Chemistry- atomic structure
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what is an atom
smallest particles of a substance that can exist while still possessing all the unique chemical properties of that substance.
They make up everything in the universe and are the basis of chemistry.
what is the structure of an atom
An atom consists of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons that orbit in energy levels
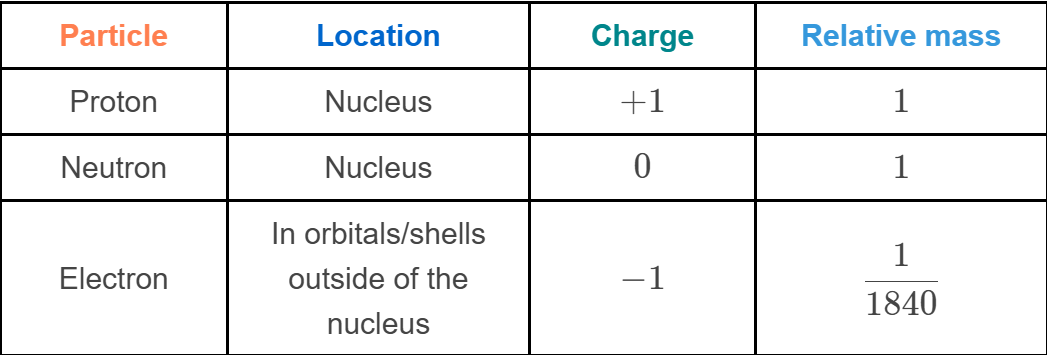
what charges or protons neutrons and electrons
protons= positive charge
neutron= no charge
electrons= negative charge
Atoms have equal numbers of positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons, making them neutral (uncharged) overall.
atomic mass
Most of an atom's mass (about 99.9%99.9%) is made up of the protons and neutrons.
Protons and neutrons each have a mass of 1.67×10−24 g.1.67×10−24 g. This
Electrons are 1840 times smaller than protons and neutrons, with a mass of 0.00549 amu.
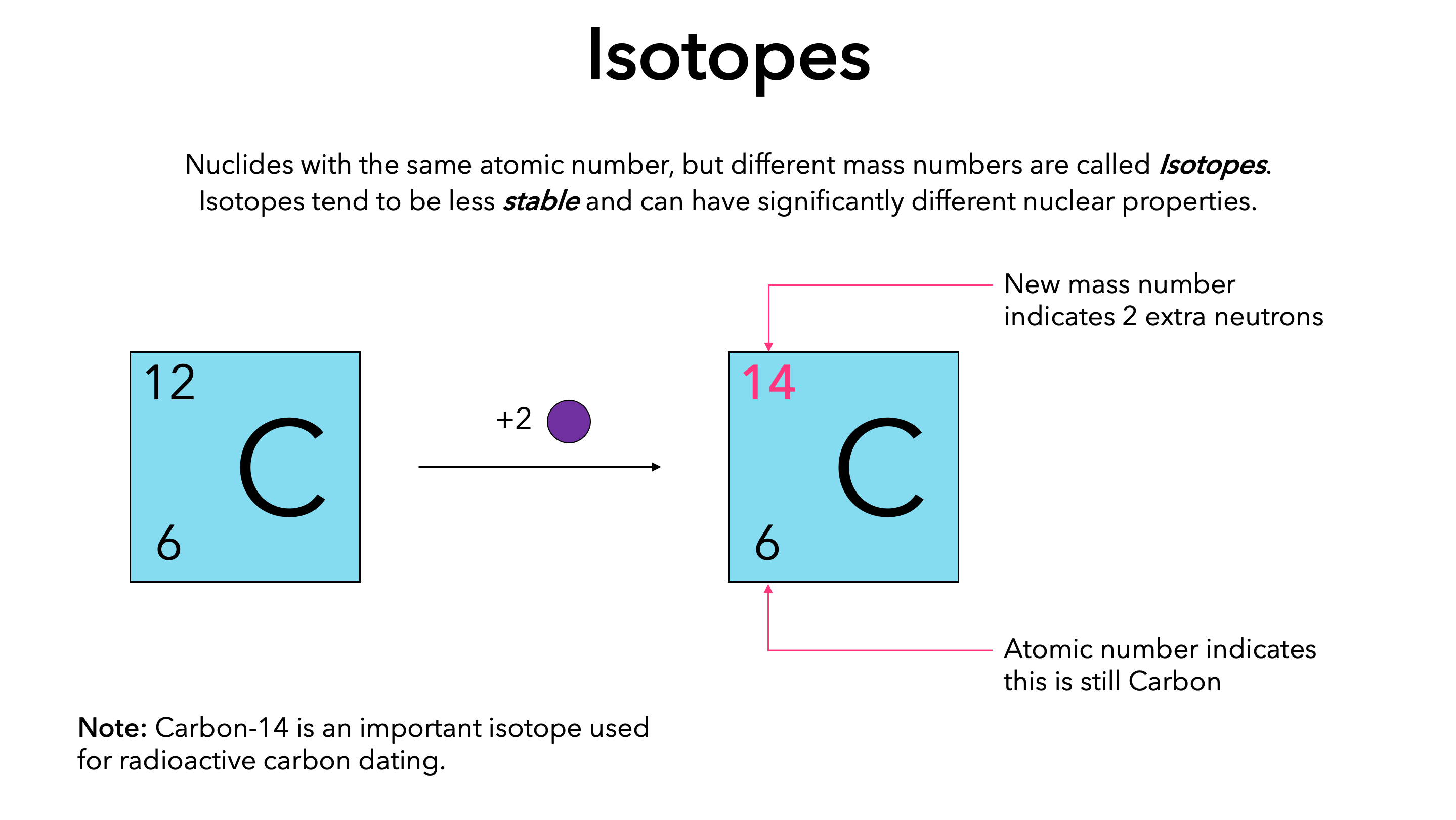
what is an isotope
Isotopes are variations of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon.
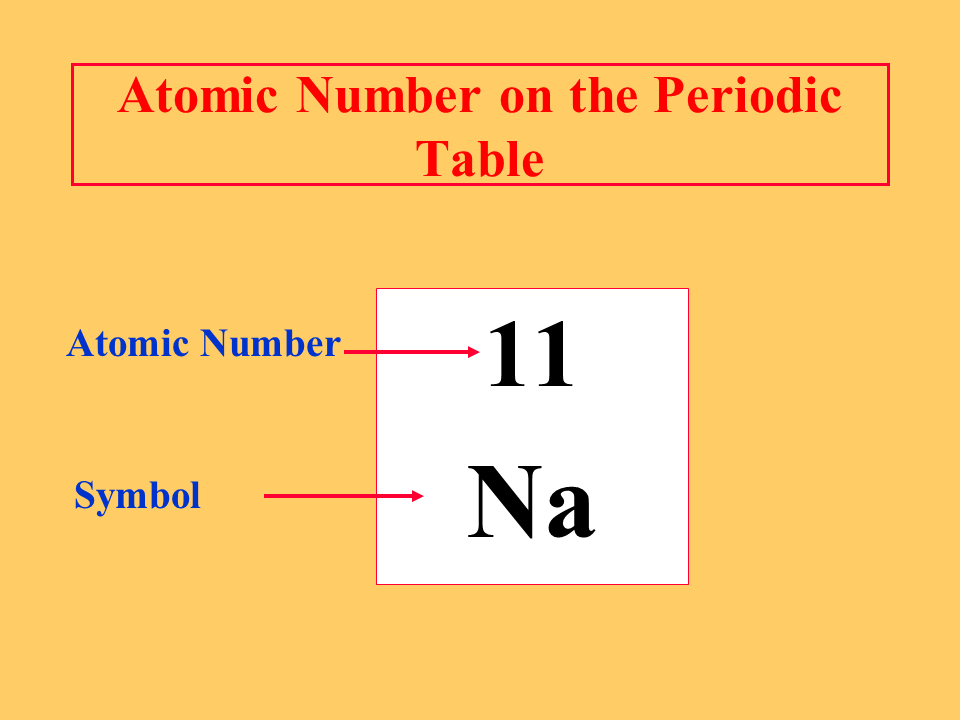
what does the atomic number represent
The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
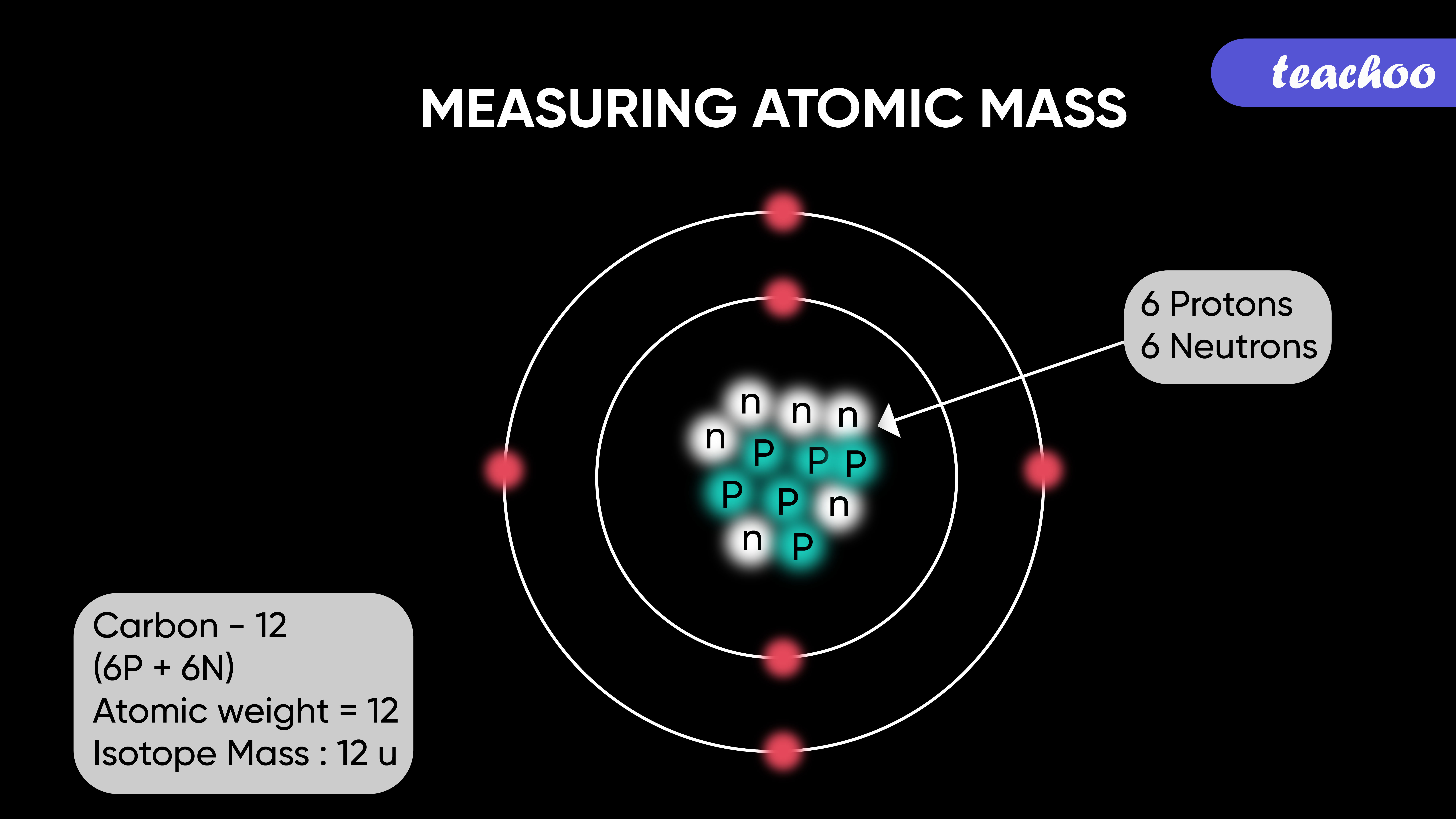
what does the atomic mass represent
Atomic mass refers to the total mass of an atom, which is determined by the sum of the protons and neutrons
how do you find subatomic partials from atomic number and mass
Protons: The atomic number equals the number of protons.
Electrons: In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
Neutrons: To find neutrons, subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass:
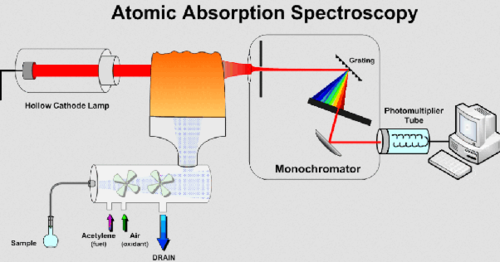
what is atomic absorption spectroscopy
Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) is an analytical technique used to determine the concentration of elements in a sample by measuring the absorption of light by free atoms in the gaseous state.
what is emission spectrum
when atoms absorb energy, their electrons move to higher energy levels- this is often observed as light with distinct colours
subshell notation
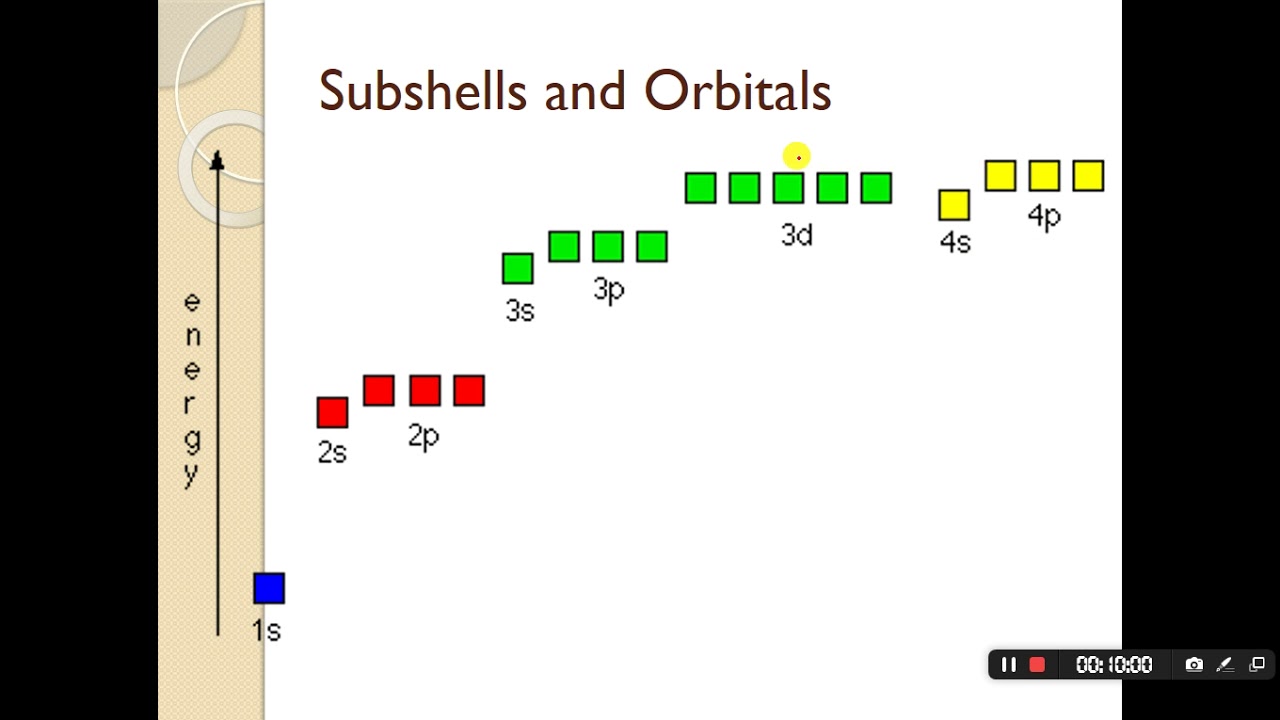
what is the difference between main shell and subshell
Main Shell (Energy Level): This refers to the broad energy levels where electrons reside, defined by the principal quantum number (n). The shells are labeled K, L, M, N or 1, 2, 3, 4, with higher numbers indicating greater distance from the nucleus and higher energy.
Subshell: Each main shell is divided into subshells, which are determined by the angular momentum quantum number (l). These subshells define the shape of the electron orbitals and are labeled s, p, d, f.
why do isotopes have the same identical chemical properties
Isotopes have identical chemical properties because they have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines how they interact in chemical reactions. Since chemical behavior is governed by electron configuration, and isotopes of an element have the same electron arrangement, they react in the same way.