2 Chemistry of Biology
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
atoms
the smallest chemical units of matter
what do atoms consist of?
neutrons, electrons, protons, nucleus
electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles circling a nucleus
nucleus
structure containing neutrons and protons
neutrons
uncharged particles
protons
positively charged particles
element
composed of a single type of atom
electron shells
energy rings
What does the nucleus contain?
protons and neutrons
where are electrons placed?
on the rings/shells
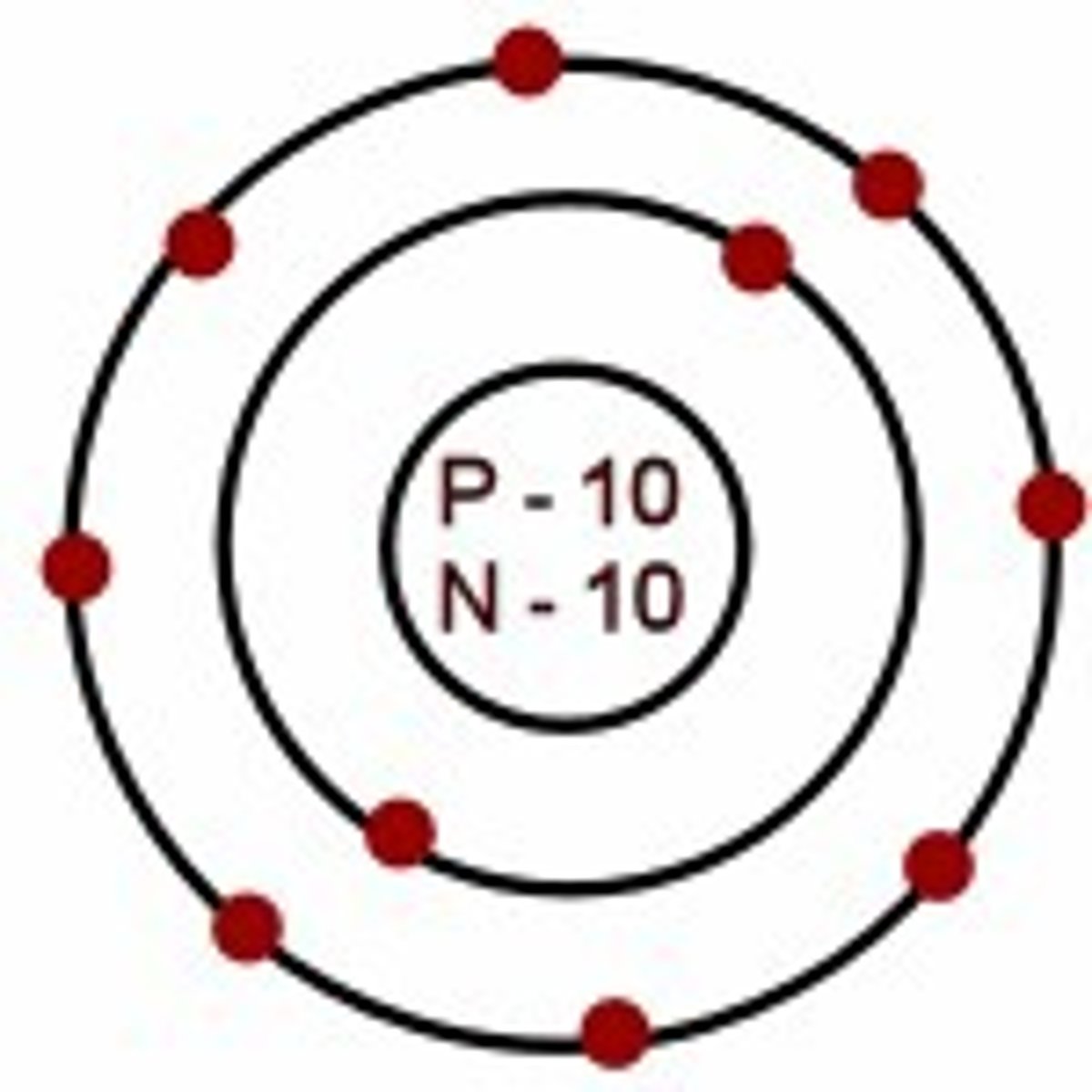
atomic number
equal to the number of protons in the nucleus
atomic mass
sum of masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons
valence electrons
electrons in outermost shell that interact with other atoms
-combining capacity of an atom (number of extra or missing electrons in outermost shell)
chemical bonds
attachment of atoms combined by sharing or transferring valence electrons
molecule
two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
compound
a molecule composed of more than one element
ex) H2O
covalent bond
sharing of a pair of electrons by two atoms
electronegativity
attraction of atom for electrons; the more electronegative an atom, the greater the pull its nucleus exerts on electrons
-O & N super electroneg
Electronegativity Values (Linus Pauling)
F>O>N>C>H
types of chemical bonds
ionic bonds, non/polar covalent bonds, and intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonds
Ionic bond
charged ions formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another
-occur when two atoms with vastly different electronegativities come together
-Typically form crystalline ionic compounds known as salts
anion
A negatively charged ion
cation
A positively charged ion
Aqueous Interactions
hydrophilic, hydrophobic, amphipathic
Amphipathic
"feeling both" molecules have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties (polar and nonpolar parts)
hydrophobic
"water-hating" molecules repel water (nonpolar)
hydrophilic
"water-loving" molecules attract water to their surface (polar)
nonpolar covalent bonds
a chemical bond where atoms share electrons equally, resulting in a balanced molecule with no partial charges. (The most common bonds in living cells)
-Strongest covalent bonds in solution
what do nonpolar covalent bonds form between
Form between C, H, O, N, S, and P.
hydrogen bonding
weak attractions involving hydrogen and electronegative atoms that help hold molecules together and give many biological molecules their shape and properties
Polar Covalent Bonds
Unequal sharing of electrons due to significantly different electronegativities
-Most important polar covalent bonds involve hydrogen (Allows for hydrogen bonding)
which bond is weaker than covalent bonds but essential for life
hydrogen bonding
synthesis
to build
hydrolysis
splitting with water
what doesn't have a cell wall
animal cells
types of intermolecular forces
London dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding, ion dipole
what's the weakest force?
London dispersion forces
Common Elements in Living Organisms
CHNOPS (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur)
pH
Measures the acid concentrations of solutions
-Ranges from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic); 7 is neutral pH = -log[H+]
functional groups of organic molecules
hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino group, phosphate, ester, ether
Chemical Reactions
the making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter (involve reactants and products)
Macromolecules
Many biological molecules are composed of monomer Units
what are polymers broken down by?
hydrolysis reactions
Organic Macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
carbohydrates
Organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CH2O)n
function of carbohydrates
-Medium or Long-term storage of chemical energy
-Ready energy source
-Part of backbones of nucleic acids
-Converted to amino acids
-Form cell wall
-Involved in intracellular interactions between animal cells
types of carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
proteins
Mostly composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur
function of proteins
-Structure
-Enzymatic catalysis
-Regulation
-Transportation
-Defense and offense
what are proteins composed of?
amino acids
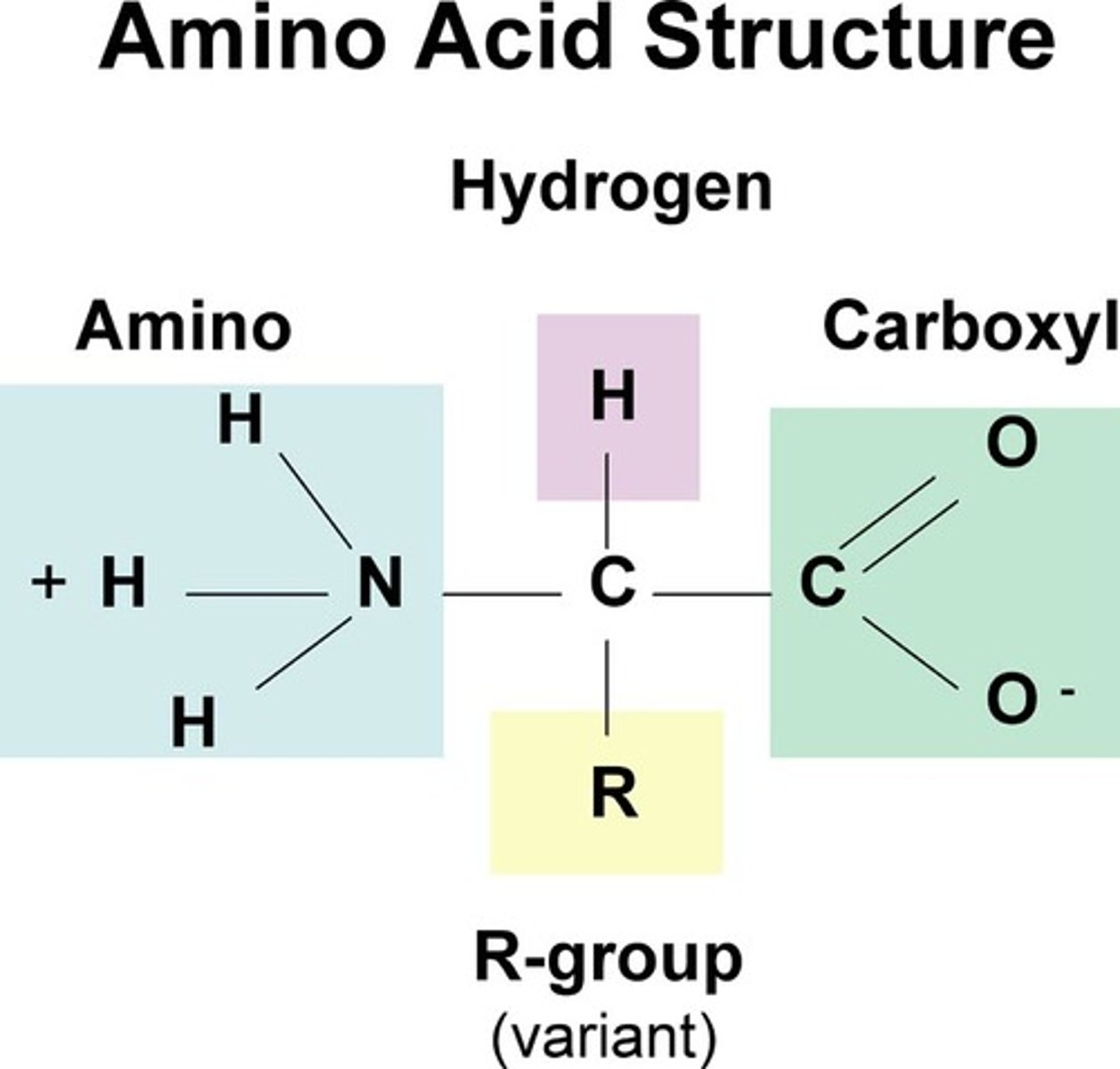
amino acids
monomers that make up proteins
amino acid structure
isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
stereoisomers
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement of the atoms in space. ex) hands
protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
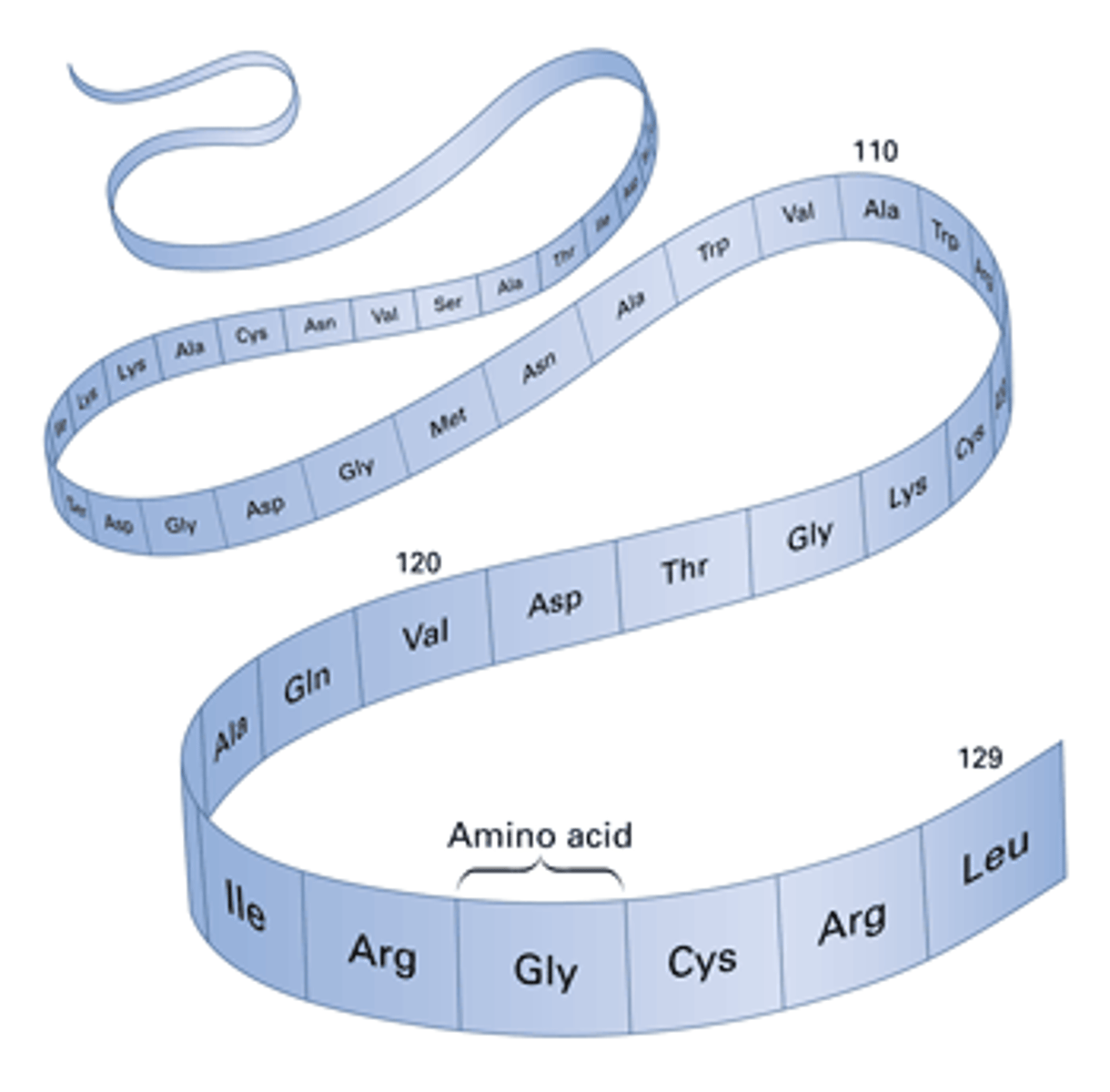
primary protein structure
the sequence of amino acids
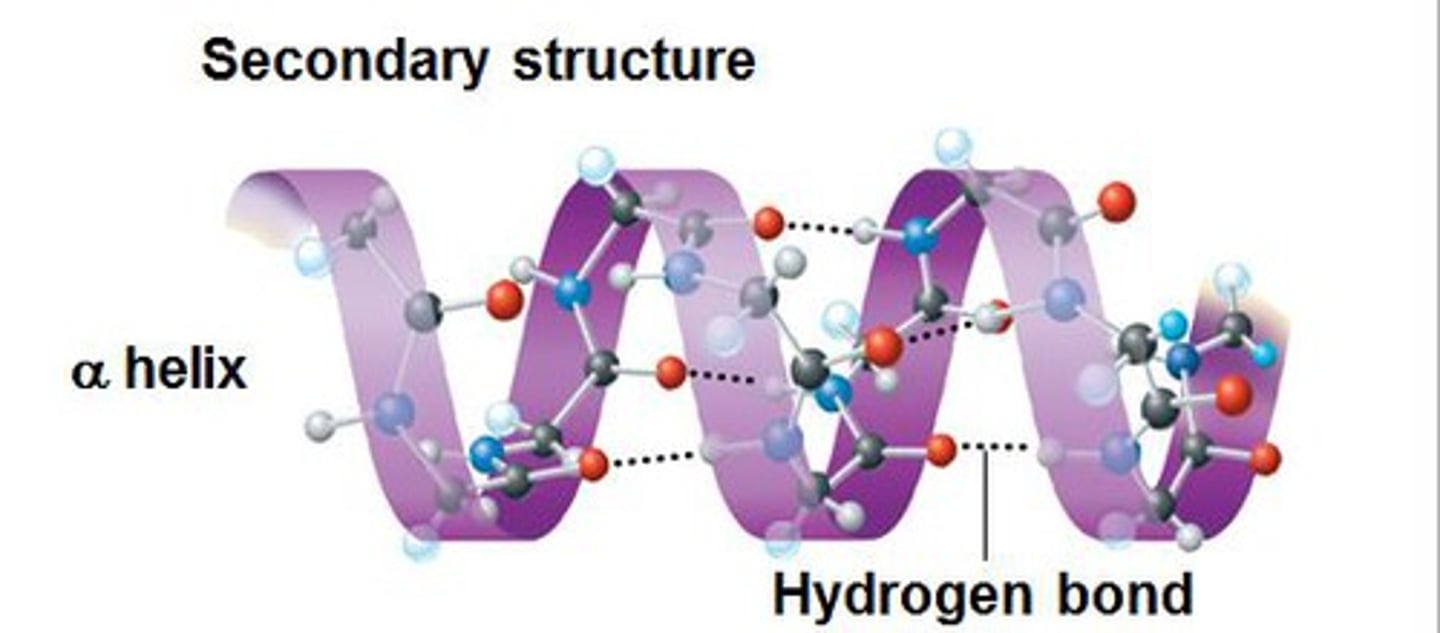
secondary protein structure
a localized (short distance) 3D structure based on hydrogen bonding on the peptide backbone
tertiary protein structure
a globular 3D structure of the protein based on the interaction of the R groups
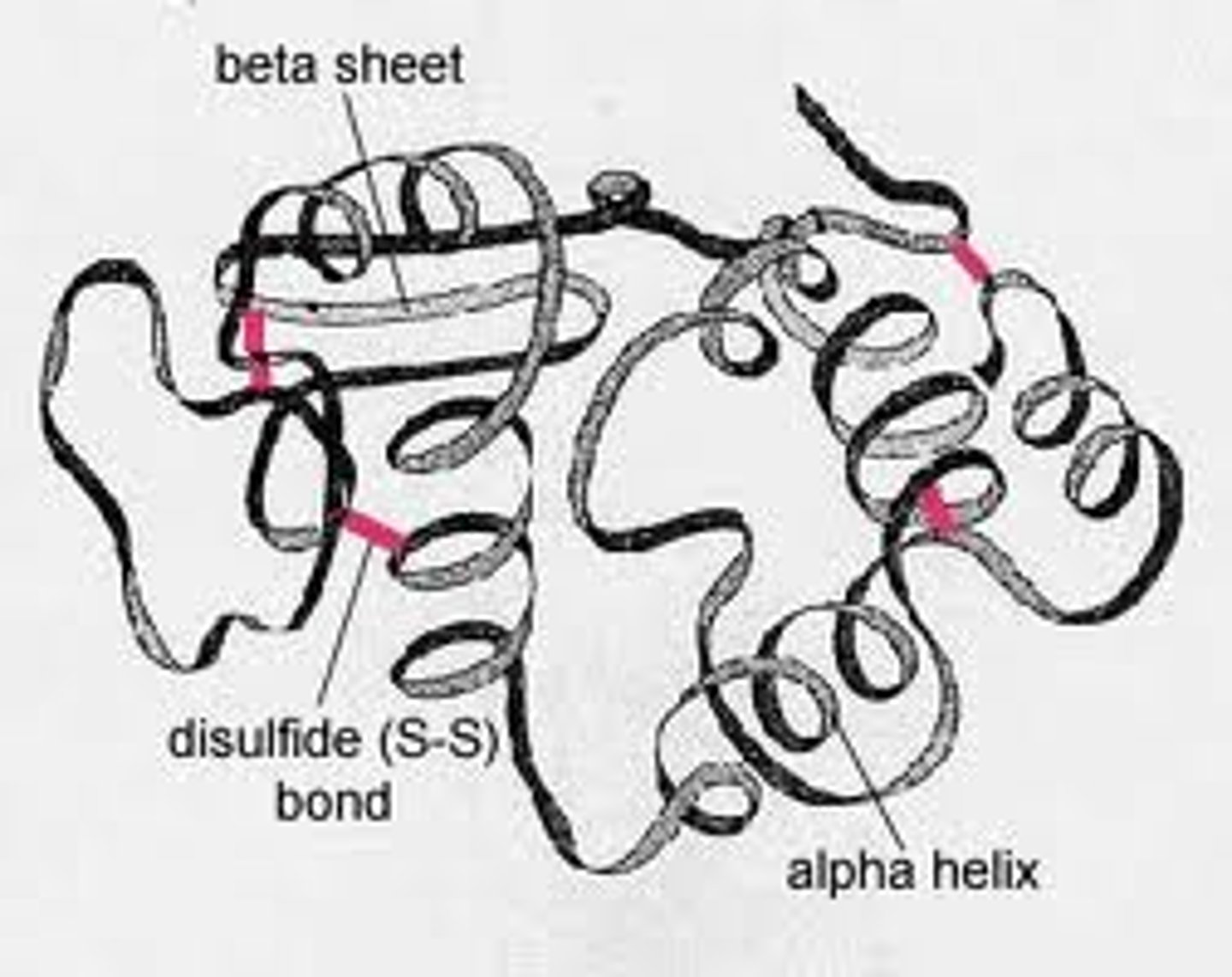
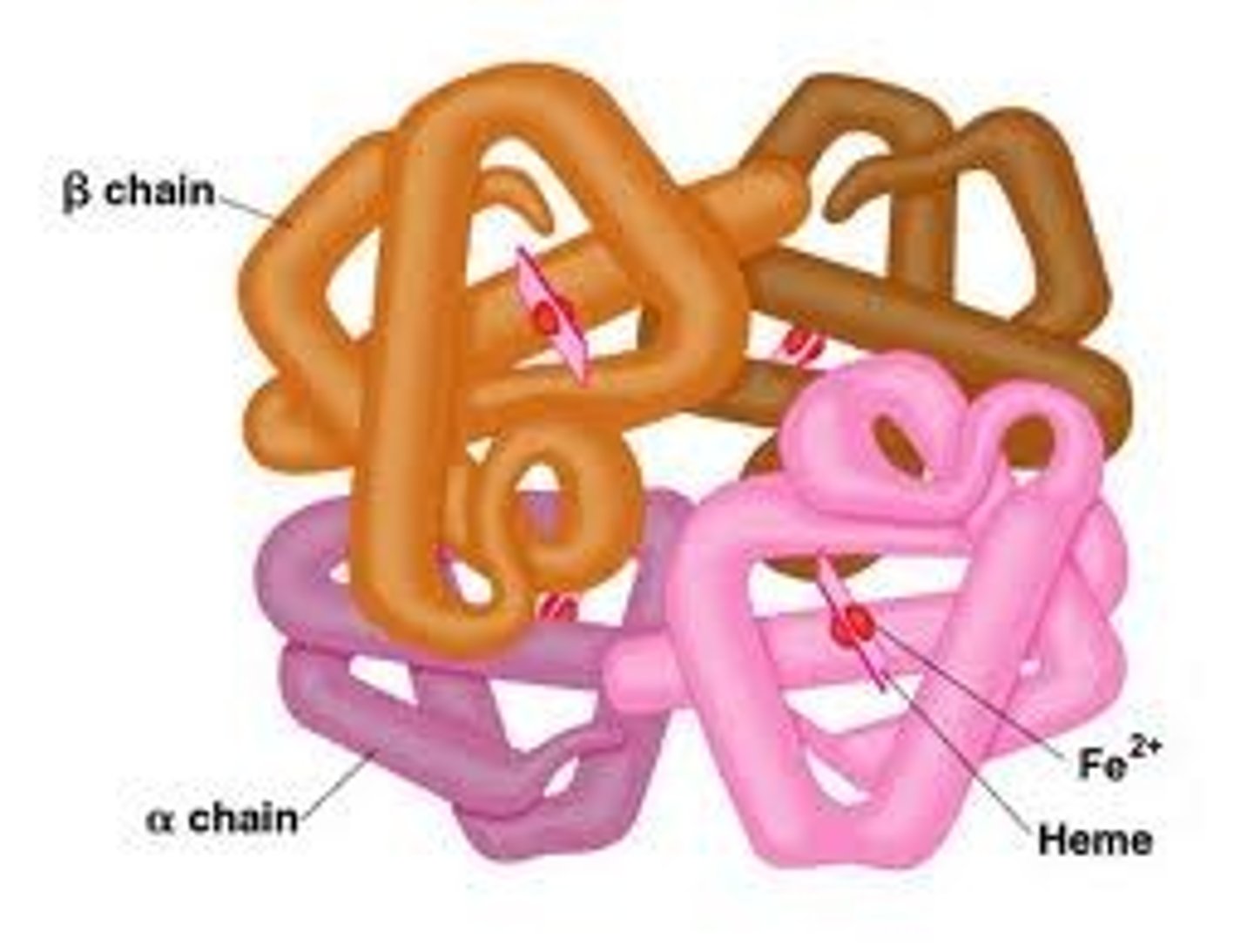
quaternary protein structure
the association of more than one peptide
protein denaturation
when proteins are subject to heat, acid or other conditions that disturb their stability; protein uncoils, loses its shape, and loses its function
enzymes
proteins that act as biological catalysts (nearly always proteins)
Cofactors
non-protein chemical compounds that assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions
nucleic acids
dna & rna
DNA
genetic material of all organisms and of many viruses
-Carries instructions for synthesis of RNA and proteins; controls synthesis of all molecules in an organism
RNA
the genetic material of some viruses
-functions in protein synthesis (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA)
nucleotides
Monomers that make up nucleic acids
-Composed of three parts (Phosphate, Pentose sugar - deoxyribose or ribose, One of five cyclic nitrogenous bases)
lipids
Not composed of regular subunits, but are all hydrophobic
what 4 groups consist of lipids?
• Fats
• Phospholipids
• Waxes
• Steroids
unsaturated fats
liquid at room temperature (colder melting points)
-contain double bonds
saturated fats
solid at room temperature (warmer/higher melting points)
Phospholipids
a molecule with a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails that forms the structural foundation of all cell membranes
sterols
ring-structured lipids crucial for membrane stability and serve as precursors (transitions) for many important biological molecules like hormones, vitamins, bile acids
precursors
something that comes before and is transformed into another molecule through a biological process.
ex) "cholesterol is a precursor to steroid hormones", we mean that the body uses cholesterol as the raw material to chemically produce those hormones through metabolic pathways.
cells
fundamental unit of life
what do all cells have?
-a cytoplasmic membrane
-chromosomes made of DNA
-ribosomes for protein synthesis
-Reproduce to form progeny cells
-Obtain energy from their environment