gcse pe paper 1
1/105
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
functions of the skeleton
support, movement, red blood cell production, mineral storage, protection, provides points of attatchment
types of bones
long, flat, short, irregular
definition of joint
where two or more bones meet
what are the three types of joint and examples
immovable (cranium) , partially moveable(spine) , freely movable joint( elbow)
liagament
connects bone to bone
tendons
connects muscle to bone
function of cartilage
aid movement, absorb shock, prevent bones rubbing together
function of joint capsule
surrounds and seals joint, provides stability
function of bursae
fluid filled sacs which reduces friction in between bones and tissue
what movements can occur at hinge
Flexion and extension
What movements can occur ball and socket
Rotation, flexion, extension ,abduction ,adduction ,circumduction
Definition of rotation
Rotating movement around an axis
Definition of extension
When the angle of the joint increases
Definition of flexion
When the angle at a joint decreases
Definition of abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Definition of adduction
Movement towards the midline of the body
Definition of plantar flexion
Movement at the ankle joint that points the foot downwards away from the shin
Definition of dorsiflexion
Movement at the ankle joint that points the foot upwards towards the shin
What movement does the deltoid cause
Abduction of the arm at the shoulder eg bowling a cricket ball
What movement does the bicep cause
Flexion of the arm at the elbow joint eg pulling a paddle and kayaking
what movement does the tricep cause
Extension of the arm at the elbow joint eg throwing a javelin
What movement do the quadriceps cause
Extension of the leg at the new joint EG pushing the pedals when the cycling
what movements do the hamstrings cause
Flexion of the leg at the knee joint eg lifting your leg to kick a football
what movements does the tibialis anterior cause
Dorsi flexion of the ankle eg lifting of the toes off the ground when walking and running
what movement does the gastrocnemius cause
Flexion of the foot at the ankle joint for example taking off when performing a high jump
Agonist and antagonist of flexion of the arm
Bicep is agonist and contracts to allow flexion. Tricep is antagonist and relaxes to allow flexion
Agonist and antagonist of extension of arm
Tricep is agonist and contracts to allow extension. bicep is antagonist and relaxes to allow extension
Agonist and antagonist of flexion of leg
Hamstrings are agonist and contract to allow flexion. Quadriceps are antagonist and relaxed to allow flexion
Agonist and antagonist in extension of leg
Quadriceps are agonist and contract to allow extension. Hamstrings are antagonist and relaxed to allow extension.
Definition of isometric muscle contraction
There is no change in joint angle and muscle length eg plank
Definition of concentric isotonic contraction
Muscles shorten as muscle fibres contract eg upward phaser bicep curl
Definition of eccentric isotonic contraction
Muscles lengthen as muscle fibres contract eg The downward phase of a bicep curl
Pathway of air
Through nose or mouth —trachea—bronchi—bronchioles—-alveoli and gas exchange
Features that assist in gaseous exchange
- Large surface area of alveoli
- Aveoli walls are only one cell thick
-There's a short diffusion distance between alveoli and capillaries
- There are lots of capillaries around the alveoli that provide a large blood supply for gas exchange
During inspiration
-Chest volume increases
- Intercoastal muscles contract to expand rib cage
-Diaphragm contracts and moves down
-Contractions of the pectorals and sternocleidomastoid muscles
During expiration
- Chest volume decreases as air is forced out of lungs
- Intercostal muscles relaxed to lower rib cage
- The diaphragm relaxes and moves up
- Contraction of abdominal muscles pulls the rib cage down faster forcing the air out quicker
Tidal volume definition
The volume of air normally inhaled and expelled by breath
inspiritary reserve volume definition
The additional amount of air that can be inhaled above tidal volume
expiratory reserve volume definition
The additional amount of air that can be exhaled beyond tidal volume
Residual volume definition
The amount of air left in the lungs after maximal exhalation
Pathway of blood through heart
- deoxygenated blood from body is carried into right atrium through vena cava
- The right atrium contracts pushing blood into right ventricle
- The right ventricle contracts pushing blood into pulmonary artery
- the pulmonary artery transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs where gas exchange occurs
- Oxygenated blood from lungs is carried by pulmonary vein into left atrium
- the left atrium contracts pushing blood into left ventricle
- the left ventricle contracts pushing blood into aorta
- the aorta transports oxygenated blood to body
vasodilation definition
Blood vessels leading to working muscles dilate to increase blood flow
Vasoconstriction definition
Blood vessels leading to digestive system constructs to reduce blood flow
what do arteries carry
-Oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery
-thick walls small lumen
What the veins carry
-deoxygenated blood except Pulmonary vein
- Thin walls large lumen
What do capillaries do
Allow gas exchange
one cell thick
Cardiac output definition
The amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one minute
stroke volume definition
The amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in one contraction
Cardiac output equation
Stroke volume x heart rate
Methods to recover from exercise
Rehydration, consuming carbohydrates, massage ,ice bath
Immediate effects of exercise
- Increase body temperature
- Increased breathing rate
- Increase heart rate
Short term effects of exercise up to 36 hours
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Nausea
- Doms
Long term effects of exercise
- Change in body shape
- Increased in heart size
- Lower resting heart rate
- Improvements in components of fitness
Mechanical advantage
Turning a small force into a bigger force. mechanical advantage = effort arm divided by load arm.
- When the effort arm is longer than the load arm
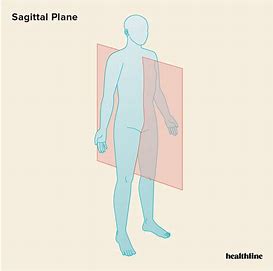
What movements occur in the sagittal plane and transverse axis
flexion and extension -eg bicep curl and front flip
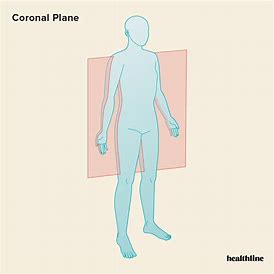
What movements occur in the frontal plane and sagittal axis
Abduction and adduction eg star jump and cartwheel
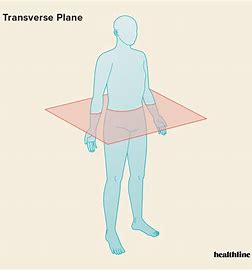
What movements occur in the transverse plane and longitudinal axis
Rotation eg discus throw and 360 spin in ice skating
Reasons for fitness testing
- can be used to show a starting level of fitness and develop training requirements
- Can provide variety to training and help you monitor improvement
- Can help determine the success of a training programme
Reasons against fitness testing
- Can be too general and not sport specific
- Do not include the movements of the actual activity
- Do not account for the competitive conditions of sport
- Take motivation to complete
Definition of agility
The ability to change direction quickly and accurately
What is the test for agility and how to do it
- The Illinois agility test
- Lie face down at start cond and on command jump up and complete the course
Definition of balance
The ability to retain centre of mass above the base of support while stationary or moving
Fitness test for balance and how to do it
-stork test
- Stand with hands on hips and place soul of right foot against inside of left knee rise up on toes and hold
Cardiovascular endurance definition
The ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen to working muscles
Test for cardiovascular endurance and how to do it
- Multi stage fitness test
- Run back and forth between two cones twenty metres apart
Coordination definition
The ability to use a combination of body parts at the same time
What is the test for coordination and how to do it
- wall toss test
- Stand two metres from wall and throw a ball against the wall with one hand and catch it with other during thirty seconds
Flexibility definition
Range of movement possible around a joint
Test for flexibility in how to do it
- Sit and reach test
- Sit with feet against test reach forward as far as you can and record
Muscular endurance definition
The ability of a muscle group or muscle to work for prolonged period of time without tiring
Test for muscular endurance and how to do it
- Sit up bleep test
- As many sit ups as you can in time with bleeps
Definition of power
Combination of explosive strength and speed of movement
Test for power and how to do it
- Vertical jump test
- Reach your hand as high as you can up a wall and mark. Jump as high as you can and touch the wall up to the highest point
Reaction time definition
The time taken to react to a stimulus
Test for reaction time and how to do it
- Ruler drop test
- One person holds a ruler level with the other persons fingers at 0cm. The partner then unexpectedly drops the ruler and the other person catches it.
Strength definition
Applying a force to overcome a resistance
Test for strength and how to do it
-Handgrip dynamometer test
- Grip the dynamometer with maximum effort
Definition of speed
The ability to move your body or part of your body quickly
Test for speed and how to do it
- Thirty metres sprint test
- Involved running thirty metres as fast as possible with a rolling start
what does sport mean
Specificity-tailored to sport and performer
Progressive overload-to improve and develop, a training programme must gradually be made more difficult
Reversibility-fitness levels drop if regular exercise stopped
Tedium-using a variety of methods helps you stay motivated
key principles of overload
Frequency-how often you exercise
Intensity-how hard you exercise
Time-how long exercise
Tedium-how your training matches your chosen activity
benefits of circuit trainings
-develops both anaerobic and aerobic systems
negatives of circuit training
-can require lots of space, equipment and time to set up
-can difficult to maintain work rate
positives of continuous training
-improves aerobic fitness, cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance
-easy to monitor rate and progression
-don’t need equipment
negatives of continuous training
-does not develop other components of fitness
-time consuming
-can be repetitive and boring
positives of fartlek training
-develops both anaerobic and aerobic systems
-improves cardiovascular fitness and muscular endurance
-can be adapted to suit most sports and improve other components of fitness
negatives of fartlek
-can be repetitive and boring
-difficult to monitor work rate and progession
-can be difficult to maintain work rate
benefits of interval training
-develops both aerobic and anaerobic systems
-can be adapted to suit specific sports and improve other components of fitness
-easy to monitor work rate and progression
negatives of interval training
-can be repetitive and boring
-can be difficult to maintain work rate
weight training benefits
-improves muscular strength, endurance, size and power
-low reps, high weight for strength
-high reps, low weight for muscular endurance
-easy to monitor work rate and progression
disadvantages of weight training
-requires specialist equipment
-can cause serious injury if incorrect technique used
benefits of plyometric training
-improves muscular strength , power and speed
-can use all muscles
-no equipment needed
negatives of plyometrics
-very demanding on muscles and joints
-high risk of injury
benefits of static stretching
-increases flexibilty
-can be relaxing
disadvantages of stretching
-can be time-consuming
-some muscles are difficult to stretch
benefits of altitude training
-improves cardiovascular and muscular endurance which benefits anaerobic athletes
negatives of high-altitude training
-little benefits of anaerobic athletes
-travel to training areas can be expensive
-altitude sickness
-effects only last for a limited time
how high is altitude training
2000m above sea level
anaerobic %
80-90%