Week 4 (2/3) Long Bones
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
diaphysis
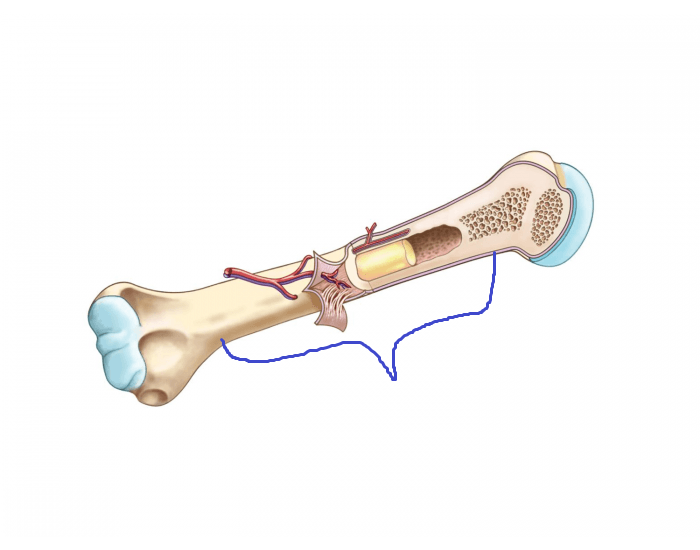
the bulk of the long “axis” of the long bone - forms a tube of compact bone around medullary cavity
epiphysis
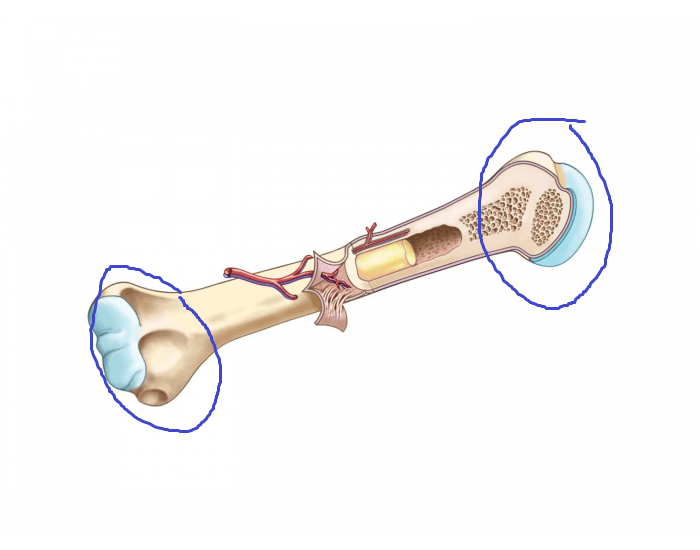
the thick ends of the long bone that are formed from an outer shell of compact bone and inner spongy bone filling
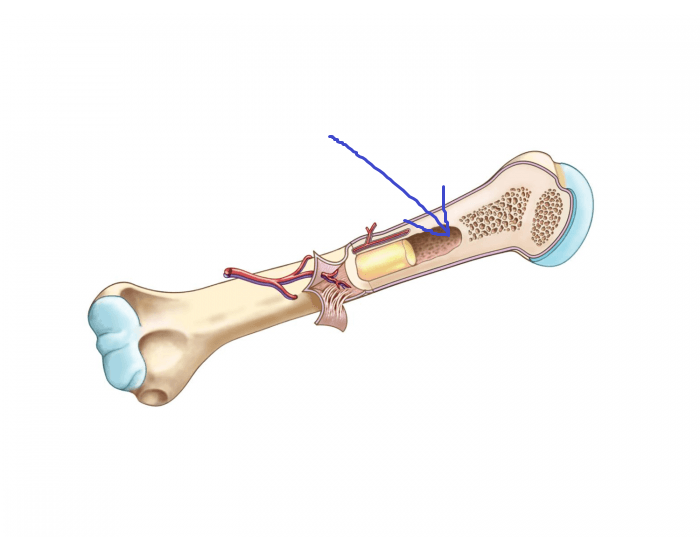
medullary cavity
the bone cavity underneath the diaphysis containing yellow bone marrow
epiphyseal line
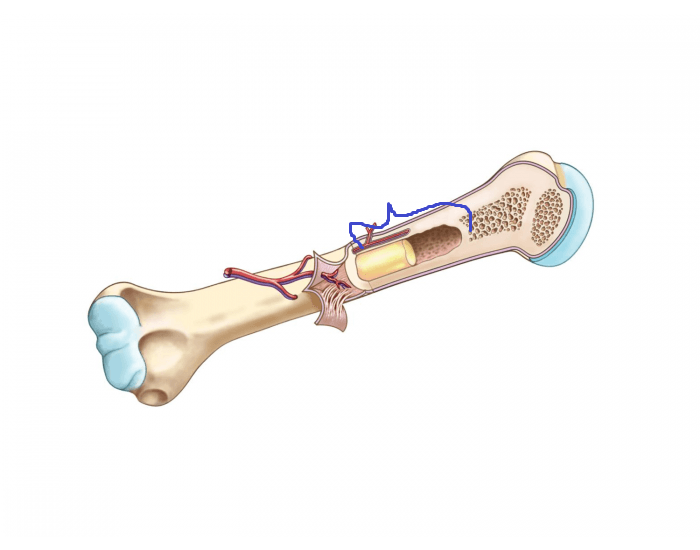
a remnant of the epiphyseal plate in early development that separates the diaphysis and epiphysis
compact bone
a type of hard, calcified bone tissue with osteons as the primary structural unit
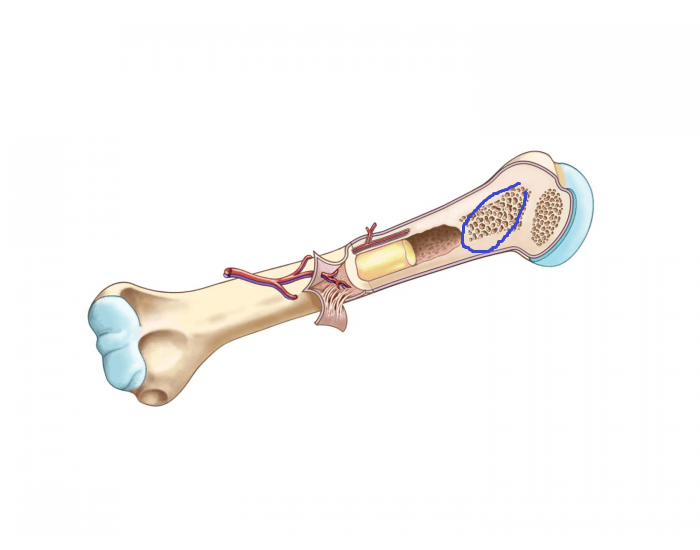
spongy bone
a porous, honey-comb-like bone tissue make of flat trabeculae and bone marrow
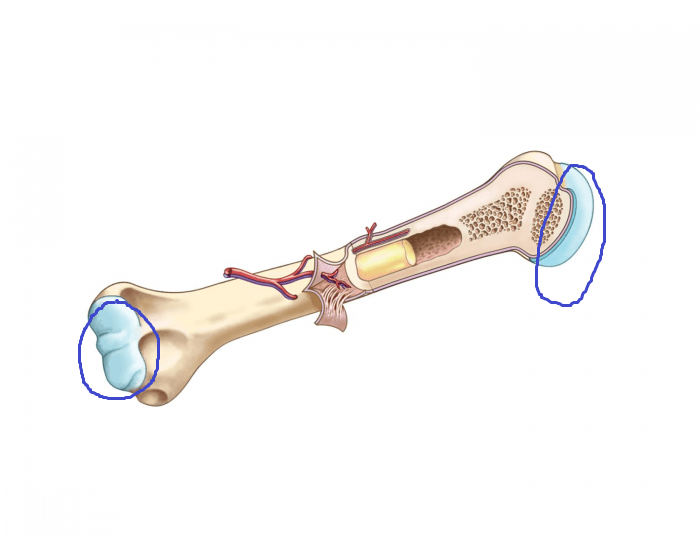
articular cartilage
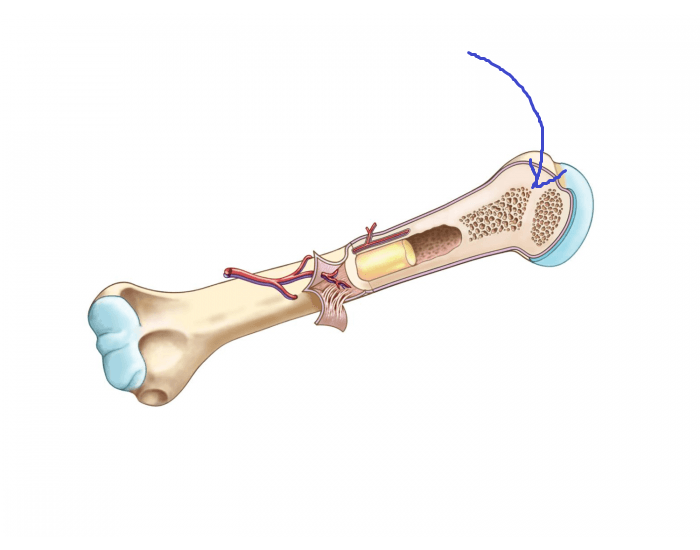
a type of hyaline cartilage that covers the end of bones at movable joints
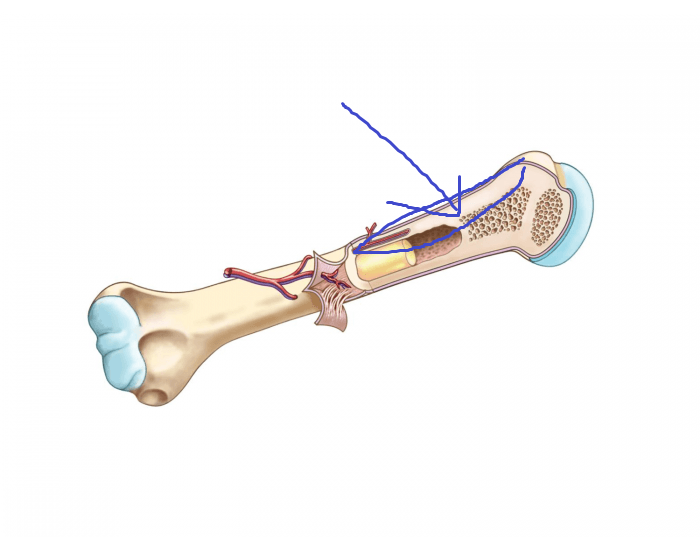
endosteum
connective tissue membrane that lines the medullary cavity
periosteum
a denser, more fibrous membrane covering the outside of the long bones (but not at the joint epiphysis ends)
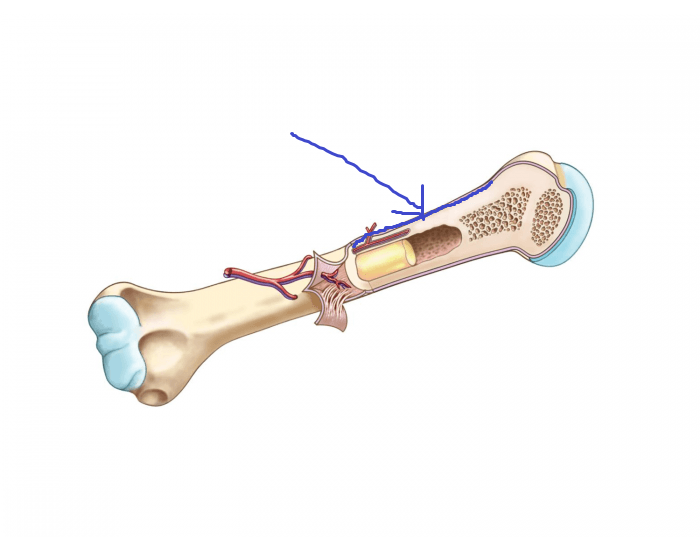
yellow marrow
fat-containing marrow in the medullary cavity of long bones that serves as energy storage and can revert to red marrow
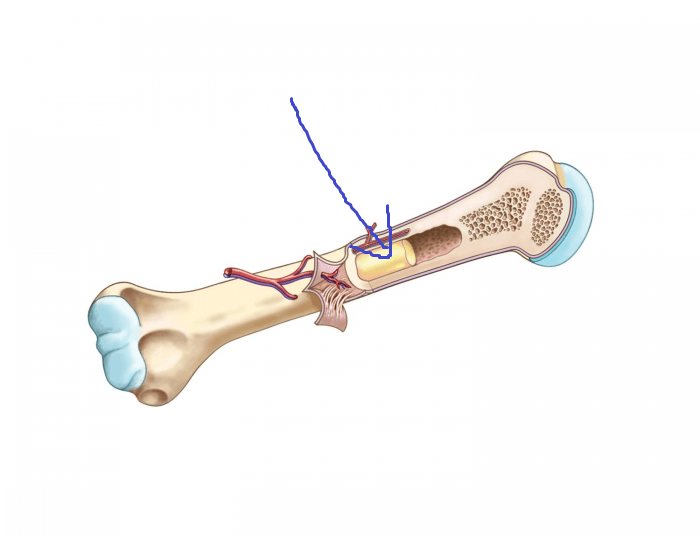
nutrient arteries
blood vessels that run into the bone marrow, spongy bone, and then compact bone to supply them
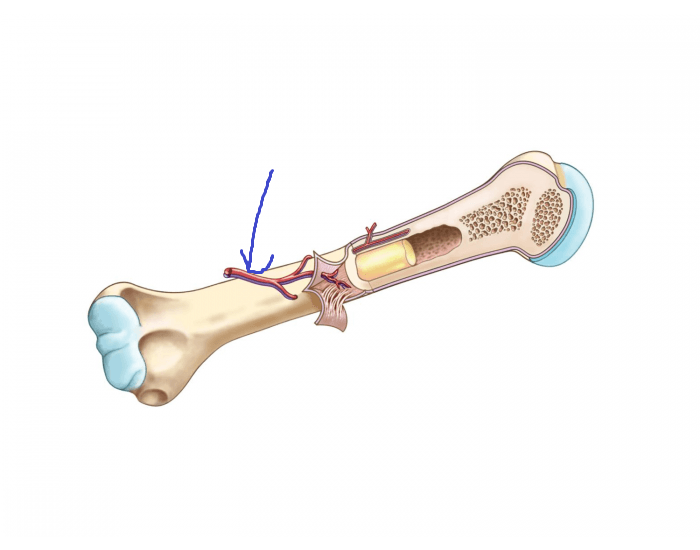
red marrow
responsible for hematopoiesis, found in the cavities of spongy bone