22.11 Final Review
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
Binding Energy
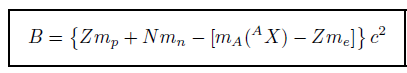
Semi-Empirical Mass Formula (SEMF)

Radius of a Nucleus Estimate
R~R0*A^1/3 where R0=1.25fm
SEMF Volume Term Reasoning
Because nucleons are closely packed and the nuclear force has a short range the Volume force is proportional to A (R³) instead of A*(1-A).
av
15.5 MeV
SEMF Surface Term Reasoning
Correction to the volume term since there are less nuclides to interact with on the surface of the nucleus. Proportional to A^(2/3) (R²)
as
13-18 MeV
SEMF Coulomb Term Reasoning
Comes from the energy of a uniformly charged sphere ~Q²/R —> Q² = e²Z(Z-1)
ac
ac = 0.691
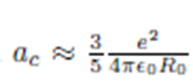
SEMF Symmetry Term Reasoning
Comes from the shell model of the nucleus and Pauli Exclusion Principle. IF you want to add more of one type of nucleon it must be more energetic which lowers the total binding energy. The (N-Z) term is squared because it better matches empirical data.
asym
23 MeV
SEMF Pairing Term Reasoning
Having even-even numbers of nucleons is the most energetically favorable configuration, while odd-odd is the least energetically favorable. Even-odd has no overall effect.
ap
34 MeV
How to find optimal numbers (N, Z, etc.) from the SEMF?
Differentiate with respect to the number of interest.
Q value
Difference in rest masses or kinetic energies
Center of Mass Kinetic Energy
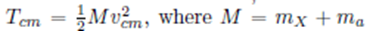
Center of Mass Velocity
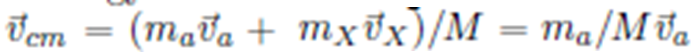
Available Energy
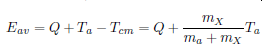
Reaction Condition
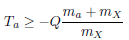
Radioactive Decay
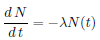
Mean Lifetime
tau = 1/lambda
Half-life
t1/2 = ln(2)/lambda
Activity
A = lambda*N(t)
Chain of Decays
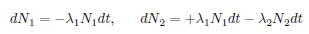
What nuclides is alpha decay observed for?
A > 200
Geiger-Nuttall Rule
log(t1/2) ~ 1/sqrt(Qalpha)
Beta Decay Parabolas
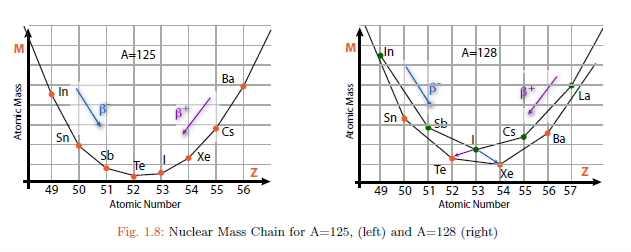
When doing Q-value equations for beta decay…
The mass of electrons matter
Gamma Energies
E = hbar*k*c = hbar * omega_k
Steps of a Quantum Mechanical Experiment
Preparation: determines the probabilities of the various possible outcomes (states)
Measurement: retrieve the value of a particular outcome, in a statistic manner (measurement of observables)
First Axiom of Quantum Mechanics
States: The properties of a quantum system are completely de ned by speci fication of its state vector. The state vector is an element of a complex Hilbert space H called the space of states.
Second Axiom of Quantum Mechanics
Hermitian Operators: With every physical property (energy, position, momentum, angular momentum, ...) there exists an associated linear, Hermitian operator “A” (usually called observable), which acts in the space of states H. The eigenvalues of the operator are the possible values of the physical properties.
Third Axiom of Quantum Mechanics
a. Probability of States (Born Rule): The modulus squared of the inner product of two states gives the probability of finding one state in the other.
b. Probability of Operators and Wave Function Collapse: If A is an observable with eigenvalues a_n and eigenvectors |n>, the probability of obtaining a_n as the outcome of the measurement of A is p(a_n) = |<n|f>|². After the measurement, the system is left in the state projected on the subspace of the eigenvalue a_n.
Fourth Axiom of Quantum Mechanics
The evolution of a closed system is unitary (reversible). The evolution is given by the time-dependent Schrodinger equation.
Momentum operator in position basis
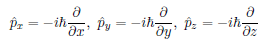
Position operator in momentum basis
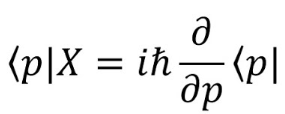
Momentum eigenfunctions and values
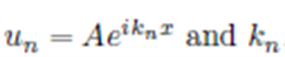
Kinetic energy wavenumber relation
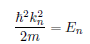
Properties of eigenfunctions
The eigenfunctions of an operator are orthogonal functions
The set of eigenfunctions forms a complete basis (any other vector functions belonging to the same space can be written in terms of the set)
Fourier Transform
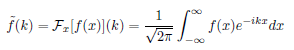
Inverse Fourier Transform
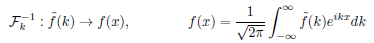
Procedure for calculating all of the probabilities of each outcome for each observable
Find the eigenfunctions of the observable’s operator
Find the probability amplitude of the wavefunction with respect to the eigenfunction of the desired eigen-value outcome
The probability of obtaining the given eigenvalue in the measurement is the probability amplitude modulus square
Position probability function
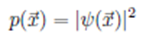
Momentum eigenfunctions…
cannot be normalized, they are a Fourier Transform of the position eigenfunction
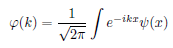
Probability flux
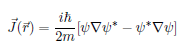
Conservation Equation
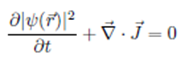
Free particle flux
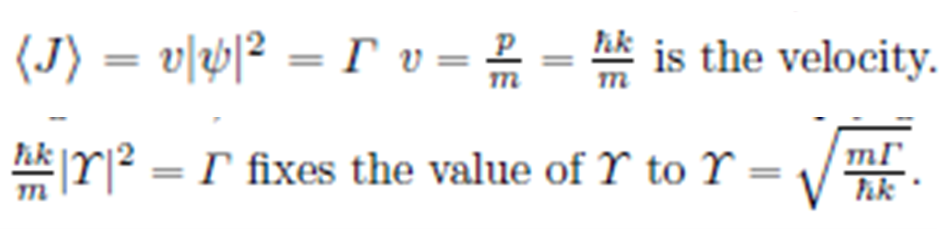
Wavefunction expectation value
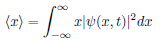
Operator Expectation Value
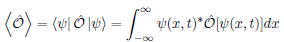
Position and Momentum Commutator
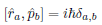
Commutator Properties
Any commutator commutes with scalars [A, a] = 0
[A, BC] = [A,B]C + B[A,C] and [AB,C] = A[B,C] + [A,C]B
Any operator commutes with itself [A,A] = 0 and with any power or functions of itself
Energy eigenfunctions are also…
momentum eigenfunctions
Eigenvalue degeneracy
Energy eigenfunctions are degenerate, there are two eigenfunctions associated with the same eigenvalue. The degeneracy is broken by measuring the momentum eigenvalue.
Complete Set of Commuting Observables
A set of operators that completely define the state. The eigenvalues are called good quantum numbers.
Time Dependent Schrodinger Equation
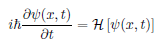
Time Independent Schrodinger Equation
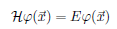
Position representation Hamiltonian
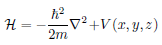
Total wavefunction
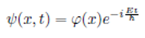
General solution of Schrodinger equation
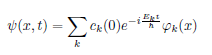
Energy eigenfunctions
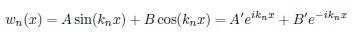
Finite Potential Wall Boundary Conditions
YI(0) = YII(0) Y’I(0) = Y’II(0)
Finite Potential Wall Coefficients E>V and E<V
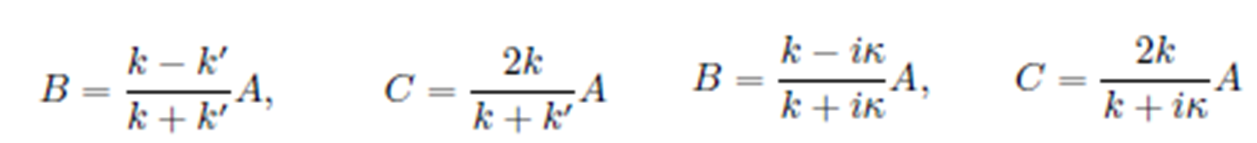
Tunneling probability
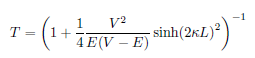
The initial energy in an alpha decay is equal to
the Q value of the reaction
Size of alpha decay potential well
R = R’ + R_alpha = R_0*((A-4)^1/3 + 4^1/3)
Alpha coulomb potential height
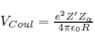
Alpha decay rate
(Probability of tunneling) x (Frequency at which the initial nuclei and alpha particle are found separately)
Alpha separation frequency
f = v_in/R = (velocity of particles in the nucleus)/(Potential well radius)
v_in
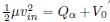
R_C
Solve for Q_alpha = V_C
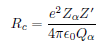
Alpha decay rate
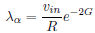
Gamow factor (approx)
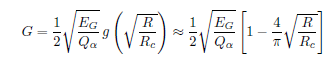
Gamow energy
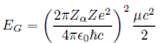
Why are alpha decay more likely than spontaneous fission?
The Coulomb barrier becomes too large for other types of decay even though the Q-value is much larger
Infinite well boundary conditions
YI(0) = YII(0) (no derivative)
Infinite well wavenumber values
k_n = n*pi/L
Infinite well eigenfunction
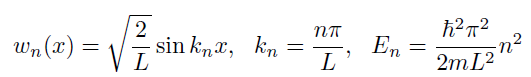
Finite well odd solution constraints

Harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian
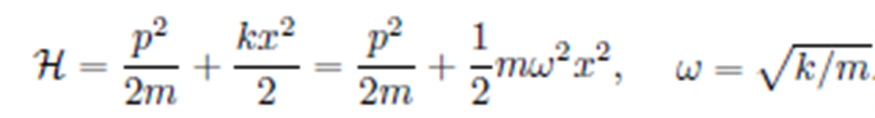
Annihilation and creation operators
a|n> = sqrt(n)|n-1> a*|n> = sqrt(n+1)|n+1>
Number operator
N = a*a
Spherical coordinates
x = r*sin(t)*cos(p)
y = r*sin(t)*sin(p)
z = r*cos(t)
3D SE Radial
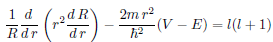
3D SE Angular
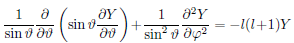
Angular Momentum Commutators
[Li, Lj] = i*hbar*Lk
Angular momentum uncertainty relation
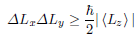
L² eigenvalue
L² |l,m> = hbar²l(l+1)|l,m>
Lz eigenvalue
Lz|l,m> = m*hbar|l,m>
Range of m values
-l, -l + 1, …, l - 1, l
<L²> in terms of Lz, Ly, and Lx
<L²> = <L²x> + <L²y> + <L²z>
Uncoupled representation
|l1, m1, l2, m2>
Coupled representation
|l, m, l1, l2>
Uncoupled representation to coupled representation
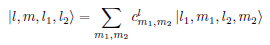
Angular momentum degeneracy
D = 2*l + 1
Total angular momentum bounds
|l1 - l2| < l < l1 + l2
u(r) SE equation
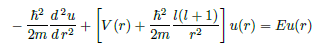
3D Potential well effective potential
V(r) + centrifugal potential
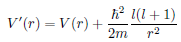
Fermions
Particles with half-integer spin that cannot occupy identical states
Bosons
Particles with integer spin that can occupy identical states
Particles subject to the nuclear force
Protons and neutrons