peptides L2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
How can you make something more activated for amines to attack?
What is the problem with this solution?
Use an acid chloride instead of a carboxylic acid
It makes a mixture (R/S on the carbon between the NH and C=O gps) ie racomisation
Hence acyl chlorides are rarely used
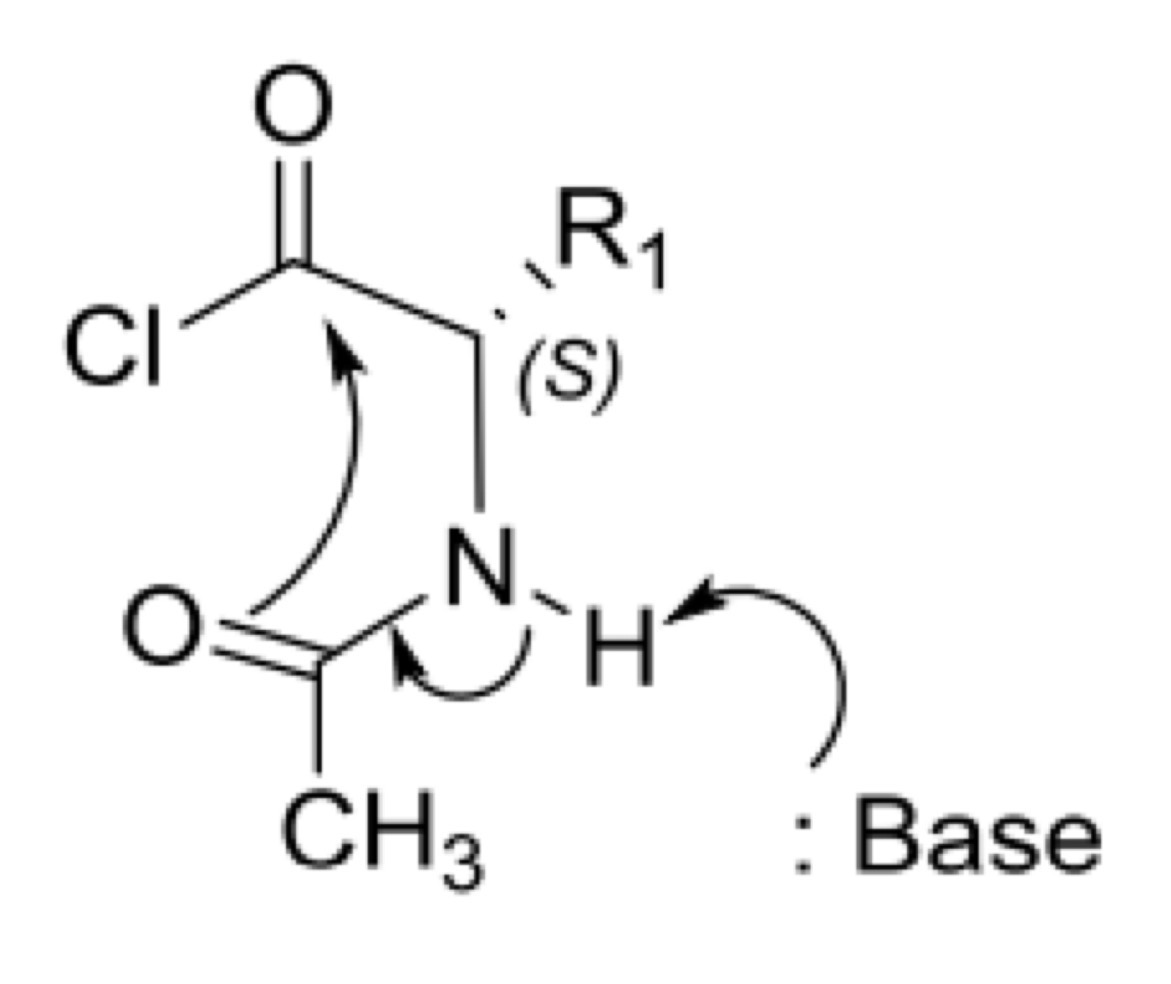
Peptide bond formation: racemisation via oxazolone
What is the product formed and how is it formed?
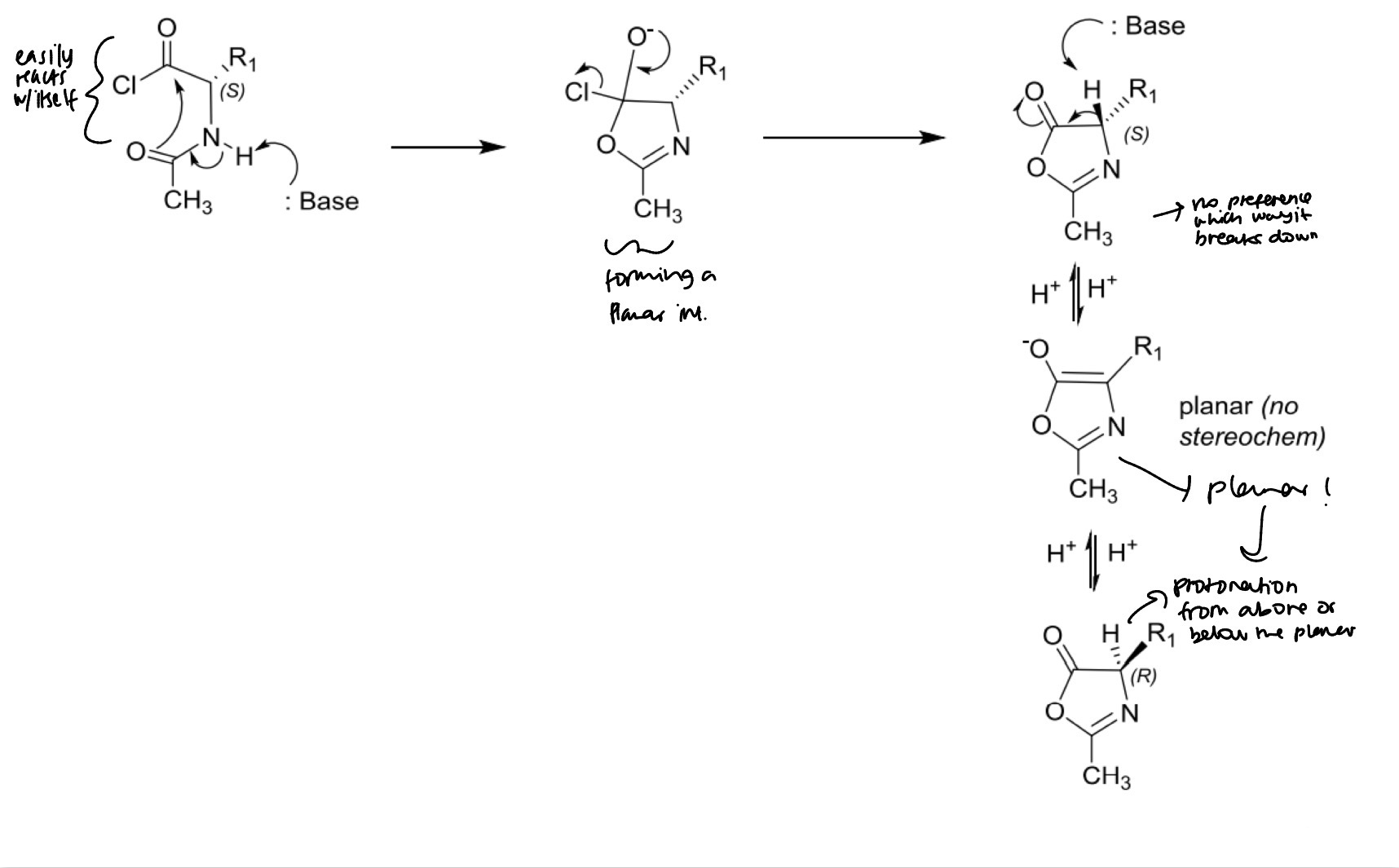
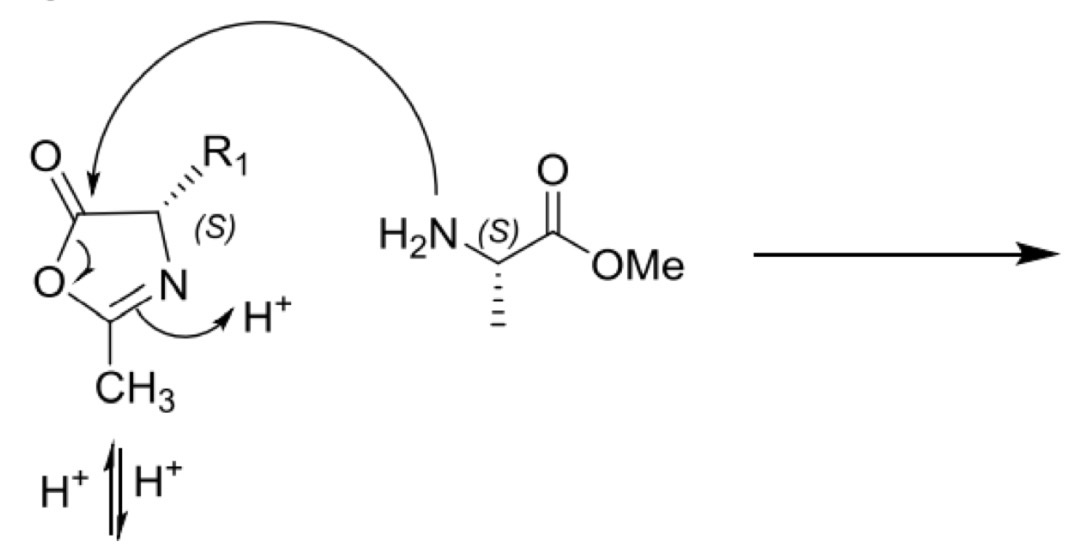
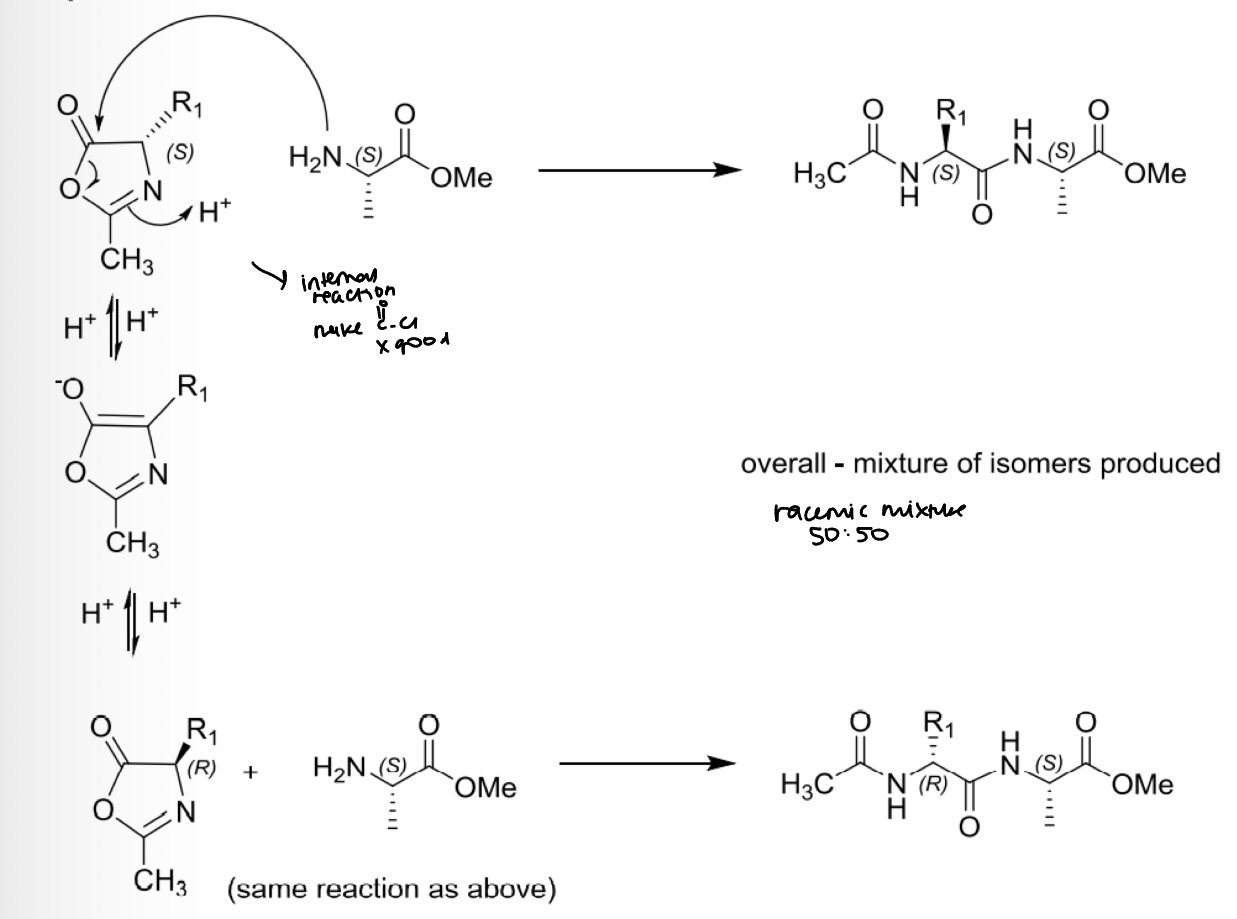
Peptide bond formation: racemisation via oxazolone
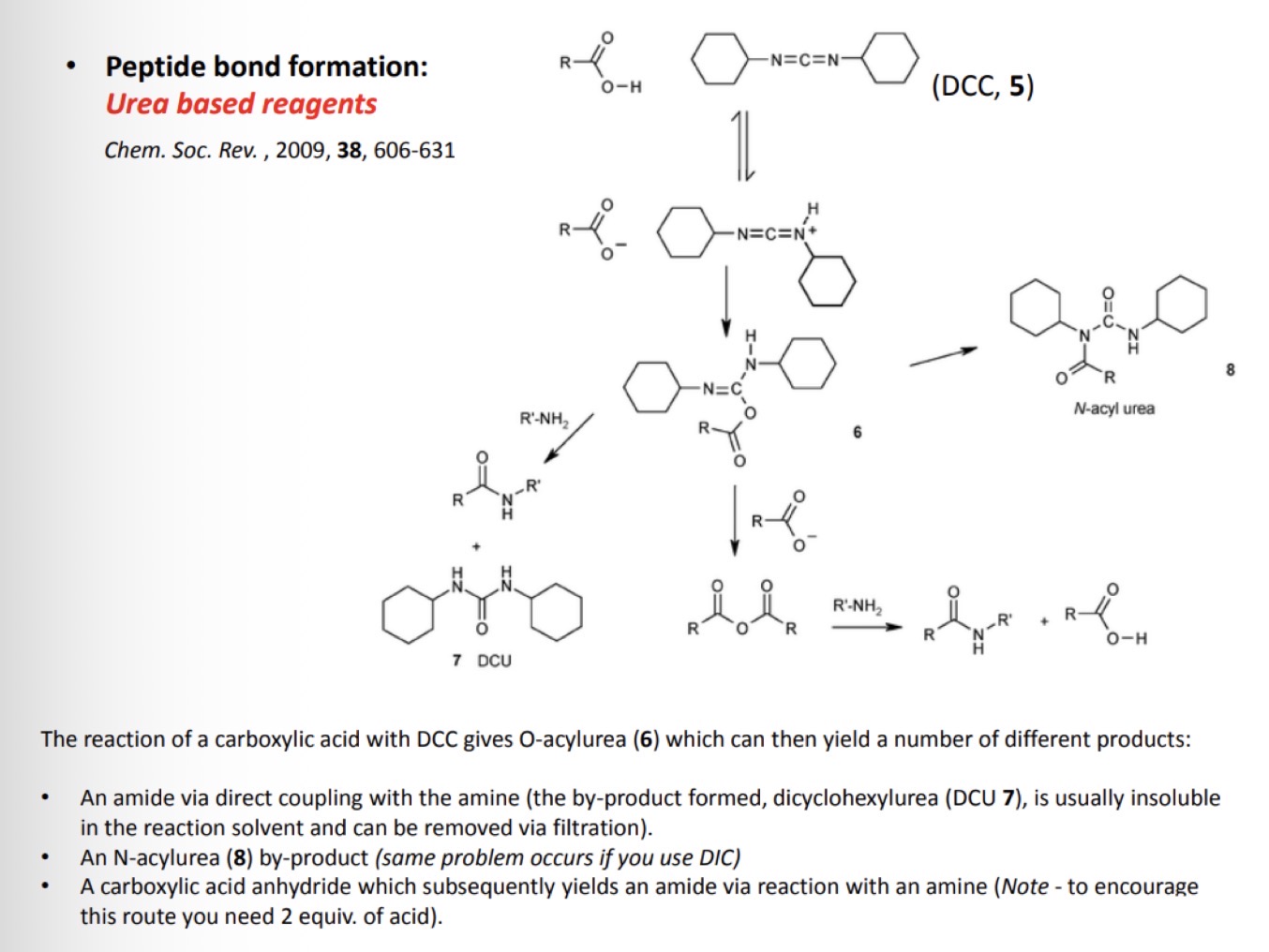
Peptide bond formation: Urea based reagents (ie contains N=C=N)
Finish the equation: R”COOH + R’-NH2 —R-N=C+N-R→ ?
R”COOH + R’-NH2 → R”-CO-NH-R’
Where the CO-NH ius an amide bond
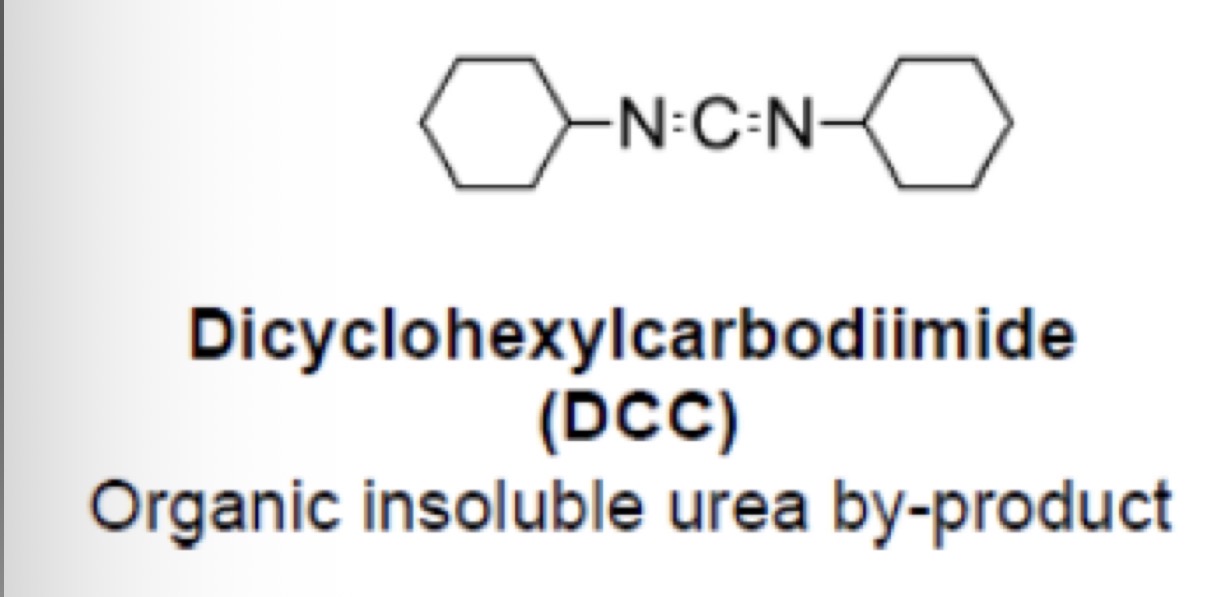
Types of urea based reagents: DCC
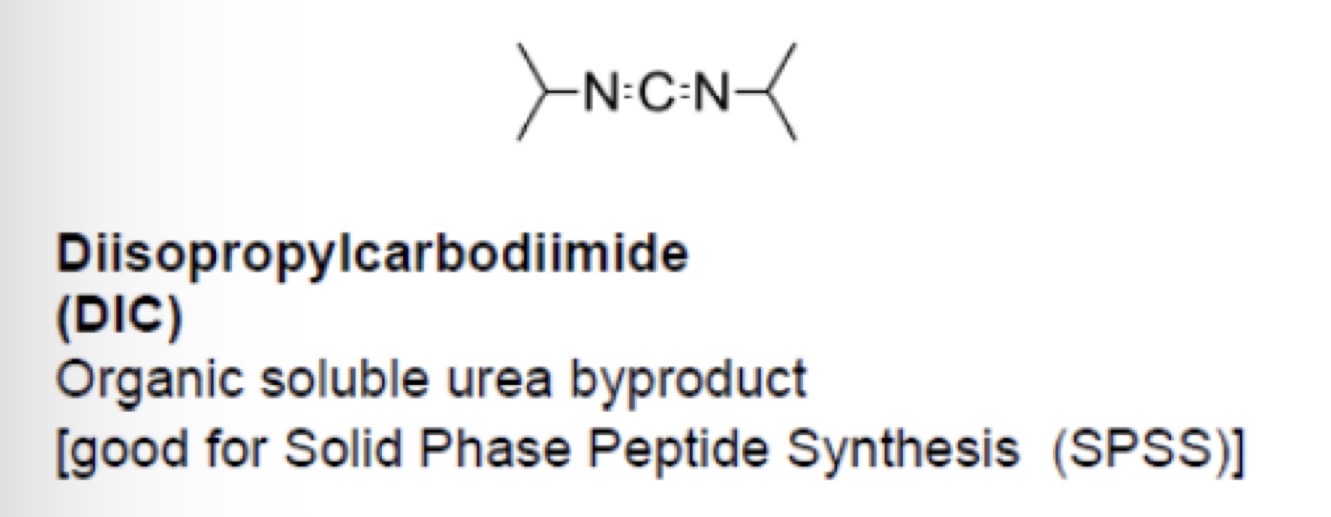
Types of urea based reagents: DIC
Types of urea based reagents: EDCI

How would you pick which urea based reagents to use?
The R’ groups are all different, meaning the urea based reagents have different solubilities, so use one with the correct solubility
Peptide bond formation: using DIC
Write out any potential side reactions
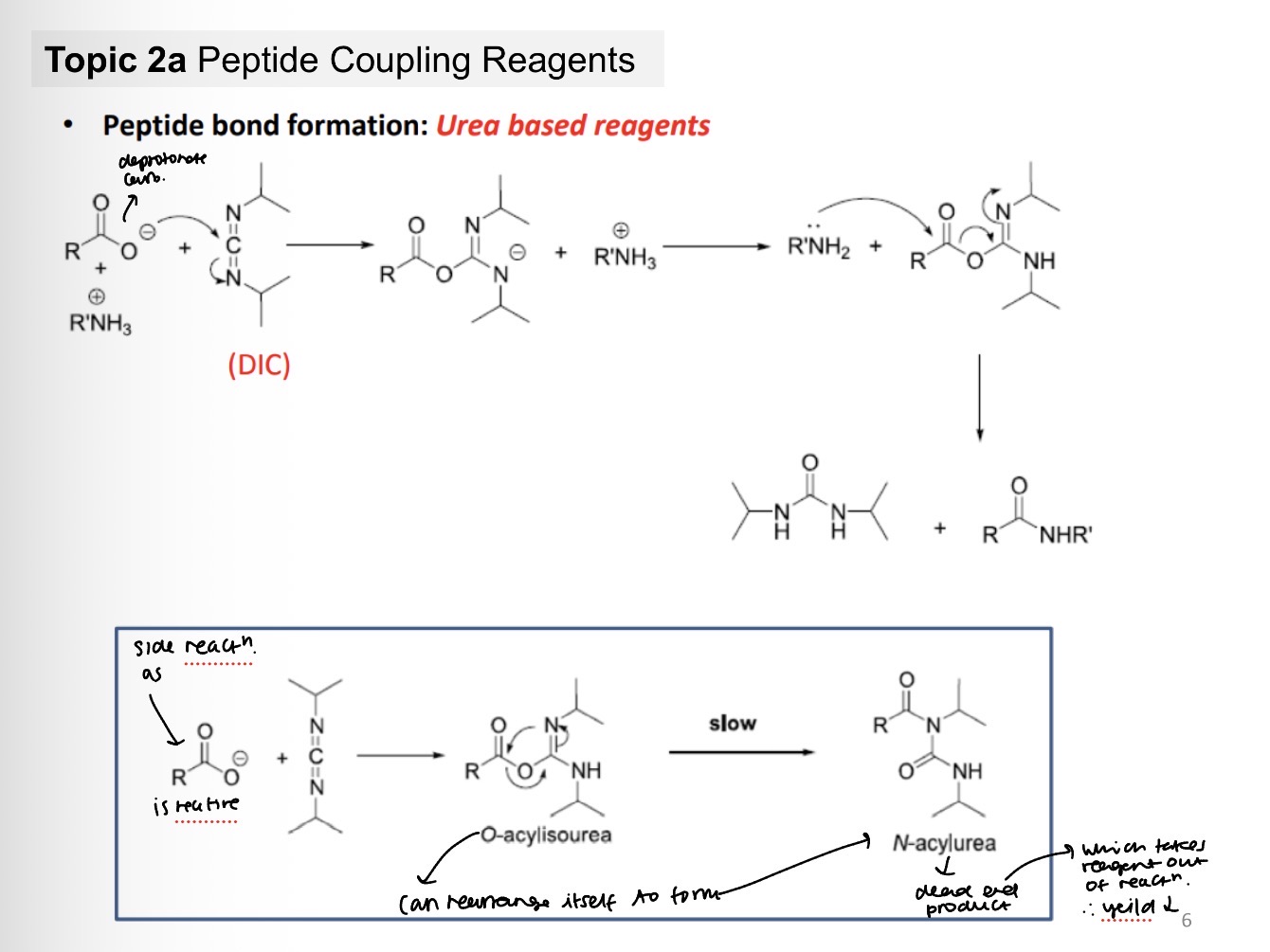
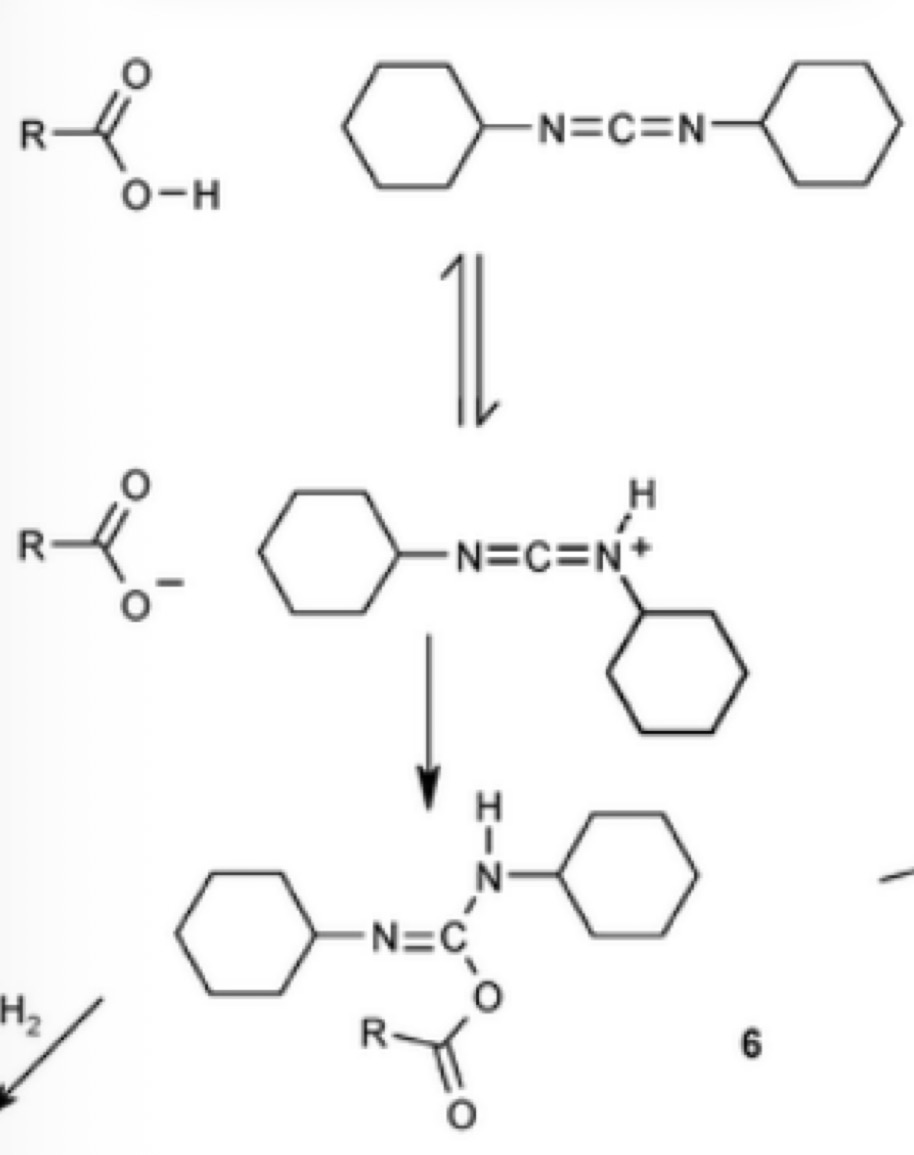
What potential products can be made from this reaction?
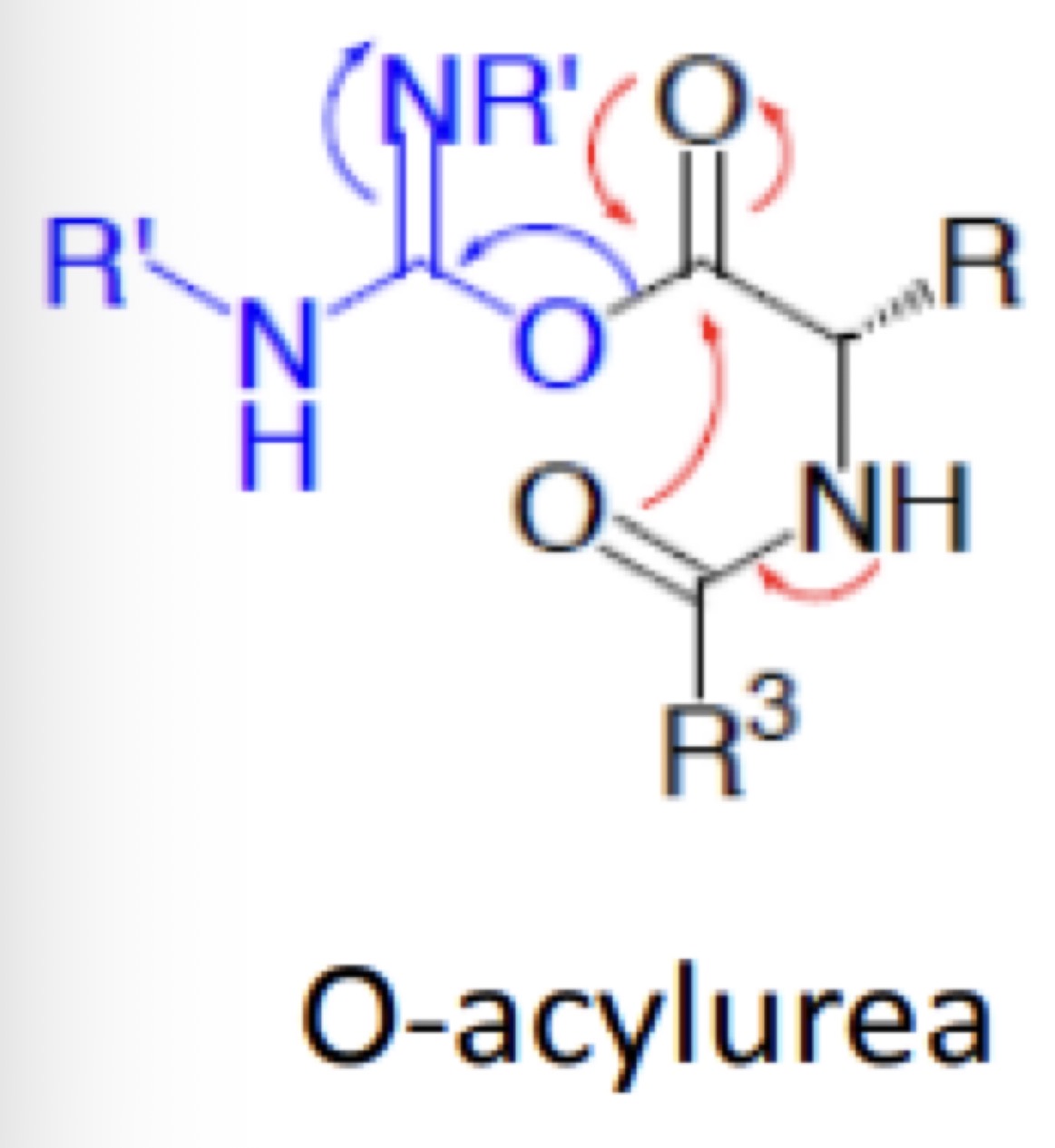
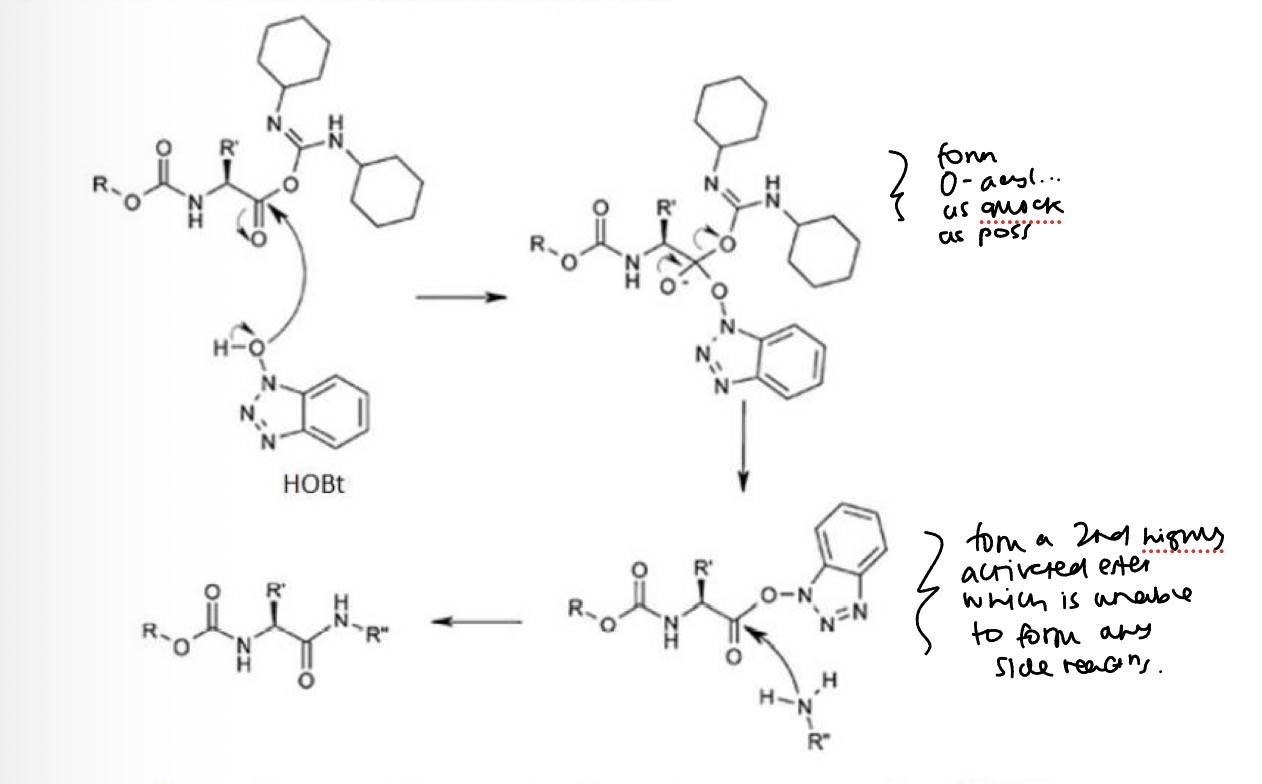
Racemisation in Peptide Synthesis using O-acylurea
Draw the resonance structures for this reaction
Draw the product formed when reacting these structures with a carboxylic acid protected amino acid
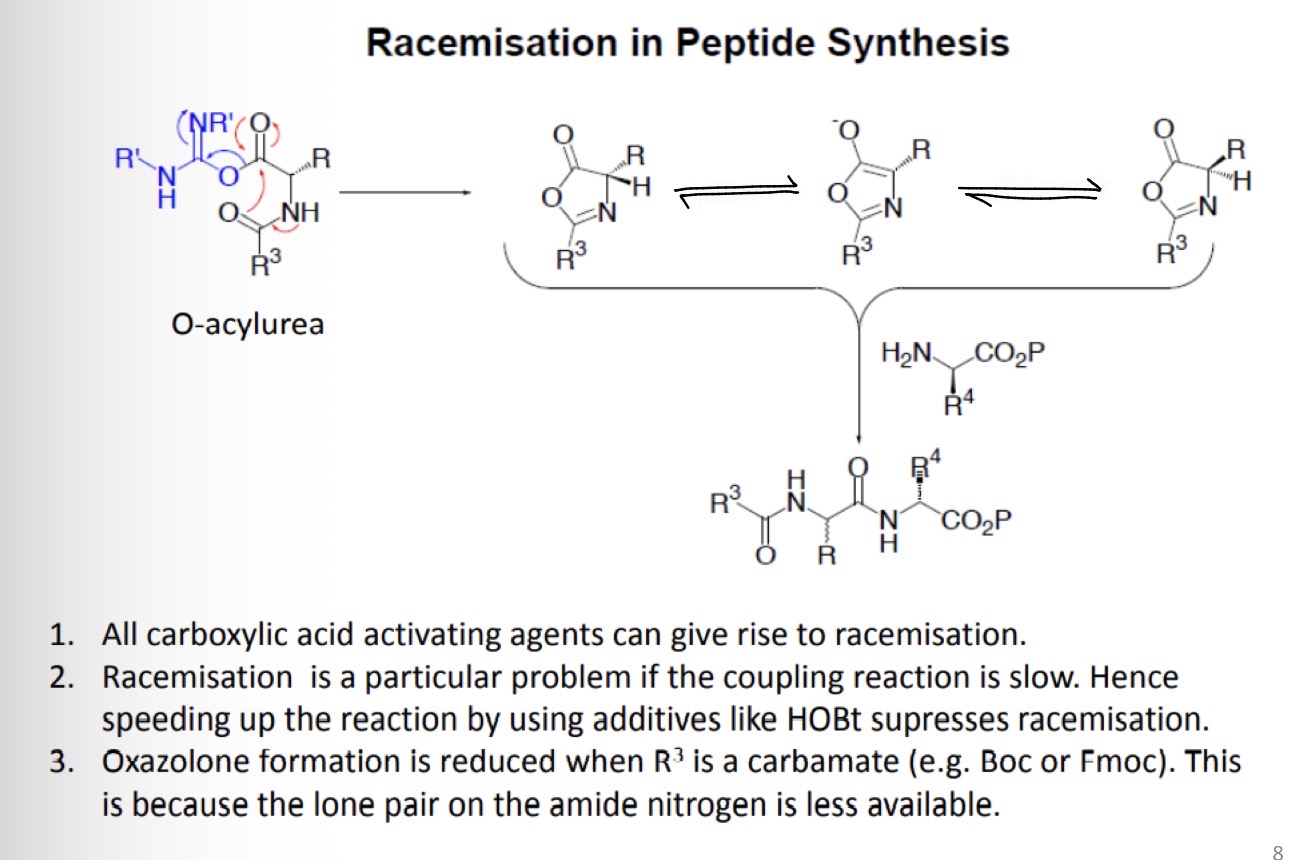
Additives can be used with carbodiimides to modulate the reactivity of the activated esters
This can help with racemisation and the formation of unwanted N-acyl urea by-products
Peptide coupling reagents: Urea based reagents
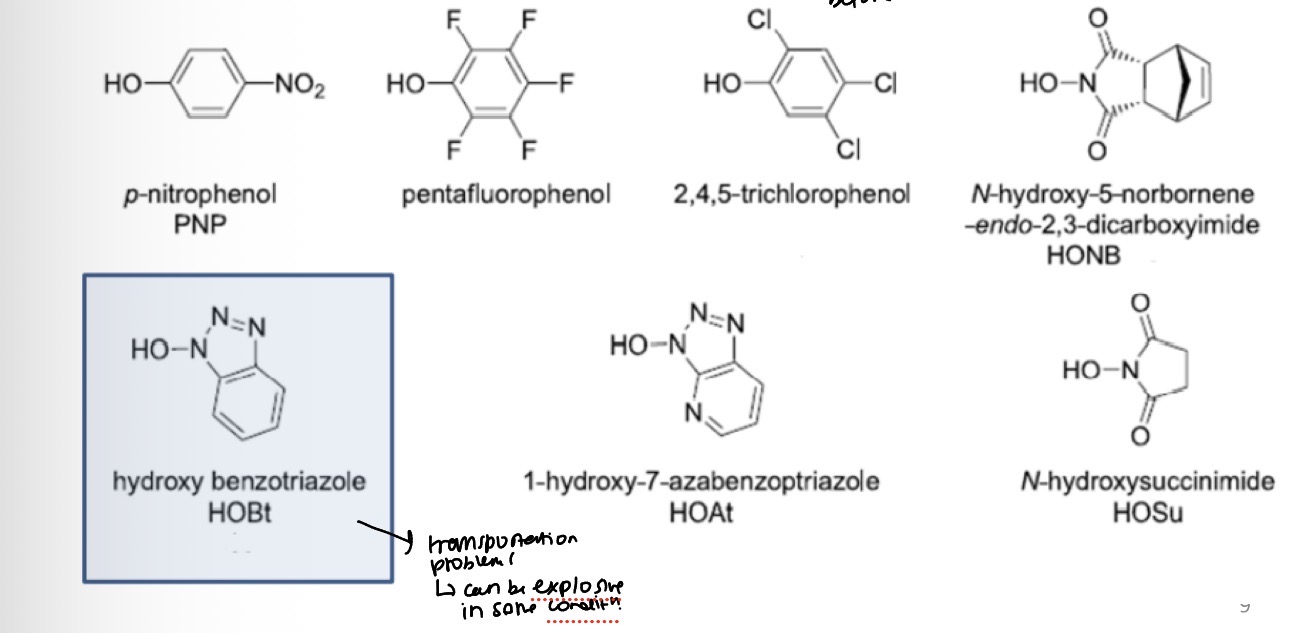
To reduce racemisation and prevent by-product formation reagents like (HOBt) can be used as an additive in the coupling reaction.
Coupling reactions run with DIC (or DCC) AND HOBt tend to have higher yields and low racemisation levels.
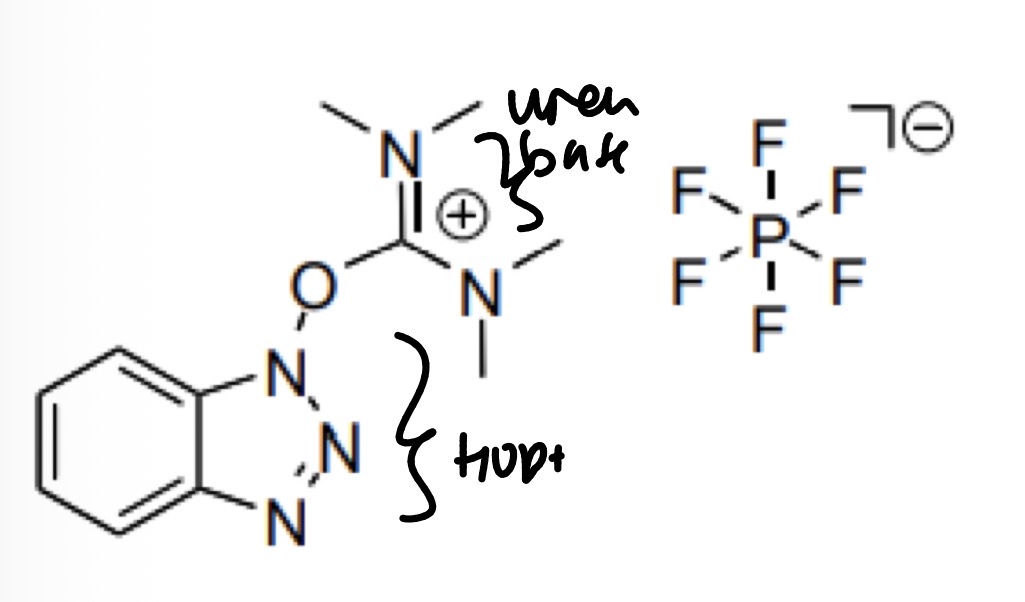
Uranium coupling reagents: HBTU (HOBt) additive added to it
What is its structure
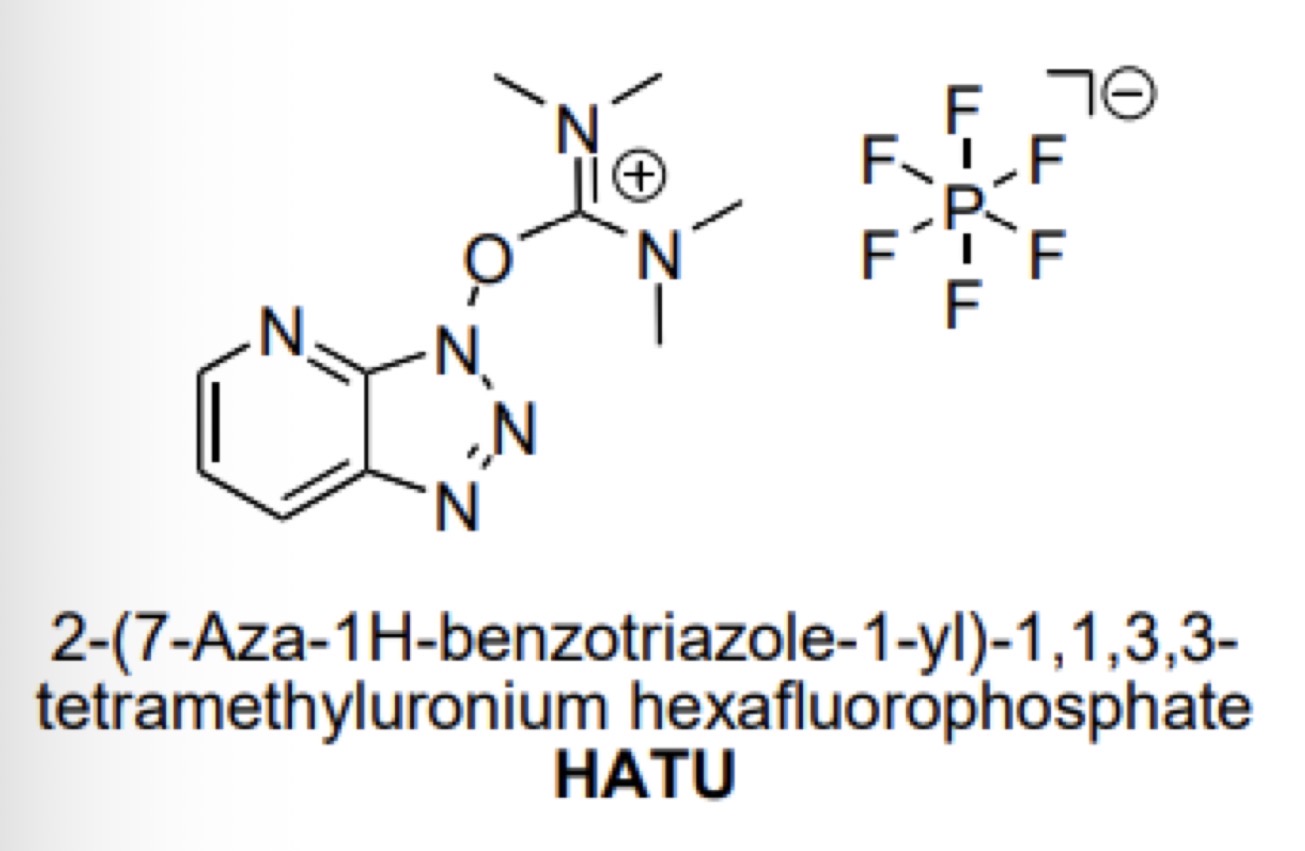
Uranium coupling reagents: HATU
What is its structure
Uranium coupling reagents: BOP
What is its structure
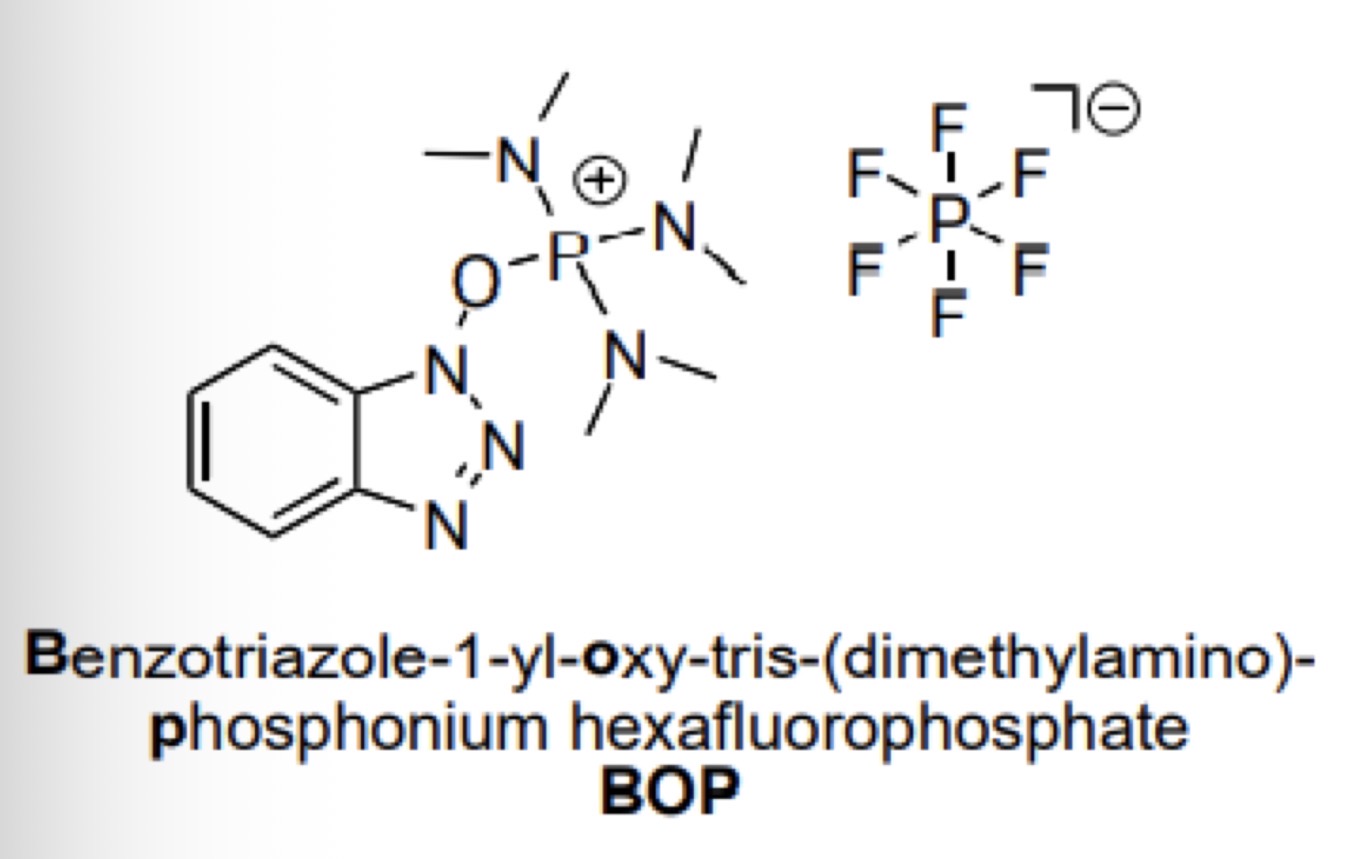
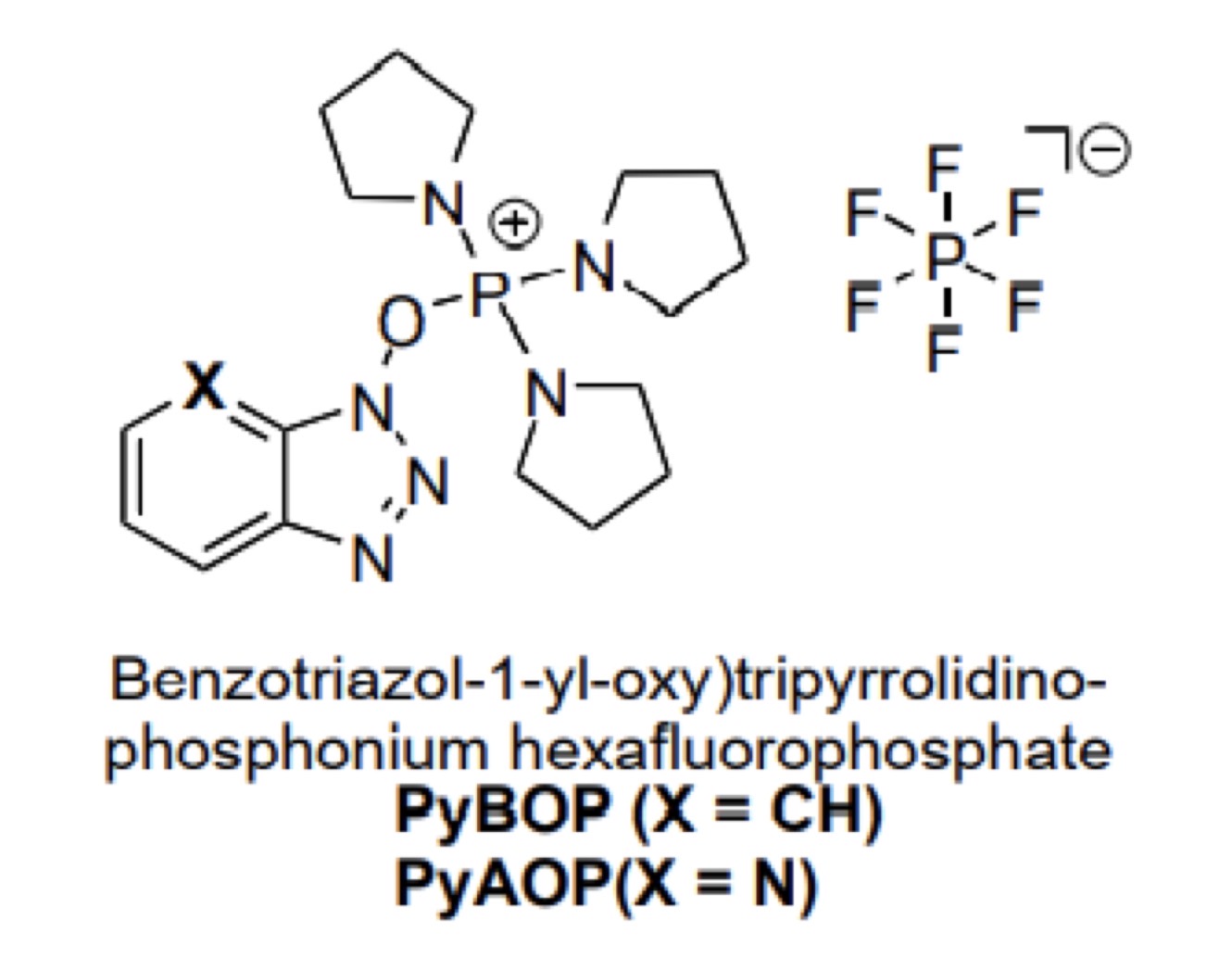
Uranium coupling reagents:
What is its structure PyBOP and PyAOP
Draw the mechanism for the peptide bond formation using phosphonium coupling reagents, for example using BOP, RCOO-, R’NH3 and NEt3
What is the by product?
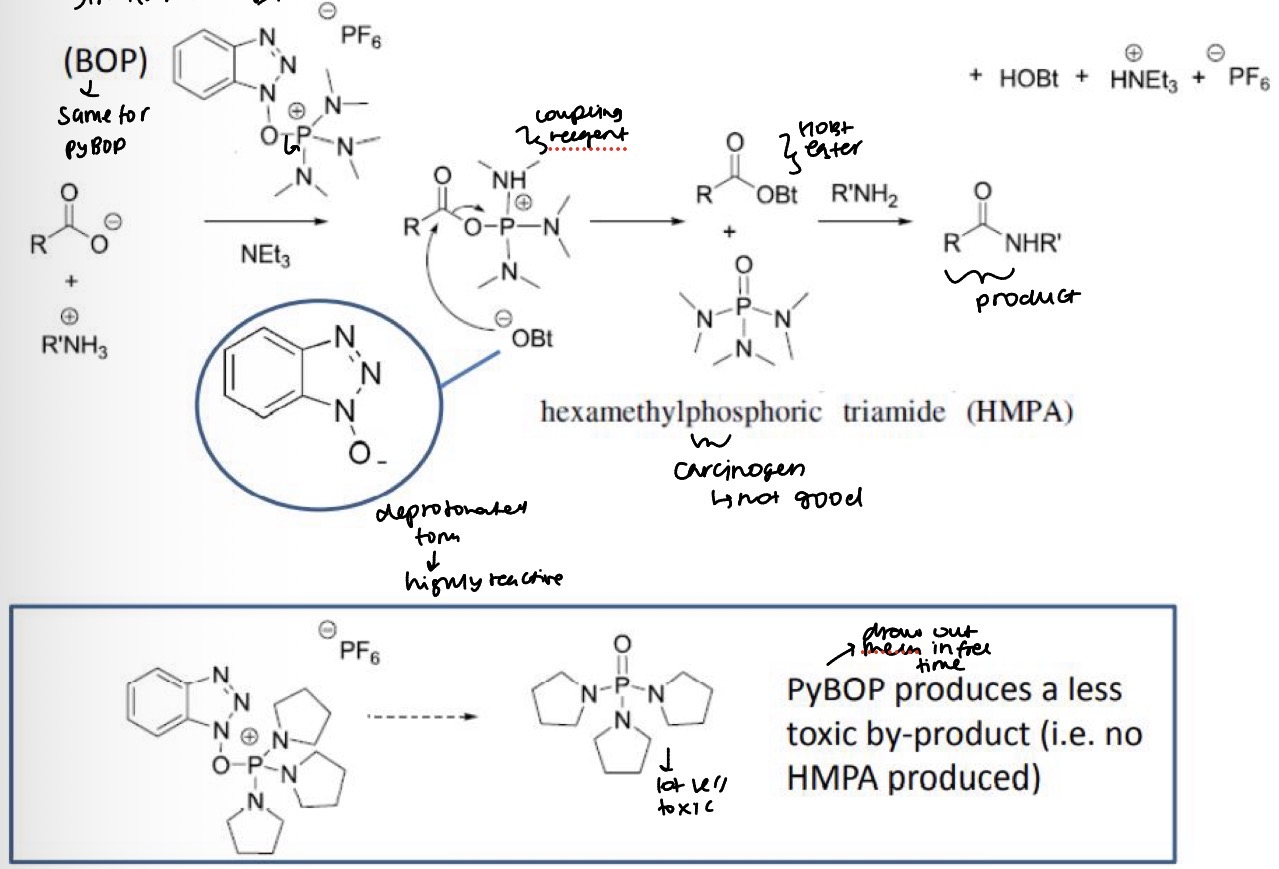
What is bad about HMPA
What is common about the by products when using HATU, HBTU and HCTU etc?
HMPA is toxic
The by-process are all toxic - must use fumehoods
General Mechansim for Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS):
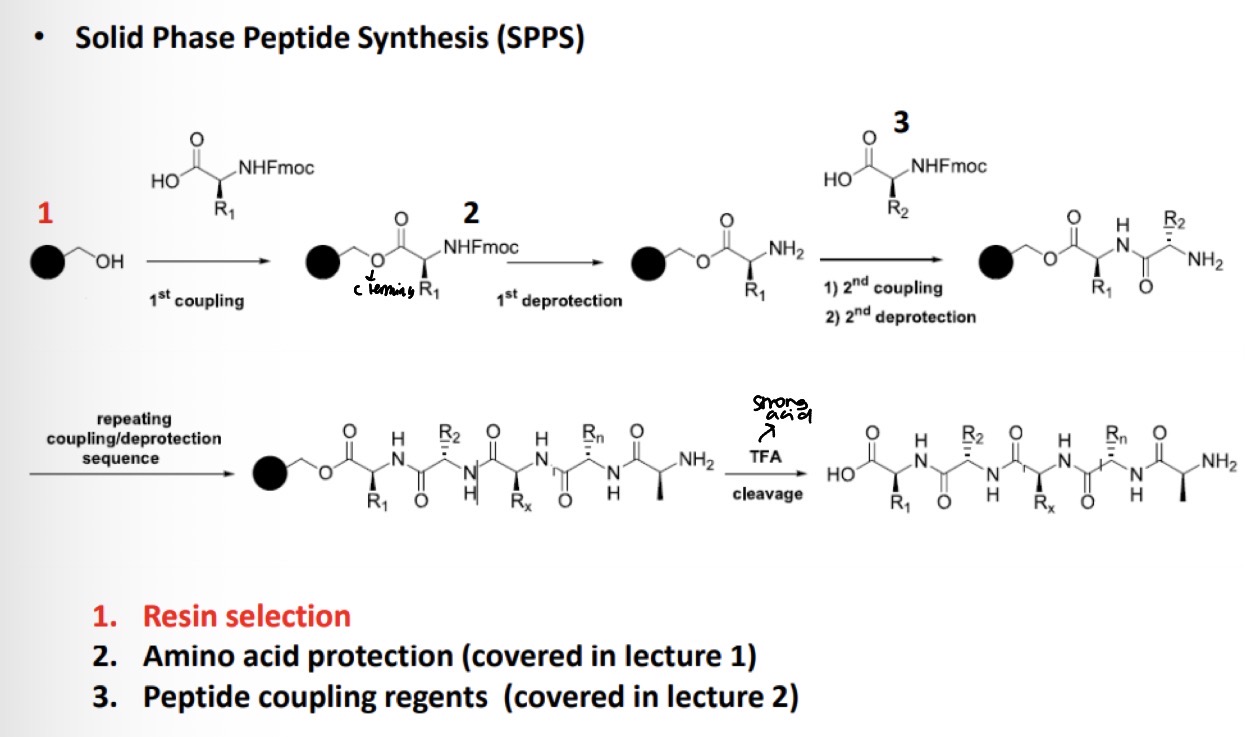
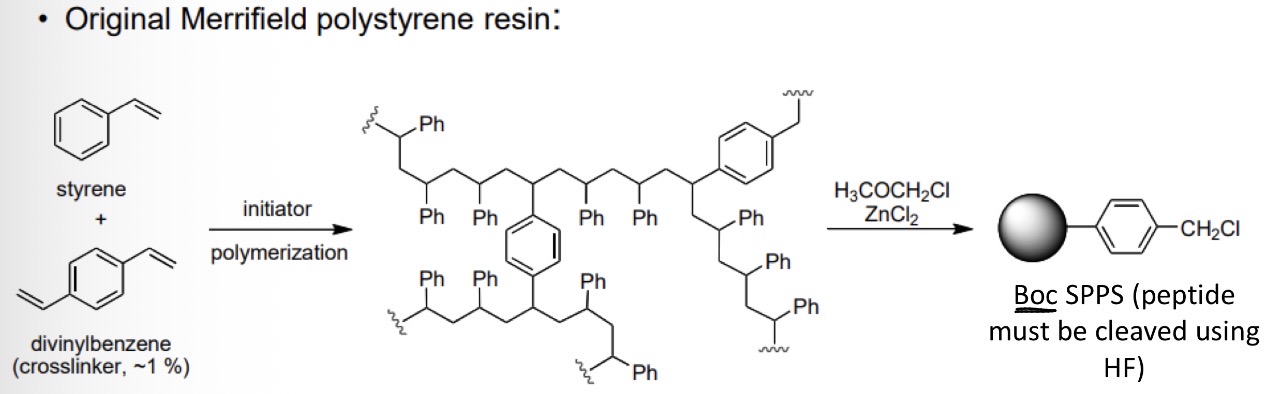
SPPS: Reaction for the original Merrified polystyrene resin
using styrene and divinylbenzene
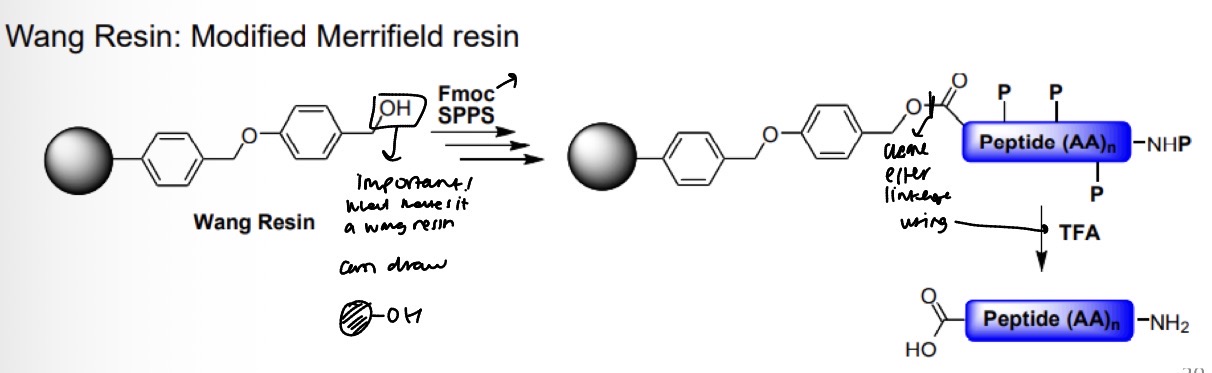
Wang Resin: Modified Merrifield resin reaction
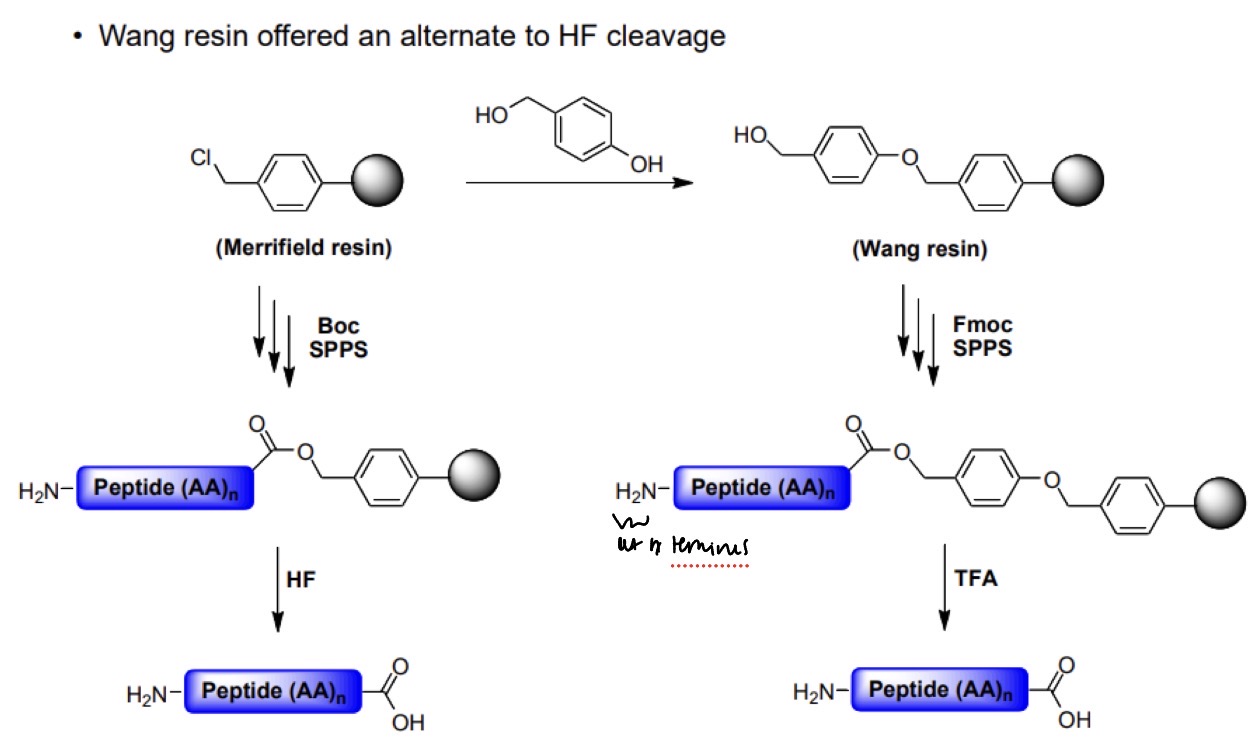
SPPS: Wang resin offered an alternate to HF cleavage.
What is the overall reaction
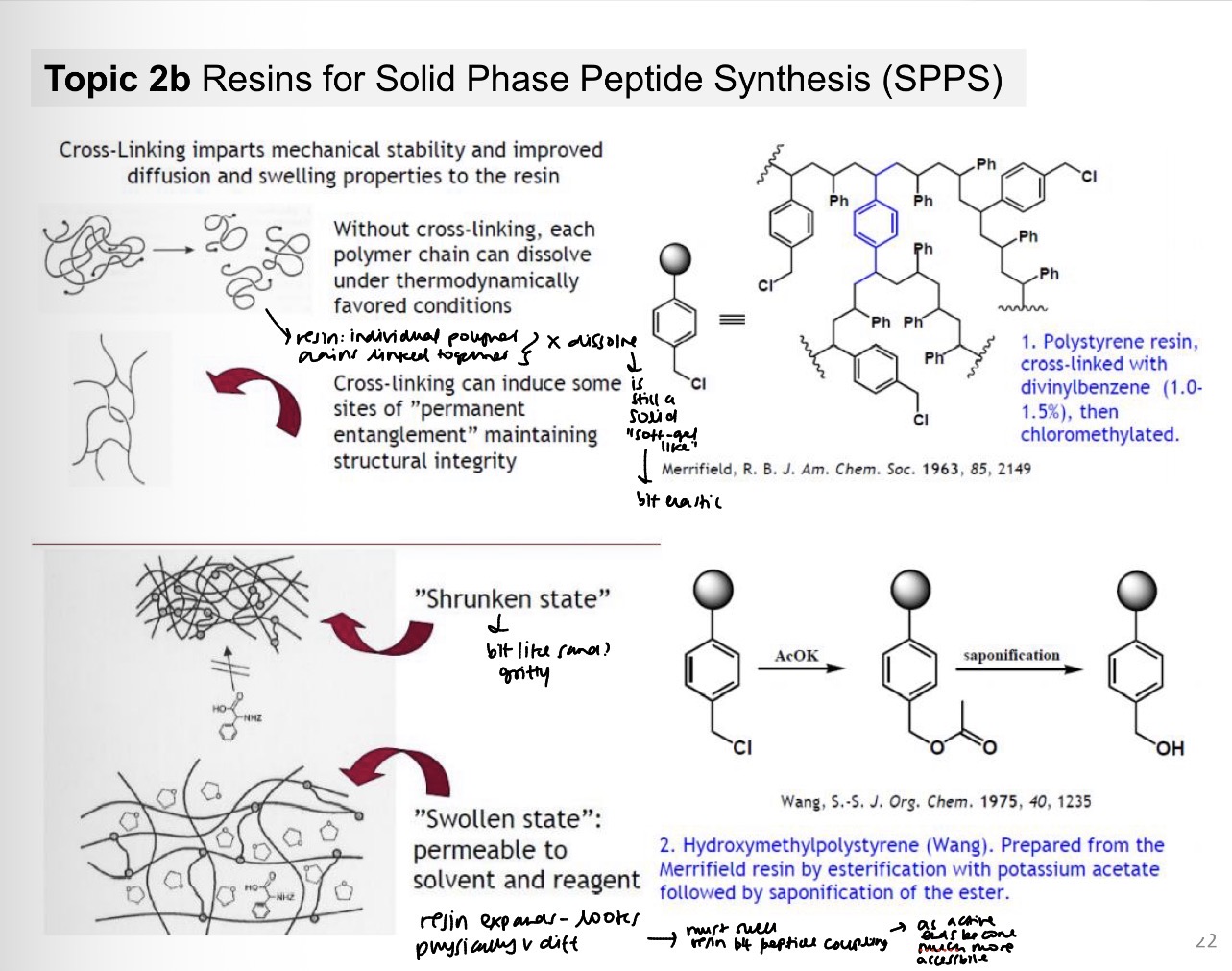
Resins properties: cross linking imparts
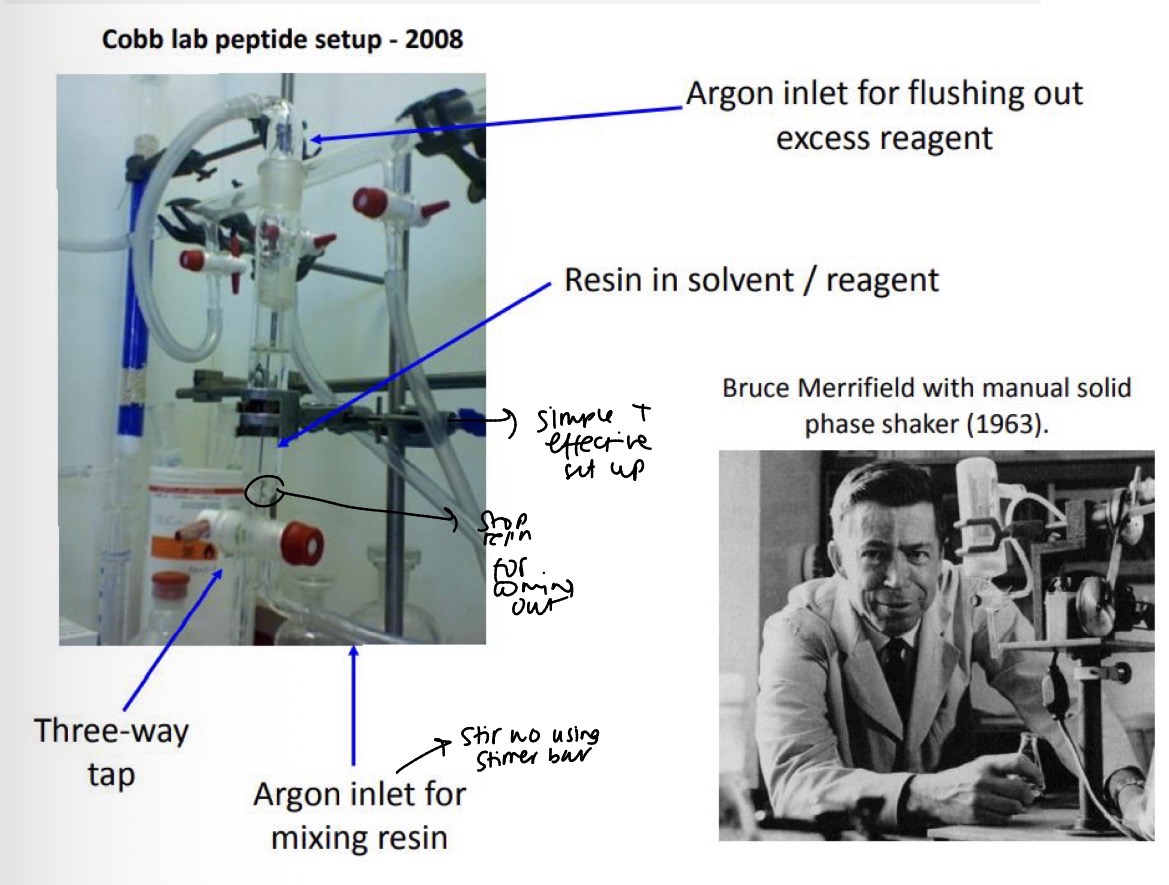
What does the Cobb lab peptide setup look like for SPPS?
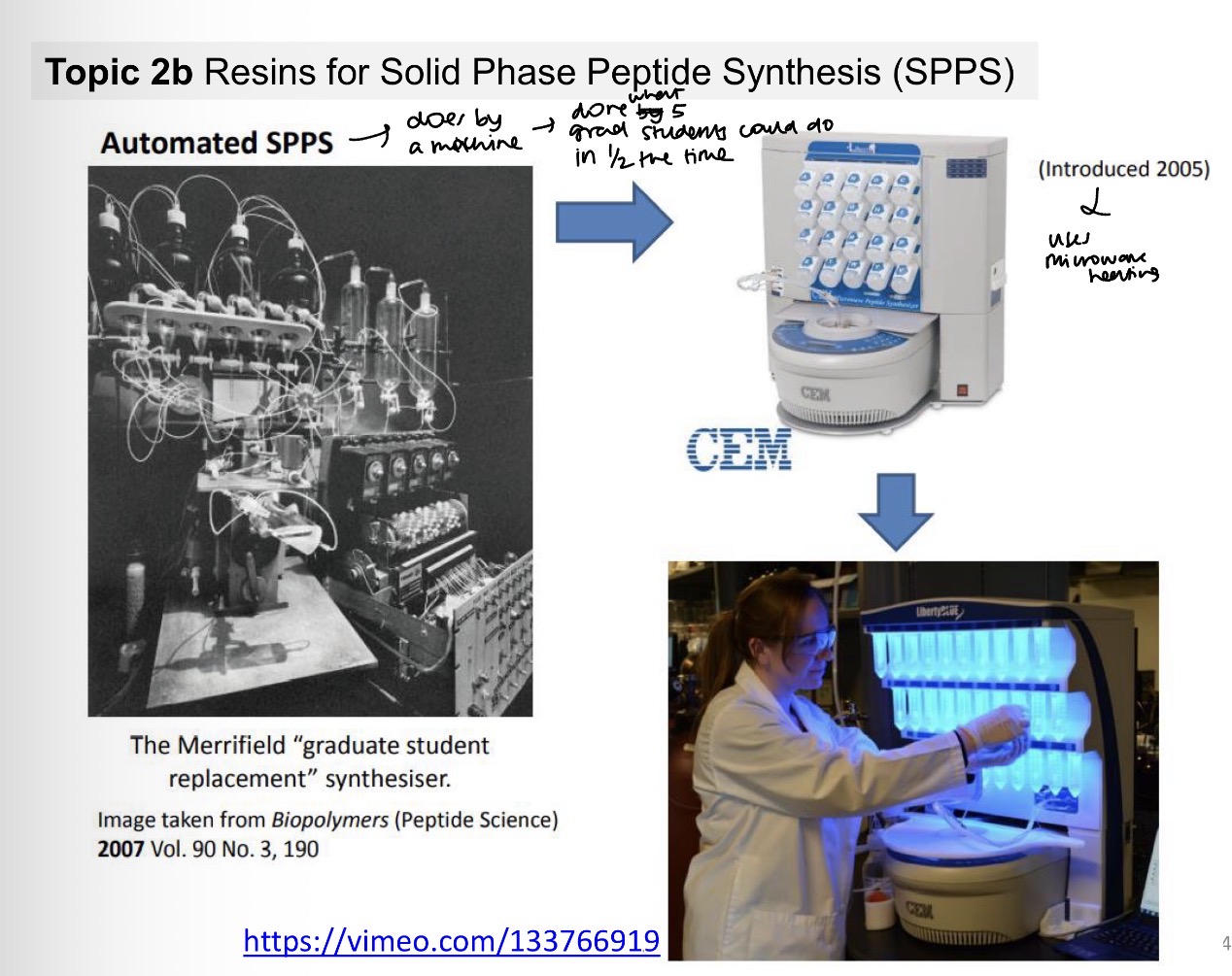
What does automated SPPS look like now?
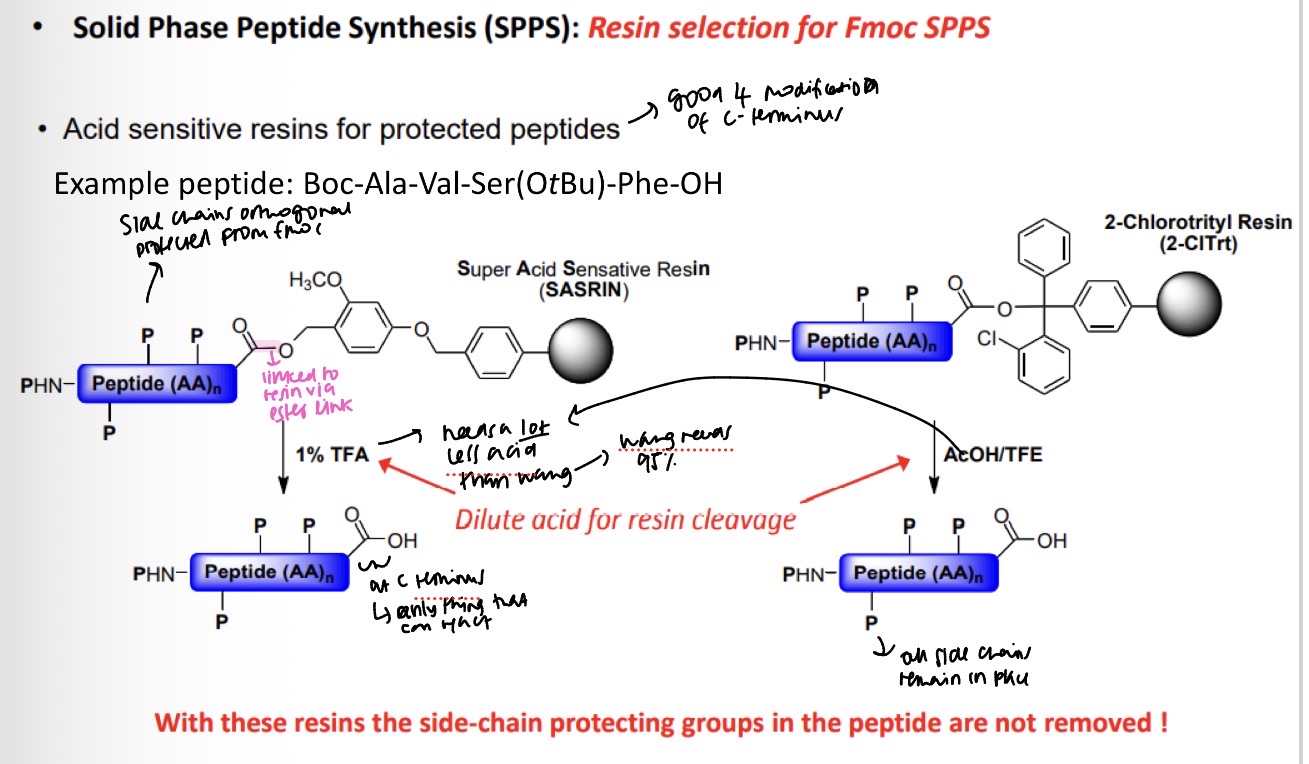
Resin selection for Fmoc SPPS
What conditions does the resin need to be sensitive towards? Example Boc-Ala-Val-Ser(OtBu)-Phe-OH
Resin selection for Fmoc SPPS.
Amide resin steps to:
Deprotect Fmoc
SPPS
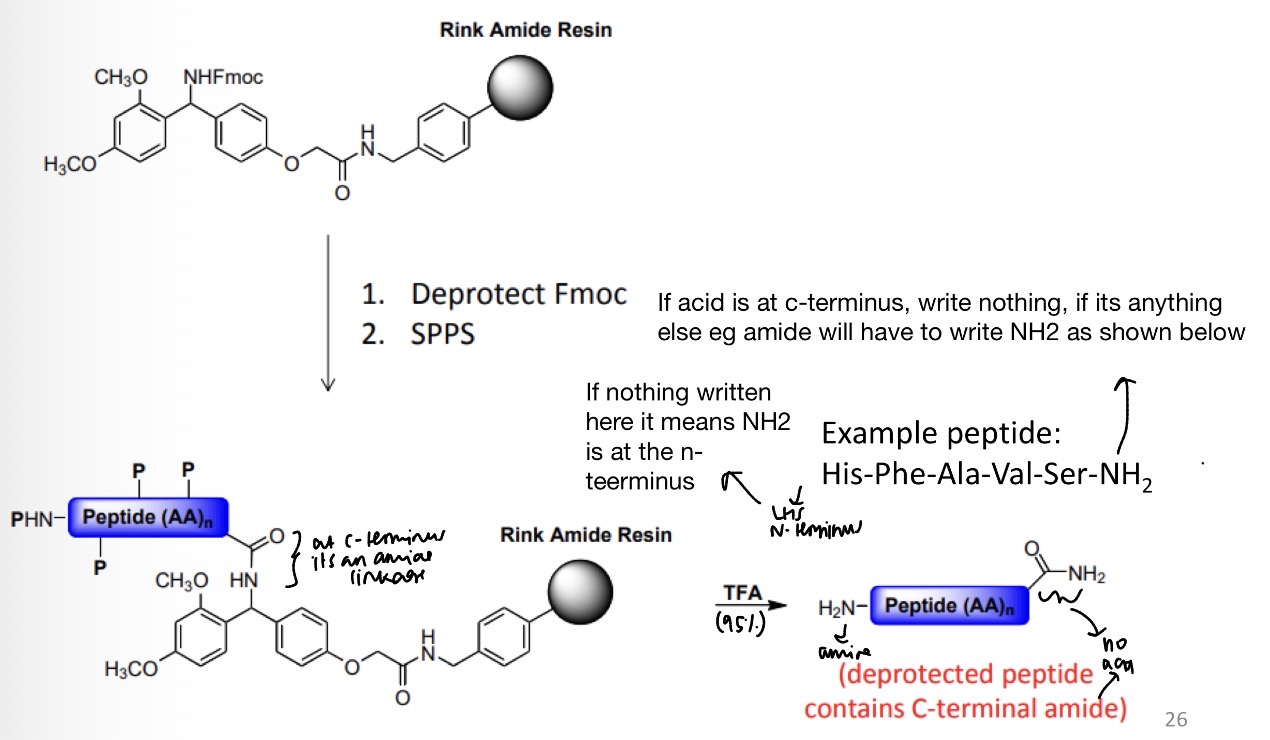
SPPS: Resin selection for Fmoc SPPS using Wang linker
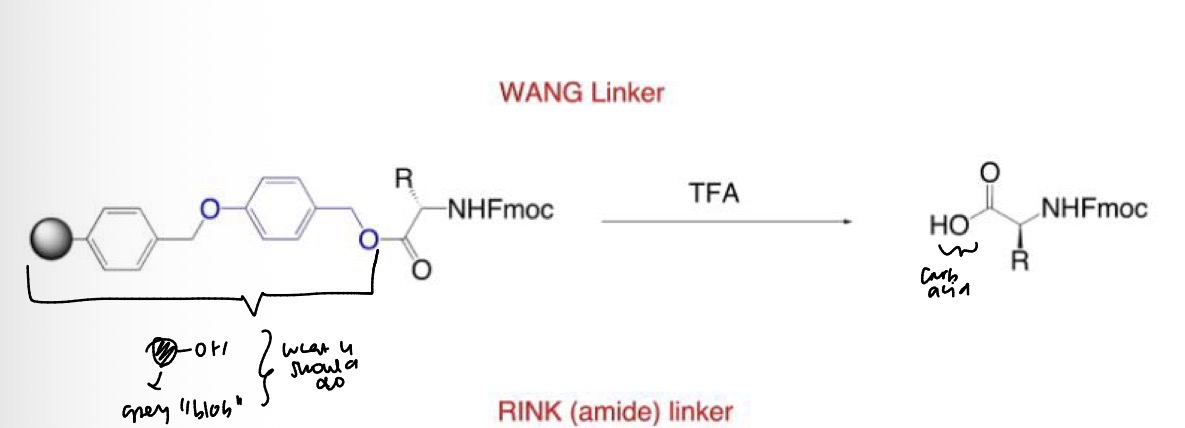
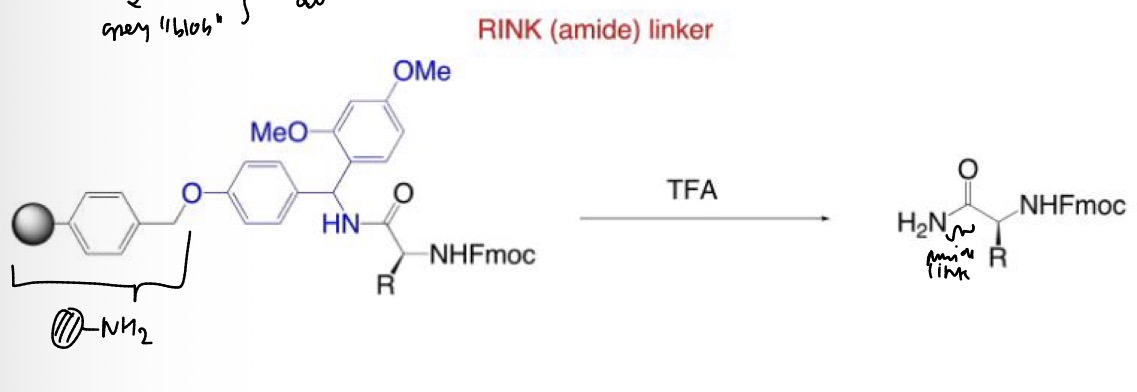
SPPS: Resin selection for Fmoc SPPS using RINK (amide) linker
Summary of key points in L2
Acid chlorides are not good to use as "activated" amino acids in peptide bond formation - Racemisation occurs via oxazolone formation
Amide bond formation in peptide synthesis requires the use of a coupling reagent.
There are many different types of coupling reagent see review reference on DUO but they all act by forming an activated ester that can be readily attack by an amine.Racemisation of the alpha carbon of amino acids can occur with all coupling reagents used. Some supress racemisation better that others.
The amount of racemisation that can occur varies with the coupling reagent, amino acid protecting group etc.
Additives like HOBt can be used in combination with coupling reagents like DIC or
DCC to suppress racemisation and increase reaction yields.Many peptide coupling reagents can be toxic and they must be handled in a laboratory with care.
get as cose to 99% yeill as poss
There are a range of different solid supports (resins) available for peptide synthesis.
Regardless of the resin type peptides are prepared from the C to the N terminus (e.g. last amino acid added will be located at the N-terminus).
Specific resins can be selected to: a) modify the C-terminus upon cleavage of the peptide (i.e. Rink Amide) and b) leave all of the side chain protecting groups on the peptide (i.e. 2-Chloro-trityl resin).