AP Psychology NEED TO KNOW
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:40 PM on 4/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
Structuralism
used introspection; the use of looking INWARD to determine underlying structures of the mind
2
New cards
Functionalism
Analyze the purpose of behavior - what function does it serve?
3
New cards
Evolutionary approach
natural selection, genes
4
New cards
Humanist
free will, choice, ideal, self-actualization
5
New cards
Biological
brain, neurotransmitters
6
New cards
Cognitive
perceptions, thoughts
7
New cards
Behavioral
learned, reinforced
8
New cards
Psychoanalytical/psychodynamic
unconscious, childhood
9
New cards
Biopsychosocial
combo, eclectic
10
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
father of modern psychology- structuralist
11
New cards
Mary Calkins
first female president of APA
12
New cards
Charles Darwin
natural selection and evolution
13
New cards
Dorothea Dix
reformed mental institutions in the U.S.
14
New cards
Stanley Hall
first president of APA
15
New cards
William James
father of American psychology - functionalist
16
New cards
Margaret Floy Washburn
first female PhD
17
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
observe people in their own setting
18
New cards
Correlation
relationship between two variables, but not CAUSATION
19
New cards
Positive Correlation
variables move in the same direction; one increases, the other increases
20
New cards
Negative Correlation
variables move in opposite directions; one increases, the other decreases
21
New cards
Mean
average
22
New cards
Median
middle number
23
New cards
Mode
most occuring number
24
New cards
Normal Distribution
mean, median, and mode are the same
25
New cards
Positive Skew
\
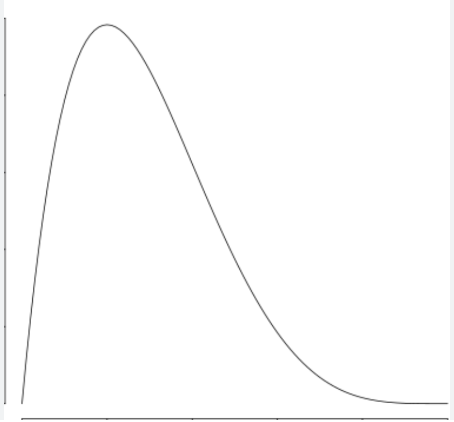
26
New cards
Negative Skew
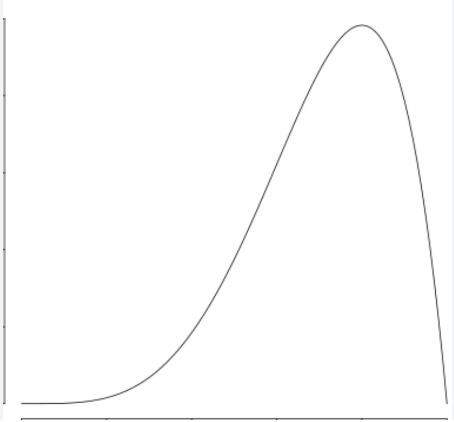
27
New cards
Absolute Threshold
identify stimulus 50% of the time
28
New cards
Sensory Adaptation
diminished sensitivity to stimuli
29
New cards
Top Down Processing
using brain/experiences to interpret information
30
New cards
Bottom Down Processing
taking in sensory information and then assembling and integrating it
31
New cards
Perceptual Set
past experiences influence interpretation
32
New cards
Inattentional Blindness
failure to notice something because attention is elsewhere
33
New cards
Beta Waves
awake
34
New cards
Alpha Waves
drowsy
35
New cards
Stage 1
drifting/jerking
36
New cards
Stage 2
most of night, sleep spindles, light sleep
37
New cards
Stage 3
deep sleep, delta waves, growth
38
New cards
REM
rapid eye movement - dream
39
New cards
Night Terrors
mainly in children, in stage 3, screaming, flailing, sleepwalking, while still asleep
40
New cards
Sleepwalking/Parasomnia
stage 3 movement
41
New cards
REM Sleep Disorder
acting out dreams
42
New cards
Place Theory
sound based on location of hair cells
43
New cards
Frequency Theory
rate of neuron firing
44
New cards
Cones
color
45
New cards
Rods
black and white
46
New cards
Feature Detectors
specialized cells for motion, shapes, lines
47
New cards
Blindspot
where optic nerve converges
48
New cards
Trichromatic Vision Theory
3 cones (red, green, blue)
49
New cards
Opponent Process Theory
in ganglion cells, three opposing channels in vision
50
New cards
Visual Capture
vision dominates senses
51
New cards
Phi Phenomenon
adjacent blinking lights look like movement
52
New cards
Interposition
overlapping objects
53
New cards
Freud’s Wish Fulfillment
symbolism and unconscious wishes in dreams
54
New cards
Activation Synthesis
dreams are random
55
New cards
Cognitive
problem solving in dreams
56
New cards
Information Processing
dreams are for memory storage
57
New cards
Unconditioned Stimulus
something that naturally causes a response
58
New cards
Unconditioned Response
natural response
59
New cards
Neutral Stimulus
does not cause any response
60
New cards
Conditioned Stimulus
previously the neutral stimulus
61
New cards
Conditioned Response
previously was unconditioned response (now in response to neutral stimulus)
62
New cards
Contiguity
timing of pairing
63
New cards
Contingency
predictability of nuetral stimulus
64
New cards
Overjustification
reinforcements diminish intrinsic motivation
65
New cards
Continuous Reinforcement
reward for every response
66
New cards
Fixed Ratio
reward response every (x) time
67
New cards
Fixed Interval
reward when (x) time has passed
68
New cards
Variable Ratio
reward after random number of responses
69
New cards
Variable Interval
reward after a random amount of time
70
New cards
Inight
aha! moments (Kohler)
71
New cards
Episodic Memory
memory of specific events
72
New cards
Semantic Memory
facts about something
73
New cards
Hierarchies
memories are stored according to a hierarchy
74
New cards
Semantic Networks
linked memories are stored together
75
New cards
Instinct
complex behaviors that are not learned (animal motivation)
76
New cards
Drive Reduction
physiological need creates aroused tensions (drive) that motivates you to satisfy the need
77
New cards
Homeostasis
equilibrium
78
New cards
Primary Drive
unlearned drive based on survival (hunger, thirst)
79
New cards
Secondary Drive
learned drive (wealth or success)
80
New cards
Optimum Arousal
humans aim to seek optimum levels of arousal, easier tasks require more arousal, harder tasks need less
81
New cards
Stomach Contractions
tell you when you are hungry
82
New cards
Glucose
level is maintained by the pancreas (if this drops, hunger increases)
83
New cards
Insulin
decreases glucose
84
New cards
Orexin
released by the hypothalamus, tells us to eat (increase in this results in hunger)
85
New cards
Lateral Hypothalamus
makes you hungry when stimulated
86
New cards
Ventromedial Hypothalamus
when stimulated you feel full (without it you would not stop eating)
87
New cards
Leptin
signals the brain to reduce appetite (end of meal)
88
New cards
Anorexia
distorted body image, weight loss of at least 15% of ideal weight
89
New cards
Bulimia
normal body weight, binge
90
New cards
Sexual Response Pattern
excitement, plateau, orgasm, refractory period
91
New cards
James- Lange
stimulus, physiological arousal, then emotion
92
New cards
Cannon-Bard
\
stimulus, physiological arousal and emotion simultaneously
stimulus, physiological arousal and emotion simultaneously
93
New cards
Schacter Two Factor
adds in cognitive labeling, stimulus, arousal, interpret cues, label emotion
94
New cards
Facial Feedback Hypothesis
being forced to smile will make you happier, facial expressions influence emotion
95
New cards
General Adaptation Syndrome
three phases of a stress response (alarm, resistance, exhaustion)
96
New cards
Alarm
body/you freak out in response to stress
97
New cards
Resistance
body/you are dealing with stress
98
New cards
Exhaustion
body/you cannot take any more, give up
99
New cards
Big Five
OCEAN, openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, neuroticism, each person varies on each of these
100
New cards
Openness
imaginative, independent, like variety