Urinalysis unit 3
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
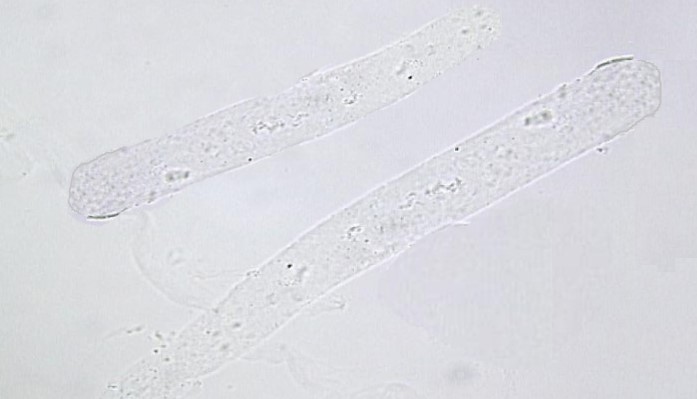
Name this cast? What is it associated with?
Hyaline cast, renal disease in high amounts
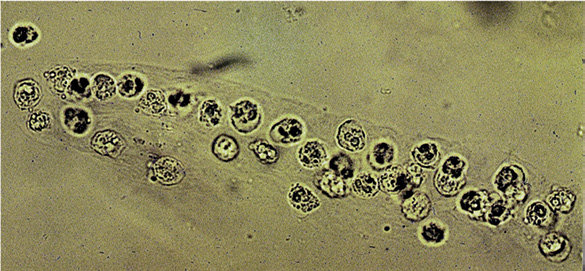
Name this cast? what is it associated with?
WBC cast, renal inflammation and acute pyelonephritis
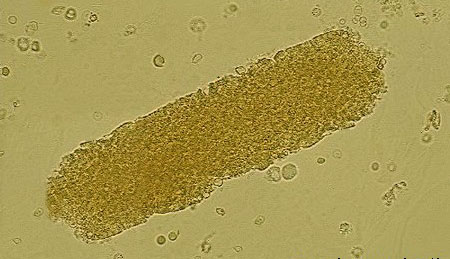
Name this cast? What is it associated with?
granular cast, prolonged renal disease
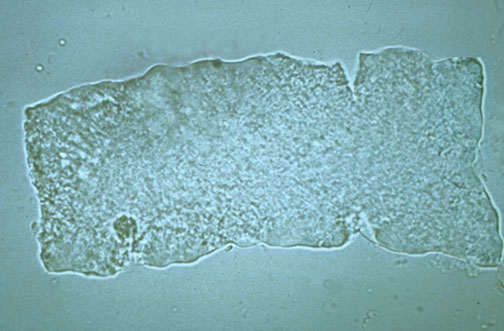
Name this cast? What is it associated with?
Waxy cast, renal failure, kidney transplant rejection and diabetic nephropathy
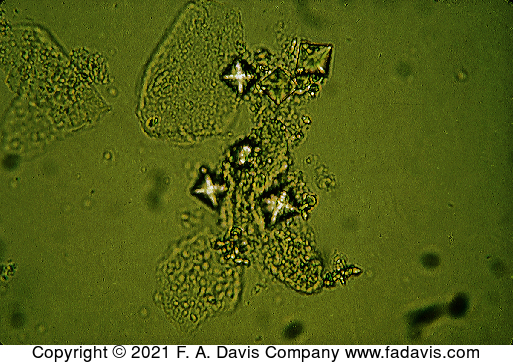
Name this crystal? What is the disease its associated with? what is its ph? normal or abnormal?
calcium oxalate, kidney stones, acidic (and normal), normal
ON TEST
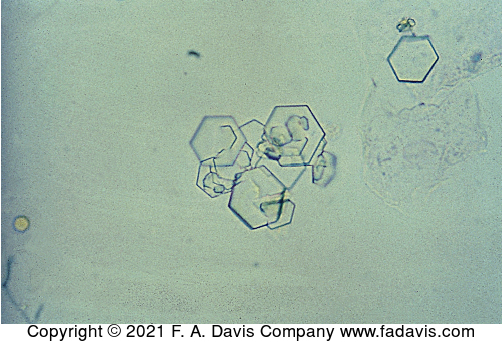
Name this crystal? what is it associated with? what is its ph? normal or abnormal?
cystine, cystinuria, acidic, pathogenic (abnormal)

name this crystal, what disease is it associated with? What is its ph? Normal or abnormal?
Uric acid, gout, acidic, normal

Name this crystal? What is it associated with? what is its pH? normal or abnormal?
ammonium biurate, dehydration and old samples, alkaline, normal
ON TEST
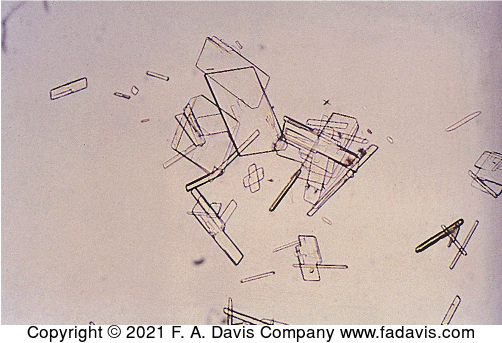
name this crystal? what is it associated with? what is its pH? normal or abnormal? what is a key feature?
cholesterol, nephrotic syndrome, acidic, pathogenic (abnormal), notched edges, and they tend to stack on top of eachother
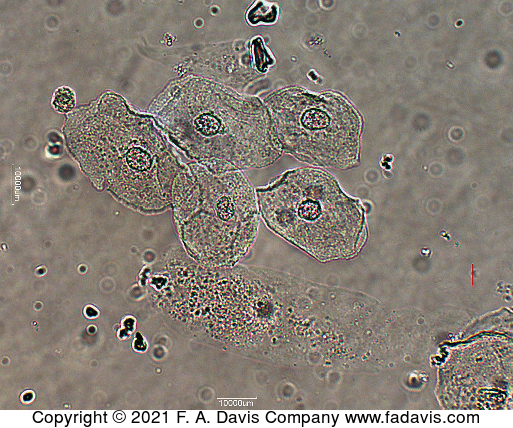
name this cell? What is it associated with?
squamous epithelial, non cleancatch urine
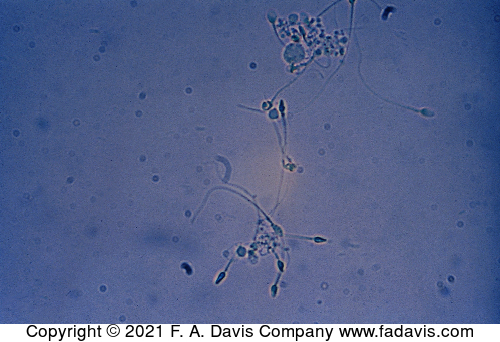
name this cell
sperm
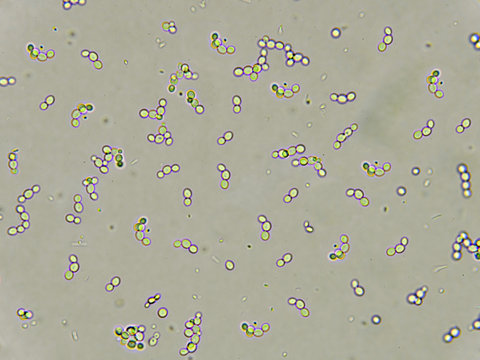
name this cell? What is it associated with?
yeast, UTIs
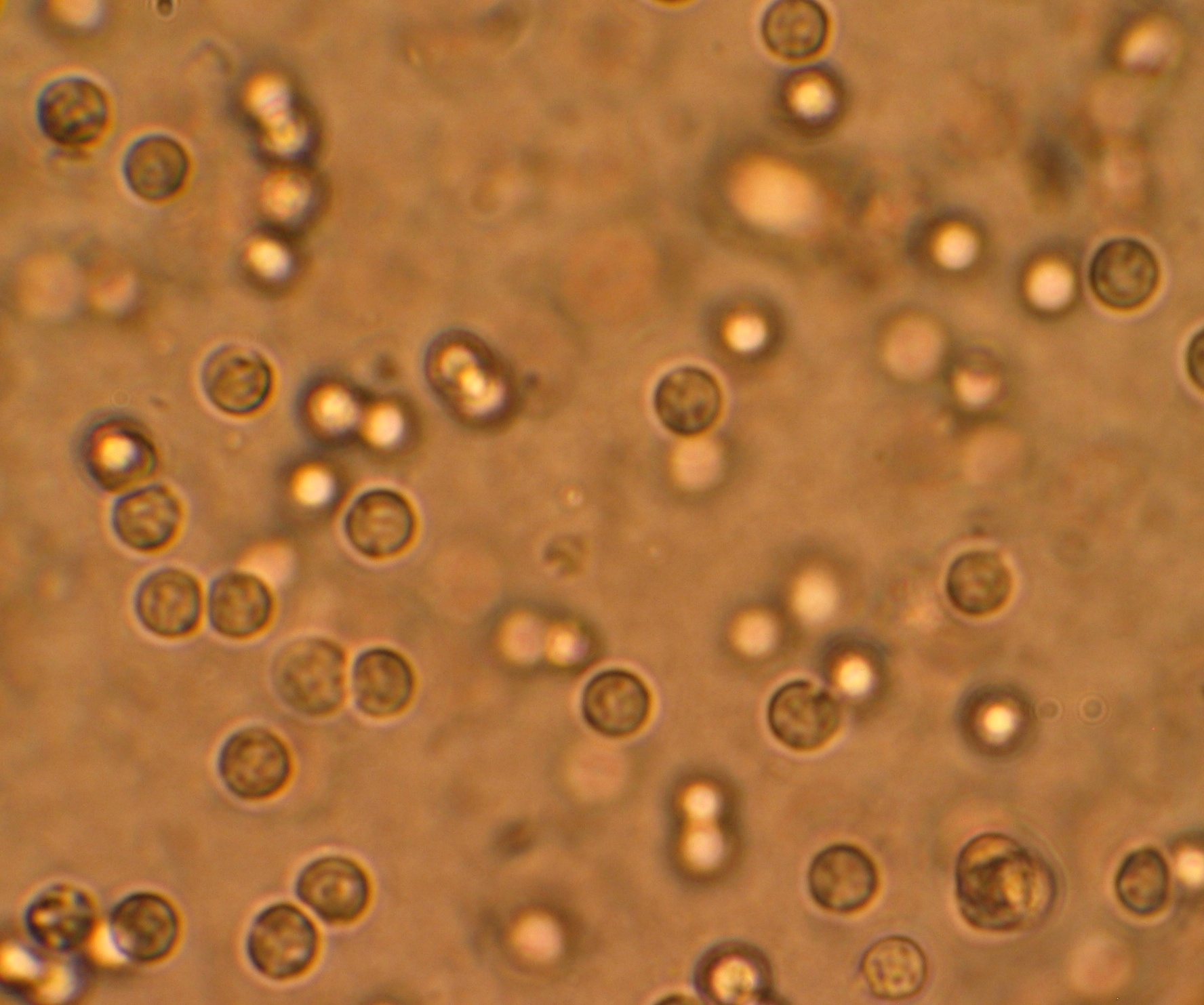
name this cell
WBC
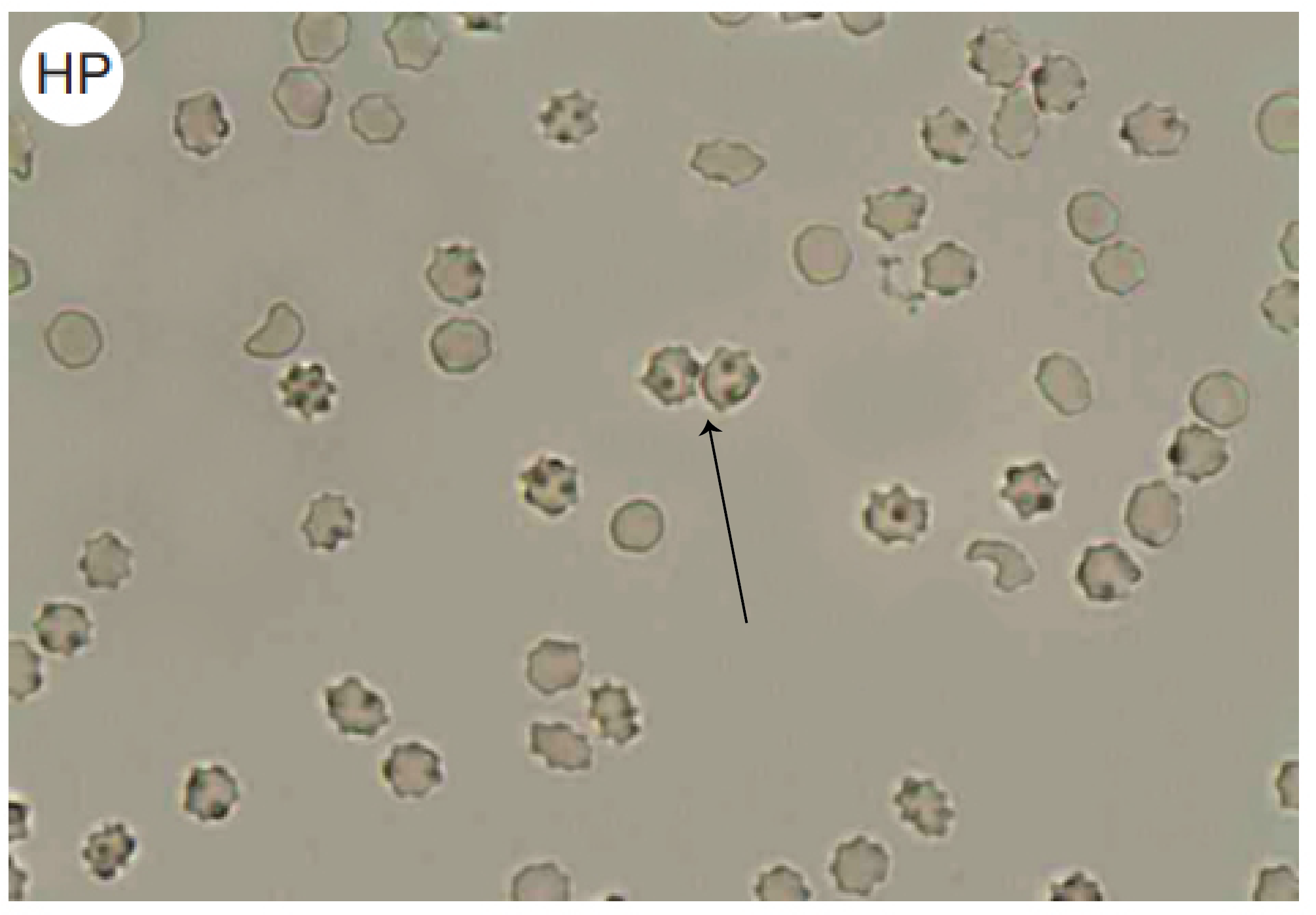
Name this cell
crenated RBC (found in hypertonic)
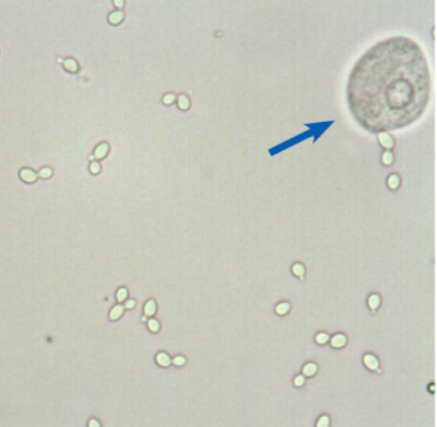
name this cell (blue arrow), what is it associated with?
Transitional epithelial, UTI and carcinoma (in large amounts)
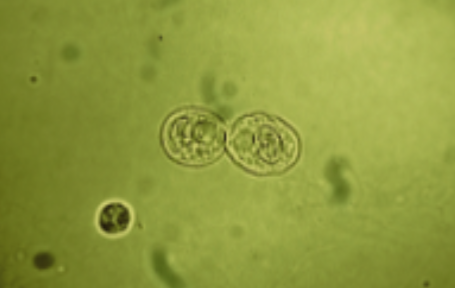
name this cell? What is it associated with?
Renal tubular epithelial, acute tubular necrosis, kidney infection
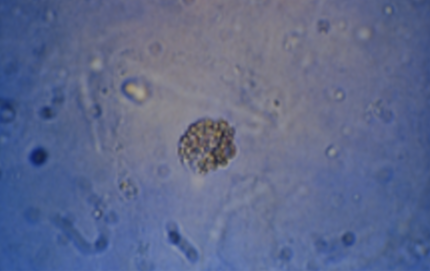
Name this cell? What is it associated with?
Oval fat bodies, lipid nephrosis, terminal kidney disease
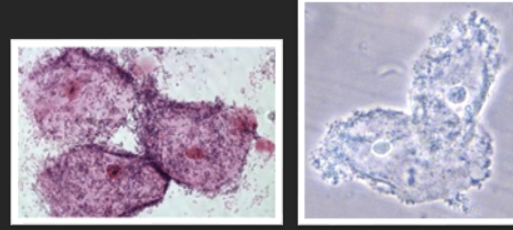
What are these? What are they associated with?
Clue cells, bacterial vaginosis
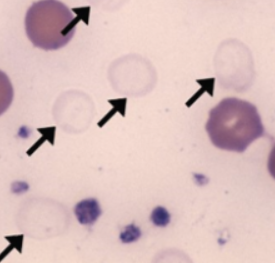
Name the cells (black arrow)
Ghost cells

What is this?
WBC clump
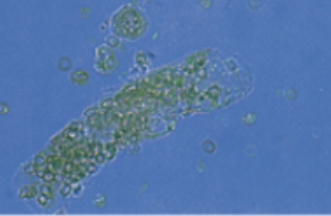
What cast is this? What is it associated with?
RBC cast, acute glomerulonephritis
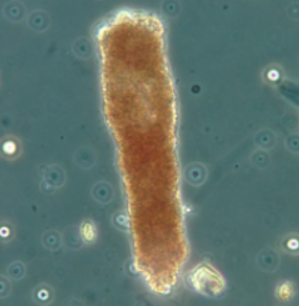
what cast is this? What is it associated with?
hemoglobin cast/ muddy brown cast, acute glomerlonephritis
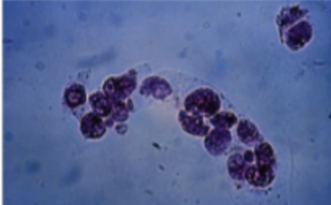
What cast is this? What is it associated with?
Renal tubular cast, severe renal disease and kidney transplant rejection
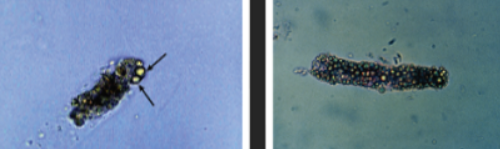
What casts are these? What diseases are associated?
Fatty casts, Crush injury, diabetes mellitus, nephrotic syndrome
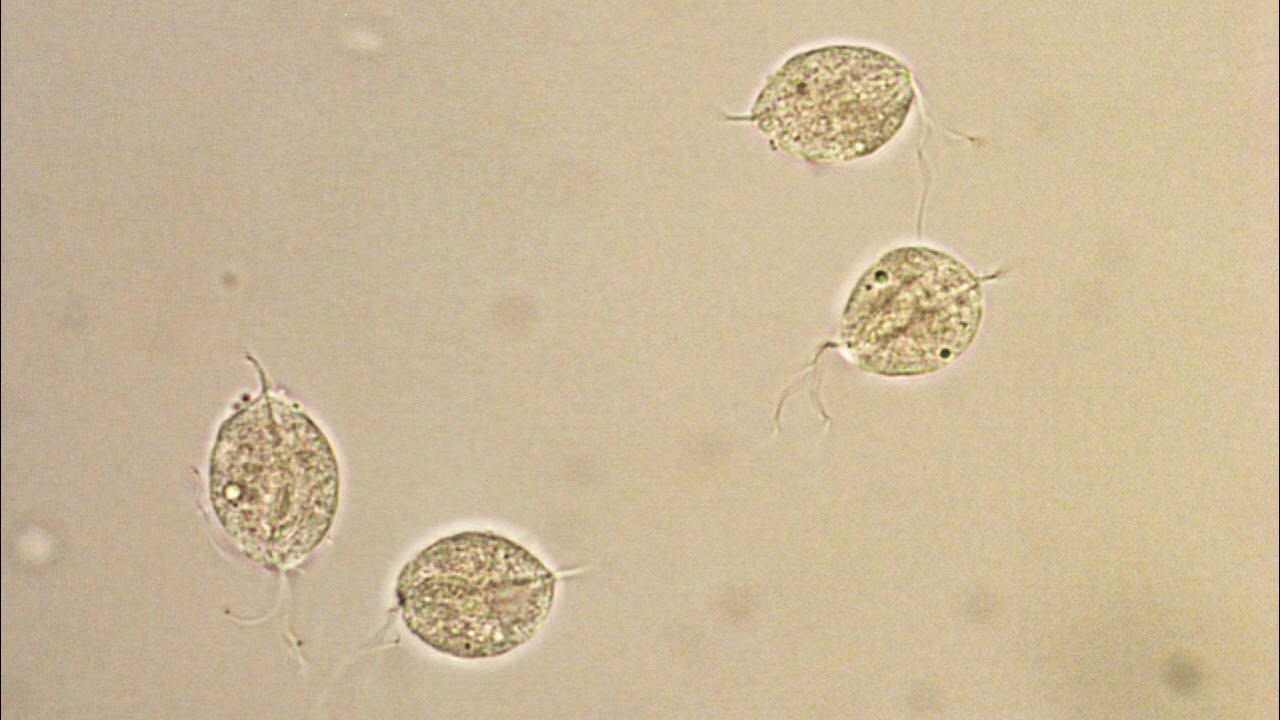
What is this? What must it be doing to diagnose it?
Trichomonas, moving

What is this crystal? what disease is it associated with? what is its pH? normal or abnormal?
Sodium citrate, no disease association in urine, acidic, normal
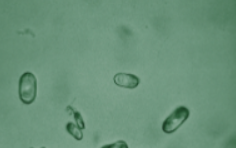
Name this pathogenic dumbbell form of a typically normal acidic crystal, and what the pathogenic form indicates:
calcium oxalate, ethylene glycol (antifreeze poisoning)
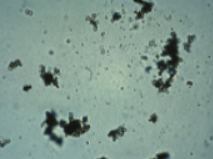
Name this ACIDIC crystal that resembles sand in an old urine? What is it associated with? Normal or abnormal?
Amorphous urate, old specimens, normal
Name this ALKALINE crystal that resembles sand in an old urine, what is it associated with? normal or abnormal?
Amorphous phosphate, refrigeration, normal

Name this crystal? What is it associated with? What is its pH? normal or abnormal?
calcium phosphate, kidney stones, alkaline, normal

Name this crystal? What is it associated with? what is its pH? normal or abnormal?
triple phosphate, no association (sometimes UTI), alkaline, normal
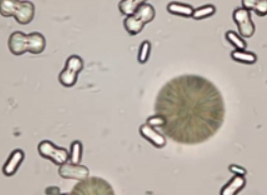
Name this crystal? what is it associated with? what is its pH? normal or abnormal?
Calcium carbonate, no significance, alkaline, normal

Name this crystal, what is it associated with? what is its ph? normal or abnormal?
tryosine, liver disease and inborn error of metabolism, acidic, pathogenic (abnromal)
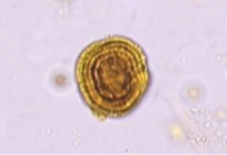
Name this crystal? what is it associated with (3 things)? what is its ph? normal or abnormal?
Leucine, liver disease inborn error of metabolism and maple syrup urine, acidic, pathogenic (abnormal)
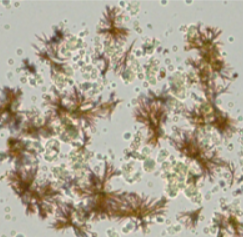
name this crystal? what is it associated with? what is its ph? normal or abnormal?
bilirubin, hepatic disorders, acidic, pathogenic (abnormal)
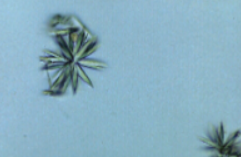
Name this drug associated crystal? what is it associated with?
sulfonamide, dehydration while taking sulfa drugs
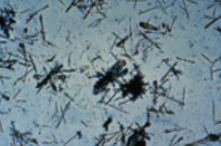
Name this drug associated crystal? what is it associated with?
ampicillin, dehydration and impaired kidney function
What is the preferred specimen for microscopic examination?
12 mL of room temp sample, spun down for sediment. fresh or preserved ON TEST
What is the speed of centrifugation?
1500-2000 RPM for 5 minuets ON TEST
What is the most common microscope used for microscopic examination?
Bright field with reduced light ON TEST
What does acetic acid do?
lyses RBCs ON TEST
What cell is most often associated with vaginal contamination?
Squamous epithelial
What parts of the body does the transitional epithelial cells reside in?
The lining of the renal pelvis, ureter, bladder, and urethra ON TEST
What are Oval Fat bodies?
Renal tubular cells (or sometimes WBCs) that have absorbed lipids ON TEST
What (single thing) forms a Maltese cross when polarized?
Oval fat bodies
What cast indicates end stage renal disease?
waxy cast ON TEST
What are ghost cells and how are they formed?
Lysed RBCs, due to a highly alkaline urine
What are glitter cells?
Swollen WBCs due to (hypotonic) alkaline urine ON TEST
What is pyuria?
Increase in WBCs
What is the major protein constituent of casts?
Uromodulin/ Tramm-Horsfall mucoprotein ON TEST
Where are urinary casts formed?
The renal tubules ON TEST
Which cast can be seen in a healthy patient or due to strenuous excersize ?
Hyaline ON TEST
Crystals are formed by precipitation of urinary solutes; precipitation is due to changes in what three factors?
Changes in temperature, increase in solute concentration, pH
How much supernatant should be left in the conical tube for examination?
12 mL
What is used to detect fat, fatty casts, and oval fat bodies?
polarized light to detect the formation of a maltese cross
Which urinary cast is most often seen in glomerular injury?
RBC cast ON TEST
What result is the most important on the reagent strip with relation to crystal formation?
pH ON TEST
What crystal indicates an abnormal metabolic condition?
Crystine ON TEST
Which nonpathogenic crystals are found in acidic urine?
Uric acid, sodium urate, calcium oxalate, amorphous urate
Which pathogenic crystals are found in acidic urine?
Cystine, cholesterol, tyrosine, leucine, bilirubin KNOW FOR TEST
Which nonpathogenic crystals are found in alkaline urine?
Amorphous phosphate, calcium phosphate, triple phosphate, ammonium biurate, calcium carbonate
What can uric acid dissolve in?
10% KOH
How can you tell the difference between uric acid shards/needles and sodium urate shards/needles?
Uric acid will dissolve in 10% KOH
Where are most kidney stones found in America from?
Calcium oxalate
What pathogenic association can uric acid crystals have?
Gout or from chemotherapy
What pathogenic association can calcium oxalate crystals have?
Glycol poisoning (antifreeze)
Which crystal can precipitate in acidic, neutral, or alkaline urine, and is associated with a diet rich in oxalic acid from foods like spinach, chocolate, and tea?
Calcium oxalate
What pathogenic association do cystine crystals have?
Cystinuria (metabolism issue)
What should you see microscopically and in a urinalysis if you see cholesterol crystals? What is the pathogenic association?
Fat globules, oval fat bodies, and protenuria. associated with nephrotic syndrome.
What would you see on urinalysis if you see tyrosine crystals?
Positive bilirubin
what pathogenic associations does tyrosine have?
liver disease, inborn error of metabolism
What should you see microscopically and on urinalysis if you see leucine crystals?
tyrosine crystals, and positive bilirubin. ON TEST ( that cystine pairs with tyrosine)
What pathogenic associations do leucine crystals have?
liver disease, inborn error of metabolism, maple syrup urine disease
Which crystal is associated with sulfa drugs, indicates inadequate hydration and can mean tubular damage in a fresh sample?
Sulfonamide
Which crystal is associated with high doses of ampicillin, indicate poor hydration, and impaired kidney function?
ampicillin
which crystals are associated with CT?
radiographic dye crystals
What do fat droplets show on a urinalysis strip that starch artifacts will not?
a positive protein ON TEST
How to tell the difference between radiographic dye and cholesterol crystals?
Cholesterol crystals have notches and polarize
radiographic dye urine has high SG
What can amorphous phosphate crystals indicate in urine?
refrigeration
Calcium phosphate crystals are associated with what?
kidney stones
Triple phosphate crystals can be associated with what?
UTI from a bacteria with urease
How do you tell the difference between amorphous urate crystals and amorphous phosphate crystals?
The urines pH. Amorphous phosphate likes alkaline urine, amorphous urate likes acidic. ON TEST
A patient recieving sulfonamide antibiotics who is dehydrated presents with crystals in their fresh urine, which crystal do you expect?
Sulfonamide
A patient presents with heavy proteunria and lipiduria, rectangular plates with notched corners that are highly birefringent are seen. What crystal do you suspect?
Cholesterol
A refrigerated urine specimen shows abundant crystal formation that obscures sediment, what is the primary reason for this?
Crystals form rapidly in low temperatures
Which factor most significantly aids in differentiating uric acid crystals from cystine crystals?
Uric acid is highly bifringent under polarized light, cystine crystals will not polarize light
The most valuable tool for identifying crystals in urine is what?
pH
What temperature should urine be tested at?
room temp
What happens to the Ph of a urine when left at RT for a prolonged period?
The pH goes up
what do Supravital stains do?
stain living cells
What do lipid stains do?
stains triglycerides but not cholesterols
Transition epithelial cells are clinically significant in what regard?
Can be increased with UTIs, large amounts can indicate carcinoma.
Clinical significance of renal tubular epithelial cells?
Acute tubular necrosis, kidney infection, drug or heavy metal toxicity.
How to tell renal tubular epithelial cells from squamous epithelial cells?
RTC are MUCH smaller with a large nuclei and granular cytoplasm
Clinical significance of oval fat bodies
lipid nephrosis, or terminal kidney disease
What is the clinical significance of clue cells?
Bacterial vaginosis ON TEST
What is the clinical significance of seeing greater than the normal (0-5/HPF) RBCs?
Glomerulonephritis, kidney stones, UTIs, trauma
RBCs appear __ in a hypotonic urine
swollen (can lyse)
RBCs appear __ in a hypertonic urine
crenated (spiky) ON TEST
What is the clinical significance of seeing greater than the normal (0-5/HPF) WBCs?
UTIs or prostatis