Intro Psychology Chapter 2: Biology of the Mind
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
Neurons
structure of communication between body, brain, and outside world; allows us to create memories, how to feel, signaling growth/movement
How many neurons do we have in the brain
100 billion
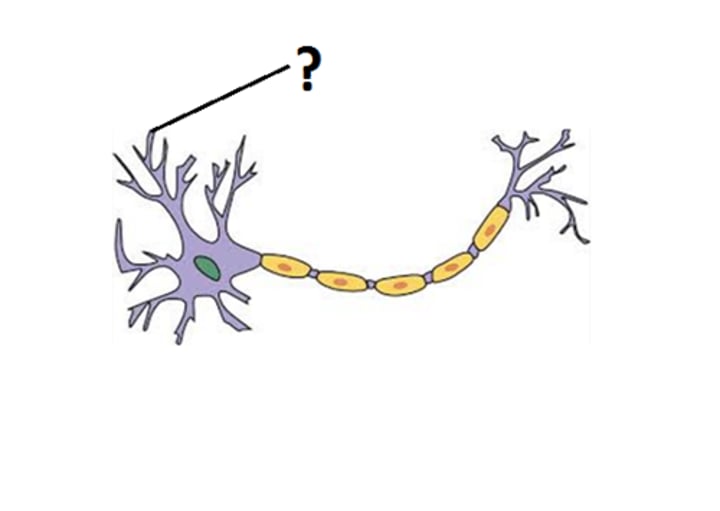
Dendrites
branch like structure on head of neuron that receives incoming signals from other neurons
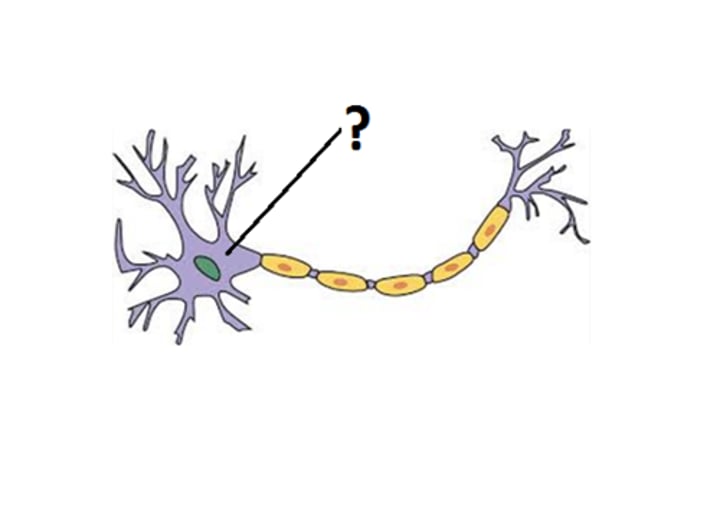
Cell Body
contains the nucleus and DNA
Excitatory/Excitation
When a neurotransmitter makes the postsynaptic cell more positive inside, becoming more likely to fire an A.P.
Inhibitory-Inhibition
When a neurotransmitter makes the postsynaptic cell more negative inside.
Threshold of Excitation
Potential difference at which a neuron will fire an action potential(-55 mv)(inside of neuron becomes more positive, inside of neuron may become positive enough to reach TOE.)
Messages are transmitted through...
the axon and down to the terminal branches and terminal buttons
Axon
tail-like structure growing out of cell body of neuron that carries action potentials that convey info from cell body to synapse
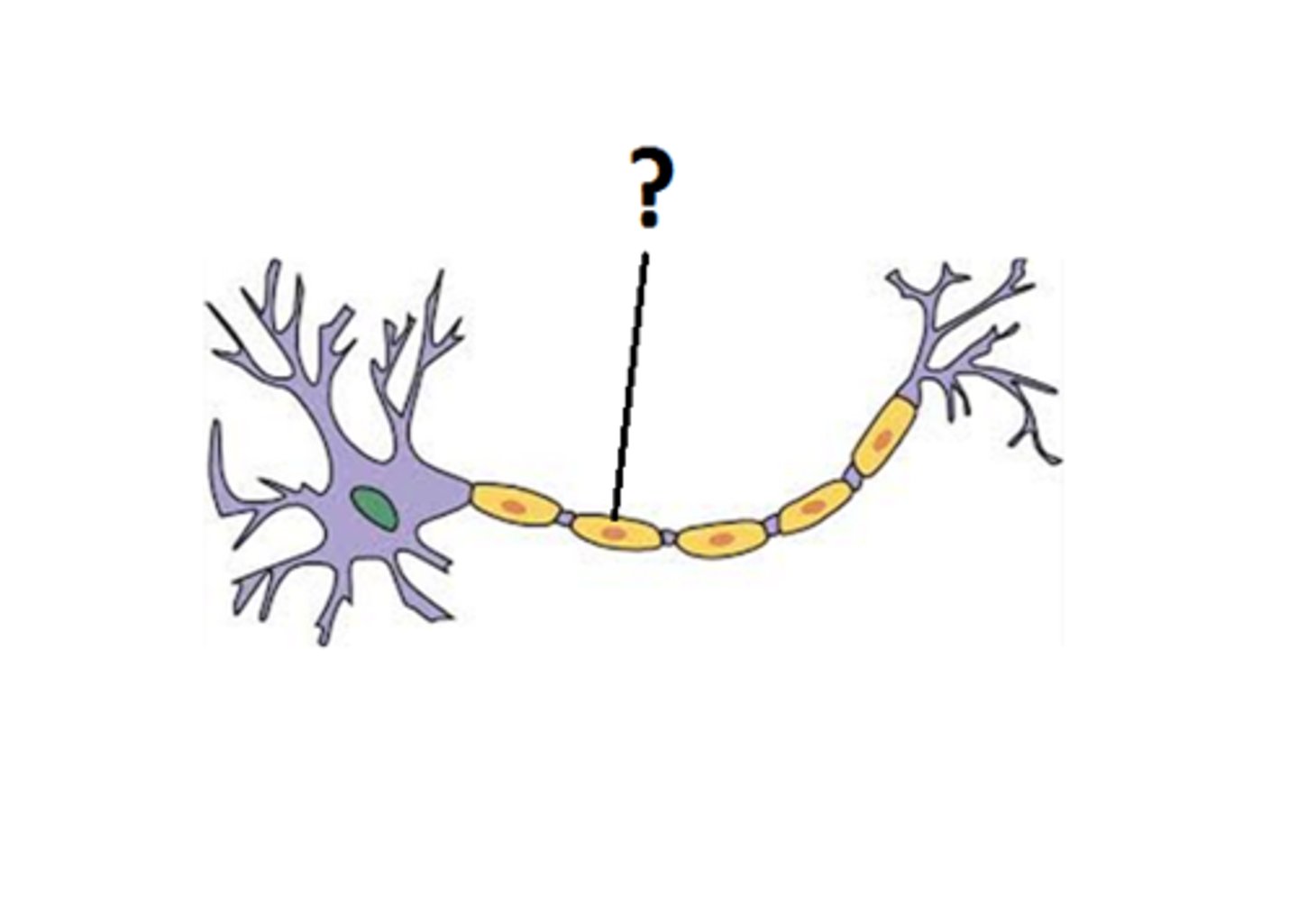
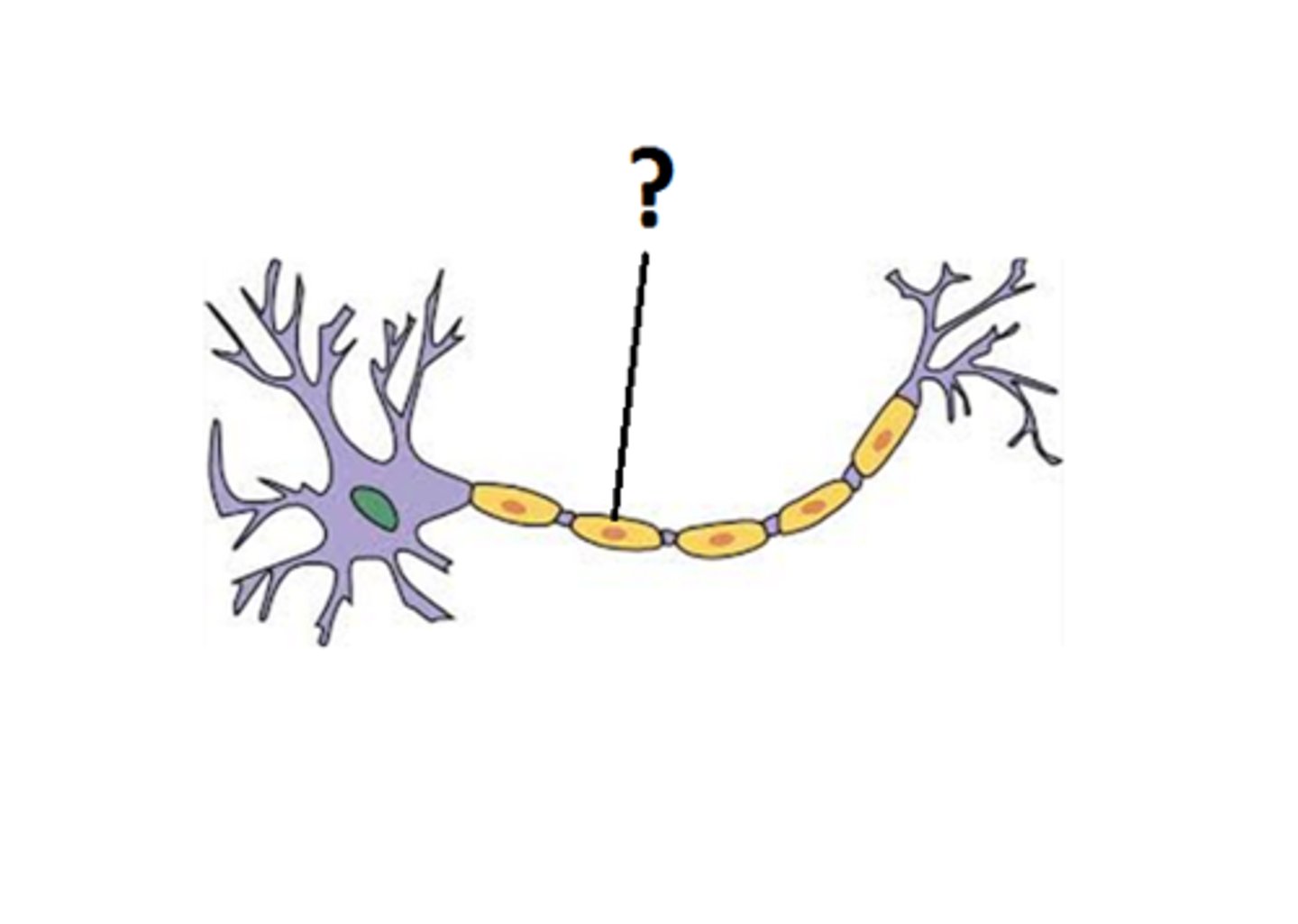
Myelin Sheath
protects messages traveling from one side to the other
Messages
neural impulse/action potential
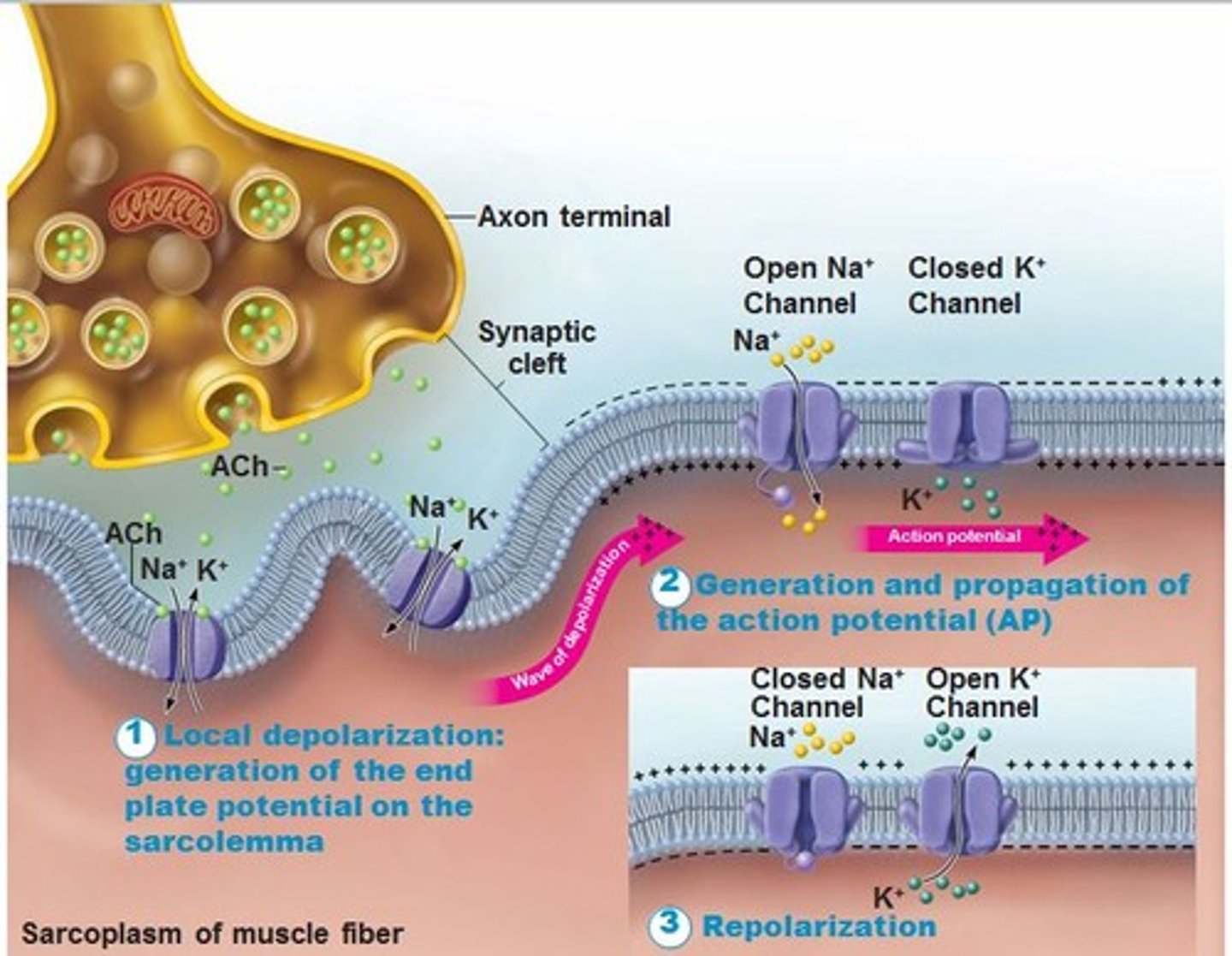
Action Potential
neural impulse; brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane; never leaves the neuron;When it reaches -55 MV
All-or-None Fashion
a strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed
Intensity
of an cation potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon
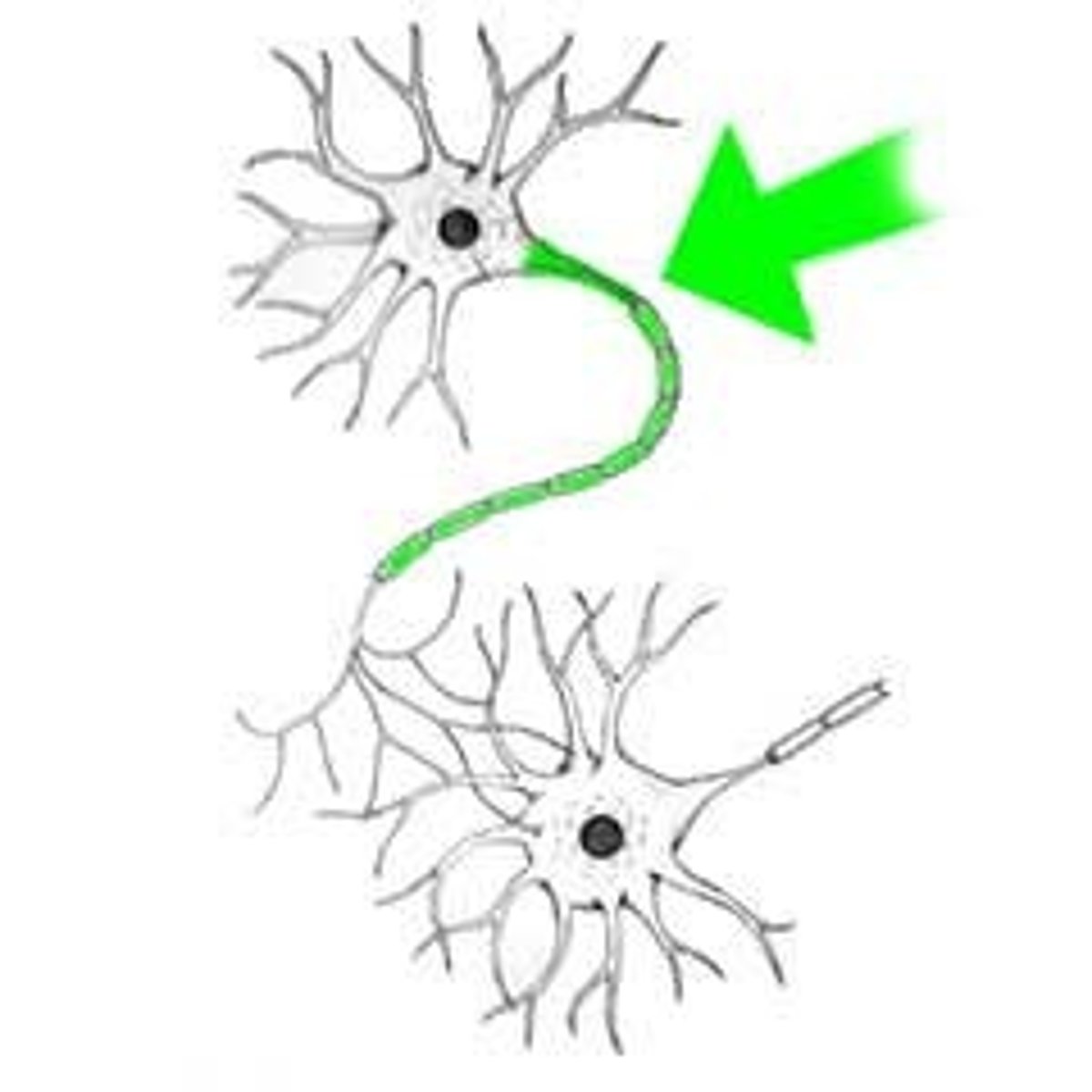
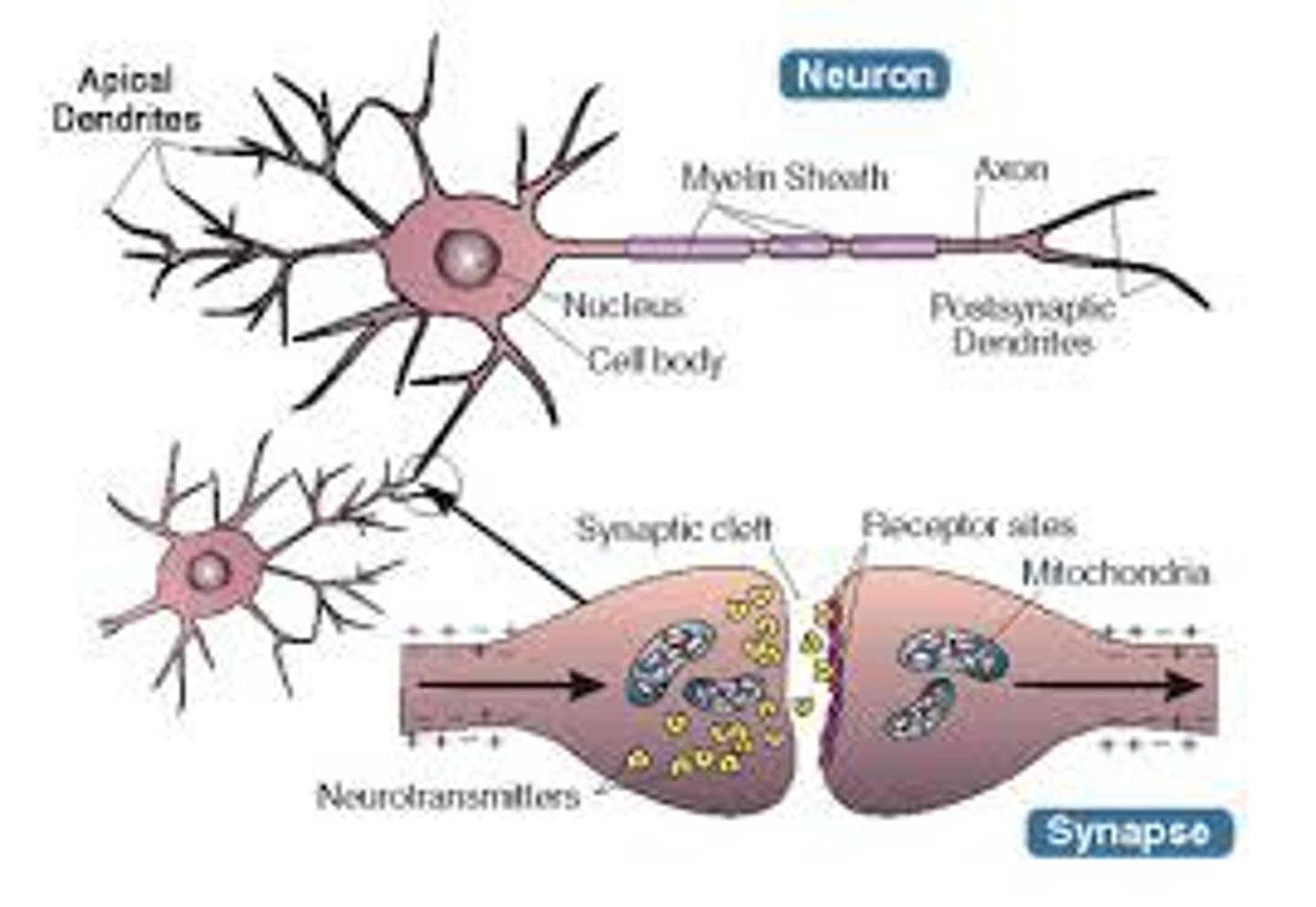
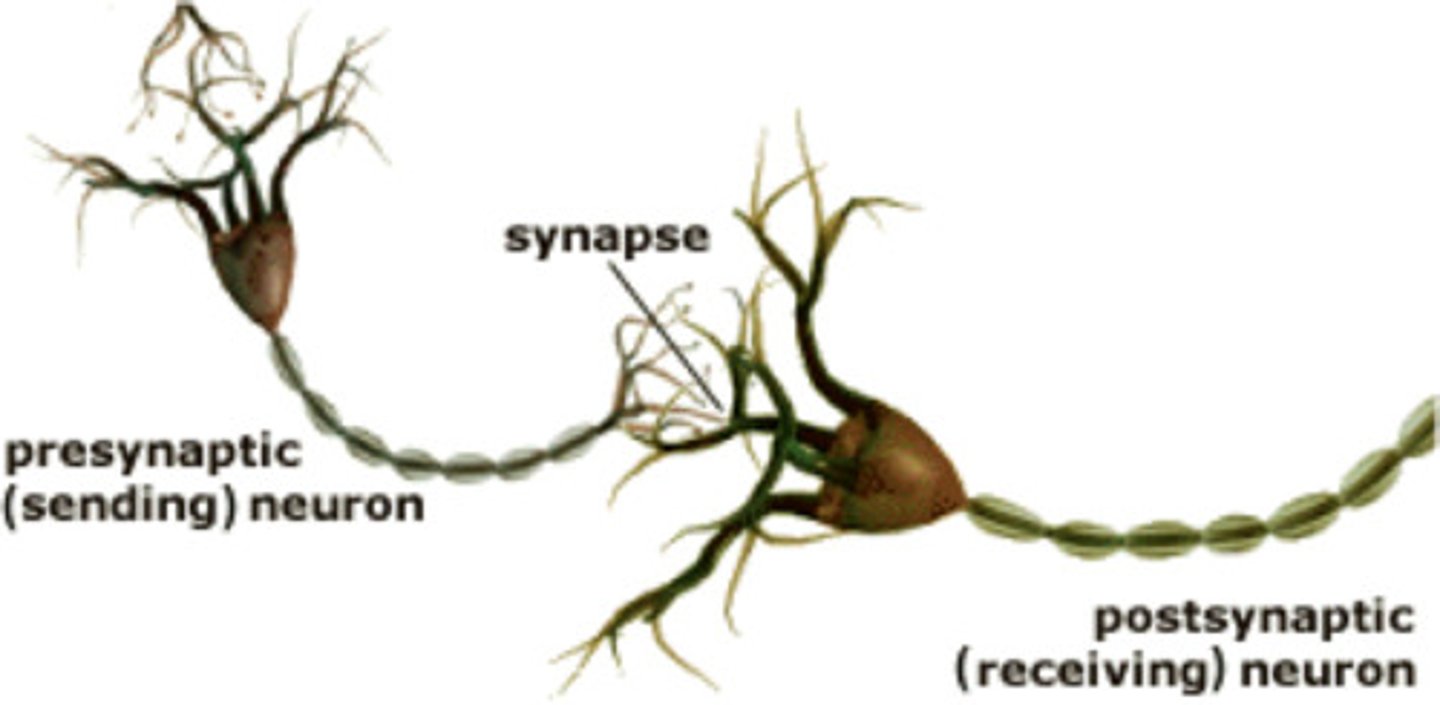
Synapse
tiny gap; neurons communicate via a tiny gap separating the two structure; neurons do not touch each other
Suki's Dentist game her a drug that froze the sodium ion channels along her neural axons. What is likely the effect of this drug?
a. Her neuron's will fire more action potential
b. Her neurons will fire stronger action potentials
c. Neurons will fire weaker action potentials
d. neurons will fail to fire action potentials
D
Sabrina has contracted a disease that is destroying her myelin sheath. What effect would you expect this disease to have on the functioning of Sabrina's nervous system?
a. It will speed up neural signals traveling through her NS
b. It will slow down the neural signals traveling through her NS
c. It won't affect the functioning of her NS
d. Her NS will speed up and slow down in random fashion
B
A drug that causes potassium ions to leave one's neurons is likely to produce what type of effect on the neuron?
a. increasing firing
b. Excitation
c. Inhibition
d. Bothe excitation and inhibition
C
Neurotransmitters are released from...
the sending neuron travels across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron
Norepinephrine(NOR)
- Plays role in regulating sleep, arousal, mood.
excitatory, happy, alert, motivated, appetite control, energy, sexual arousal
-might play role in development of synapse
Acetylocholine(ACh)
-Related to muscle movement and consciousness, learning, and memory. Help store/process memories
-first neurotransmitter discovered
-Alzheimers
-alertness, memory, appetite control, release of growth hormone, sexual performance
Phenylethylime
feeling of bliss, involved in feelings of infatuation
Reuptake
neurotransmitters bind to the receiving sites on the dendrites of the next neuron, then are released and taken back up by the sending neuron
Key-Lock Mechanism
neurotransmitter molecule has a molecular structure that precisely fits the receptor site on the receiving neuron, much as a key fits a lock
All-or-Nothing Fashion
all action potentials are equal in strength; once a neuron begins to fire an action potential, it fires all the way down the axon.
Refractory Period
Brief period of time after neuron has fired an action potential during which the neuron is inhibited and unlikely to fire another A.P.
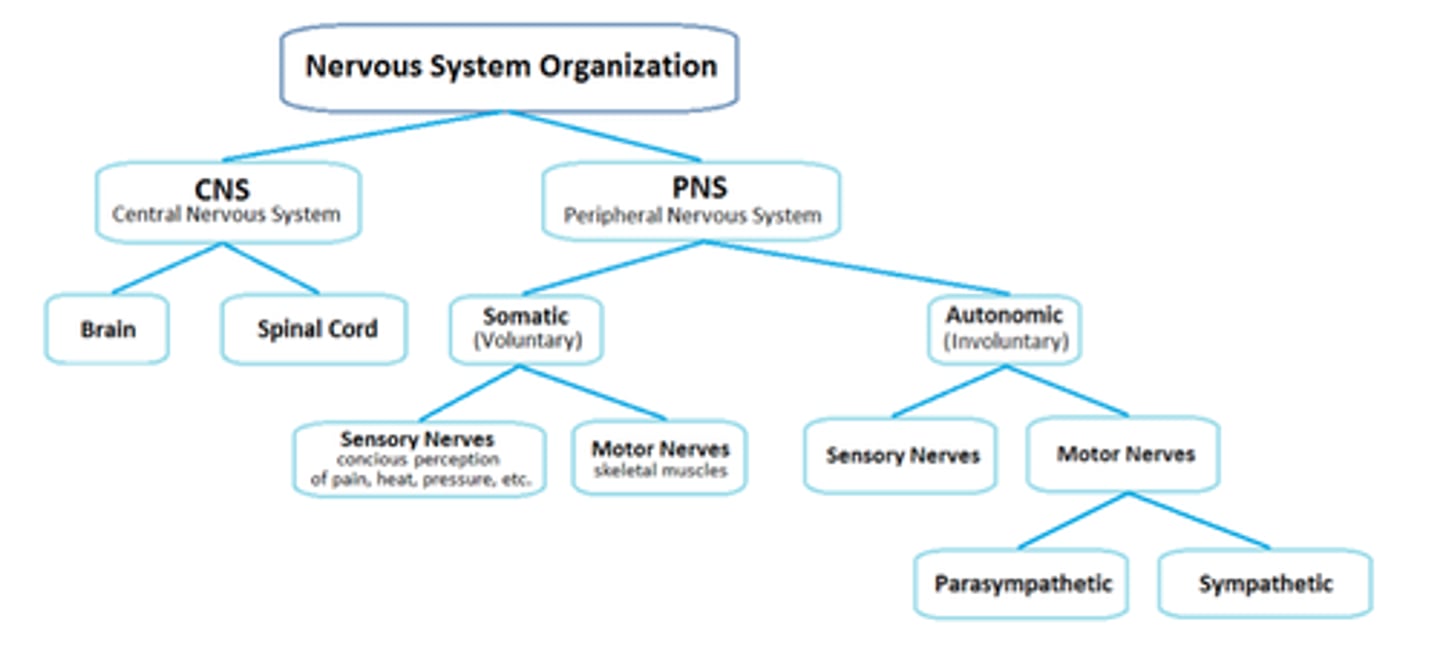
2 Major Division of the Nervous System
CNS, PNS
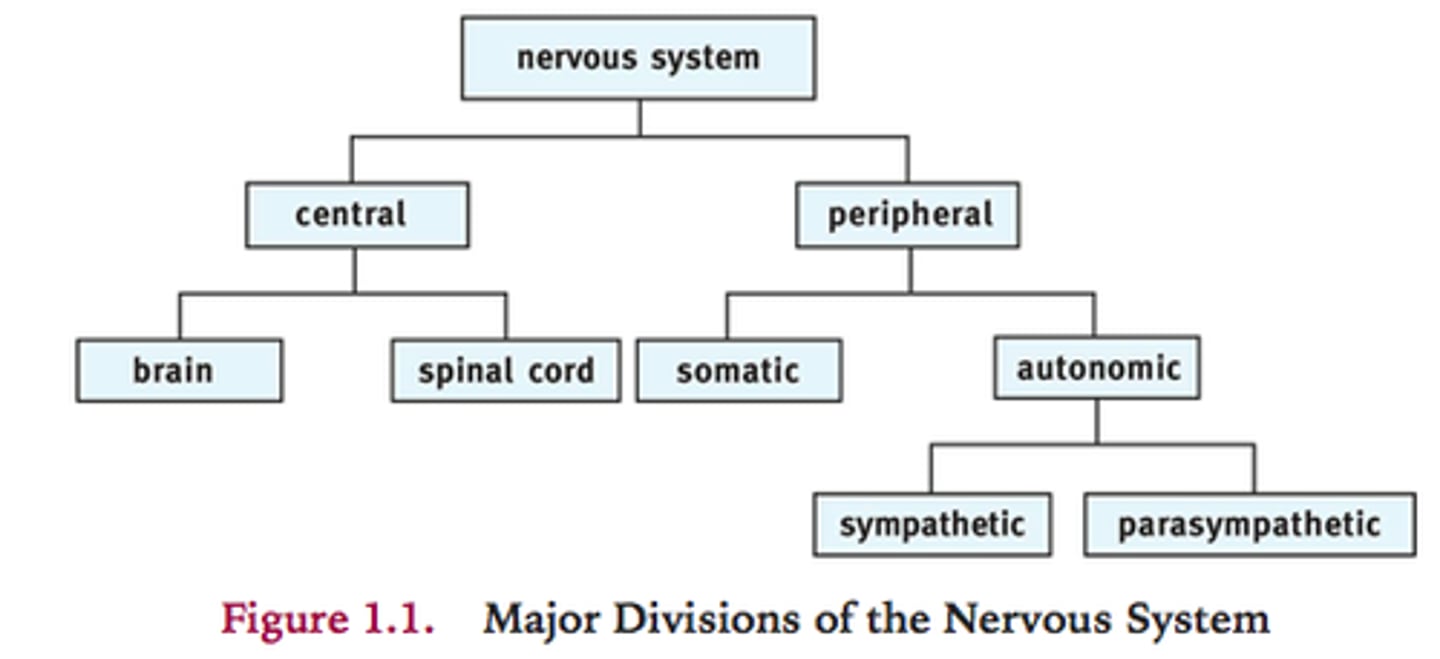
CNS
central nervous system; brain and spinal cord
PNS
peripheral nervous system; all nerves emanating from the spinal cord and the brain
Autonomic Nervous System(involuntary)
controls self-regulated action of internal organs and glands; cannot control; feeds off emotions/reactions accordingly; involuntary
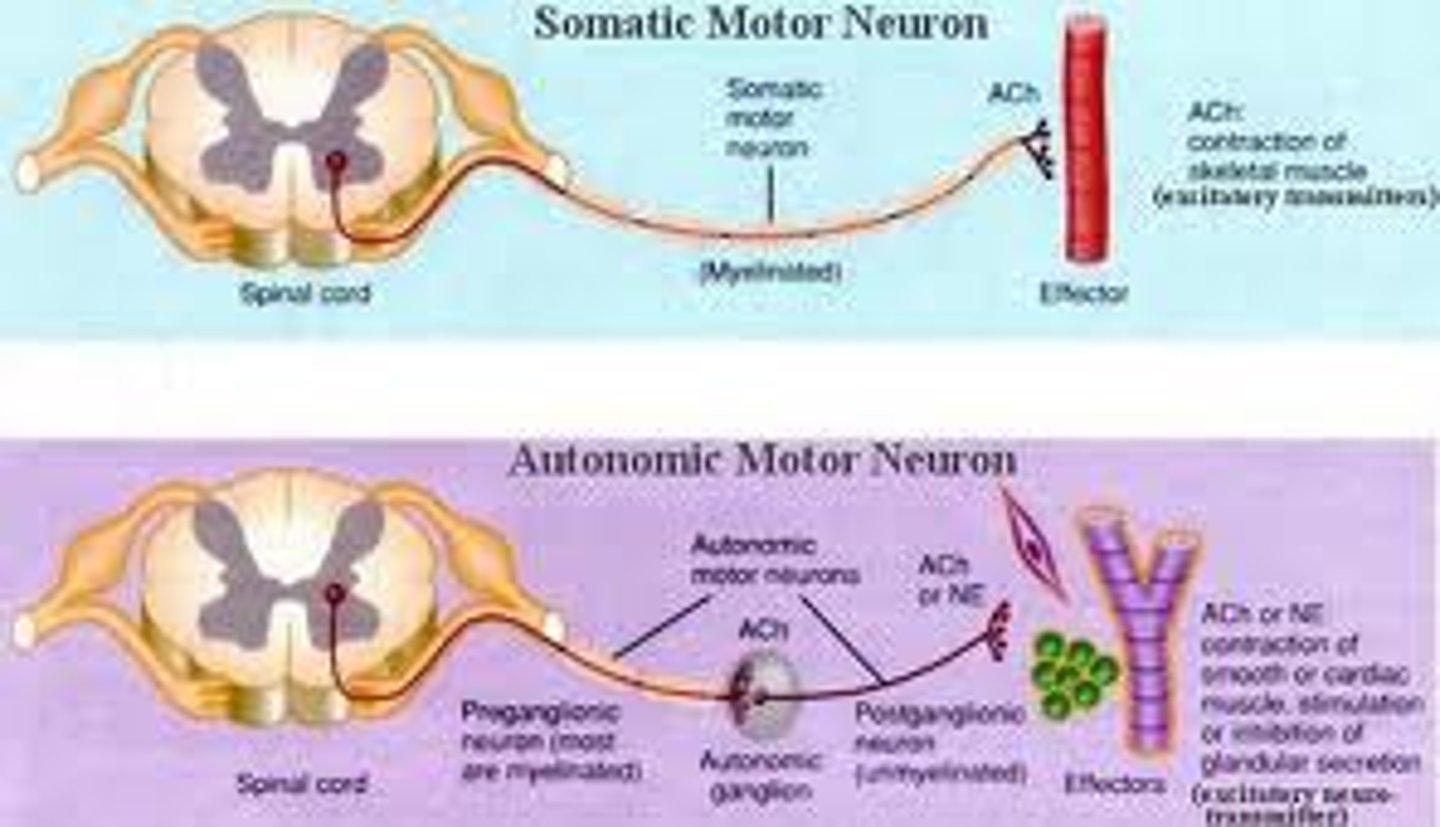
Sympathetic Nervous System
Branch of Autonomic System
-fight or flight response; arousing
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Branch of Autonomic system;
-calming; rest and digest
-Responsible for interval organ function
Juanita was hiking in the woods when she stumbled upon a rattlesnake. Immediately she saw the snake, which division of the NS was most likely in control of internal organ functions?
a. Parasympathetic
b. Sympathetic
c. Endocrine
D. Spinal
B
Moving your arm is an example of behavior that is governed by which branch of the NS?
a. Somatic Nervous System
b. Autonomic Nervous System
c. Sympathetic NS
d. Parasympathetic NS
A
The sensory neurons in your fingertips are part of the ___________ NS.
a. Central
b. Peripheral
c. autonomic
d. Sympathetic
B
Somatic Nervous System
Branch of PNS; controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles; voluntary
1800 Franz Gull
suggested that bumps on the skill represented mental abilities
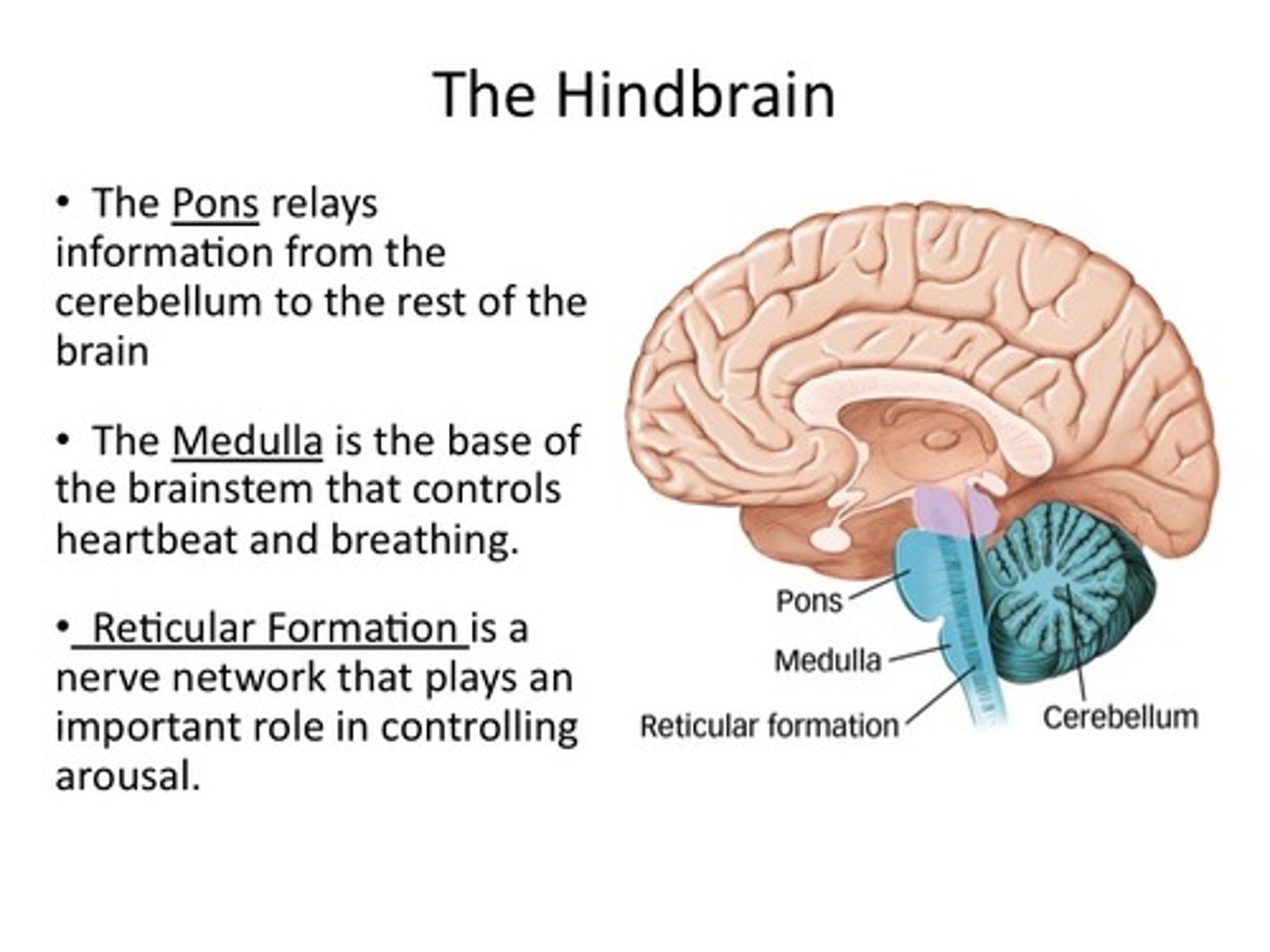
Brainstem
oldest part of the brain; beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull; responsible for automatic survival functions
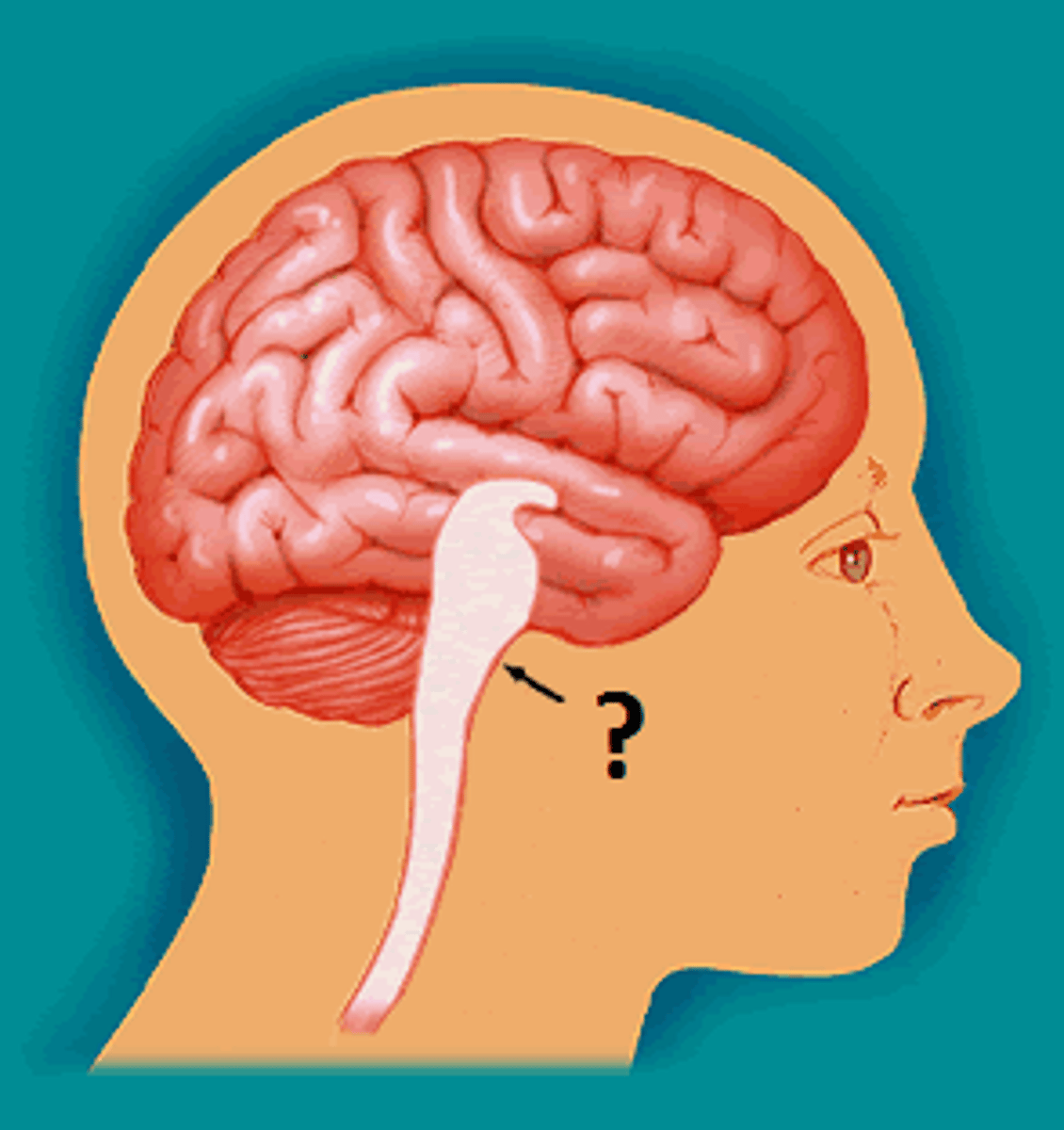
Medulla
base of the brainstem that controls heartbeat and breathing, blood pressure, sneezing, coughing, swallowing, digestion
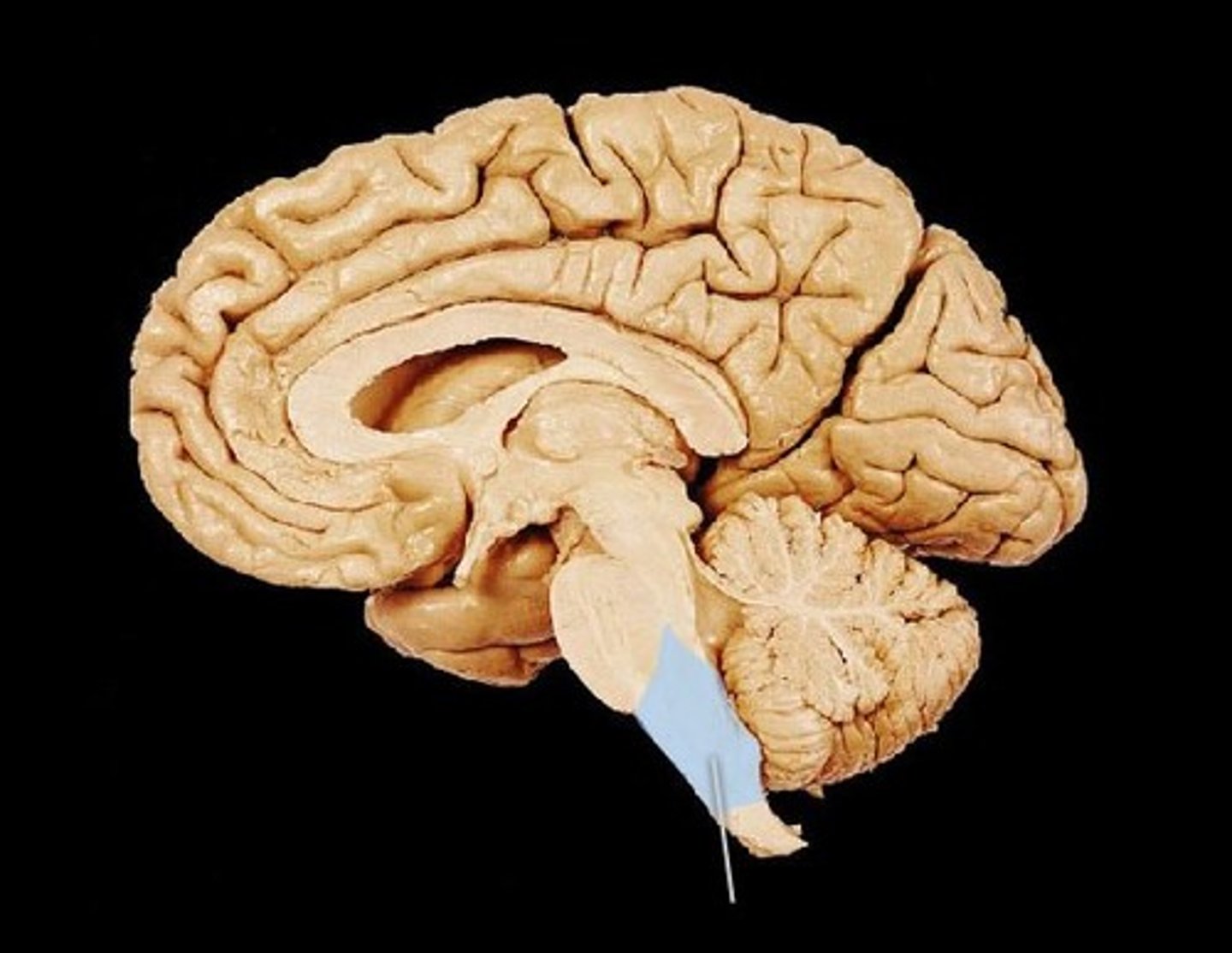
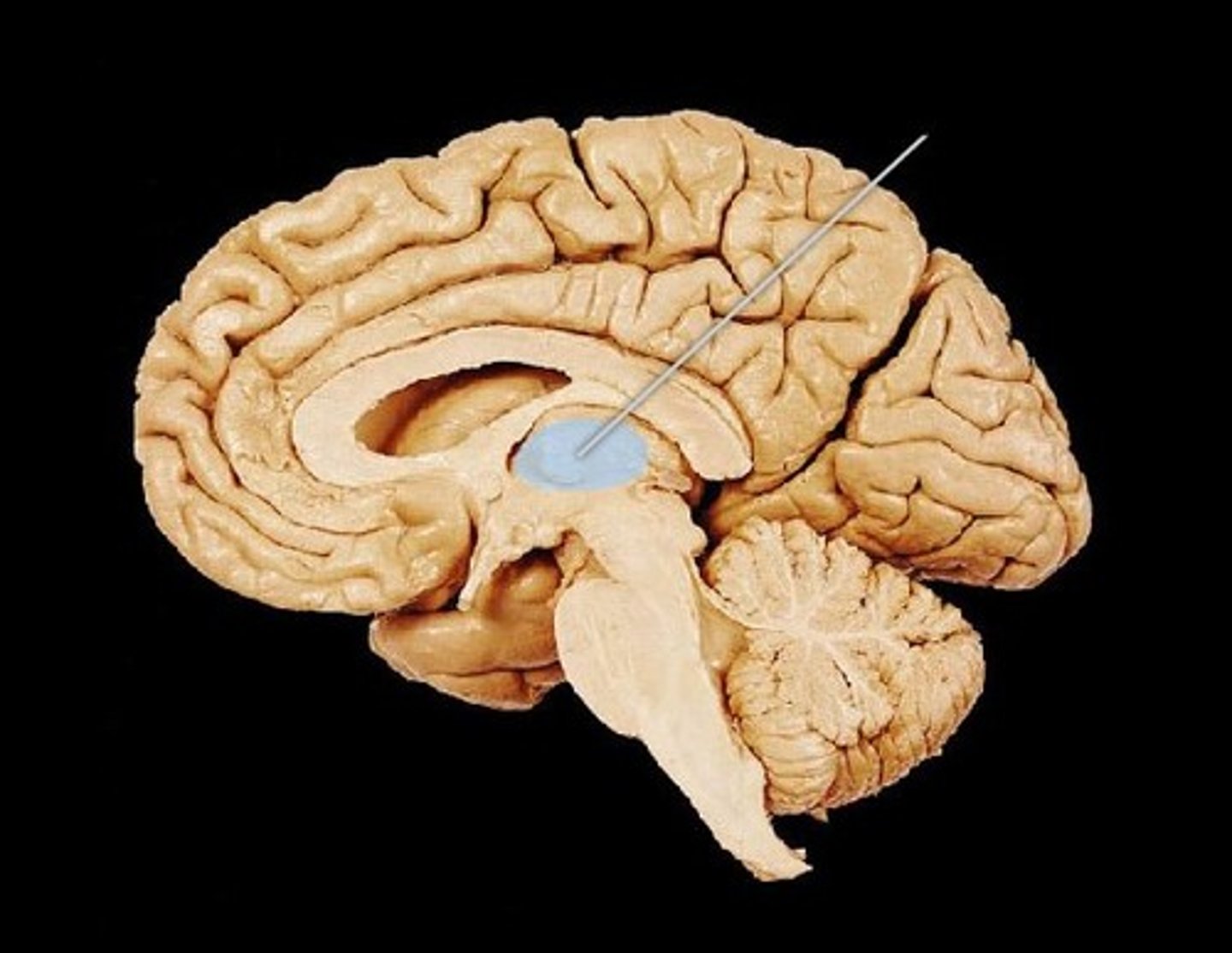
Thalamus
brain's sensory switchboard, located on the top of the brainstem; directs messages to the sensory areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
*~part of forebrain that functions as a sensory relay system
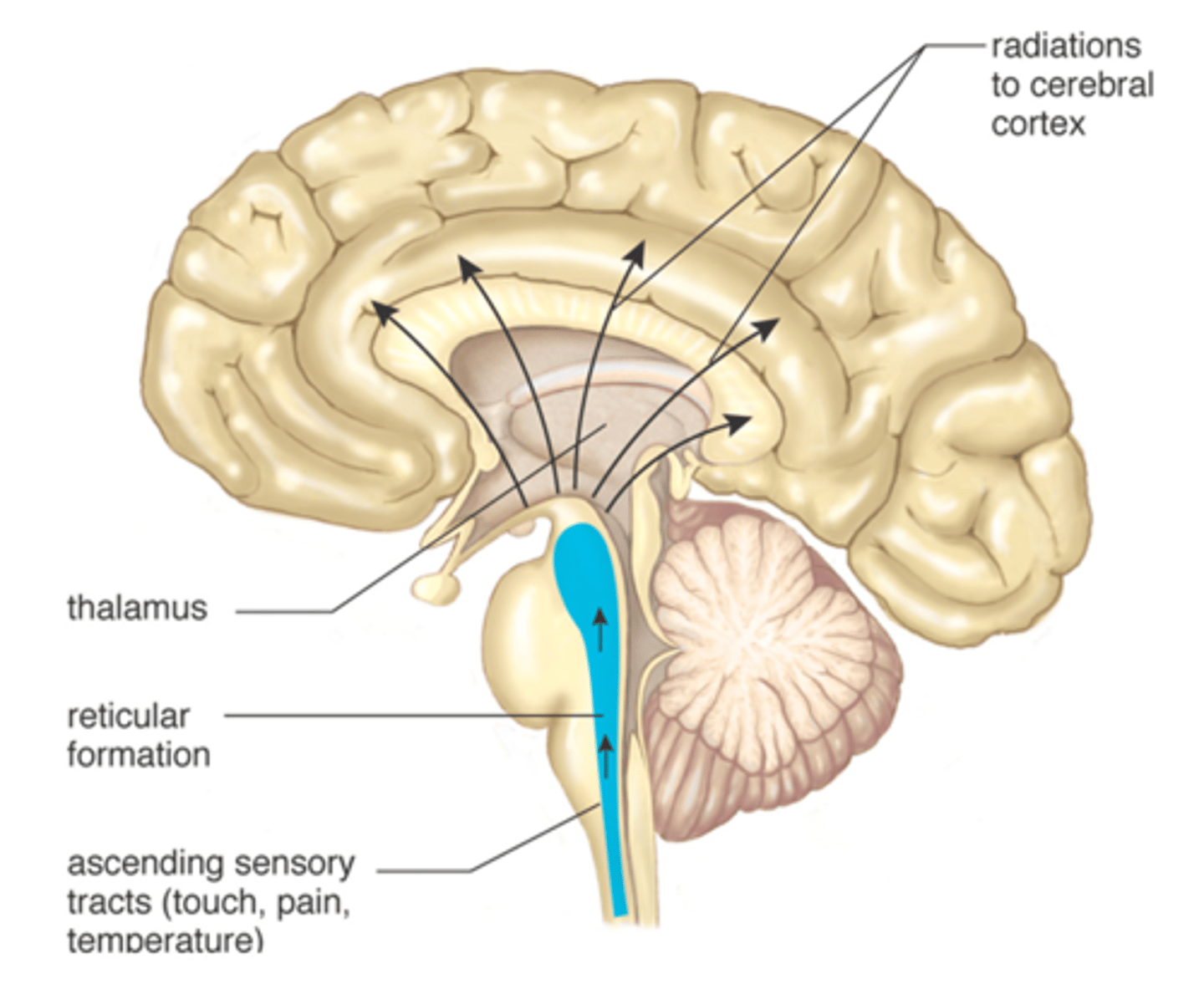
Reticular Formation
Part of midbrain nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal, attention, sleep, and consciousness
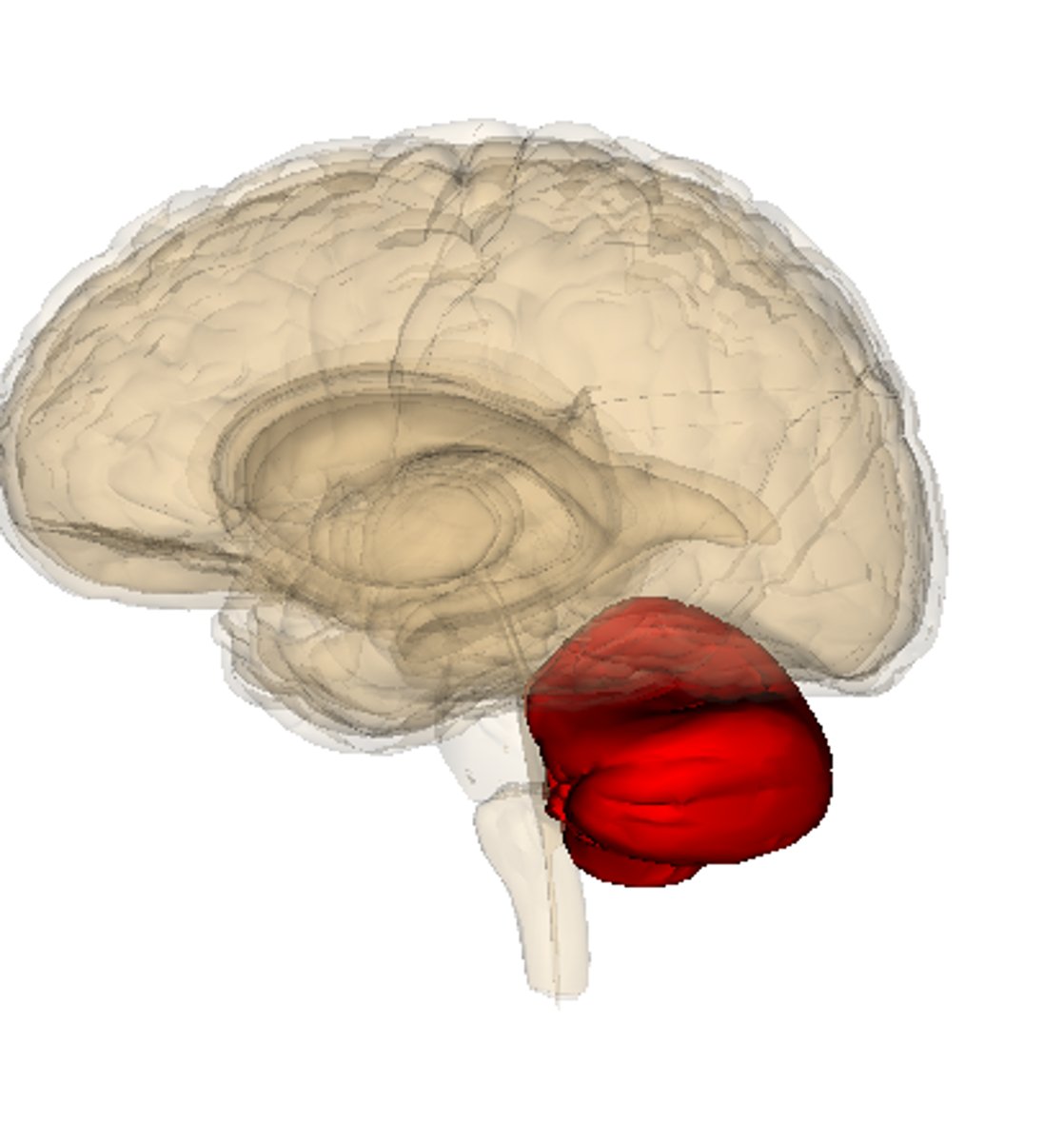
Cerebellum
the "little brain" attached to the read of the brainstem; helps coordinate voluntary movements and balance; allows us to stand up straight/run/process some types of memory/emotions
How many lobes does each hemisphere have
4 lobes
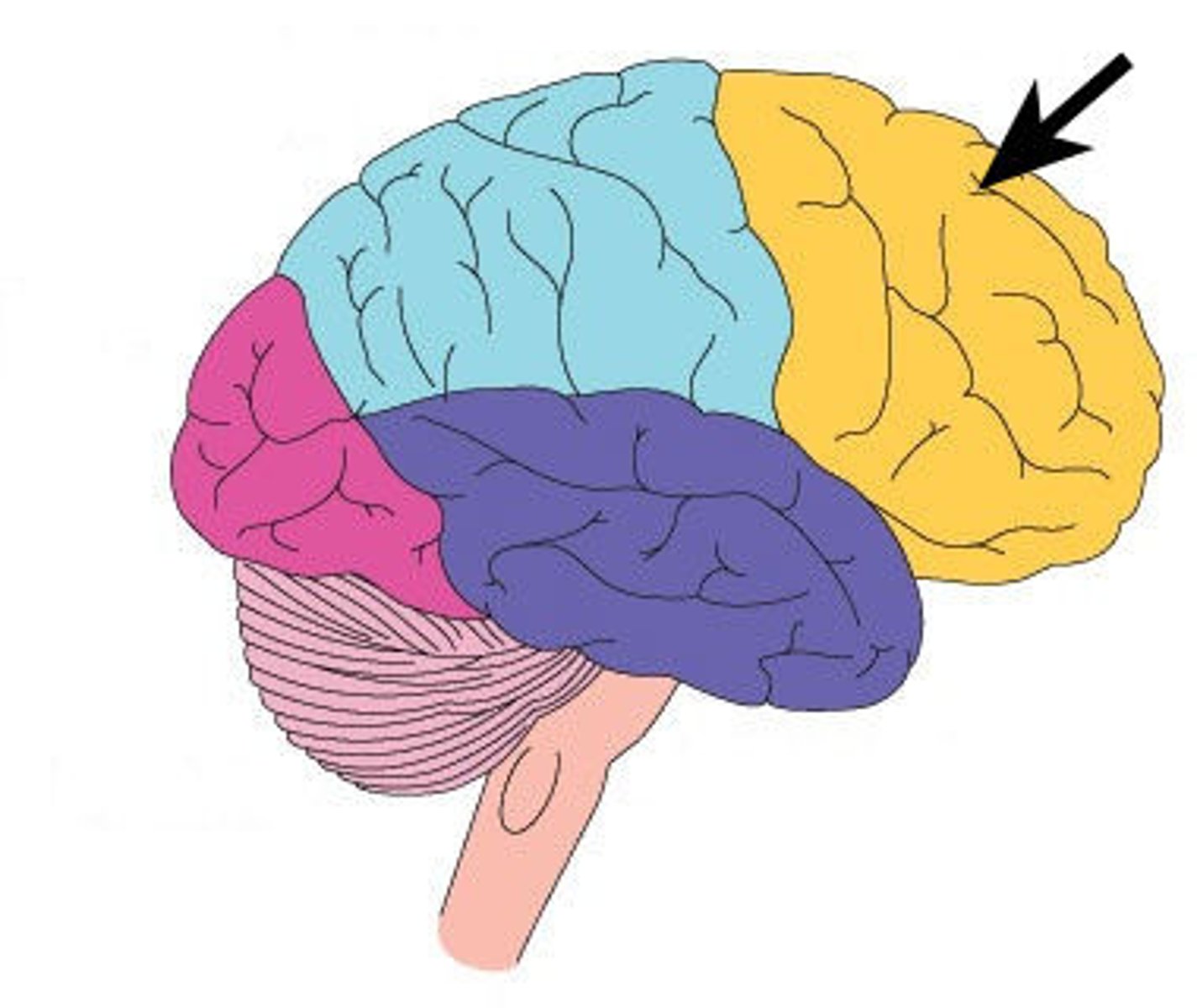
Frontal Lobe
forehead; judgement, personality, thinking, planning, decision making, language, motor movements
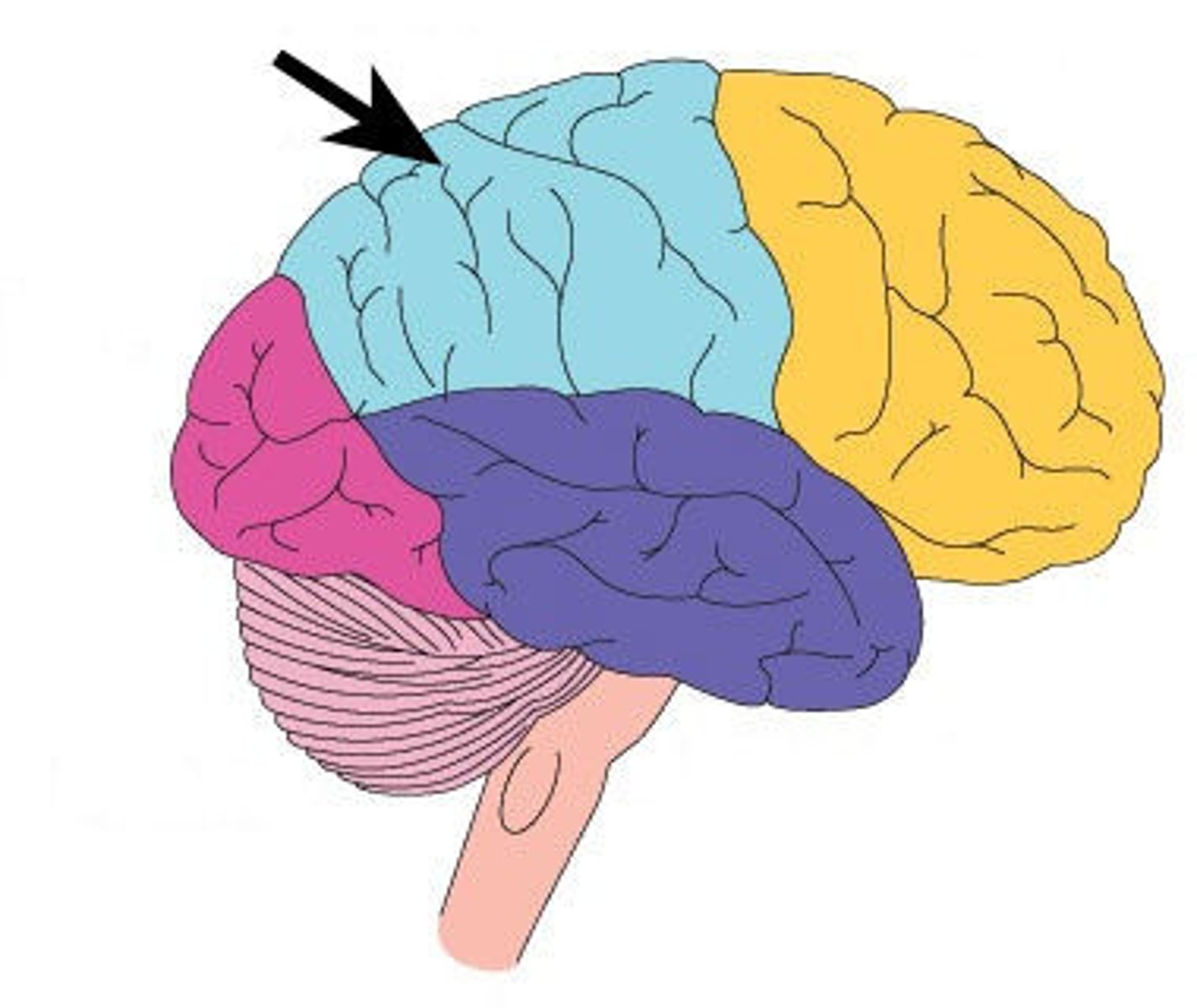
Parietal Lobe
top of rear head; regulates sensory information and cognitive processes
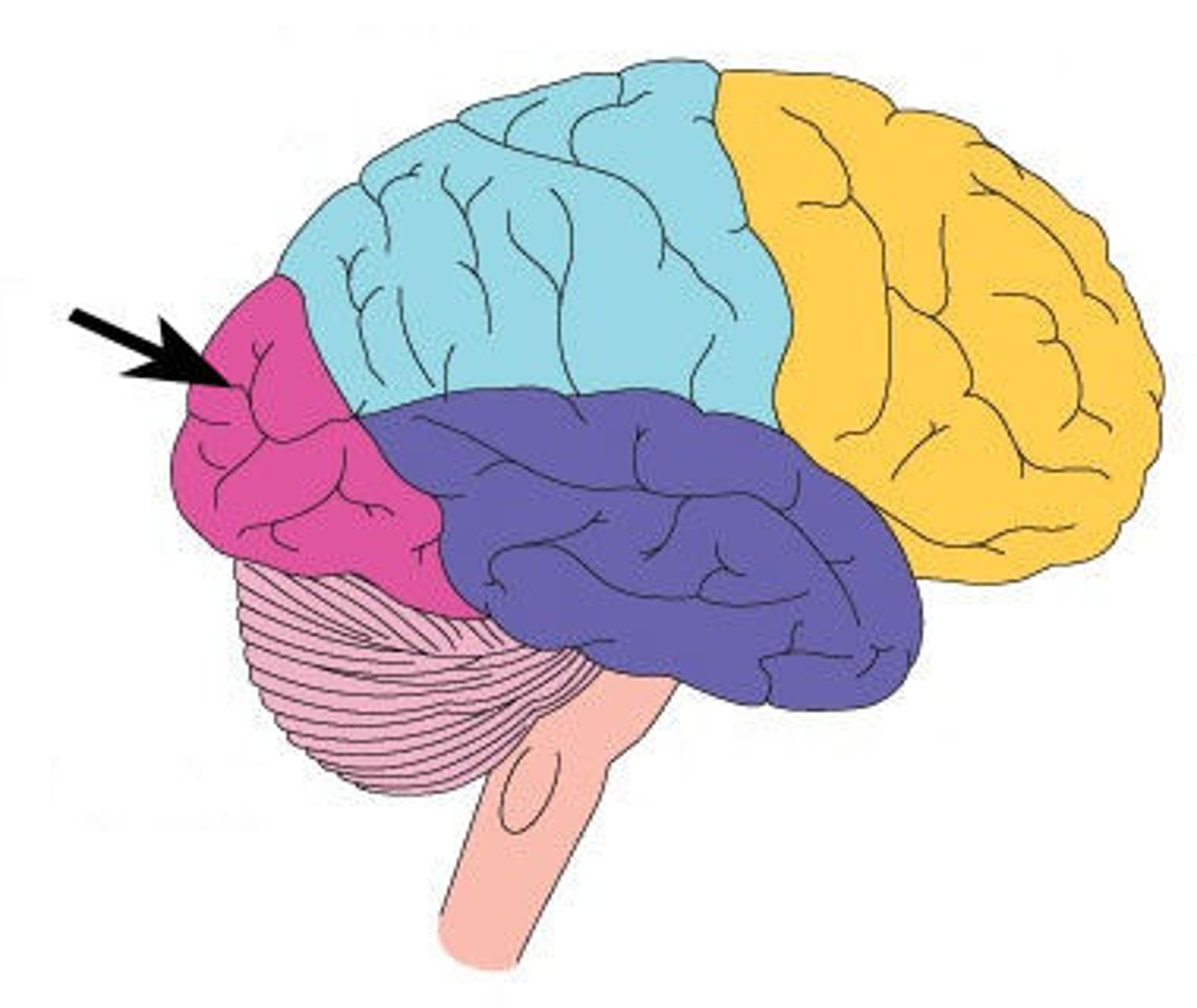
Occipital Lobe
back of head; vision, allows you to process sight/color your eyes pick up
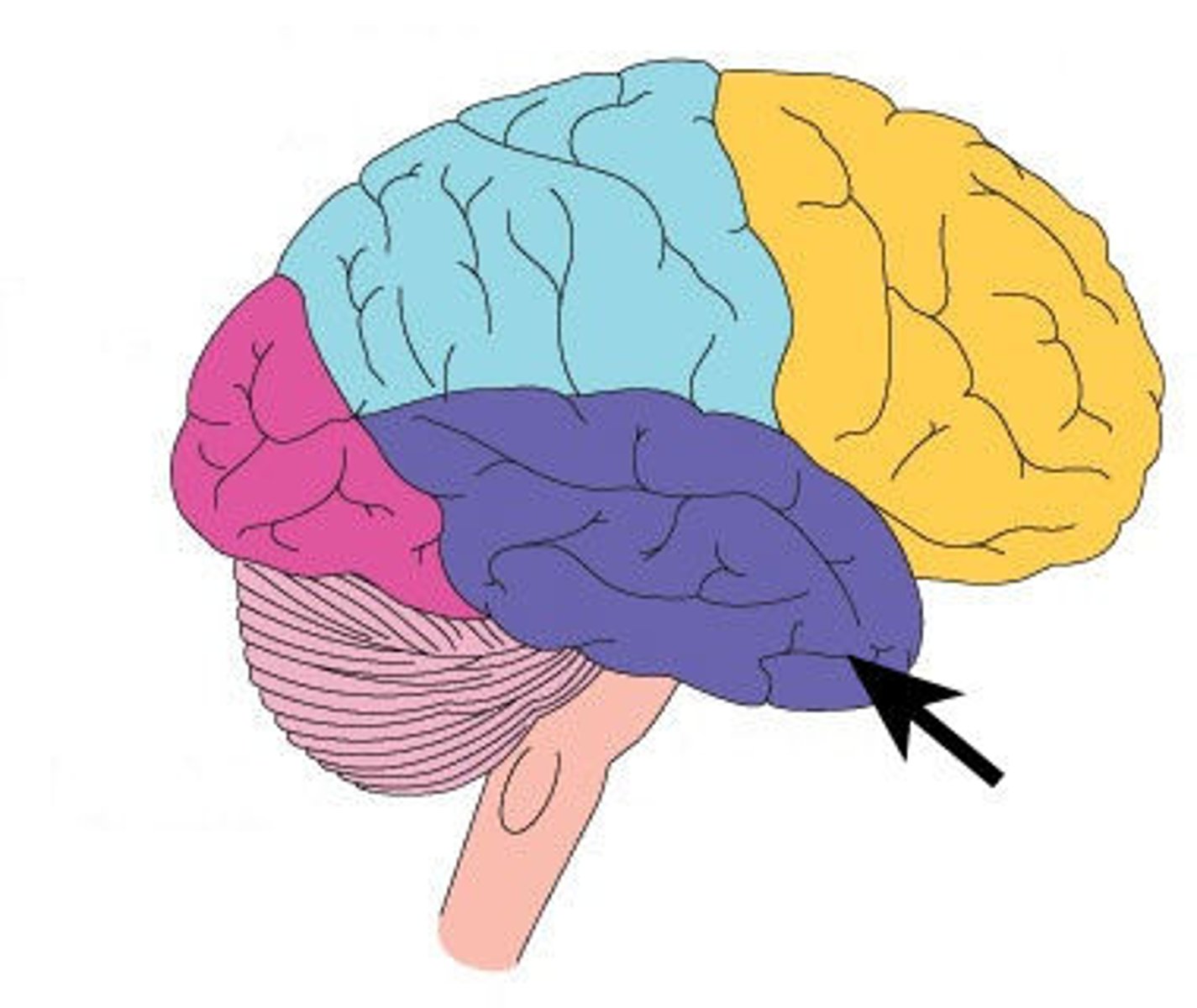
Temporal Lobe
side of head; contains auditory cortex, allows you to process sound/ language
Functions of the Cortex
motor cortex, sensory cortex
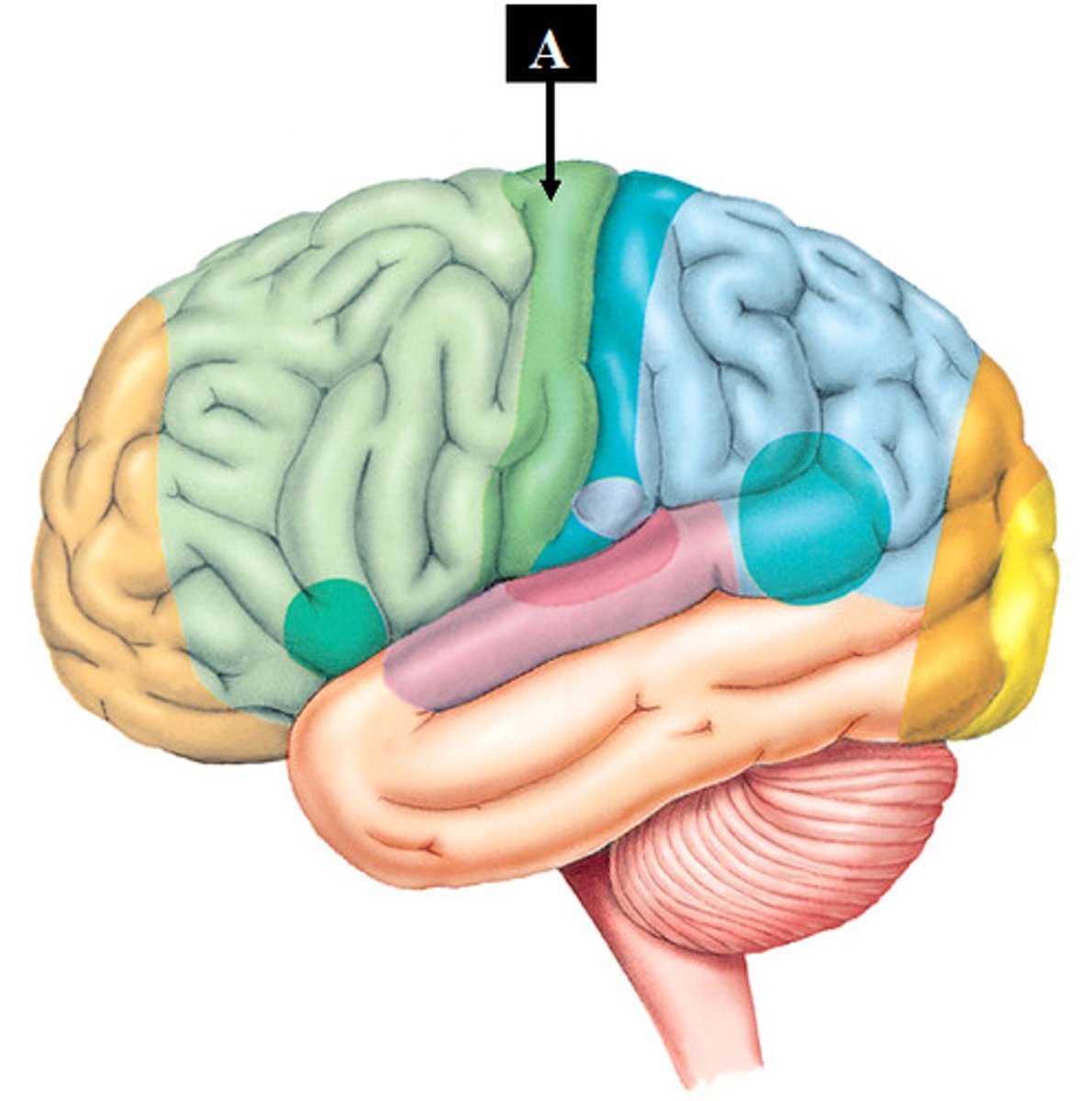
Motor Cortex
located in the back of the frontal lobe; control voluntary movements; Execution of movement. output
Sensory Cortex
located in the front of the parietal cortex; receives information from skin surface and sense organs; input
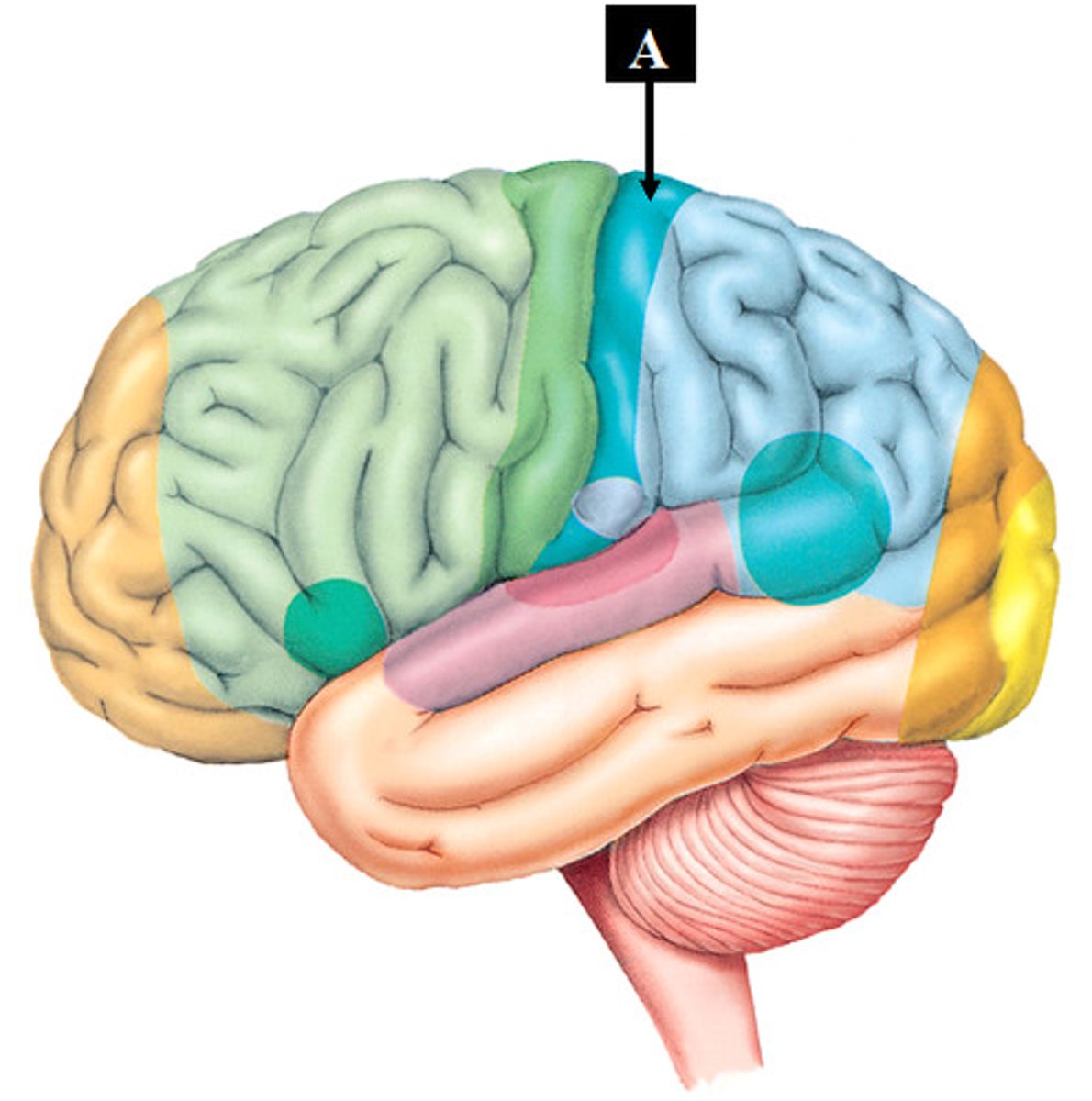
Left Hemisphere section controls...
the body's right side
Right Hemisphere section controls...
the body's left side
Auditory Cortex
located in the temporal lobes; responsible for processing auditory information
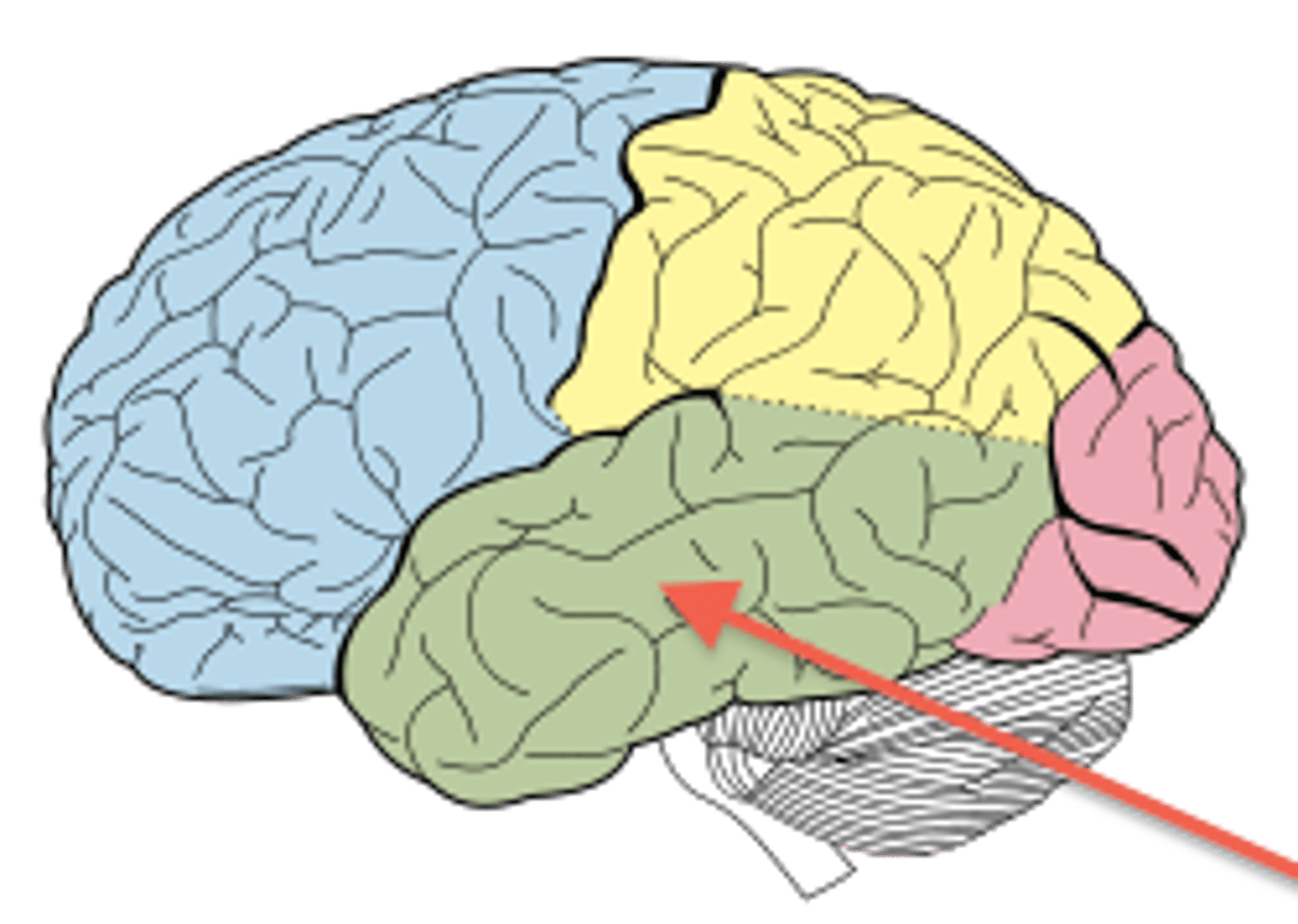
Association Areas
uncommitted planes of neural wiring that can take on multiple responsibilities
Plasticity
refers to the brain's ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness; the brain will overcome whatever/everything
Myelin
waxy substance that insulates portions of some neurons in nervous system
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that carry neural signals across synapse
presynaptic Neuron
The neuron that is sending the signal at a synapse in NS
Ions
charged particles that play an important role in firing of action potentials
Resting Potential
Difference in charges found inside and outside of neuron. (mammals are about -70MV-meaning inside is 70 MV more negative than outside)
Dopamine
Plays role in movement, motivation, learning, and attention.
-motivation by making sex and eating very pleasurable
-Parkinson's disease
Serotonin
Plays role in different behaviors, sleep arousal, mood, eating, and pain perception.
Gamma Amino Butyric Acid
Body's chief INIHIBITORY neurotrans., that plays role in regulating arousal(general level of alertness and energy)
-produce seizures with lose of
Glutamate
Chief EXCITATORY neurotrans. Found at more than 50% of synapses in brain.
Endorphins
Act as a natural painkillers
-may play role in making eating pleasurable.
-working out or stress releases this to protect us from pain
Lamont Developed a disease that reduces the amount of serotonin in his brain. What symptoms would you expect Lamont to have?
a. Hallucinations
b. Trouble with motor skills
c. Symptoms of depression
d. Seizures
C
Jackson is a normal, healthy adult main. Jackson's brain likely contains more__________ than any other neurotransmitter.
a. Glutamate
b. GABA
c. Dopamine
d. Acetylcholine
A
Sasha has been drinking herbal tea that she believes boosts her body's ability to manufacture acetylcholine. Why do you suppose Sasha is so interested in drinking this tea?
a. She is trying to improve memory
b. She is trying to treat her depression
c. She is hoping it will help her have more energy
d. She is hoping it will help her sleep better
A
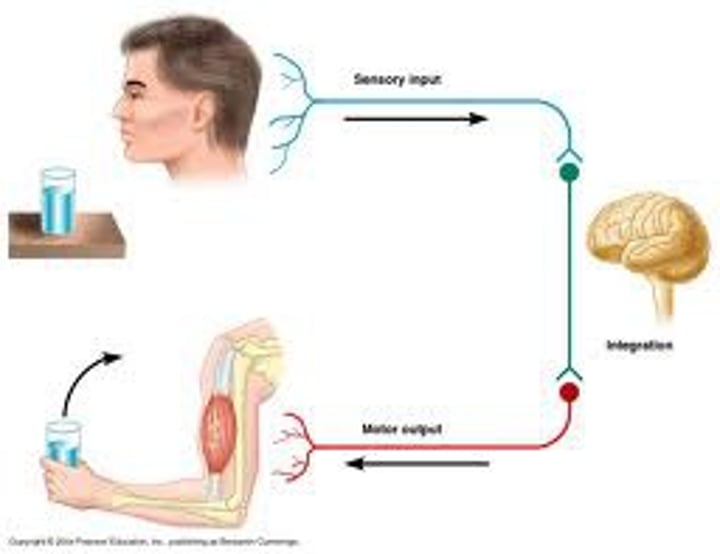
Sensory Neurons
Transmit info from sense organs to CNS
-sights and sounds and aches and pains to CNS
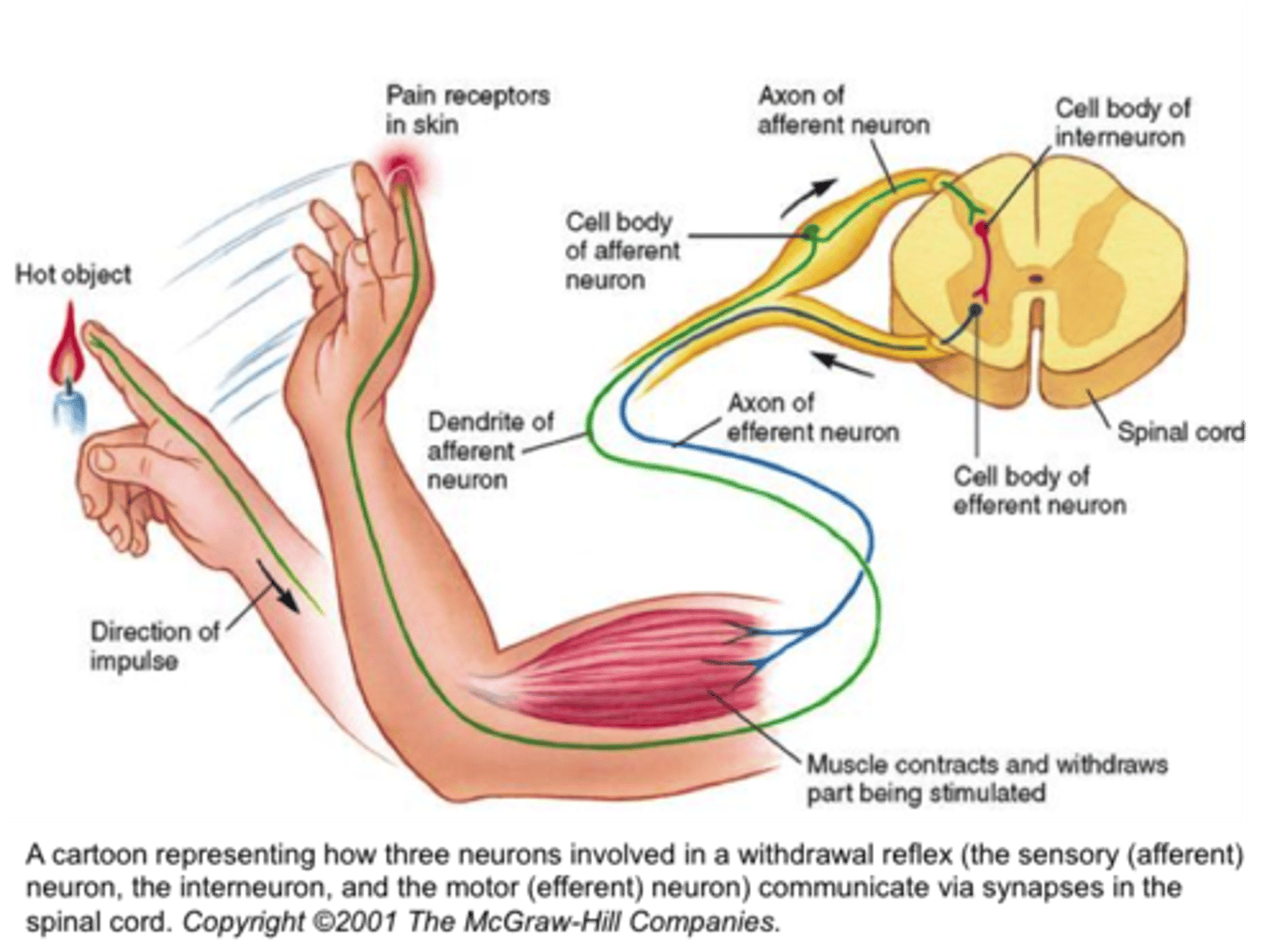
Nervous system Picture
Motor Neurons
Transmit commands from brain to the muscles of body
Hindbrain
Primitive part of brain that comprises the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
-most basic life-sustaining function
Forebrain
*~Regulates complex mental processes like thinking and emotional control
Structures include limbic system, thalamus, hypothalamus, and cortex.
-Govern higher-order mental processes
-structures regulate emotional, motivation, and cognitive processes
-W/o it, no ability to problem solve, remembering, language, etc.
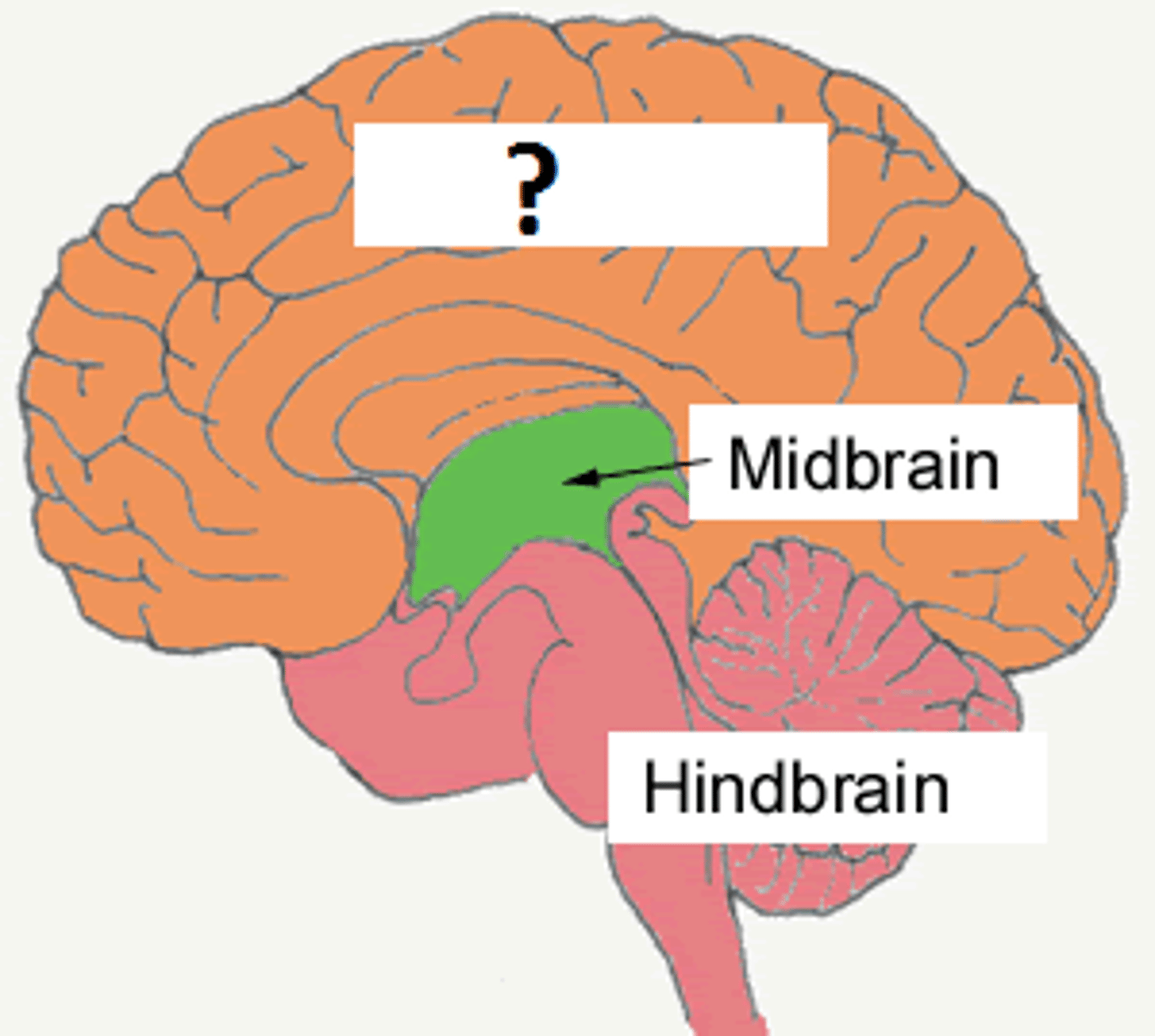
Midbrain
Structures that connect hindbrain to forebrain
-w/o it, hindbrain could not supply forebrain with neural impulses
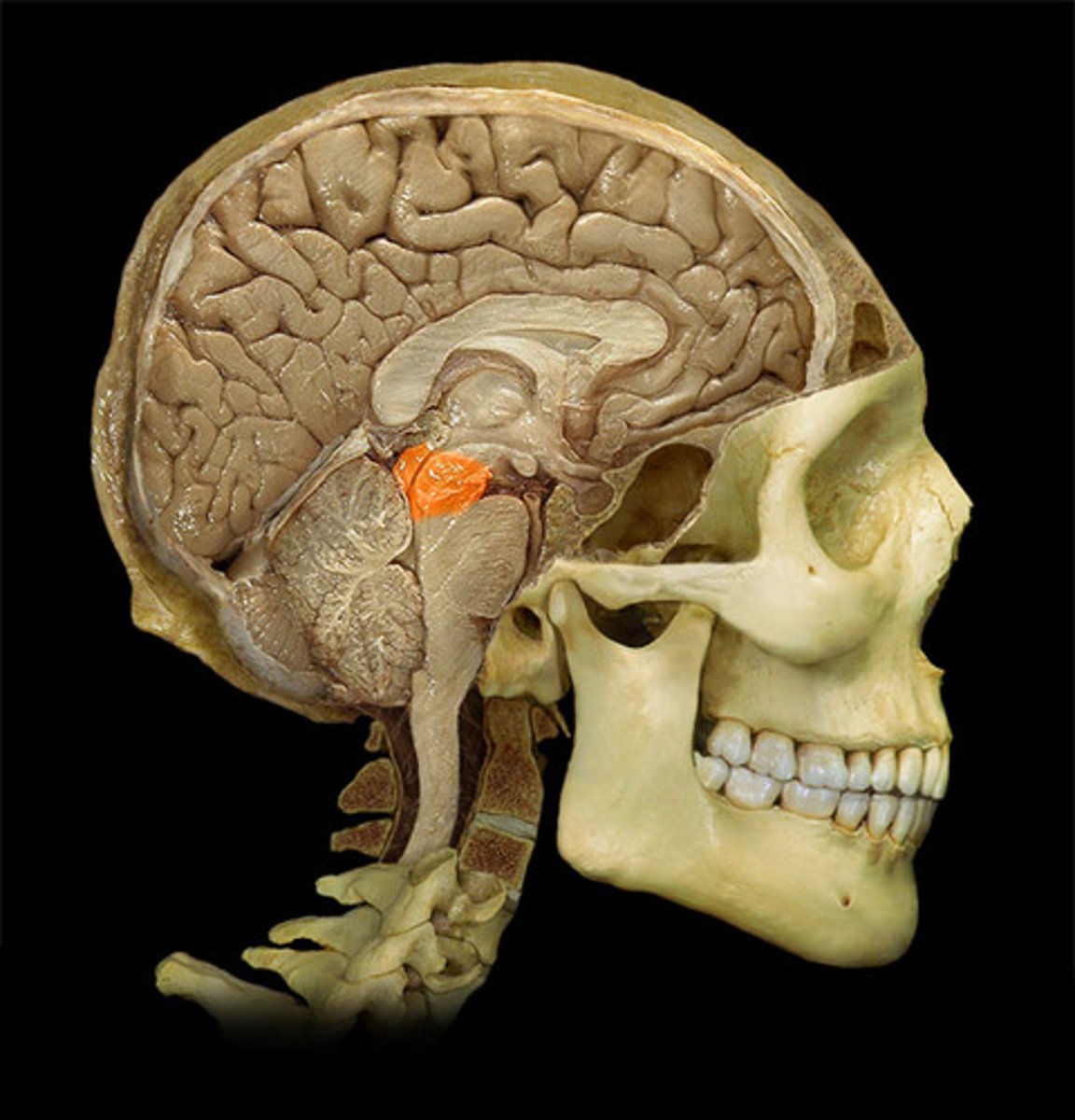
Pons
Hindbrain structure that plays role in respiration, consciousness, sleep, dreaming, facial movements, sensory processes, and transmission of neural signals to different parts of brain
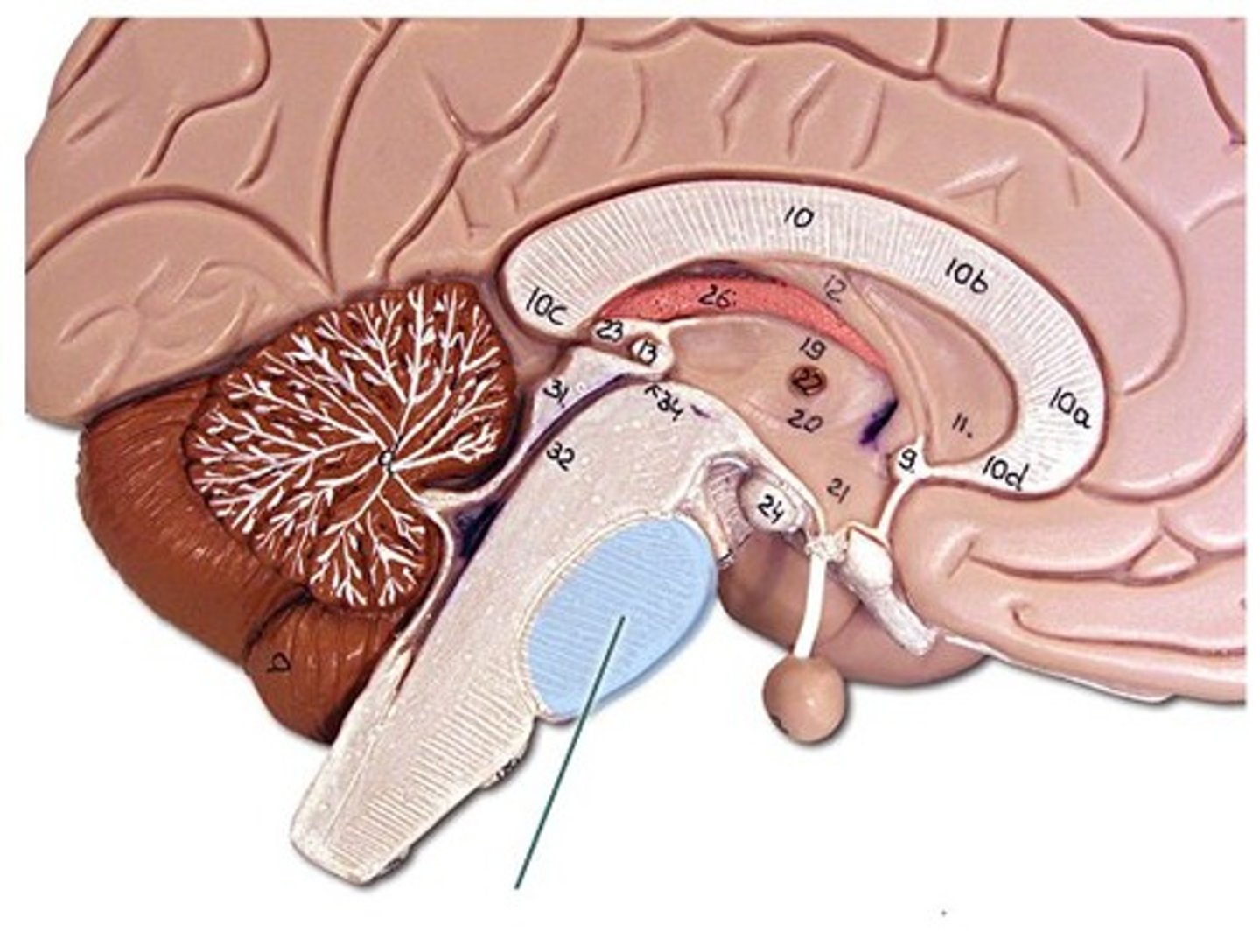
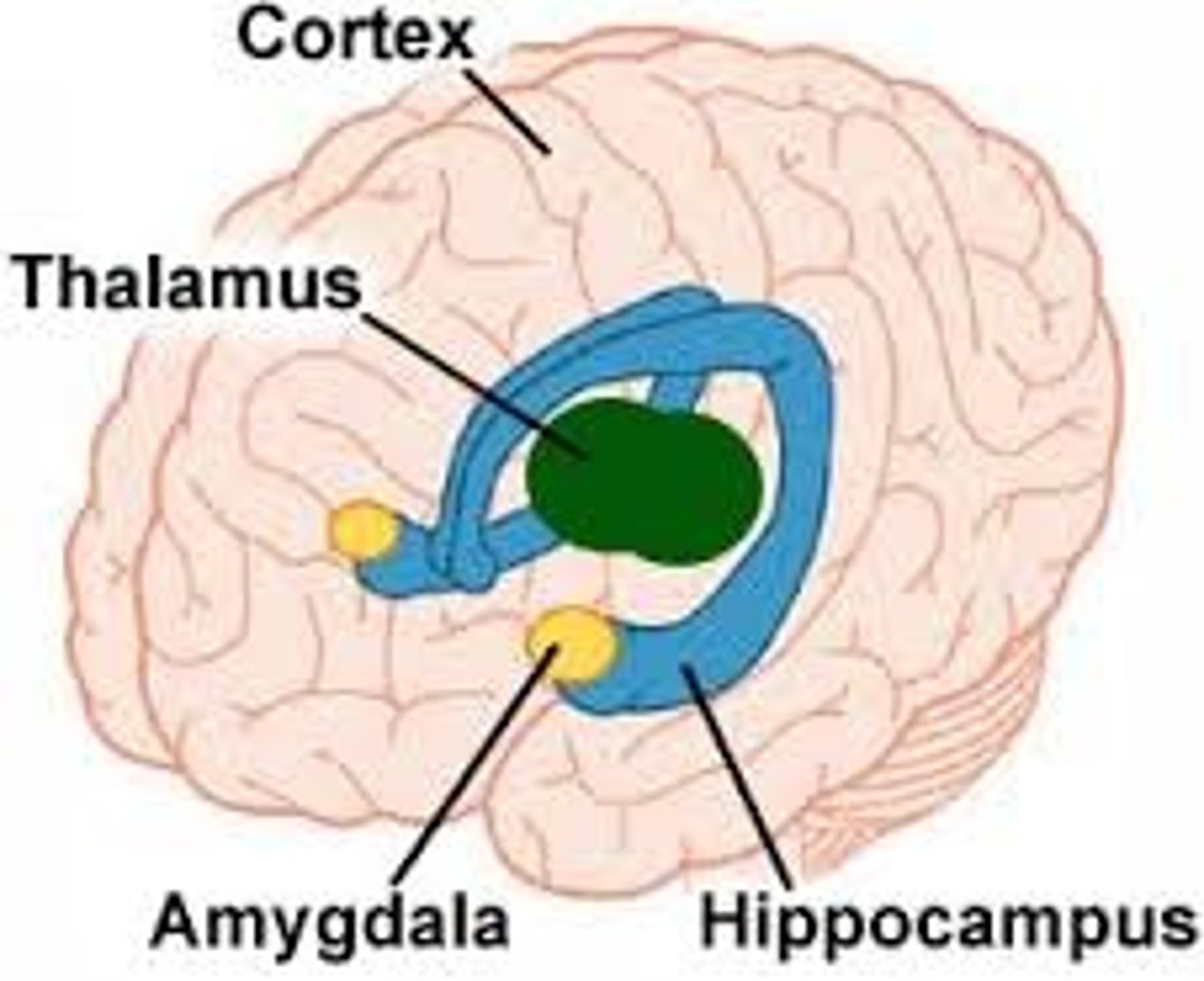
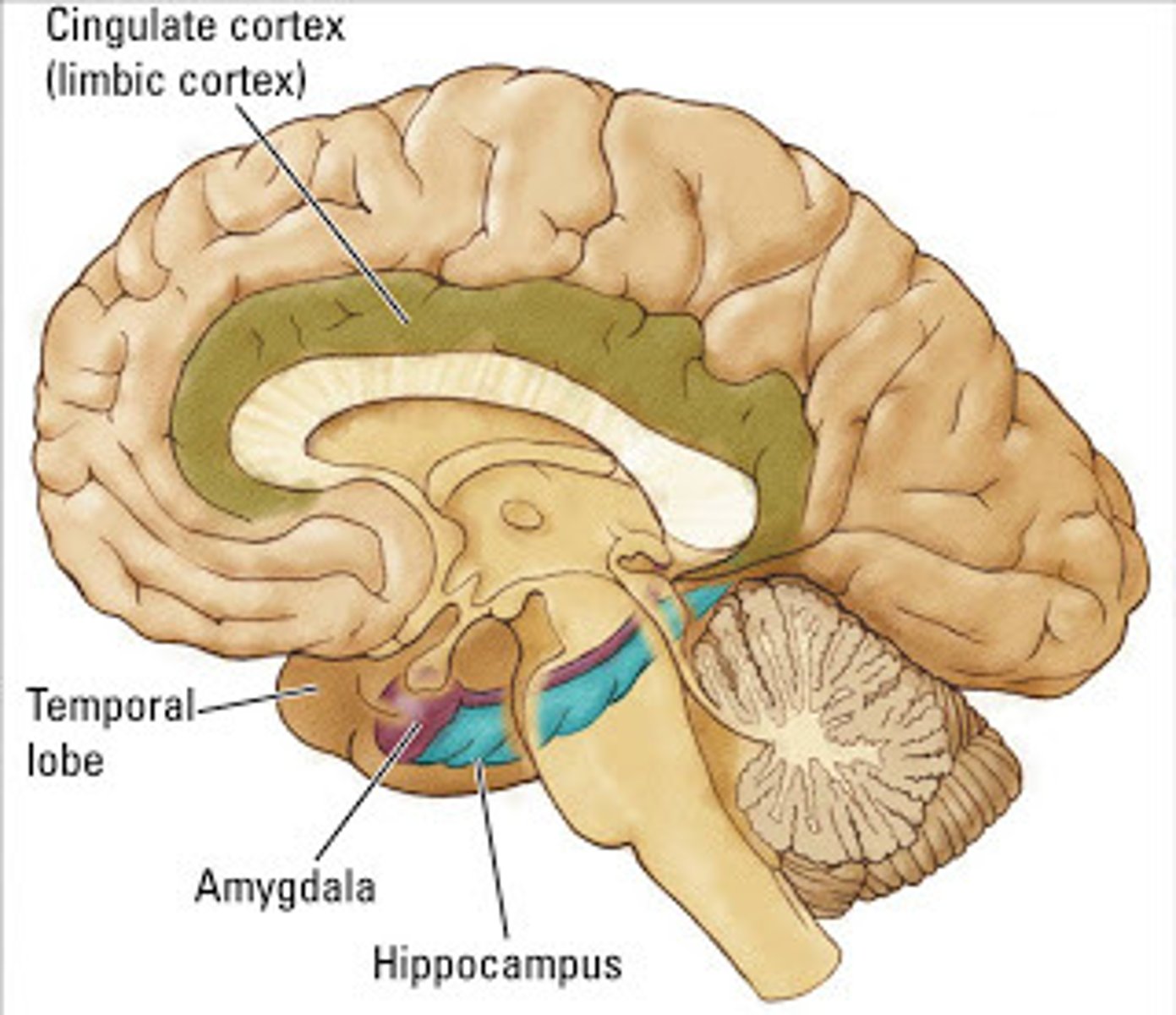
Limbic System(FOREBRAIN STRUCTURES)
System that includes amygdala and hippocampus, governing emotion, motivation, and memory
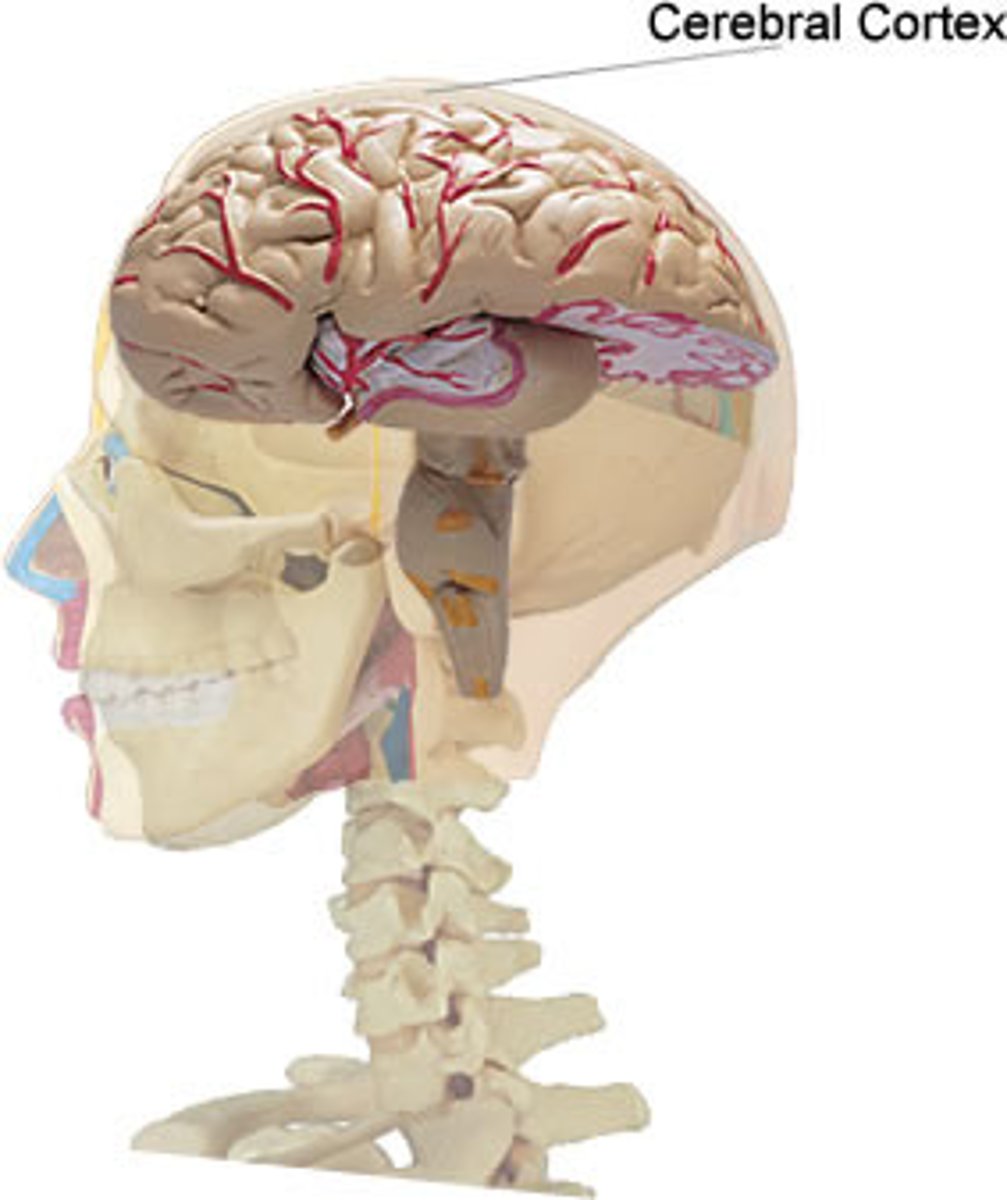
Cerebral Cortex
Thin, wrinkled outer covering of brain in which high-level processes like thinking, planning, language, interpretation of sensory data, and coordination of sensory and motor info take place
Cerebral Hemisphere
Right and left sides of brain that govern different functions in the body
Amygdala
Part of Limbic system that plays role in emotions of fear/aggression
Hippocampus
Plays role in transfer of info from short to long term memory
-Those with epilepsy have this destroyed.
H.M hippocampus Destroyal
He could no longer create new memories(anterograde amnesia) but he could perform new motor skills
Neuroplasticity
Nervous System's ability to rewire its structures as a result of experience
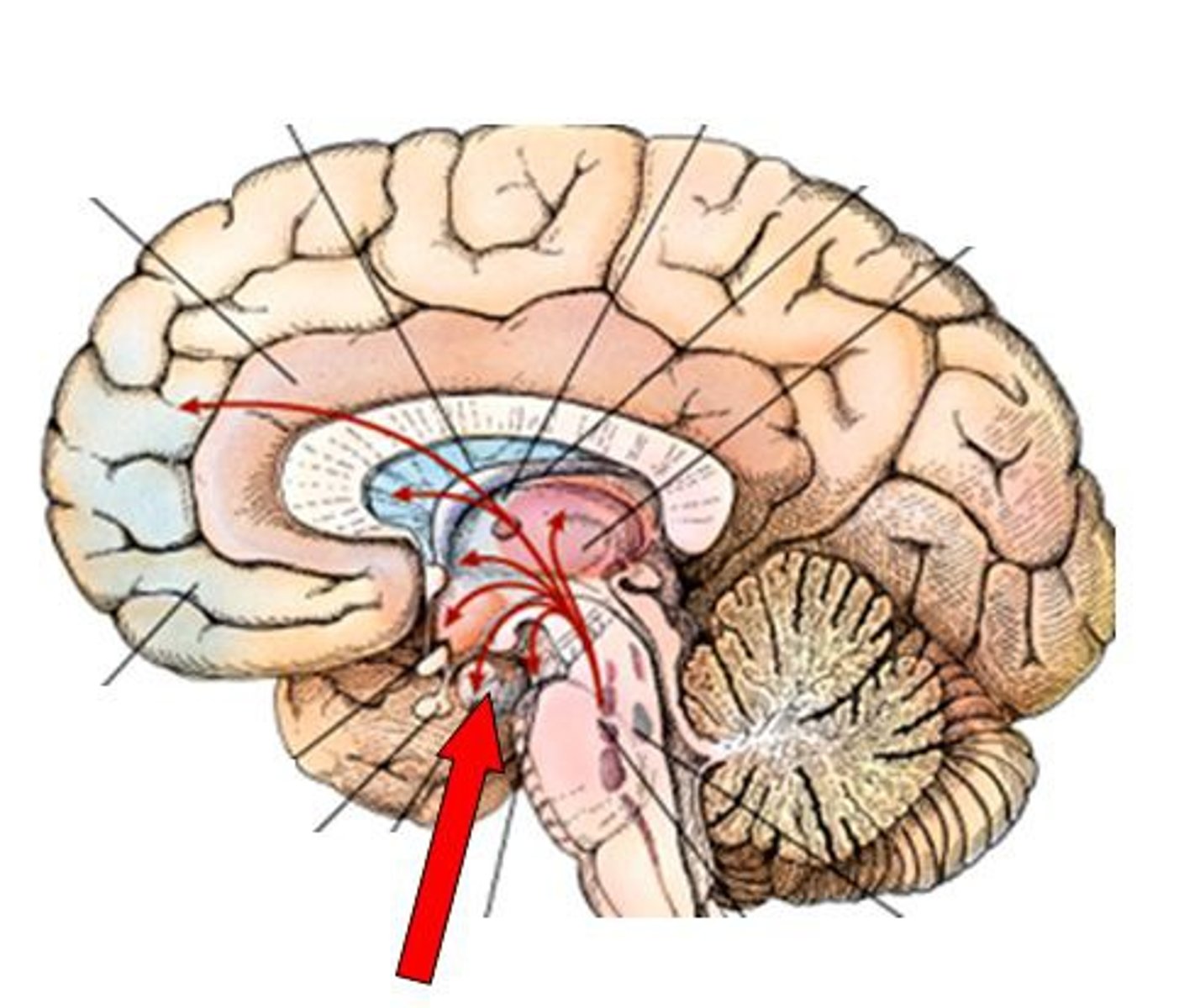
Hypothalamus
Forebrain that plays role in homeostasis in body,including sleep, body temp, sexual behavior, thirst, and hunger.
-where endocrine and nervous system intersects
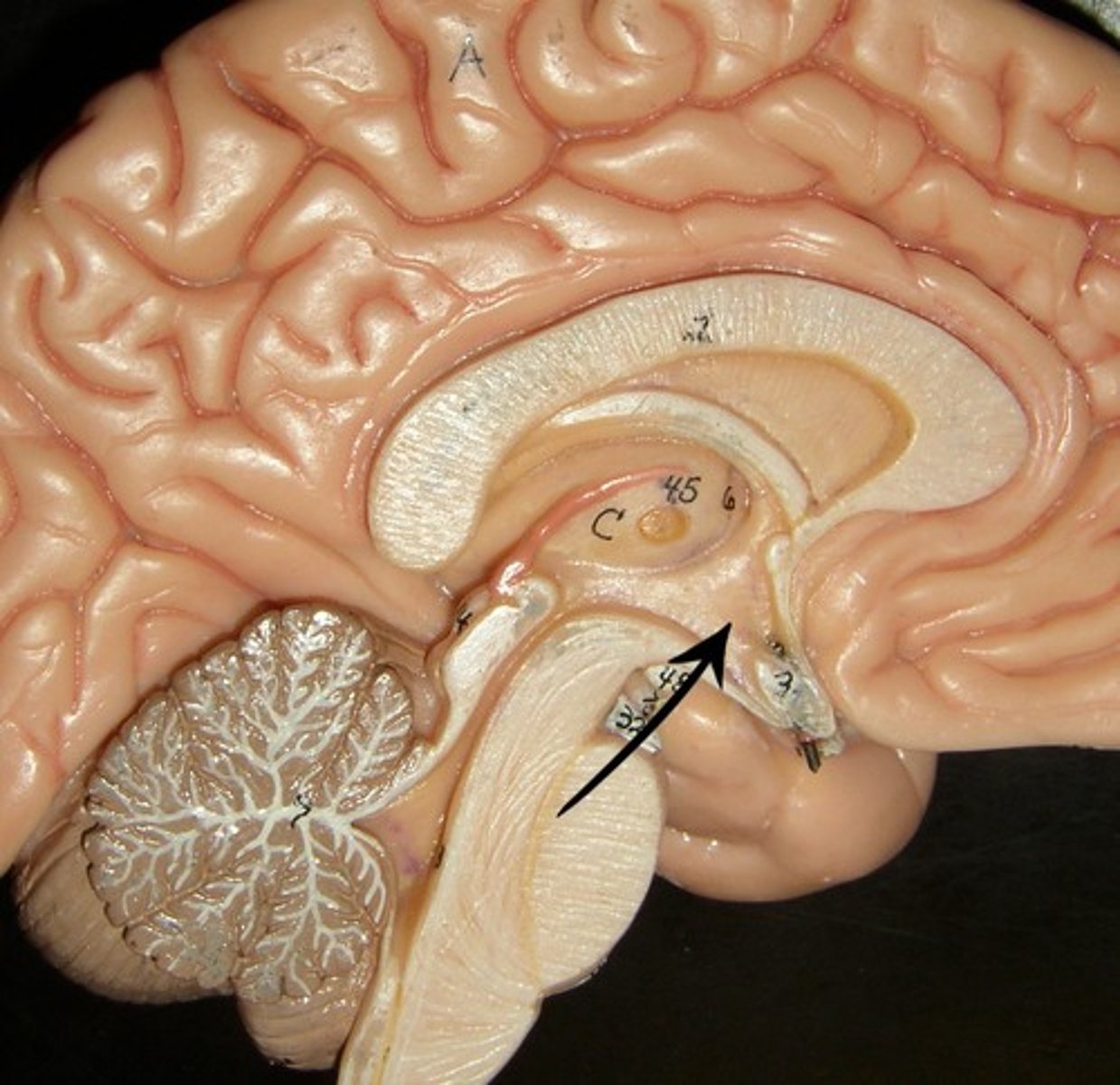
Homeostasis
Internal state of equilibrium in the body
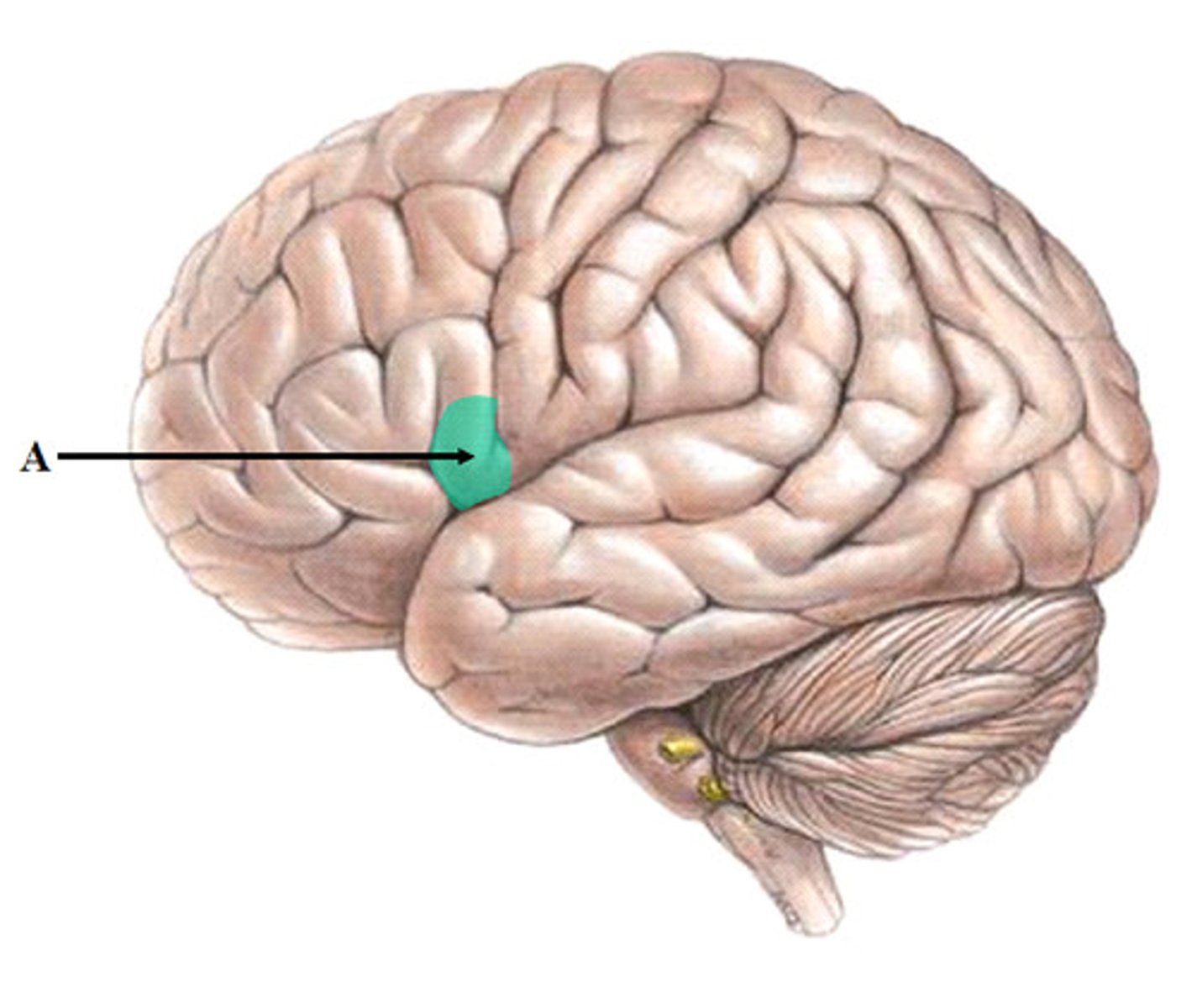
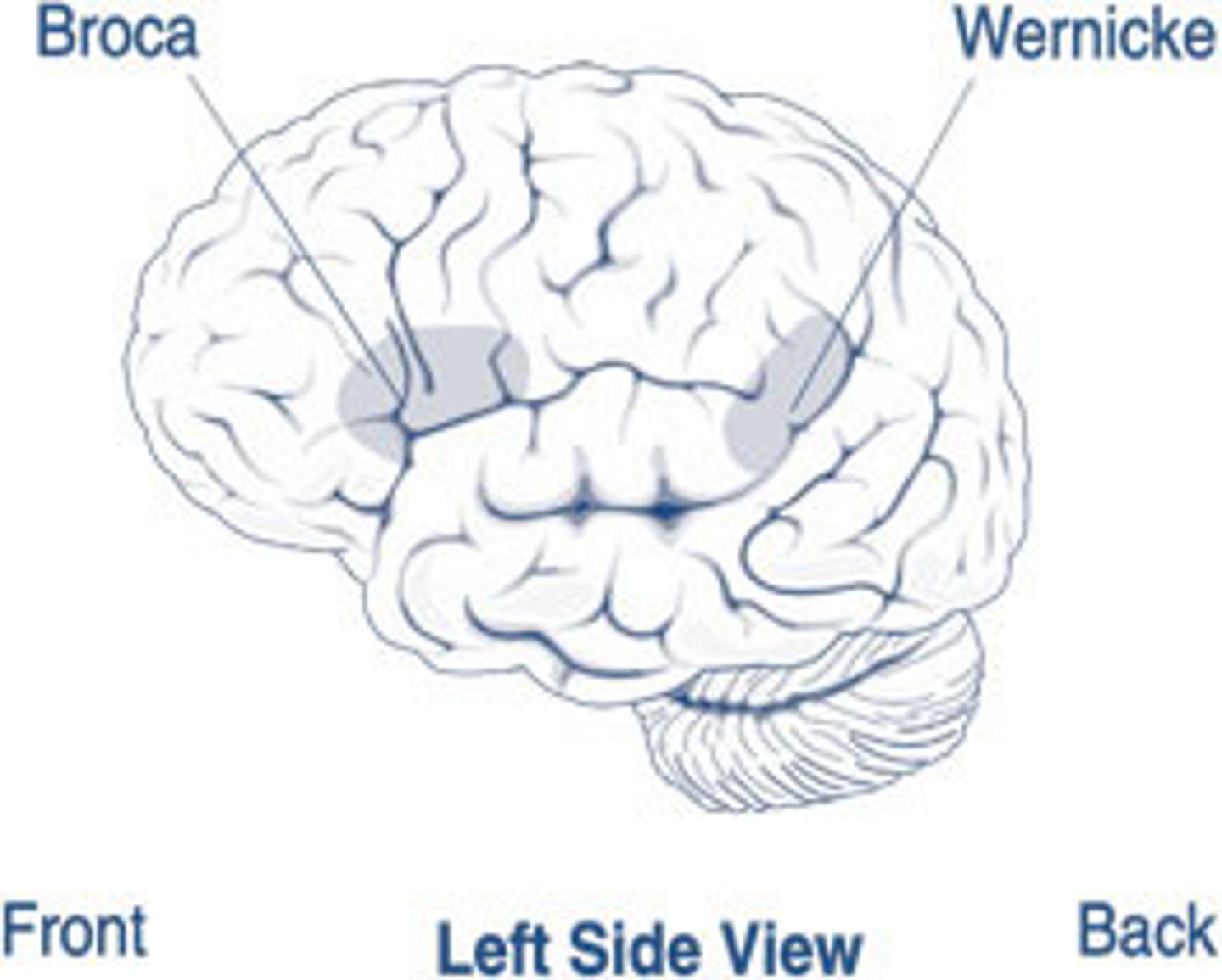
Broca's Area
region in left frontal lobe that plays role in production of speech
Wernicke's Area
a region of left temporal lobe that plays role in comprehension of speech
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of neurons that connects right and left hemispheres of brain.
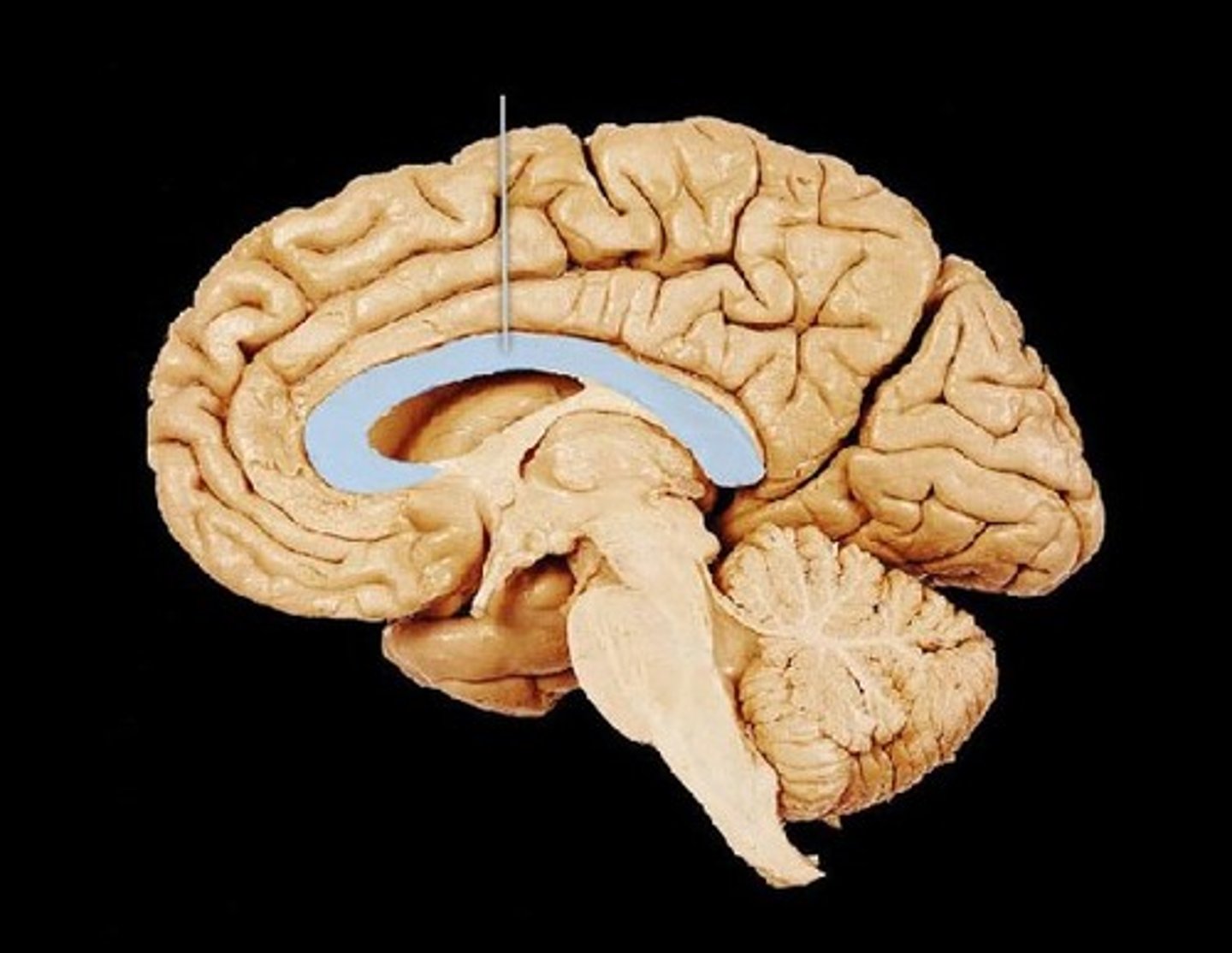
Split Brain
Brain with its Corpus Callosum severed; done to control effects of epilepsy in people
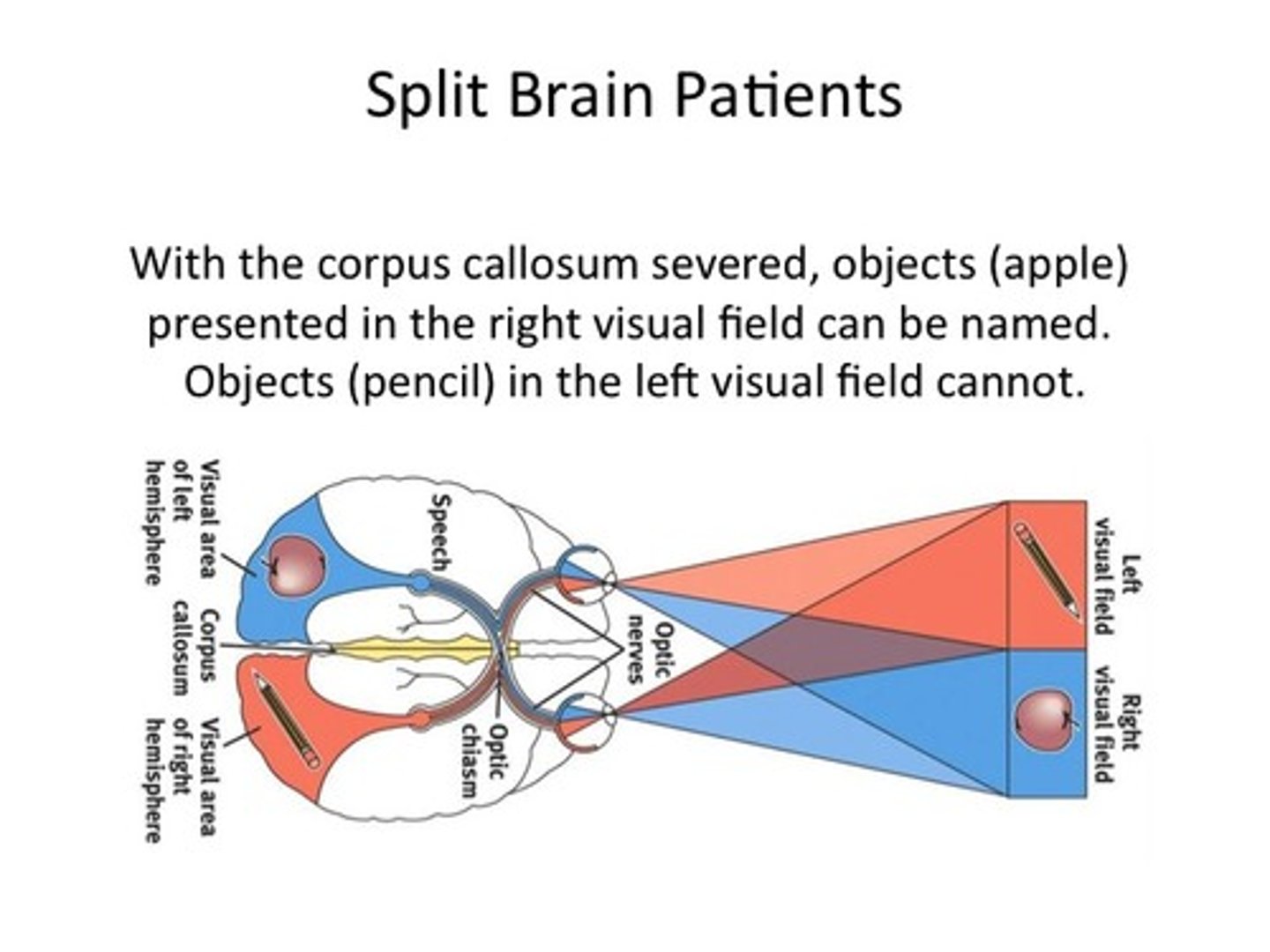
Split Brain facts
Left side produces speech. Images were flashed to the right and left visual fields and were asked to identify object. When right field is shown, the visual info is sent to left hemisphere. Broca's are is on left so they could verbally identify it
-When presented to left side, it is sent to right hemisphere. The right brain knee what it was but could not SPEAK it out.
-Could point oout object using left hand since it is controlled by right side of brain.
Association Cortex
Areas of cortex involved in association or integration of info from motor-sensory areas of cortex
-thinking, planning, decision making, etc.
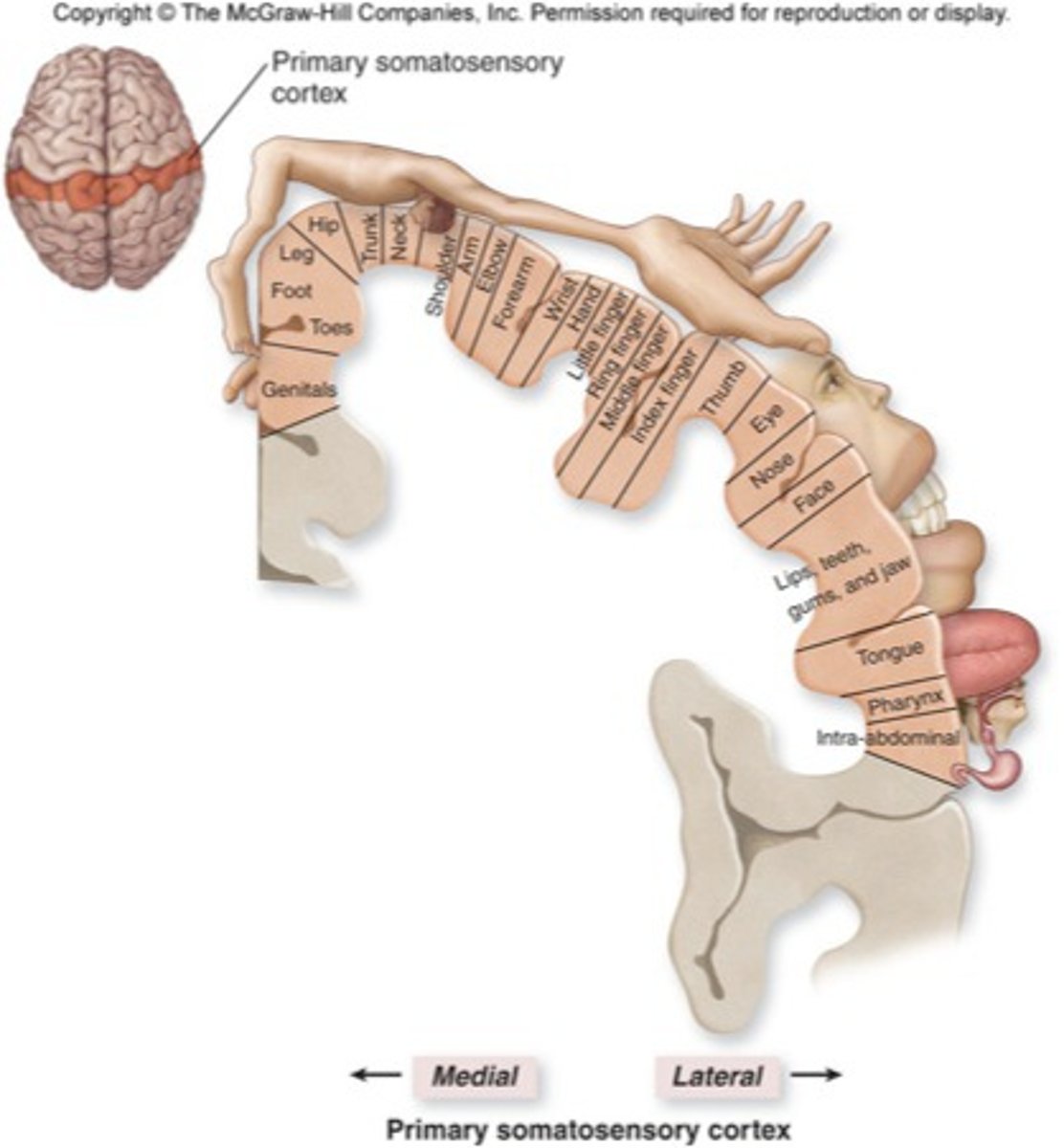
Somatosensory Cortex
Strip of cortex in back of parietal lobe that governs execution of motor movements in body
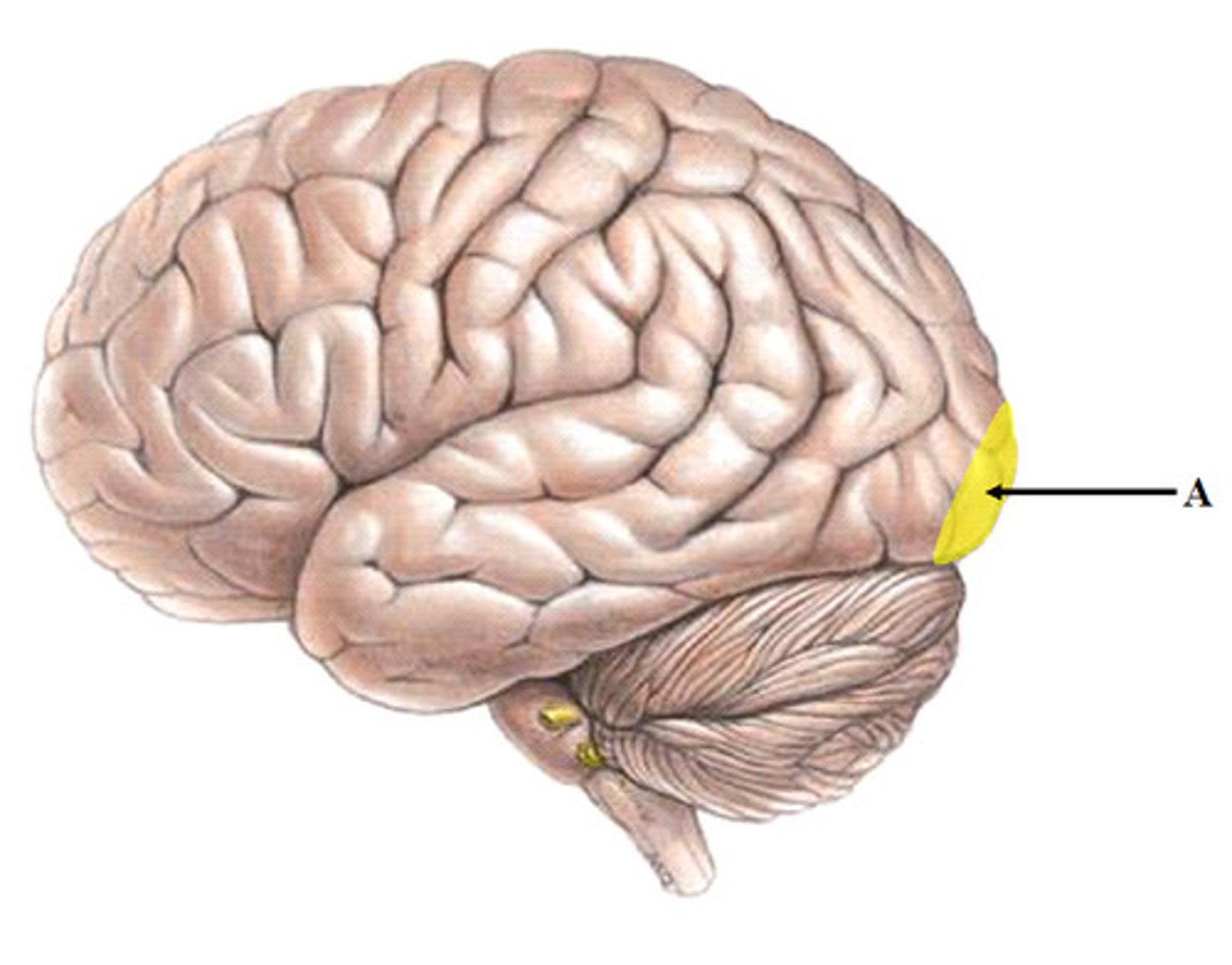
Visual Cortex
Found at back of occipital love that processes visual information in brain
Damage to which of the following brain structures would be MOST likely to cause death?
a. Frontal Lobe
b. Amygdala
c. Medulla
d. Hippocampus
C
Billy had a stroke on the left side of his brain. Most of his frontal lobe was destroyed. What symptoms would you expect to see in Billy as a result of this damage?
a. Paralysis on right side of body and inability to speak
b. Paralysis on the right side of his body and inability to understand speech
c. Paralysis of his left leg, partial deafness, and stuttering
d. Paralysis on left side of body and an inability to understand speech
A
Juanita experienced a brain injury that left her with an inability to store new memories for events and concepts. Which part of Juanita's brain was most likely damaged?
a. Hippocampus
b. Hypothalamus
c. Thalamus
d. Midbrain
A
Endocrine System
chemical system of communication in body that uses chemical messengers, called hormones, to affect organ function and behavior
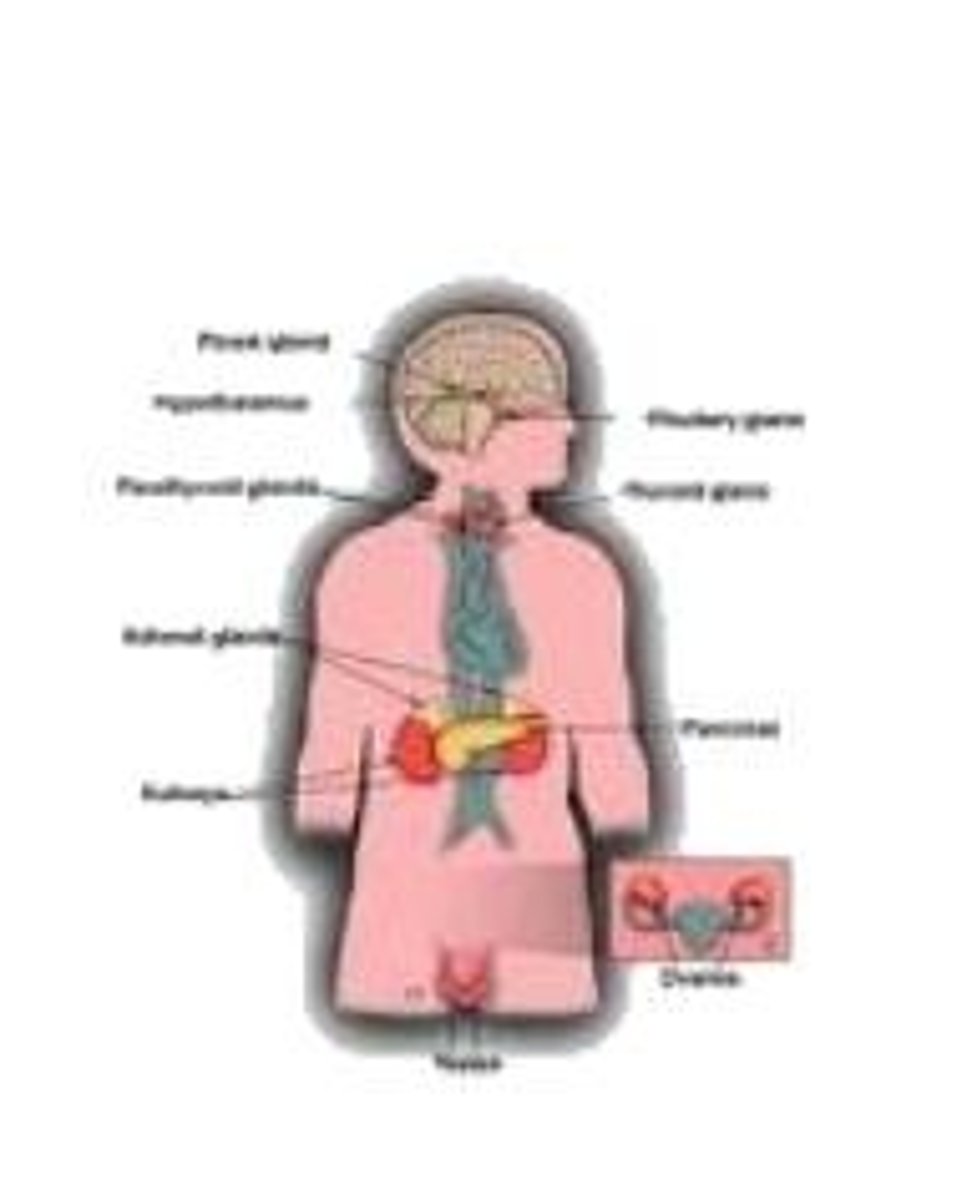
Endocrine Glands
Organs of endocrine system that produces and releases hormones into blood
Hormones
Chemical messengers of endocrine system
Pituitary Gland
Master gland of system that controls action of all other glands
Hypothalamus in Endocrine System
It sends a signal to the pituitary gland