AP Chemistry Unit 3.7-13
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
tf even is light
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Solvent
The substance that dissolves another
Solute
The substance that is dissolved by another
In a mixture, there is usually __________ solvent than solute
more
__________ is the universal solvent
Water
Molarity equation
(Moles of solute)/(liters of solution)L
Larger molarity = _________ concentration
larger
A solution in which a substance is dissolved completely in water is known as an _______ solution
aqueous
How do you perform a dilution?
Add distilled water to s solution
What formula can you use to figure out molarity in a dilution?
M1V1 = M2V2
Why do you rinse the weighing paper when adding solute to a solvent?
Solute may stick to the weighing paper/container
What kind of flask is used for a dilution?
Volumetric flask
The components of a liquid solution cannot be separated by…
filtration
What are the two methods in which a liquid solution can be separated?
Chromatography, distillation
Chromotography
Separates chemical species by taking advantage of the differential strength of the IMFs between and among the components of the solution/mobile phase and with the surface components of the stationary phase
Chromatography can help infer the relative _____________ of components in a mixture
polarities
Stationary phase
A solid that provides support for the chromatography experiment, but does not move → can be piece of paper, piece of metal/glass coated with a porous solid, or a glass column filled with a porous solid
Mobile phase
A liquid or gas that moves, carrying the components of the mixture over or through the stationary phase
In a chromatography experiment, if Component X travels farther away from a nonpolar solvent/mobile phase than Component Y, Component X is more ___________
nonpolar
Substances with ____________ IMFs tend to be more soluble in one another; in other words, _________ dissolves _________
similar; like dissolves like
Solvent front
In a chromatography experiment → the mark on the paper that indicates how far the solvent has moved up the paper
Retention factor (Rf) formula
(Distance traveled by one component)/(distance traveled by the solvent)
The larger the Rf value is the farther _____ the paper he component of the mixture has traveled relative to the solvent front
up
Distillation
Separates chemical species by taking advantage of the differential strength of IMFs between and among the components and the effects these interactions have on the vapor pressures of the components in the mixture; separates components of a mixture that have different boiling points
In a distillation, the mixture is heated gently until the component with the ________ boiling point begins to boil. The vapor rises up through the glassware, and reaches the ____________, which is the portion of the apparatus that is surrounded by cool _____________. The vapor condenses into a liquid and is collected in a separate container, The liquid that is produced in a distillation experiment is known as the _______________. The component of the mixture that appears first in that is the one with the _____________ boiling point.
lowest, condenser, water, distillate, lowest
Ionic compounds MUST dissolve in _________
water
Polar and nonpolar only refers to _____________ molecules
nonmetal
What are the three types of electromagnetic radiation (EMR)?
Microwave, infrared, ultraviolet
Microwave radiation causes a molecule to…
rotate
Infrared radiation (IR) causes the bonds in a molecule to…
vibrate
Visible/ultraviolent (UV) radiation causes electrons in the molecule to…
move up to higher energy levels
Wavelength (𝜆)
Length of wave (period) in meters/nanometers
Frequency (v)
Number of cycles passing a point in a given time (cycles per second → hz)
Speed (c)
The speed of light, at which all electromagnetic radiation travels at
How do wavelength, frequency, and speed relate?
c = 𝜆v
What is represented by h?
Planck’s constant
How can you find the energy of a photon?
E = hv
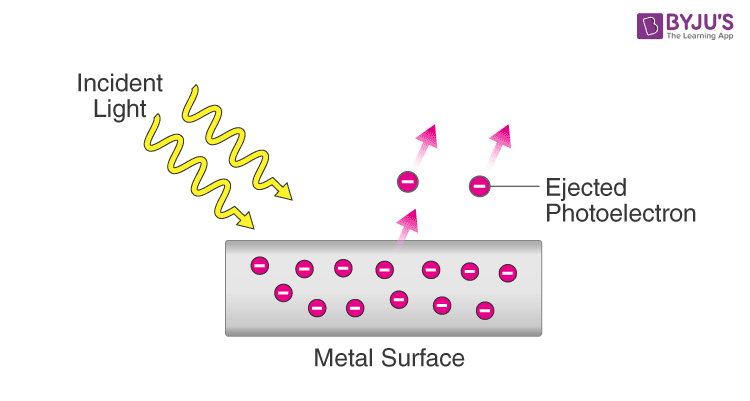
Photoelectric effect
When light shines on the surface of a metal, electrons can be ejected from the surface (and thus, E = hv)
If E = hv, and c = 𝜆v, how can you combine the equations for simplicity?
E = (hc)/𝜆
Amount of energy needed to remove an electron is measured by…
threshold frequency (v0)
Ionizing energy
Any wavelength/energy that causes the loss of electrons
Which color of light can’t remove electrons from any element?
Red
Colors result from _______________ (______________) between energy levels in atoms
quantum leaps, electron jumps
Is this unit real
no
Beer-Lamber law relates the ____________ of light to three variables according to the equation…
absorption; A = εbc
Molar absorptivity (ε)
Describes how intensely a chemical species absorbs light of a specific wavelength (L / mol cm)
The pathlength (b) and concentration (c) are proportional to the number of __________________________ in the light path
light-absorbing particles
In most experiments, the pathlength and wavelength and held ___________
constant
What value do we assume the pathlength (b) is, unless told otherwise?
1
Color absorbed is the ___________ of the color observed
opposite
When a substance absorbs light, electrons in the ground state become _____________ and move to __________ energy levels
excited, higher
A ______________ or _________________ is an instrument that consists of a light source and a diffraction grating that separates the light into different ____________. The light passes through a ____________, which is a small test tube or square container used to hold the sample that is being analyzed. After the light passes through the sample, a detector measures how much ____________ passes through the sample. Most spectrophotometers are designed to measure absorbance in the ___________ or ____________ region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
spectrophotometer, colorimeter; wavelengths; cuvette; light; visible, ultraviolet
Incident light
The original beam of light in a spectroscopy experiment
Transmittance (T)
Ratio of amount of light transmitted to the incident light
Transmittance formula
T = I1 / I0
OR
T = (light out)/(light in)
How does absorbance (A) relate to transmittance (T)?
A = -log(T)
As concentration increases, absorbance…
increases
Molarity is a way of expressing…
concentration (mol/L)
What is a calibration curve made from?
Constructed from absorbances of solutions with known calculations, using a line of best fit to determine concentration of an unknown solution based upon its measured absorbance
What does the slope equal on a calibration curve (given y = mx + b)?
The molar absorptivity (ε)
Will there be more or less absorbance if a cuvette has finger prints on it?
More
Why is it important to wipe a cuvette clean before placing it into a spectrophotometer?
It may have fingerprints on it, which would cause absorbance to be higher than it should be
According to Beer’s Law, absorbance should increase ___________ with concentration
linearly
Which colors are opposites of red, blue, and yellow?
Red → green, blue → orange, yellow → purple
A substance that can create hydrogen bonds tends to be ________ soluble in water
more
1 Nanometer = _________ meters
1 × 10-9
1 Meter = ________ nanometers
1 × 109
As wavelength (𝜆) lets larger, energy (E) gets __________
smaller
When an electron jumps down an energy level, a photon is ____________, and thus the energy of the atom _____________
emitted, decreases
To calculate the minimum amount of energy required to ionize an atom, divide its ________________ by _______________
first ionization energy, Avogadro’s number