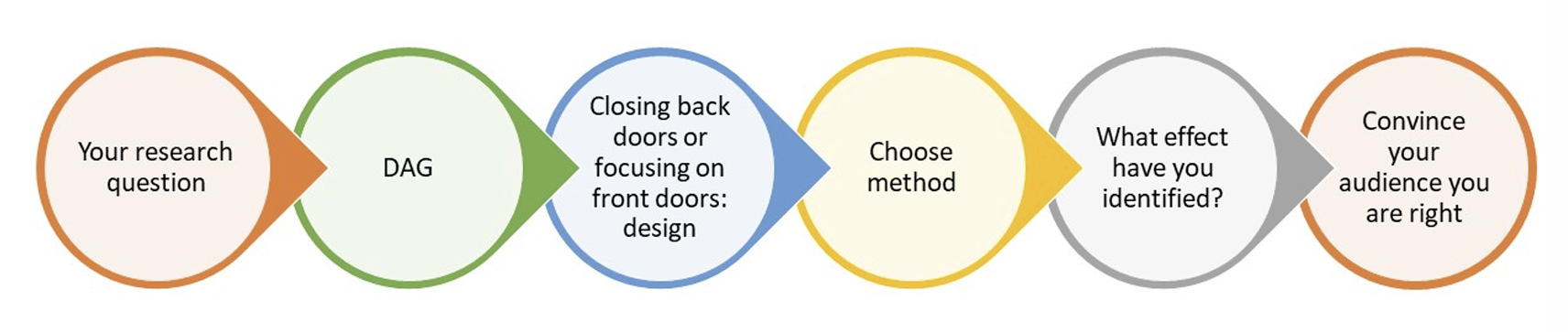
Lecture 2: Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) and Treatment Effect
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What does DAG stand for?
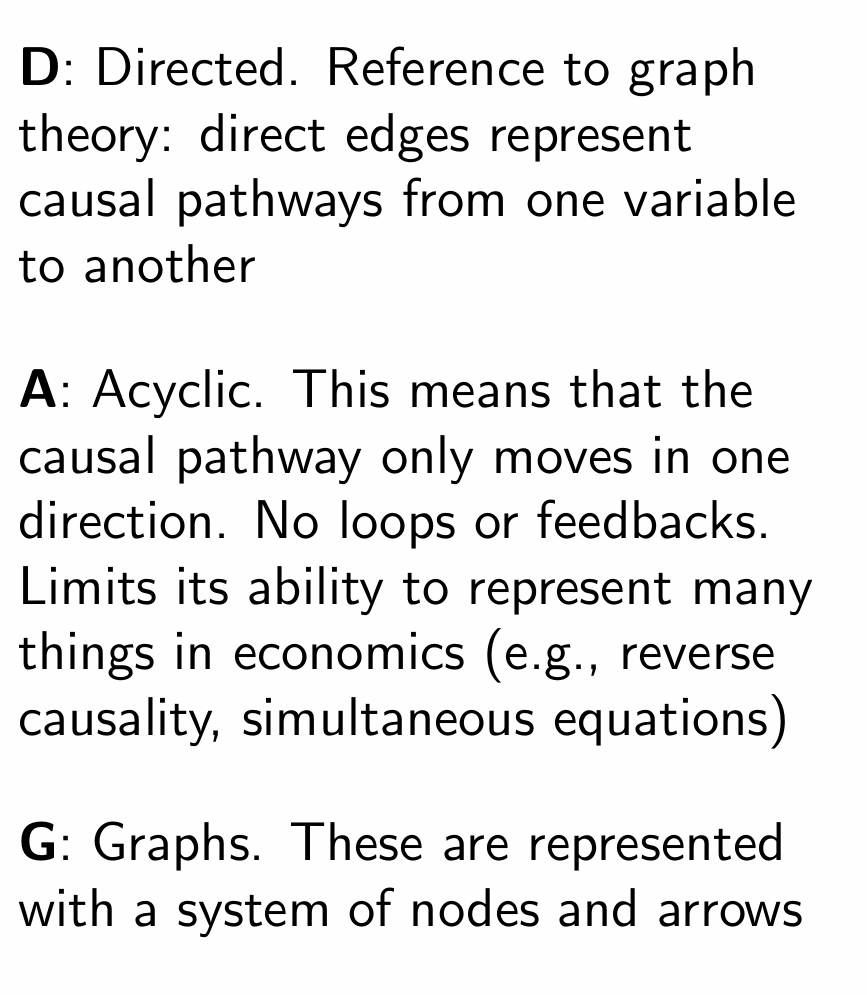
What does a DAG model show?

What is an advantage and a disadvantage of DAGs?

How do we put together a DAG?


X
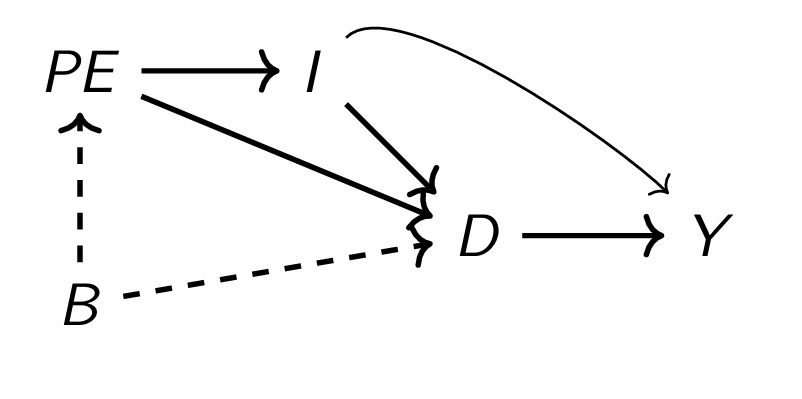
Describe the relationships between each variable

When should you create the DAG in relation to data collection and why?

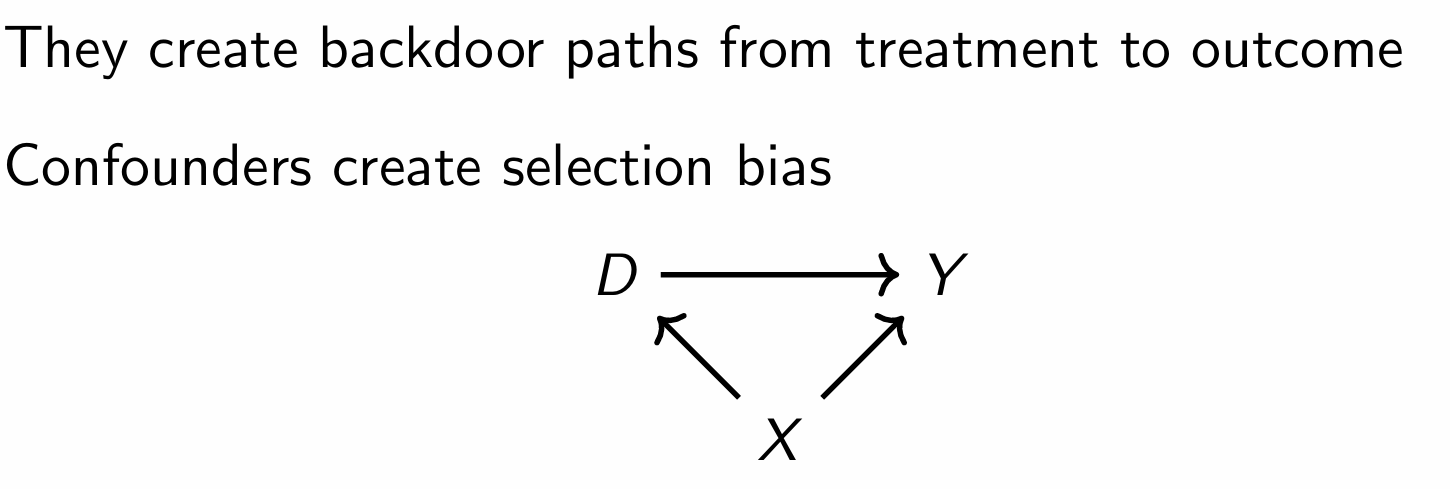
What are confounders?

What do confounders create?
Only a concern when the variable impacts both treatment and outcome (i.e. X)
What does knowledge of confounders allow us to do?

How do backdoor paths compare to collider and mediator (indirect) paths?

How can we block a backdoor path?
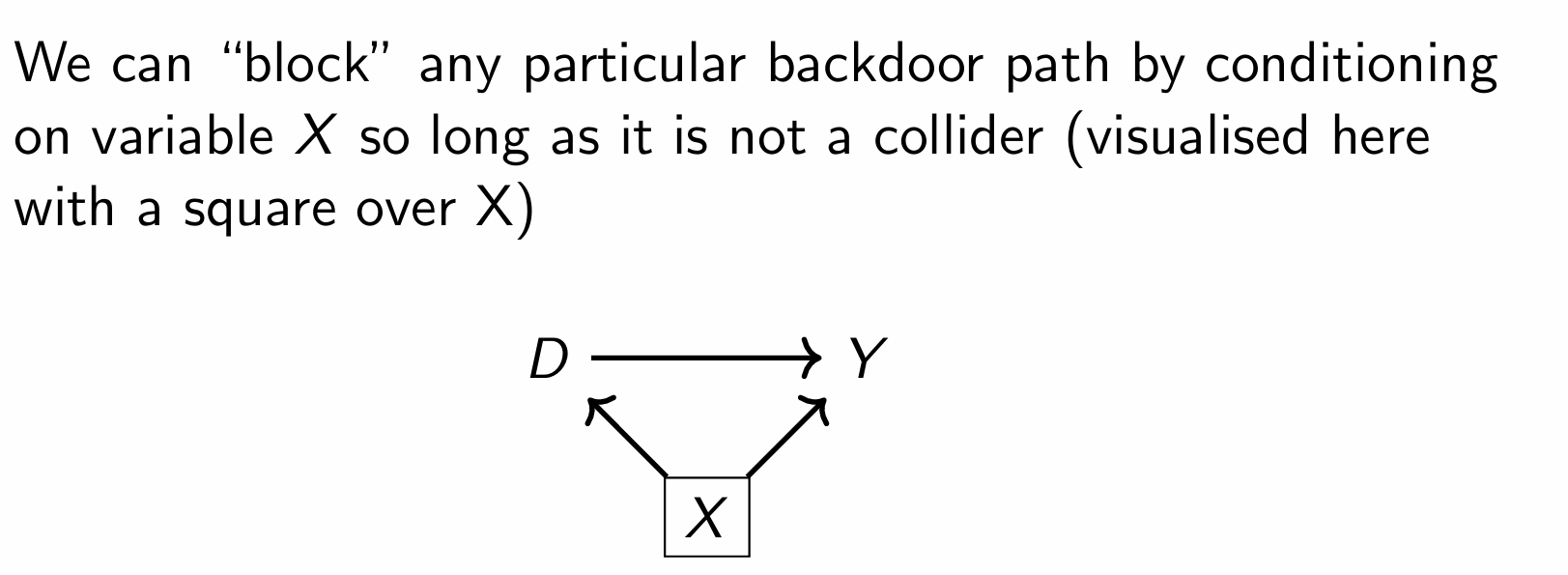
What can we calculate once we condition on X (the backdoor)?

What methods can we use to calculate the average differences in Y?
Regression, Matching, Stratification, Weights
What do all of these methods achieve?
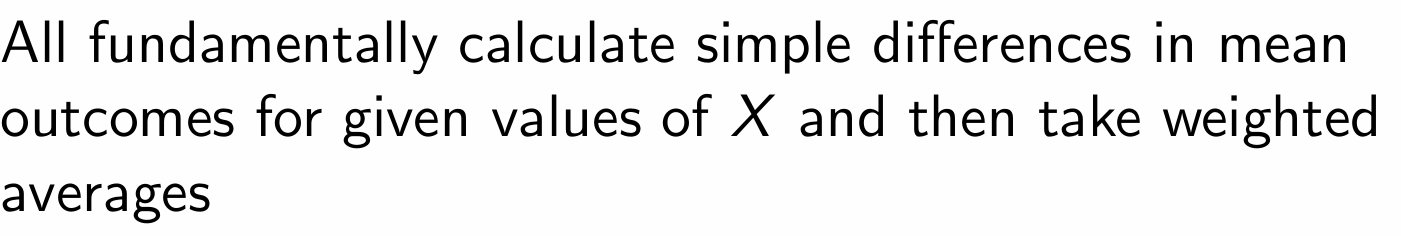
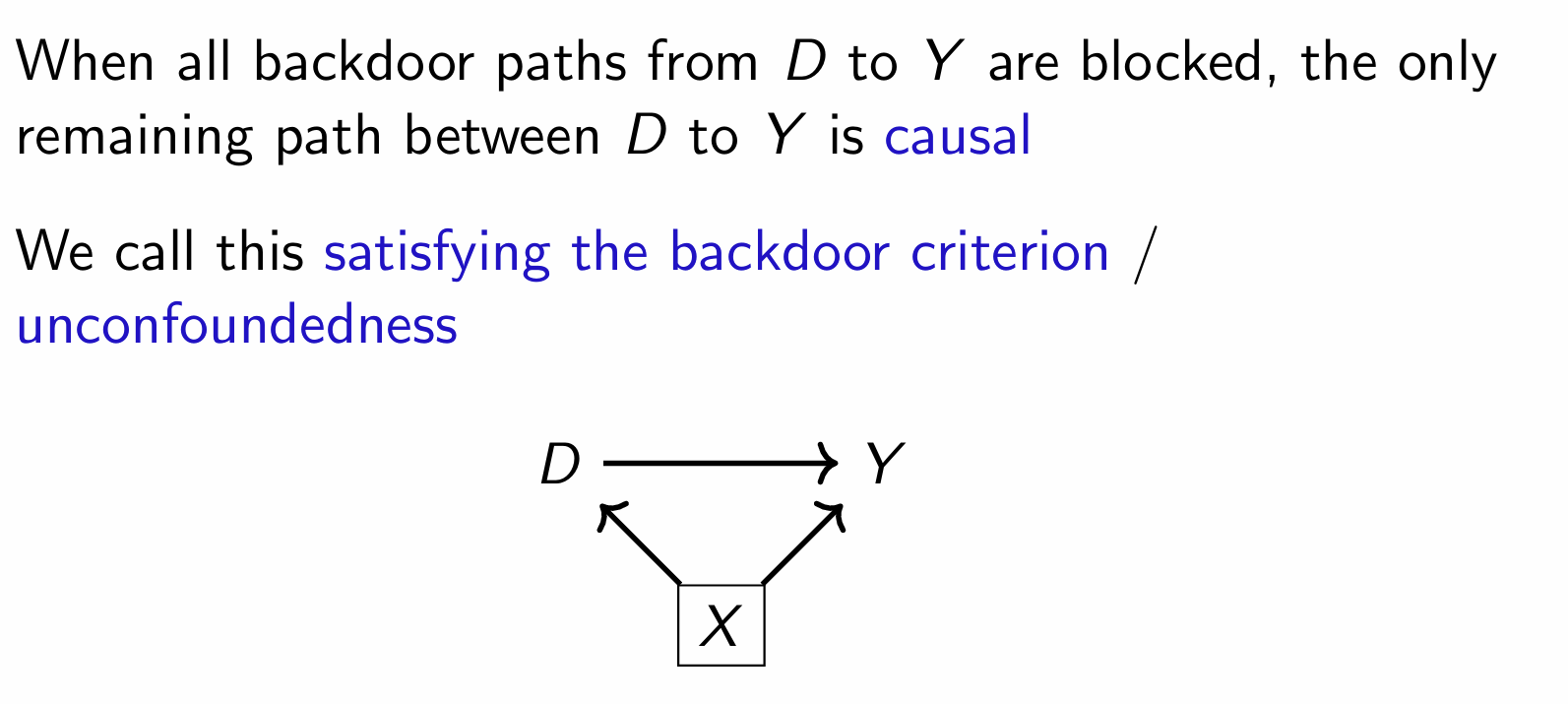
When all backdoor paths are blocked, what is this known as and what is the only remaining relationship?


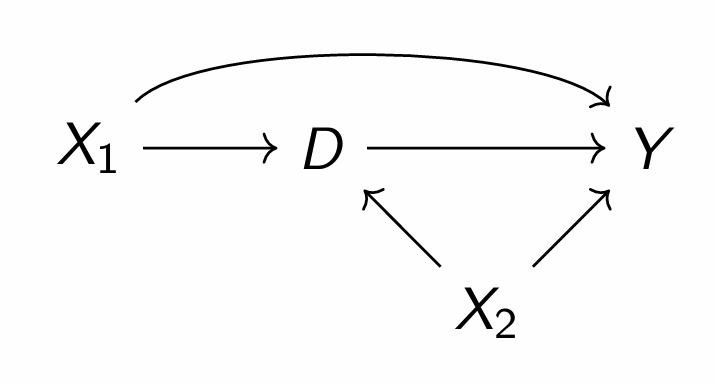
What relationship are we interested in and what are the various front and back doors?

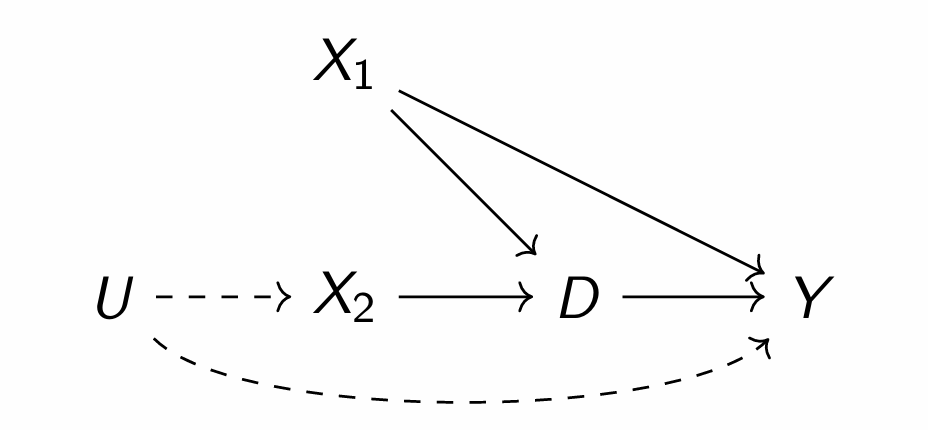
What relationship are we interested in and what are the various front and back doors?


No, due to it being a front door path (directly effects D but indirectly effects Y); D is a mediator in this path
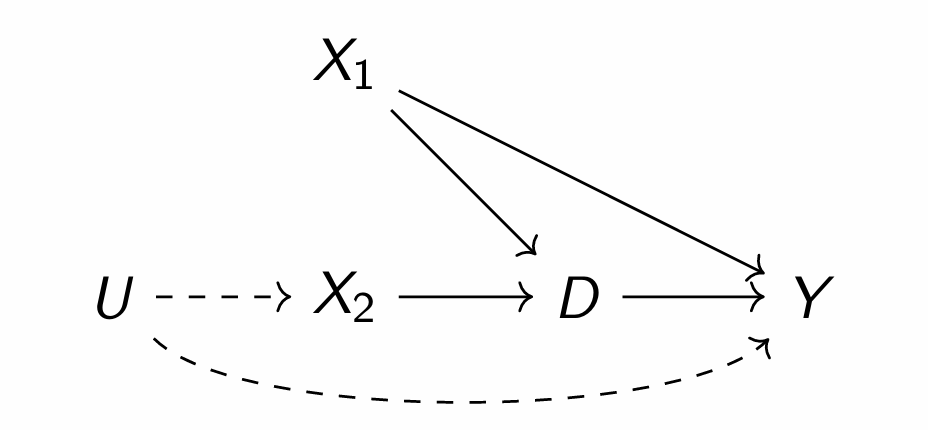
How could you try to close the backdoor from U?
Condition on X2 as its the only way to capture some of the effect of U as there is no effect between the direct relationship of U and Y
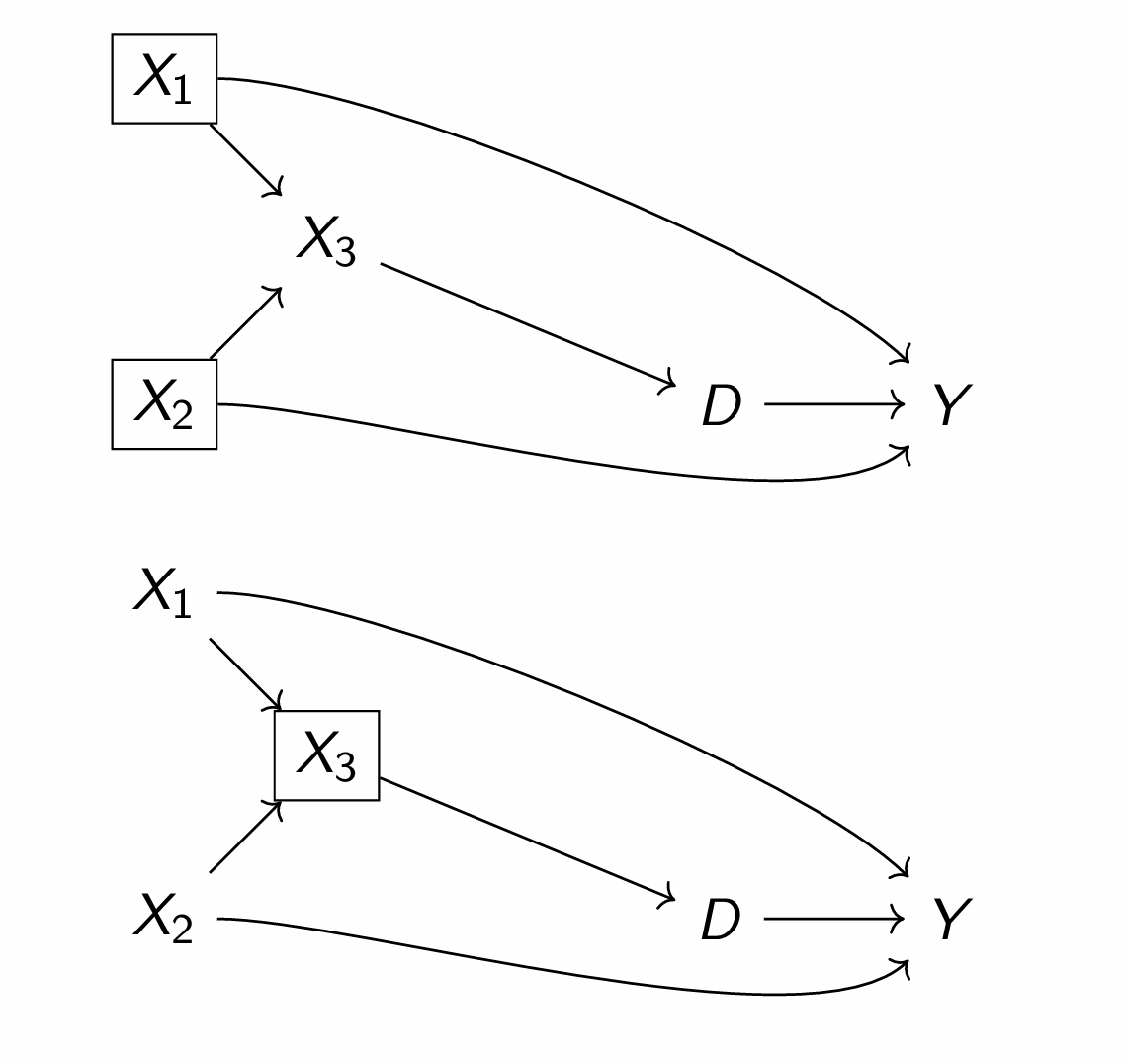
What is going on here and which is more precise?
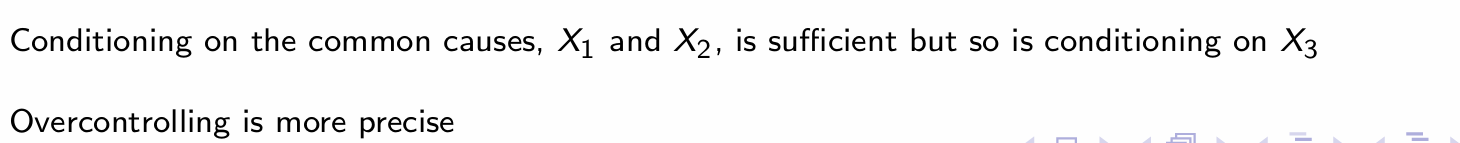
Why might backdoor paths remain open?

Colliders are not a problem in the actual design but why are they bad controls?


Plots represent sample selection which could mask the true effect(s)
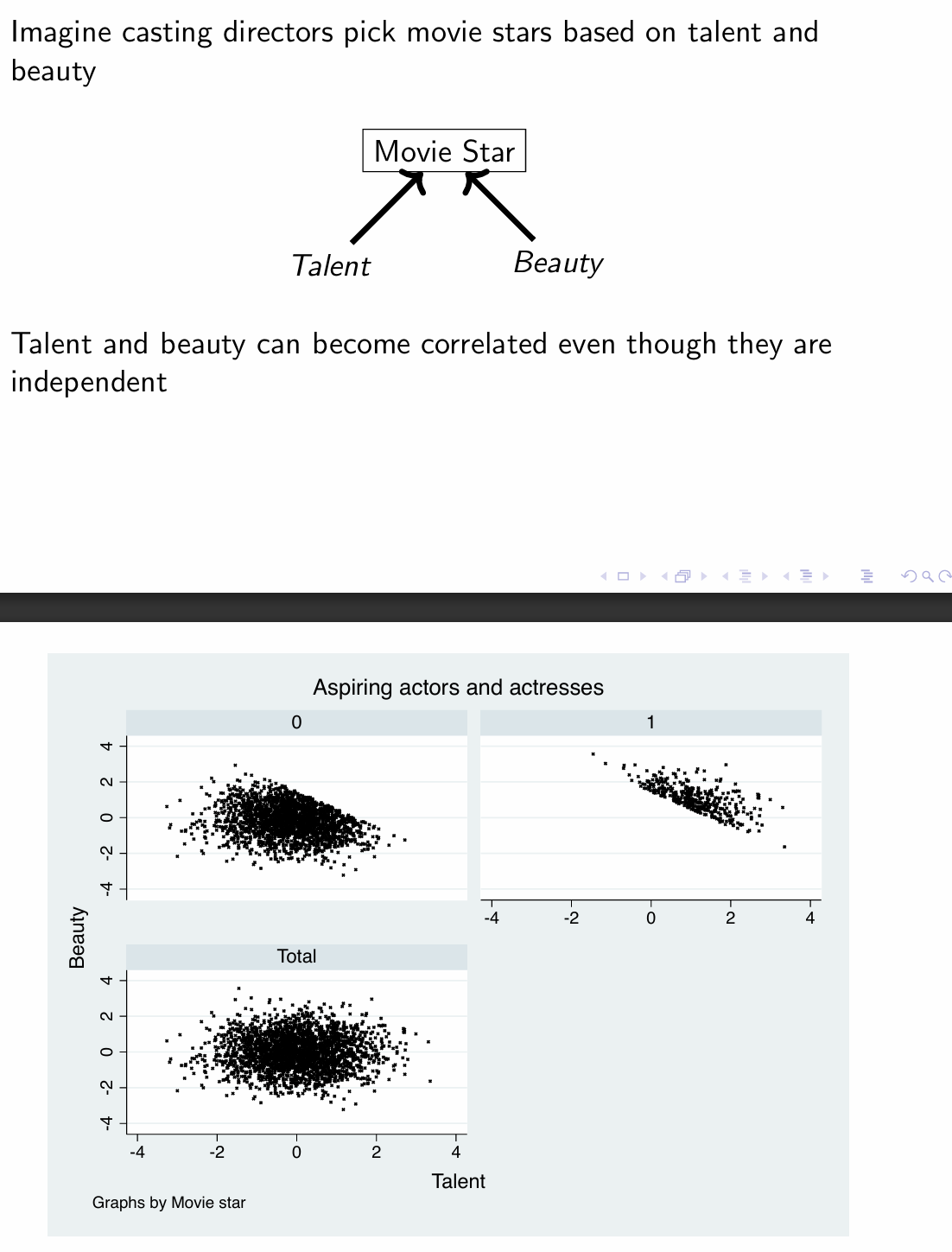
What would happen if we framed the analysis through a regression?


Controlling for occupation in a wage regression searching for discrimination can lead to strange results

Draw a DAG and describe the relationships between variables
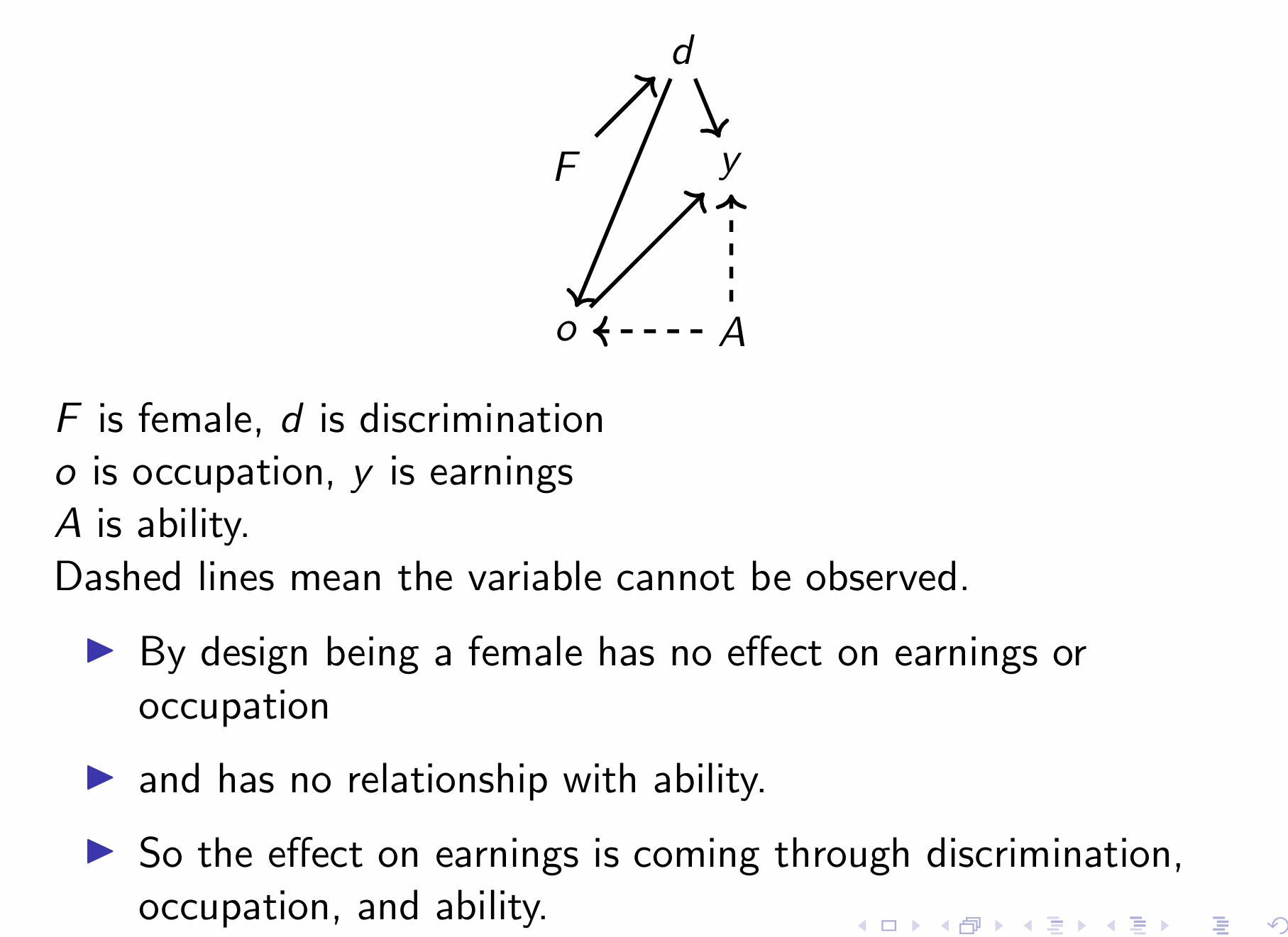
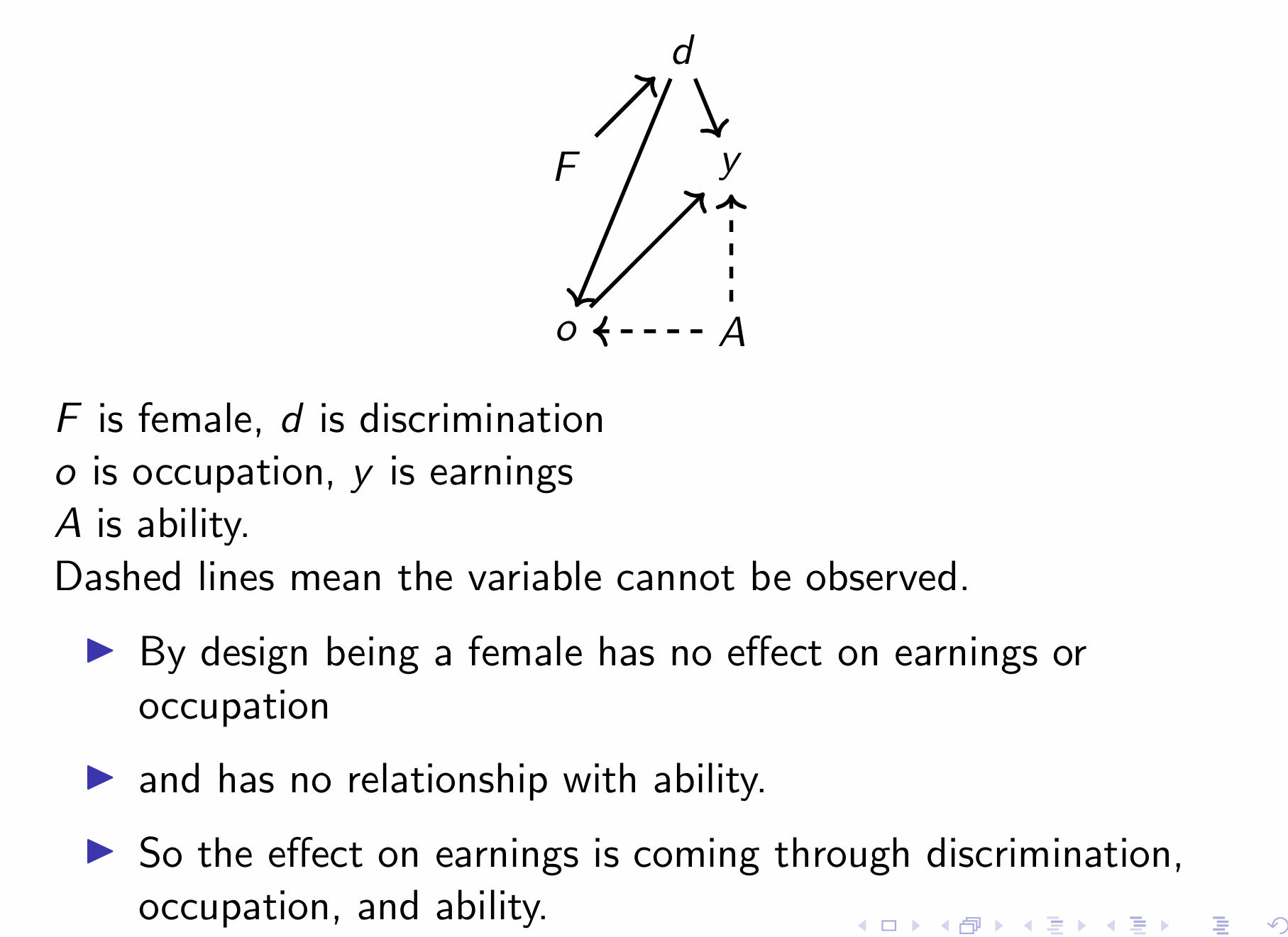
What relationship are we interested in and what are the front and back doors?

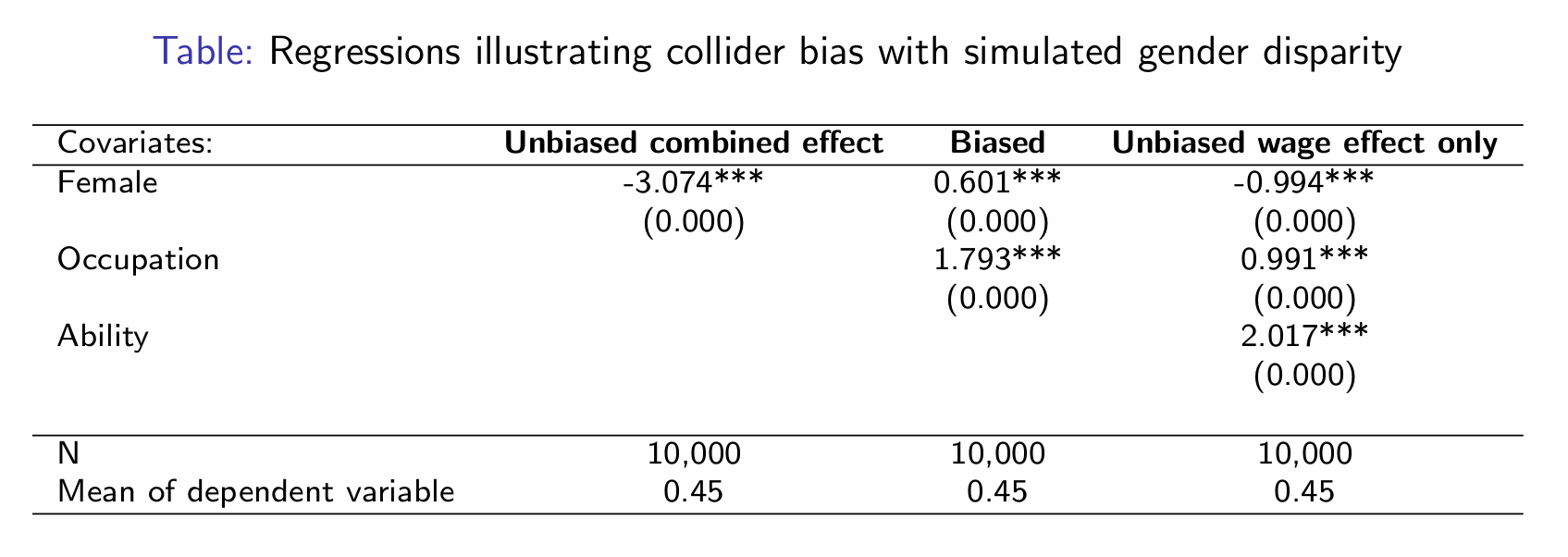
What can we infer from the regression output?

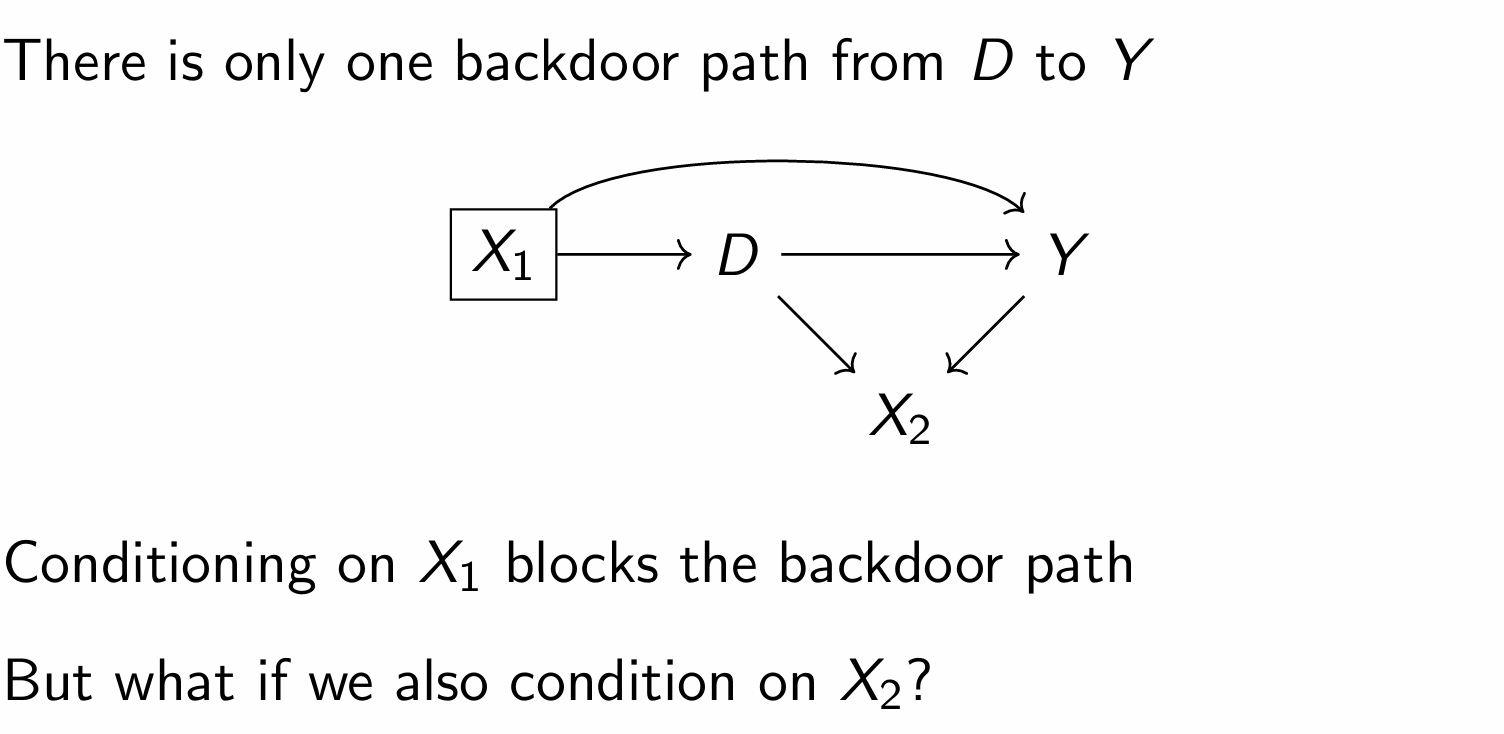
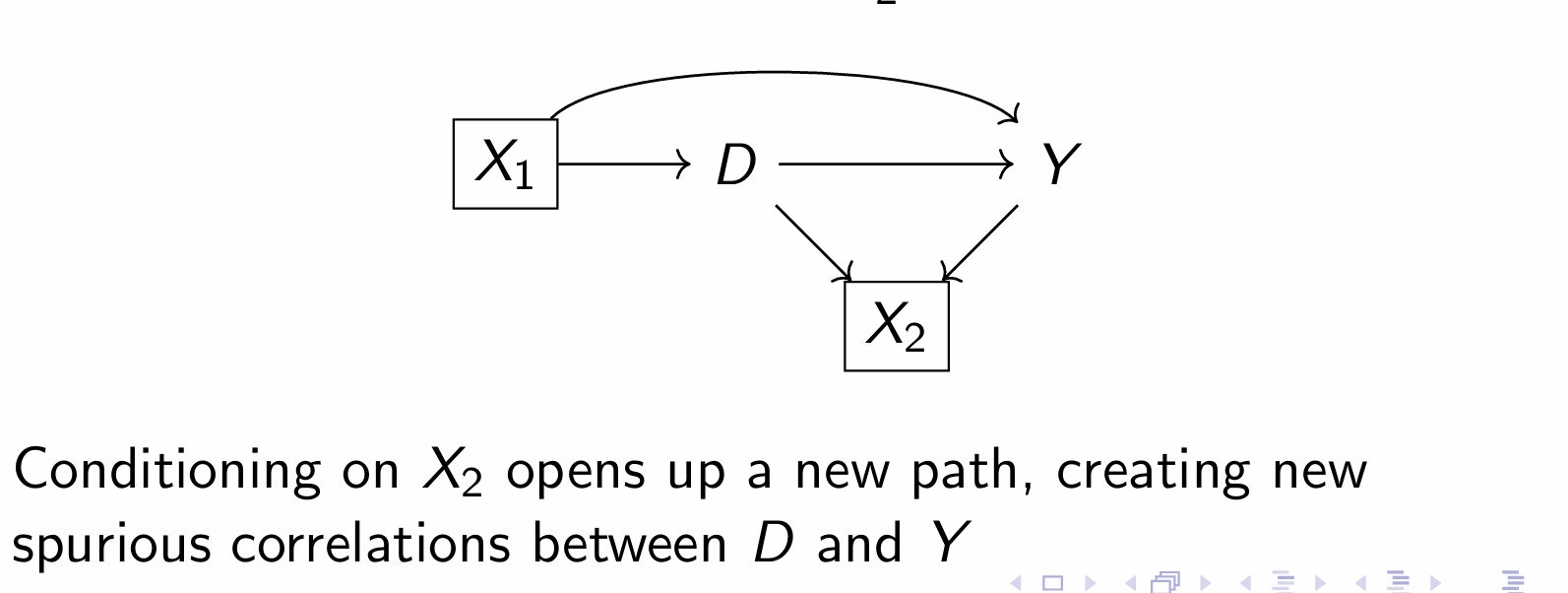
When colliders are pre-treatment covariates, what do we call the bias?
M-bias
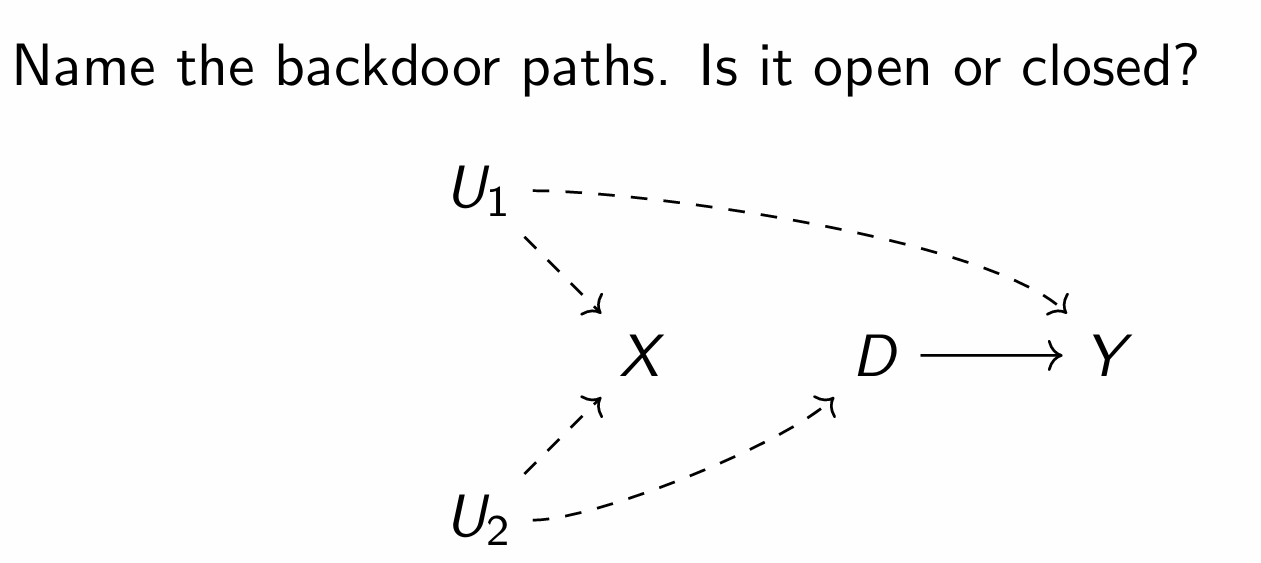
D ← U2 → X ← U1 → Y
Would be closed due to collider X but as U1 and U2 are unobserved, the backdoor technically remains open
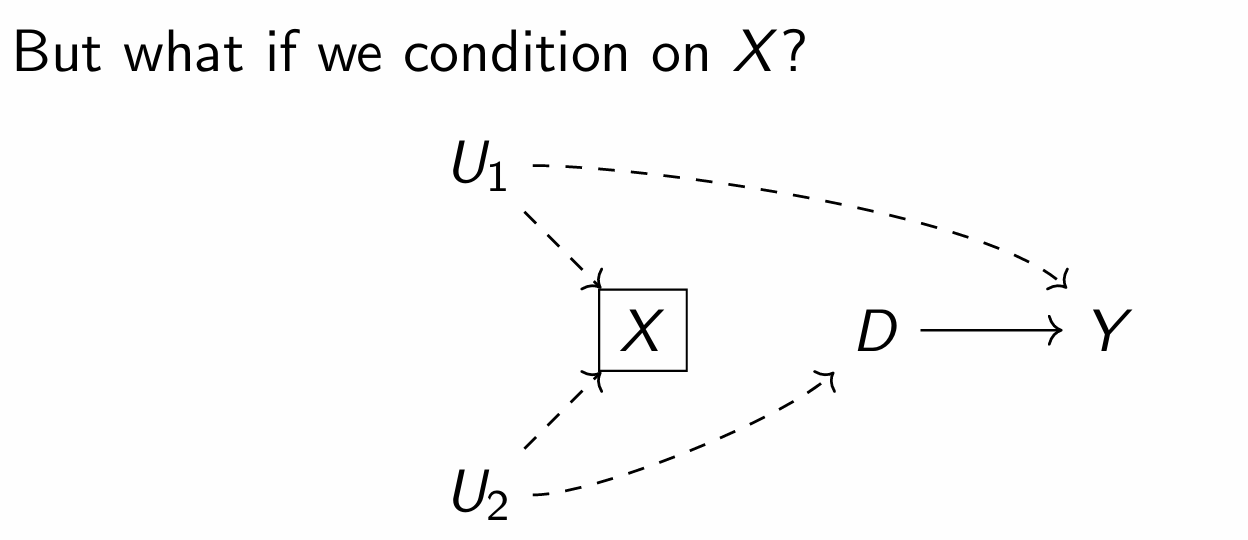
Conditioning on a collider but nothing changes as the backdoor was already open from the unobserved factors
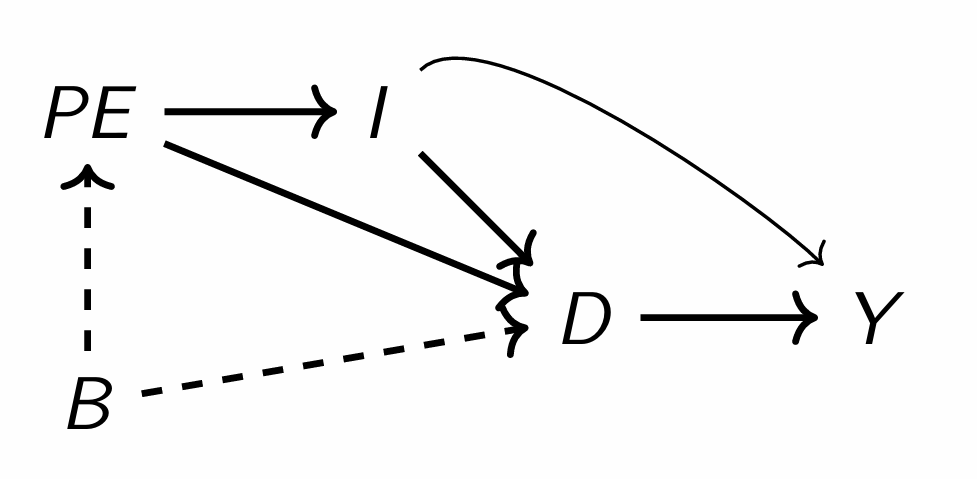
What happens if we condition on D and I?

How does a kitchen-sink regression compare to the considerations of DAG?

What if you are not confident about the DAG, how can you improve it?
DAGs will be less formalised than other methods but will provide reasoning about the treatment assignment mechanism

What is included in the design phase for causal inference?

How should you frame your study and how should you utilise potential outcomes?

How do you define the hypothetical experiement?

What can happen as a result of having different hypothetical experiments for the same dataset?

Why might you reconstruct the assignment mechanism in a study?

How can we assess covariate quality and availability?

Why are known and observed confounders useful in the design?

What are some examples of different estimators and how do their assumptions vary?





What assumptions do we make to estimate causal effect with inclusion of controls?


Which of the assumptions are needed to estimate casual parameters (e.g. ATE, ATU, ATT)?

How do we define unconfoundedness?


How can we write this using expectations?
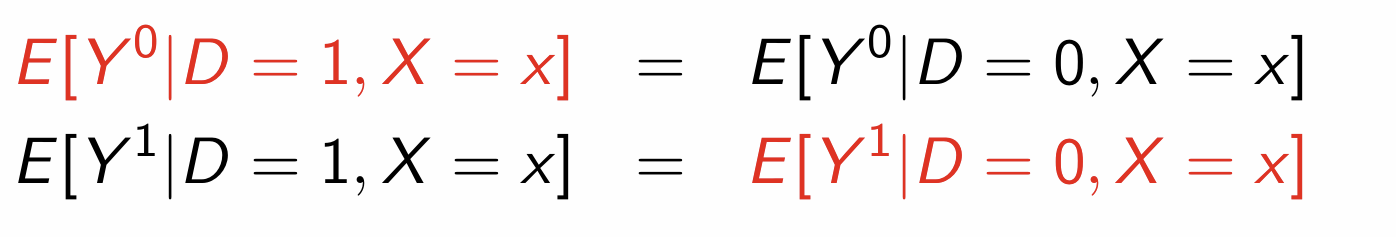
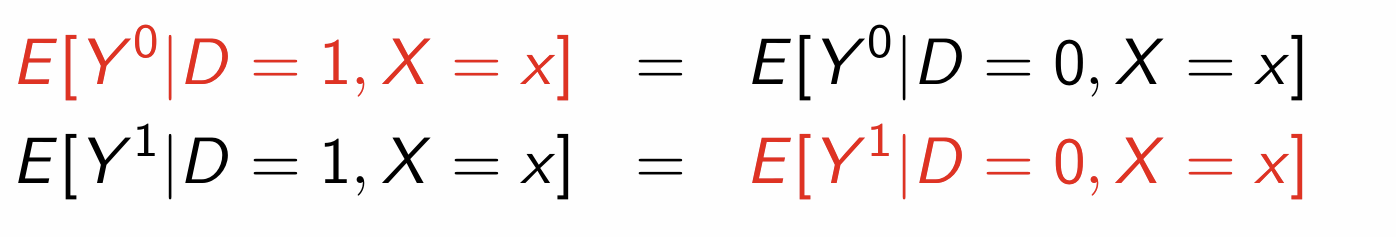
What does unconfoundedness justify?


Why do we sometimes weaken the assumption?

How do we define weak unconfoundedness?


How can we write this using expectations?
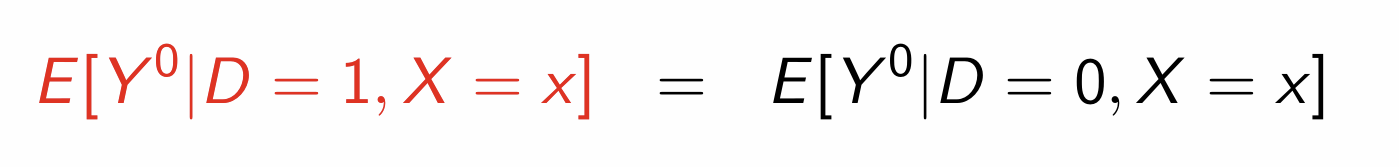
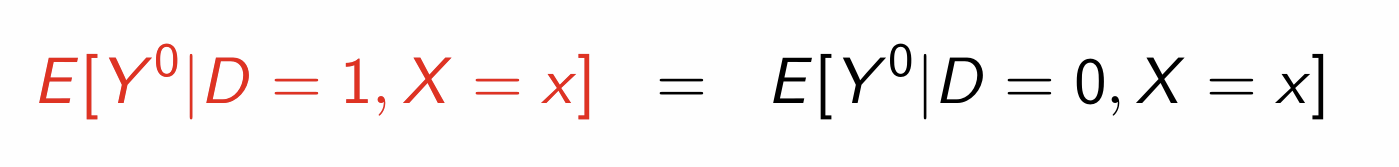
What can we use weak unconfoundedness for?
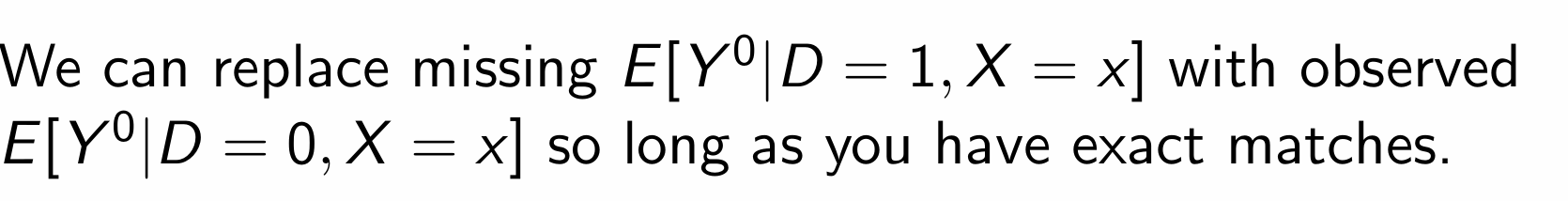
Which causal parameters are weak and strong unconfoundedness used for?

How do we define common support?

What allows us to make substitutions under common support?

Why is common support testable?

What happens if the dimensions of X get very large regarding common support?

If we have both assumptions, how can we estimate ATE outside of an RCT?


How can we use unconfoundedness to estimate ATE and is it testable?


How can we use common support to estimate ATE?
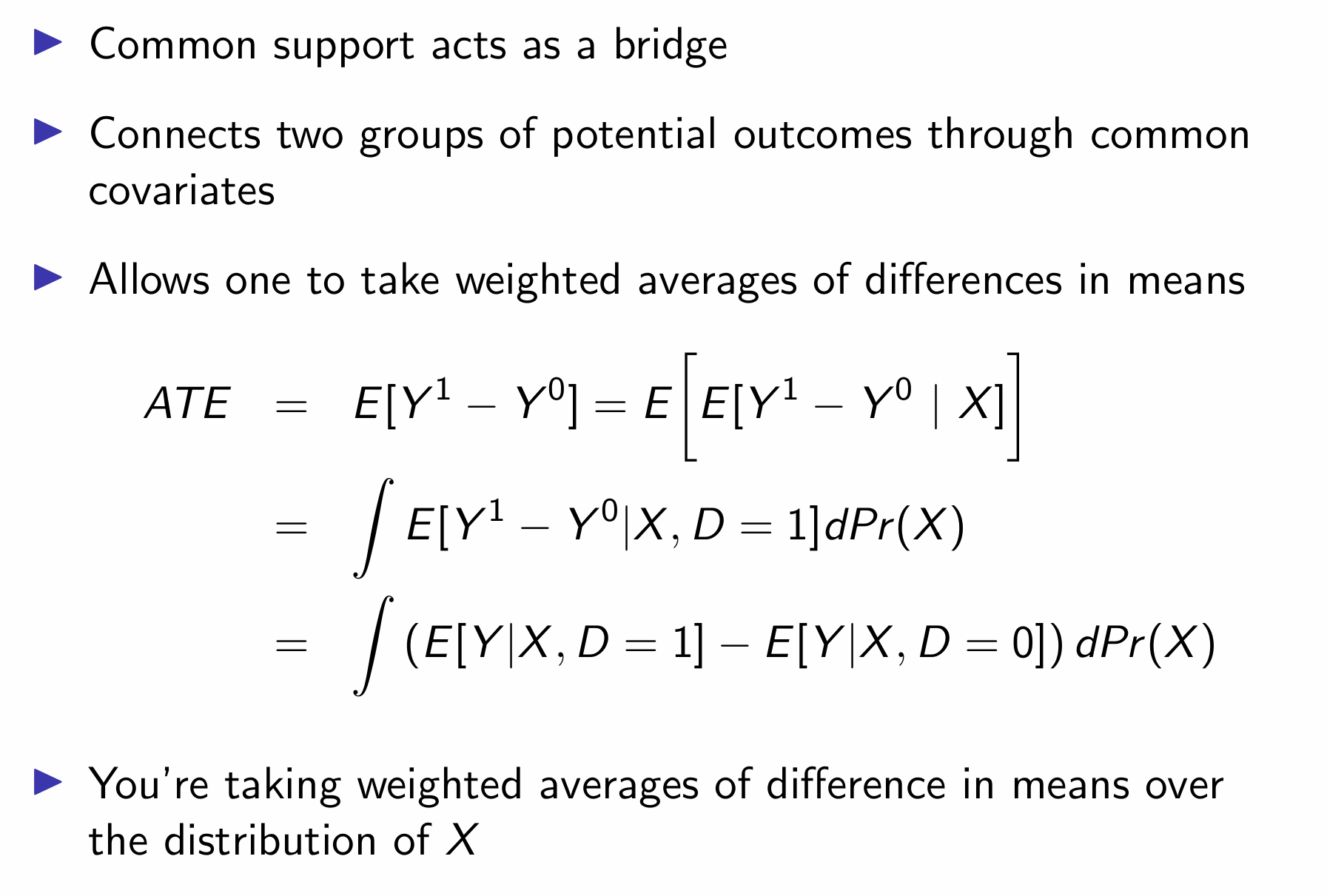
Why is the ATT more likely to be evaluated than the ATE?

What assumptions are required to estimate the ATT?


Why do we only need weaker assumptions to estimate the ATT?


How can we use the weaker assumptions to estimate the ATT?
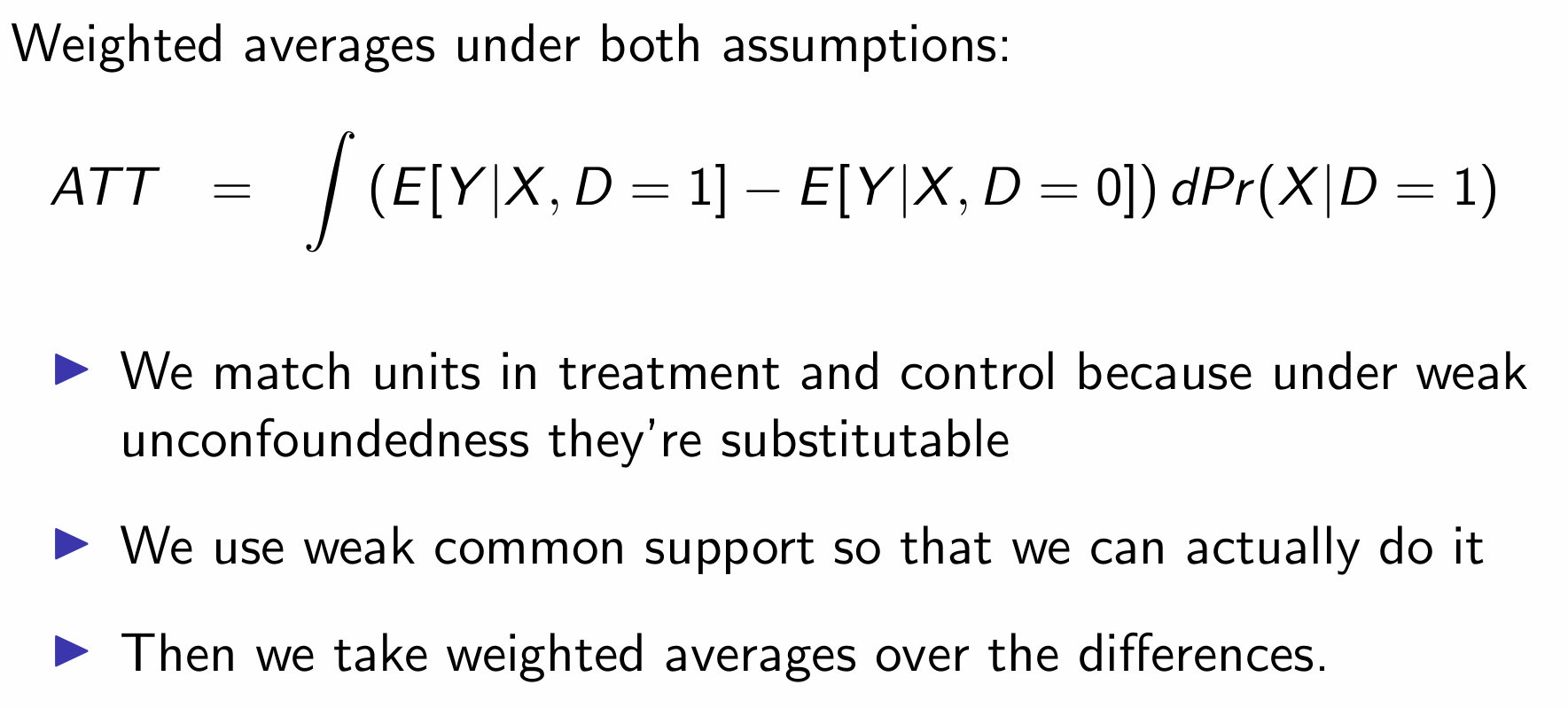
How would we estimate the ATU?
Similar to the ATT

What are three other examples of treatment effects and how are they defined?
CATE and WATE come in many forms depending on the conditions or weights applied

What are some common examples of WATEs and how are they defined?

What is the Intent-to-Treat Effect and what are the properties of it?

If you want to know how effective a treatment was when applied, which causal parameter would you use?
ATT
If you want to know how effective a treatment would be if applied randomly, which causal parameter would you use?
ATE
If you want to know how effective it would be if applied just a little more broadly, what casual parameter might you use?
MTE

Which casual parameter would we use if the sample is not representative?
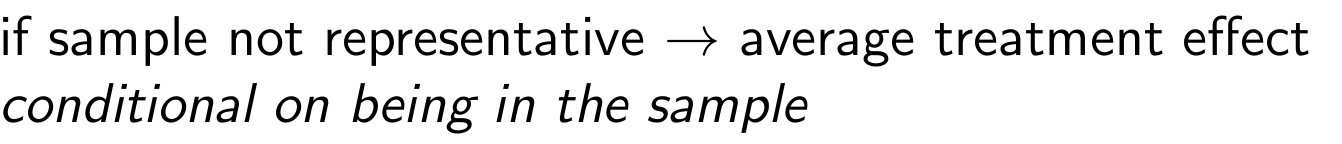

What are the treatment effect averages for each of the rules of thumb for research design?
ATE
CATE
WATE
ATT
LATE
How does the design of the study compare to the estimators? What is the usage of both?



What methods can we choose to close various backdoors?

How can we test the assumptions we have made in our method?

What is the order of events for the empirical research process?