Haloalkanes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What mechanism do haloalkanes to alcohols undergo
Nucleophilic substitution
What is hydrolysis
The breaking of a bond in a molecule in a solution with hydroxide or water
Name 3 main nucleophiles
Water, ammonia and OH- ion
What reagents and conditions are there for the hydrolysis of a haloalkane
NaOH and heated under reflux
How does carbon-halogen bond strength vary down the group
The average bond enthalpy decreases
How does bond enthalpy of carbon-halogen bond affect the rate of hydrolysis
The larger the bond enthalpy of the carbon-halogen bond, the slower the reaction rate
How to measure rate of hydrolysis
Add aqueous silver nitrate, so precipitate is formed as halide is released into solution. This has to be done with ethanol and water so the haloalkane doesn’t form a separate layer
What is a cfc
Chlorofluorocarbon
Why is depletion of the ozone layer dangerous
Because more UVB radiation will hit humans which can cause genetic damage and skin cancer
Is hydrolysis quicker in tertiary or primary haloalkanes and why
Tertiary because it uses a two step mechanism instead of a one step mechanism like primary
Where does the nucleophile attack in hydrolysis
The opposite side of the carbon atom to the functional group
How does a nitrogen oxide radical react in the ozone layer (equations)
Acts as a catalyst

How does a chlorine radical (as a catalyst) react in the atmosphere
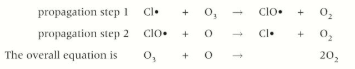
How do OH radicals react in the ozone layer

Test for haloalkanes
add silver nitrate and ethanol and heat to 50 C
Chloroalkane = white precipitate
Bromoalkane = cream precipitate
Iodoalkane = yellow