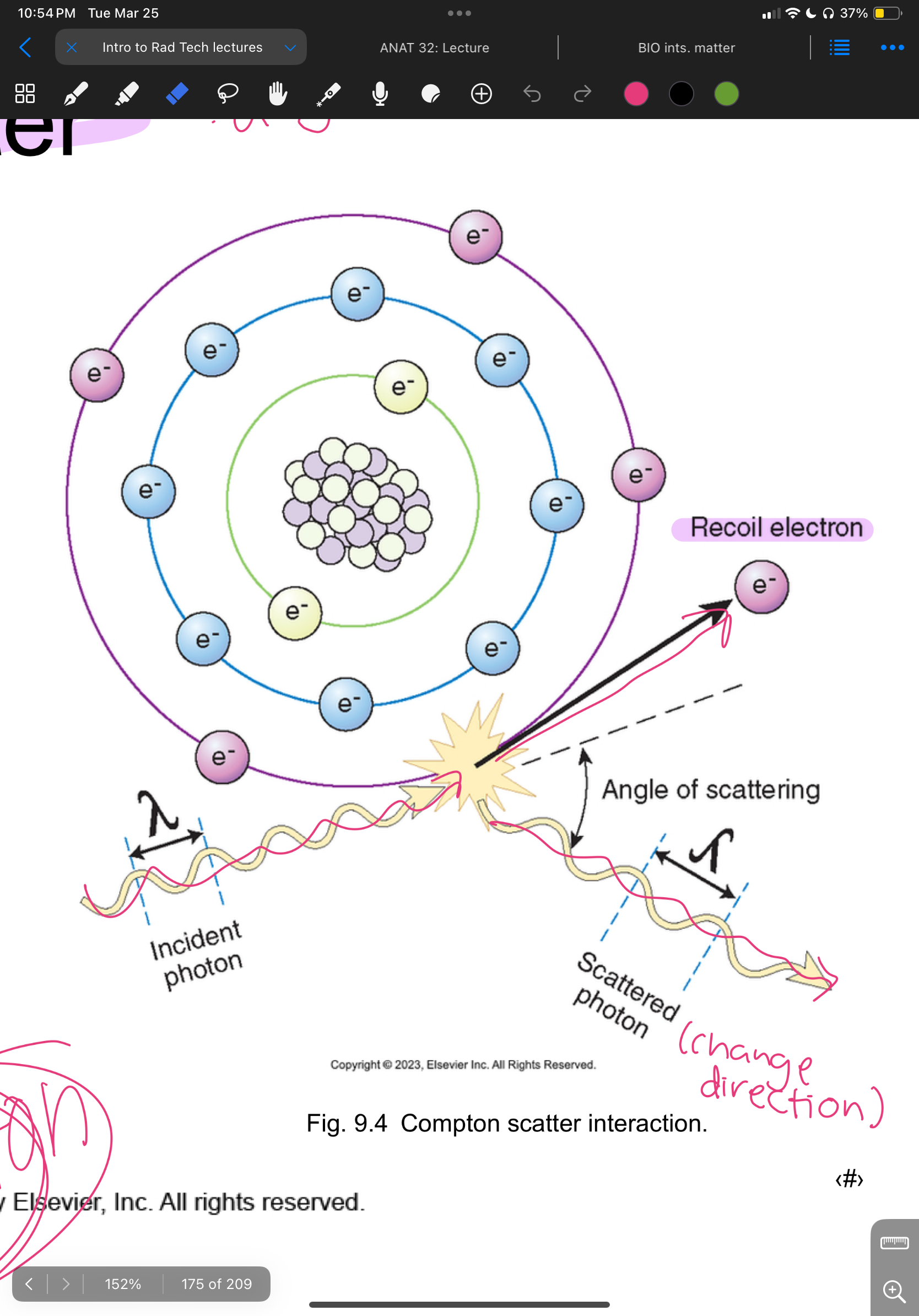
Compton Scatter
occurs when incoming photon collides w/ outer-shell electron, causing the photon to lose energy and change directions creating “recoil electron” and ion pair
Techs get exposure from Compton
Degrades images
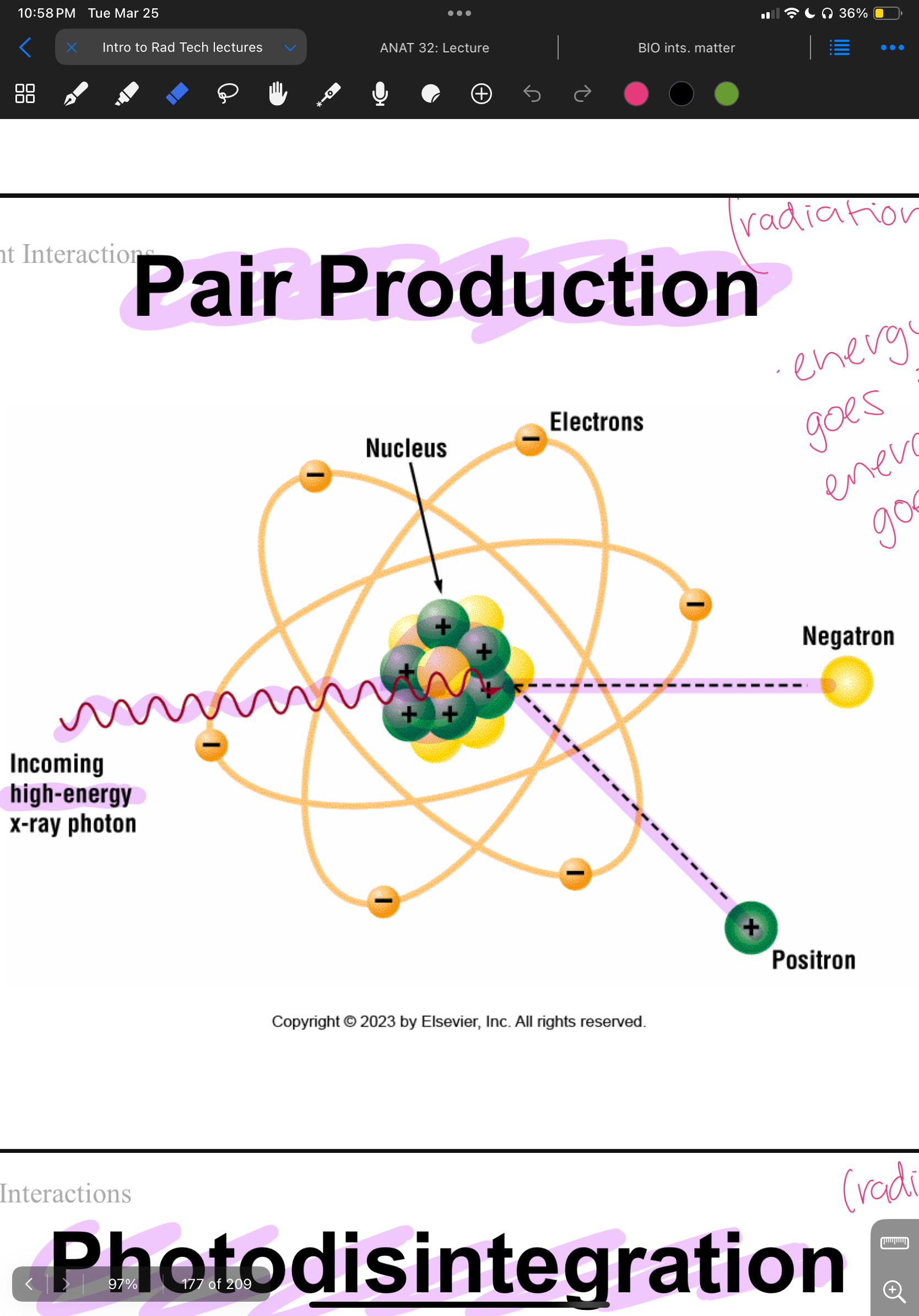
Pair production
When high energy photon interacts w/ nucleus creating negation/positron pair. Same energy that goes in comes out.
used in radiation therapy
Cultural Competency
Value/diversity
Possessing capacity for cultural self assessment
consciousness of dynamics of cross cultural interactions
Institutionalizing cultural knowledge
Developing adaptation of service delivery that reflect understanding multicultural environment
Human rights law
Autonomy
Dignity
Equality
Solidarity
Diagnostic efficiency
Accuracy of diagnostic info on a medical image
Human diversity characteristics
Age
Race
Sexual Orientation and gender
Ethnicity and nationality
Largest growing population is
Geriatric (65+)
Globalization
People cross board to other countries for school/work/ etc.
Assimilation vs. Biculturalism
Assimilation = blending in
Biculturalism = bi-racial
Diagnostic yield
Clinically useful information on a diagnostic image
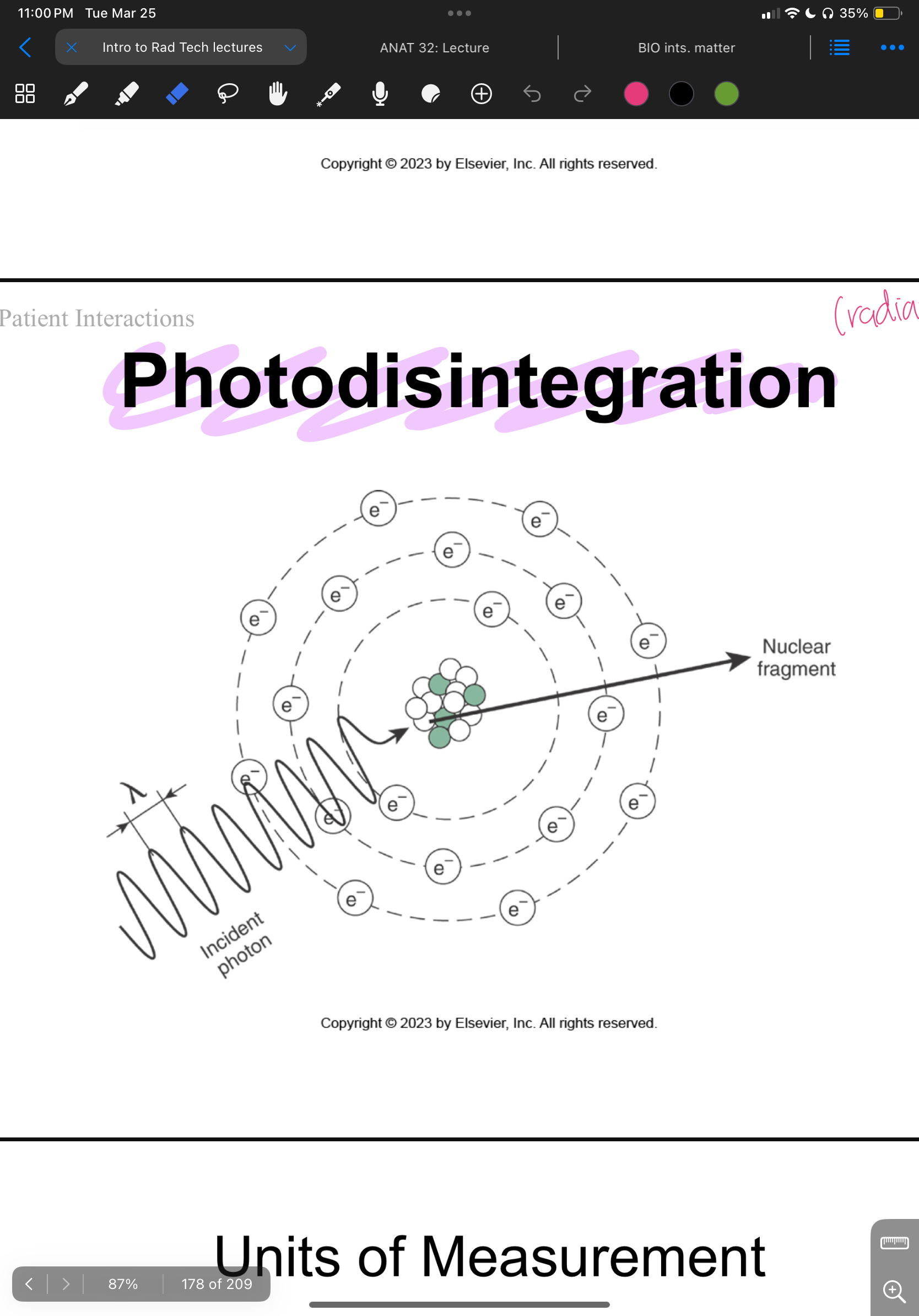
Photodisintegration
When incoming photon is captured by nucleus, then will release “fragment” of the nucleus due to amount of energy used
also used in radiation therapy
General population whole body dose
5 mSv (0.5 rem)
Radioactivity (Bq)
Used in radiation therapy and nuclear medicine
Bq/Cu = units used to measure
Effective dose
Occupational exposure
measured in Sv
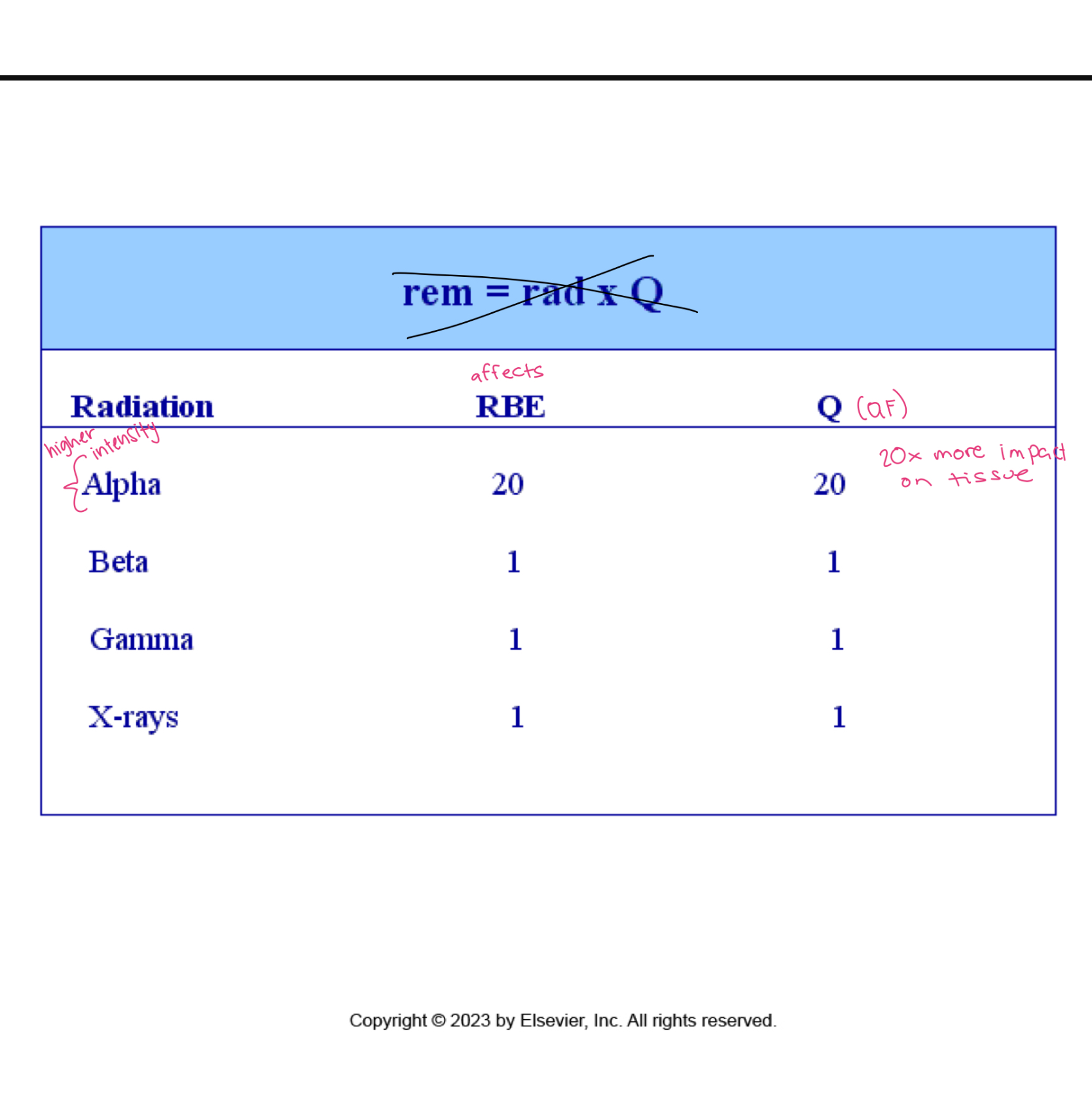
QF of x-ray is 1
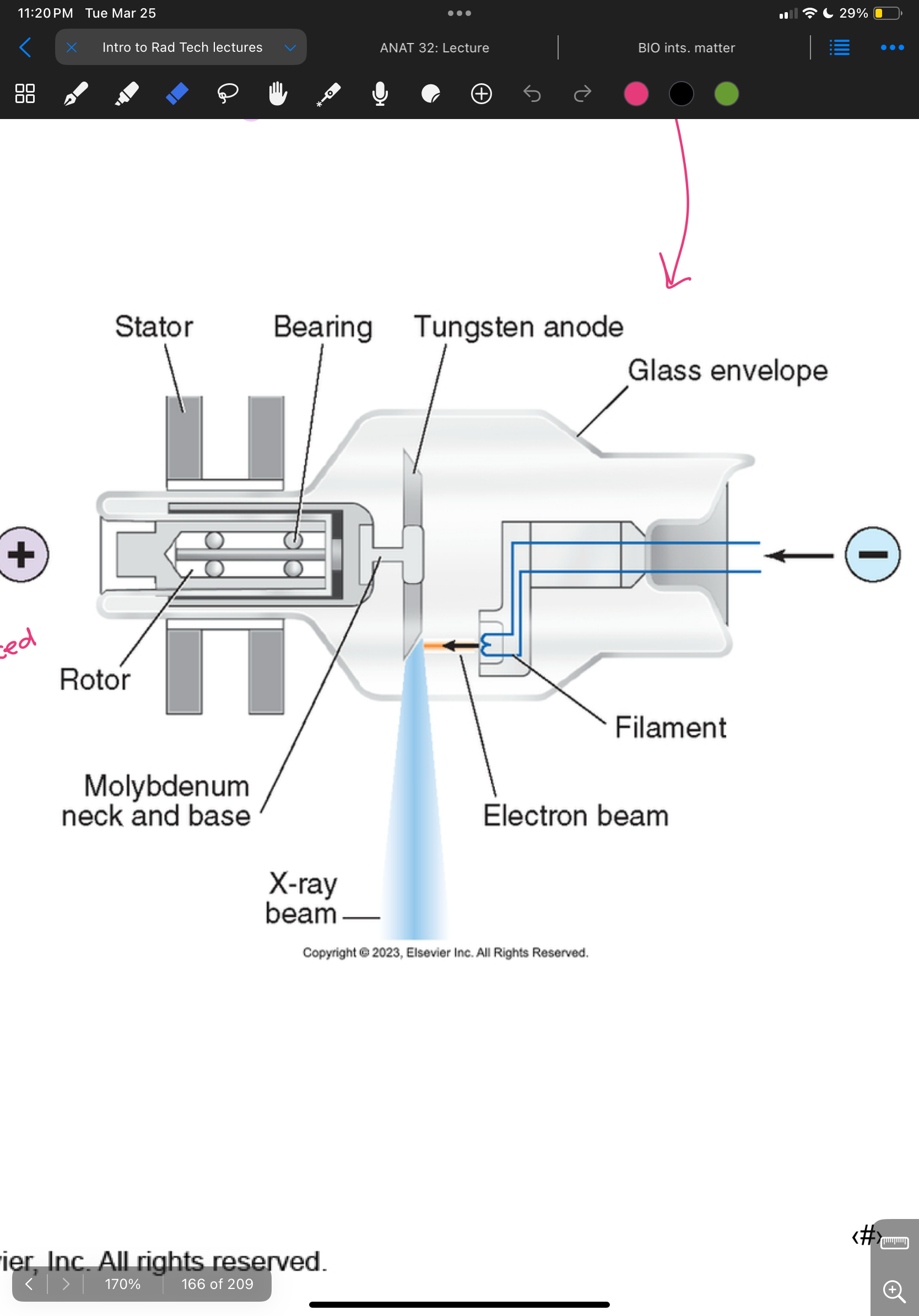
X-ray tube design
Annual effective dose
50 mSv/ 5 rem
Max cumulative whole body dose
10 mSv x age
Cellular response to radiation
-cellular death
-delayed mitosis
-altered mitotic rate
Cellular irradiation damage theories
Direct
Indirect
Attenuation
Loss of radiation energy as it passes thru absorbing matter (human)
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
minimize radiation exposure.
Radiation Monitoring Dosimeters
Optically stimulated luminescence dosimeter (OSL)
most commonly used
Total Body response
acute radiation syndrome
Stages
-padromal (vomit, diarrhea)
-Latent (cool off)
-manifest (get better or die)
No dose = safe dose
No dose is considered totally risk free
Exposure
Measures exposure in AIR
Measured in R/ Gya
Absorbed dose
Measures amount of radiation absorbed in tissue
assured in (gray) Gyt/Rad
Cardinal Rules of Protection
Time -least time possible
Distance- inv. Sq. Law (far from x-ray beam)
Shielding - always shield
Inside X-ray tube
- BREMS 20%
-CHARACTERISTIC 80%
-HEAT
3 general interactions btwn x-ray photons and matter
No interaction
Complete absorption
Partial absorption w/ scatter
What patient interactions ate important
-Compton scatter
-photoelectric absorption
5 patient interactions
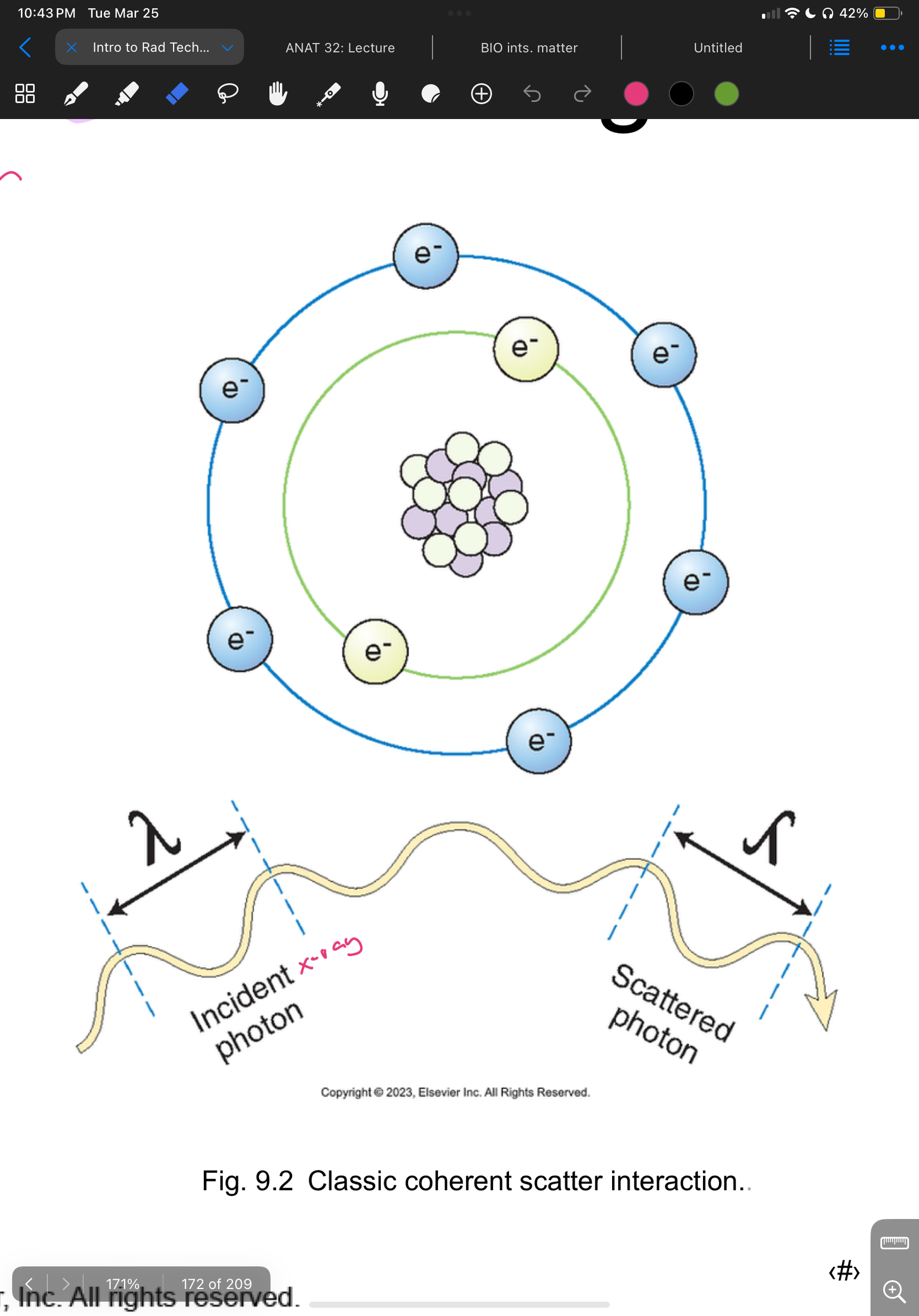
Classic coherent scatter
Compton scatter
Photoelectric absorption
Pair production
Photodisintegration
Classic coherent scatter
Incoming photon hits atom and is absorbed, atom releases excess energy creating another X-ray photon in a different direction aka scattering
(<10 kVp)
Radiation syndromes
-bone marrow syndrome
- gastrointestinal syndrome (GI)
-central nervous syndrome (CNS)
Dose limit for full term pregnancy is..
5 mSv
Geiger meter
occupational workers use to measure presence and exposure in real time