Computer Systems
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Definition of Hardware
Hardware are the physical components that make up a device or computer system. These include both the internal components and also peripheral devices.
Definition of Software
Software is the computer code, which is programs and algorithms that give instructions to the hardware to make it perform the desired tasks. Without the software the hardware will not get any instructions, and will not do anything.
Label these logic gates
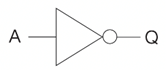
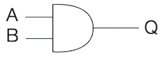
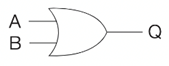
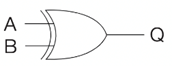
A = NOT
B = AND
C = OR
D = XOR
What is the rule for the AND truth table?
Output is True (1) only when all the inputs are True(1)
What is the rule for the OR truth table?
Output is True when at least one of the inputs are True
What is the rule for the XOR truth table?
Output is True only when the inputs are different
What is the rule for the NOT truth table
The output is the inverted input
Label these truth tables
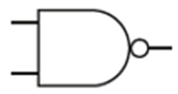
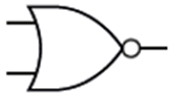
E = Nand
F = Nor
What is the rule for the NAND truth table?
Output is True unless all the inputs are True
What is the rule for the NOR truth table?
Output is True only when all the inputs are False
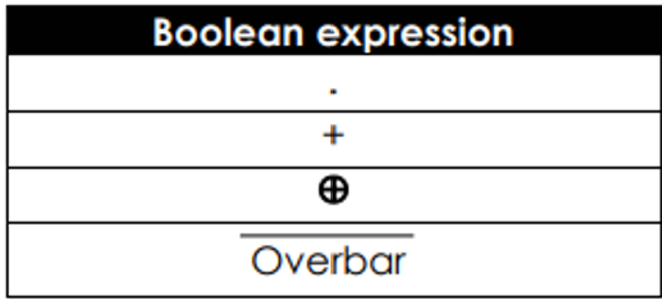
What are these Boolean expressions
1 = AND
2 = OR
3 = XOR
4 = NOT
What are the two types of software?
Application and System software
What is application software?
A program designed to perform a specific task that the user interacts directly with.
Examples of application software
Spreadsheets, web browser, word processor
What is system software?
Software that enables the computer to function and to control the computer hardware. It is concerned with running and maintaining the computer
Examples of system software
IOS, Windows
What is an operating system
A group of programs than manages the processor, memory, input/output devices, applications and security
What is application management?
Application software runs on top of operating systems which is an intermediary and takes care of interactions with the hardware.
What does the Operating System do for applications?
The operating system will maintain a directory of where each application and each data file is stored on disk. When the application is run, the OS will allocate space in memory for it to be loaded and the job will enter the queue of jobs being allocated processor time.
What does processor resources do?
Allows multiple applications to be run simultaneously by managing the processing time between applications and core and switching processing between applications very quickly. High priority applications will have more CPU time, but it means that lower priority applications will take longer to run.
What does memory management do?
Distributes memory resources between programs and manages transfer of data and instruction code in and out of main memory. It ensures that each application does not use excessive memory.
What does security do?
It ensures safety from threats and attacks by:
Controlling access to a computer by setting up passwords for different users, without the password others will be unable to access the software applications and files on your computer
Setting different access rights and privileges for different users
Automatically downloading security updates
Encrypting files that are stored on the hard disk
How does the OS control the interactions with input and output devices?
OS controls interaction will input, output, and storage using hardware drivers. This allows users to save files to the hard disk and print documents.
Advantages of High level languages
Easier to test/identify mistakes
Faster to develop
Better documented
Contain complex data structures
Code is more portable
Disadvantages of High level languages
Needs a translator
Runs slower because of the layers of abstraction and there is inefficiency in the translator
Advantages of low level languages
Produce code that is faster and better optimised
Programs written in assembly language can interact directly with hardware
Assembly language programs require less memory when executing
Programs written in assembly language have no unnecessary code added by a compiler
Appropriate for developing new operating systems, embedded systems and hardware device drivers
Disadvantages of Low level languages
Difficult to understand and modify
Assembly code is written for a specific processor architecture and so is not portable to other computer architectures.
What is Machine code?
This is the language computers understand. All codes whether assembler or high level programming languages need to be translated into machine code. Machine code is specific to a processor. Machine code instructions are made up of two parts the operator and the operand. The processor decodes the operator to identify the task that is to be carried out. The operand is the value or memory address that the instruction is to be operated on.
What is assembly language?
It provides basic computer instructions for programs to run. There is a one to one relationship between machine code and assembly code instructions. One assembly language instruction maps to one machine code instruction, thus the structure of assembly language and machine code is the same, but where machine codes uses 0 and 1 which are very difficult for programmer to understand, assembly language uses mnemonics which is easier for the programmer.
What are the types of program translators?
Interpreters, and compilers
What does an interpreter do?
converts high level languages into machine code one instruction at a time on-the-fly while the program is running. Each instruction is converted to machine code once the previous instruction has been executed. Interpreters are good for debugging code because the program stops as soon as the error has been found. However running code this way is much slower than running compiled code. The machine code is not saved.
What do compilers do?
A program that converts high level languages into machine code before the program is run. A compiler saves the machine code, so the source code is no longer needed A compiler allows a program to be run faster than interpreted code. Software is normally distributed as compiled machine code. For proprietary software this is good because other people cannot copy the code and use it for their own applications.
What is the Von Neumann architecture?
It is the stored program concept, where program instructions and the data to be processed can be stored in the same memory?
What does the processor contain?
Arithmetic Logic Unit, Control Unit, clock, bus
What does the Arithmetic Logic Unit do?
Carries out the following instructions:
Logical operations – these include AND, OR and NOT
Shift operations – the bits in a computer word can be shifted left or right by a certain number of places
Arithmetic operations – these include addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
What does the Control Unit do?
The Control Unit coordinates all the activities taking place, inside the CPU. Its functions may be summarised as follows:
It controls the execution of instructions in the correct sequence
It decodes instructions
It regulates and controls processor timing using regular pulses from the system clock
It sends and receives control signals to and from other devices within the computer
What does the system clock do?
The system clock controls processor timing, switching between zero and one at rates exceeding several million times per second. It synchronises all CPU operations.
What is the clock frequency?
Number of clock cycles which occur per second
What is the bus?
The bus is the internal connections of the CPU, it passes data between the components of the CPU. Data and instructions are passes between registers and other components along the buses.
What is the system bus?
A collection of buses connecting the system components
What is the steps to the fetch-execute cycle?
When a program is to be run it needs to be loaded into main memory first, then it can be accessed by the processor, which runs each instruction in turn. When the program is loaded, the processor fetches an instruction, decodes it and then executes it. The processor executes one instruction at a time. This is the fetch-execute cycle.
What is the fetch-part of the fetch-execute cycle?
The address A of the next instruction to be executed is fetched from the register where it is held
This register is incremented so it points to the next instruction to be fetched
The instruction at address A is fetched from the memory and out into a special register ready to be decoded.
What is the decode part of the fetch-execute cycle?
The Control Unit decodes the instruction to see what has to be done next
What is the execute part of the fetch-execute cycle?
The instruction is executed
What factors affect CPU performance?
Clock speed, Cache memory and Processor cores
What is the clock speed?
The number of cycles that a processor carries out per second whereby each cycle of the CPU allows a single instruction to be carried out. The greater the clock speed, the greater the number of operations and the faster the computer will run
What does the number of processor cores do?
Having multiple cores allows instructions to be carried out concurrently, whereas a single core will only allow carry out instructions in serial.
What is cache size and what does it do to the CPU performance?
Frequently used data and instructions within an application can be stored in cache instead of fetching from RAM which is quite slow. The bigger the cache the greater the volume of data and instructions that can be stored thereby reducing latency and improving performance of the CPU.
What is volatile memory?
When the computer is turned off the contents of volatile memory is lost. When there is no power, volatile memory is erased. Volatile memory can be accessed directly from the CPU. E.g RAM
What is non-volatile memory?
Even when there is no power, the data remains unchanged and can be accessed once again once power has been resumed. This allows you to store files for the long term. It cannot be accessed directly by the CPU so data and instructions have to be read from storage into memory first. E.g. Hard disks and solid state devices
What is RAM used for?
RAM is used to hold programs currently being executed, and the data the programs are using. When a program needs to be executed the program and any data needed for that program to run needs to be loaded into main memory so that the processor can access the instructions. The main purpose of RAM is to act as temporary storage for programs and data while the program is being executed.
What is ROM?
Data can only be read from the device, and the memory cannot be edited or deleted. It is only used for situations where you can be sure that updates will not be needed. The computer’s basic input output system which controls the boot up sequence is stored on a ROM chip. You cannot write over the contents once it has been created, it is non-volatile
RAM vs ROM
RAM | ROM |
Volatile – data is lost when the power is turned off | Non-volatile – data is NOT lost when power is turned off |
Stores user data/programs/part of operating system which is currently in use | Used to store the BIOS which is required at start-up of the computer |
Memory can be written to or read from | Memory can only be read from but NOT written to |
What is secondary storage?
Secondary storage is a long term storage and refers to hard disk drive, optical disks and more recently solid state drives. It generally holds much more data than main memory and is relatively inexpensive per MB, however it tends to have slower access speeds than main memory, it also needs to be robust and reliable.
What do you need to consider when choosing a storage device?
Capacity, Speed, Portability, Durability, Reliability
How does a magnetic disk work?
A hard disk uses rotating platters coated with magnetic material. Iron particles on the disk are polarised to become either a north or south state. This represents 0 and 1. The disk is divided into tracks in concentric circles, and each track is subdivided into sectors. The disk spins very quickly at speeds of up to 10,000 RPM. A drive head moves across the disk to access different tracks and sectors. Data is read or written to the disk in order to prevent damage from movement.
Advantages of Magnetic disks
Cheap form of storage
Large capacity
Very reliable
Disadvantages of Magnetic disks
Not very portable because of moving parts, so it can be damaged when carried or dropped
Electromagnetic surge can corrupt the data held
Slow speed of read/write access
Examples of Magnetic storage
HDDs, Magnetic tapes, Floppy disks
How do solid state drives work?
Sold state devices all use flash memory. They are built from special types of transistors that do not lose their state when the power is switched off.
It uses millions of switches called floating gate transistors or microchips to store data.
Electrons are stored in gates and this is encoded as 0 when there is an electron present and encoded a 1 when there is no electron present.
The electron remain trapped even when there is no flow of electricity
Advantages of Solid State Drives
No moving parts making them more reliable
Considerably lighter than HDDs making them portable
Faster access time because they don’t spin and data can be accessed instantaneously
Low power consumption
Don’t rely on magnetic properties so are unaffected by magnetic fields
Quiet
Disadvantages of Solid State Drives
More expensive per volume of storage
May deteriorate over time and not last as long as HDDs
How do optical devices work?
An optical disk works by using a low-powered laser to read the disk by bouncing light onto its surface – which is covered in pits and lands. At the point where a pit starts or ends, light is scattered and therefore not reflected so well. A land, and the bottom of a pit reflects the light well. Non-reflective and reflective areas are read as 1s and 0s. There is only one single track on an optical disk, arranged as a tight spiral.
Advantages of optical devices?
Cheap to produce
Easy to send through the post for distribution purposes
Disadvantages of optical devices
Con be corrupted or damaged easily by excessive sunlight or scratches
Examples of optical devices
CD, DVD, Blu-ray disks
Examples of Solid State devices
SSDs, memory sticks, and memory cards (SD cards)
What is cloud storage?
Cloud Storage refers to saving data in an off-site storage system maintained by a third party for example Microsoft/google. Instead of saving data on the computer’s hard drive or other local storage devices you save it in a remote storage facility and access it via the internet. The data is stored usually on hard disks but increasingly on solid state drives in remote locations in different countries.
Advantages of cloud storage
Able to access from anywhere in the world
You can share the data with other people in different locations
Backup is no longer such an issue, as it is the responsibility of the provider to keep the data safe
Disadvantages of cloud storage
To access the data a strong internet connection is required
Some users are concerned about security in the cloud, and whether their data could be attacked by a hacker
What is an embedded system?
An embedded system is a computer system that is designed for a specific function. For example, the circuits inside a washing machine, car engine or MP3 player were created to perform tasks and cannot be re-programmed to perform something else. You couldn’t install the circuitry from your washing machine in your ca and expect it to work.