Chapter 11 - Acid & Base Reactions In Water
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Common Acids
Hydrochloric Acid - Stomach Acid (Strong)
Sulfuric Acid - In car batteries (strong)
Ethanoic Acid - Batteries, fertilizers (strong)
Carbonic Acid - Carbonated Drinks (weak)
Phosphoric Acid - Fertilizers, drinks (weak)
Citric Acid - In citrus fruits (weak)
Ascorbic Acid - In citrus fruits (weak)
Common Bases
Sodium hydroxide - Oven cleaners (strong)
Ammonia - Fertilisers, explosives (weak)
Calcium hyrdoxide - Cement and mortar (strong)
Magnesium Hydroxide - For acid reflux (strong)
Sodium hydroxide - Powder, glass (strong)
Alkalis
Soluble/aqueous bases
Properties Of Acids
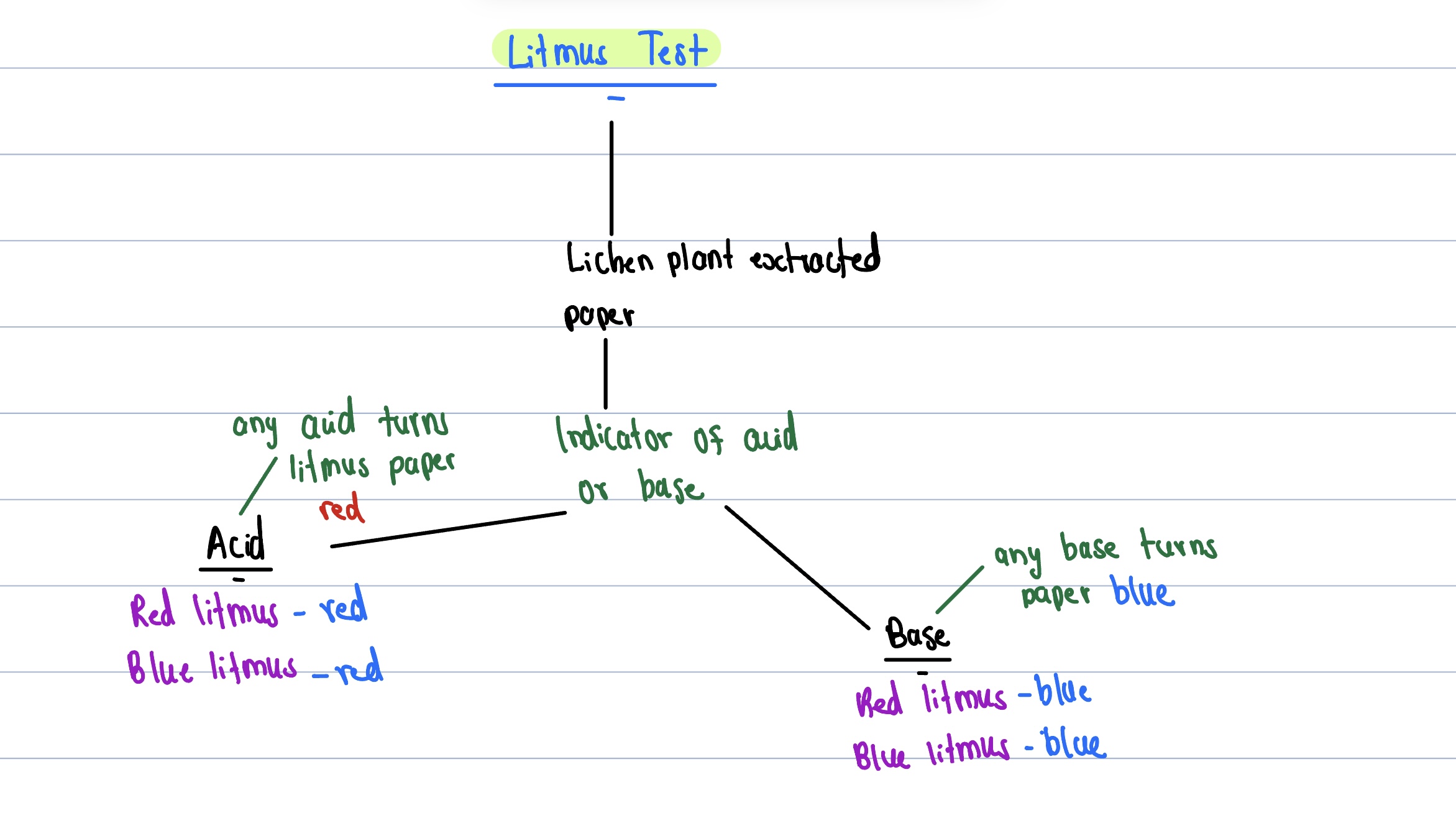
Turns litmus paper red
Tend to be corrosive
Taste Sour
Reacts With Bases
Solutions have low pH
Solution conducts an electrical current - because aqeous solution has free moving hydrogen protons (mobile)
Properties Of Bases
Turns litmus paper blue
Caustic, Slippery
Taste bitter
Reacts with acids
Solutions have pH
Solution conducts electrical current
Litmus Test
Robert Boyle deduced acids based on:
Taste
Action as solvents
How they change the color of vegetable extracts
Soluble bases (alkalis) could reverse the effect of acids
Antoine Lavoisier’s Suggestion
Acid properties due to Prescence of oxygen
Sir Humphrey David’s Discovery
Acidic properties are associated with hydrogen
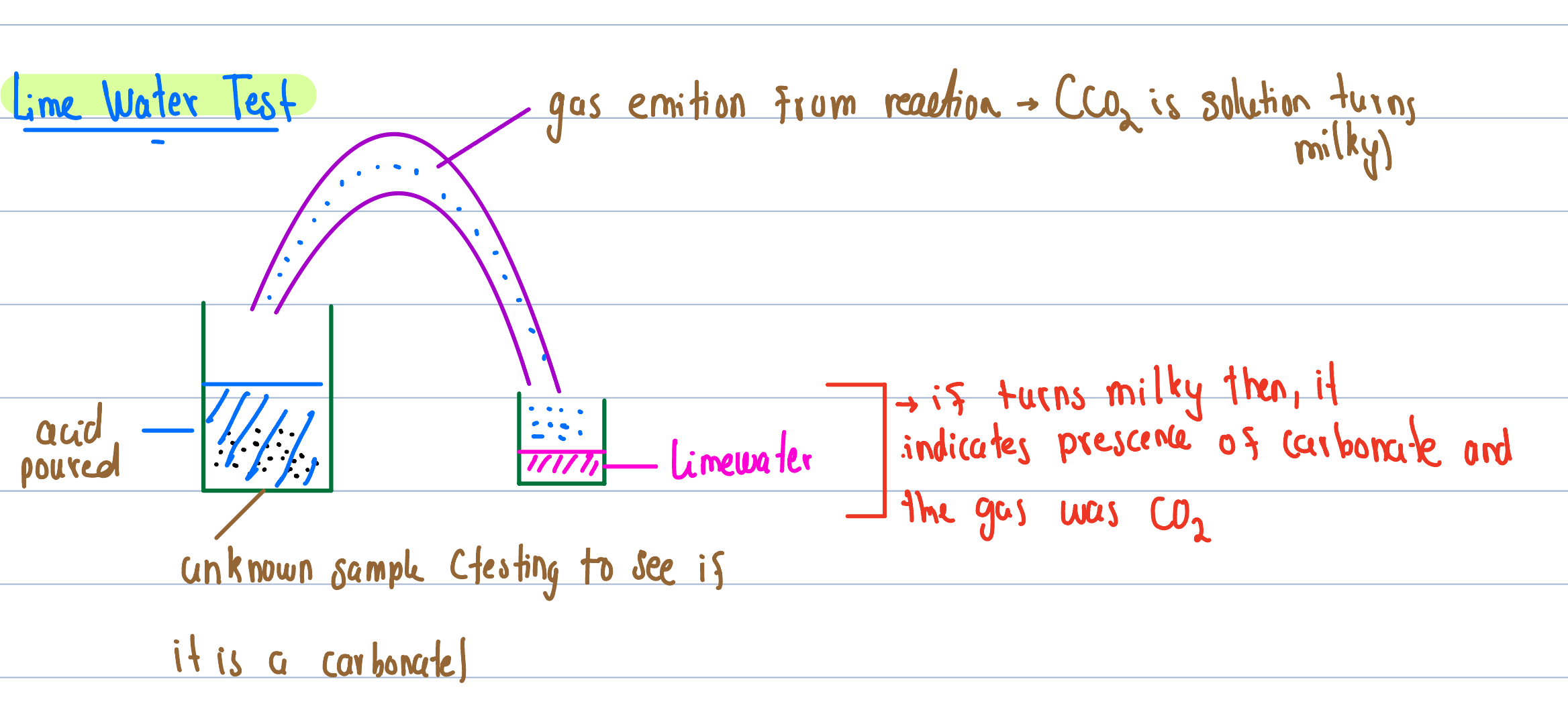
Lime Water Test
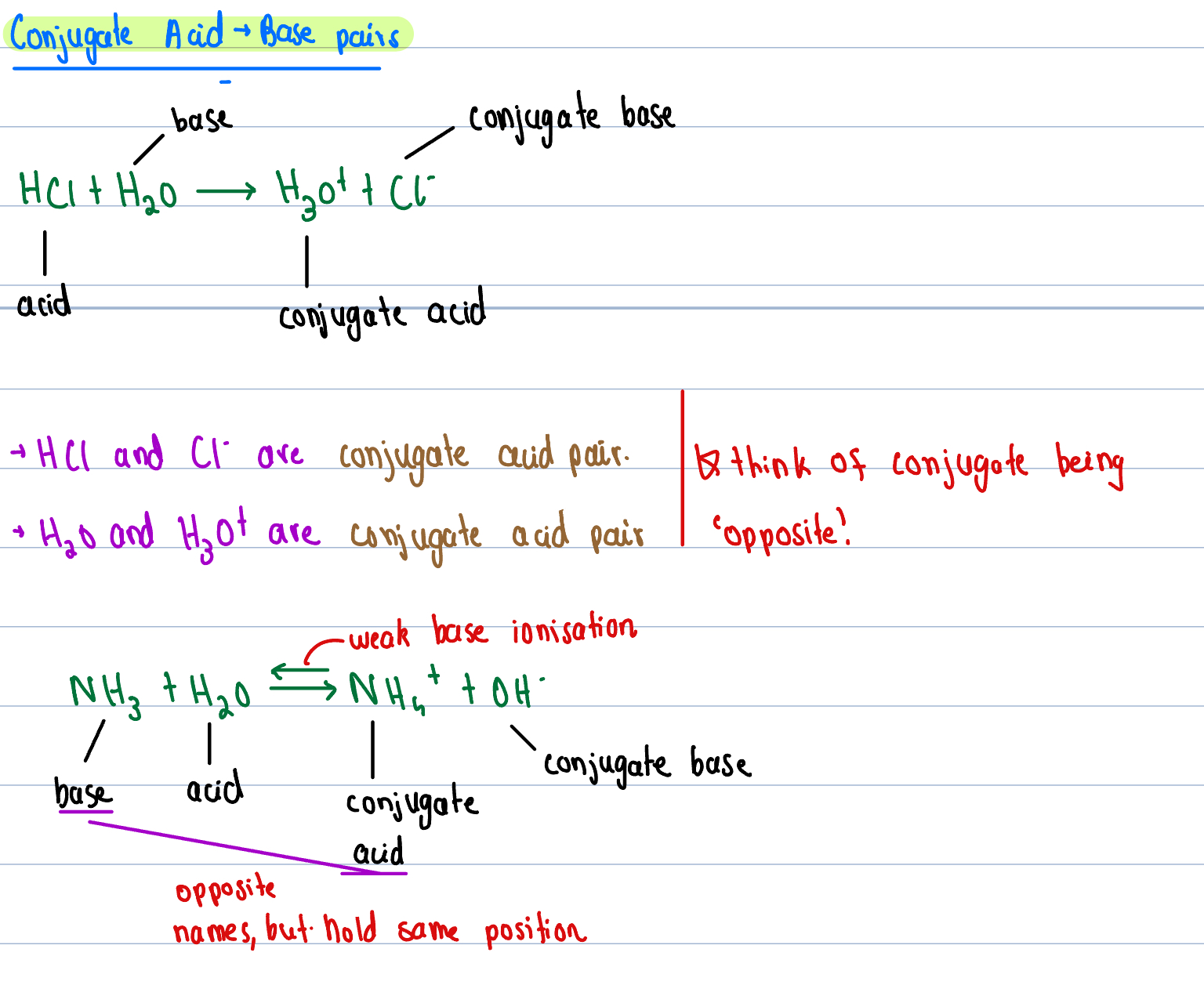
Bronsted-Lowry Theory Of Acids and Bases
When substance donates (H+) proton - acid
When substance receives (H+) proton - base
Conjugate Acid Pairs
Amphiprotic Substances
Substance can receive or donate an electron - must have at least on hydrogen proton
Monoprotic Substances
Can have only one hydrogen that can be donated (eg.HCI or H20)
Polyprotic Acids
Acids that can donate more than one hydrogen atom
Don’t donate all protons at once
Donate protons in steps
Ionization Energy Across Steps
Harder to loose hydrogen protons as steps increase, due to the increase of electrostatic attraction.
Triprotic Acids
Have 3 protons that can be donated (done in three steps)
Diprotic Acids
Have 2 protons (done through 2 steps)
Water in all ionisation reactions
Water is a reactant in all ionization reactions
Why do Amphiprotic substances have a double reversible arrow
They can behave as either a base or an acid meaning that the reaction can happen in both ways.
Can only be straight arrow if the first proton (oly if strong acid)
Other protons are less likely to ionise due to increased electrostatic attraction
Why must Hydrogen be next to a highly electronegative atom to be donated?
It creates a partial positive charge
Enables it to be transferred as a proton easily.
e.g. only a bond with O-H can be donated with acids such as CH3COOH (acidic proton)
What is strength of a acid or base measured by?
By its ability to donate or accept protons
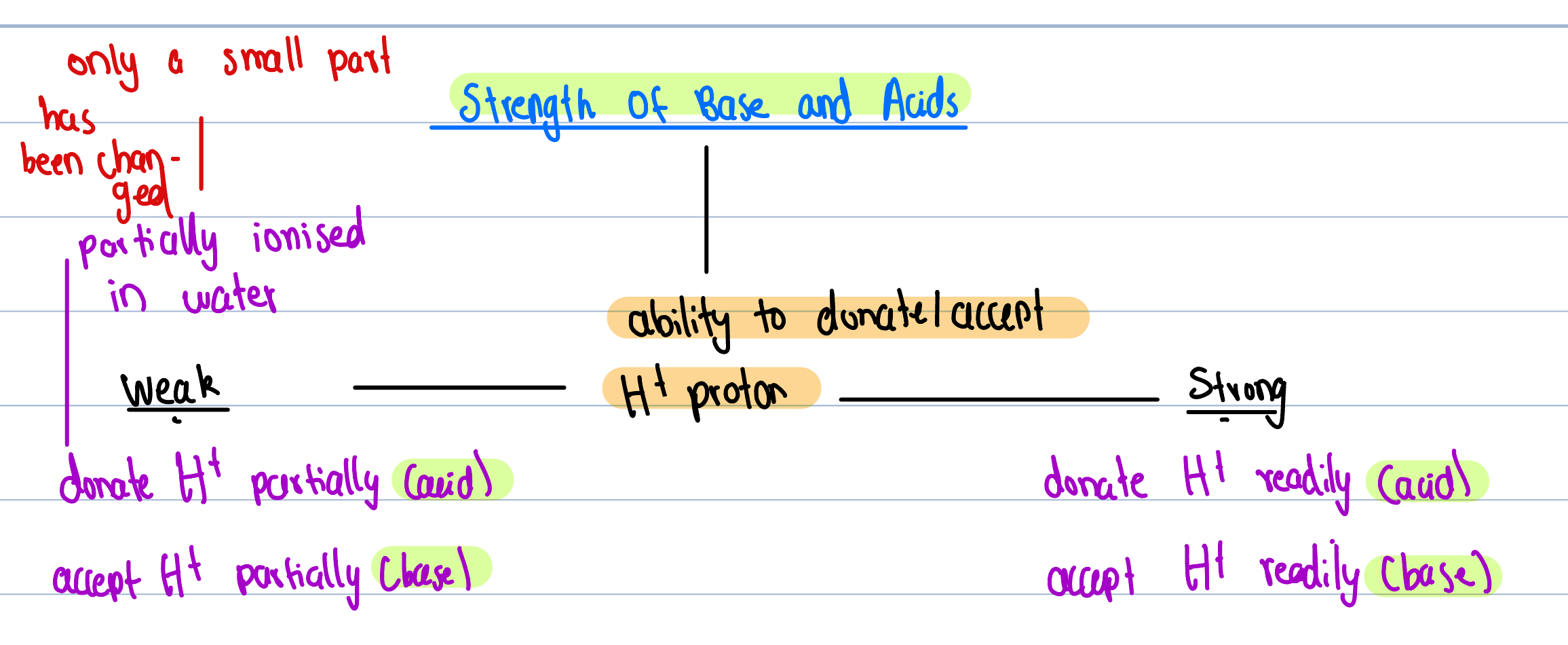
Dissolving into water
Strong acids completely ionize in water
Weak acids partially ionize in water
Weak acids
HCI
H2S04
HN03
Strong Acids
CH3C00H
H2C03
H3PO4
Strong Bases
NaOH
KOH
Ca(OH)2
Weak Bases
NH3
What is concentration?
Measuring “solute” to “solvent” ration
Solute - Solvent ratio low?
Less solute
More solvent
Diluted solution
Solute - Solvent ratio high?
More solute
Less solvent
Concentrated solution
Acid & Base relationship with conjugates
Stronger the acid - weaker the conjugate base
Stronger the base - weaker the conjugate acid
Neutralization Reactions
Acid + metal hydroxide (base) ——- Salt + water
Acid + bicarbonate ——- Salt + C02 + H20
Acid + metal carbonate —— Salt + H20 +C02
Acid + metal hydrogen carbonate —- Salt + H20 + C02
Acid + Reactive Metal ————- Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Oxide ——— Salt + Water
Acid + Ammonia ——- Ammonia Salt (eg. NH4CI)
Neutralization (real life)
Sting of bee (methanoic / formic acid) neutralized by ammonia or lime water
venom of wasp is alkaline - ethanoic acid can be used to treat it
Stomach acid treated with antacid (milk or magnesia)
Harmful bacteria in tooth enamel deteriorate teeth and can be neutralized with a weak base
Dissassociation
Ionic compounds seperate into ions
Water in a reaction
Weak acid and base
Only a small amount reacts
What does “M” stand for?
Concentration of moles per litre
Acidity of water at 25 degrees
[H30+]=[OH-]=10-7M
Hydronium = 10-7M
Hydroxide = 10-7M
They both multiply up to 10-14M (half-half)
![<p>[H<sub>3</sub>0<sup>+</sup>]=[OH<sup>-</sup>]=10<sup>-7</sup>M</p><p>Hydronium = 10<sup>-7</sup>M</p><p>Hydroxide = 10<sup>-7</sup>M</p><p>They both multiply up to 10<sup>-14</sup>M (half-half)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f5221b4e-12d1-494e-ba70-07c83b693963.jpg)
Acid Ionisation
[H30+] > 10-7M - more hydronium ions than hydroxide ions make the solution more acidic
Base Ionisation
[OH-] > 10-7M - more hydroxide ions than hydronium ions make the solution more basic
Neutral
[H30] = [OH-] - Both have 10-7M
Measuring of acidity
pH = -log10[H30+]
[H30+] = 10-pH
Notes on pH
pH decreases as [H30+] increases (more hydronium = more acidic)
Indicators
Litmus - purple dye from lichen plant
Rose petals, blackberry, red cabbage - organic indicators
Converting to moles and finding concentration
n=m/n
C = n/v
n= moles
v = volume
c = concentration
Ocean acidity
Increase in C02 in atmosphere increases ocean acidity
Steps of CO2 entering water
CaCO3(s)+H+(aq)−>Ca2+(aq)+HCO3−(aq)
The more H2C03 (from C02 mixing with H20) the more h+ ions attack the calcium carbonate

Why Is Ocean Acidity Bad
Krill eggs won’t hatch at lower pH (high acidity)
Stops food chain
Stops calcification for coverings of sea animals (decalcification) - acidity in sea water
Impact of Ocean Acidity On Humans
Social, Economic Impacts
Reduce sea life in water
Destroy coastal reefs - reduce tourism and increases erosion on land
Common Acids
Acid | Formula | Strength |
|---|---|---|
Hydrochloric acid | HCl | Strong |
Nitric acid | HNO₃ | Strong |
Sulfuric acid | H₂SO₄ | Strong |
Ethanoic (acetic) acid | CH₃COOH | Weak |
Carbonic acid | H₂CO₃ | Weak |
Phosphoric acid | H₃PO₄ | Weak |
Citric acid | C₆H₈O₇ | Weak |
Hydrofluoric acid | HF | Weak (but corrosive) |
Common Bases
Base | Formula | Strength | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Sodium hydroxide | NaOH | Strong | Soap and detergent production, drain cleaner, paper manufacturing |
Potassium hydroxide | KOH | Strong | Fertilizers, liquid soap, alkaline batteries |
Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)₂ | Strong | Limewater, water treatment, cement and plaster |
Barium hydroxide | Ba(OH)₂ | Strong | Laboratory reagent, sugar refining |
Ammonia | NH₃ | Weak | Fertilizer, cleaning products, refrigeration gas |
Methylamine | CH₃NH₂ | Weak | Chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals |
Sodium carbonate | Na₂CO₃ | Weak | Glass manufacturing, water softening, detergents |
Magnesium hydroxide | Mg(OH)₂ | Weak | Antacids, laxatives, wastewater treatment |
Aluminium hydroxide | Al(OH)₃ | Weak | Antacids, water purification, fire retardants |
Ammonium hydroxide | NH₄OH | Weak | Cleaning products, pH adjustment, chemical manufacturing |
If ph falls or rises based on reaction
Reaction Type | Reaction Example | pH Change | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|
Acid + Metal hydroxide | HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H₂O | Rises (if acid in excess) | H⁺ ions are neutralised by OH⁻ |
Acid + Base (general) | HNO₃ + KOH → KNO₃ + H₂O | Rises | H⁺ removed → less acidic |
Acid + Metal carbonate | HCl + CaCO₃ → CaCl₂ + H₂O + CO₂ | Rises | H⁺ ions react with CO₃²⁻ → acid partially neutralised |
Acid + Metal hydrogen carbonate / Bicarbonate | HNO₃ + NaHCO₃ → NaNO₃ + H₂O + CO₂ | Rises | H⁺ reacts with HCO₃⁻ → pH increases |
Acid + Reactive metal | 2HCl + Zn → ZnCl₂ + H₂ | Slightly rises | H⁺ removed to form H₂ gas |
Acid + Ammonia / Weak base | HCl + NH₃ → NH₄Cl | Rises | NH₃ consumes H⁺ ions → solution less acidic |
Acid + Metal oxide | H₂SO₄ + CuO → CuSO₄ + H₂O | Rises | H⁺ reacts with O²⁻ ions to form water → pH rises |
Real life Neutralization Reactions
1) Hydrochloric Acid (HCI) + Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) -
Mg(OH)₂ + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + 2H₂O
2. Treating acidic soil using lime
Acid: Sulfuric acid (acidic soil often contains H₂SO₄)
Base: Calcium hydroxide or Calcium oxide (lime)
Reaction (with calcium hydroxide):
Ca(OH)₂ + H₂SO₄ → CaSO₄ + 2H₂O
6. Baking soda for bee sting
Acid (from sting): Methanoic acid (formic acid)
Base: Sodium hydrogen carbonate (baking soda)
Reaction:
NaHCO₃ + HCOOH → NaCOOH + CO₂ + H₂O
When and how to use stoichiometry for getting correct concentration
for strong bases - just dissassociate - and find the ratio
for strong acids - include water and balance - find ration
ubstance | Reaction for stoichiometry | Include water as a reactant? | Why? |
|---|---|---|---|
Strong bases (e.g. KOH, NaOH) | KOH→K++OH−\mathrm{KOH \to K^+ + OH^-}KOH→K++OH− | ❌ No | Complete dissociation → directly gives OH⁻ |
Strong diprotic acids (e.g. H₂SO₄) | donates 2 H⁺ in steps | ✅ Yes | Use water to track how many H⁺ (or H₃O⁺) are formed |
Weak acids/bases | equilibrium with water | ✅ Yes | Water donates/accepts protons, affects pH |
Universal Indicator
