Comprehensive Review of Gonadal, Male, and Female Reproductive Hormones and Disorders
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the common substrate for all adrenal steroids?
Cholesterol
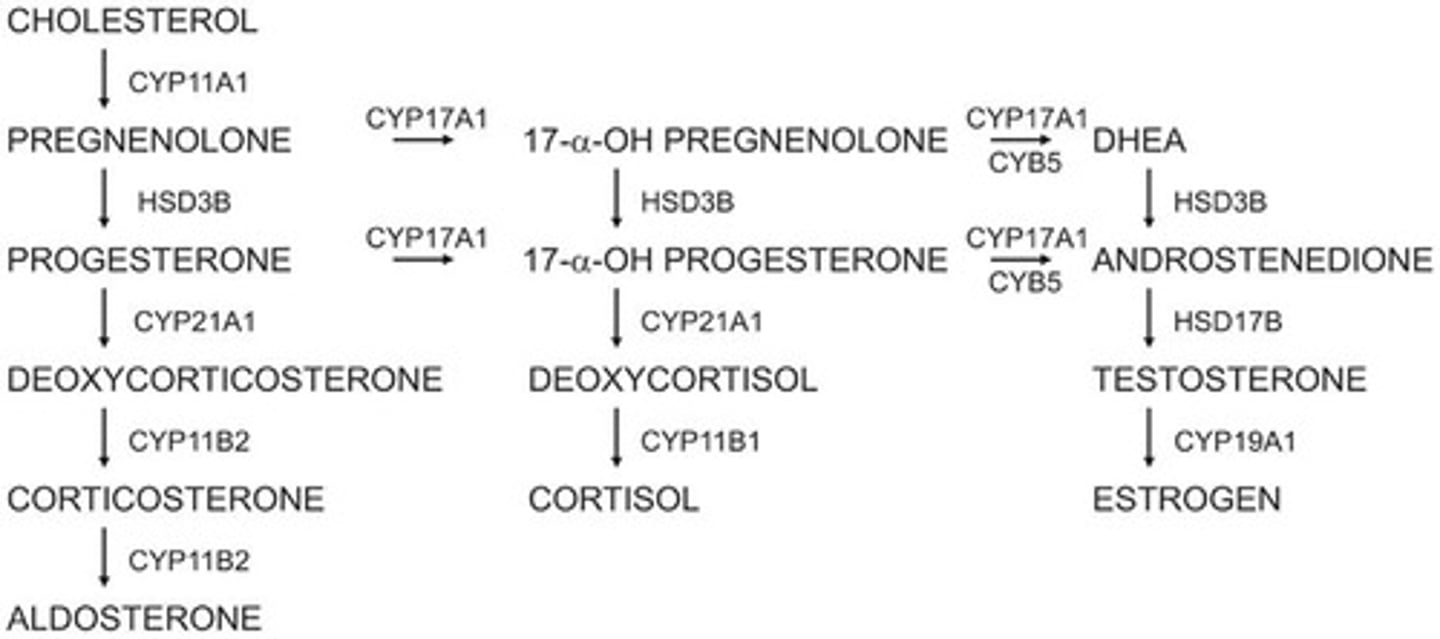
What are the main endogenous male sex hormones?
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), androstenedione, testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
What is the role of Sertoli cells in the male reproductive system?
They secrete Androgen Binding Protein, inhibin B, and activin, and respond to FSH to initiate spermatogenesis.
What is the function of Leydig cells?
They produce testosterone in response to LH.
What is the significance of seminal vesicle secretions?
They are rich in vitamin C and fructose, which are important for sperm motility.
What hormonal changes indicate the onset of puberty in males?
Rising levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
What percentage of circulating testosterone is produced by the testes?
95%
How does testosterone affect LH secretion?
Increased testosterone inhibits LH secretion.
What is the role of Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)?
It stimulates the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary.
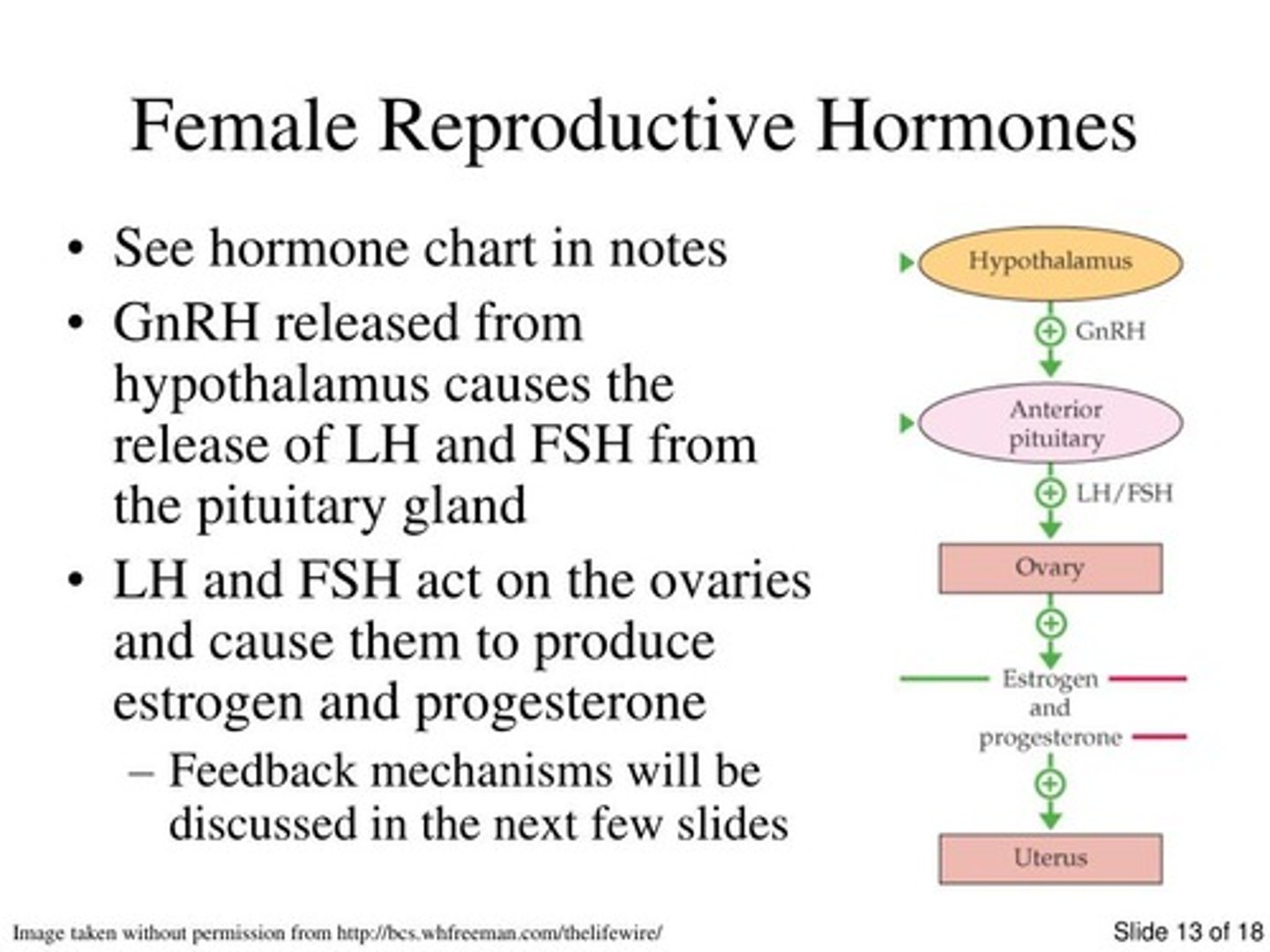
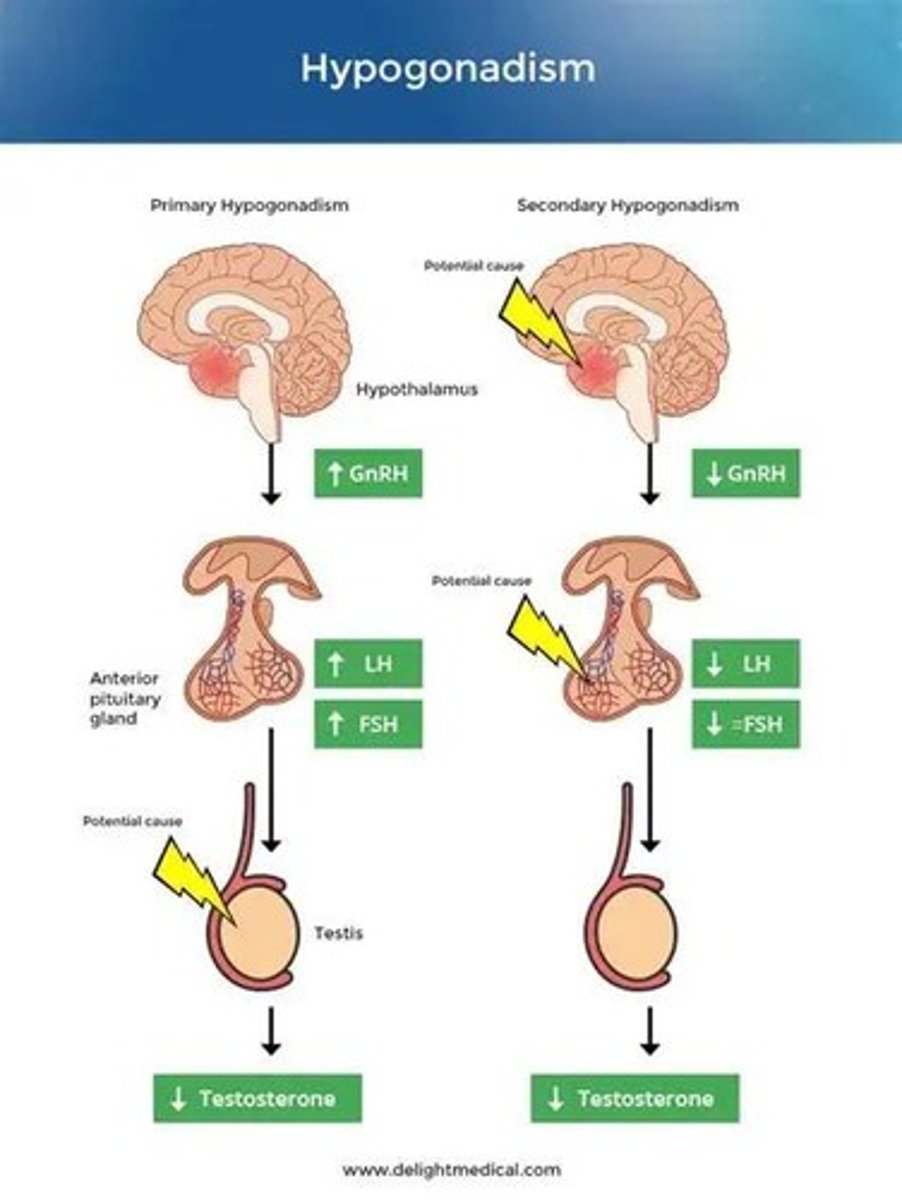
What is the difference between hypergonadotropic and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
Hypergonadotropic hypogonadism is characterized by high levels of pituitary gonadotropins, while hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is due to insufficient secretion from the pituitary or hypothalamus.
What genetic condition is associated with Klinefelter's syndrome?
Presence of an extra chromosome (karyotype 47 XXY).
What is the primary characteristic of 5α-reductase deficiency?
Decreased conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), leading to a female-like appearance until puberty.
What is Sertoli cell-only syndrome?
A condition where there are no germ cells to develop into sperm, resulting in infertility due to azoospermia.
What is androgen insensitivity syndrome?
A condition where there is androgen receptor dysfunction, leading to feminization of male babies despite normal testosterone and DHT levels.
What are the two main functions of the ovaries?
To produce eggs during ovulation and to synthesize estrogen.
What happens to the follicles at the start of every ovarian cycle?
Several follicles are selected to mature, but typically only one becomes the graafian follicle; the others undergo atresia.
What is the average duration of the menstrual cycle?
25-35 days, lasting 3-6 days.
What is the role of estrogen and progesterone in the reproductive system?
They have positive and negative feedback effects on the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus.
What is positive feedback in hormonal regulation?
A loop where the release of a hormone initiates actions that lead to additional release of that same hormone.
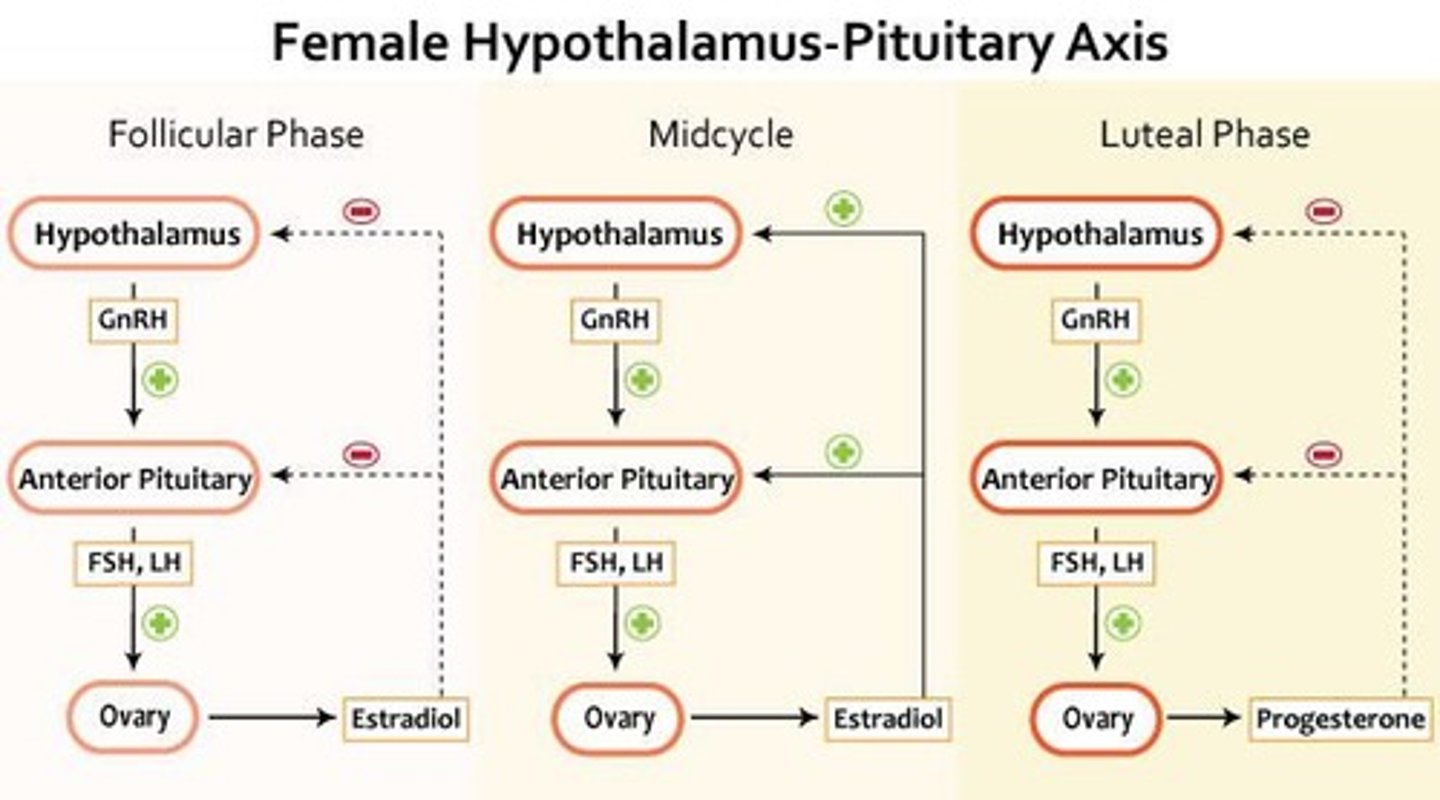
What is negative feedback in hormonal regulation?
A loop that leads to reduced release of a hormone.
What is the role of inhibin secreted by Sertoli cells?
It signals the hypothalamus to stop the release of GnRH, creating a negative feedback loop.
What is the main metabolite of testosterone?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is more potent.
How is testosterone metabolized in non-target tissues?
It is converted into estradiol.
What is the function of the endometrium?
It thickens during the menstrual cycle and sloughs off if no implantation occurs.
What occurs during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
It begins on the first day of the menstrual period and ends on the day of the LH surge.

What is the effect of low estrogen during the start of the follicular phase?
It results in negative feedback.
What happens to estrogen levels during the mid-cycle?
Estrogen levels peak, resulting in positive feedback.
What is the role of progesterone after ovulation?
It stabilizes the endometrium (uterine lining) and prepares it for embryo implantation.
What triggers the shedding of the uterine lining?
A drop in progesterone levels.
What are the primary hormones produced by the ovaries?
Estrogen and progesterone.
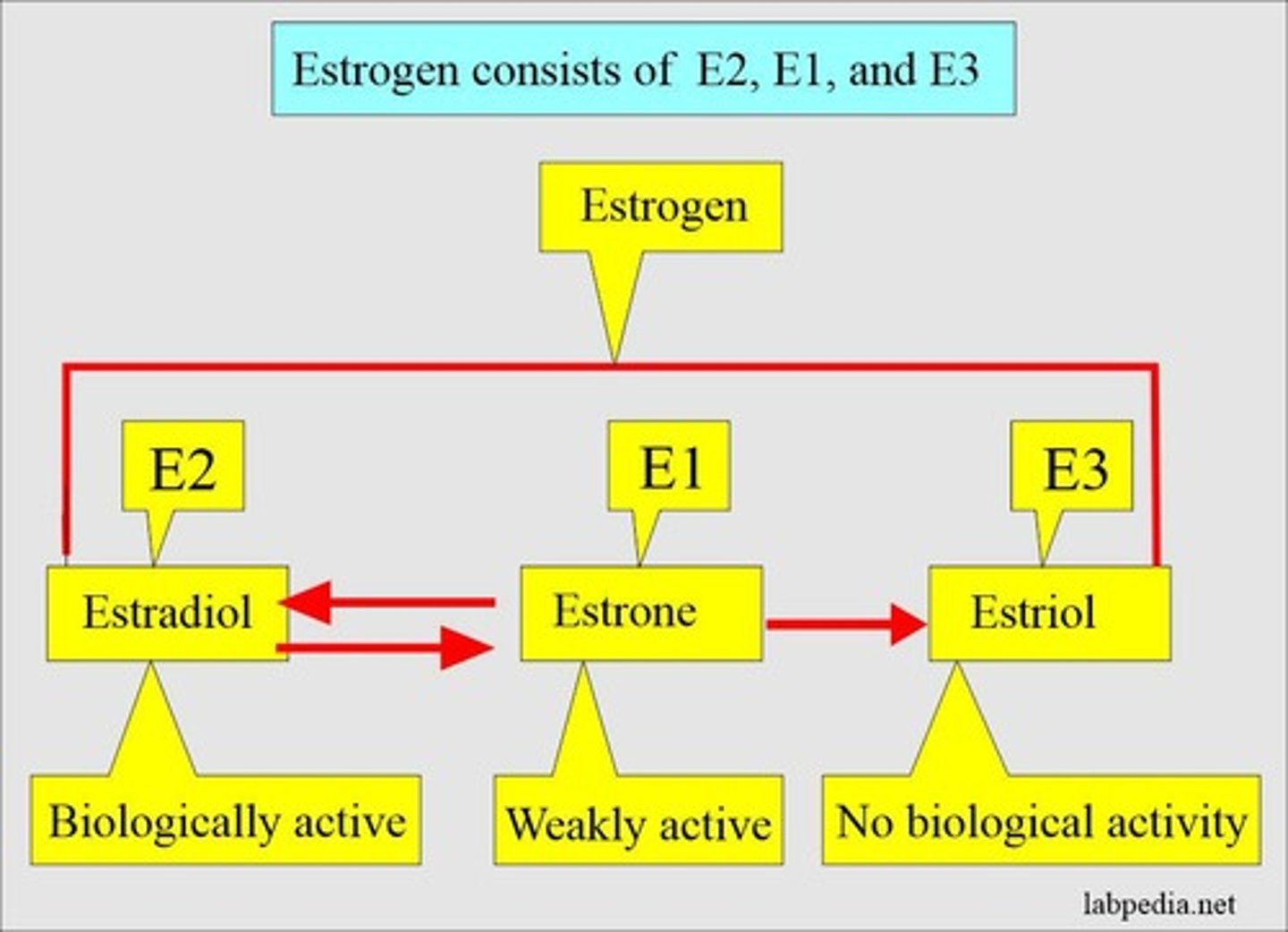
What is Estradiol?
The most abundant and biologically active estrogen produced by the ovary.
What is the function of estrogen during the follicular phase?
It thickens the uterine lining.
What is the consequence of estrogen deficiency during the follicular phase?
Irregular and incomplete development of the endometrium.
What is the role of progesterone during pregnancy?
It reduces cytokine production to protect the fetus and prevents ovulation.
What is primary amenorrhea?
A condition where a woman has never menstruated by age 16.
What is secondary amenorrhea?
The absence of menstrual cycles for a minimum of three to six months after having at least one cycle.
What is oligomenorrhea?
Infrequent irregular cycles in excess of 35 to 40 days.
What is menorrhagia?
Menstrual bleeding that lasts over seven days.
What is hypogonadotropic hypogonadism?
A condition characterized by FSH and LH deficiencies, which can cause secondary amenorrhea.
What is hypergonadotropic hypogonadism?
Ovarian failure that causes a rise in FSH and LH levels.
What is Turner's syndrome?
A condition where part or all of one of the X chromosomes is missing, leading to ovarian failure.
What is polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)?
A condition characterized by enlarged ovaries with small cysts, irregular menstrual periods, and excess hair growth.
What is Kallman's Syndrome?
A disorder that delays or prevents puberty, often associated with an impaired sense of smell.
What is the role of inhibins A & B?
They inhibit FSH production.
What does activin do?
It enhances FSH production.
What is the significance of the corpus luteum?
It secretes progesterone to aid in implantation of the embryo.
What happens to hormone levels if fertilization does not occur?
There is a decline in progesterone and estrogen production, leading to the shedding of the endometrium.
What is the typical duration of the luteal phase?
It lasts about 14 days.
What is the effect of androgens in females?
Overproduction can lead to hirsutism and other male characteristics.
What triggers ovulation?
A surge in LH levels, occurring about 36 hours after the peak in estrogen.