MODELS OF DISABILITY
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
the loss of how many teeth is considered ‘disabling’
21 or more teeth



define disability in the medical model
disability (medical model): the activity limitations that result from one or more chronic conditions (Bury, 2004)
define disability in the social model
disability (social model): disability is something produced by society through ‘disabling structures’ and ‘disabling societies’ (Bury, 2004)
define disability in the biopsychosocial model
disability (biopsychosocial model): disability results from the complex interplay of social, biological and psychological factors
define impairment
impairment: any loss or abnormality of psychological, physiological or anatomical structure or function (WHO)
define disability
disability: a restriction or lack (resulting from an impairment) of ability to perform an activity in a manner or within the range considered normal for a human being (WHO)
define handicap
handicap: a (social) disadvantage for a given individual, resulting from an impairment or a disability, that limits or prevents the fulfilment of a role that is normal (depending on age, sex and social and cultural factors) for that individual (WHO)
outline the International Classification of Impairments Disability and Handicap (ICIDH) model of disability

outline Locker’s model of oral health (follows ICIDH model)
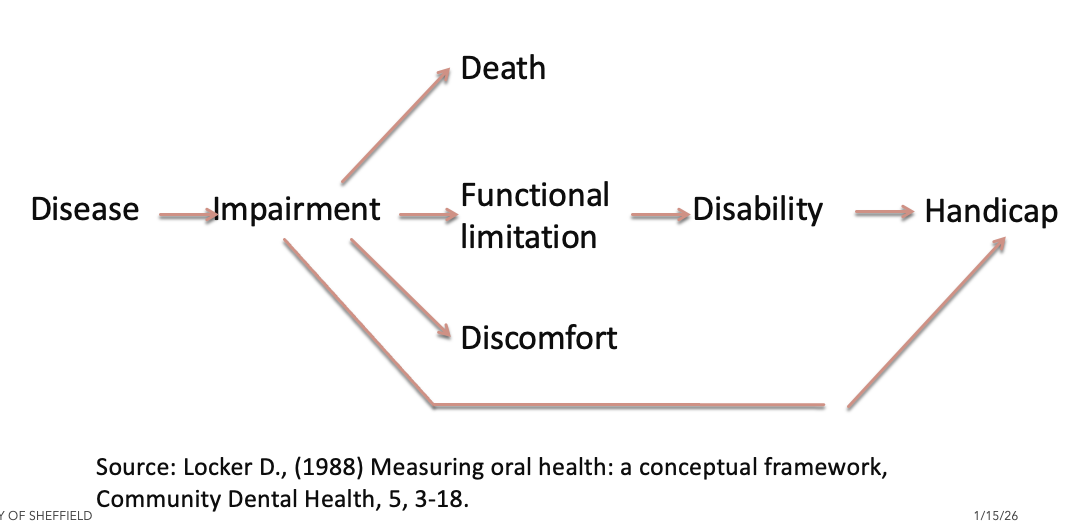
interrelations between impairment, disability and handicap

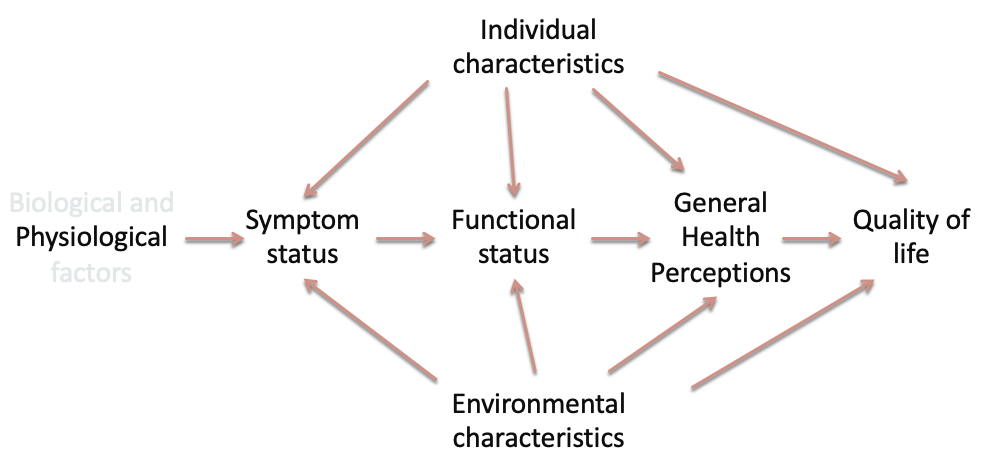
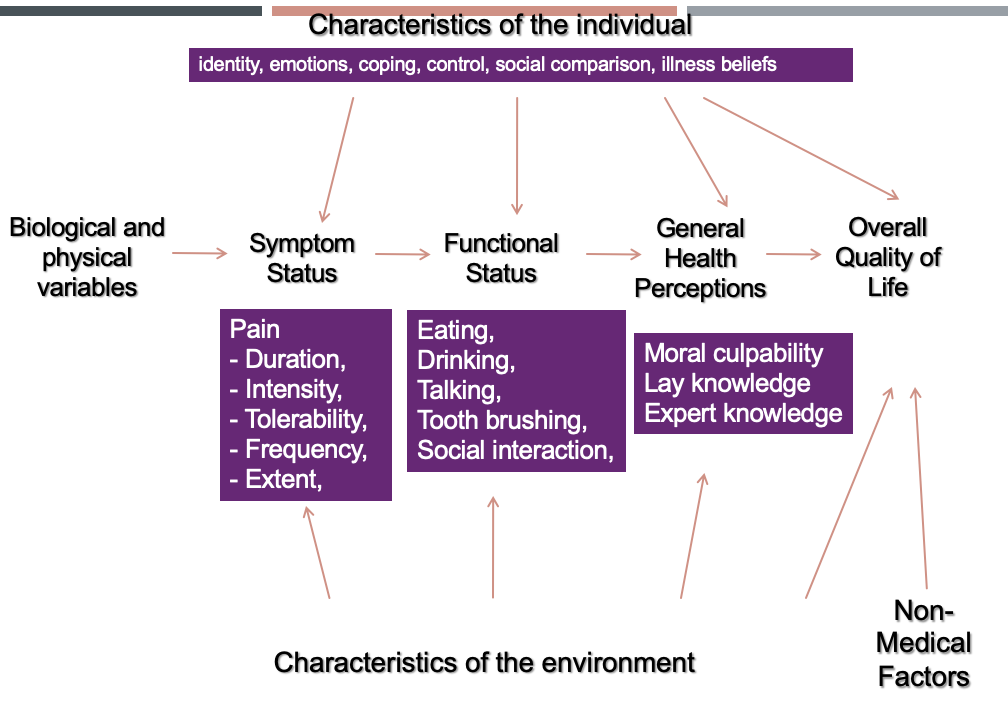
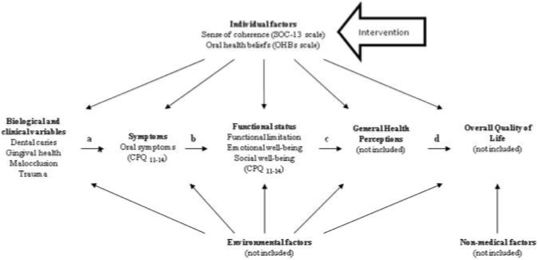
outline Wilson and Cleary’s model of health-related QoL
(links clinical variables to outcomes of QoL)
outline problems with the medical model of disability
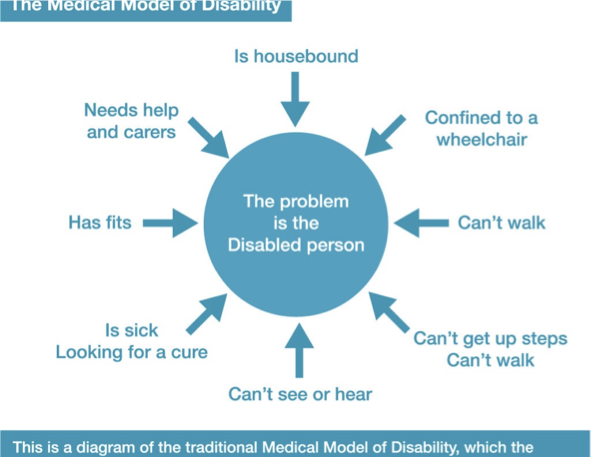
the medical model of disability

what does the social model of disability state that the issue is
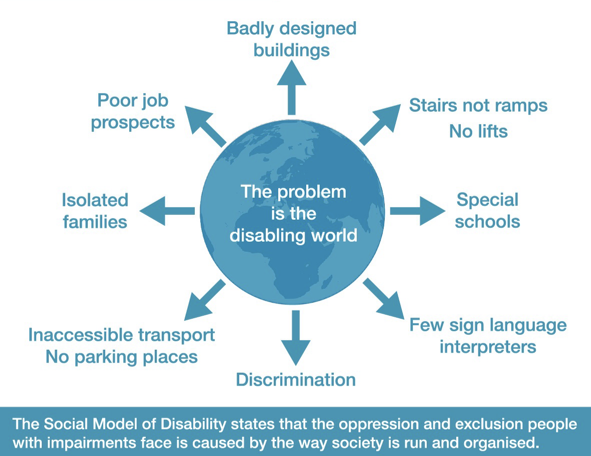
what does the social model of disability state the cause of disability is
“caused solely through the inadequate adaptation of the environment to the needs of people with impairments”
what are criticisms of the social model of disability
failure to appreciate the body (Pinder, 1995; Synder and Mitchell, 2001)
simplistic, a doctrine rather than a scientific model (Shakespeare and Watson, 2010, Thomas, 2010, Scambler and Scambler, 2010)
ignores impairment (Shakespeare and Watson, 2010)
only applies to white males with spinal injuries - it is very narrow and does not appreciate the diversity of disabling conditions (Thomas, 2010, Shakespeare and Watson, 2010)
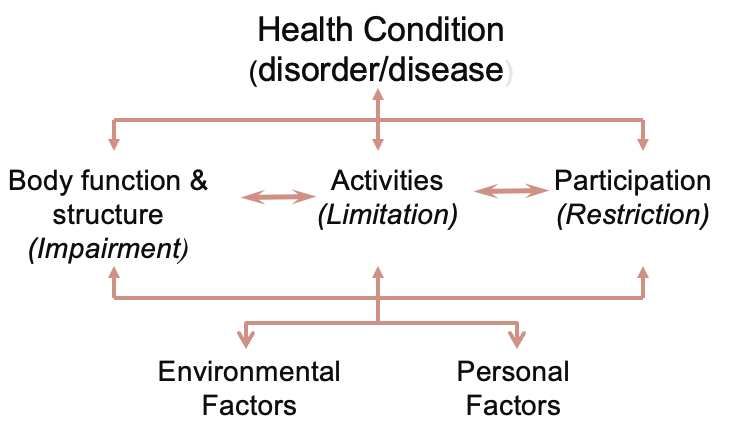
outline the International Classification of Functioning Disability and Health model (WHO, 2001)

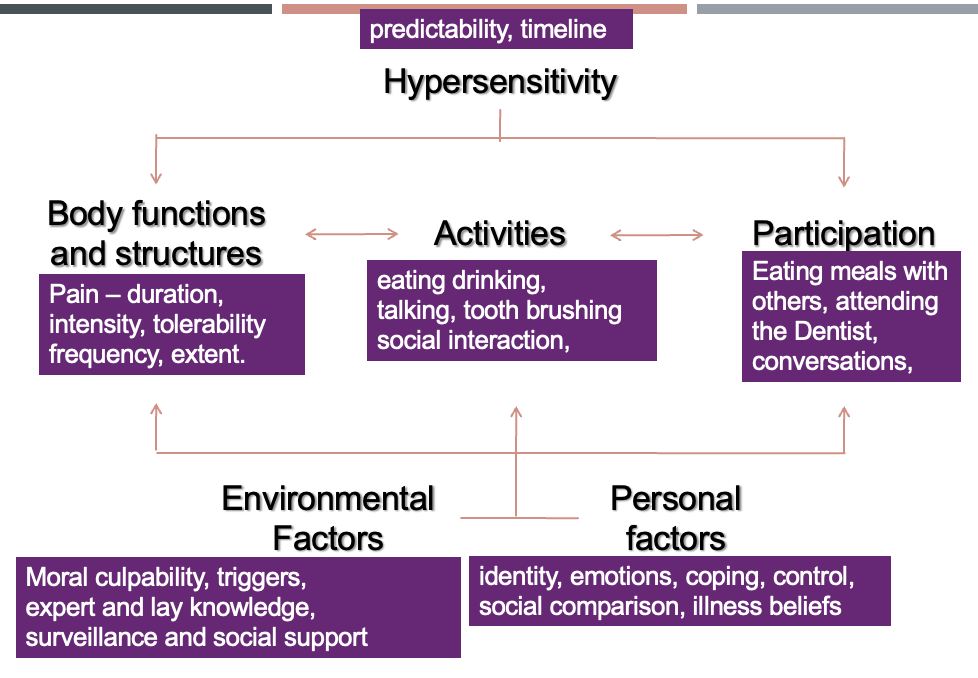
Wilson and Cleary framework applied to dentine sensitivity
Wilson and Cleary model applied to dry mouth
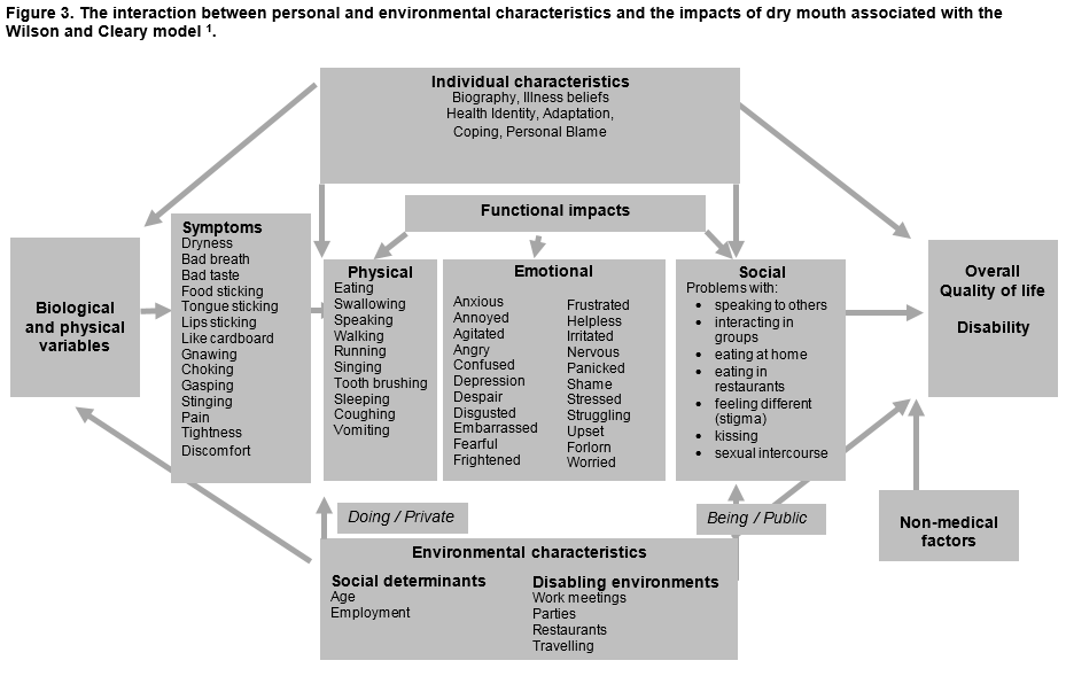
where in the Wilson and Cleary model should intervention be given
what are the types of barriers in disability
individual
organisational






conclusions
