Retina
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
retina
innermost layer of the eye b/t the vitreous and choroid; continuous with epithelial layers of ciliary body
phototransduction
complex biochemical process by which the retina changes light energy into a signal that can be transmitted along neural pathways in the retina, exits the eye through the optic nerve, and transmitted to various parts of the brain for processing
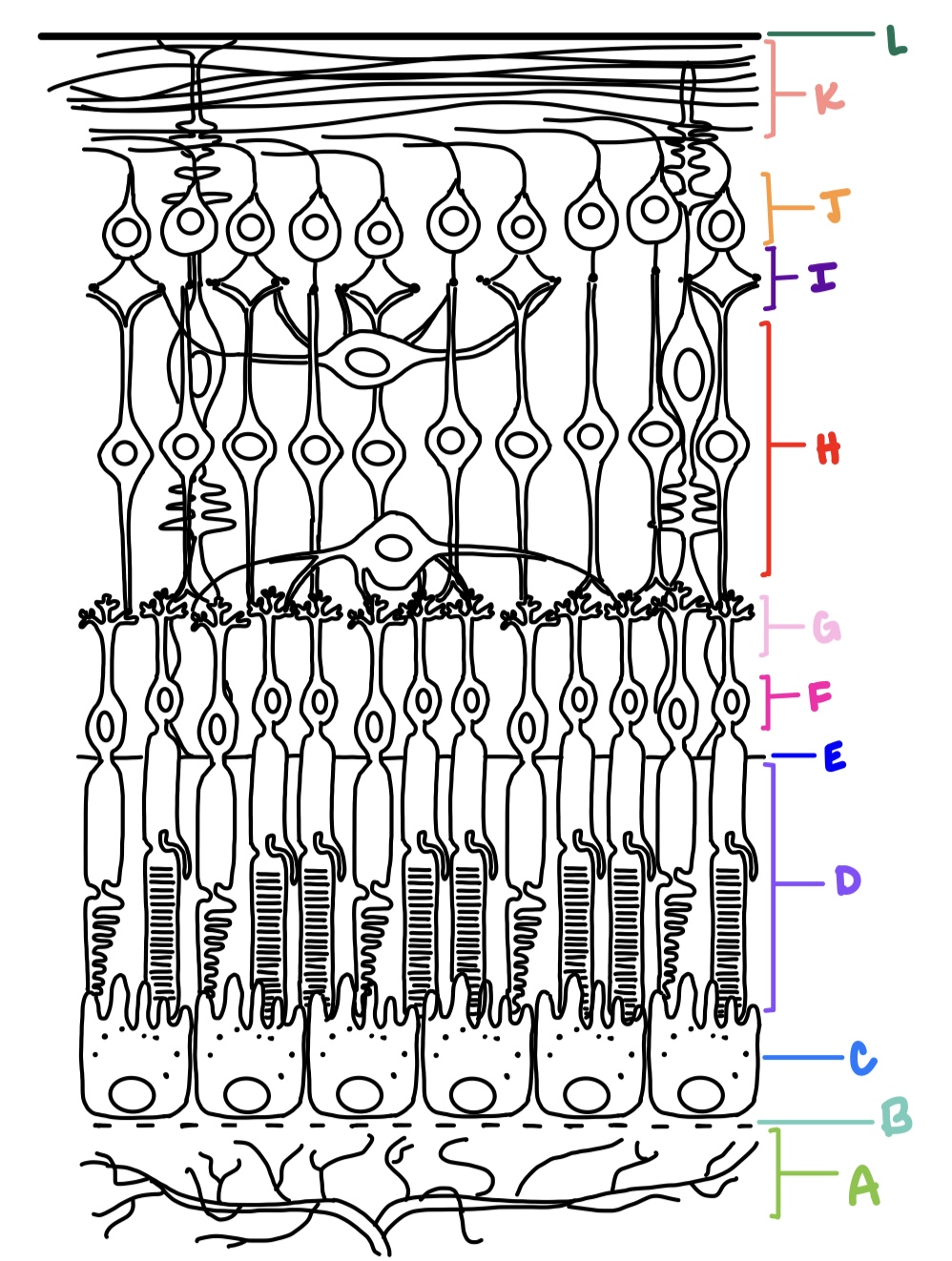
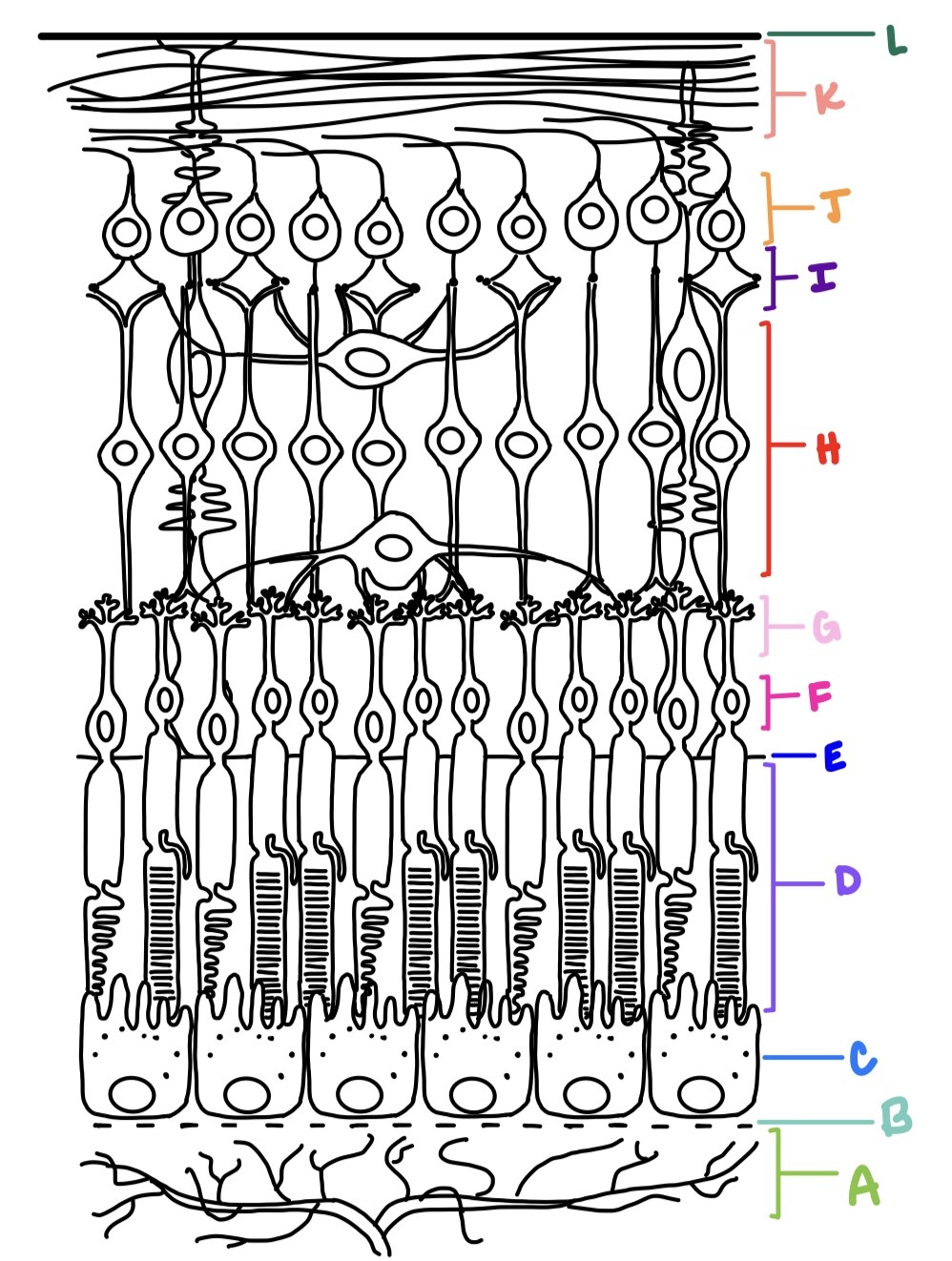
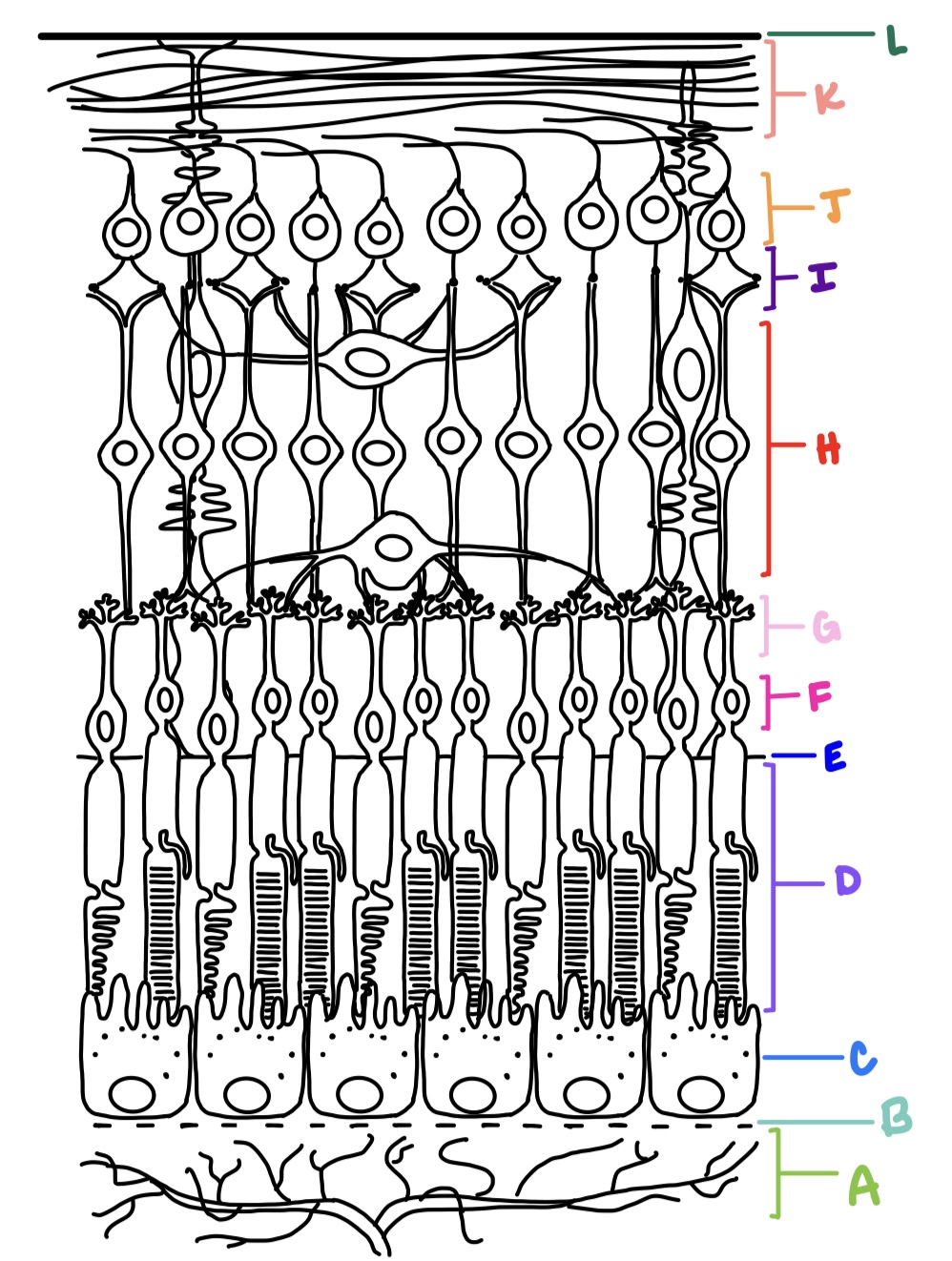
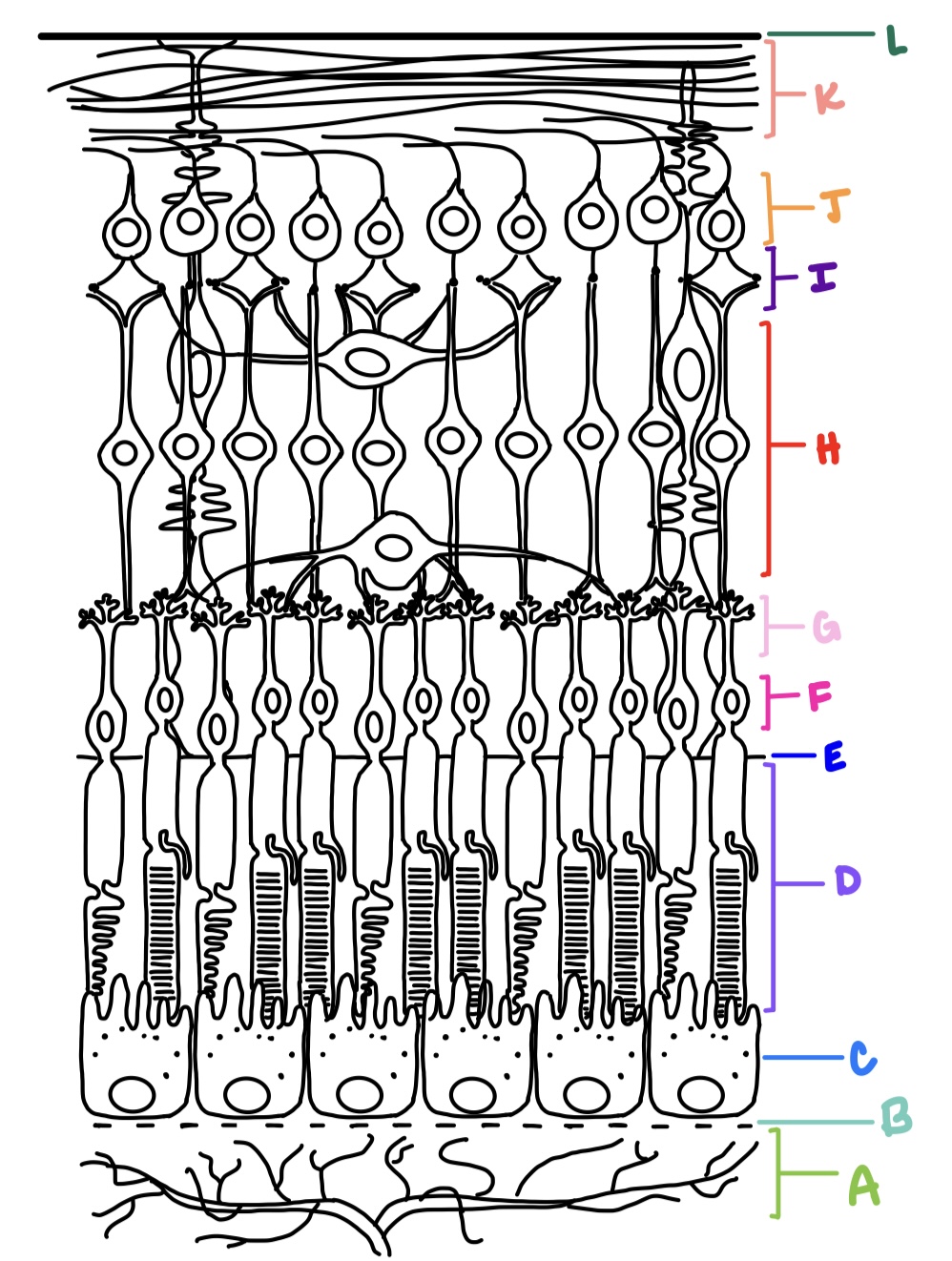
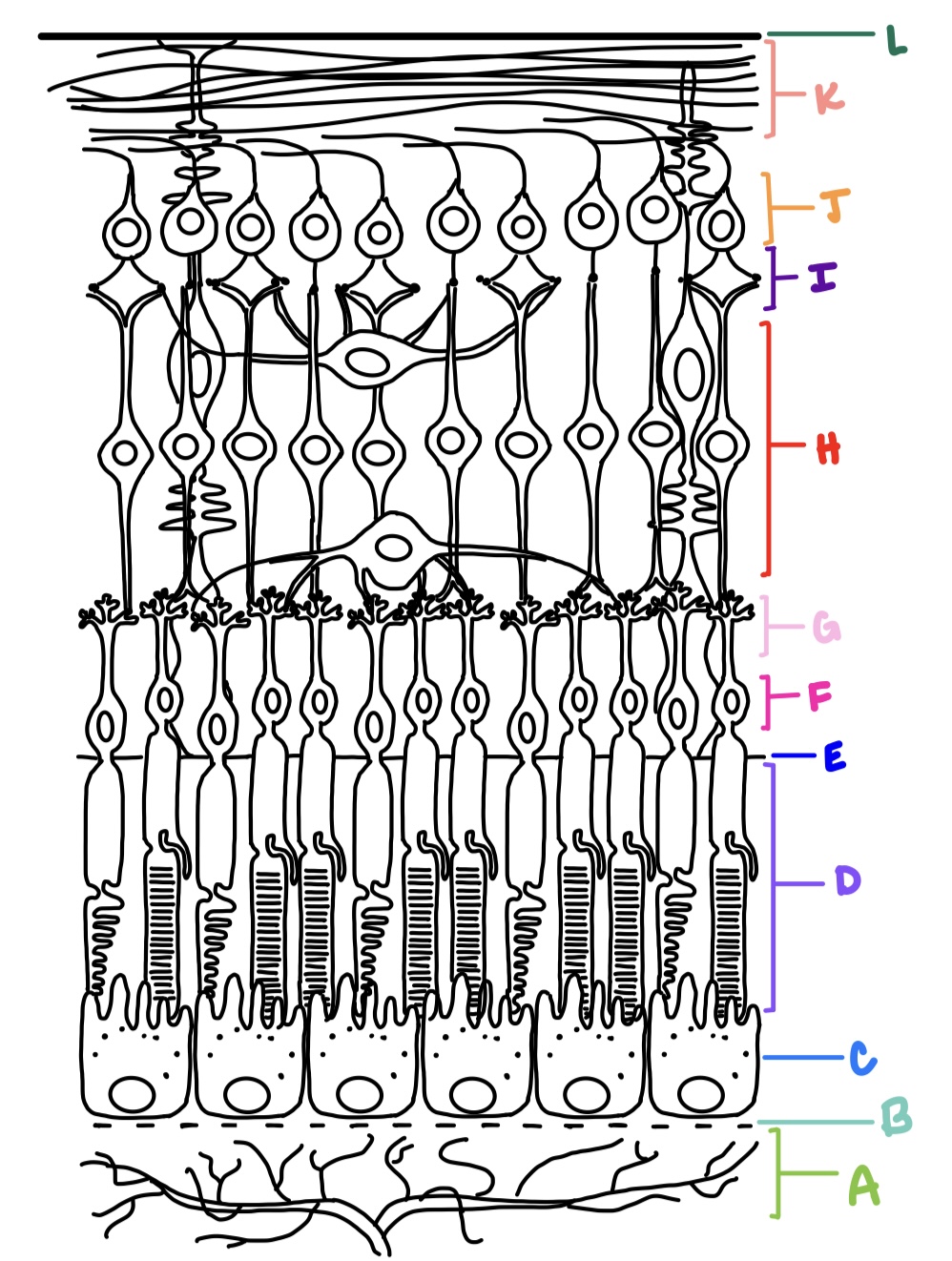
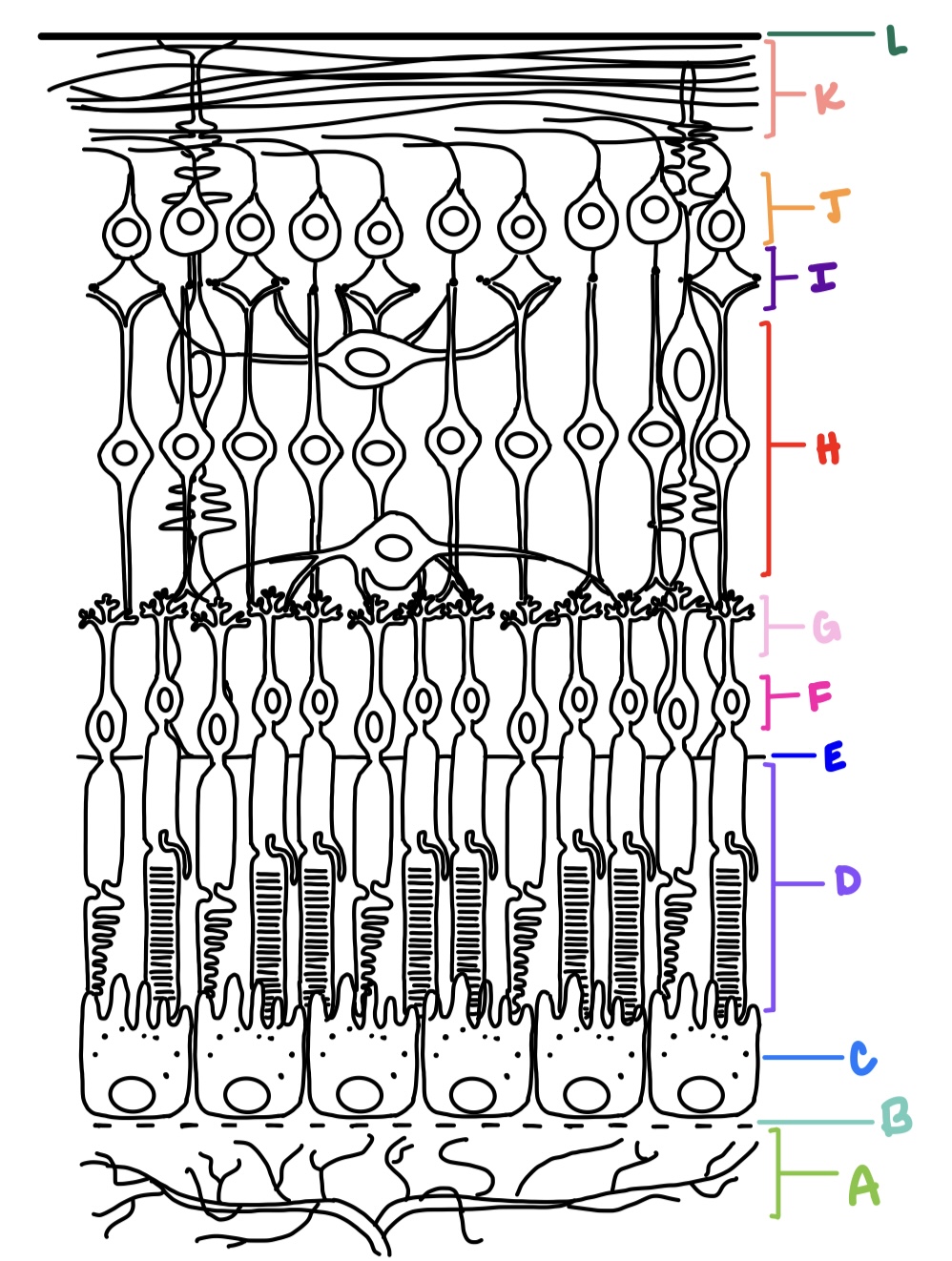
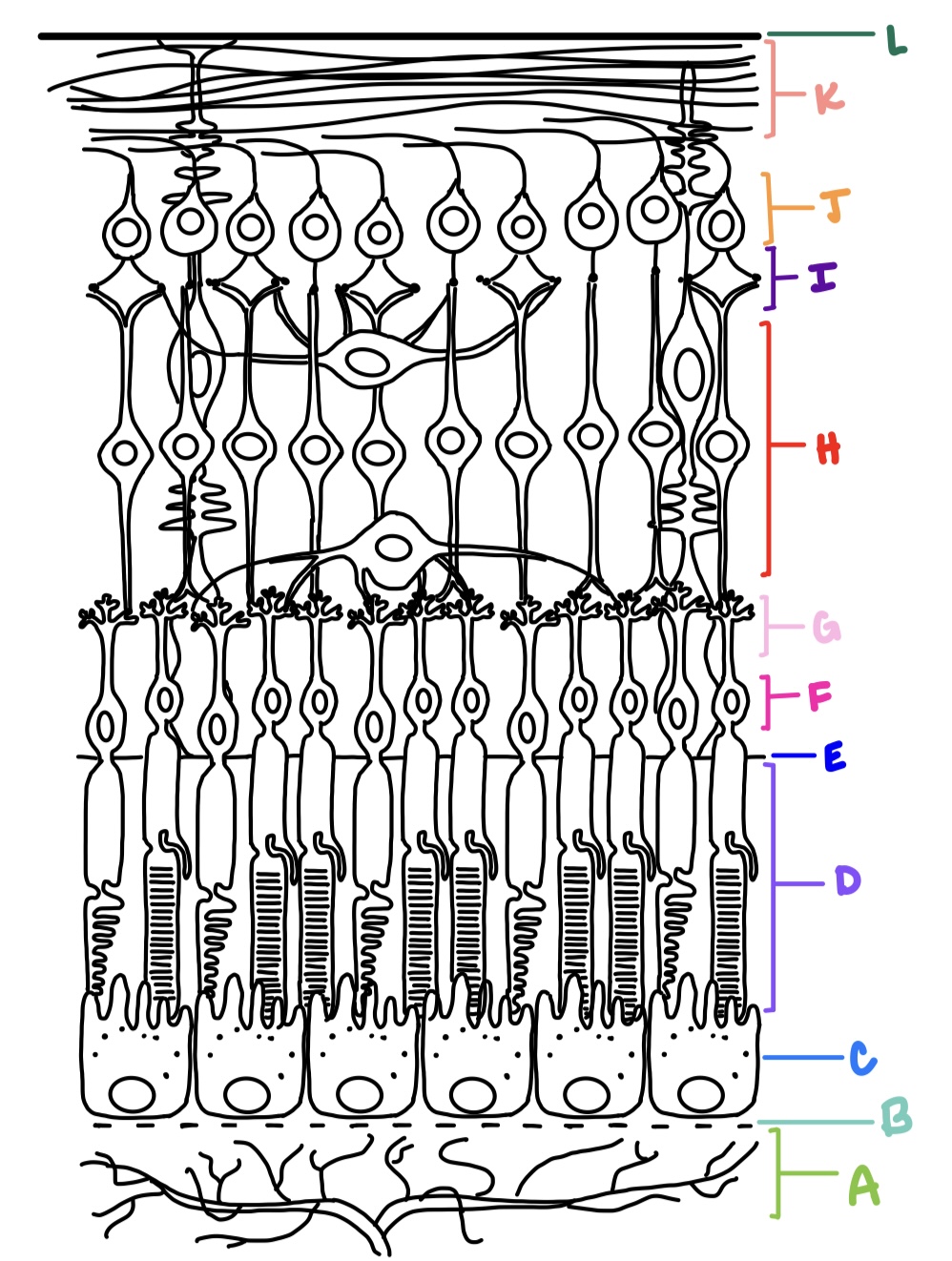
ILM, NFL, GCL, IPL, INL, OPL, ONL, ELM, PRL, RPE
what are the layers of the retina from inner most to outer most?
photoreceptors
first order neurons; rods and cones; site of phototransduction
bipolar cells
second order neurons, transmit signals from photoreceptors to retinal ganglion cells; synapse with horizontal cells and photoreceptor at OPL, synapse with amacrine cells and ganglion cells at IPL
retinal ganglion cells
3rd order neurons; transmit signals from bipolar and amacrine cells to brain via optic nerve
horizontal cells
form connections with photoreceptors & bipolar cells; modify & integrate signals
amacrine cells
project to ganglion and bipolar cells; modify & integrate signals
Bruch’s membrane
acellular extracellular matrix that lies b/t the metabolically active RPE and choriocapillaris; transports H2O, ions, metabolites, nutrients, and waste products
B
elasticity
the ______ of Bruch’s membrane helps the eye withstand changes in IOP or choroidal blood flow
blood retinal barrier
Bruch’s membrane forms part of this to keep choroidal vessels from passing into the retina
increases
Bruch’s membrane _______ with age
thicker
Bruch’s membrane is _____ centrally than peripherally
basement membrane of RPE, inner collagenous zone, elastic fiber area, outer collagenous zone, basement membrane of choriocapillaris
what is the order of layers of bruch’s membrane from inner to outermost?
brittle
elastic fibers in Bruch’s membrane become more ______ over time due to degradation and calcification
increasing collagen synthesis
what may contribute to trapping and accumulation of cellular debris in the collagenous zones?
lipofuscin
incomplete lysosomal degradation of photoreceptor outer segments causes accumulation of this
drusen
deposits of lipids, proteins, and other cellular debris
retinal pigment epithelium
outermost retinal layer
monolayer of hexagonal cells
cells do not divide
barrier between choroid and neural retina
contains many melanosomes
C
columnar
what shape are RPE in the macula?
cuboidal
what shape are RPE near the ora serrata
highly folded
the basement membrane of the RPE is said to be what?
microvilli
apical surface of RPE has ______ that extend up into photoreceptors and envelop photoreceptor outer segment tips
4-6 million
how many RPE cells are there?
30-40
how many photoreceptors does each RPE cell interact with?
melanosomes
located in RPE, help absorb stray light and reduce light scatter
pigment, vitamin A metabolism, secrete growth factors, transport nutrients & metabolites, phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer discs, blood retinal barrier, sub retinal space helps balance ions/pH/fluids
what are functions of the RPE?
blood-retinal barrier
prevents components of blood plasma to enter the retina, which could impede light
no
are retinal capillaries fenestrated?
zonula occludens
located between RPE cells and form tight junctions and prevents movement of large molecules
constantly
how often are discs shed?
10%
during disc shedding ___ of photoreceptor volume is shed
circadian rhythm
what controls the timing of disc shedding
disc shedding
old discs are pinched off at the tips, captured by microvilli, and engulfed by RPE
RPE
what cells are the most active phagocytic cells in the entire body?
phagosomes
engulfed outer segments in membrane bound sac, fuse with lysosomes
phagolysosome
formed when phagosome fuses with lysosomes
decreases, accumulates, retinal degeneration
with age, lysosome function ______, lipofuscin ______, and this can lead to ___________________
hyper
lipofuscin is ____fluorescent
fundus flavimaculatus
autosomal recessive genetic disorder affecting RPE ability to remove cellular waste, which accumulates
lactate
byproduct of anaerobic metabolism
aquaporins
aid in the movement of water with Cl- and K-
glucose transporter
located on both apical and basal sides of RPE to maintain a steady supply of nutrients to photoreceptors
rods
sensitive to low light (scotopic) conditions
poor VA
low spatial resolution
absent color vision
very sensitive to light
rhodopsin (OPN2)
what is the opsin type in rods?
cones
sensitive to bright light (photopic) conditions
good VA
high spatial resolution
color vision present
less sensitive to light
S, M, L
what are the 3 types of opsins in cones?
498nm
what is the peak wavelength for rhodopsin/OPN2?
420nm
what is the peak wavelength for S/blue/OPN1SW?
531nm
what is the peak wavelength for M/green/OPN1MW?
588nm
what is the peak wavelength for L/red/OPN1LW?
fovea
where are cones most concentrated at?
tapered tip
what is the shape of cones?
blunt tip
what is the shape of rods?
around fovea, not at
where are rods concentrated at?
outersegment
part of photoreceptors that contains photo discs for converting light into neural signal
spherule
synaptic terminal for rods
G on left
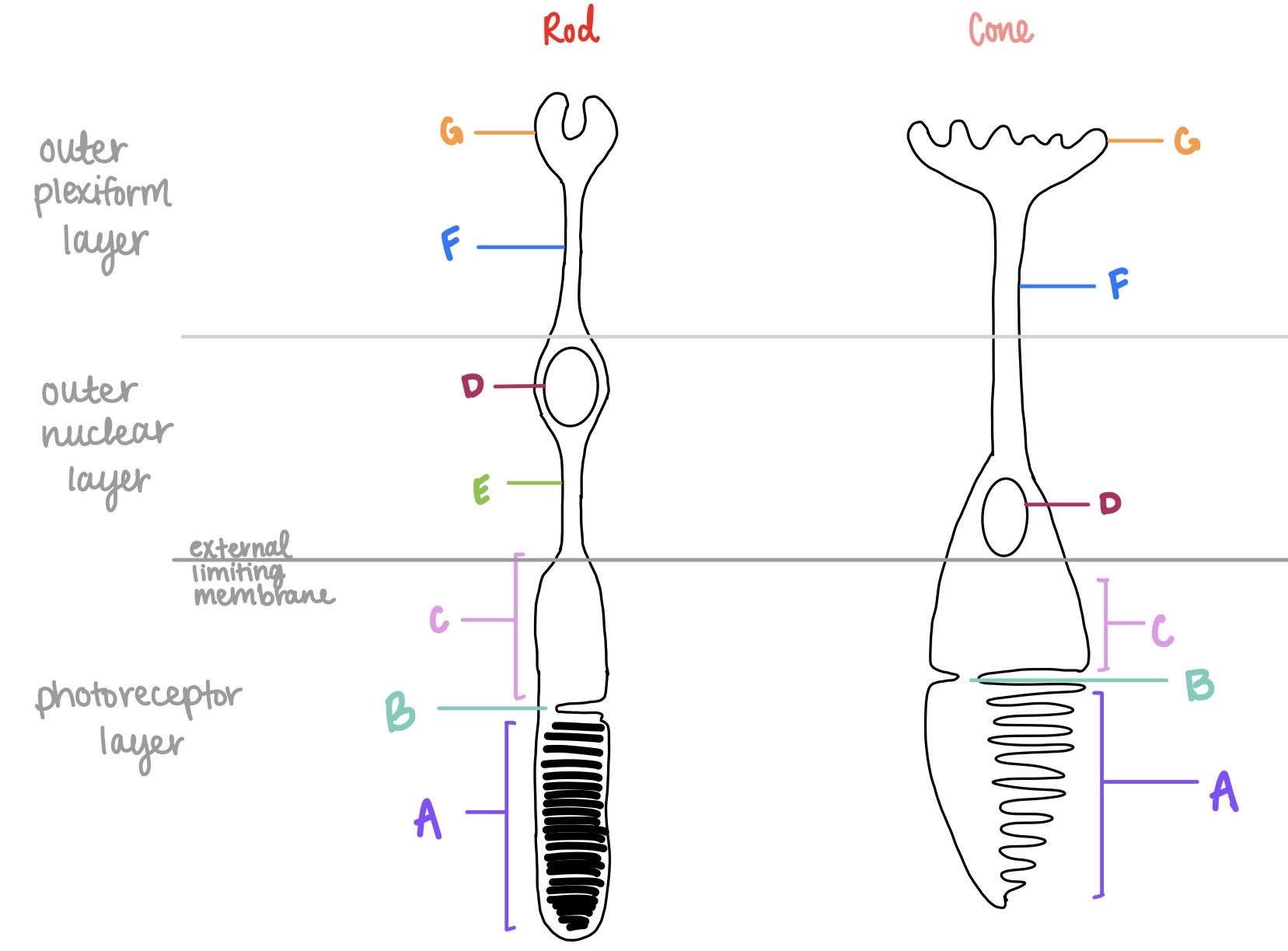
pedicle
synaptic terminal for cones
G on right
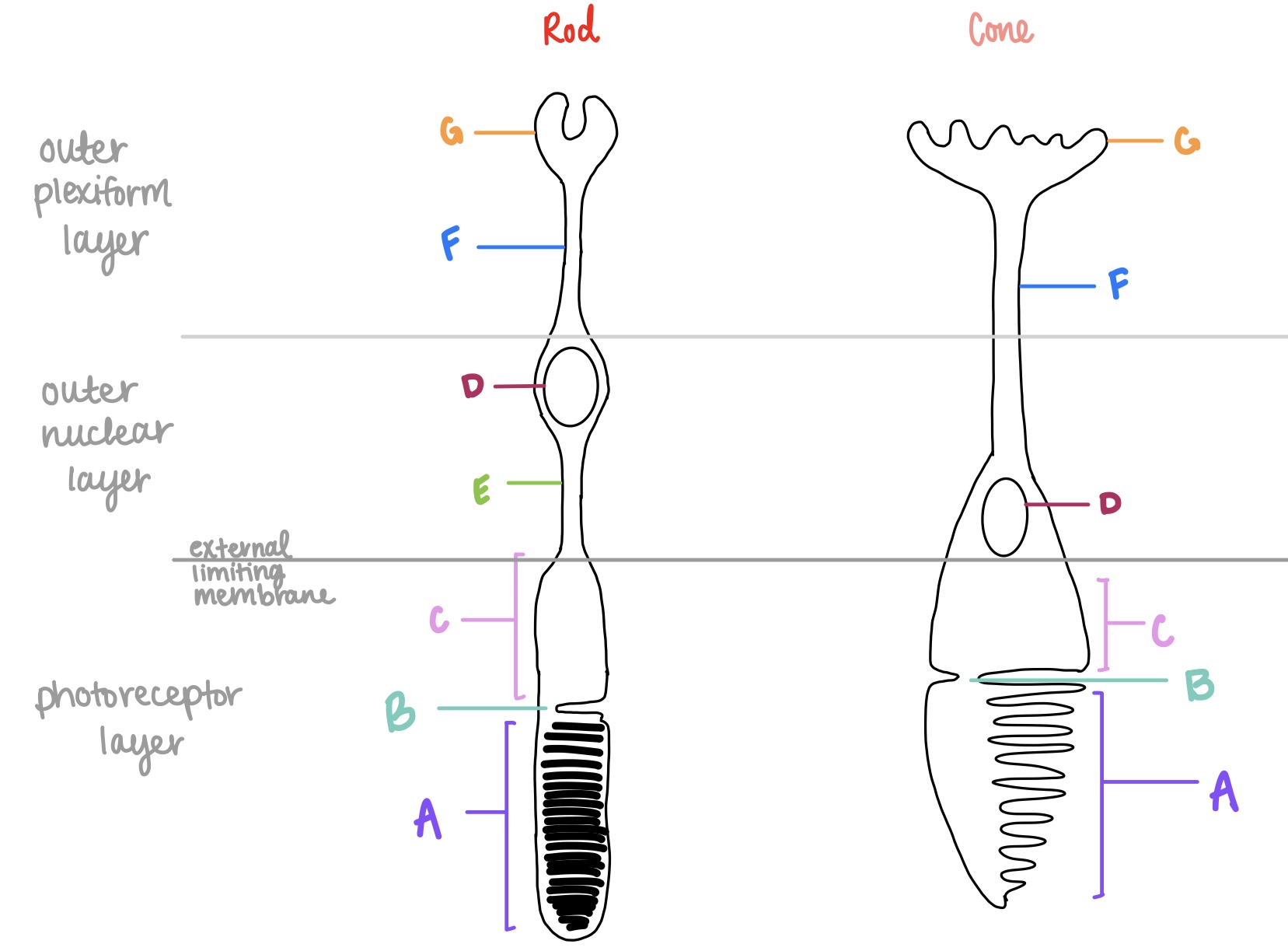
outer nuclear layer
where are the cell body nuclei located for photoreceptors?
F
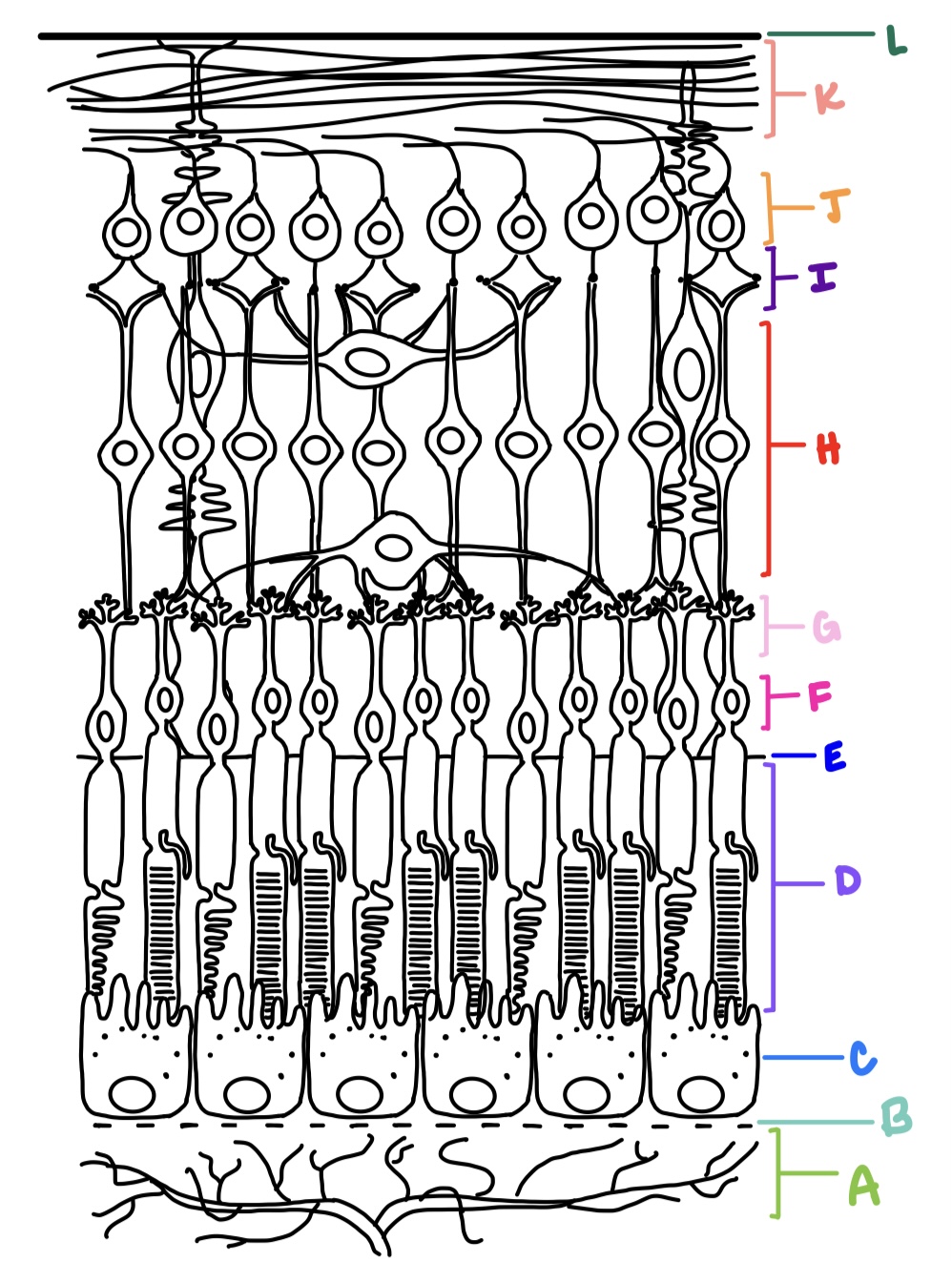
outer plexiform layer
where are the axon terminals located for photoreceptors?
G
outer segment, connecting cilium, inner segment, outer fiber, cell body, inner fiber
what are the parts of the photoreceptor from outermost to innermost?
inner segment
metabolic apparatus for photoreceptors, higher concentration of mitochondria
C
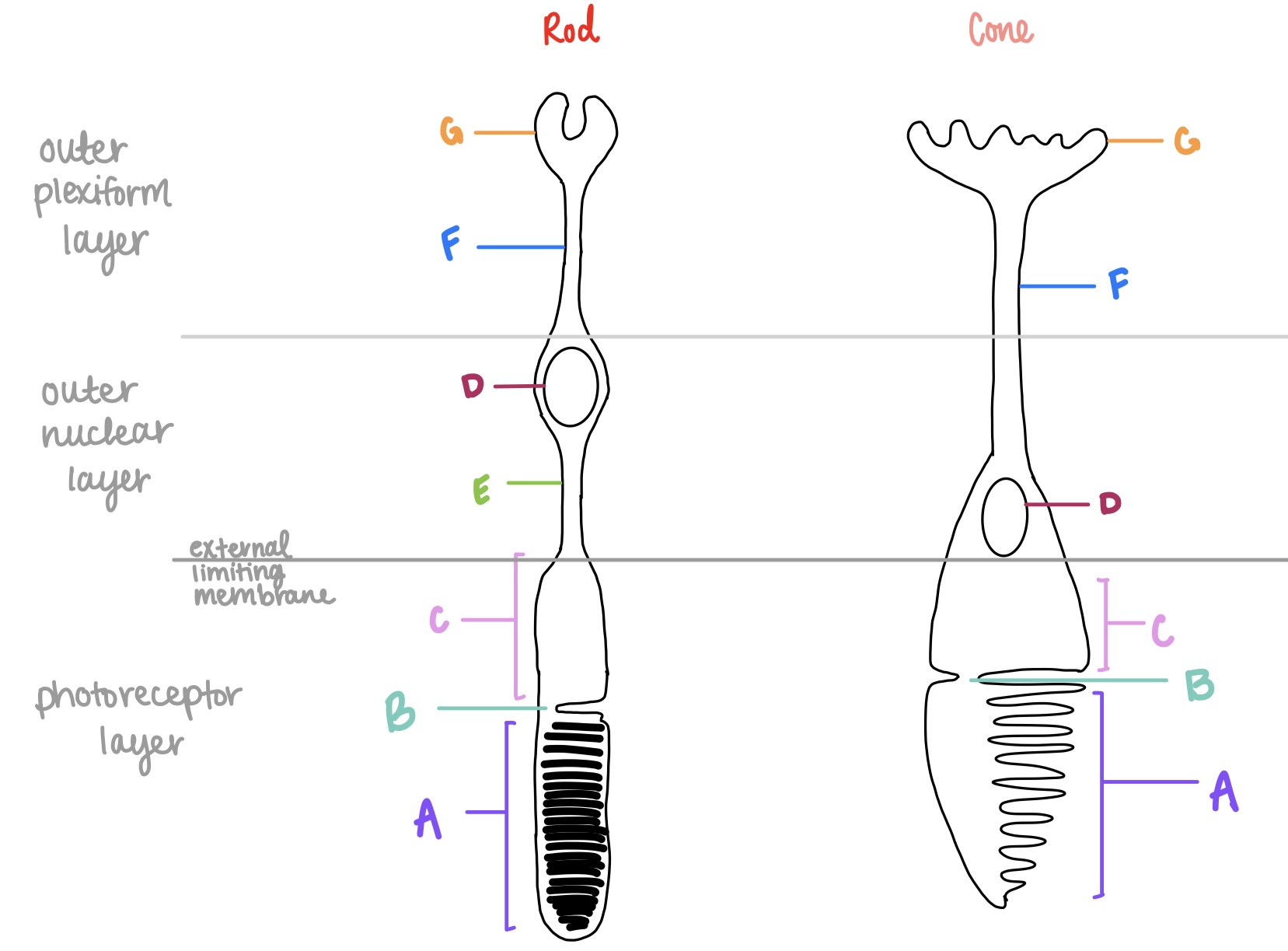
photopigment
opsonin + chromophore
chromophore
11-cis-retinal
opsin
determines the wavelength the pigment responds to
shape
chromophore changes _____ in response to opsin wavelength
vitamin A
where does 11-cis-retinal come from?
no
can the human body synthesize vitamin A?
all-trans-retinal
what does 11-cis-retinal transform into when activated?
interphotoreceptor retinoid binding proteins (IRBP)
moves all-trans-retinal into the RPE where it is converted to 11-cis-retinal
no
are there any intercellular junctions b/t the RPE and photoreceptors?
retinal detachment
caused by vitreous fluid getting into the retina and separating the photoreceptor from the RPE if a retinal tear or hole occurs?
outer plexiform layer
contains synapses of photoreceptors with bipolar cells and horizontal cells; common site for retinoschisis
retinoschisis
separation of retina at the OPL
inner nuclear layer
contains cell bodies of bipolar cells, horizontal cells, and amacrine cells
H
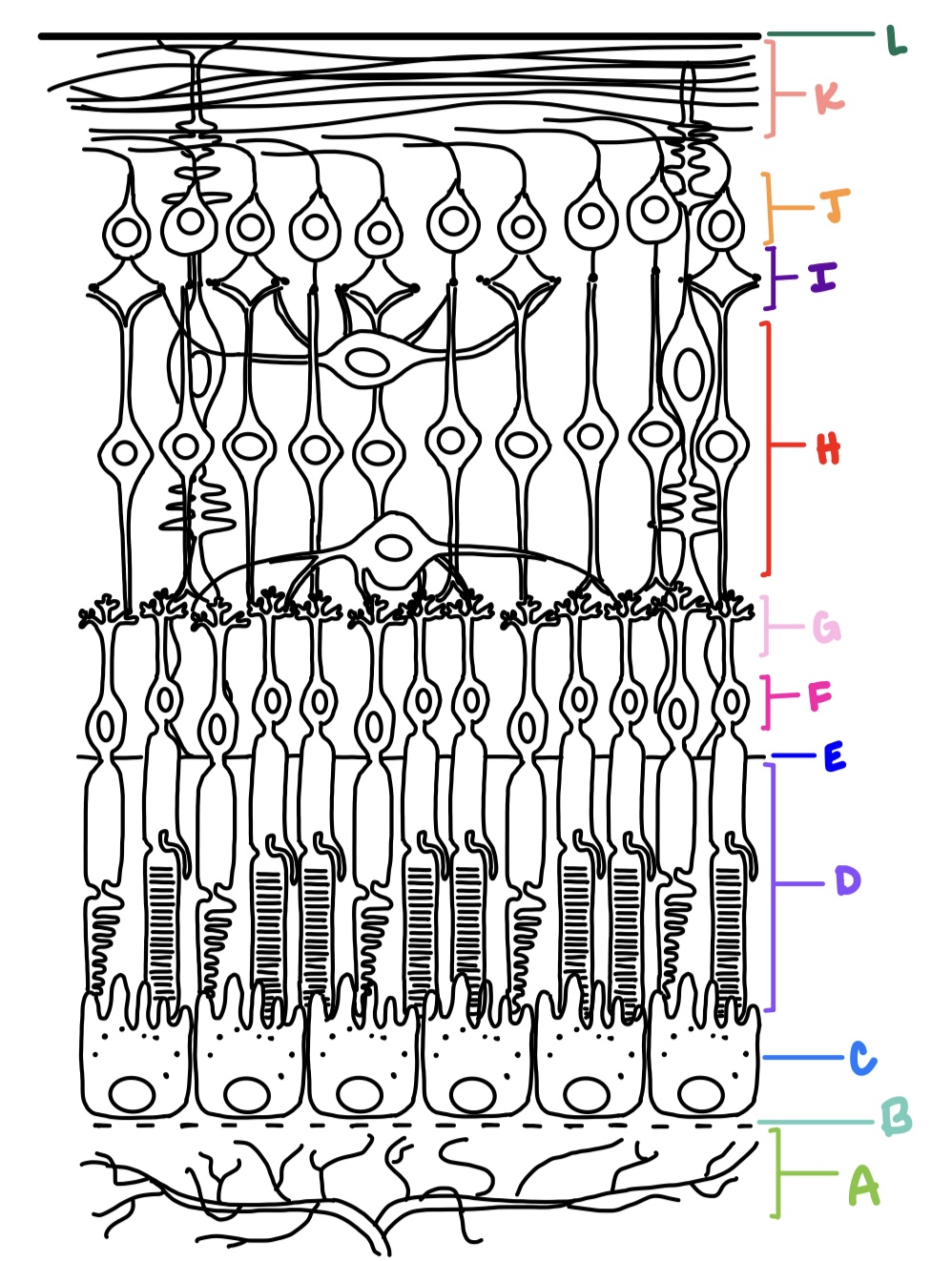
amacrine cells
processes are in IPL; synapses w/ bipolar cells, ganglion cells, and other amacrine cells; generally inhibitory (GABA/glycine)
horizontal cells
processes are in OPL; synapses with photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and other horizontal cells; releases both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
1
how many types of rod bipolar cells are there?
10
how many types of cone bipolar cells are there?
ON
__ bipolar cell synapses with cone photoreceptor, and its axons synapses to the ON ganglion cell
sublamina B of IPL
where do ON bipolar cells synapse with ON ganglion cells
depolarized
how are ON ganglion cells affected by light?
OFF
__ bipolar cell synapses with cone photoreceptor, and its axons synapses to the OFF ganglion cell
sublamina A of IPL
where do OFF bipolar cells synapse with OFF ganglion cells?
hyperpolarized
how are OFF ganglion cells affected by light?
A2 amacrine cell
what is responsible for relaying rod signals to both ON and OFF ganglion cells?
greater
there is ____ convergence of rods onto ganglion cells than cones
1:1
ratio for bipolar to cone cells at the fovea
inner plexiform layer
consists of synaptic connections made between bipolar cells, amacrine cells, and ganglion cells
I
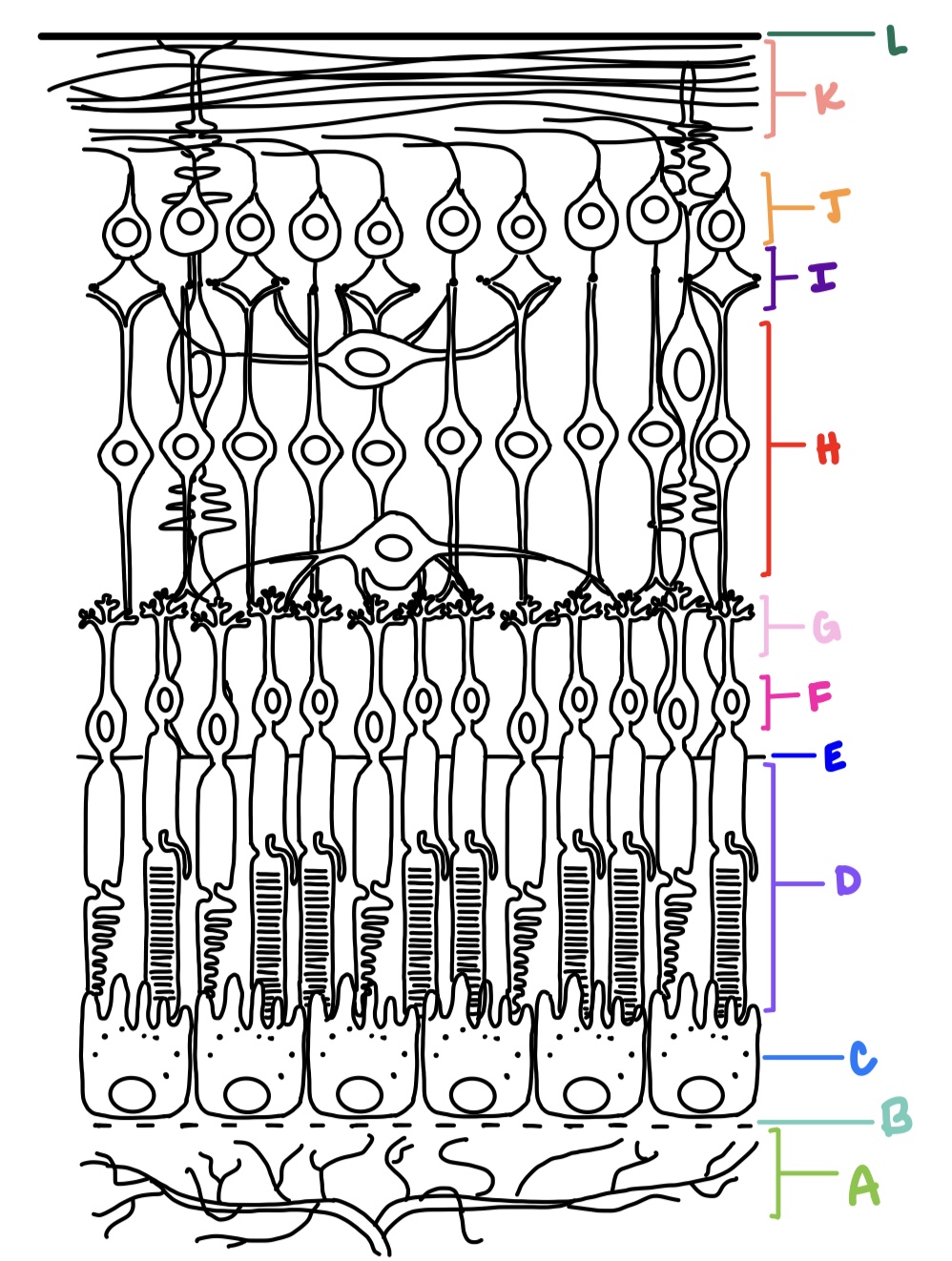
ganglion cell layer
consists of retinal ganglion cells and displaced amacrine cells
J
parvo (p-type) ganglion cells
90% of RGCs
axons terminate in parvocellular layers of LGN
small cell bodies
small receptive fields
sensitive to high spatial frequency stimuli and color
concentrated at fovea
magno (m-type) ganglion cells
5% of RGCs
axons terminate in magnocellular layers of LGN
large cell bodies
large receptive fields
sensitive to high temporal frequency stimuli
carries luminance signals
achromatic
aka parasol cells
P1 cells
aka midget ganglion cells
most common type
1:1:1 cone: bipolar: ganglion
P2 cells
densely branched and compact dendritic trees that spread horizontally
konio (k-type) cells
axons terminate in koniocellular layers of LGN
large cell bodies
large receptive fields
carries blue-yellow color signals
not well understood
intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells
>1% of RGCs
contain melanopsin
can respond to light independently of and in absence of rods and cones
non-image forming
axons project to SCN and PON
nerve fiber layer
made up of 1-2 million ganglion cell axons that converge at optic disc; makes right angle turn to exit the eye; forms optic nerve which carries electrical impulses to various areas of the brain
K
internal limiting membrane
faces the vitreous, formed by basal aspect of Muller cells called Muller end feet and covered by basement membrane
L
external limiting membrane
not a true membrane, located between ONL and photoreceptor layer; formed by apex of Muller cells
E
neural glial cells
cells not directly involved in visual information processing; Muller cells, microglial cells, astrocytes; provide support, nutrients, waste removal, homeostasis, response to injury/inflammation/infection