IB Cell Biology-
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
glycosylation
The term used to describe the attachment of a carbohydrate to another compound
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
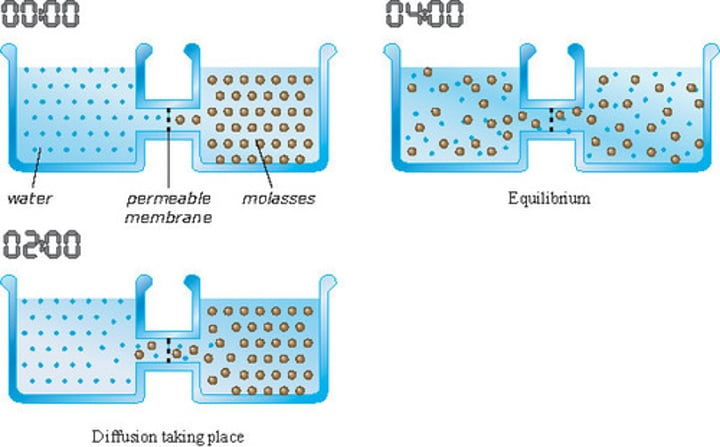
facilitated diffusion
The spontaneous diffusion of molecules assisted by specific transmembrane integral proteins involving channel proteins
active transport
energy-requiring movement of molecules across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
ribosome
organelle that synthesises proteins.
Rough and Smooth ER
differ in structure and function, and are formed of continuous membranes, and transport systems in the cell.
mitochondria
supplies energy to the cell and has its own ribosomes and DNA.
Totipotent
Can form any cell type including extra-embryonic (placental) tissue.
Can give rise to an entire organism.
Pluripotent
Can form most cell types, except extra-embryonic.
Cannot give rise to an entire organism.
Multipotent
Can differentiate into a number of closely related cells.
Ex. blood cells, skin cells and nerve cells.
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
DNA organisation in prokaryotes
One circular chromosome and additional plasmids
Sensitivity
the ability to detect or sense stimuli in the internal or external environment.
Nutrition
the process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
embryonic cells
are able to differentiate into the required cell type.
bone marrow
The stem cell niche that gives rise to different types of blood cells
Geonome
The term used to describe the complete set of genetic instructions within a cell
peripheral protein
A protein loosely bound to the surface of a membrane or to part of an integral protein and not embedded in the lipid bilayer.
Selectivity
The term used to describe a membrane's capacity to control the passage of certain materials
endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Hypertonic
solution that has a higher concentration of dissolved particles compared with another solution. It has a higher osmotic pressure
cytoplasm
jellylike substance inside cells that contains molecules and in some cells organelles.
golgi apparatus
involved in secretion and intracellular transport.
chloroplasts
used to convert solar energy into chemical energy.
Differentiation
The expression of some genes and not others in a cell's genome. A process when newly formed cells become more specialised and distinct from one another as they mature.
lysosomes
digest excess or worn out organelles, food particles, and engulfed viruses or bacteria.
morphogen
The name given to chemicals that trigger embryonic development according to expression gradients
Role of cholesterol and proteins in membrane
maintaining the structural integrity and regulating the fluidity of cell membranes
Metabolism
The cell function that is affected by volume
stem cells
unspecialized cells that can renew themselves for long periods by cell division.
osmosis
diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of higher solute concentration to an area of lower solute concentration
What is the Cell Theory?
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. Cells are the smallest units of life
3. All cells come from pre-existing cells
Equation for magnification?
Magnification = size of image / actual size
centrosome
Organelle made up of a pair of centrioles. It organises the microtubules during cell division.
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
Analysis of the proteins
provides biochemical evidence that cells have begun to differentiate
surface area
The factor that determines the rate of material exchange
Hydrophobic interactions
The major interaction responsible for stabilising plasma membranes is
Cell recognition
The role of carbohydrates in cell membranes
plasmolysis
plant tissue is placed in a hypertonic solution
Osmolarity
A measure of solute concentration, as defined by the number of osmoles of a solute per litre of solution
Isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution. The type of solution used in medical procedures to prevent cellular desiccation