Anatomy II: Practical II
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/276
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:15 AM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
1
New cards
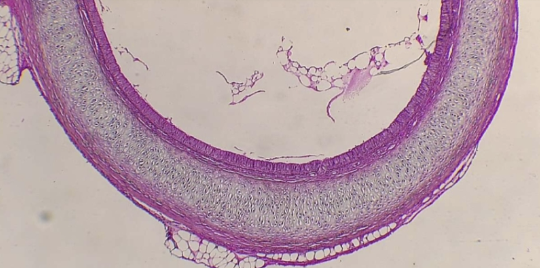
What is the histology?
Trachea
2
New cards
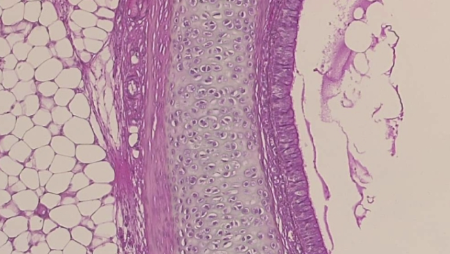
What is the histology?
Trachea
3
New cards
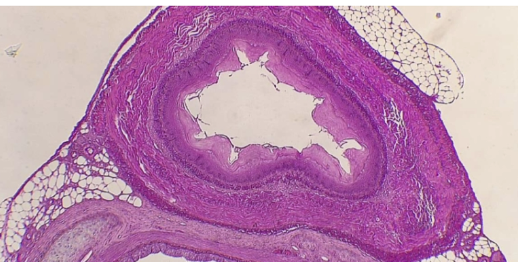
What is the histology?
Esophagus
4
New cards
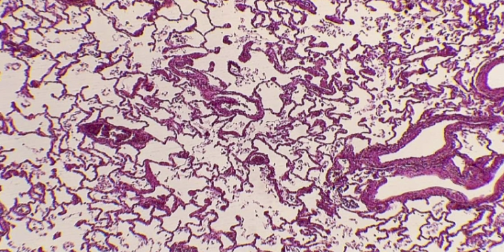
What is the histology?
Healthy lung tissue
5
New cards
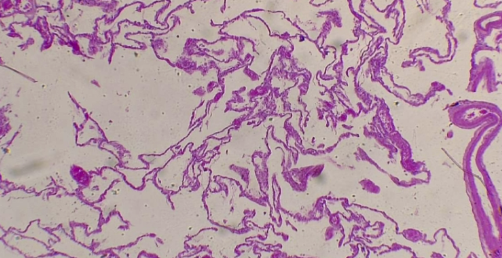
What is the histology?
Emphysema
6
New cards
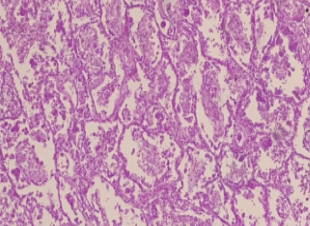
What is the histology?
Viral Pneumonia
7
New cards
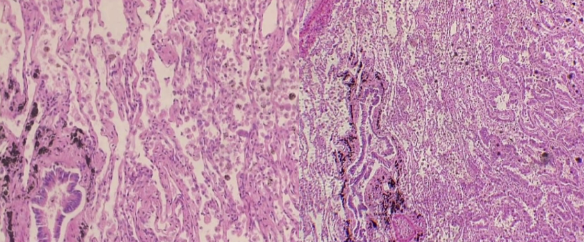
What is the histology?
Anthracosis
8
New cards
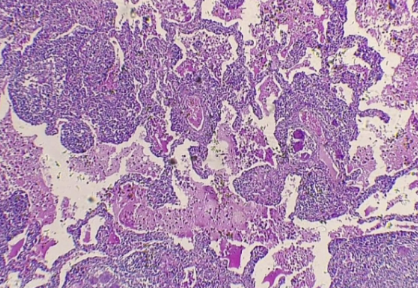
What is the histology?
Tuberculosis
9
New cards
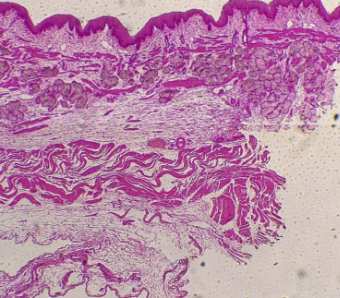
What is the histology?
Cardia (Stomach)
10
New cards
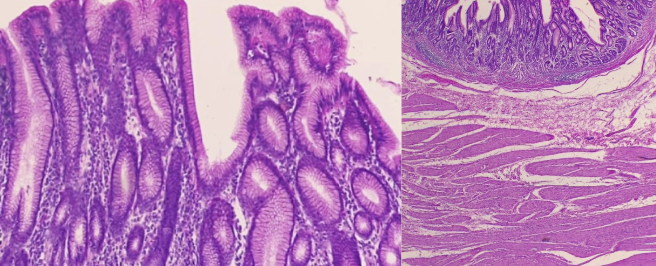
What is the histology?
Fundus (Stomach)
11
New cards
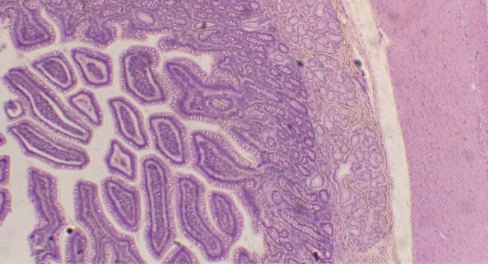
What is the histology?
Duodenum
12
New cards
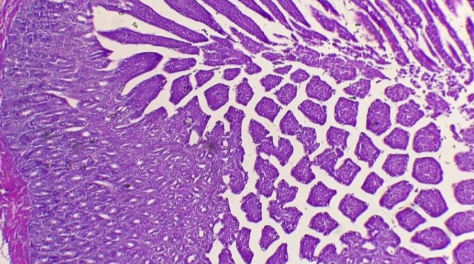
What is the histology?
Duodenum
13
New cards
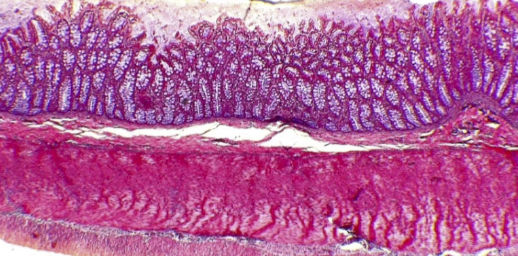
What is the histology?
Colon
14
New cards
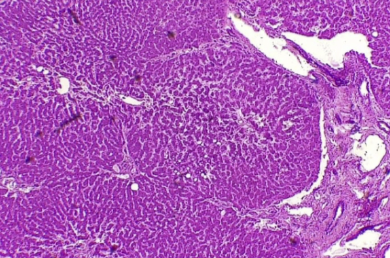
What is the histology?
Liver
15
New cards
Diagnose the Pathology: Looks and feels like a sponge. Pink, squishy, and flexible.
Healthy Lung Tissue
16
New cards
Diagnose the Pathology: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease characterized by elasticity breaks down in alveoli. Results in shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing.
Emphysema
17
New cards
Diagnose the Pathology: Infection, either bacterial or viral, of the lungs that can be caused by a variety or bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Symptoms may include fever, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Alveoli is filled with fluid and debris.
Pneumonia
18
New cards
Diagnose the Pathology: also known as black lung disease. Is cause by the inhalation of coal dust and cal lead to scarring and inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include difficulty breathing. Alveoli filled with fine coal dust.
Anthracosis
19
New cards
What is the normal sound of healthy lungs in the trachea and bronchi?
Rushing/wooshing
20
New cards
what is the normal sound of healthy lungs in the alveoli?
rustling leaves
21
New cards
What auscultatory sound would expect to hear when a patient is experiencing fluid in the lungs due to pneumonia?
Rales/crackles
22
New cards
What auscultatory sound would you expect to hear from a patient who is experiencing restricted airways due to asthma?
Rhonchi/wheezing
23
New cards
What is the normal amount of inspired/expired air at rest?
Tidal Volume
24
New cards
What is the amount of air forcibly inhaled after normal tidal inhale?
Inspiratory reserve volume
25
New cards
What is the amount of air forcibly exhaled after normal tidal exhale?
Expiratory reserve volume
26
New cards
What is the leftover air after forcible exhale?
Residual volume
27
New cards
What are all four volumes together?
= IRV + ERV + TV + RV
= IRV + ERV + TV + RV
Total Lung Capacity
28
New cards
This capacity is all but residual and is the range used in daily life.
= IRV + ERV+ TV
= IRV + ERV+ TV
Vital Capacity
29
New cards
This is all you can inhale.
=IRV + TV
=IRV + TV
Inspiratory capacity
30
New cards
This is all below tidal volume.
=ERV + RV
=ERV + RV
Functional residual capacity
31
New cards
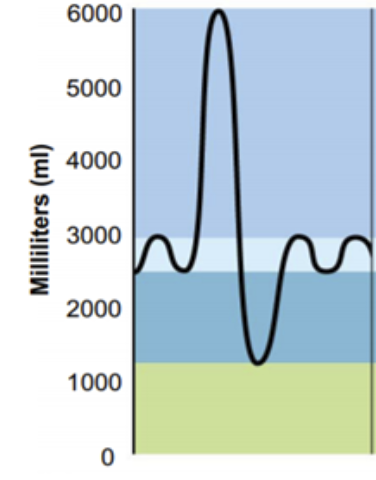
What is the volume that includes goes from 2500 -3000 mL? (Lightest blue)
Tidal Volume
32
New cards
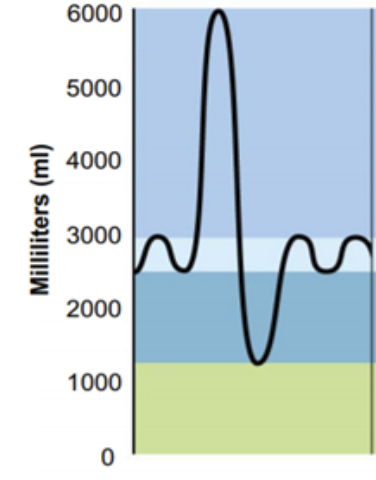
What is the volume that includes goes from 3000 - 6000 mL? (Periwinkle)
Inspiratory Reserve Volume
33
New cards
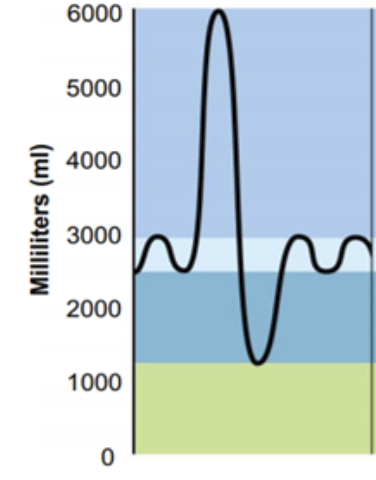
What is the volume that includes goes from 1000 - 2500 mL? (Dark blue)
Expiratory Reserve Volume
34
New cards
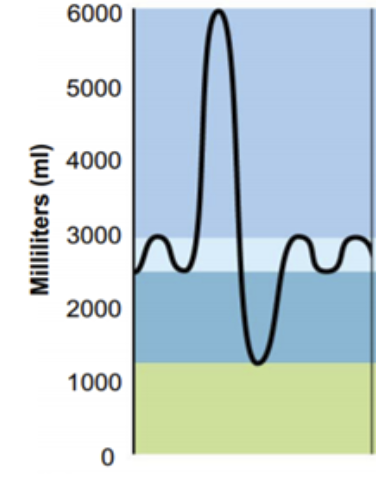
What is the volume that includes goes from 0 - 1200 mL? (Green)
Residual Volume
35
New cards
What is the ideal range for blood pH?
7\.35-7.45
36
New cards
Rapid, deep breathing causes a decrease in blood CO2 and increase of H+ ions, which results in?
Respiratory acidosis
37
New cards
Slow, shallow breathing cause an increase in CO2 and a decrease in H+ ions which results in:
respiratory alkalosis
38
New cards
During _______, the diaphragm contracts and lowers increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and intrapulmonary pressure decreases.
Inspiration
39
New cards
During ______, the diaphragm relaxes and rises decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and raising the intrapulmonary pressure.
exhalation
40
New cards
What pressure prevents against collapsed lung and allows tension for lungs to recoil and be elastic?
Intrapleural pressure
41
New cards
What are the four walls of the trachea?
Mucosa, submucosa, hyaline cartilage, and adventitia
42
New cards
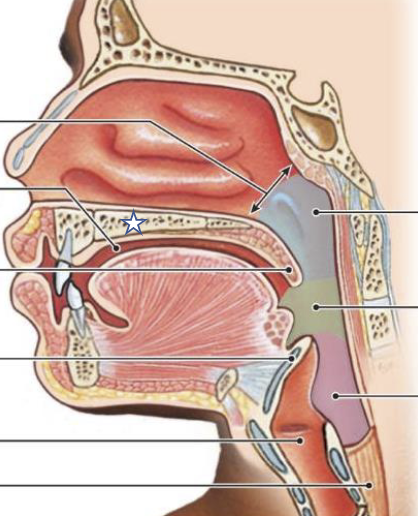
What is this structure?
Hard palate
43
New cards
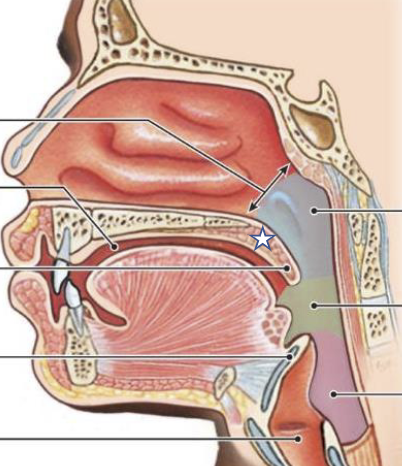
What is this structure?
Soft palate
44
New cards
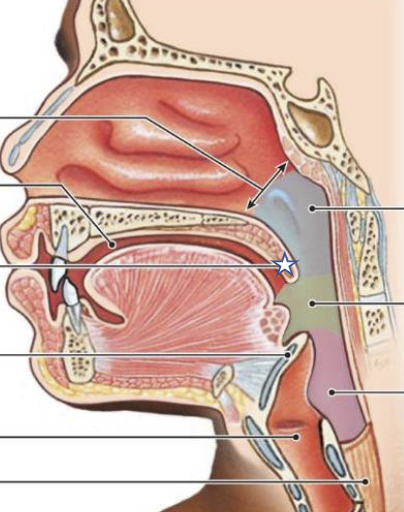
What is this structure?
Uvula
45
New cards
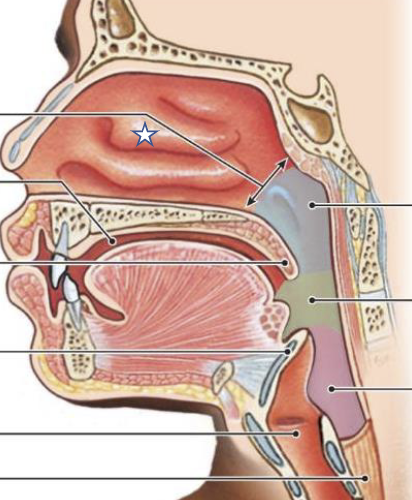
What is this structure?
Nasal conchae
46
New cards
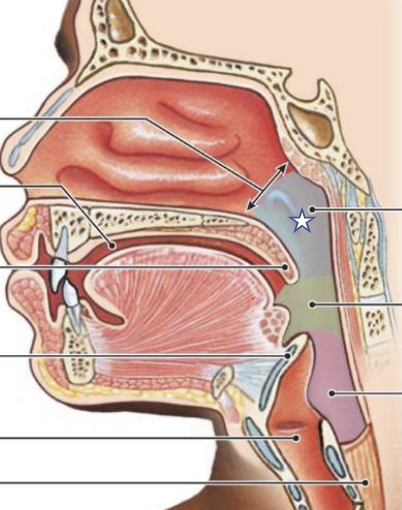
What is this structure?
Nasopharynx
47
New cards
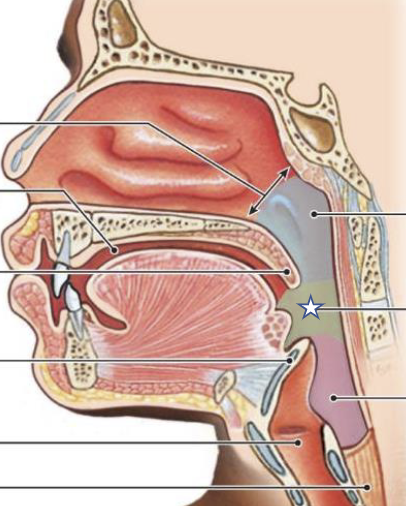
What is this structure?
Oropharynx
48
New cards
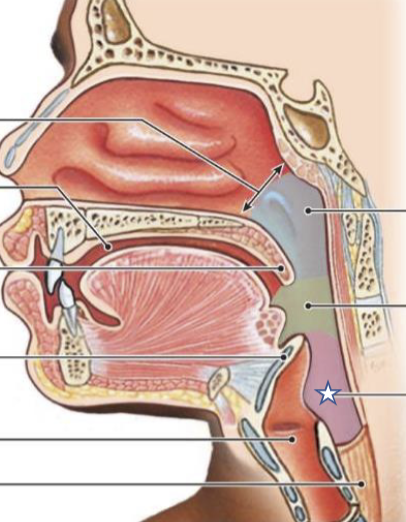
What is this structure?
Laryngopharynx
49
New cards
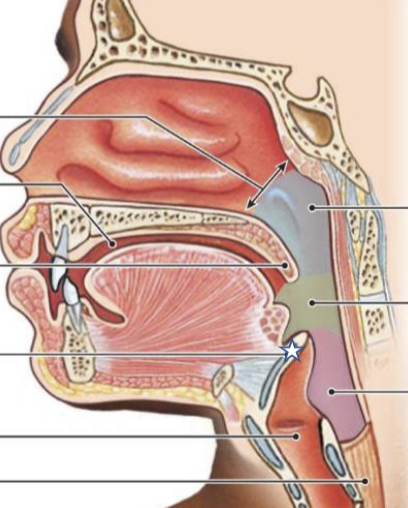
What is this structure?
Eppiglotis
50
New cards
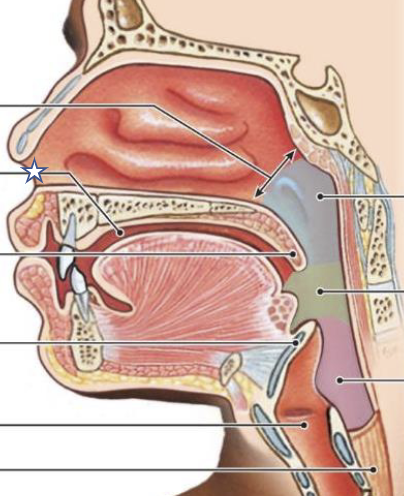
What is this structure?
Nostril
51
New cards
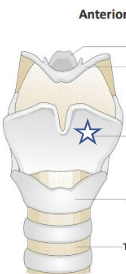
What is this structure?
Thyroid cartilage
52
New cards
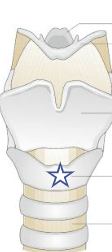
What is this structure?
Cricoid cartilage
53
New cards
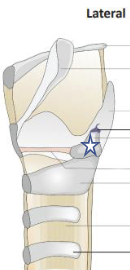
What is this structure?
Arytenoid cartilage
54
New cards
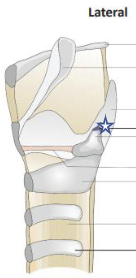
What is this structure?
Corniculate cartilage
55
New cards
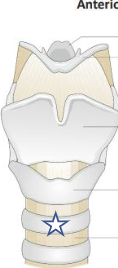
What is this structure?
tracheal cartilage
56
New cards
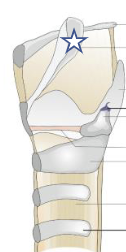
What is this structure?
Epiglottis
57
New cards
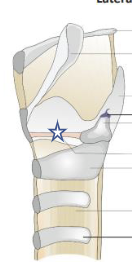
What is this structure?
Vocal folds
58
New cards
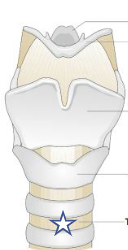
What is this structure?
Trachea
59
New cards
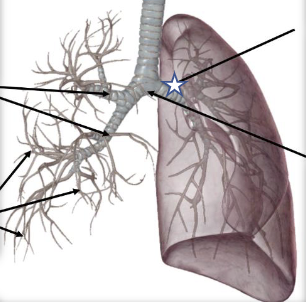
What is this structure?
Left bronchus
60
New cards
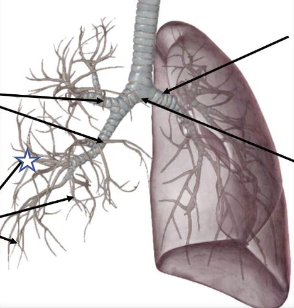
What is this structure?
Bronchioles
61
New cards
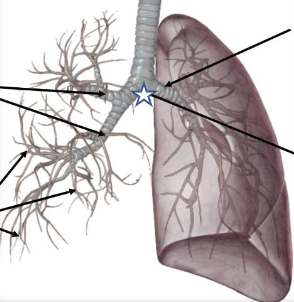
What is this structure?
Carina
62
New cards
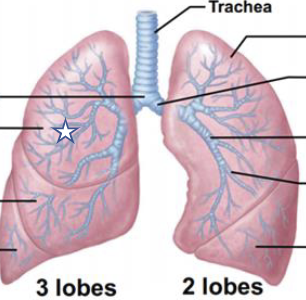
What is this structure?
R superior Lobe
63
New cards
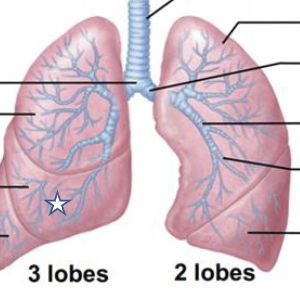
What is this structure?
R middle lobe
64
New cards
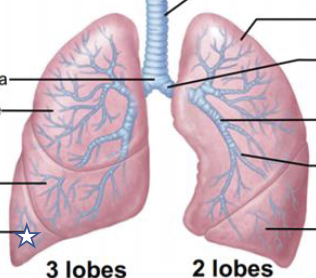
What is this structure?
R inferior lobe
65
New cards
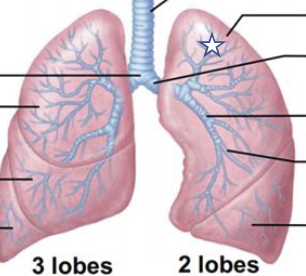
What is this structure?
L superior lobe
66
New cards
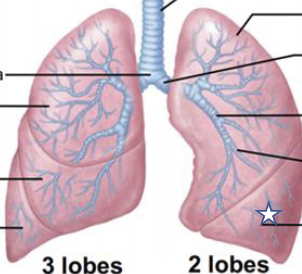
What is this structure?
L inferior lobe
67
New cards
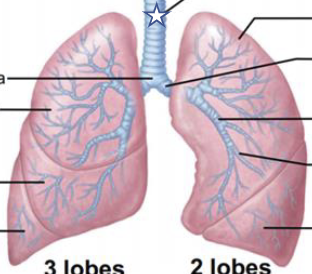
What is this structure?
trachea
68
New cards
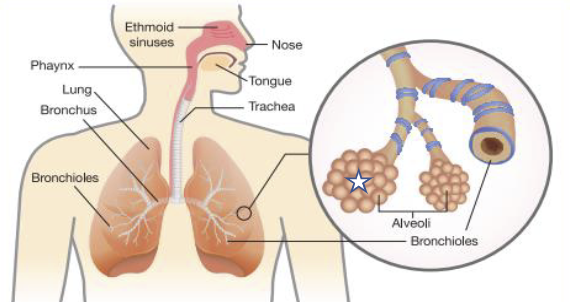
What is this structure?
Alveoli
69
New cards
What structure prevents food from entering the trachea?
epiglottis
70
New cards
What is the purpose of teeth?
Mastication
71
New cards
What is the purpose of the uvula and salivary glands?
Moistening
72
New cards
What organ produces bile?
Liver
73
New cards
What organ stores concentrated bile?
Gallbladder
74
New cards
What is the duct system order of bile?
Pancreatic duct to common bile duct to duodenum at ampulla vater
75
New cards
What pathology is consistent with ulcers and inflammation of the colon?
Ulcerative colitis
76
New cards
What condition results in small pouches called diverticula that form in the walls of the large intestine and become inflamed or infected?
Diverticulitis
77
New cards
What condition results in liver scarring and causes the liver to not function properly, often as a result of alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis?
Liver cirrhosis
78
New cards
What are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts and can cause pain?
Gall stones
79
New cards
What is a sore or erosion that forms in the lining of the stomach or duodenum as a result of the acid and pepsin produced in the stomach?
Peptic ulcer
80
New cards
What enzyme is produced by the salivary glands and begins the breakdown of starches in the mouth?
Salivary amylase
81
New cards
What enzyme is produced by the pancreas and breaks down strached into smaller molecules in the small intestine?
Pancreatic amylase
82
New cards
What enzyme is produced by the stomach and breaks down proteins into smaller peptides?
Pepsin
83
New cards
What enzyme(s) is produced by the pancreas and breaks down proteins into smaller peptides in the small intestine?
Trypsin and chymotrypsin
84
New cards
What enzyme is produced by the pancreas and small intestine and breaks down fats into smaller fatty acids and glycerol?
Lipase
85
New cards
What fluid is produced in the liver, stored in the gallbladder, and helps emulsify fats in the small intestine.
bile
86
New cards
What is the process of chewing food with teeth to break it down into smaller pieces and mix it with saliva?
Mastication
87
New cards
What is the rhythmic contraction of the stomach muscles that mix food with gastric juices to break it down into a liquid known as chyme?
Churning
88
New cards
What is the coordinated muscular contraction that propels food through the digestive tract?
Peristalsis
89
New cards
What is the periodic squeezing of the circular muscles in the small intestine that mixes and breaks down food?
segmentation
90
New cards
The inner most layer of the alimentary canal wall that is composed of three layers and secretes mucus/digestive enzymes and also helps absorb nutrients?
Mucosa
91
New cards
What layer of the alimentary canal is composed of connective tissues, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. Contains glands to secrete mucous and digestive enzymes.
submucosa
92
New cards
What layer of the alimentary canal is a layer of smooth muscle that contracts (peristalsis) to move food through the digestive tract?
Muscularis externa
93
New cards
What layer of the alimentary canal is the outermost layer composed of connective tissue and supports/protects the digestive tract?
Serosa
94
New cards
These are cells in the stomach that secrete pepsinogen, an inactive form of pepsin, which breaks down proteins.
Chief cells
95
New cards
These cells are located in the stomach and secrete hydrochloric acid to create an acidic environment which activates pepsinogen and helps kill bacteria.
Parietal cells
96
New cards
These are found in the duodenum and secrete mucus to protect the lining of the small intestine from the acidic content of the stomach.
Duodenal glands
97
New cards
This is a glandular structure located in the mucosa of the small intestine and colon that secret mucus to lubricate the intestinal surface.
crypts
98
New cards
These cells are in the mucosa of the digestive tract and secrete mucus to protect and lubricate the intestinal surface.
Goblet cells
\
\
99
New cards
What are the longitudinal bands of smooth muscle in the colon that contract to form haustra?
Taeniae coli
100
New cards
Pouch like structures found in the colon.
Haustra