Bio 11 Anatomy - Senses
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Free Nerve Endings
touch, pain, pressure
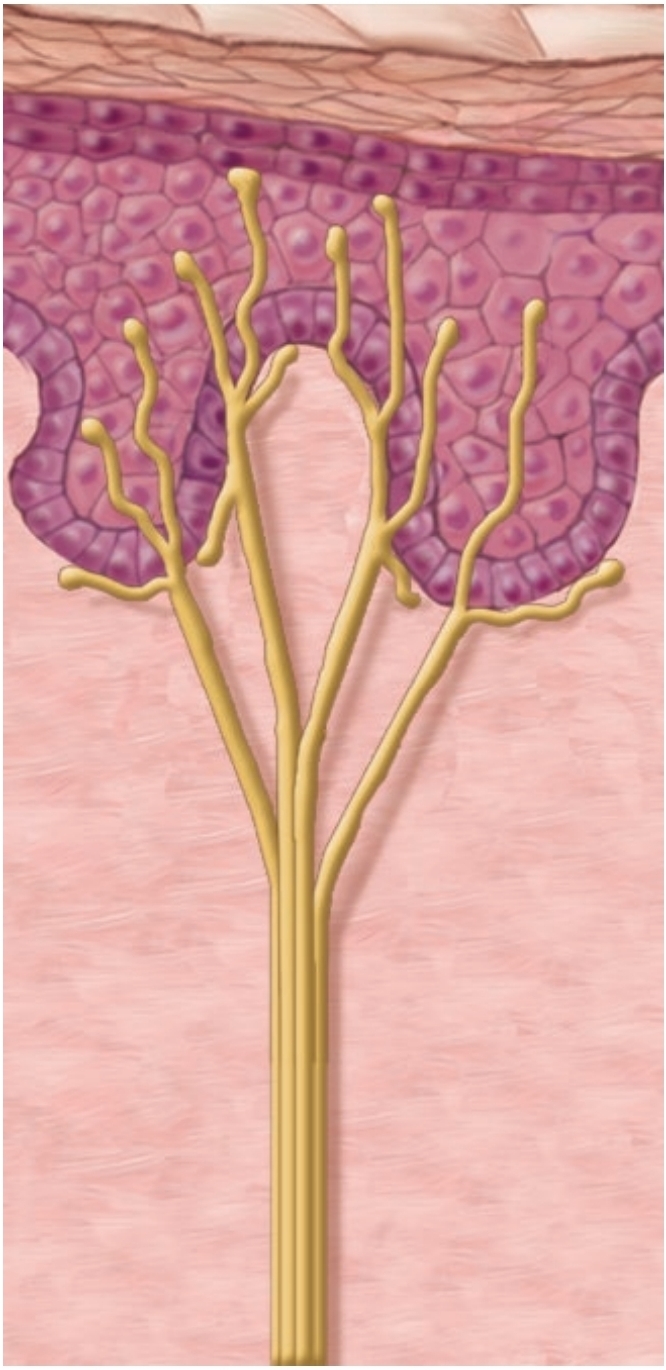
Root Hair Plexuses
hair movement
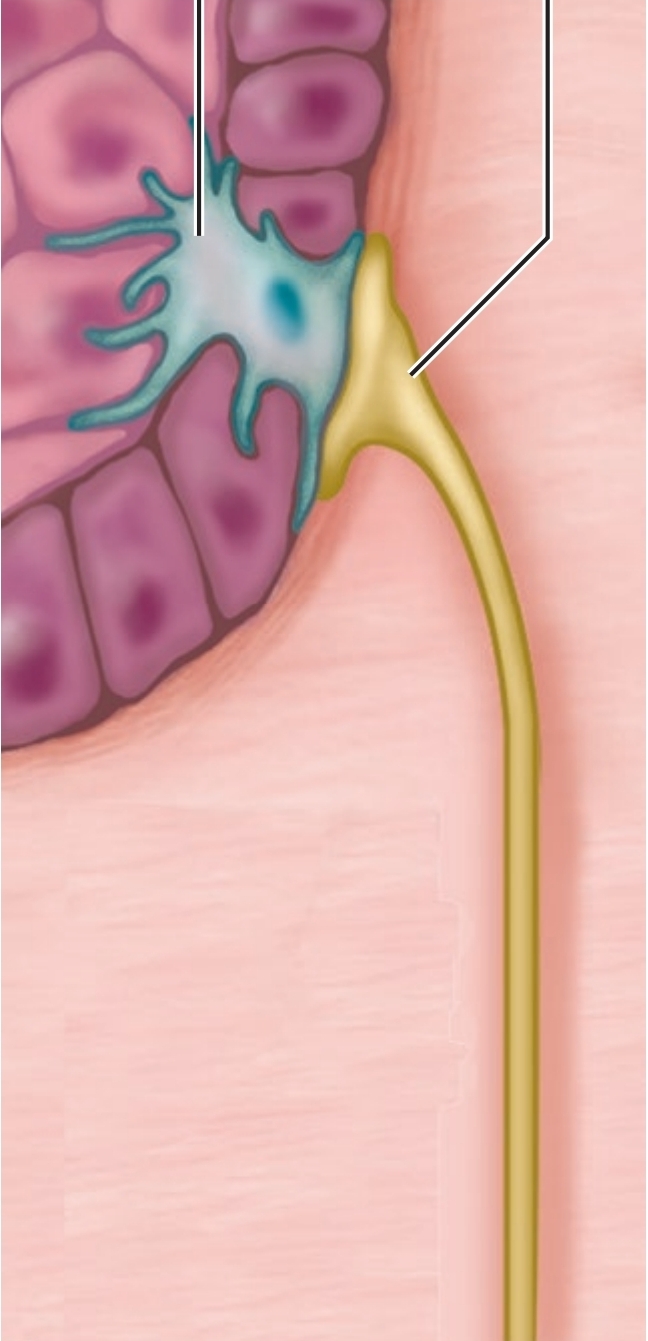
Tactile Discs
light touch
End Bulbs
light pressure, low vibration (in mucus membranes)
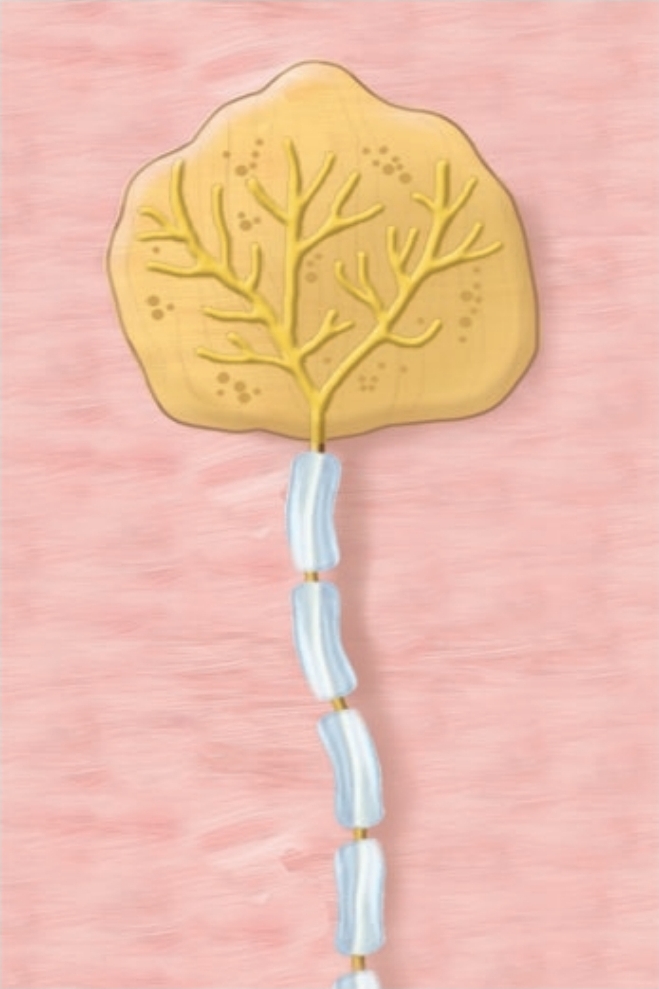

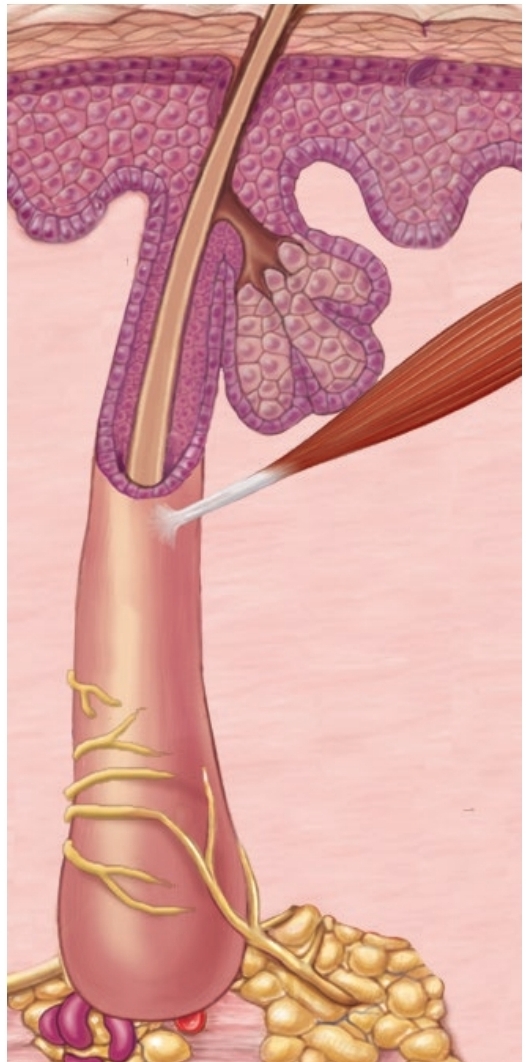
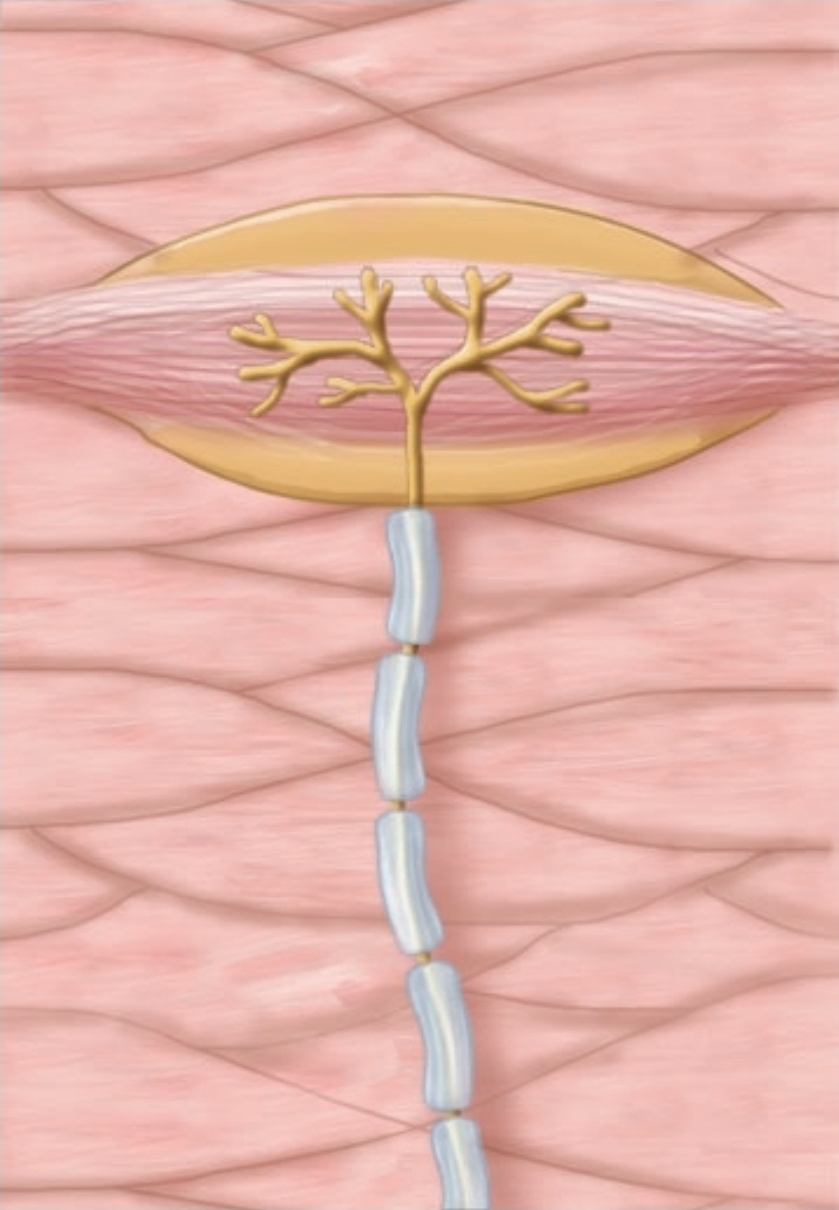
Lamellated Corpuscles
course touch, deep pressure, high vibration; Inner core of neurolemmocytes
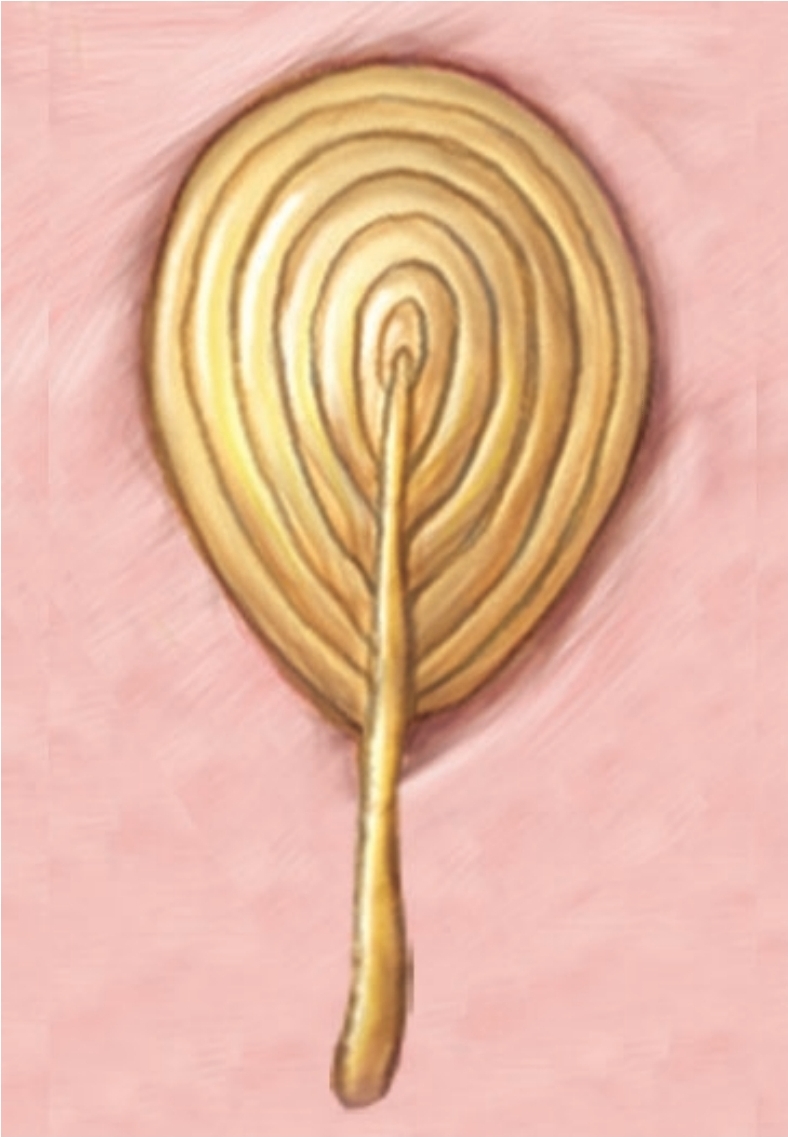

Bulbous Corpuscles
skin distortion, deep pressure
Tacticle Corpuscle
textures, shapes
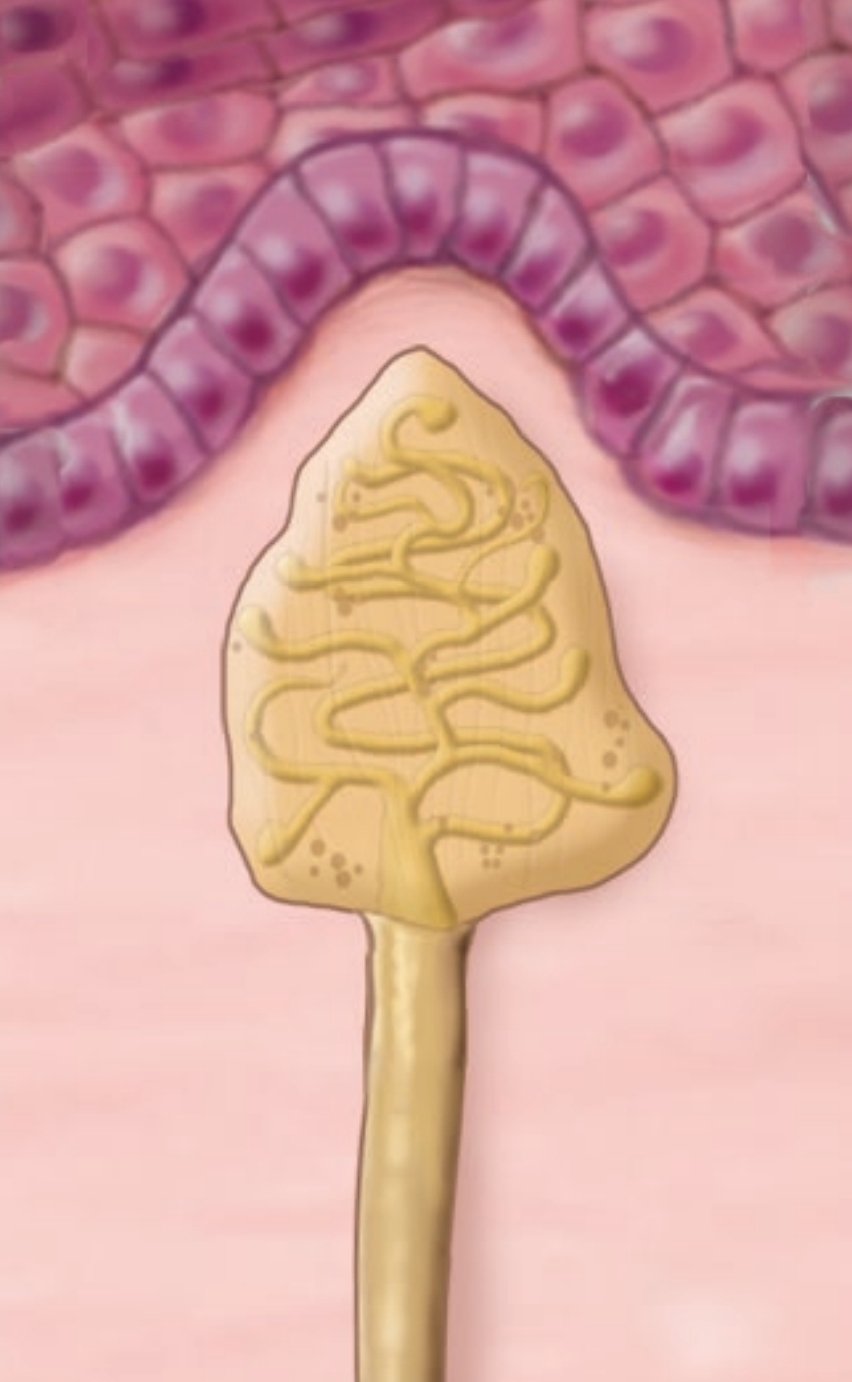
Vallate Papillae
Largest but least common. “V” shape in posterior. Most taste buds
Palpebra
Eyelid
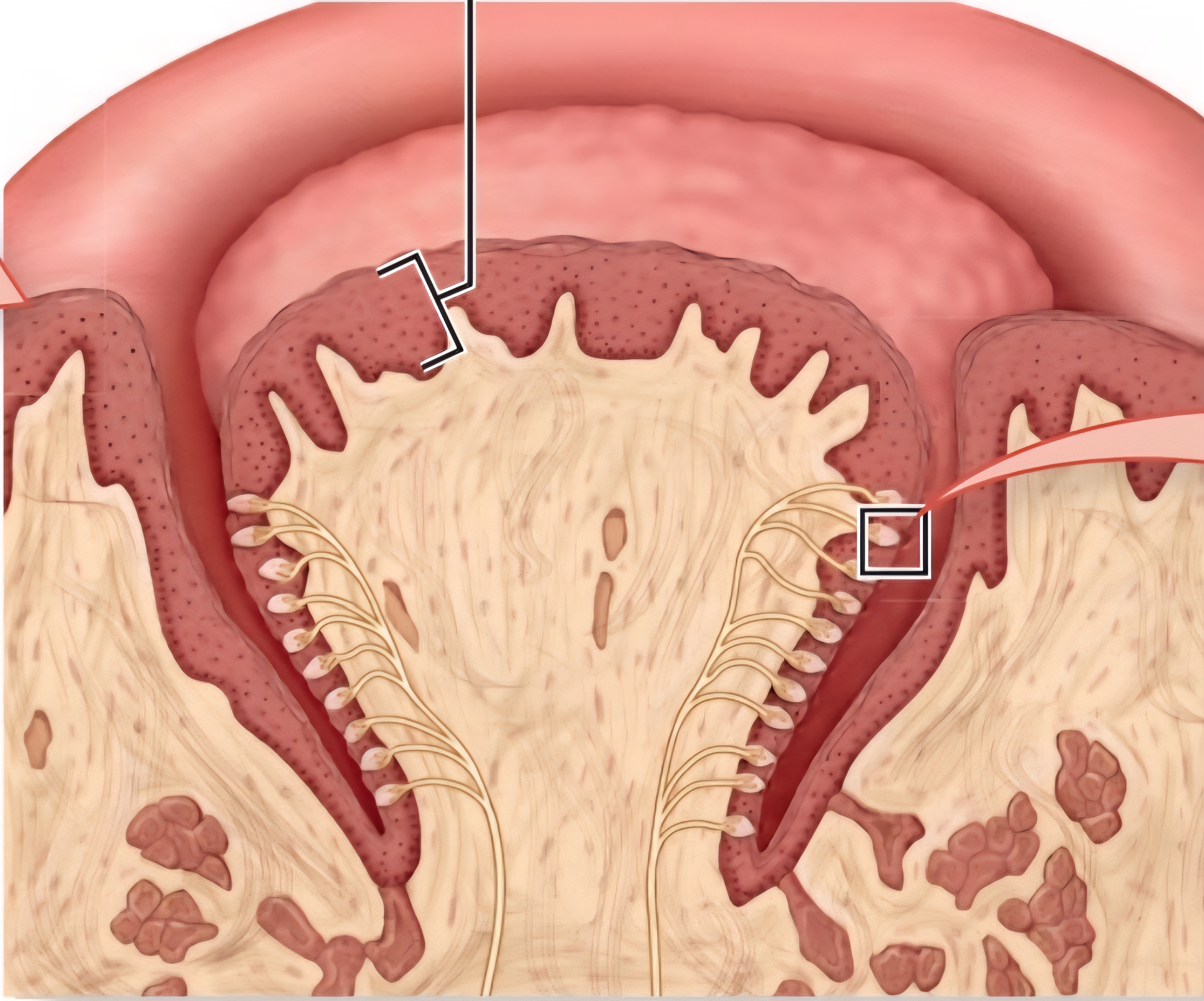
Foliate Papillae
Extend as ridges on lateral tongue; few tastebuds in infancy + childhood
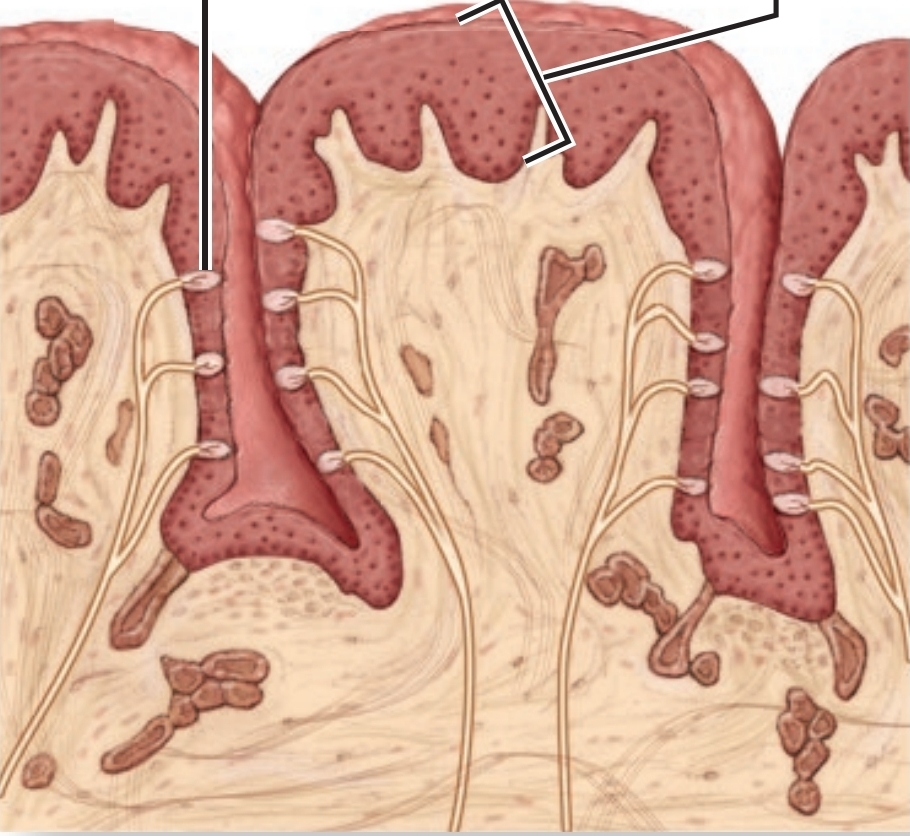
Filiform Papillae
No tastebuds, detects texture, mechanically moves food during mastication.
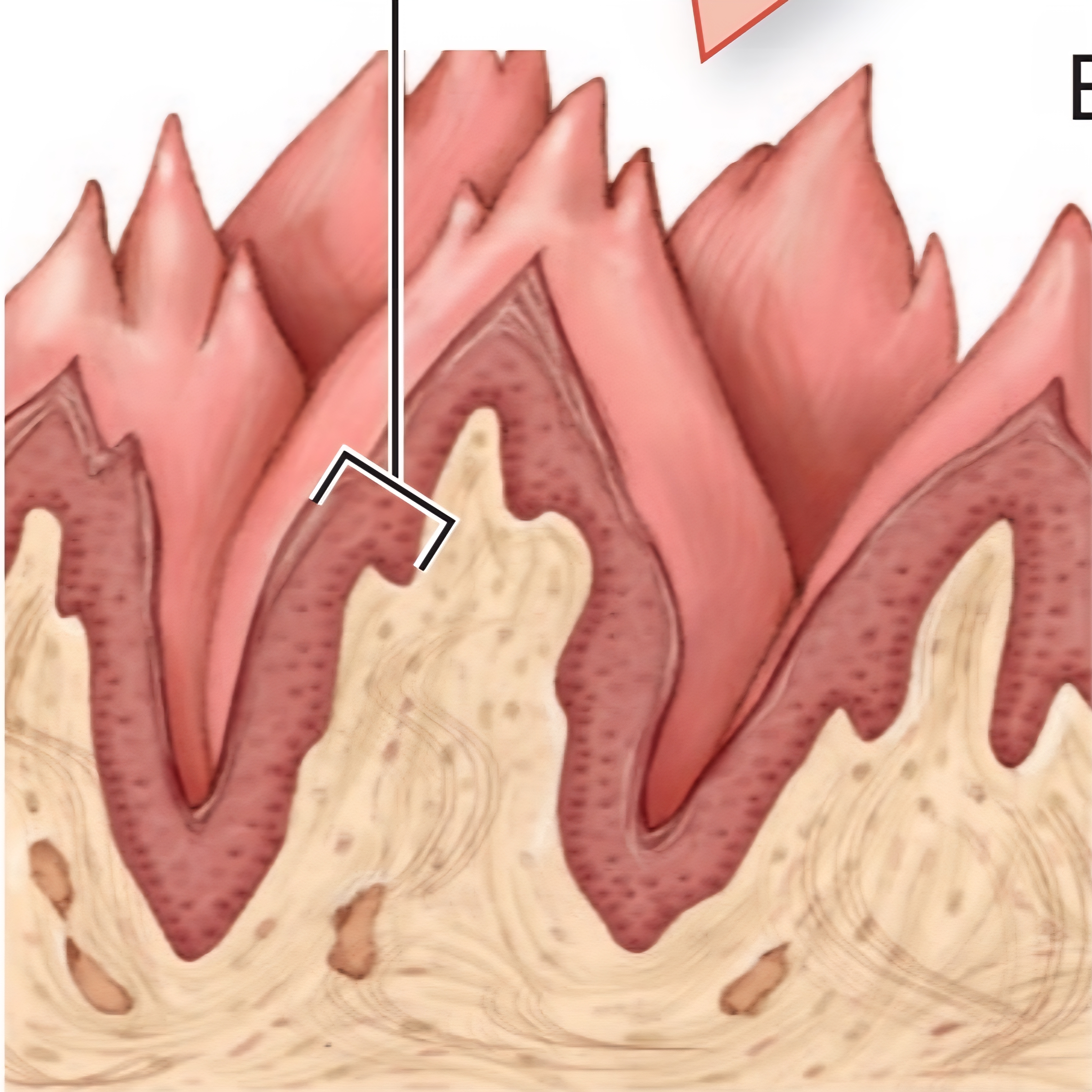
Fungiform Papillae
On tip and sides of tongue, few taste receptors
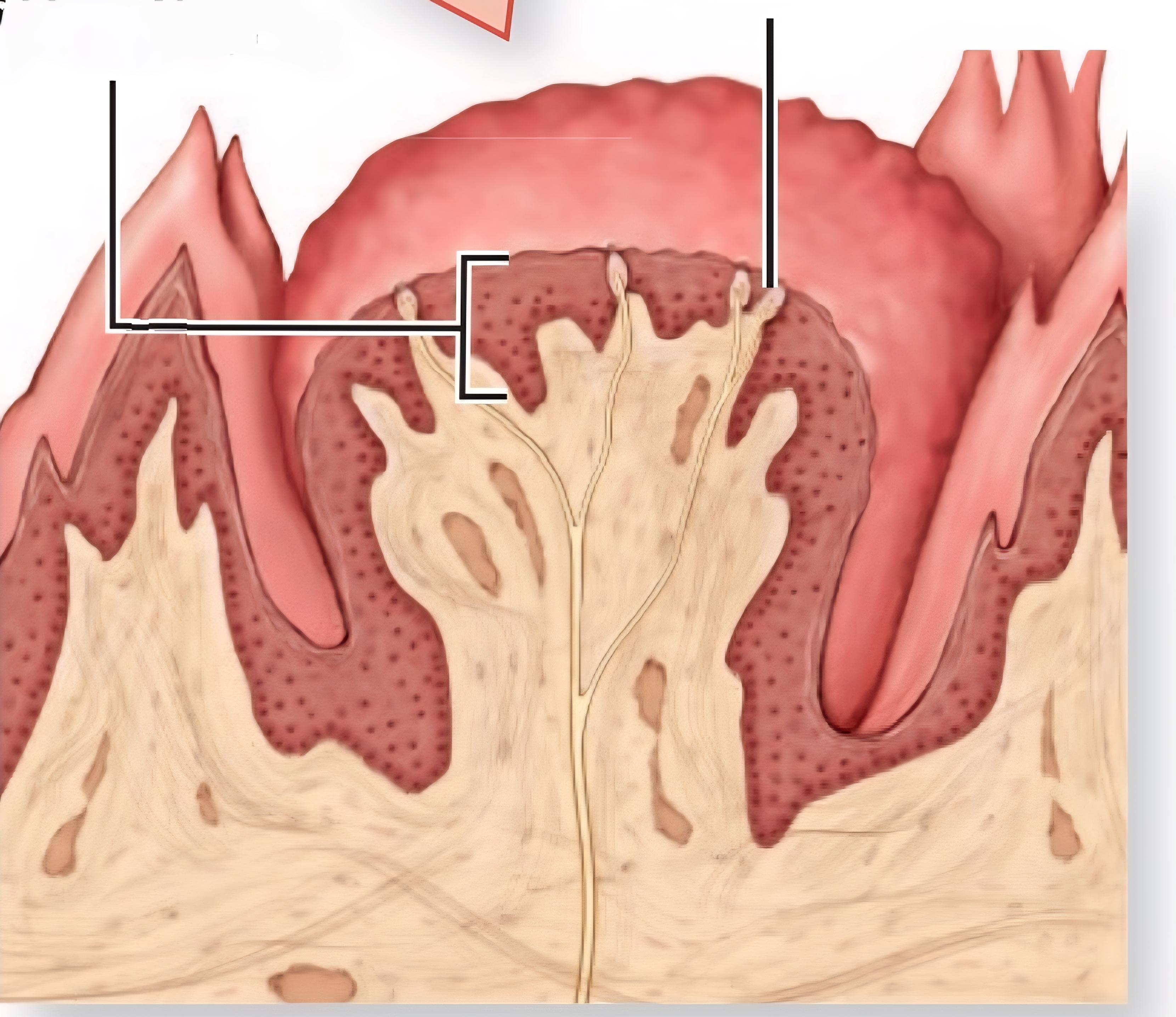
Basal Cells
neural stem cells that replace gustatory cells every 7-9 days
Cranial Nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal - responsible for taste sensations at the posterior region of the tongue, initiates swallowing, and carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information
CN VII
Facial - responsible for taste sensations at the anterior regions of the tongue
Where are parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons?
brainstem nuclei, craniosacral, and CN III, VII, IX, and X
where are sympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons?
lateral horns, thoracolumbar
Submucosal Plexus
part of enteric nervous system; controls secretion, absorption, mucosal folding.
Myenteric Plexus
part of enteric nervous system; controls GI tract smooth muscle activity
Plasma Proteins
60% albuminum, 36% globulins 4%fibrogen
Lamina Propria
deep to the epithelium; contains mucin-secreting olfactory glands
Pigmented Layer
provides vitamin A for photoreceptor cells
Emmetropia
normal vision; parallel rays of light focused on retina
Hyperopia
farsightedness, caused by short eye. corrected with convex lens.
Myopia
nearsightedness, caused by long eye. corrected with concave lens.
Presbyopia
changing from far to near; caused by age, lens cannot change shape
Astigmatism
blurry vision, caused by unequal curves of cornea or lens
Neural Layer
contains photoreceptor cells, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells;
responsible for converting light → nerve impulses
Tarsal Glands
Sebaceous glands that produce a secretion to prevent tear overflow, prevents eye from sticking together
Lacrimal Caruncle
Houses ciliary glands, modified sweat glands that causes gritty morning eyes.
lacrimal fluid is transferred here
Lysozome
antibiotic-like enzyme produced by lacrimal apparatus
Limbus
structural continuity between cornea and sclera
Lens shape for far-away things
lens flattened, suspensory ligaments taut
Lens shape for up-close things
lens thickened, suspensory ligaments relaxed
Suspensory Ligaments
holds lens in place
Utricle
detects horizontal movement via movement otolithic membrane
Saccule
detects vertical movement via movement of otolithic membrane
Kinocilia
apex of hair cells in sensory epithelium
Stereocilia
converts mechanical energy to electrical energy; communicates to CNVIII
Cochlear Duct
endolymph,
Scala Tympani
Scala Vestibuli
Otoliths
calcium carbonate (CaCo3) crystals
Olfactory Glomeruli
spherical structures in olfactory bulbs that detect and differentiate smells
Dilator Pupillae
(radial) sympathetic ANS
Sphincter Pupillae
(circular) parasympathetic ANS
Ciliary Body
relaxation / contraction change tension on suspensory ligaments;
epithelium secretes aqueous humor
Ora Serrata
transitional layer between neural retina and ciliary body