Ch2 Mitosis & Meiosis
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1 strand of double sided DNA =
1 chromosome
how many cells are there in the human body
30 trillion (3 × 1013)
somatic cells
cells that stay with you till you die (daughter cells)
46 chromosomes
mitosis
germline cells
contribute to the genetic info of the next generation (sex cells)
23 chromosomes
meiosis
what is 2n , and what does n represent
2n = diploid
n = haploid number (23 for humans)
has all the unique genetic info for that species
transmission electron microscopy
see cells’ organized structure in high resolution
the cell components involved with genetic processes are:
nucleolus, ribosome, and centriole
________ and ________ have their own genetic info
mitochondria & chloroplasts
how many base pairs does mitochondria have ?
16,000 base pairs
what is the size of a genome
3 billion (3 × 109)
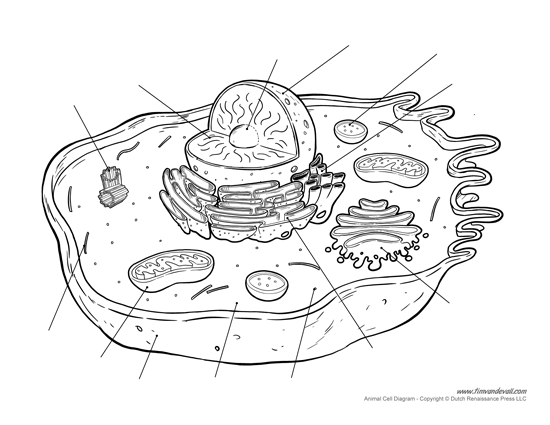
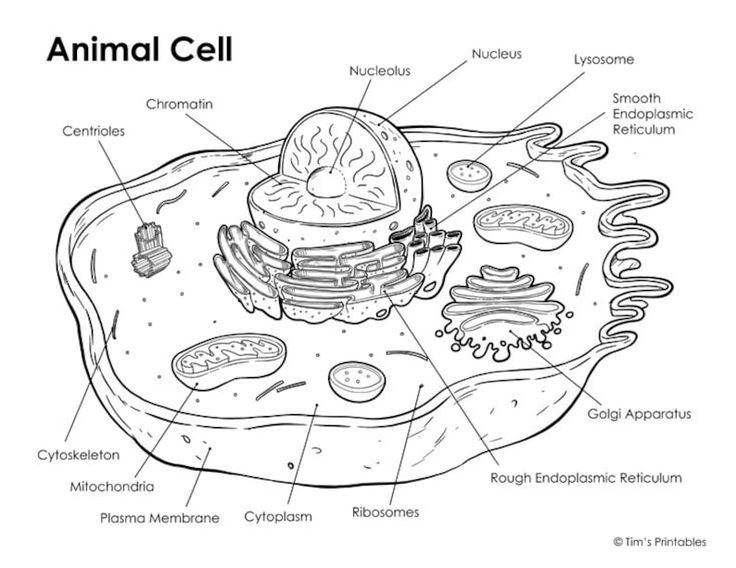
all cells are surrounded by a ________ (made of _______)
what does it do ?
plasma membrane , made of lipid bilayer
it defines cell boundary, control movement of material in & out of cell
plant cells have an outer covering in addition to plasma membrane, what is it made of?
cell wall; made of cellulose polysaccharide
animal cells are surrounded by a cell coat called _______, what is its purpose ?
Glycocalyx .
serves as recognition sites at cell surface
where is rRNA synthesized and assembled ? where are portions of DNA that encode for rRNA located?
rRNA is synthesized in the nucleolus, and in the NOR (nucleolus organizer region) is where DNA encodes rRNA
what is a cytoplasm and what are the contents inside of it and their purposes ?
cytoplasm is the remainder of the cell excluding nucleus (earth)
cytosol : liquid portion in the cytoplasm (oceans)
cytoskeleton : made of microtubules (tubulin) & microfilaments (actin) to provide support and cell movement
Italicize the name of the ______ not the ______
Italicize the name of the gene not the protein.
ER
smooth ER: lipid synthesis & detoxify
rough ER: ribosomes on the outside; protein synthesis
what do ribosomes do ?
genetic info in mRNA is translated to protein
mitochondria
site of ATP synthesis & oxidative phases in cell respiration
mtDNA
chloroplasts
site of photosynthesis
cpDNA
centrioles
organize spindle fibers for meiosis & mitosis
what are spindle fibers made of ?
microtubules
where do the sister chromatids divide ?
centromere
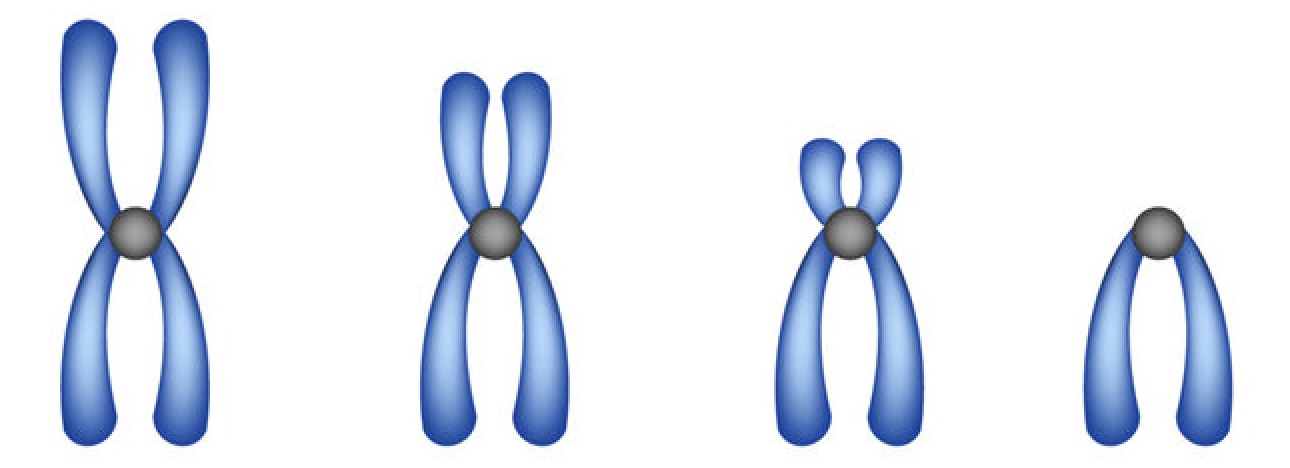
Locations of centromere
Metacentric: middle
Submetacentric: between middle & end
Acrocentric: close to end
Telocentric: at the end
what are homologous chromosomes?
a pair of chromosomes with the same genes, dif alleles
identical gene sites (loci)
karyotype
number of chromosomes
How many genes do fruit flies have ?
14,000 genes
how many genes do humans have ? and how many genes are there for 1 chromosome for humans?
20,000 genes ; 1 chromosome = 500-2000 genes
a gene is :
all the DNA sequences needed to create that gene product
Ken & Barbie fruity fly gene mutation is for what ?
mutation that causes lack of genitalia
“white” fruit fly gene mutation name is for ?
mutation that causes white eyes
zygote
first diploid cell
karyokinesis
genetic material divided into 2 daughter cells (2 nuclei) during nuclear division
cytokinesis
after karyokinesis; when the 2 daughter cells split each is enclosed by plasma membrane
Cell Cycle
Interphase:
G0: non dividing cells go here & stay (quiescent)
G1: cell grows
S phase: gene duplication creates sister chromatids with cohesin to hold them tg
G2: cell grows & checks for DNA errors
Mitosis
around 16 hours total
Mitosis stages
Prophase: chromosomes condense & centrioles divide and move apart
Prometaphase: chromosomes are visible double structures; centrioles reach opposite sides and spindle fibers form.
Metaphase: centromeres align on the metaphase plate & spindle fibers bind to kinetochore to pull the chromosomes
Anaphase: centromeres split & daughter chromosomes move to opposite sides (disjunction)
Telophase: daughter chromosomes are at opposite poles; cytokinesis divides cytoplasm, nuclear envelope reforms and interphase begins again.
what degrades Cohesin during prometaphase/metaphase? What are where is degradation prevented?
Cohesin is degraded by enzyme separase.
Enzyme shugoshin prevents degradation of cohesin at centromere
what do kinases do , and which protein is it activated by ?
tells cells when to proceed to the next phase; activated by cyclins
Where are the 3 major cell cycle checkpoints & what do they do? What happens if they fail?
G1,G2, and Metaphase
It checks for DNA errors, and if so the cell will try to repair, if it cant its removed and self destructs (apoptosis) . If failed, tumors & mutations can result.
Events of Meiotic Prophase 1
Synapsis: 1 chromosome from each parent combines to create a bivalent
Chromosomes condense and create 4 chromatids total = tetrad
Chromosome arms cross e/o = chiasma
Terminalization: Chiasmata move towards the ends
what is half of a tetrad ?
Diad
Spermatogenesis
production of male gamete in testes
Spermatogonium replicates itself and creates Primary Spermatocyte
Meiosis 1: Primary Spermatocyte divides into 2 = Secondary Spermatocytes
Meiosis 2 : Secondary Spermatocytes divide into 2 = 4 Spermatids
Spermatids develop into Spermatozoa (differentiation)
Oogenesis
production of female gamete in ovaries
Oogonium replicates itself into Primary Oocyte
Meiosis 1: Primary Oocyte divides into a smaller First Polar Body (which dies) and into a larger Secondary Oocyte.
Meiosis 2: Secondary Oocyte divides into a smaller Secondary Polar Body (which dies) and a larger Ootid.
Ootid becomes Ovum (differentiation)