Superficial Heat
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are the indications for the use of superficial heat in the clinical setting?
Promote relaxation
Pain relief
Increased blood flow
Facilitate tissue healing
Decrease muscle spasm
Decrease tissue tightness
Decrease joint stiffness
Prepare tissues for exercise
Which stages/phases of healing/rehabilitation should superficial heat be utilized?
Sub-acute or chronic stages of healing
Phases II-III of rehabilitation
Superficial heat is used to heat structures of what depth?
1-3 cm of depth
Deep heat is used to heat structures of what depth?
1-5 cm of depth (like capsules)
What temperature should superficial heat be?
104°F-113°F
What systemic changes occur in the body as a result of immersion into a hot water bath? (Whole body is exposed to heat)
Decrease BP, increased HR and minute ventilation
What affect does excess adipose tissue have on superficial heat?
Increases the amount of time for the heat to get to the muscle
The capacity of a tissue to dissipate heat is largely a factor of what 2 things?
Blood supply
How healthy the tissue is
What affect does increase in tissue temperature have on the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve? What affect does this have on tissue healing?
Shifts the curve to the right, making oxygen more available for tissue repair
Temps that go past what threshold causes human tissues to burn because the metabolic activity required to repair tissue is not capable of keeping up thermally induced protein denaturation?
113°F-122°F
Vasodilation of the heat exposed skin can occur because of what 3 factors?
Axon reflex
Release of chemical mediators
Spinal cord reflex
What is the axon reflex that causes vasodilation of heat exposed skin?
Heat on skin stimulates cutaneous thermoreceptors.
These impulses are carried through branches toward the skin blood vessels and vasoactive mediators are released.
Results in vasodilation through an axon reflex
Which causes a better axon reflex to result in vasodilation: moist or dry heat?
Moist heat
What does better than moist heat in terms of the axon reflex for vasodilation?
Exercise
Explain how release of chemical mediators causes vasodilation of heat exposed skin.
Heat produces a mild inflammatory reaction with an increase in interstitial fluid. This acts on smooth muscle and endothelial cells.
What are the chemical mediators that causes local vasodilation of heated skin?
Histamine and prostaglandin
What increases vascular permeability and causes sweat secretion?
Kallikrein, releases bradykinin
Explain the local spinal cord reflex that results in vasodilation of heated skin.
Elicited through heat activated cutaneous afferent stimulation.
Results in a decrease in post-ganglionic sympathetic adrenergic nerve activity to the smooth muscle of blood vessels.
Helps with relaxation
Is the local spinal cord reflex that occurs when skin is heated limited to the area that is specifically heated? Explain.
No. For example, heating the low back may cause an increase of blood flow to the legs.
What decreases as a result of systemic heat that the body experiences?
DECREASES:
Blood pressure
Muscle activity
Blood flow to internal organs
Blood flow to resting muscles
What increases as a result of systemic heat that the body experiences?
INCREASES:
Cardiac output
Pulse rate
Metabolic rate
Respiratory rate
Vasodilation
At what temp of water should cardiac precautions be monitored?
>104°F
What neuromuscular affects occur as a result of superficial heat?
Analgesia (decreased pain)
Decreased spasm and guarding
Does deep or superficial heat have a greater effect when combined with a stretch?
Deep
When combining stretches with heat, what results in a greater increase in comfort and ROM gains?
Low load long duration stretch
In areas of adequate blood supply, superficial tissue (skin and subcutaneous tissue) temperature will increase to a maximum in how long?
10 minutes
In areas of adequate blood supply, muscle temperature will increase to a maximum in how long?
15-30 minutes
If someone has a lot of adipose tissue, what form of heat is better to heat muscle and other targeted tissues?
Deep heat modalities to decrease risk of burn.
Fat has low thermal conductivity.
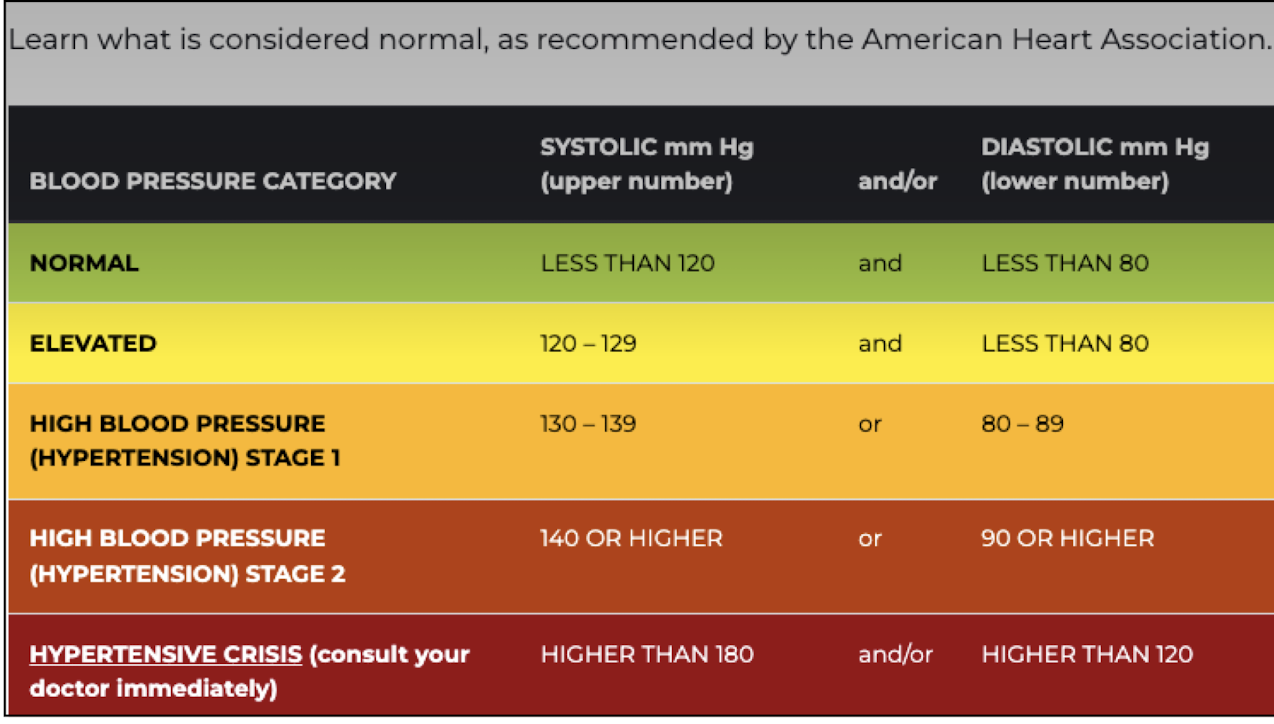
List the different values for blood pressure classifications.
What type of heat transfer requires a direct heat transfer from one molecule to another through liquid, solid, or gas?
What are some modalities that use this?
Conduction
Hot packs and paraffin
What type of heat transfer involves bulk movement of moving molecules to transfer heat from one object to another? Modality examples?
Convection
Fluidotherapy and whirpool that is turned on
What type of heat transfer involves conversion of heat energy to electromagnetic radiation and no medium is required? Modality examples?
Radiation
Diathermy
How hot should the hydrocollator be that stores moist hot packs?
158°F-167°F
How many layers should be placed between the patient’s skin and canvas pack if the patient is not laying on the hot pack?
4-6 layers
How many layers should be placed between the patient’s skin and canvas pack if the patient is laying on the hot pack?
6-8 layers (6 layers cervical, 8 layers low back)
On the first visit, when and how should you check on patient that is using the moist hot pack?
Look at skin at 5 minutes
Ask patient how they feel at 10 minutes
Treatment time of a moist hot pack is up to how many minutes?
20 minutes
Does the paraffin bath have high or low specific heat and conduction? What does this mean?
Low specific heat and low conduction.
Does not feel as hot as water of the same temperature; decreases the risk of a burn
Paraffin bath is a good choice for who?
People who have:
Sensation issues or sensitive skin
RA in a non-flare stage
Scleroderma patients
What are contraindications for the paraffin bath?
No jewelry
No open wounds
No skin/infection/rashes
No skin graft <10 days old
Passive, cannot perform exercises simultaneously
How long does heating last after treatment of paraffin bath?
Up to 20 minutes (treatment time: 15-30 minutes)
How many times should the patient dunk their hand in the paraffin bath?
8-10 times (Brummett says 6 is good)
How long can an air-activated wearable heat wrap be worn?
Up to 8 hours
What temp does the air-activated wearable heat wraps maintain?
104°F
What is the temp range for fluidotherapy?
102°F-118°F
What temp is a whirlpool heated to? Treatment time?
97°F-104°F
95°F-100°F for pts with CV or pulmonary disease
Treatment time: 20 minutes
When is vigorous heat (near tolerance levels of warmth: 113°F) indicated?
If someone is in the chronic stage with a lot of scar tissue. Helps heat collagen to help stretch tissues.
Ex: fluidotherapy at 112°F to increase tissue extensibility before ROM exercises, or paraffin for the hand/foot due to superficial covering of area.
When is mild heat (near tolerance levels of warmth: 113°F) indicated?
For pain/muscle spasms.
Ex: hot packs for reducing muscle spasm in upper traps
What are absolute contraindications specific to thermotherapy?
Application over:
Areas with a lack of intact thermal sensation
Screen area bilaterally for sensation changes
Areas of vascular insufficiency or vascular disease
Areas of recent hemorrhage or potential hemorrhaging (active bleeding)
Known malignancy
Areas where liniments or heat rubs have been recently applied
Vessels already vasodilated, increases risk for burns (Icy-Hot)
Acute inflammation
Infection
Screen for fever, chills, night sweats, and check skin for redness/swelling
Application in any situation deemed unreliable by the practitioner
Language difficulties or cognitive impairments