Ela Practice Grammar Final
4.2(6)
Card Sorting
1/45
Last updated 12:18 AM on 1/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
In a common English sentence, does the predicate usually come before or after the subject?
%%***Most of the time*** the verb follows the subject%%. however, there are some examples where it doesn’t. Page 501
2
New cards
Is this sentence expressed or understood?
“Stop!“
“Stop!“
This is %%**expressed**%% because most of the sentence structure is gone, and you have to imply it through *expression*. This is also known as an %%**imperative**%% sentence.
3
New cards
What type of sentence is this: “Please be quiet.“
This is a %%*command*%%, but it doesn’t have a subject so it is a %%**imperative**%% sentence.
4
New cards
Which one of the sentences are inverted?
\
* “I like coffee, and Mary likes tea.“
* “There is no place like home.”
* “Who ate all the ice cream?“
* “Come here now!“
\
* “I like coffee, and Mary likes tea.“
* “There is no place like home.”
* “Who ate all the ice cream?“
* “Come here now!“
**“There** __**is**__ **no** __**place**__ **like home.”**
Explanation: Although *there* might look look like the subject, its actually acting as more of an adverb (however it is useless in the sentence). You could re-structure the sentence to be “No place is like home.“
The word *there* is used in one of the few times the subject comes after the verb
Explanation: Although *there* might look look like the subject, its actually acting as more of an adverb (however it is useless in the sentence). You could re-structure the sentence to be “No place is like home.“
The word *there* is used in one of the few times the subject comes after the verb
5
New cards
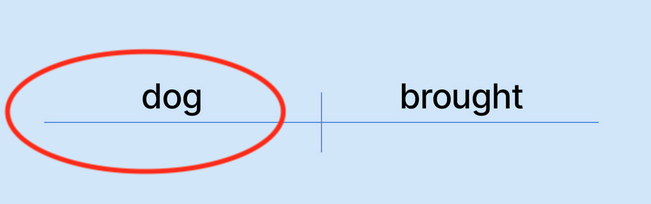
What is a simple subject?
It is **t**%%**he subject (noun)**%% that is performing the verb in the sentence. It has %%**no modifiers on it**%%, so no adjectives or adverbs.
6
New cards
Find the simple subject:
“The tired, elderly man trudged down the street.“
“The tired, elderly man trudged down the street.“
“The tired, elderly %%__**man**__%% trudged down the street.”
* Here we don’t include “The“, “tired“, or “elderly“ in the simple subject.
* Here we don’t include “The“, “tired“, or “elderly“ in the simple subject.
7
New cards
What is a complete subject?
The complete subject %%**is the subject (noun)**%% that is performing the action, BUT %%**it has all related modifiers on it.**%%
8
New cards
Find the complete subject:
“Our favorite movie from our childhood was playing on TV.“
“Our favorite movie from our childhood was playing on TV.“
“%%**Our favorite** __**movie**__ **from our childhood**%% was playing on TV.”
* All the modifiers are included onto “movie“ in this case, even the prepositional phrase. The simple subject is underlined here.
* All the modifiers are included onto “movie“ in this case, even the prepositional phrase. The simple subject is underlined here.
9
New cards
What is the simple predicate?
The simple predicate is **just the verb** without any modifiers on it. So we would exclude any adverbs that would be related to it. %%Note: A verb phrase can still be considered as simple predicate. Example: “had done“%%
10
New cards
Find the simple predicate:
“Fred Mosby will be my new tutor.“
“Fred Mosby will be my new tutor.“
“Fred Mosby %%**will be**%% my new tutor.”
* This is the simple predicate here even because there are no modifiers attached to it. However, the helping verb is also included because it is part of the *verb phrase*.
* This is the simple predicate here even because there are no modifiers attached to it. However, the helping verb is also included because it is part of the *verb phrase*.
11
New cards
What is a complete predicate?
The complete predicate is %%**the verb that has** **all modifiers**%% attached to it, and this can include adverbs, prepositional phrases, direct and indirect objects, etc.
12
New cards
Find the complete predicate:
“An early form of the bicycle was invented in France in 1690.“
“An early form of the bicycle was invented in France in 1690.“
“An early form of the bicycle %%__**was**__ **invented in France in 1690.**%%“
* This is the complete predicate because its starts with the main verb “was“, and then has all attached modifiers: a direct object, and two prepositional phrases.
* This is the complete predicate because its starts with the main verb “was“, and then has all attached modifiers: a direct object, and two prepositional phrases.
13
New cards
What is a compound subject?
A c**ompound** %%**subject is 2 or more nouns**%% **acting as the subject.** The %%compound subject includes ALL modifiers%% and conjunctions, ==*unless it is a simple compound subject.*==
14
New cards
Find the compound subject:
“The large door and small windows are broken.“
“The large door and small windows are broken.“
“%%**The large** __**door**__ **and small** __**windows**__%% are broken.”
* This would be the compound subject because it has both subjects, “door” and “windows”, and all the modifiers. Here there are 2 adjectives, an article, and a conjunction.
* This would be the compound subject because it has both subjects, “door” and “windows”, and all the modifiers. Here there are 2 adjectives, an article, and a conjunction.
15
New cards
What is a compound predicate?
A compound predicate is %%**2 or more verbs**%% that form the predicate. %%**They would include all modifiers**%% including prepositional phrases, adverbs, and conjunctions; ==Unless it is a simple compound predicate.==
16
New cards
Find the compound predicate:
“The cat chased and caught the moose.“ (not mouse)
“The cat chased and caught the moose.“ (not mouse)
“The cat %%__**chased**__ **and** __**caught**__%% the moose.“
* In this case the compound predicate is this because we have included both verbs, as well as the one modifier: the conjunction.
* In this case the compound predicate is this because we have included both verbs, as well as the one modifier: the conjunction.
17
New cards
What is a direct object?
%%The direct object is the word (or phrase) that receives the action from the verb.%% This could be seen in a sentence as: *Subject, Verb, Direct Object.*
\
Don’t get this confused: the subject does the action, but the direct object receives the action.
\
Don’t get this confused: the subject does the action, but the direct object receives the action.
18
New cards
Find the direct object:
“The students ate pizza.“
“The students ate pizza.“
“The students ate %%__pizza__%%.“
* In this sentence, the word students would be the subject, and they ate. What did they eat? They ate pizza.
* In this sentence, the word students would be the subject, and they ate. What did they eat? They ate pizza.
19
New cards
What is an indirect object?
%%An indirect object is the object that receives the direct object, its usually not the main object.%%
For example: “The teachers gave the __students__ pizza.“
* in this sentence the subject is teacher, which gives pizza (pizza is the direct object). The students are the one receiving the pizza, so “students” is the indirect object because it receives the direct Object (Pizza).
For example: “The teachers gave the __students__ pizza.“
* in this sentence the subject is teacher, which gives pizza (pizza is the direct object). The students are the one receiving the pizza, so “students” is the indirect object because it receives the direct Object (Pizza).
20
New cards
What is an object complement?
Object complements are kinda weird: %%**it’s the noun, pronoun, or adjective that follows a direct object to rename it OR say what state it’s in.**%%
* Usually, verbs like “To make“, “to create“, “to name“, or “to call“ have object complements in the sentence. (Not always tho) Example: “To call you __stupid.__“
* So in “To paint something __purple__.“
* “Something” is the direct object and “purple“ is the object complement because it shows what state it’s in (purple state). It is also an adjective.
%%When looking for an object complement, see if any words after the direct object change its state or name: Usually in the form of adjectives.%%
* Usually, verbs like “To make“, “to create“, “to name“, or “to call“ have object complements in the sentence. (Not always tho) Example: “To call you __stupid.__“
* So in “To paint something __purple__.“
* “Something” is the direct object and “purple“ is the object complement because it shows what state it’s in (purple state). It is also an adjective.
%%When looking for an object complement, see if any words after the direct object change its state or name: Usually in the form of adjectives.%%
21
New cards
What is a subject complement?
A subject complement is %%**a word (or phrase) that follows a linking verb and identifies or describes the subject.**%% ==**The object complement contains the predicate adjective and nominative.**== A subject complement can either be an *adjective, a noun, or a pronoun.*
* Example: “That pie looks __burnt to a crisp.__“
* Here the subject complement is “burnt to a crisp“, which is preceded by the linking verb “looks“. In this case, the subject complement is acting as an adjective.
* Example: “That pie looks __burnt to a crisp.__“
* Here the subject complement is “burnt to a crisp“, which is preceded by the linking verb “looks“. In this case, the subject complement is acting as an adjective.
22
New cards
What is a predicate adjective?
A predicate adjective is an %%**adjective usually describing the subject**%%, BUT it %%**comes after the predicate**%%. The predicate is 99% of the time going to *be a* %%*linking verb*%%*.* A linking verb could be: “was“, “is“, “looks”, “become“, “been“, etc. ==Don’t include any conjunctions if there are multiple predicate adjectives.==
* For example: “The cake was __sweet__.“
* In this sentence, the predicate adjective is “sweet“, because it is describing the subject: “cake“. The linking verb “was“ is used before the adjective.
* For example: “The cake was __sweet__.“
* In this sentence, the predicate adjective is “sweet“, because it is describing the subject: “cake“. The linking verb “was“ is used before the adjective.
23
New cards
What is a predicate *nominative*?
A predicate *nominative* (predicate noun) %%**renames the subject after the linking verb**%%, and it is %%**always a noun or pronoun**%%**.** This is like the predicate adjective, but with nouns. **Include any and all modifiers onto the nominative*
* For example: “John was __a nerd.__“
* In this case, nerd would be the noun that acts as the predicate nominative, and the article “a“ is included because it modifies “nerd“. There is a linking verb “was“, and it links the nominative to the subject.
* For example: “John was __a nerd.__“
* In this case, nerd would be the noun that acts as the predicate nominative, and the article “a“ is included because it modifies “nerd“. There is a linking verb “was“, and it links the nominative to the subject.
24
New cards
What is a prepositional phrase?
A prepositional phrase is %%**multiple words that start with a preposition**%%, and then %%**has an object**%% of the preposition along with %%**any modifiers.**%% \*There *must be* at least the preposition and it’s object.
* Example: “He arrived __on time.__“
* The preposition in this sentence is “on“, and the object is “time“. There are no modifiers here, so we don’t add anything.
* Example: “He arrived __on time.__“
* The preposition in this sentence is “on“, and the object is “time“. There are no modifiers here, so we don’t add anything.
25
New cards
What is an appositive phrase?
An appositive phrase is %%**a noun (or noun phrase) that gives more information to another noun/phrase.**%% It’s just extra info, and ==**can be essential or nonessential.**==
* Example: “Hermione Granger, __a witch at Hogwarts School__, is accomplished at spells“
* In this sentence, the appositive phrase is underlined where the main noun is “which“, followed by a prepositional phrase and an article. In this case, it is nonessential because it can be removed and the sentence will still make sense.
* Example: “Hermione Granger, __a witch at Hogwarts School__, is accomplished at spells“
* In this sentence, the appositive phrase is underlined where the main noun is “which“, followed by a prepositional phrase and an article. In this case, it is nonessential because it can be removed and the sentence will still make sense.
26
New cards
What is a participle phrase?
A participle phrase is %%**a group of words that start with a participle**%%, which is a word usually ending in “-ing” or “-ed” (there are also words like “gone“ which is a participle). In these phrases, %%**include any and all modifiers**%%. **You can think of the participle as an adjective phrase that describes a noun.*
* Example: “We tried to avoid the person __wearing a clown costume.__“
* In this sentence, the word “wearing“ is our participle, and it is followed by its object and modifiers: “costume“ and “a” + “clown“. This whole phrase just describes “person“.
* Example: “We tried to avoid the person __wearing a clown costume.__“
* In this sentence, the word “wearing“ is our participle, and it is followed by its object and modifiers: “costume“ and “a” + “clown“. This whole phrase just describes “person“.
27
New cards
What is a gerund?
A gerund is a %%**verb that acts as a noun**%% in a sentence, and it %%**usually ends in “-ing“**%%. Because it acts as a noun, a gerund can be the subject, direct object, indirect object, or object of the preposition. \*==Don’t add any modifiers to a gerund, unless it comes in a phrase (prepositional or gerund phrase).==
* Example: “I hope to set a new record in __swimming__.“
* “Swimming” is the gerund, and it is acting as the object of the preposition in the prepositional phrase: “in swimming“.
* Example: “I hope to set a new record in __swimming__.“
* “Swimming” is the gerund, and it is acting as the object of the preposition in the prepositional phrase: “in swimming“.
28
New cards
What is an infinitive?
Infinitives are %%**verbs that act as a noun, adjectives, or an adverb**%%. Infinitives can also act as direct or indirect objects. They are **formed when the word “to“ is in front of the base verb.**%% There are also infinitive phrases, which have all modifiers added on: “to run quickly“.
* Example: “I want __to go home__.“
* Here, the root verb is “go“, with to being added in front of it, forming the infinitive. In this case, the infinitive acts as the direct object.
* Example: “I want __to go home__.“
* Here, the root verb is “go“, with to being added in front of it, forming the infinitive. In this case, the infinitive acts as the direct object.
29
New cards
What is the main clause?
The %%main clause is the independent clause%%, a group of words that contains the subject and predicate of the sentence. A main clause forms a complete sentence if it stood on its own.
*
*
*
*
30
New cards
What is a subordinate clause?
The subordinate clause(s) is a clause that can’t stand by itself, and are dependent on the main clause. They don’t always have a direct subject or predicate.
* “*I went to bed* __*after brushing my teeth.*__“
* The underlined portion of the sentence can’t stand by itself, and thus it is dependent. In this case, the clause is a propositional phrase.
* “*I went to bed* __*after brushing my teeth.*__“
* The underlined portion of the sentence can’t stand by itself, and thus it is dependent. In this case, the clause is a propositional phrase.
31
New cards
What is the noun clause?
A %%noun phrase is a group of words that start with a noun/pronoun%%, and it includes all the modifiers for the noun. Modifiers for noun phrases can include prepositional phrases, adjectives, articles, adverbs, etc.
* “__The__ __**lawyer**__ __with the big nose__ ate cheese.“
* In this sentence, the noun is “lawyer“, with the remaining words being modifiers. There is an article and a prepositional phrase.
* \*As you can see, we didn’t include the verb or direct object in the noun phrase.
* “__The__ __**lawyer**__ __with the big nose__ ate cheese.“
* In this sentence, the noun is “lawyer“, with the remaining words being modifiers. There is an article and a prepositional phrase.
* \*As you can see, we didn’t include the verb or direct object in the noun phrase.
32
New cards
What is the adverb clause?
An adverb phrase is a dependent clause that modifies a verb, adverb, or adjective. %%The adverb clause just acts as an adverb.%%
* Example: “He bakes cakes __before he leaves for work every Sunday__.“
* The underlined portion is modifying the verb “bakes“, so it is acting as an adverb. We can also see that it can’t stand on its own, because it starts with “before“.
* Example: “He bakes cakes __before he leaves for work every Sunday__.“
* The underlined portion is modifying the verb “bakes“, so it is acting as an adverb. We can also see that it can’t stand on its own, because it starts with “before“.
33
New cards
What is an adjective clause?
An %%adjective clause is a dependent clause that acts like an adjective:%% it provides more information on a noun or pronoun. There are 2 categories: essential and non-essential.
* %%Essential:%% If you took out the clause, the sentence **WILL NOT** make sense.
* “The man __who left his wallet__ is coming back for it.“
* The underlined portion is essential because without it, the word “it“ would have no context, and so the sentence wouldn’t make sense. The clause here is also modifying the noun “man“, so we know it is an adjective clause.
* %%Non-Essential%%: If you took out the clause, the sentence **WILL** make sense.
* “Lisa, __who takes math class with Billy__, is fluent in French.“
* This is a non-essential clause because if we take it out, the sentence still makes sense: no context is lost. The underlined portion is also modifying the noun “Lisa“, so we know it is an adjective clause.
* %%Essential:%% If you took out the clause, the sentence **WILL NOT** make sense.
* “The man __who left his wallet__ is coming back for it.“
* The underlined portion is essential because without it, the word “it“ would have no context, and so the sentence wouldn’t make sense. The clause here is also modifying the noun “man“, so we know it is an adjective clause.
* %%Non-Essential%%: If you took out the clause, the sentence **WILL** make sense.
* “Lisa, __who takes math class with Billy__, is fluent in French.“
* This is a non-essential clause because if we take it out, the sentence still makes sense: no context is lost. The underlined portion is also modifying the noun “Lisa“, so we know it is an adjective clause.
34
New cards
What is a simple sentence?
A simple sentence is %%just a subject and a predicate%%, and it is an independent thought that can stand on its own.
* A simple sentence does NOT contain a dependent or subordinate clause, it is ONLY the main clause
* A simple sentence does NOT contain a dependent or subordinate clause, it is ONLY the main clause
35
New cards
What is a compound sentence?
A compound sentence is %%a sentence that contains 2 or more INDEPENDENT clauses, joined by a conjunction or a semicolon.%%
* A compound sentence is basically just 2 simple sentences joined together.
* A compound sentence is basically just 2 simple sentences joined together.
36
New cards
What is a complex sentence?
A complex sentence is a sentence with one independent (main), and one or more dependent (subordinate) clauses.
* When the dependent clause is first in the sentence, then only commas will be used.
* Other complex sentences are conjoined with subordinate conjunctions: “when“, “how“, “if“
* When the dependent clause is first in the sentence, then only commas will be used.
* Other complex sentences are conjoined with subordinate conjunctions: “when“, “how“, “if“
37
New cards
What is a Compound-Complex sentence?
A compound-complex sentence has at least 3 separate clauses: 2 independent, and at least one dependent.
* This sentence is formed by conjoining a compound sentence and a complex sentence, usually with a coordinating conjunction
* This sentence is formed by conjoining a compound sentence and a complex sentence, usually with a coordinating conjunction
38
New cards
What are the 3 types of verbs?
There are 3 types of verbs:
* Action Verbs
* Linking Verbs
* Helping Verbs
* Action Verbs
* Linking Verbs
* Helping Verbs
39
New cards
What is an action verb?
%%Action Verbs: Express action or possession%%, 2 types
* **Transitive:** Has a direct object that it is affecting
* “Bryan __raises__ his hand.“
* “Raises“ is the verb, and the direct object is “hand“, so the verb must be transitive.
\
* **Intransitive:** Sometimes has indirect objects, or no objects. Name the object to (or for) whom the action was done to.
* “Bilbo __gave__ Sid the pencil.“
* The verb here is “gave”, with “Sid“ being the indirect object.
* (To whom did Bilbo give the pencil? to Sid)
* **Transitive:** Has a direct object that it is affecting
* “Bryan __raises__ his hand.“
* “Raises“ is the verb, and the direct object is “hand“, so the verb must be transitive.
\
* **Intransitive:** Sometimes has indirect objects, or no objects. Name the object to (or for) whom the action was done to.
* “Bilbo __gave__ Sid the pencil.“
* The verb here is “gave”, with “Sid“ being the indirect object.
* (To whom did Bilbo give the pencil? to Sid)
40
New cards
What is a linking verb?
%%**A linking verb connects the subject of the sentence to the subject complement**%% (renames or describes the subject). *Linking verbs are usually: “am, are, is, was, were, become, seem, etc.”*
* “The octopus __seemed__ happy.“
* “Seemed“ is the linking verb, and happy is the subject complement because it describes “the octopus“.
* “The octopus __seemed__ happy.“
* “Seemed“ is the linking verb, and happy is the subject complement because it describes “the octopus“.
41
New cards
What is a helping verb?
%%**Helping verbs are used before action or linking verbs**%% to add additional info about %%**possibility**%% (can, could, etc.) or %%**time**%% (was, did, has, etc). A main verb + a helping verb is a verb phrase.
* “Jamie __is__ going to Ohio.“
* “is“ is the helping verb, and “going“ is the main verb. The 2 of them together combine into the verb phrase.
* “Jamie __is__ going to Ohio.“
* “is“ is the helping verb, and “going“ is the main verb. The 2 of them together combine into the verb phrase.
42
New cards
What are the types of nouns?
There are 3 different types of nouns, and they can all be either plural or singular, as well as common or proper:
\
* Abstract noun: A noun that **CANNOT** be physically seen or felt
* “Emotion” “Power” “Justice”
* Concrete noun: A noun that **CAN** be physically seen or felt
* “ Computer” “Book” “Pencil“
* Collective noun: A noun that refers to a group of people or things
* “school” “army” ”team”
\
\
* Singular noun: A noun that refers to a single object
* “Heart” ”Room” ”Suit”
* Plural noun: A noun that refers to more than one item
* “Hearts” “Rooms” ”Suits“
\
\
* Common noun: A noun that **IS** **NOT** a specific name of a place, person, or thing
* “House” ”Life” ”Race”
* Proper noun: A noun that **IS** the name of a person, place, or thing
* “George Washington” “Dallas” “The Nile River“
\
* Abstract noun: A noun that **CANNOT** be physically seen or felt
* “Emotion” “Power” “Justice”
* Concrete noun: A noun that **CAN** be physically seen or felt
* “ Computer” “Book” “Pencil“
* Collective noun: A noun that refers to a group of people or things
* “school” “army” ”team”
\
\
* Singular noun: A noun that refers to a single object
* “Heart” ”Room” ”Suit”
* Plural noun: A noun that refers to more than one item
* “Hearts” “Rooms” ”Suits“
\
\
* Common noun: A noun that **IS** **NOT** a specific name of a place, person, or thing
* “House” ”Life” ”Race”
* Proper noun: A noun that **IS** the name of a person, place, or thing
* “George Washington” “Dallas” “The Nile River“
43
New cards
What are the types of pronouns?
There are a lot of types of pronouns:
* Personal pronoun: Refers to a person or thing
* “I” “Me” “You“ “He“ “She“
* Possessive pronoun: Shows possession over something
* “My” “Mine” “Yours“
* Interrogative pronoun: Starts a question
* “Who…?” ”What…?” ”Why…?” ”Which…?“
* Relative pronoun: Starts a subordinate (dependent) clause
* “That…” “Whoever…” “Which…“
* Indefinite pronoun: Refers to a person or thing in a very general way, not very specific
* “Everyone” ”Enough” ”Another“
* Reflexive pronoun: a pronoun that refers back to another noun or pronoun
* Example: “He saw __himself__ in the mirror”
* Intensive pronoun: a reflexive pronoun but it is right after the noun or pronoun
* Example: “He __himself__ ate the cake”
* Personal pronoun: Refers to a person or thing
* “I” “Me” “You“ “He“ “She“
* Possessive pronoun: Shows possession over something
* “My” “Mine” “Yours“
* Interrogative pronoun: Starts a question
* “Who…?” ”What…?” ”Why…?” ”Which…?“
* Relative pronoun: Starts a subordinate (dependent) clause
* “That…” “Whoever…” “Which…“
* Indefinite pronoun: Refers to a person or thing in a very general way, not very specific
* “Everyone” ”Enough” ”Another“
* Reflexive pronoun: a pronoun that refers back to another noun or pronoun
* Example: “He saw __himself__ in the mirror”
* Intensive pronoun: a reflexive pronoun but it is right after the noun or pronoun
* Example: “He __himself__ ate the cake”
44
New cards
What are the types of adjectives?
Adjectives have 3 levels, and can either be regular adjectives or proper adjectives:
\
* Positive adjective: The first adjective level
* “Light, Funny, Weird”
* Comparative adjective: The second level
* “'Lighter, Funnier, Weirder“
* Superlative adjective: The final level
* “Lightest, Funniest, Weirdest“
\
* Proper Adjective: A adjective directly used to describe a name
* “Dutch, Roman, Navajo“
\
* Positive adjective: The first adjective level
* “Light, Funny, Weird”
* Comparative adjective: The second level
* “'Lighter, Funnier, Weirder“
* Superlative adjective: The final level
* “Lightest, Funniest, Weirdest“
\
* Proper Adjective: A adjective directly used to describe a name
* “Dutch, Roman, Navajo“
45
New cards
What are the types of conjunctions?
There are 3 conjunction types:
\
* Coordinating conjunction: Joins groups with equal value, or FANBOYS
* **F**or
* **A**nd
* **N**or
* **B**ut
* **O**r
* **Y**et
* **S**o
* Correlative conjunction: Two words that work in a pair to join a group of equal value to another. They don’t have to be next to each other
* “both...and” “either...or” ”neither...nor.
* Subordinating conjunction: A conjunction that joins a group of words that directly depends on another
* “Because” ”After” ”Although“
\
* Coordinating conjunction: Joins groups with equal value, or FANBOYS
* **F**or
* **A**nd
* **N**or
* **B**ut
* **O**r
* **Y**et
* **S**o
* Correlative conjunction: Two words that work in a pair to join a group of equal value to another. They don’t have to be next to each other
* “both...and” “either...or” ”neither...nor.
* Subordinating conjunction: A conjunction that joins a group of words that directly depends on another
* “Because” ”After” ”Although“
46
New cards
What is a run on sentence?
A run on sentence is a sentence when 2 complete sentences are combined without a conjunction or proper punctuation (period or semicolon). ==*A long sentence is NOT always the run on sentence, they can be short too.==
* ~~“I have a big test tomorrow I can’t go out.”~~ - This is incorrect because there is nothing to join the 2 independent sentences.
* “I have a big test tomorrow__, so__ I can’t go out“ - This is correct because now there is a conjunction and a properly placed comma.
* ~~“I have a big test tomorrow I can’t go out.”~~ - This is incorrect because there is nothing to join the 2 independent sentences.
* “I have a big test tomorrow__, so__ I can’t go out“ - This is correct because now there is a conjunction and a properly placed comma.