Bootcamp.com - Nervous System (11)
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
185 Terms
a _____ is the basic functional unit of the nervous system
neuron
what are the three main parts of neuron?
cell body (soma); dendrites; axon
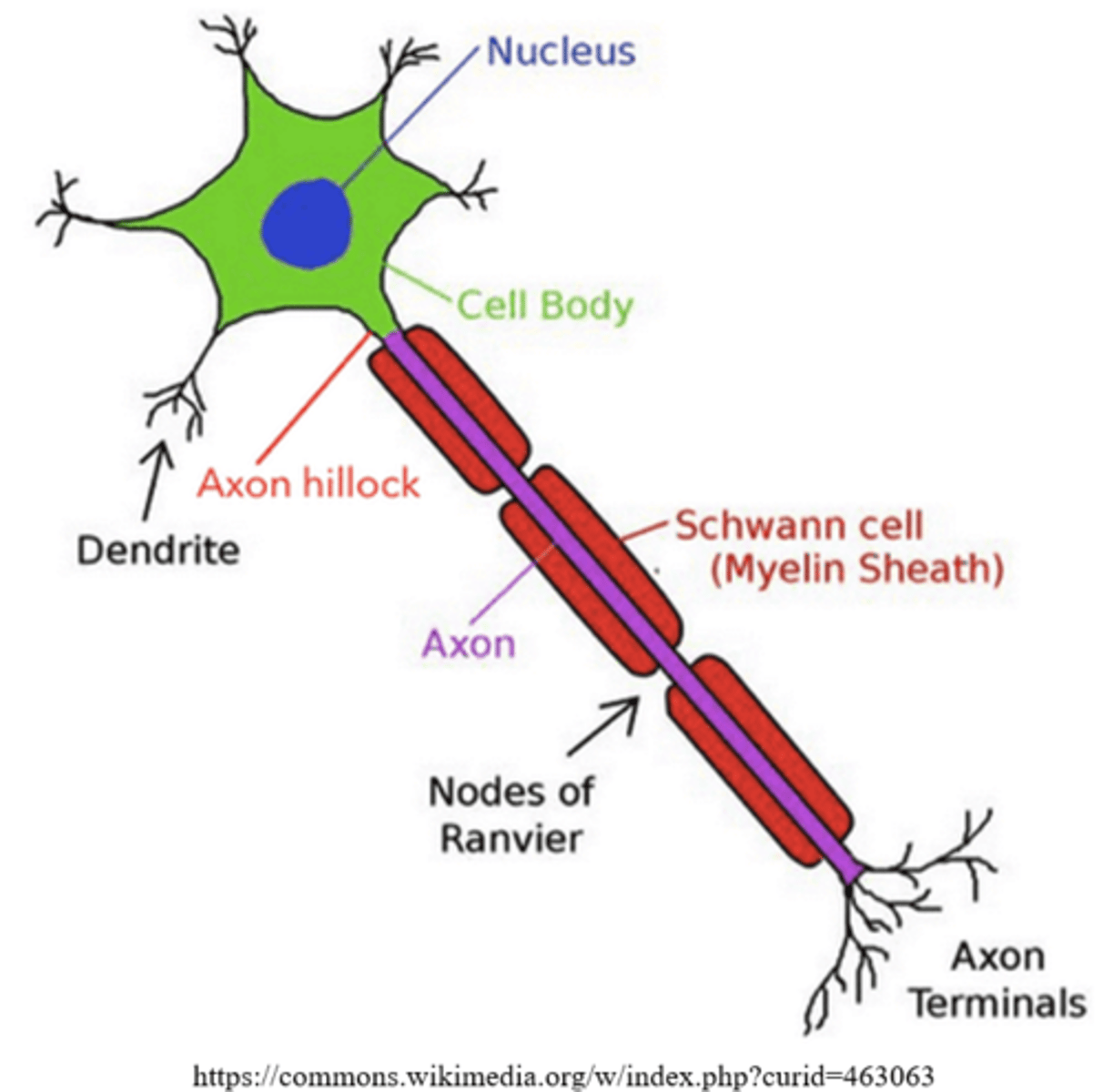
what is the name for the cell body of a neuron, and what organelle does it contain?
soma; nucleus
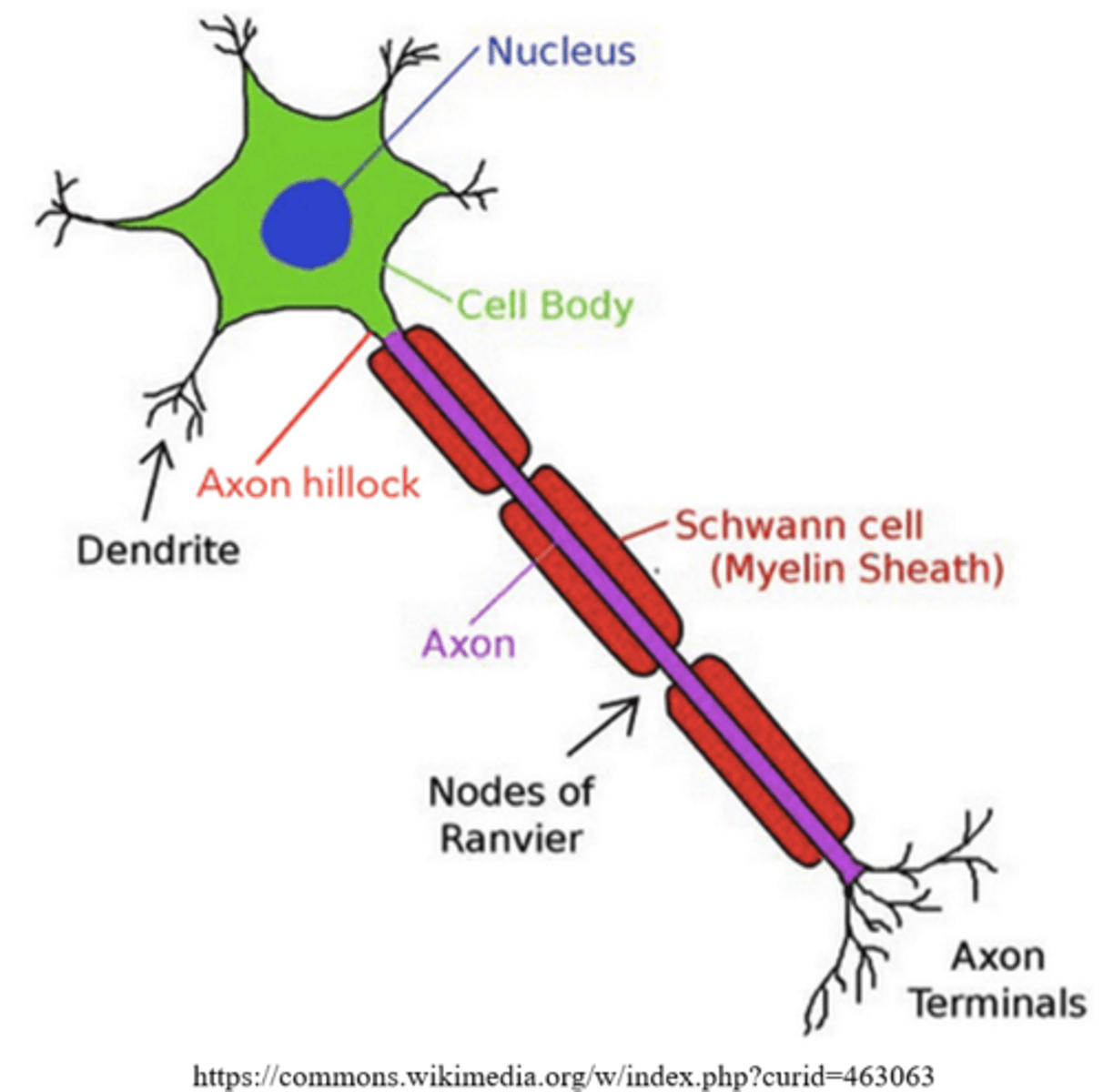
_____ are processes that receive signals from previous neurons
dendrites
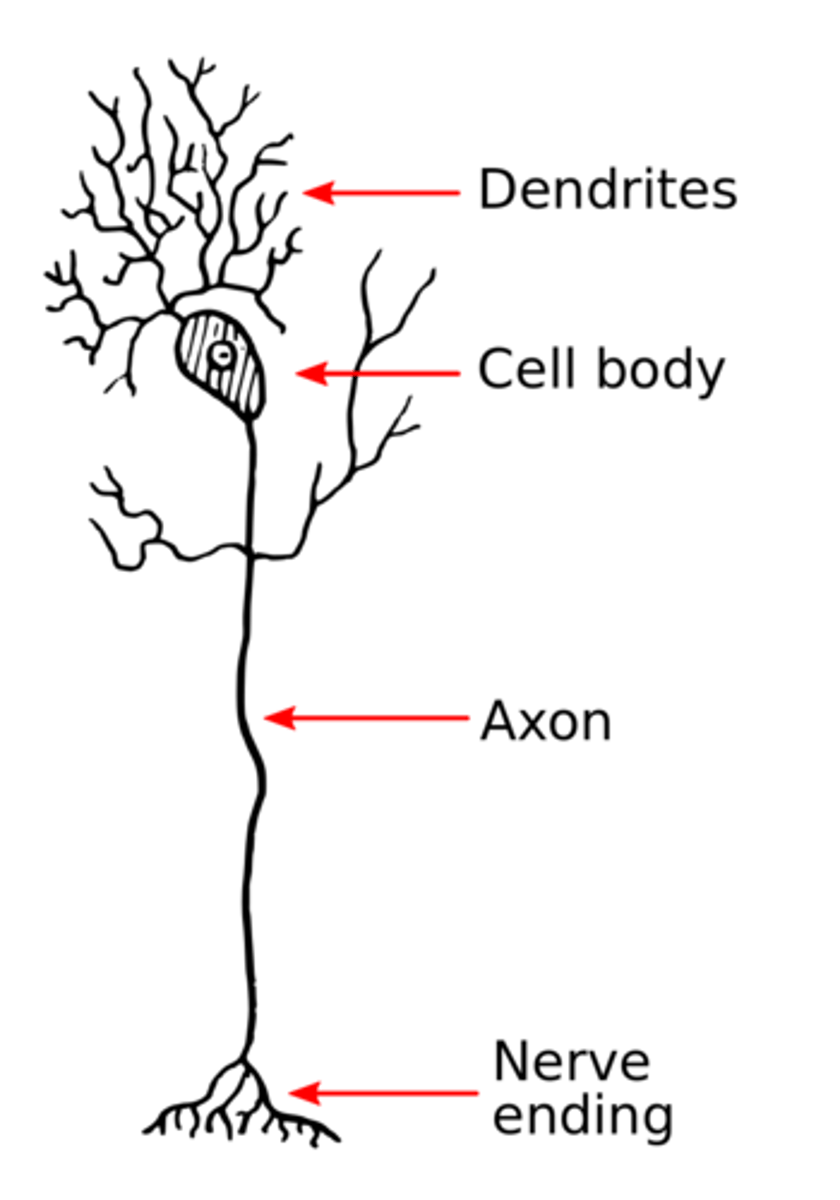
_____ are long processes that transduce signals to the next neuron
axons
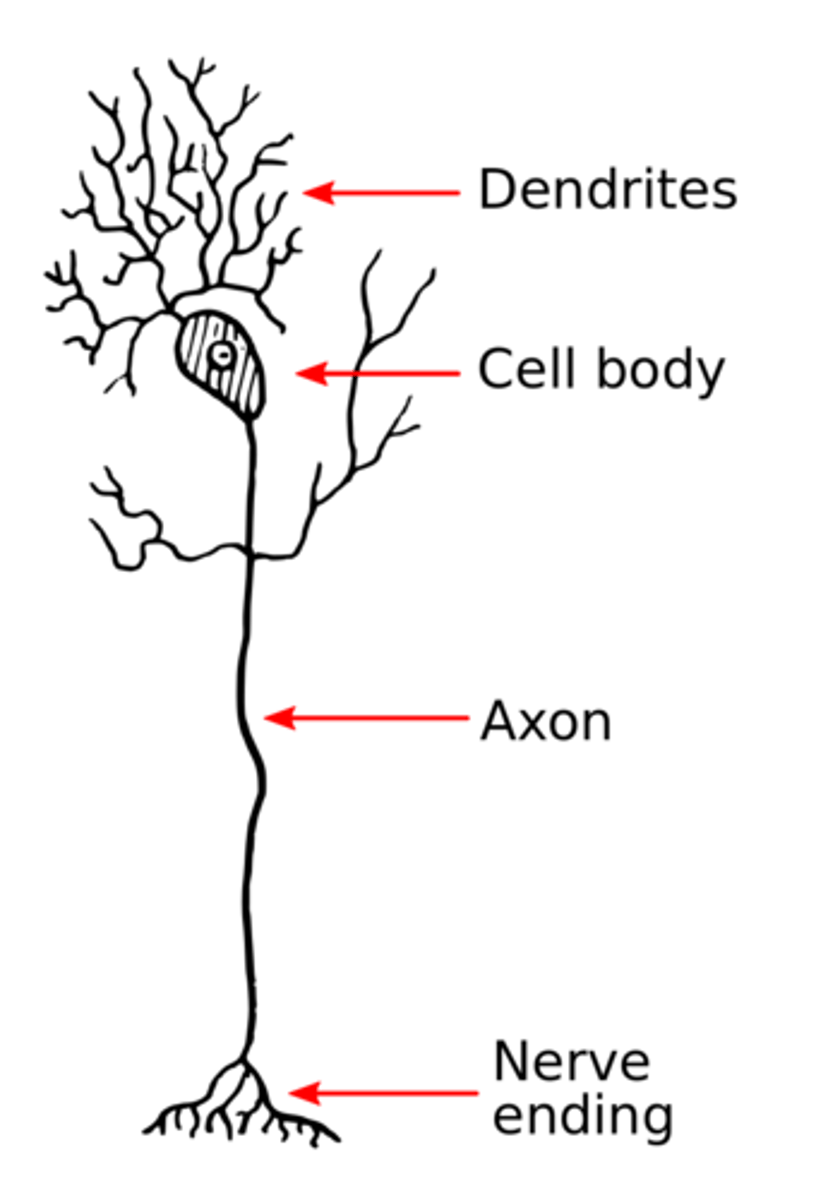
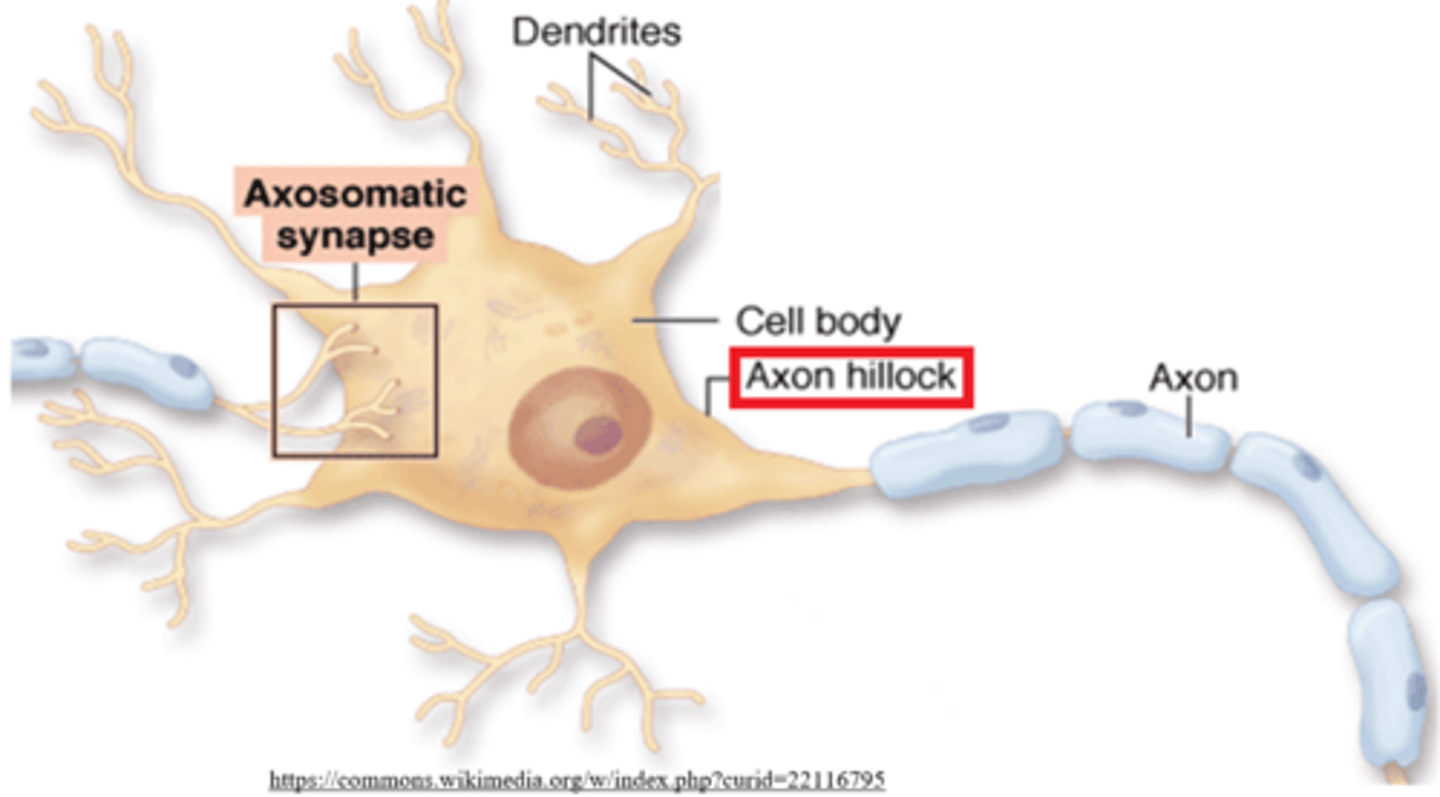
graded potential summation occurs at the _____, which connects the soma to the axon
axon hillock
what will happen if a summation is more positive than the threshold potential?
an action potential will fire
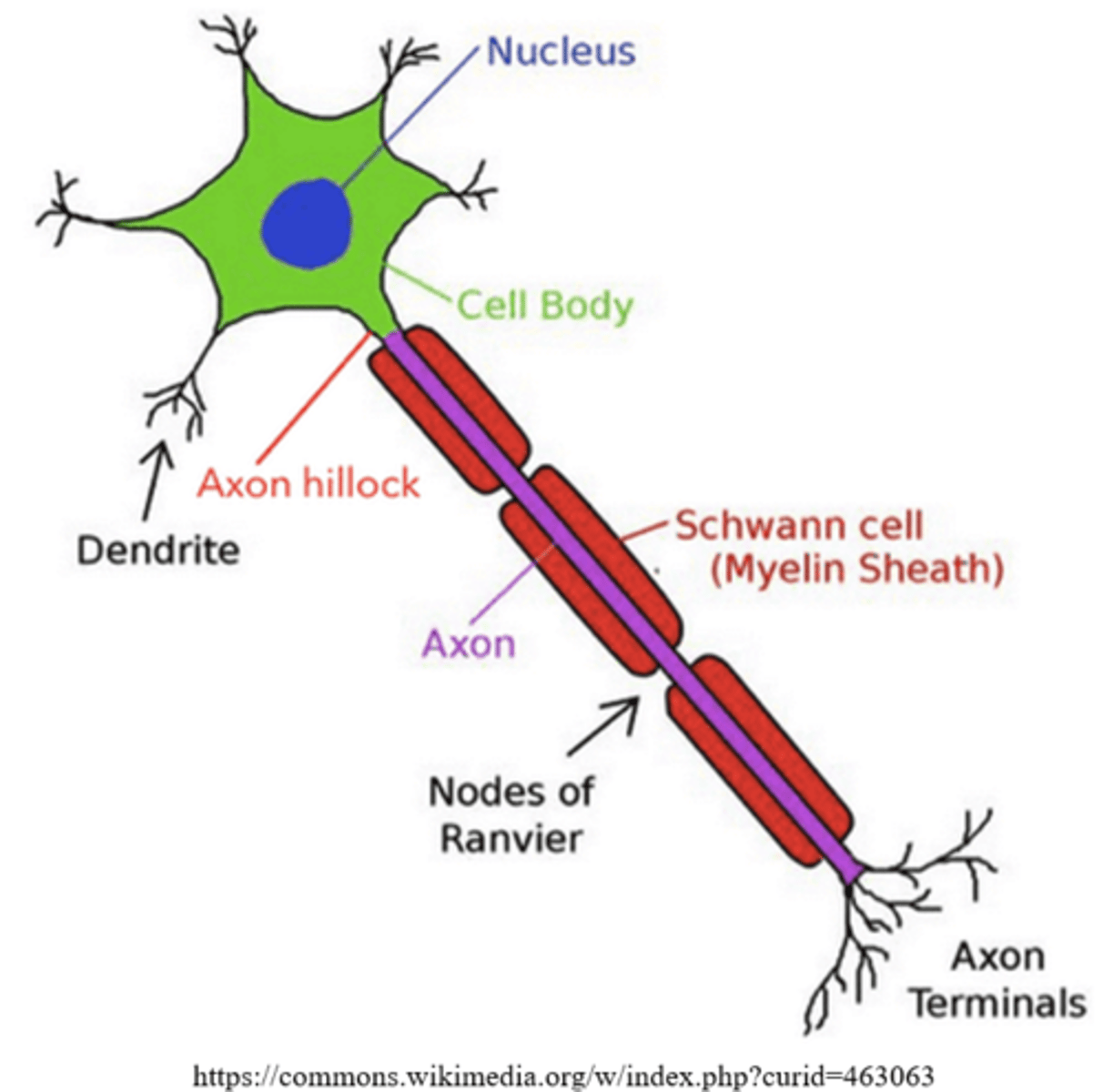
_____ is a fatty insulation of the axon, which helps for faster axon conduction
myelin sheath
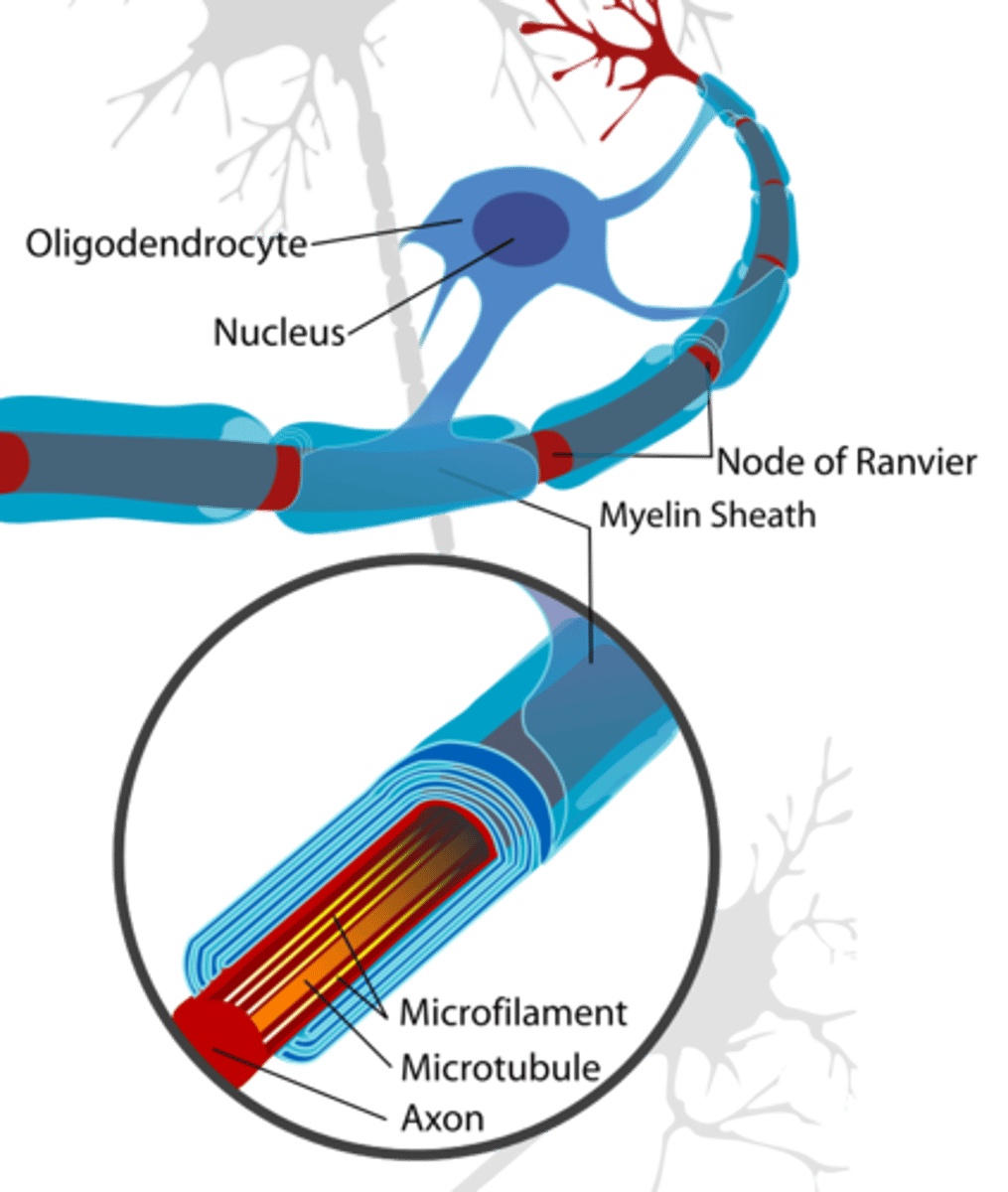
which cells produce the myelin sheath in the central nervous system?
oligodendrocytes
which cells produce the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
schwann cells
_____ are gaps between myelin sheath of the axon
Nodes of Ranvier
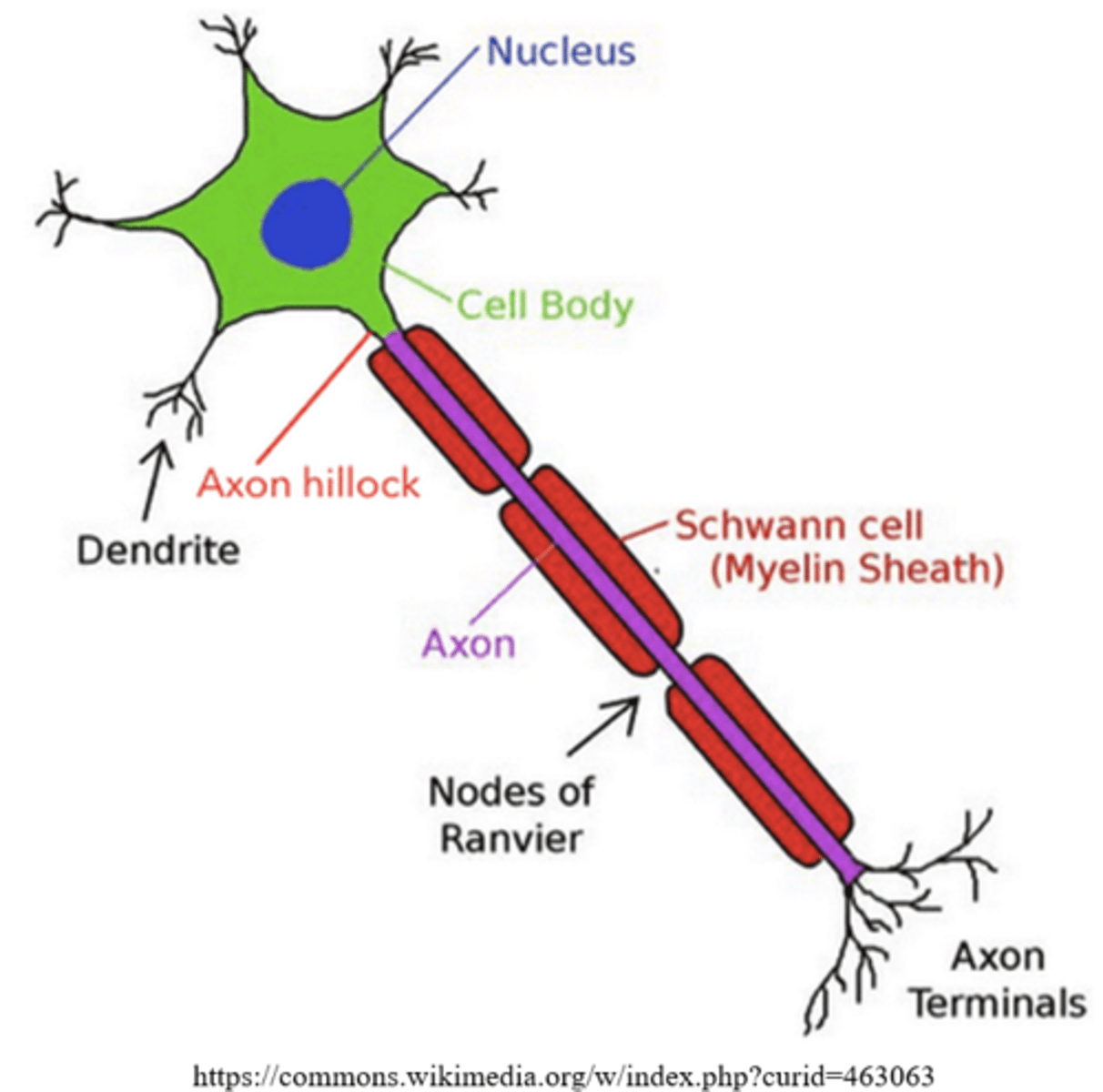
what is saltatory propagation?
the action potential "jumps" from one node of Ranvier to the next
what is the benefit of saltatory propagation?
it provides faster conduction than propagating the signal down the entire axon
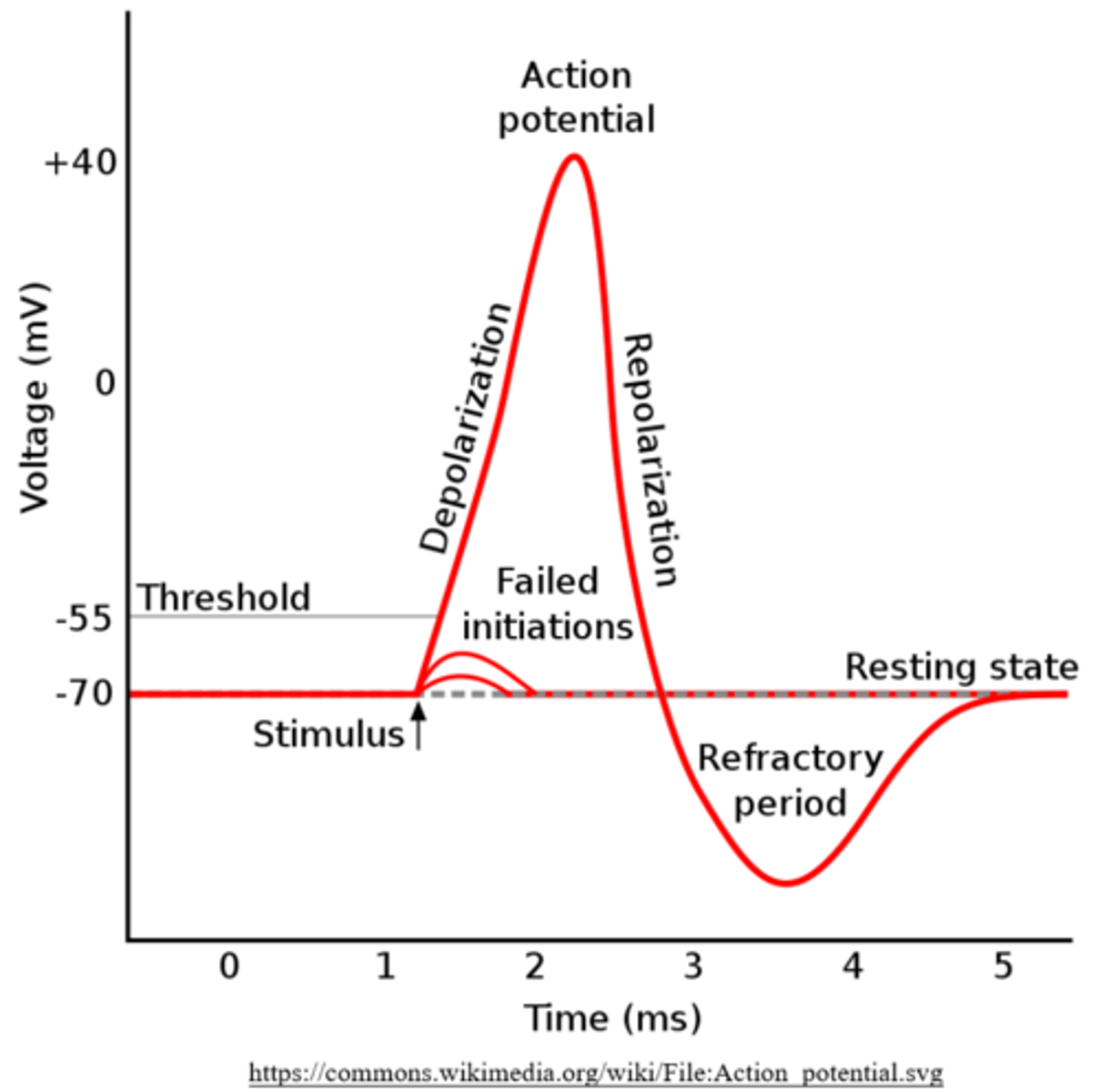
what is the resting potential for a typical neuronal cell?
-70 mV
a cell's resting potential is maintained by _____
Na+/K+ ATPases
more Na+ is _____ the neuron at the resting state
outside
more K+ is _____ the neuron during the resting state
inside
the Na+/K+ ATPase (pump) exchanges _____ out of a cell for _____ into the cell, and it consumes _____ to do so
3 Na+; 2 K+; 1 ATP
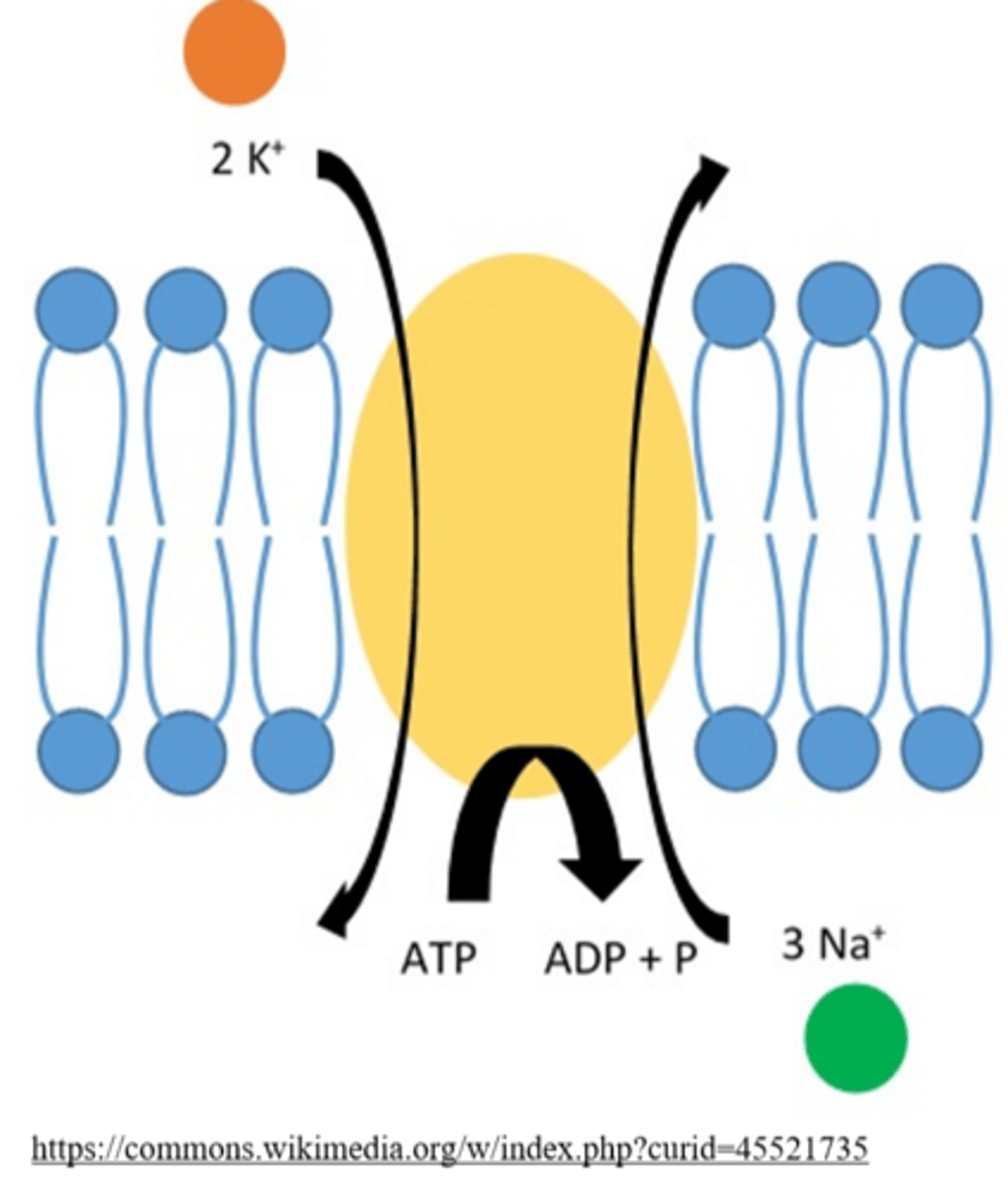
the Na+/K+ pump maintains a (positive/negative) charge in the neuron
negative
(extracellular environment is more positive)
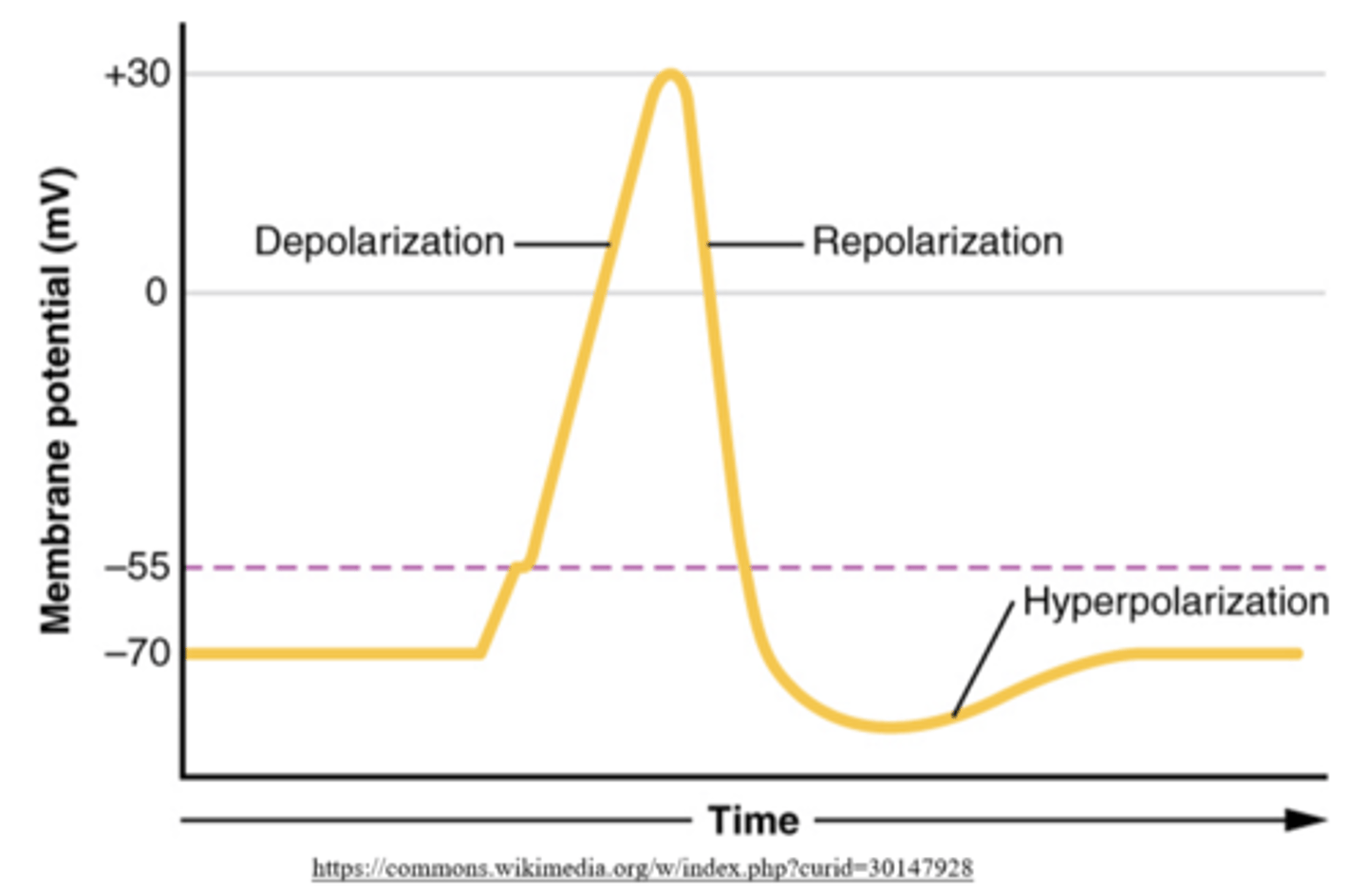
what happens when a neuron is stimulated by an excitatory potential?
depolarization
(membrane potential is made less negative)
gated Na+ channels open/close when a neuron is depolarizing
open
Na+ flows in/out of a neuron during depolarization
in
what is the threshold potential of a neuron?
minimum potential for an action potential
(typically -55 mV)
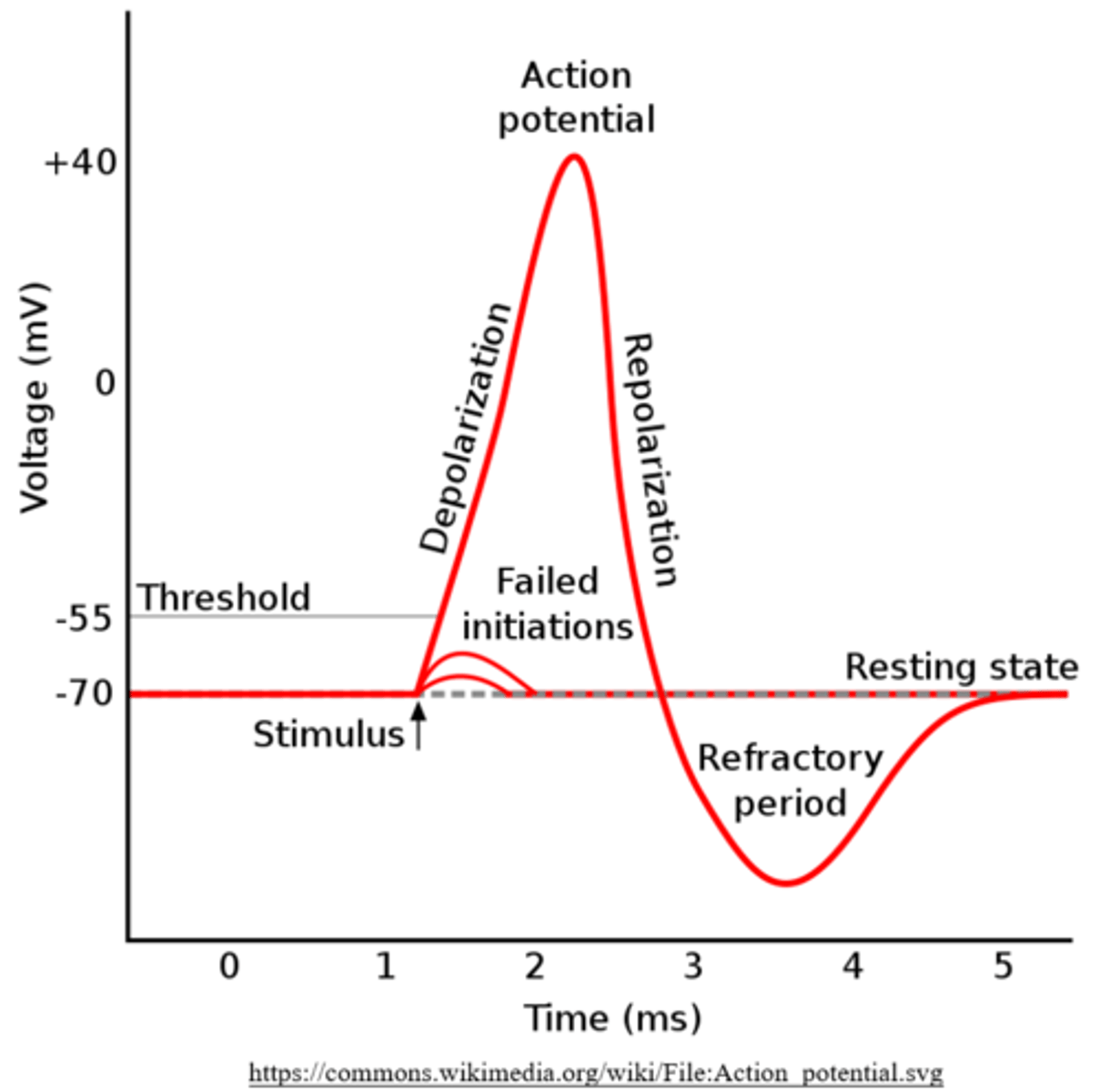
after a neuron reaches threshold, it will experience an action potential that is always the same size - what is the typical charge of an action potential?
+30 mV
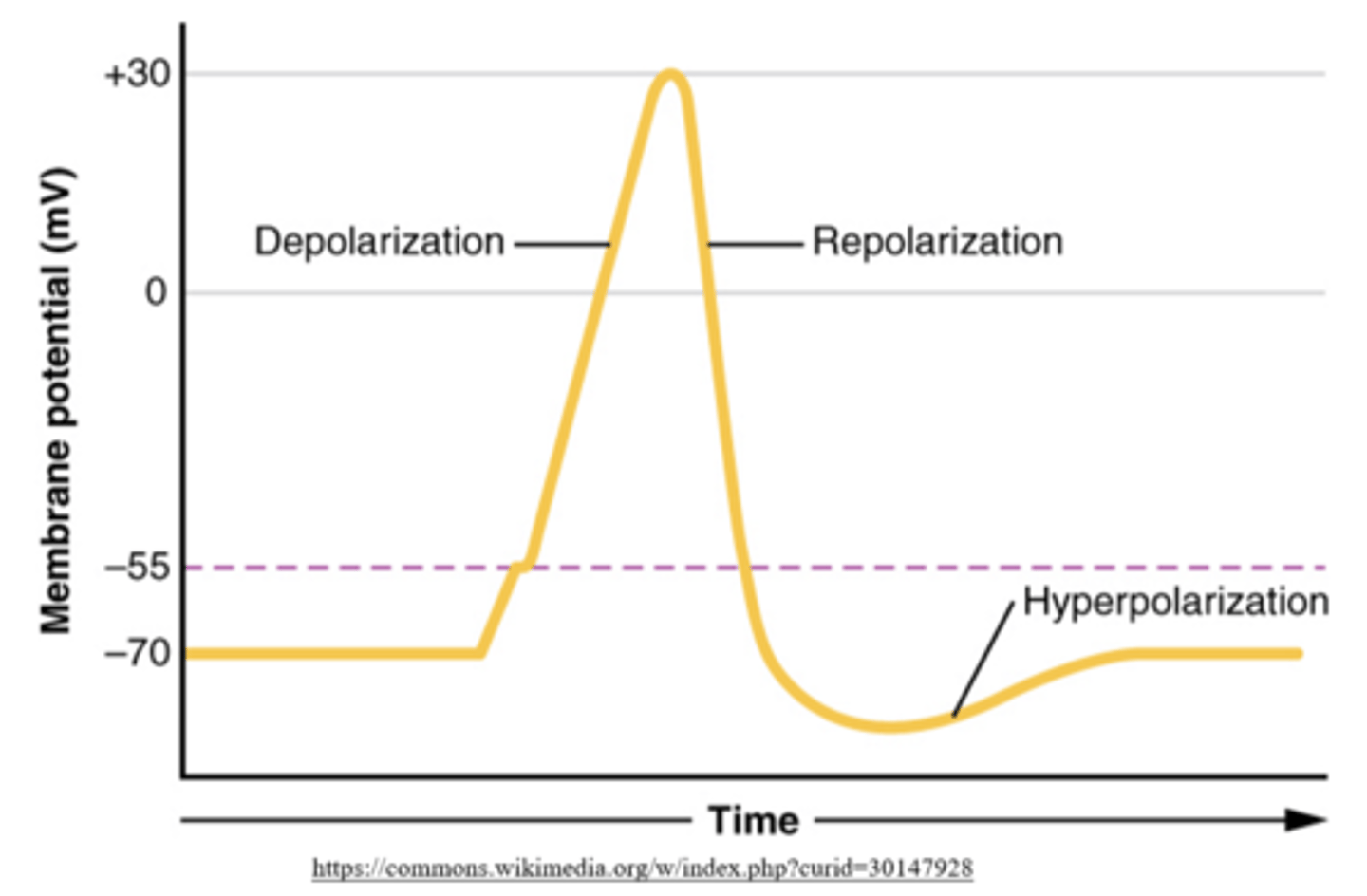
what happens at +30 mV (peak action potential)?
repolarization
(membrane potential becomes more negative)
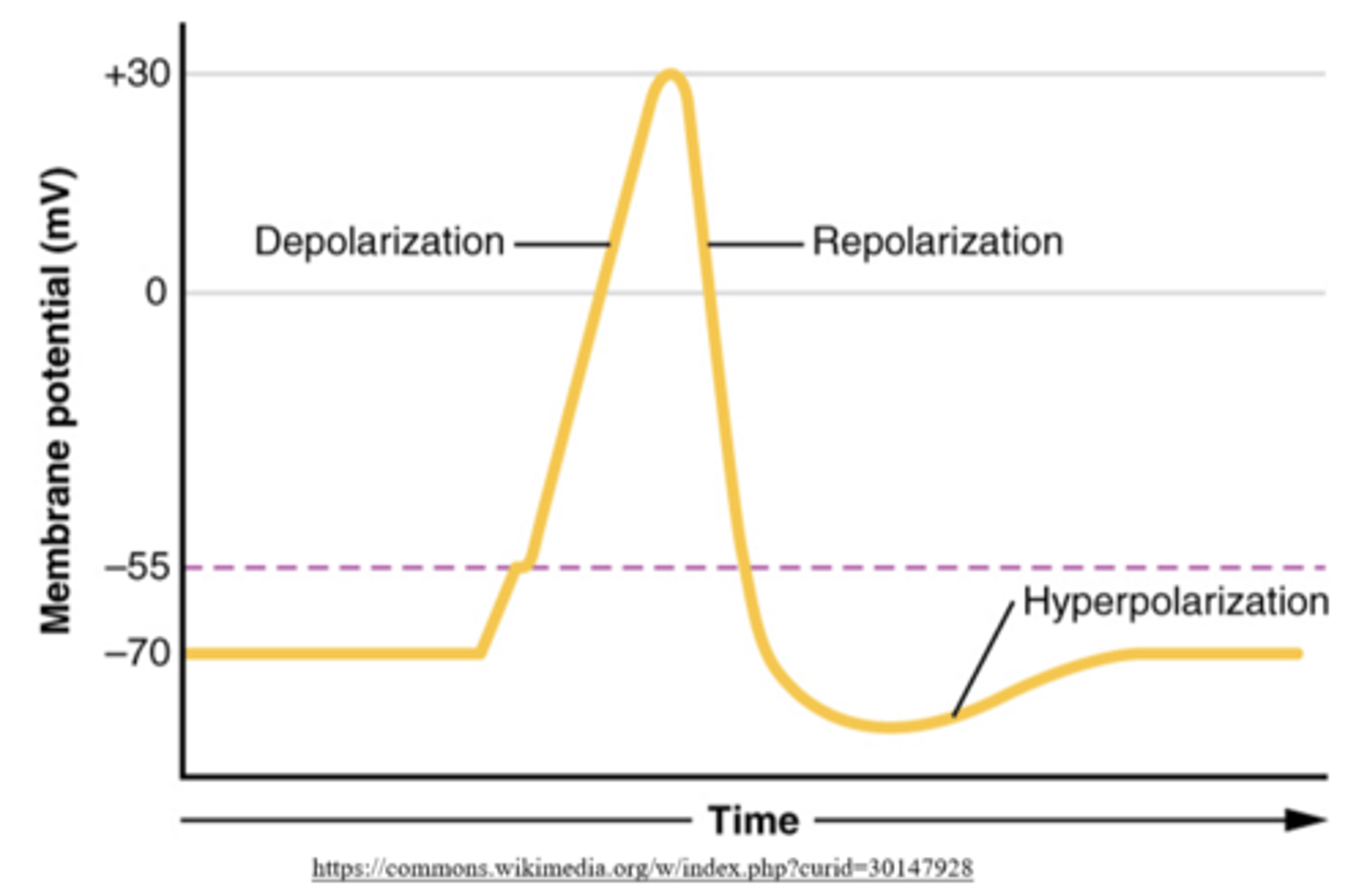
Na+ channels (open/close), while K+ channels (open/close) to initiate repolarization
close; open
K+ flows (in/out) of the neuron during repolarization
out
eventually, a neuronal cell will _____, meaning the membrane potential falls below the normal resting potential of -70 mV
hyper-polarize
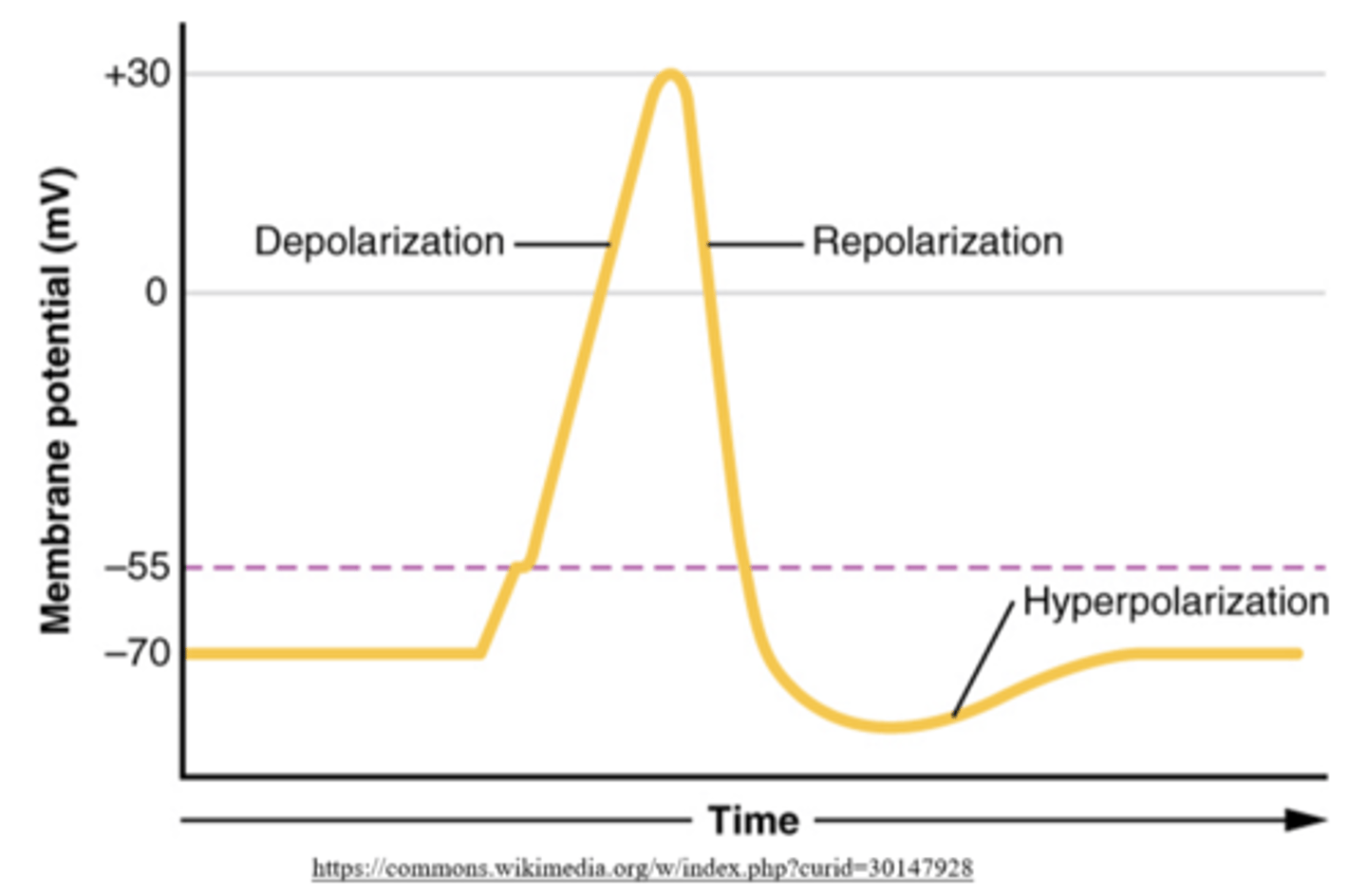
what is the typical charge of a hyperpolarized neuronal cell?
-90 mV
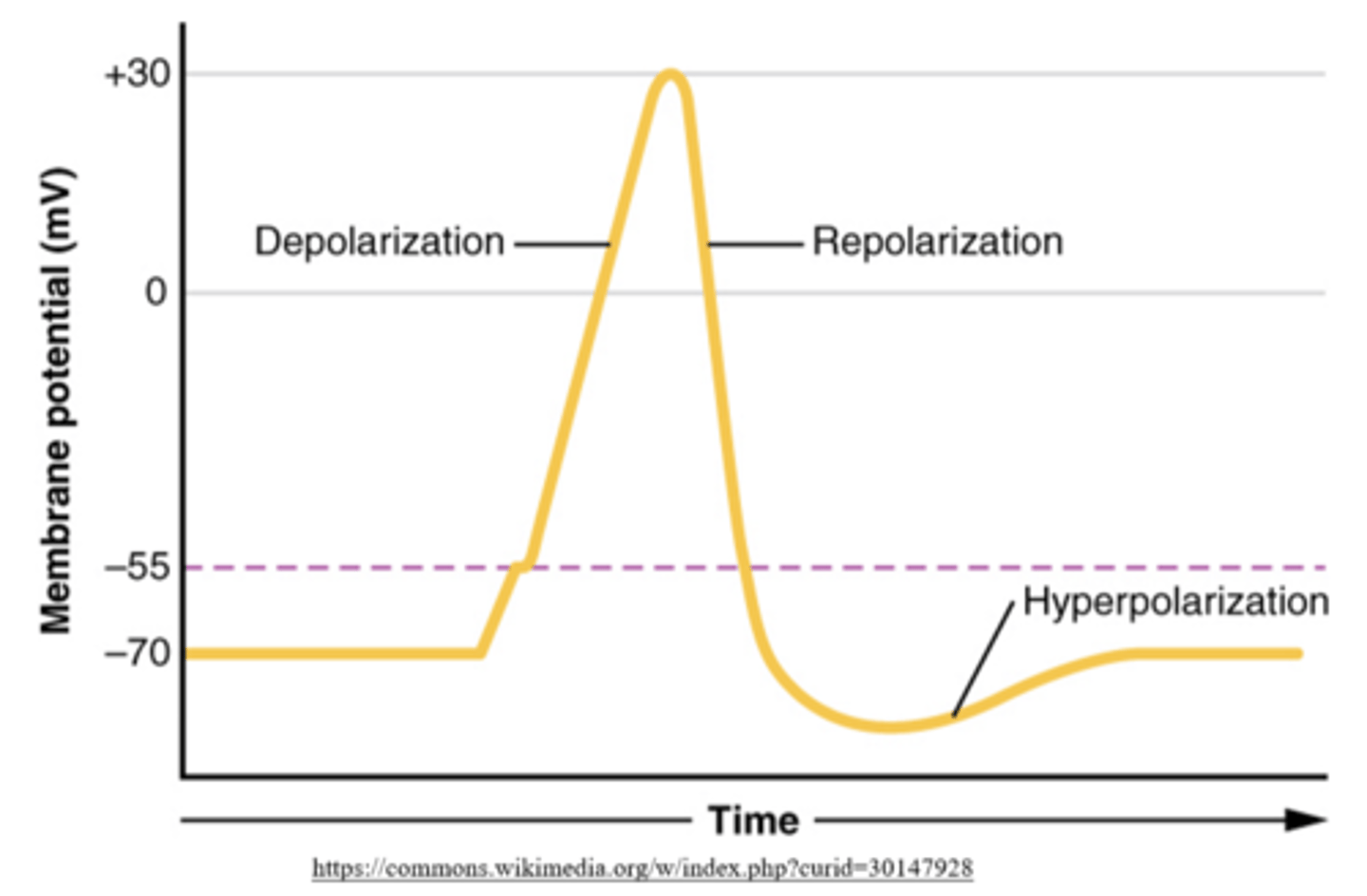
a neuron's refractory period occurs during _____ & _____, and it extends into _____
action potential; repolarization; hyperpolarization
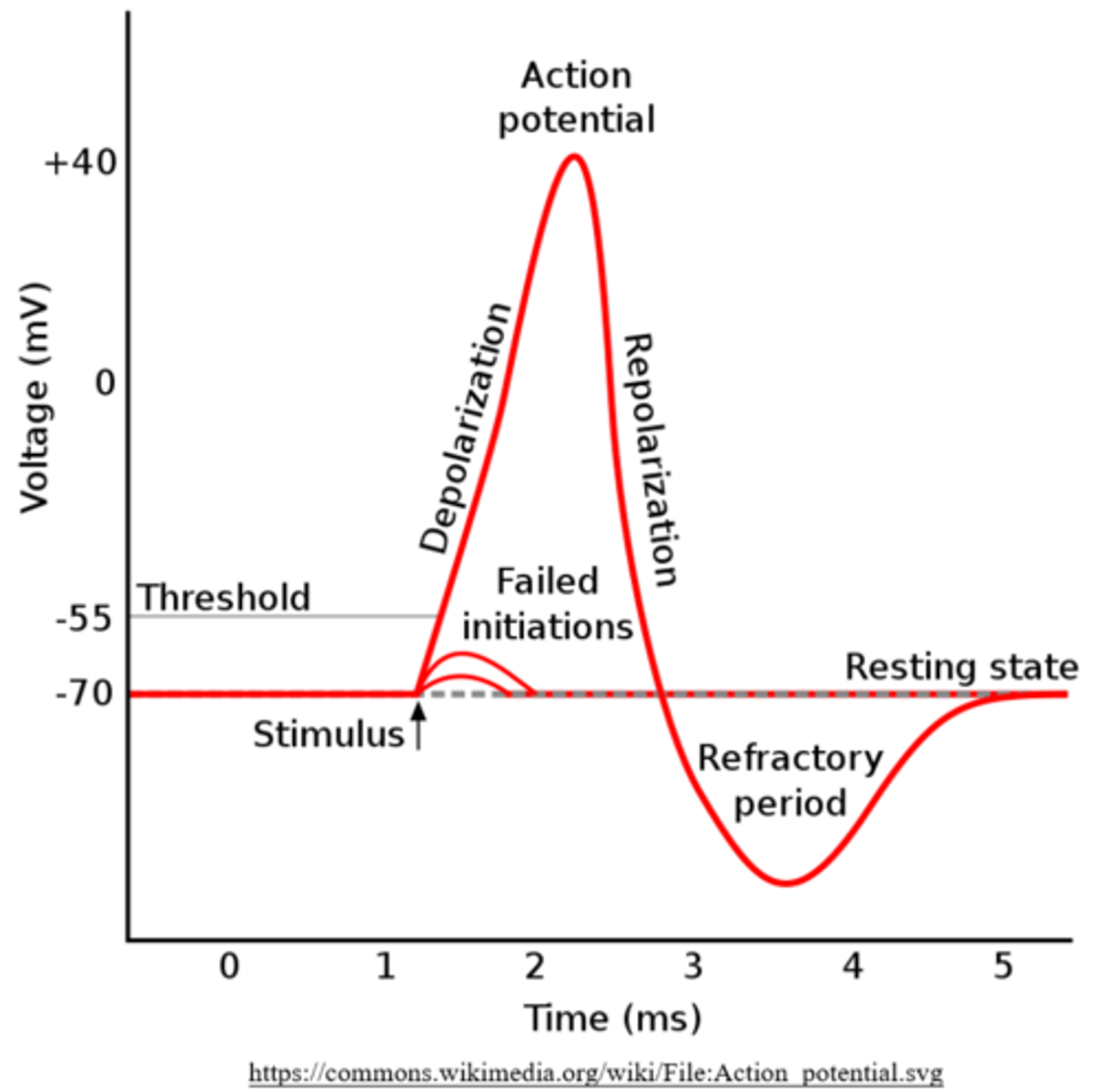
what are the two stages of the refractory period?
absolute; relative
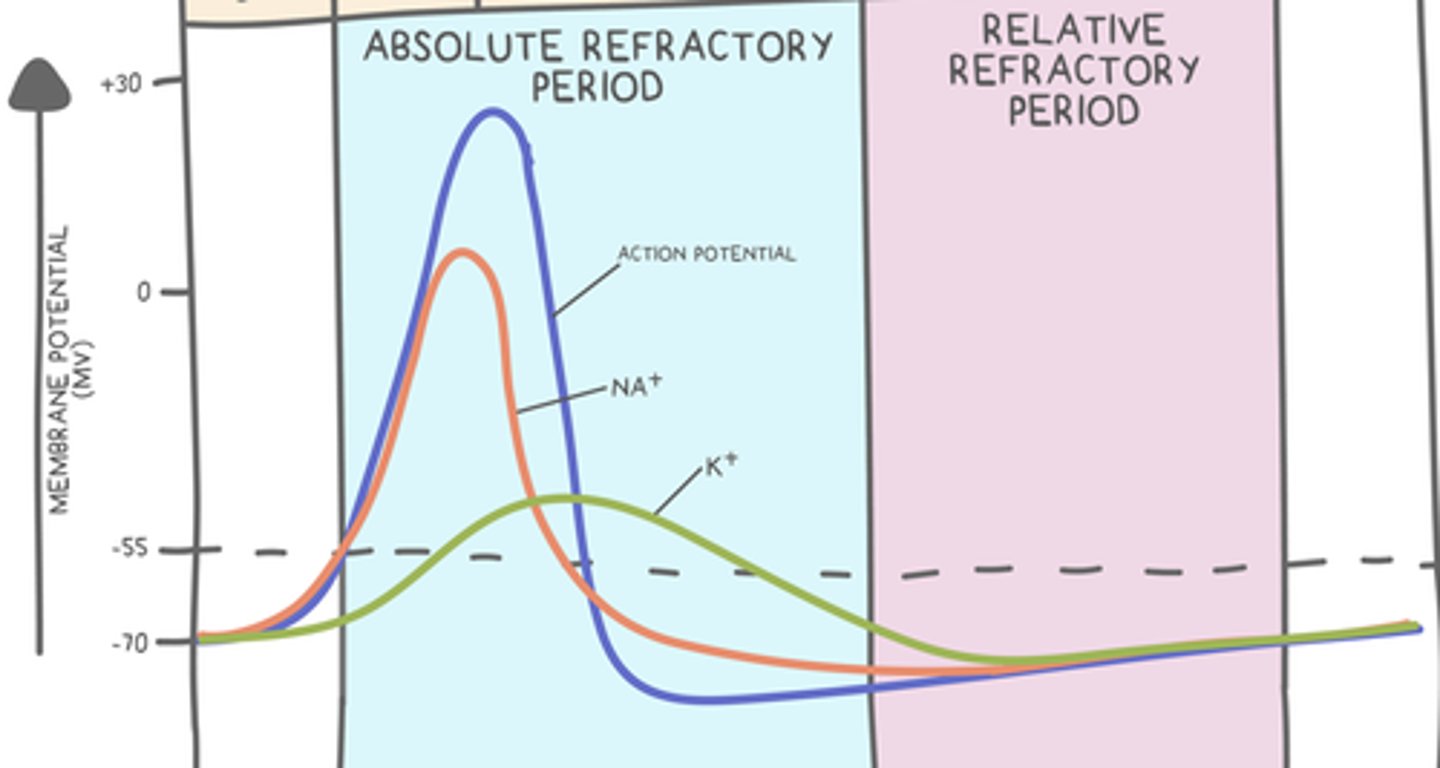
a second stimulus cannot generate another action potential during the _____ of an action potential/repolarization
absolute refractory period
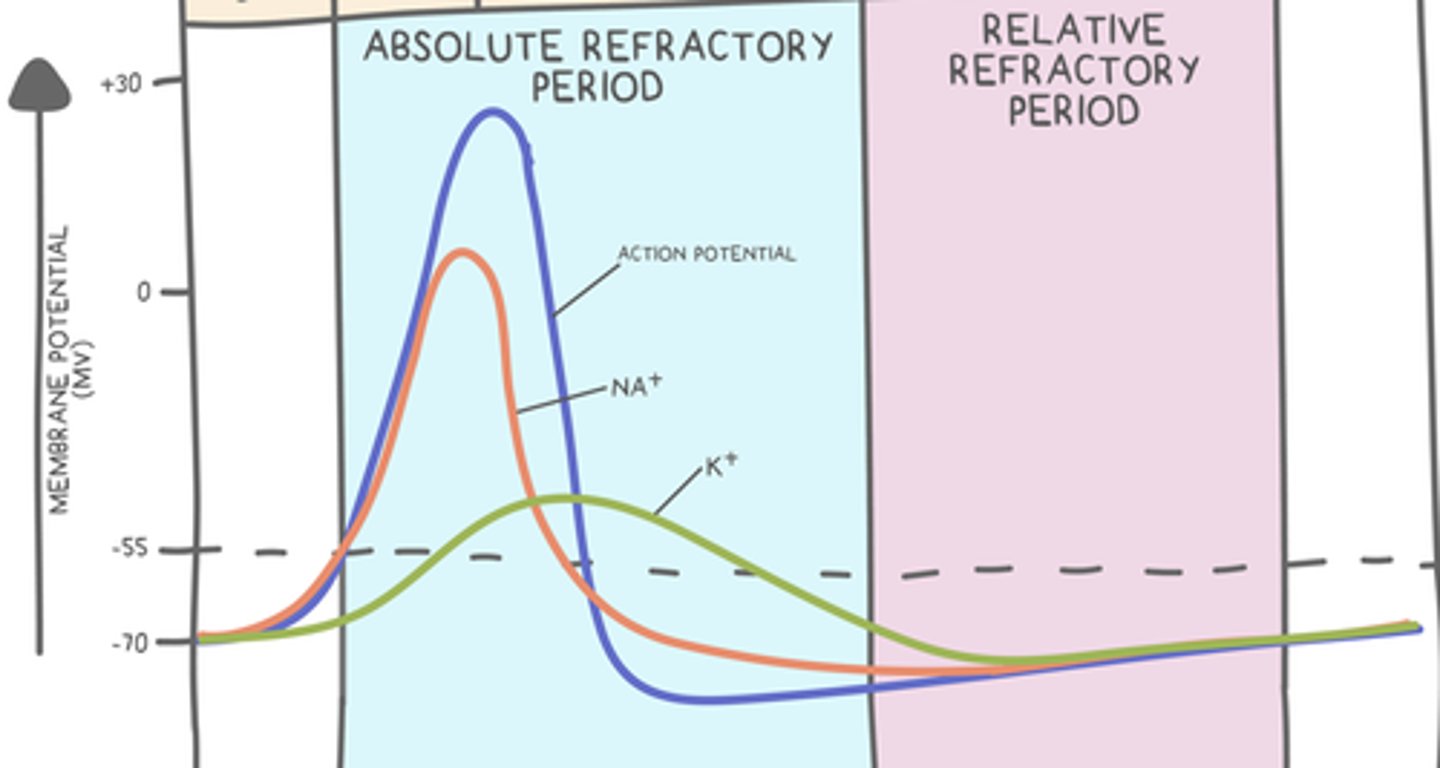
describe Na+ and K+ channels during the absolute refractory period?
gated Na+ channels are open until peak action potential, then they close
K+ channels open at peak action potential until the end of repolarization
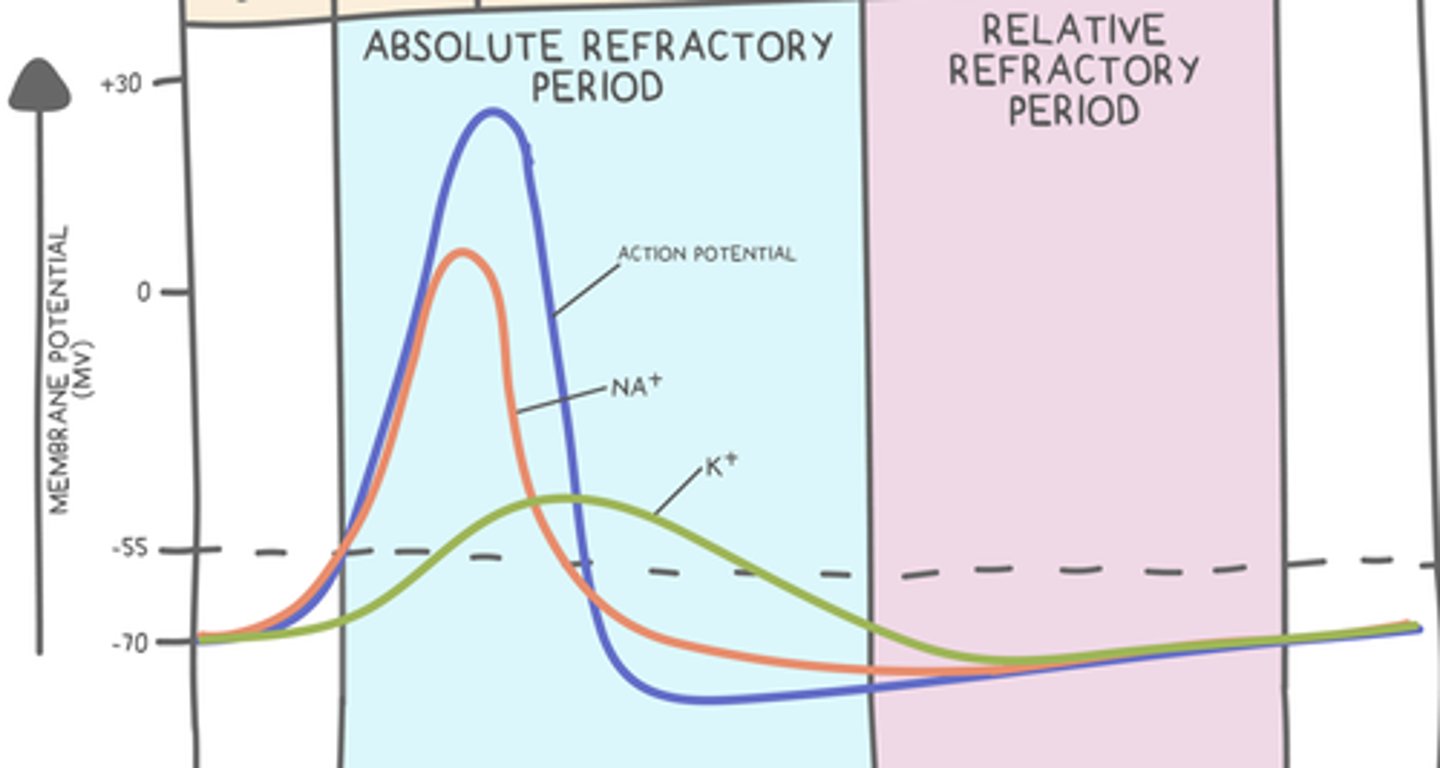
a second stimulus can stimulate an action potential if it is strong enough during a _____
relative refractory period
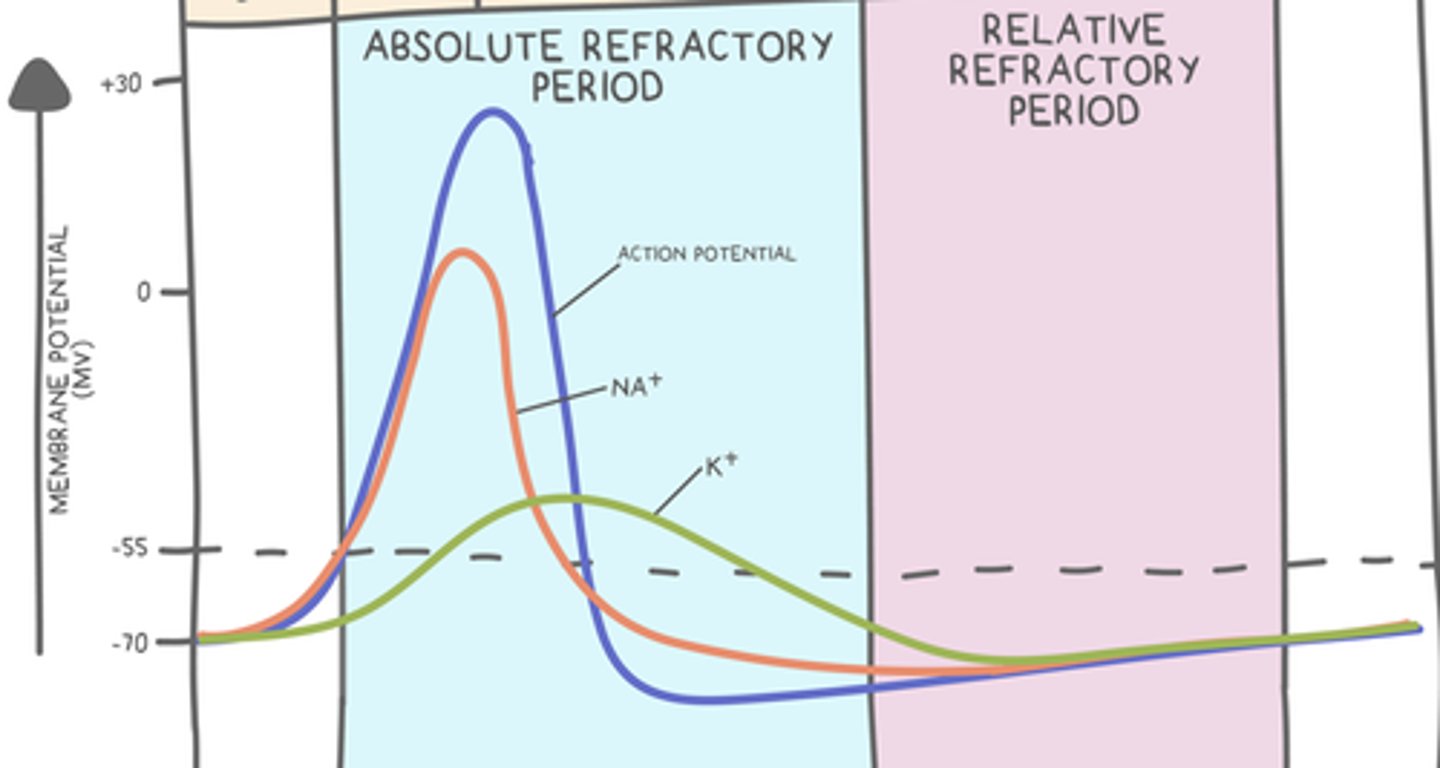
the relative refractory period occurs after the _____
absolute refractory period
(or onset of hyperpolarization)
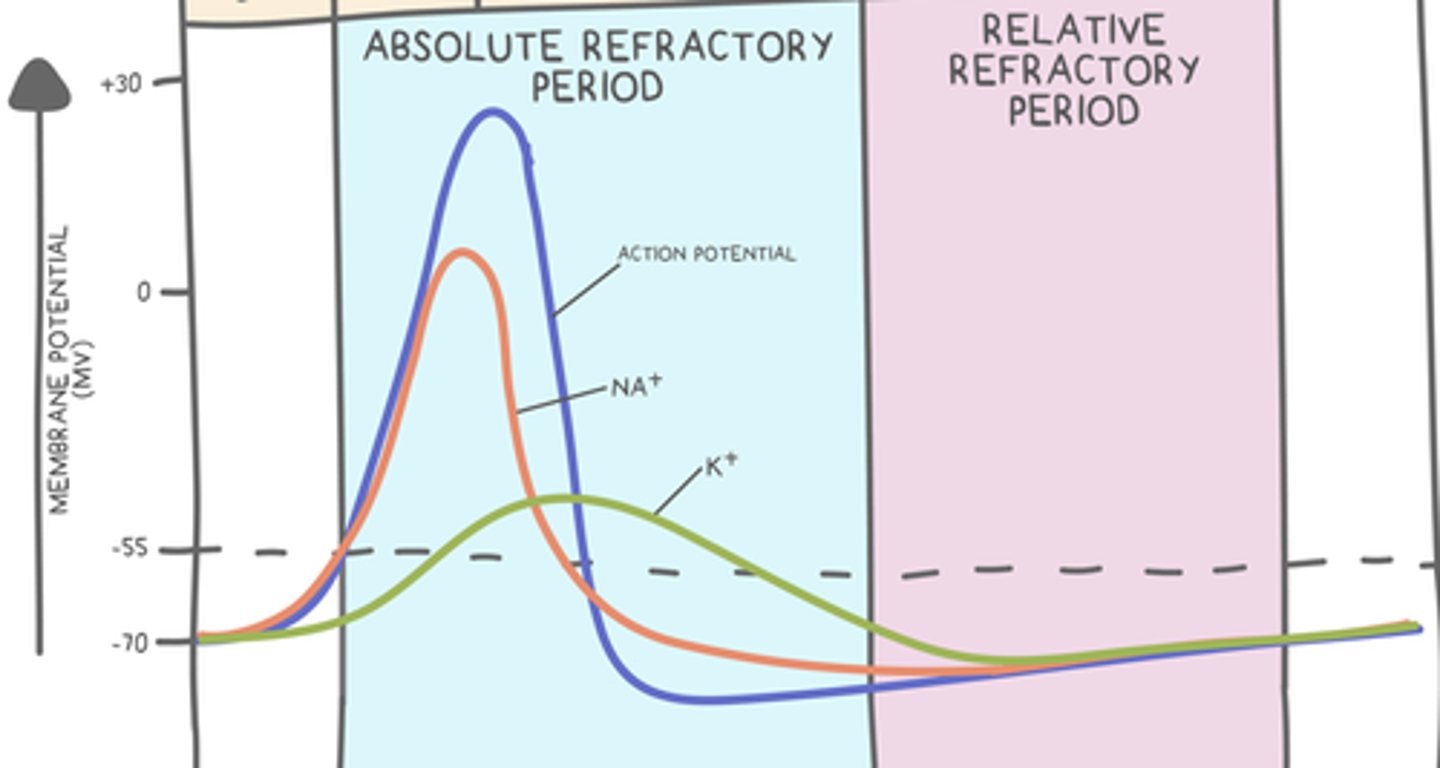
describe Na+ and K+ channels during the relative refractory period:
the Na+ channels remain closed
the K+ channels remain open until the resting potential is acheived
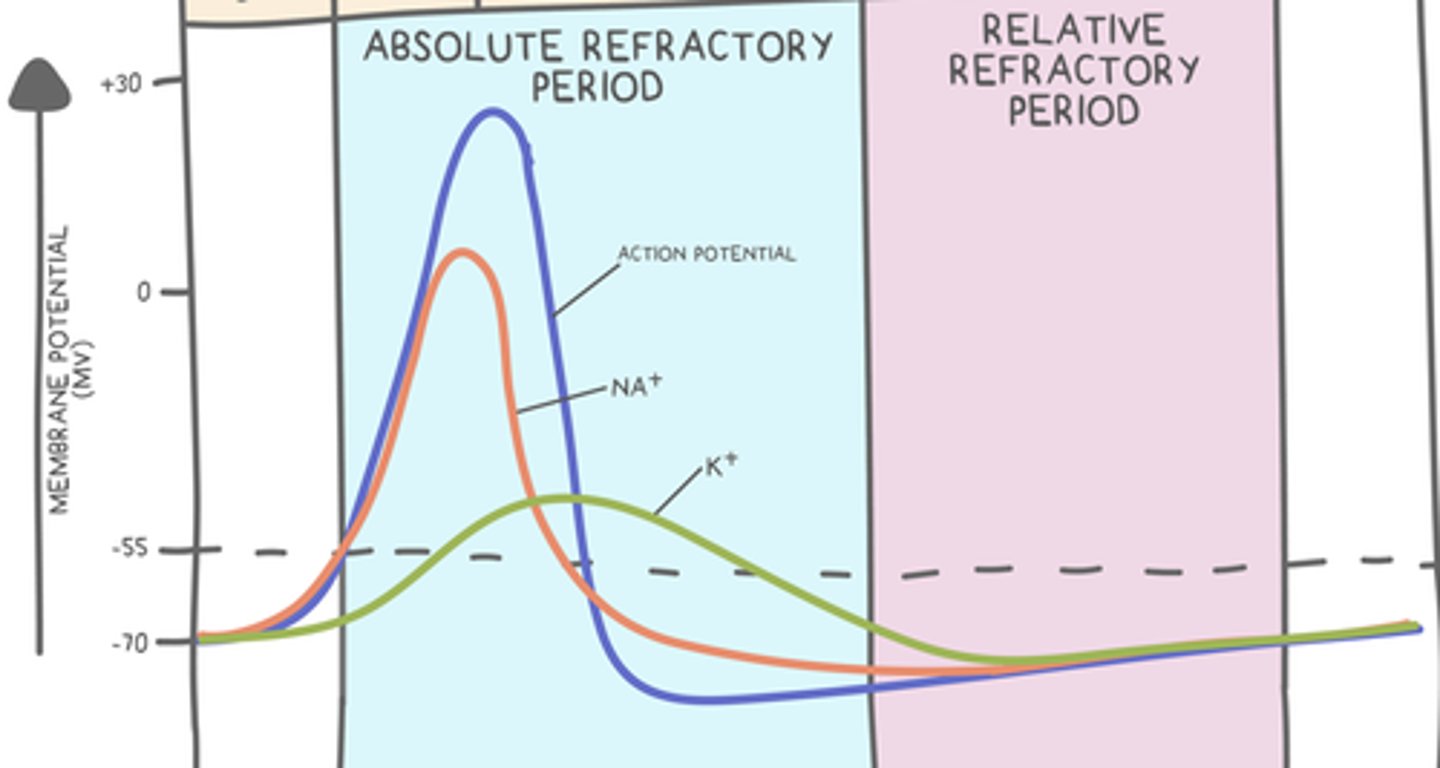
neurons are _____ during the relative refractory period
hyperpolarized
a _____ is the space between two neurons
synapse (synaptic cleft)
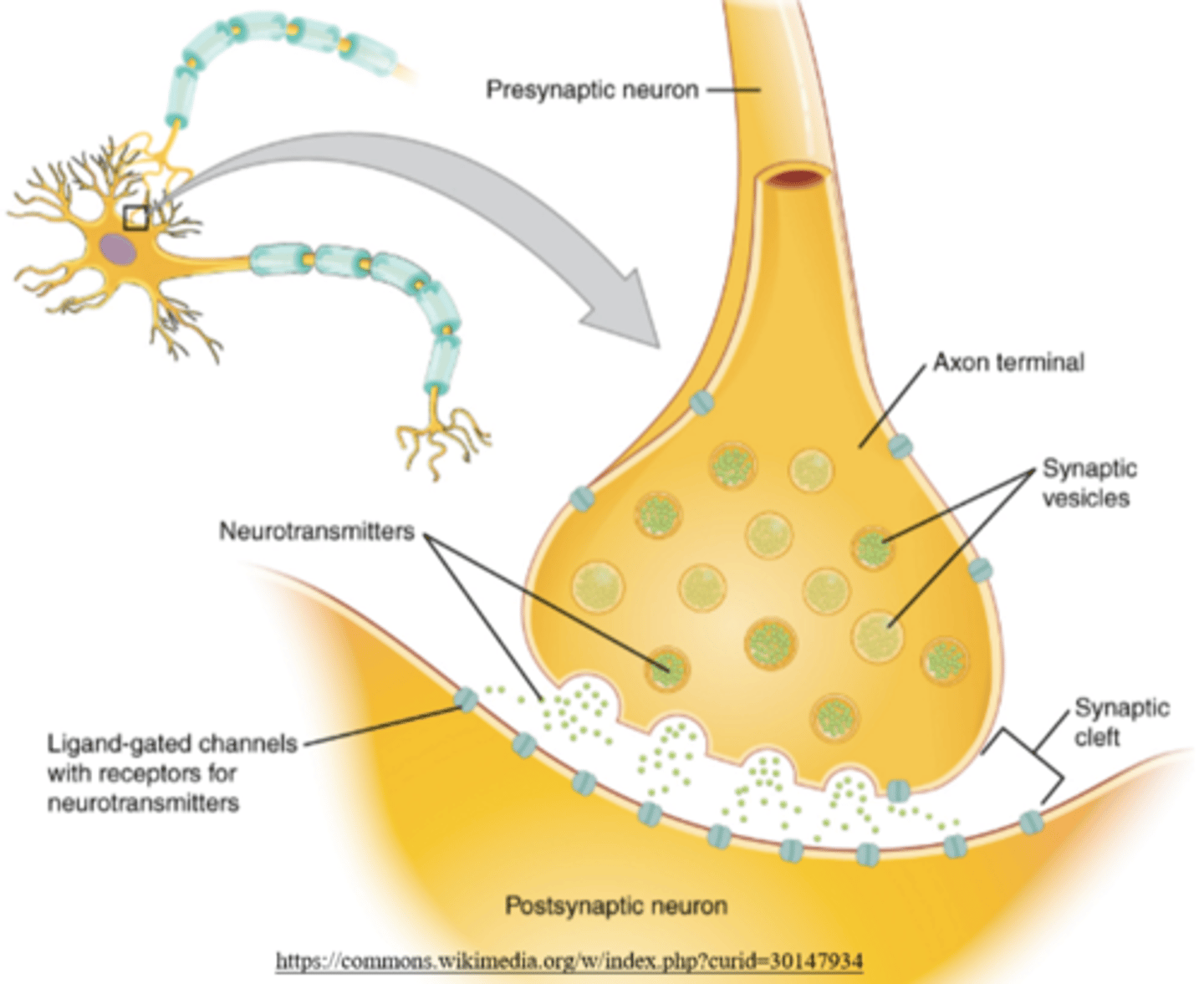
the _____ neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synapse
presynaptic
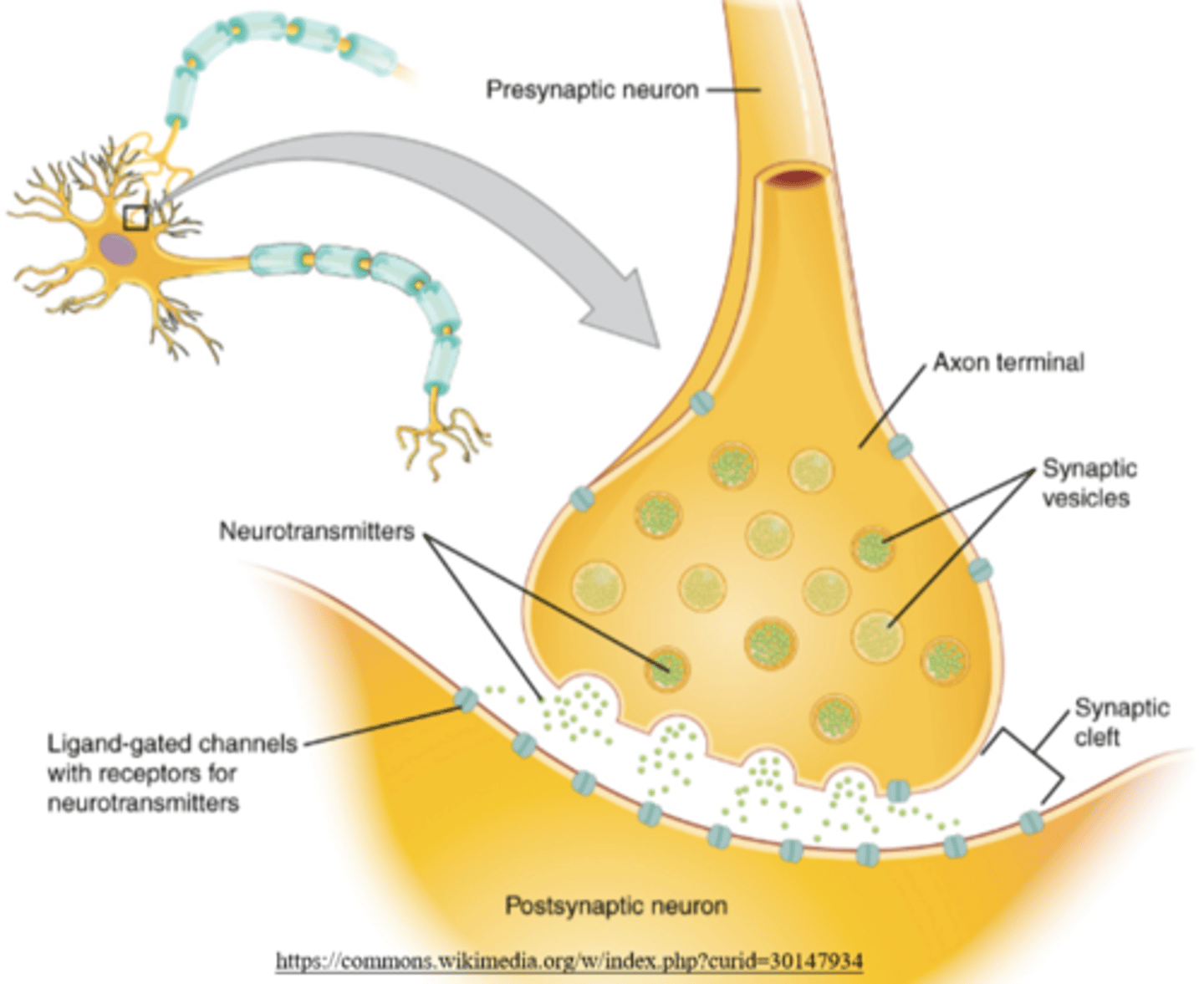
the _____ neuron receives neurotransmitters that cross the synapse
postsynaptic
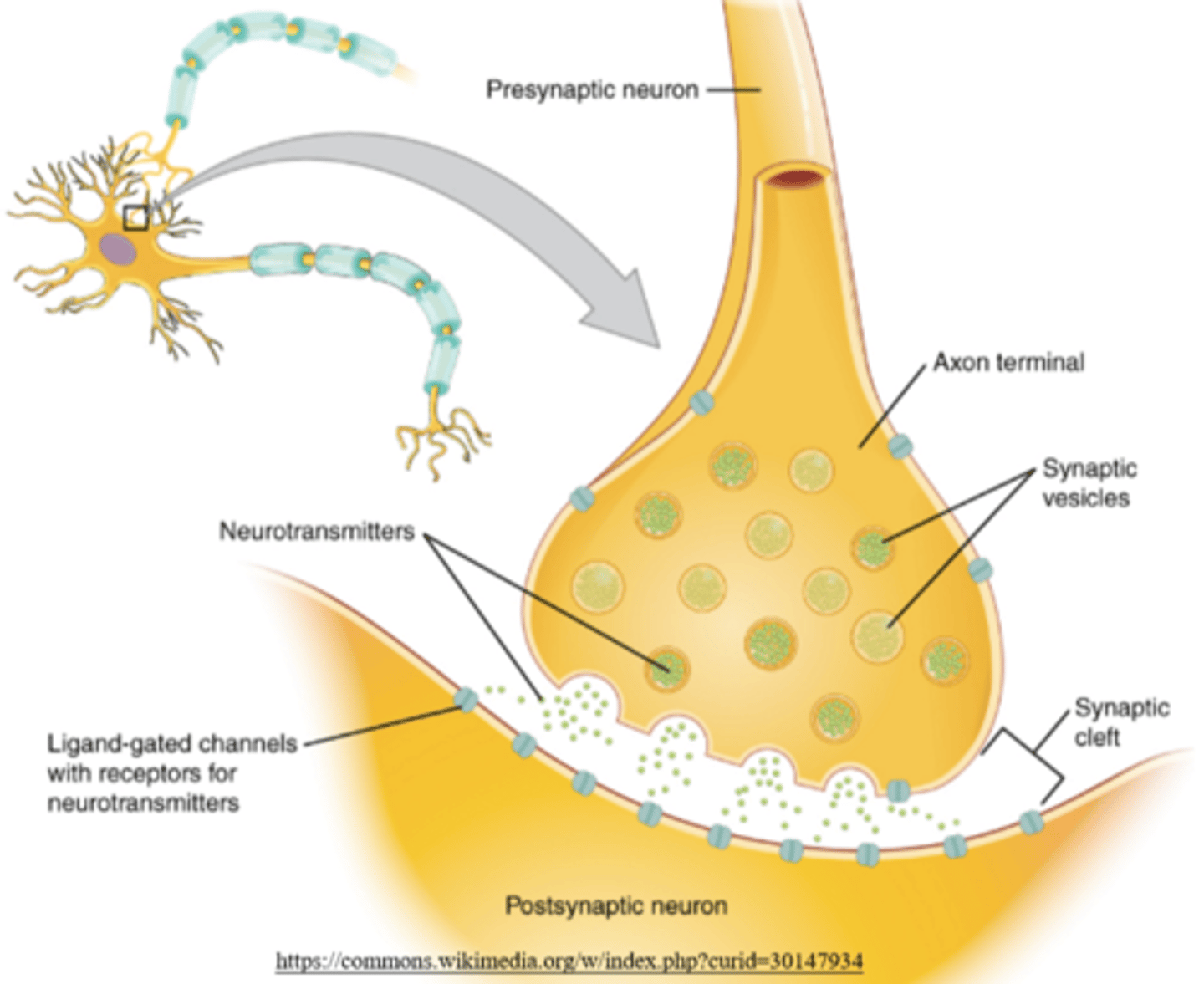
what happens when an action potential reaches the end of the presynaptic axon?
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, allowing Ca2+ to flow into the neuron
what happens when voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open to allow Ca2+ influx into the presynaptic neuron?
synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synapse by exocytosis
postsynaptic graded potentials can be _____ or _____ depending on the neurotransmitter
excitatory; inhibitory
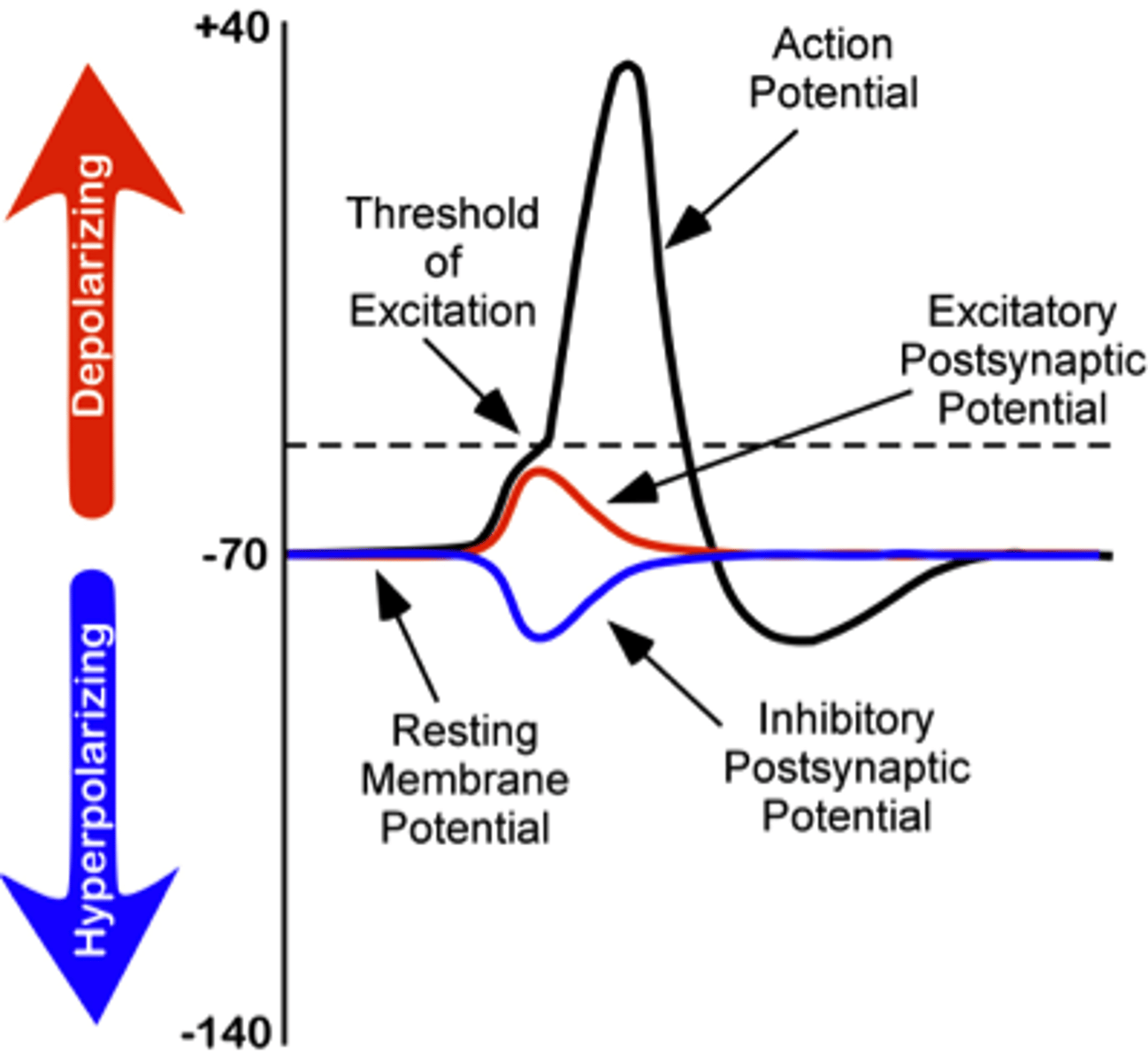
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) occur when the neuron _____ due to _____ that open
depolarizes; Na+ gates
Na+ flows (into/out of) the cell during an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
into
excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) bring the neuron _____ to the threshold
closer
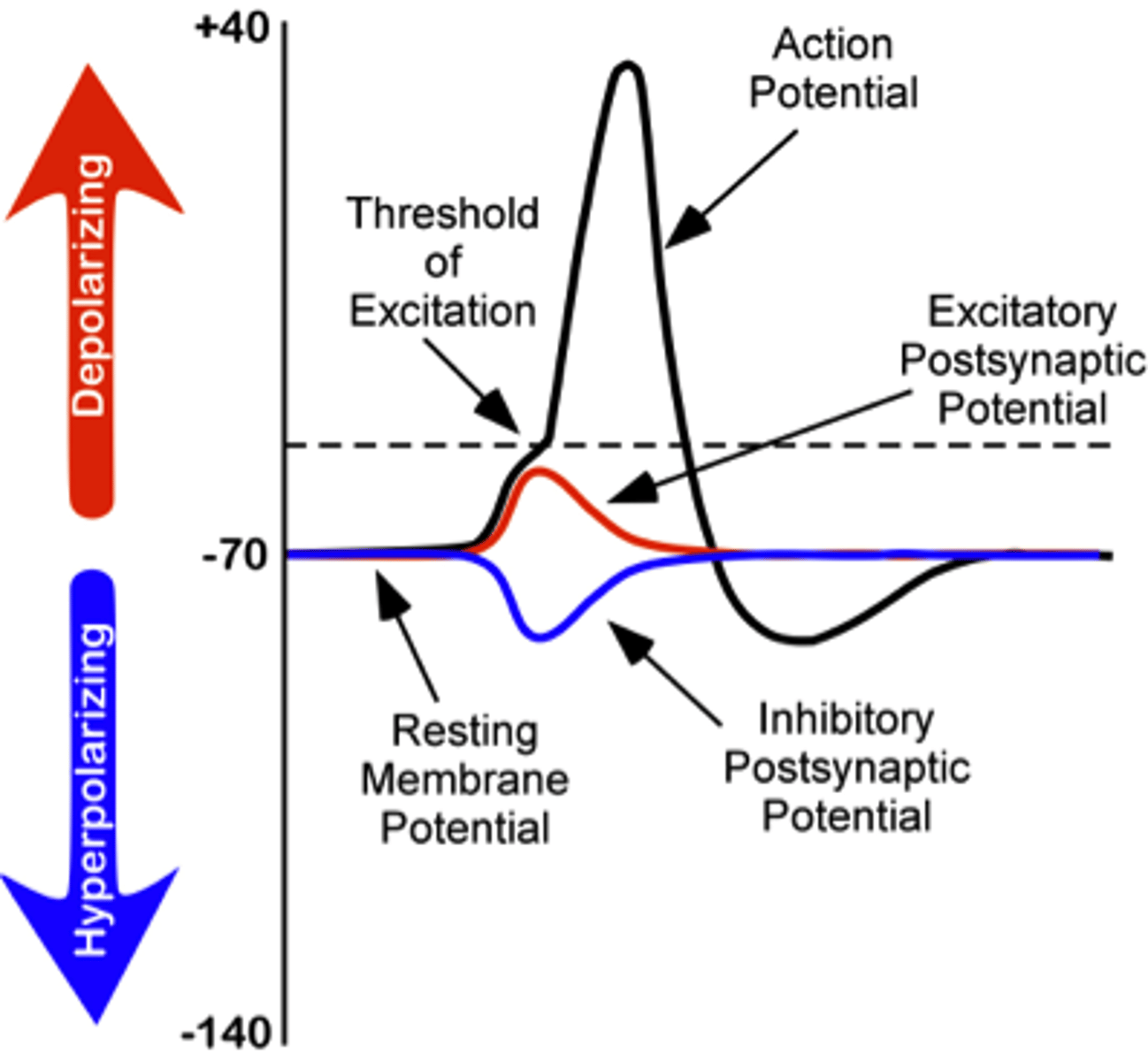
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) occur when the neuron _____ due to _____ & _____ channels that open
hyperpolarizes; Cl-; K+
in which directions do Cl- and K+ flow during an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)?
Cl- = into the cell
K+ = out of the cell
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) bring the neuron _____ from the threshold
further away
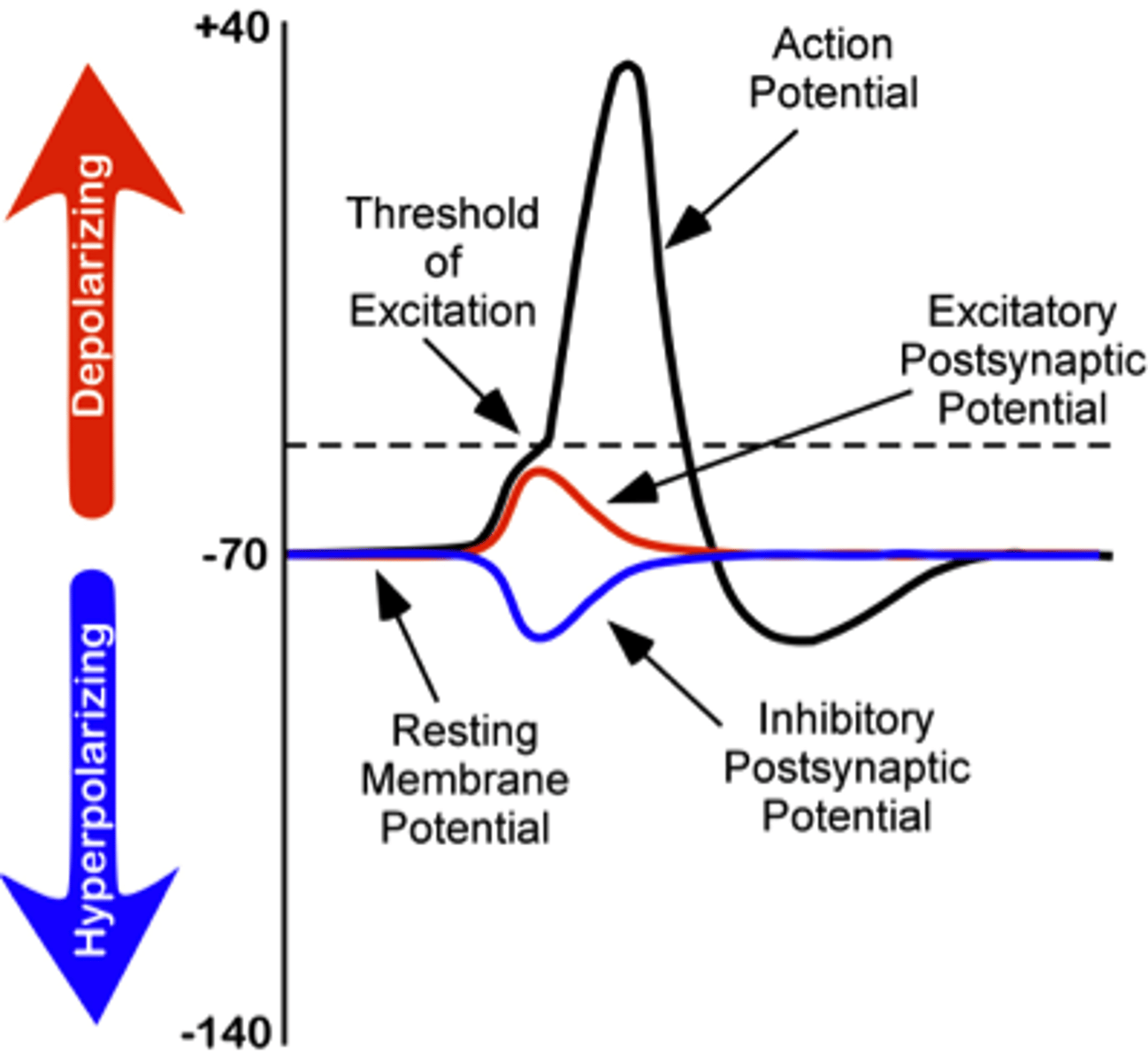
graded potentials vary in _____ and _____ (EPSP v. IPSP)
magnitude; direction
_____ occurs when all graded potentials (EPSPs and IPSPs) are added together at the _____
summation; axon hillock
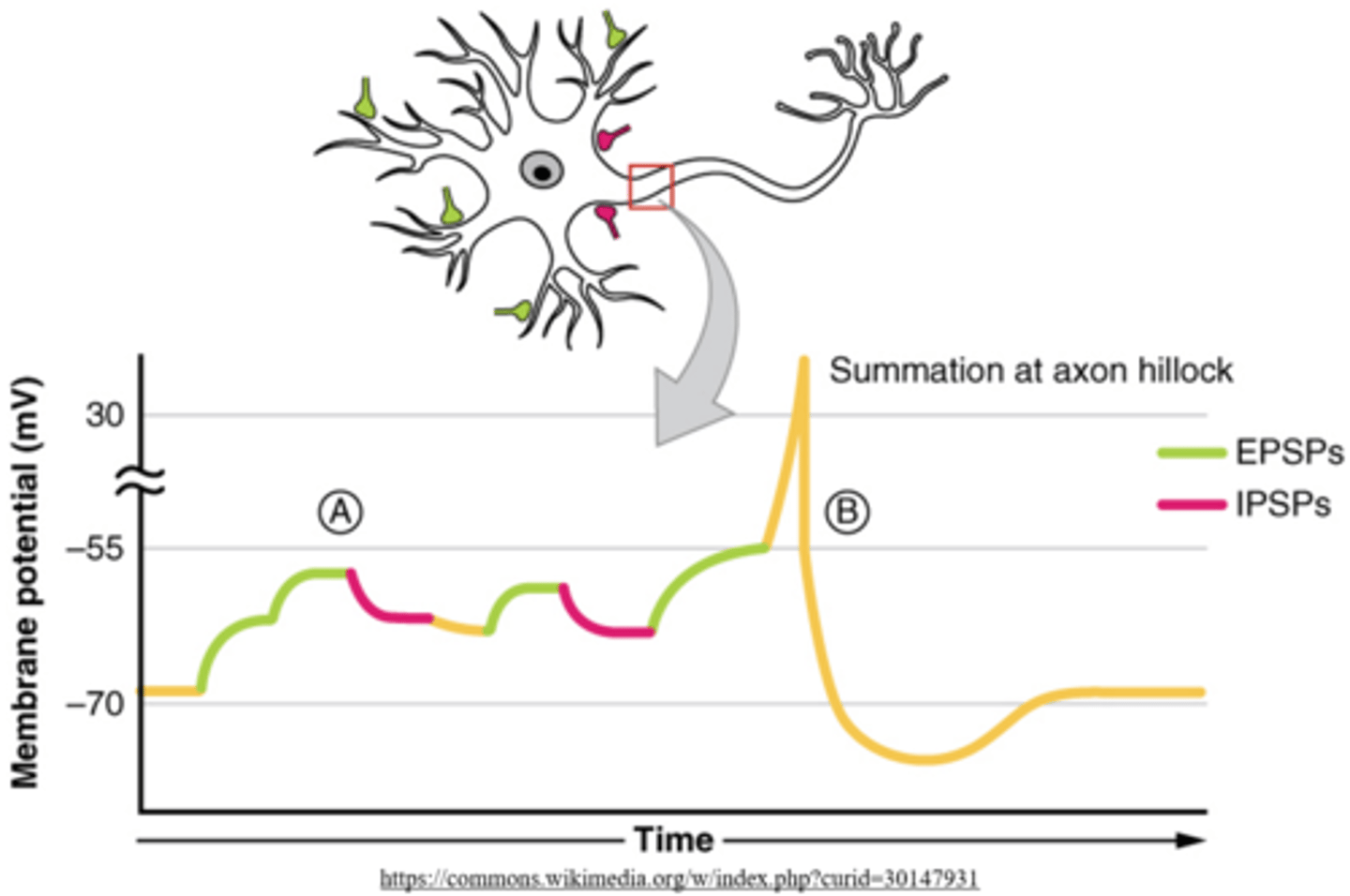
an _____ and ensuing _____ occur if the sum of EPSPs and IPSPs is higher than the threshold
action potential; refractory period
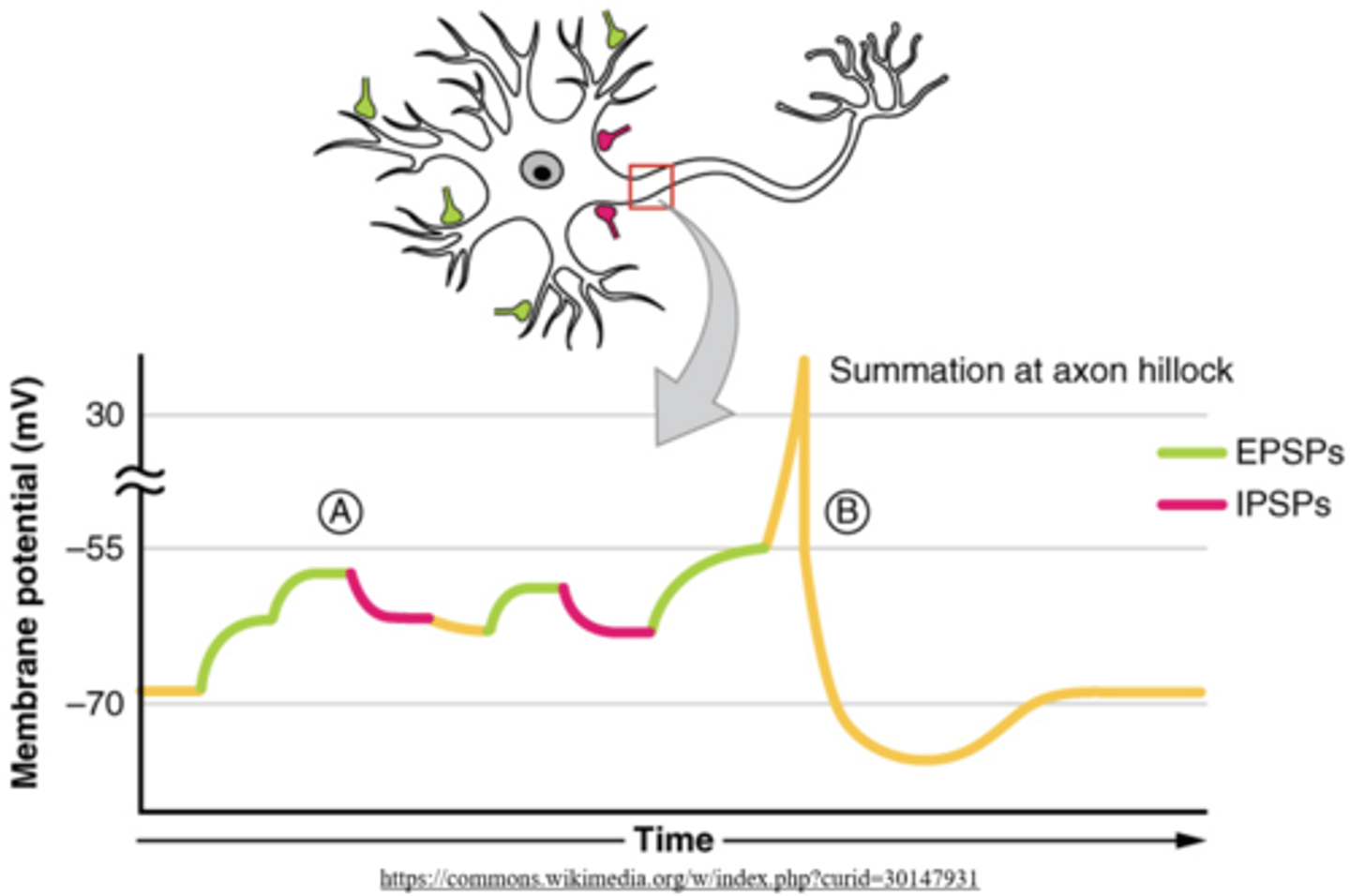
there will not be an action potential (or refractory periods) if the sum of EPSPs and IPSPs is _____
below threshold
what are neurotransmitters?
chemical messengers used during chemical neurotransmission
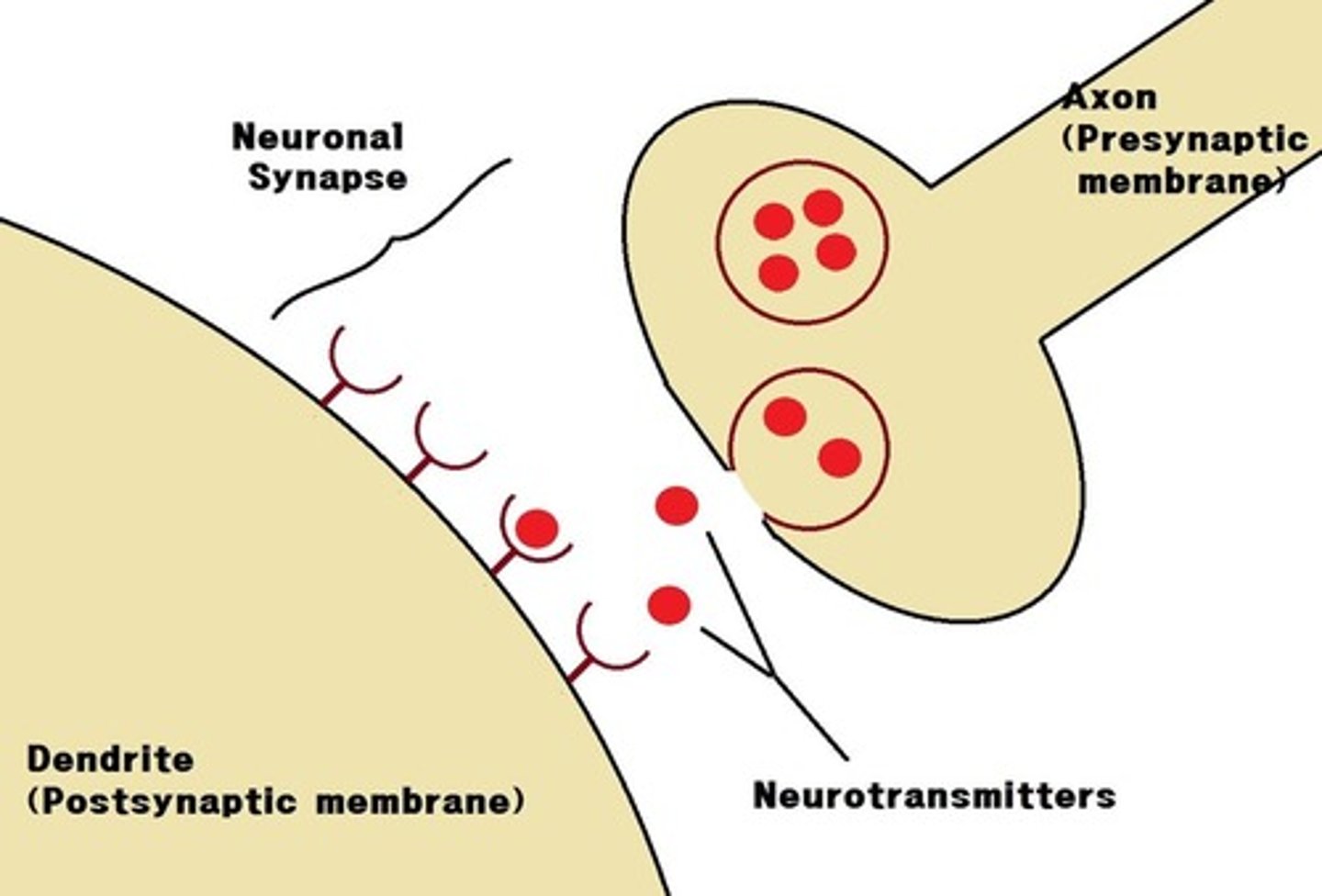
what is the main excitatory neurotransmitter of the vertebrate central nervous system?
glutamate
which category of neurotransmitter does glutamate fall into?
amino acid neurotransmitter
gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a(n) _____ (class of neurotransmitter), and it is an inhibitory/excitatory neurotransmitter of the brain
amino acid neurotransmitter; inhibitory
glycine is a(n) _____ (class of neurotransmitter), and it is an inhibitory/excitatory neurotransmitter of the spinal cord, brainstem, retina
amino acid neurotransmitter; inhibitory
epinephrine and norepinephrine are _____ (class of neurotransmitter)
amino acid-derived
epinephrine and norepinephrine are _____ postsynaptic neurotransmitters of the _____
excitatory; SNS
another name for epinephrine and norepinephrine is _____ and _____
adrenaline; noradrenaline
dopamine is a(n) _____ (class of neurotransmitter), and it is an _____ neurotransmitter of the brain
amino acid-derived; excitatory
_____ is an amino acid-derived neurotransmitter that is responsible for reward-motivated behavior
dopamine
serotonin is a(n) _____ (class of neurotransmitter), and it is an inhibitory/excitatory neurotransmitter of the brain
amino acid-derived neurotransmitter; inhibitory
for which bodily functions is serotonin responsible?
mood, appetite, sleep, and learning
serotonin increases/decreases contraction of the GI tract in response to food intake
increases
which category of neurotransmitter is involved in diverse roles for many brain functions?
short chain amino acid neurotransmitters (neuropeptides)
what is a common example of a short chain amino acid neurotransmitter?
substance P
_____ is a gaseous neurotransmitter (gasotransmitter)
nitric oxide
nitric oxide gasotransmitter causes relaxation of the smooth muscle in blood vessels (_____)
vasodilation
nitric oxide gasotransmitter is synthesized and released _____
on demand
what is the excitatory neurotransmitter of a neuromuscular junction?
acetylcholine
acetylcholine is the presynaptic/postsynaptic neurotransmitter of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
presynaptic
What is the postsynaptic neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system?
acetylcholine
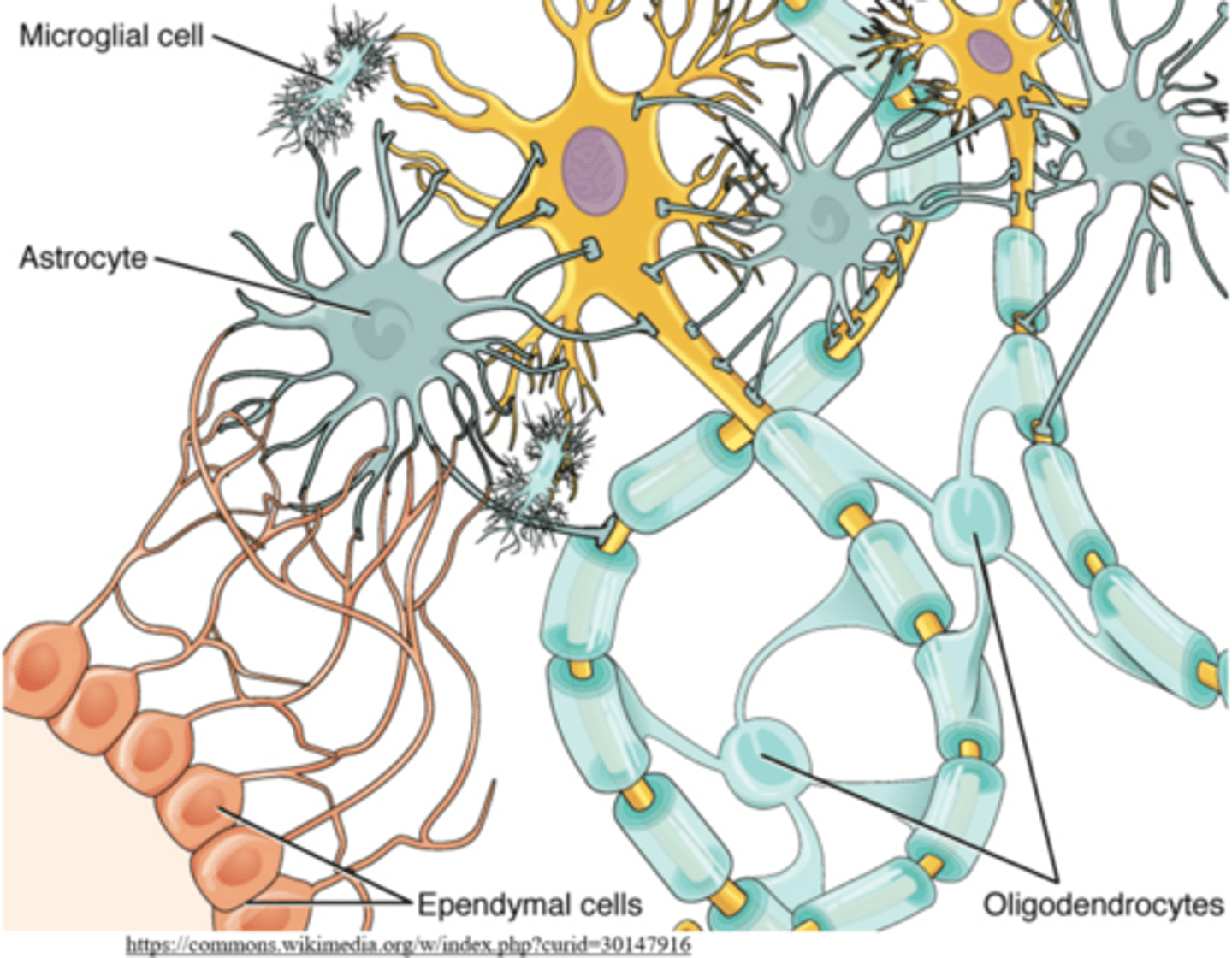
_____ are non-neuronal cells that nourish, support, and protect neurons
glial cells
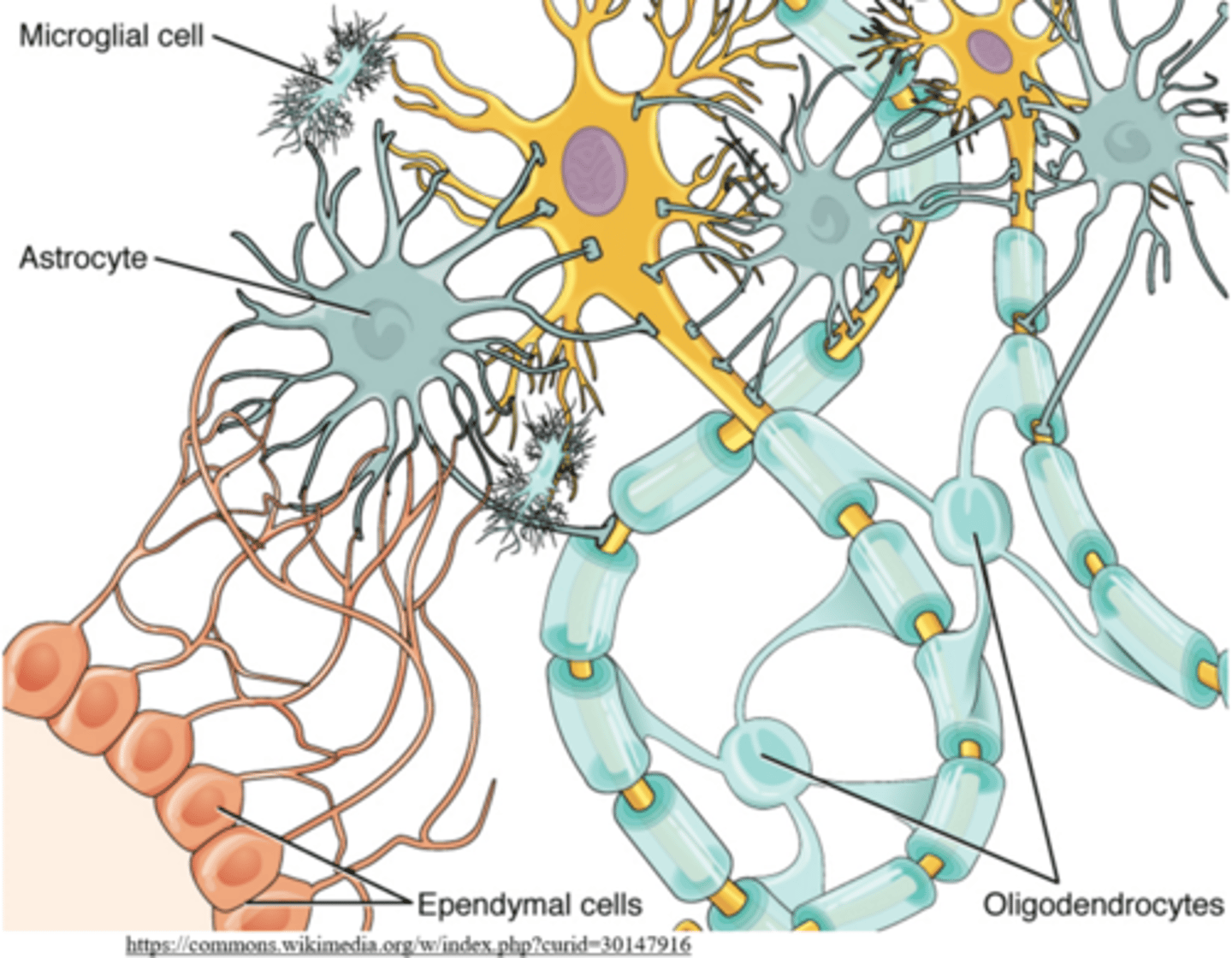
what are the two subcategories of glial cells?
microglia; macroglia (various types)
_____ are specialized macrophages that protect the CNS
microglia
what are the various types of macroglial cells?
schwann cells; oligodendrocytes; astrocytes; satellite cells; ependymal cells
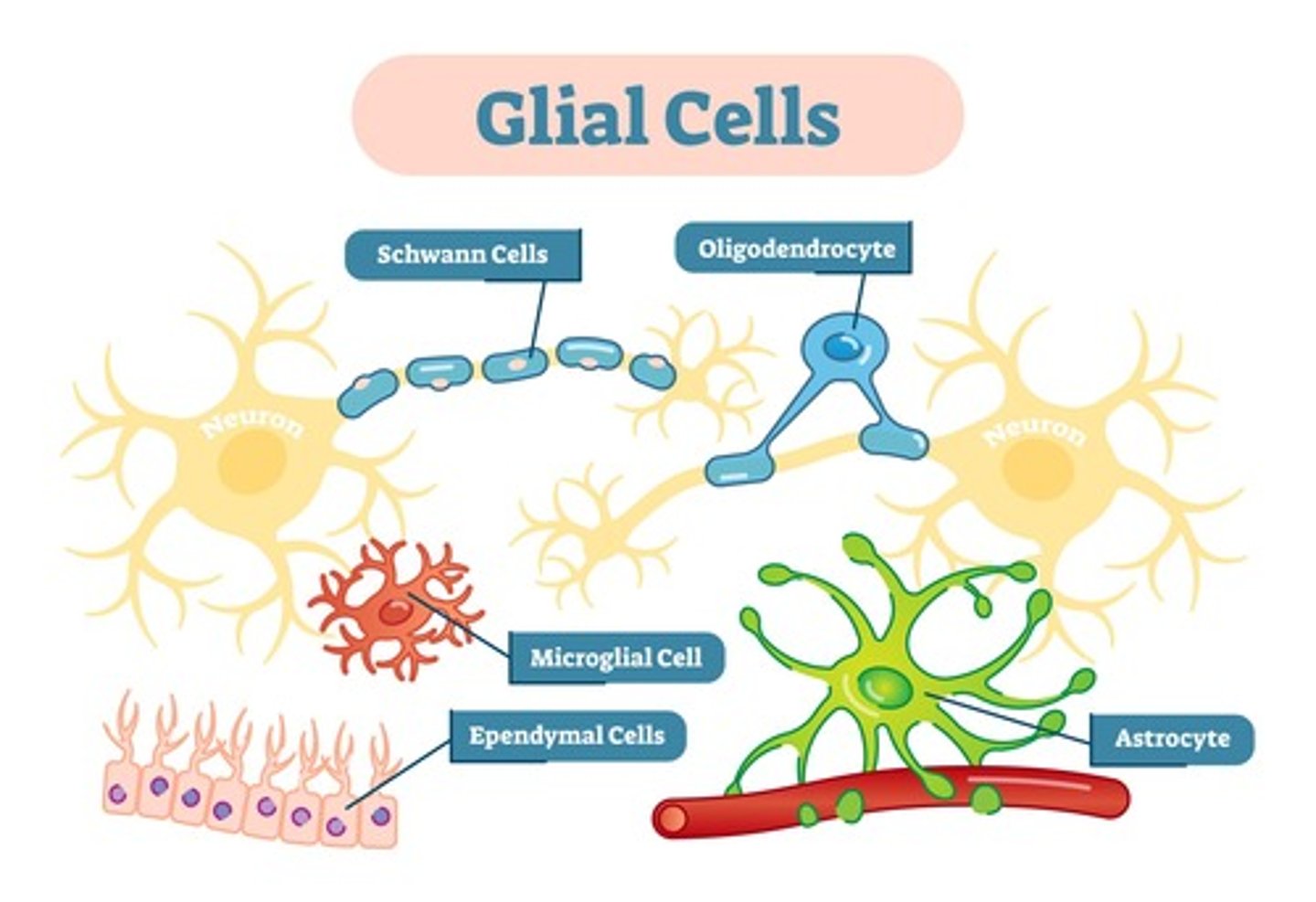
_____ form the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system
schwann cells
_____ form the myelin sheath in the central nervous system
oligodendrocytes
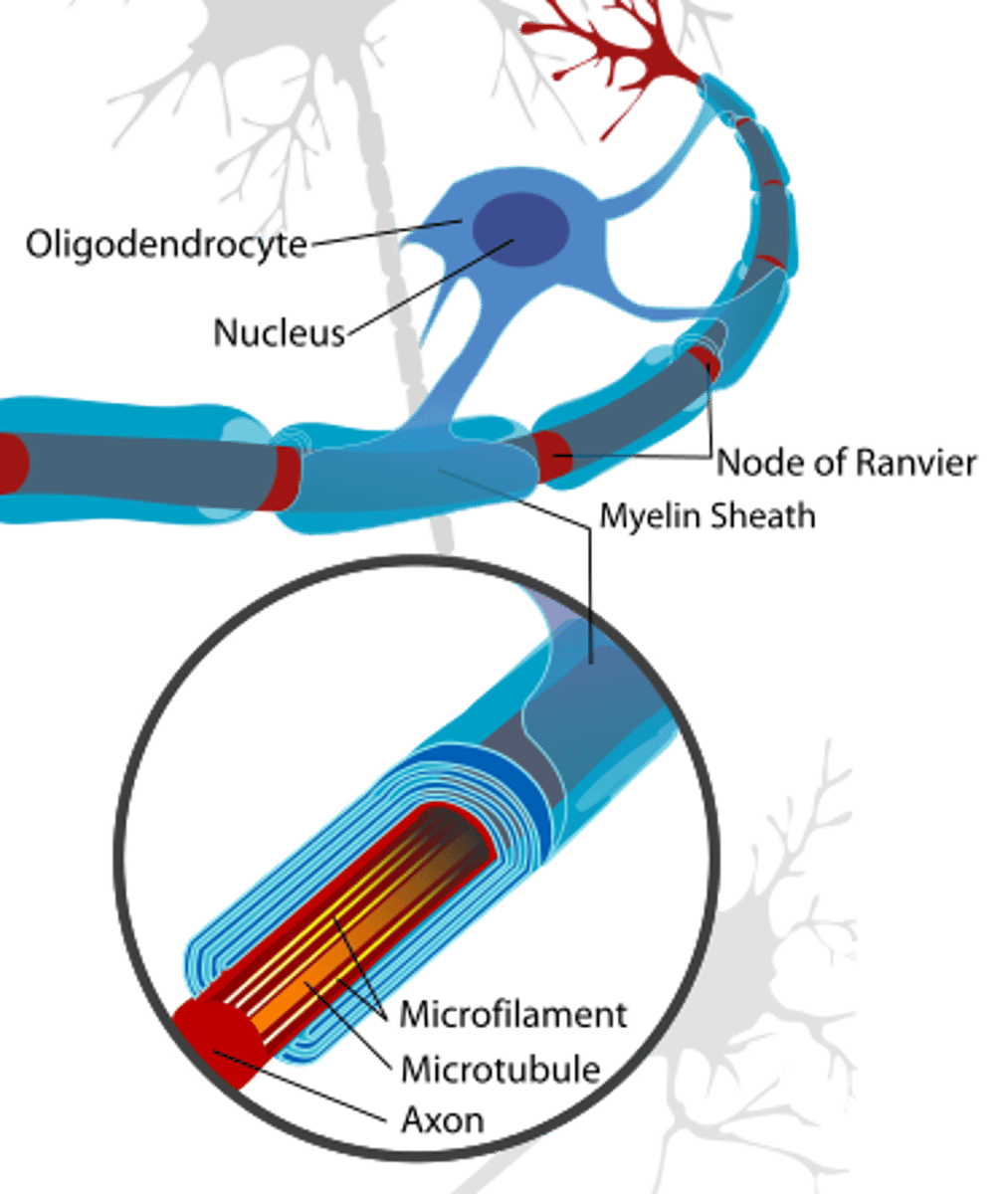
what is the most abundant type of CNS neuroglia?
hint: it is a type of macroglial cell
astrocytes
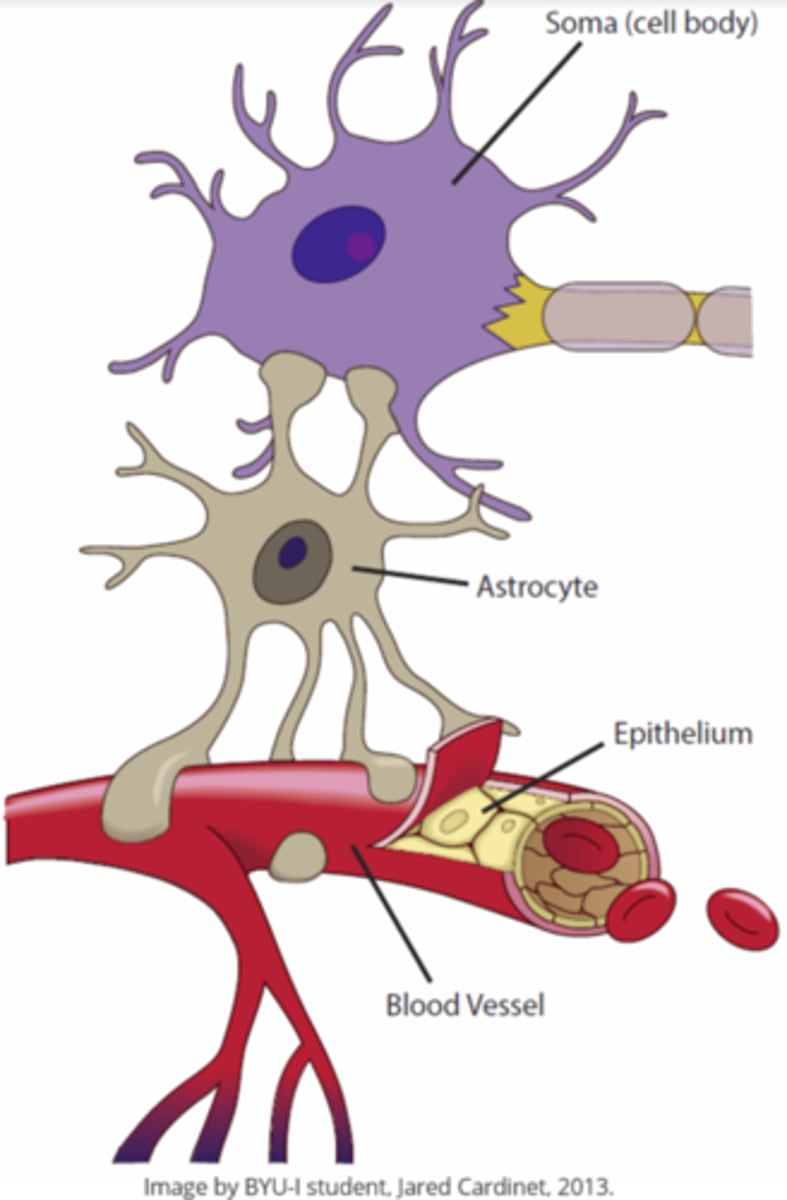
astrocytes provide blood to _____ neurons and help form the _____
CNS; blood brain barrier
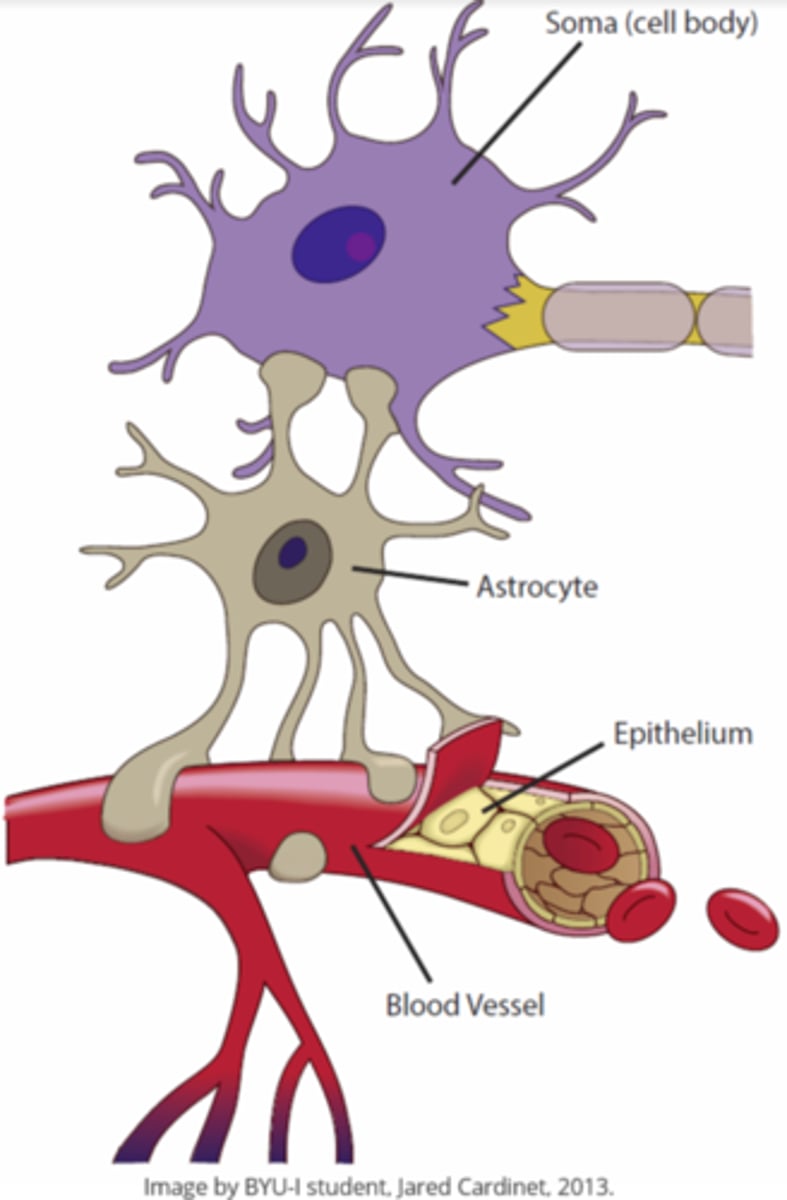
_____ are macroglia that recycle neurotransmitters and maintain ion levels
astrocytes
satellite cells ensheathe the _____ of central/peripheral nerves
soma; peripheral
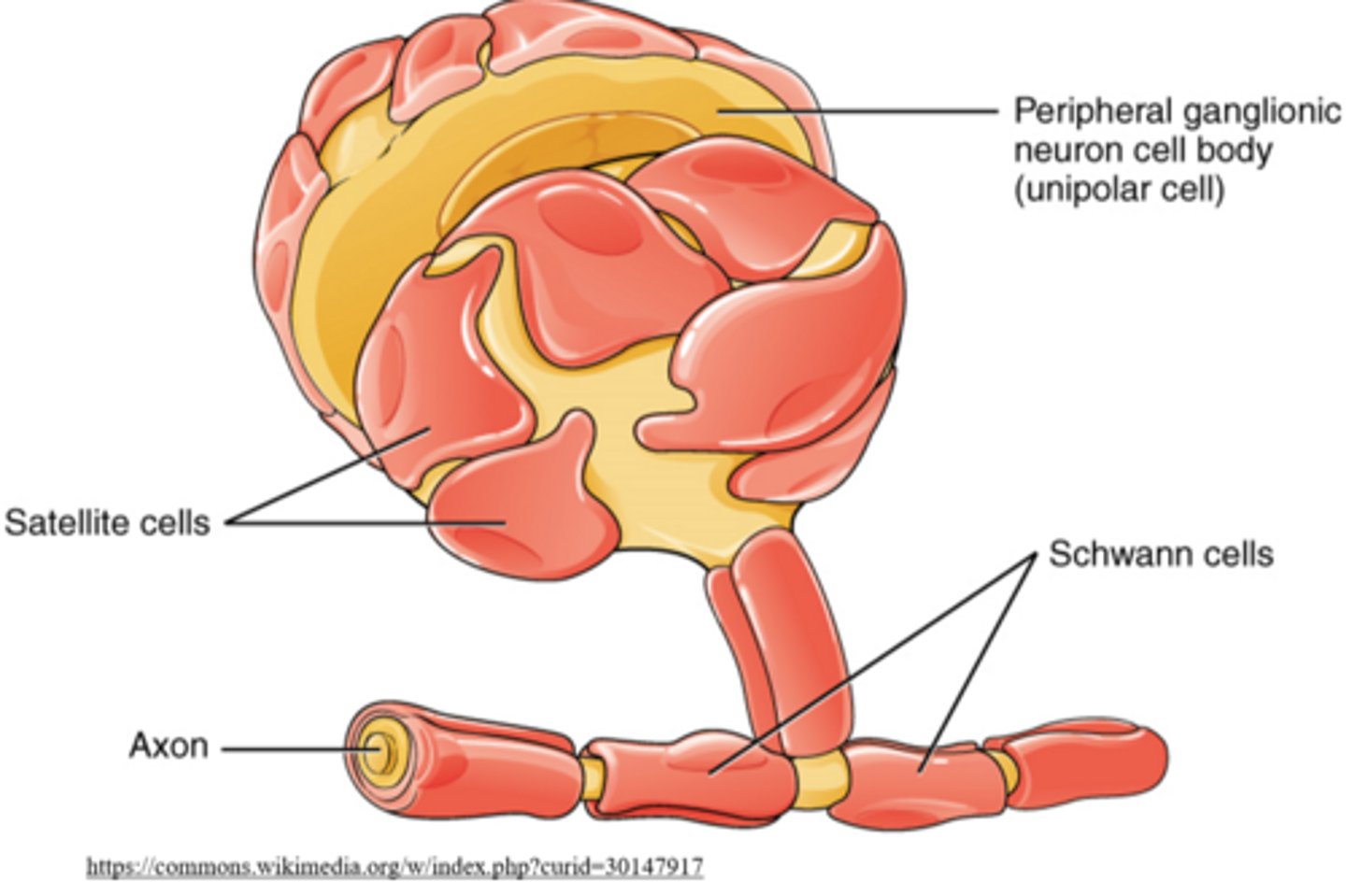
_____ are similar to astrocytes; however, they function in the peripheral nervous system
satellite cells
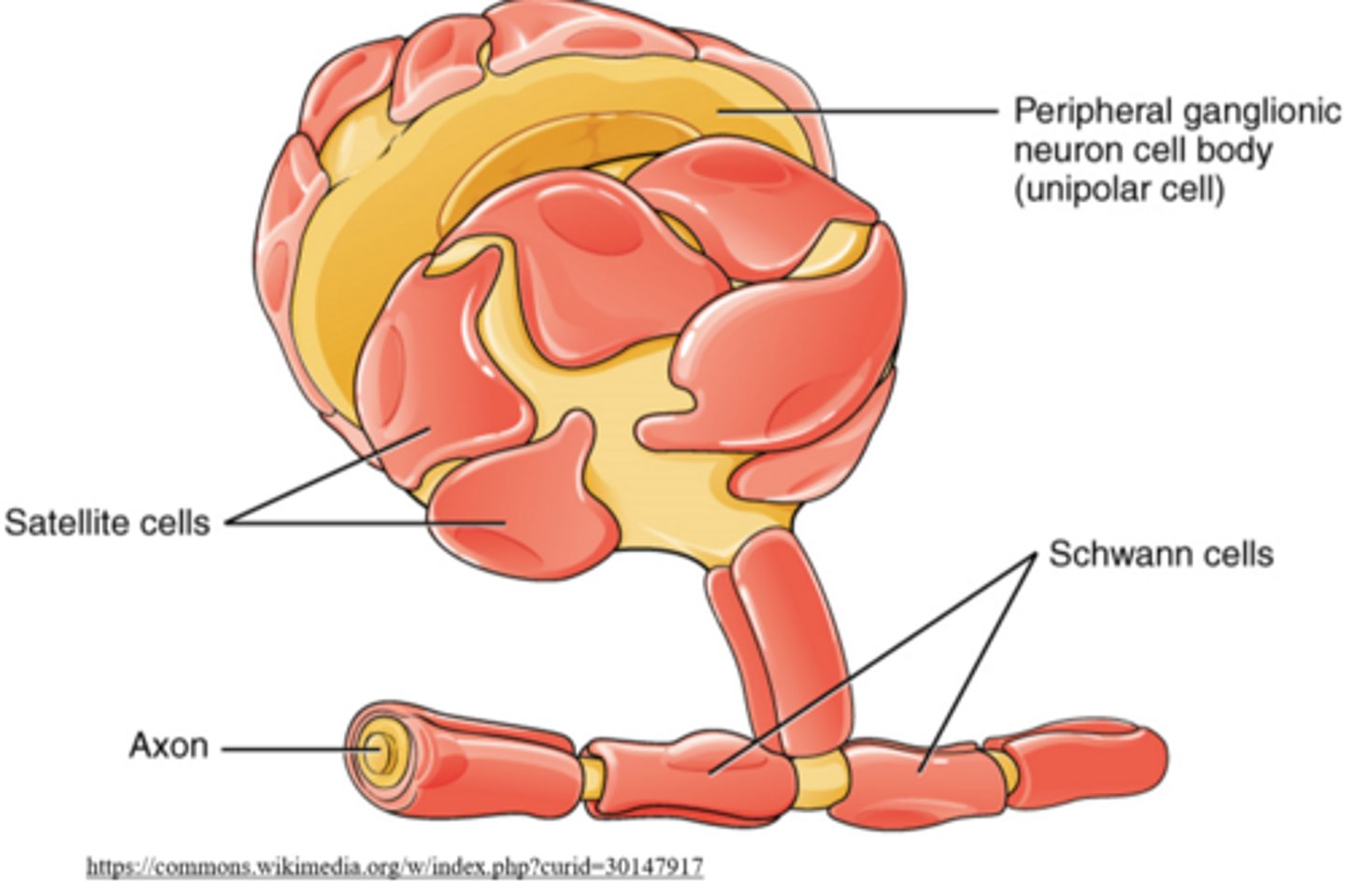
ependymal cells are macroglia that create the _____
cerebrospinal fluid
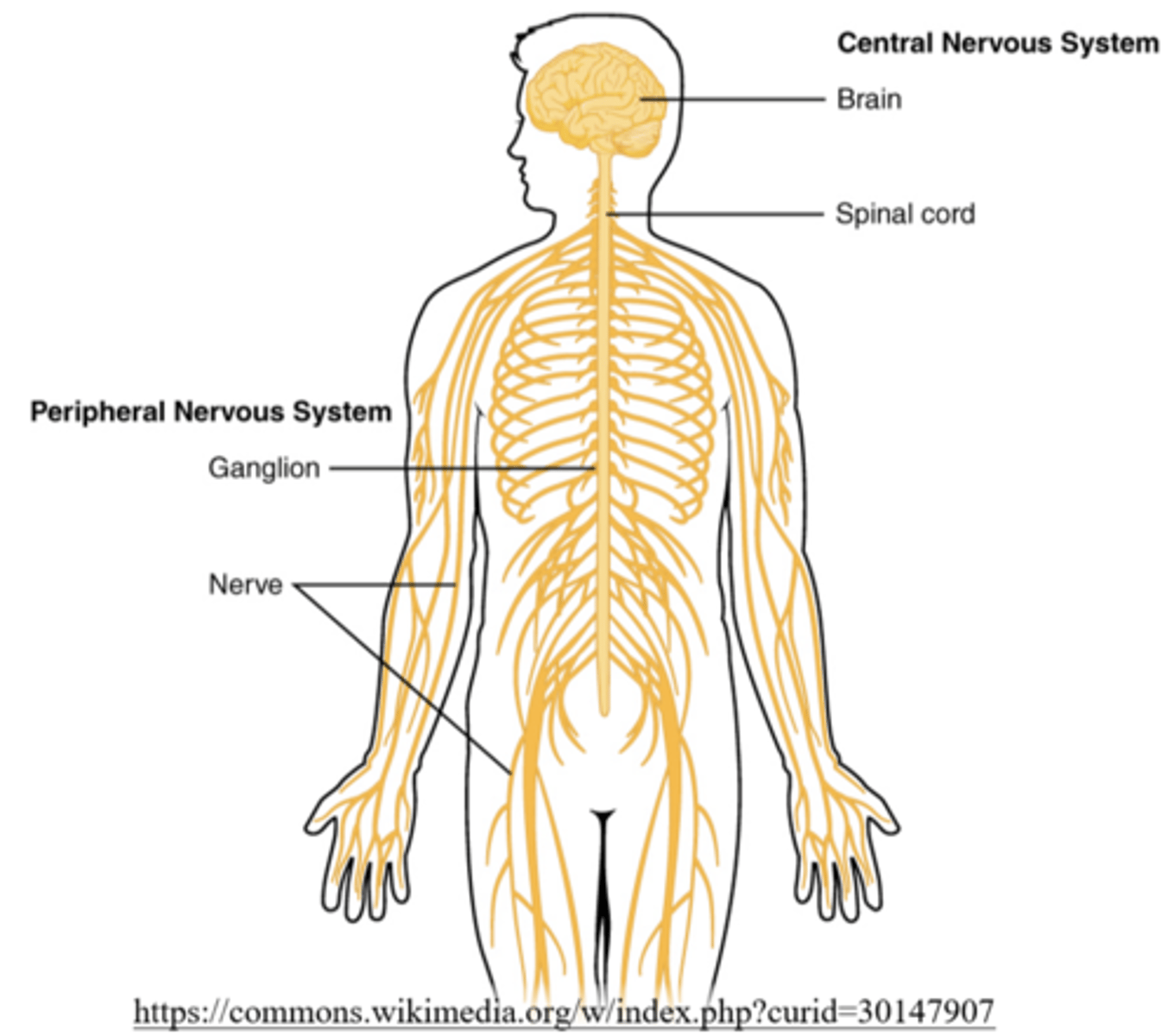
what are the major components of the central nervous system (CNS)?
the brain and spinal cord
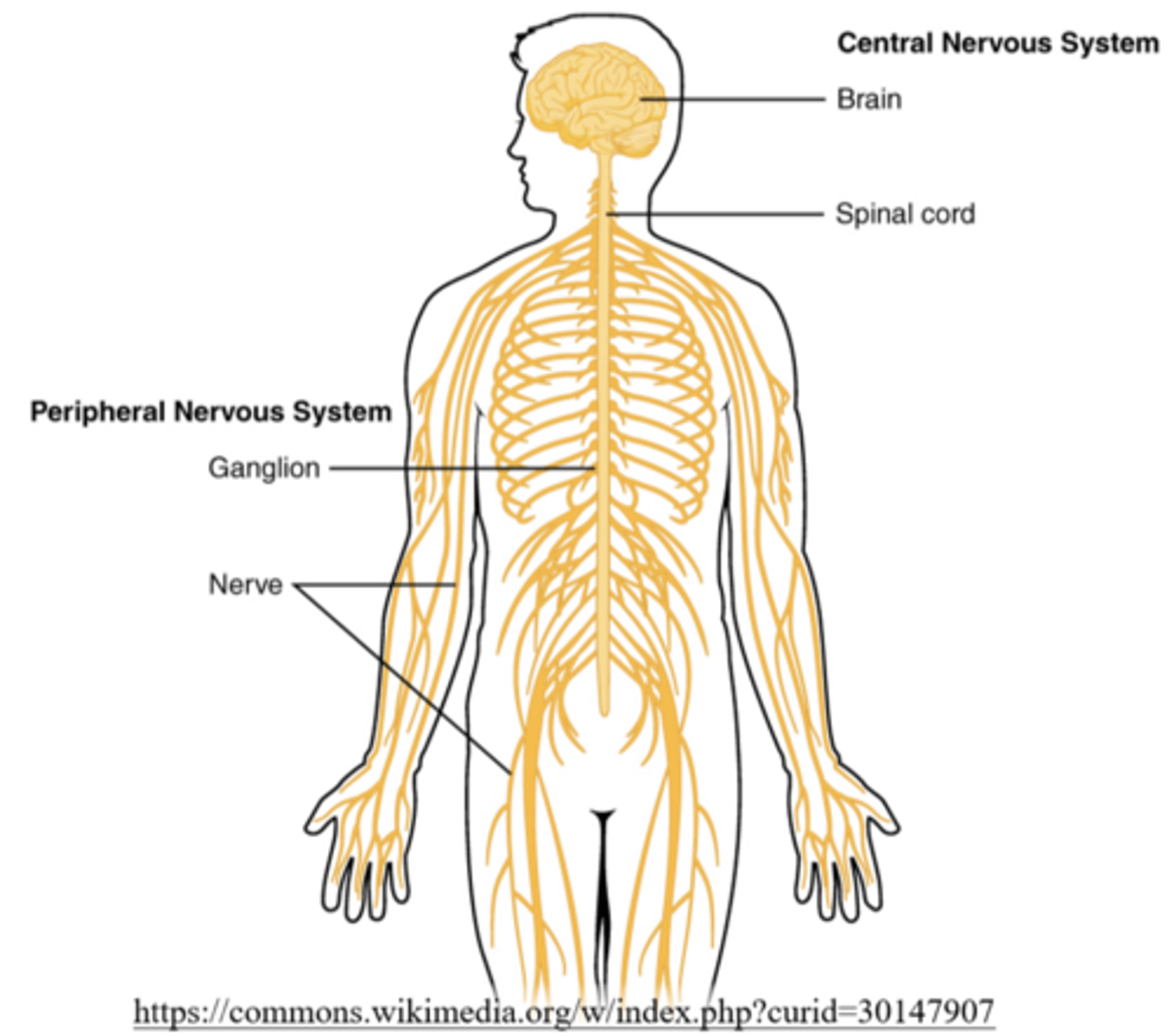
what are the major components of the peripheral nervous system?
all the nerves that branch off the CNS
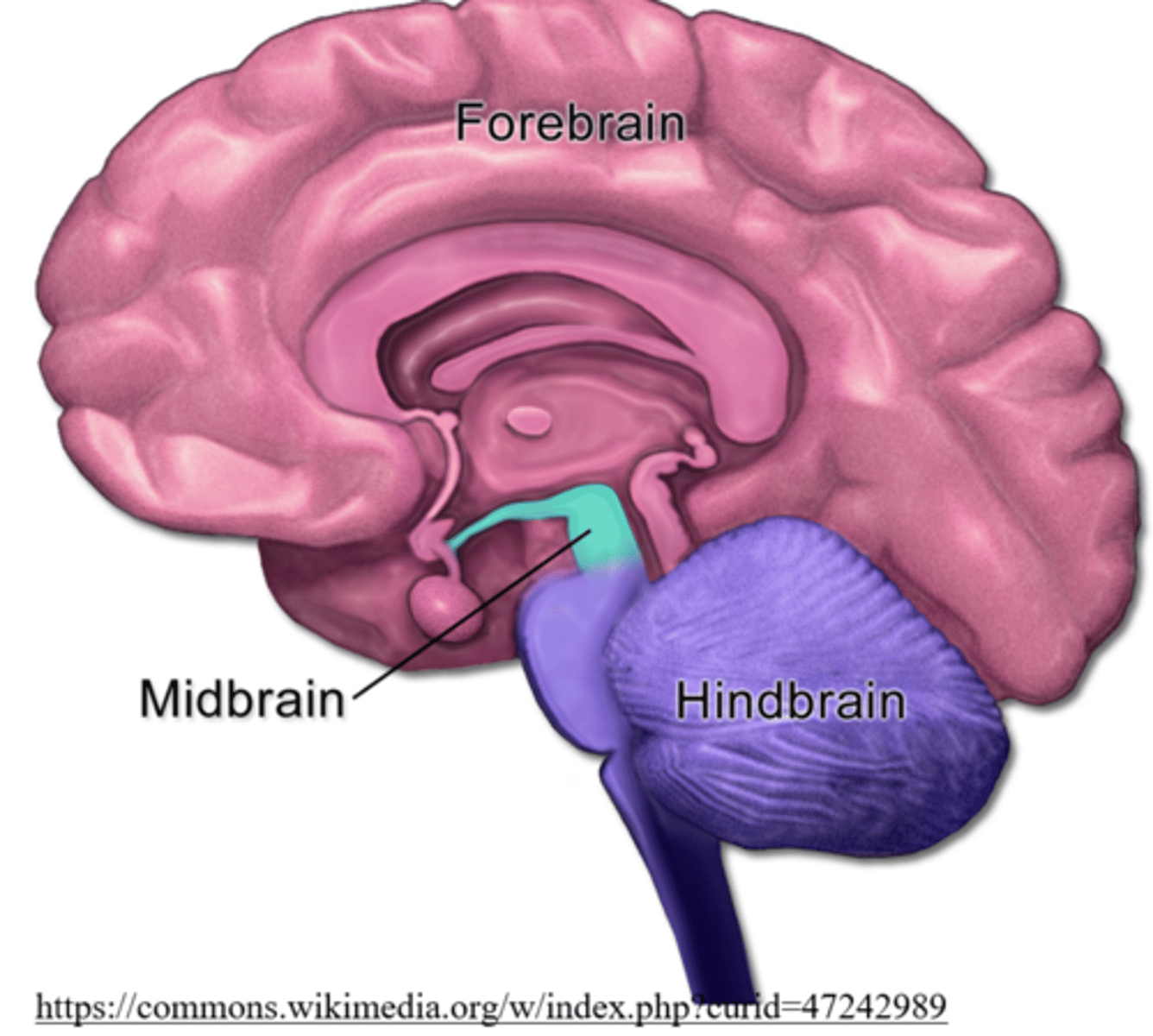
what are the three areas of the brain seen during embryonic development?
forebrain; midbrain; hindbrain
what does the forebrain develop into?
telencephalon and the diencephalon
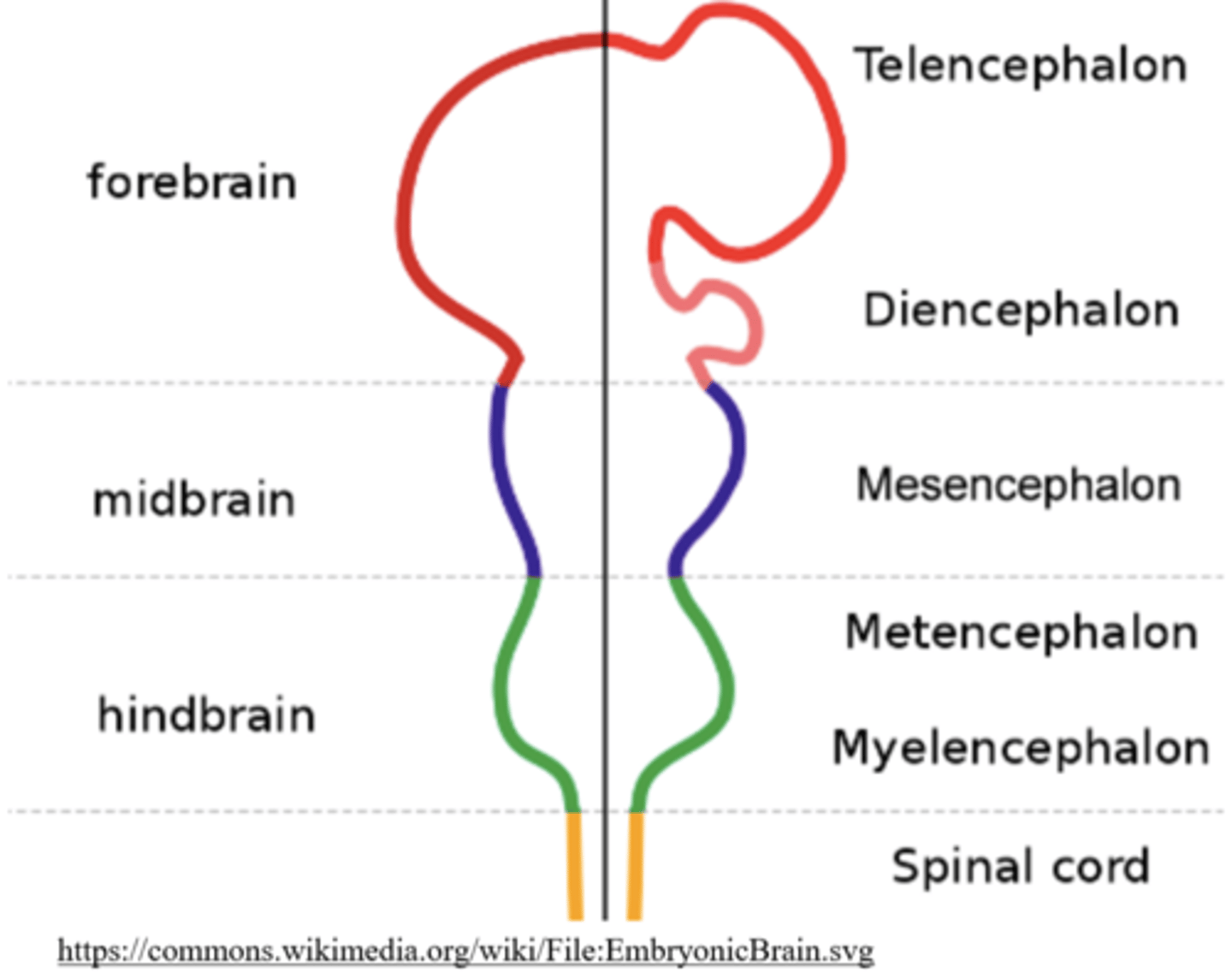
the telencephalon gives rise to the _____
cerebrum
the _____ gives rise to the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and retina
diencephalon
what does the midbrain develop into?
mesencephalon
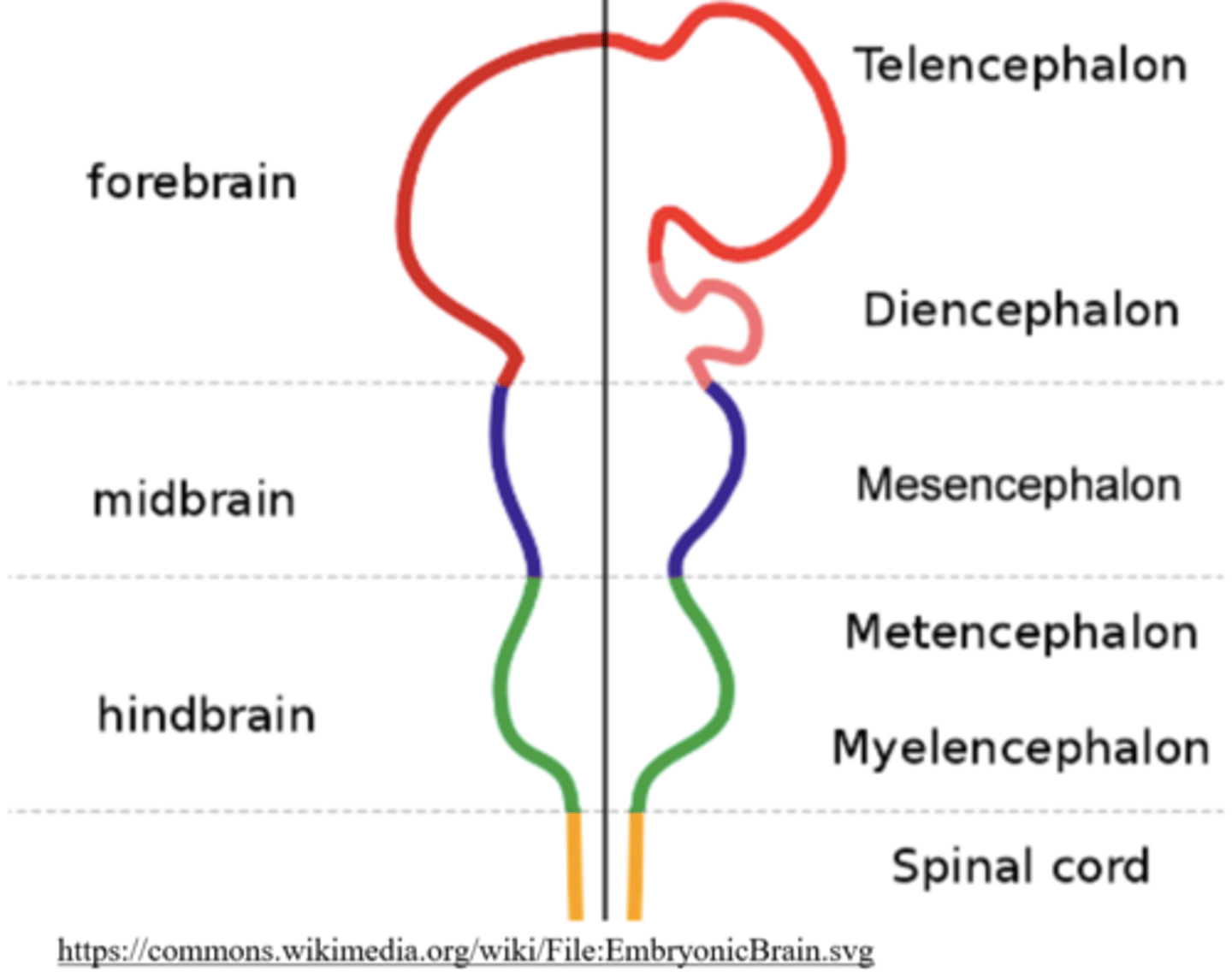
the mesencephalon gives rise to the _____
midbrain
what does the hindbrain develop into?
metencephalon and the myelencephalon
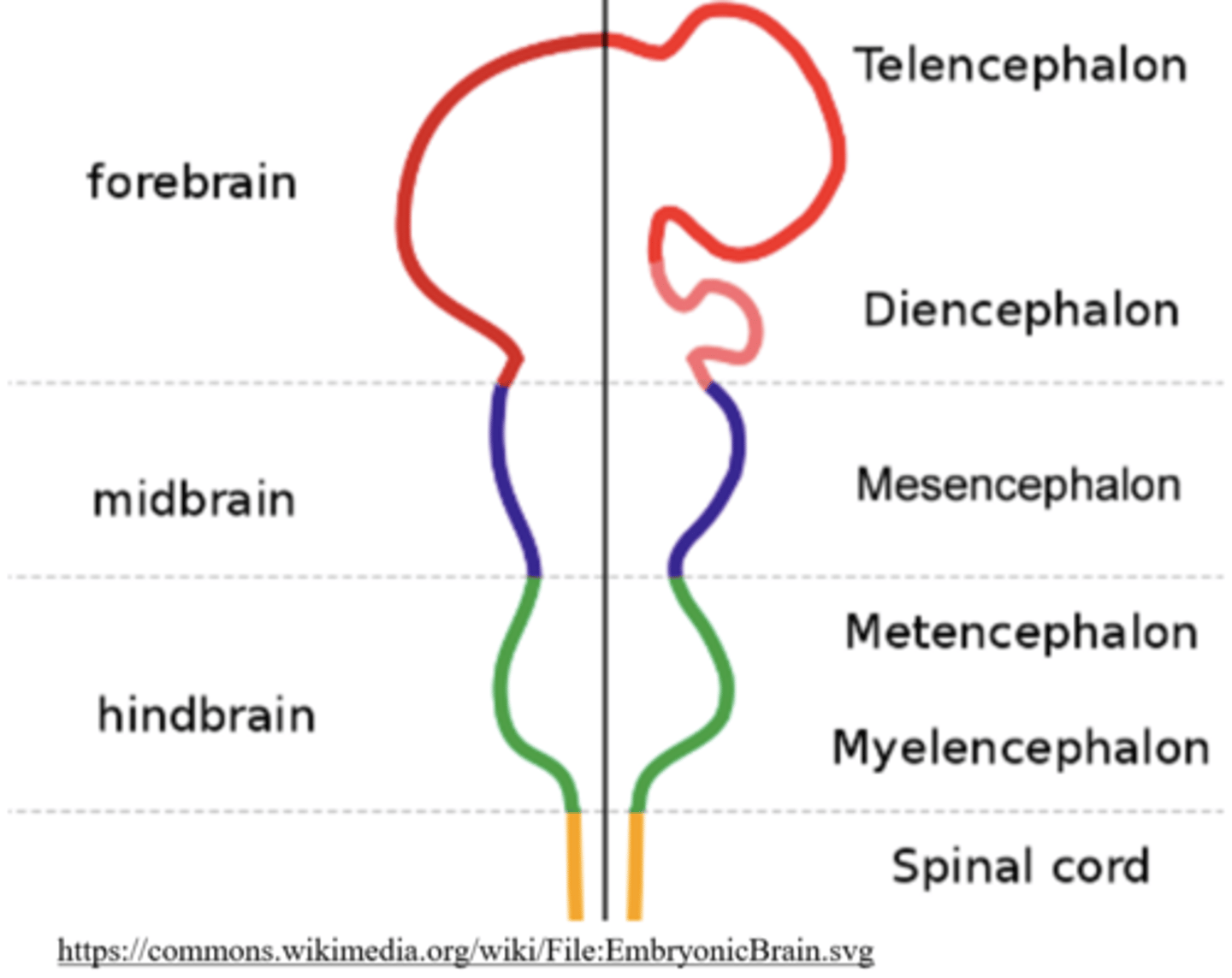
the metencephalon gives rise to the _____ & _____
pons, cerebellum
the myelencephalon gives rise to the _____
medulla oblongata
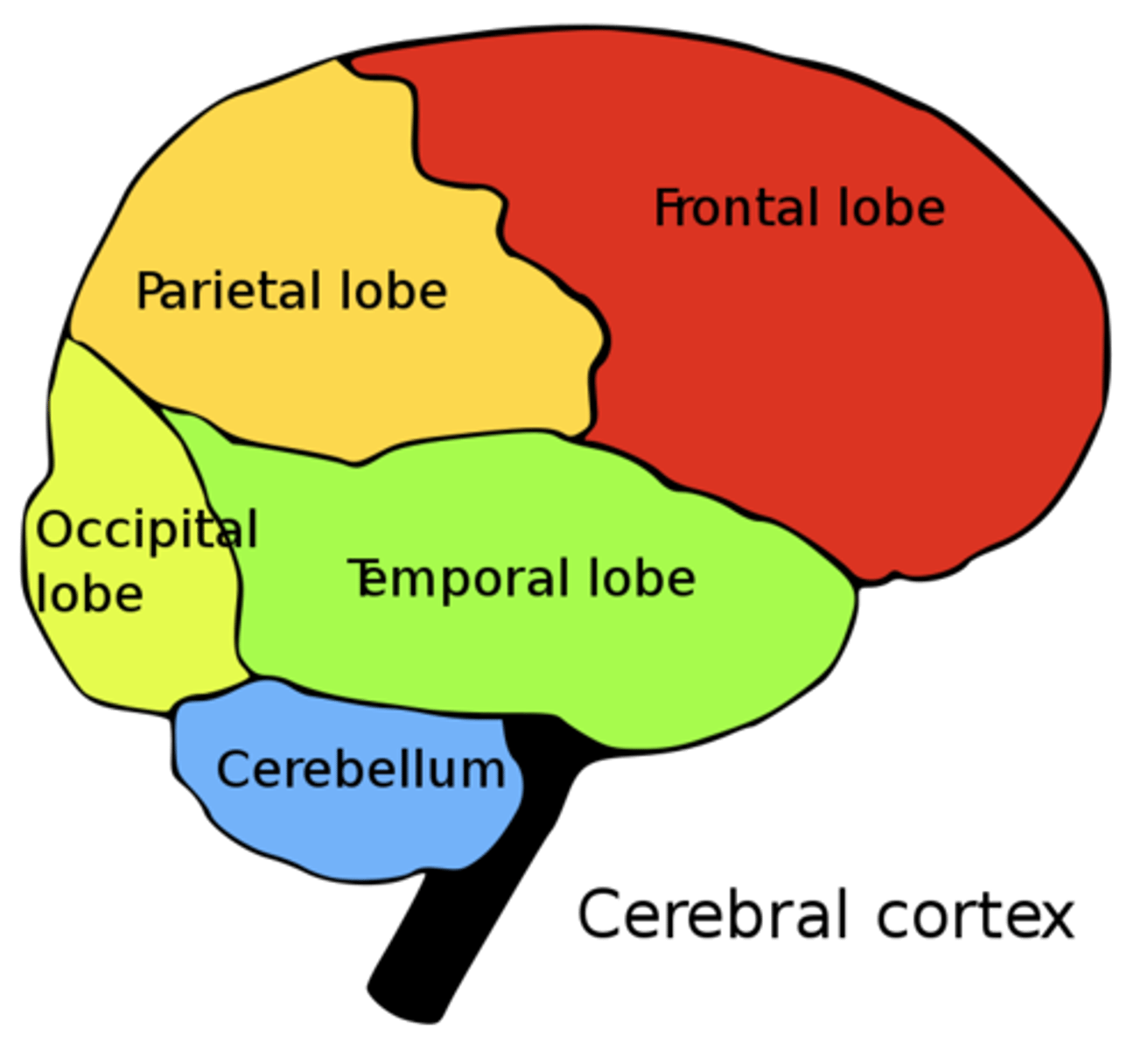
the _____ is the brain cortex, which has two hemispheres and is involved in higher cognitive functions
cerebrum
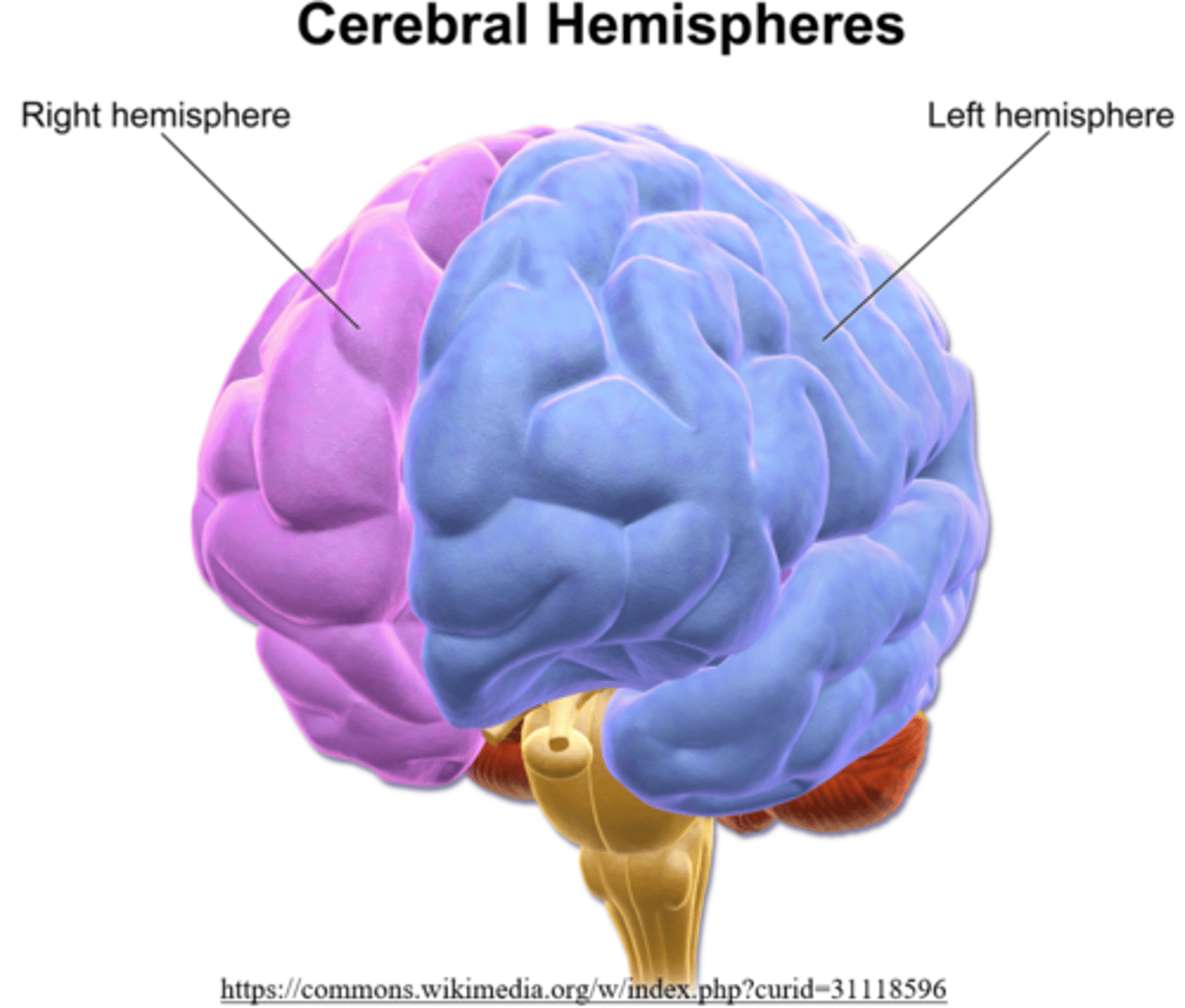
what are the four lobes of the cerebrum?
frontal; temporal; occipital; parietal
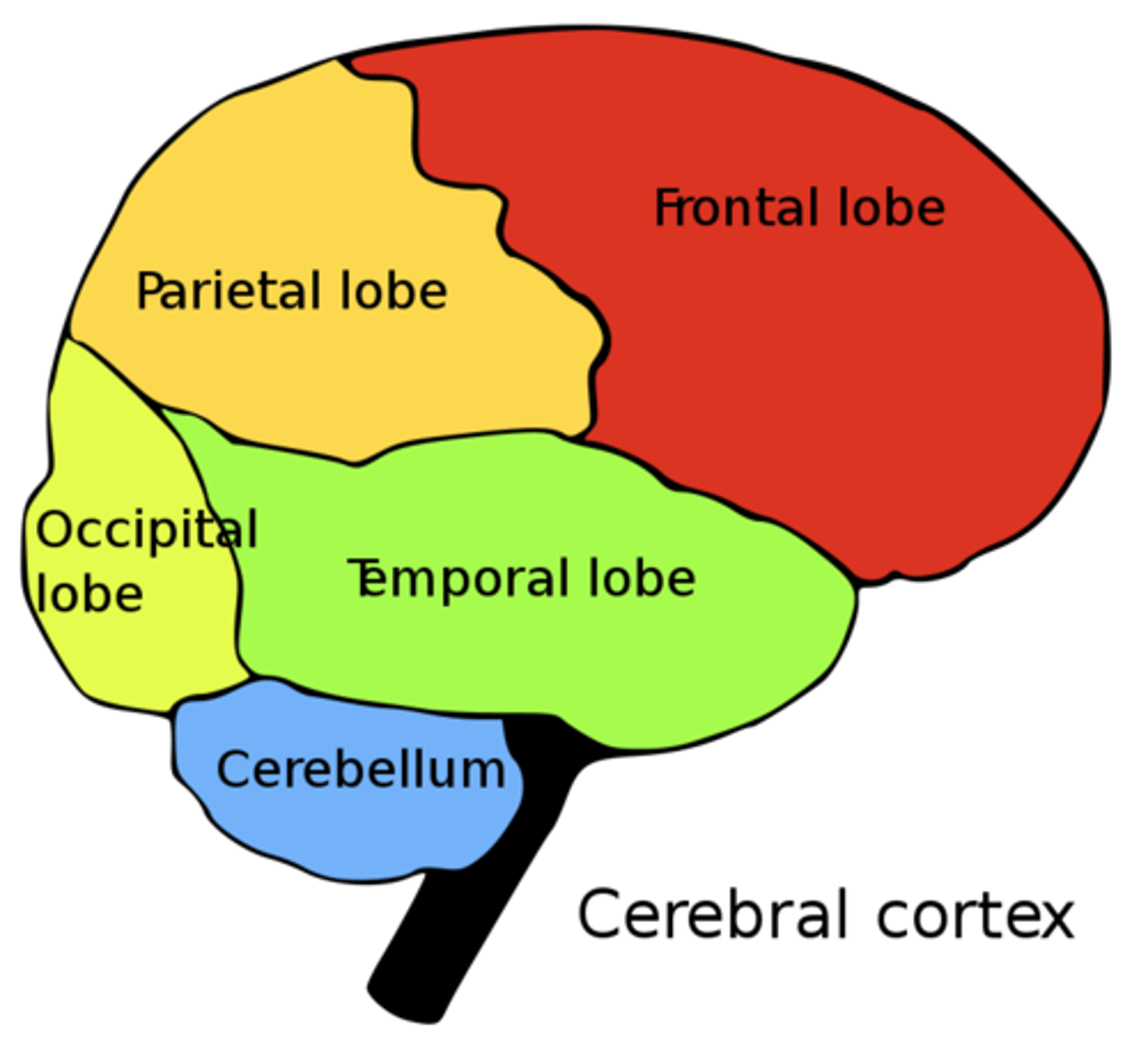
where is the cerebellum located?
under the occipital lobe of the cerebrum