Reproduction
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
*** = unsure of description, or incomplete description There are a couple extra bullet points I wasn't able to incorporate in properly
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Sex determination in males
SRY gene on the Y chromosome causes embryonic gonads to develop as testes and secrete testosterone; SRY codes for TDF, which stimulates the expression of other genes that cause testis development
Testosterone
Testes develop testosterone secreting cells early in embryonic development (8th week, 30mm long embryo), and make testosterone until week 15; causes male genitalia to develop
Male primary and secondary sex characteristics
Primary - sperm production in the testes
Secondary - enlargement of the penis, growth of pubic hair and deepening of the voice due to growth of the larynx
Sex determination in females
Lack of SRY gene leads to ovary development, and estrogen and progesterone secreted (first by mother’s ovaries, then placenta), leading to female genitalia
What happens during puberty to testosterone and estrogen/progesterone?
Increase, leading to development of secondary sex characteristics
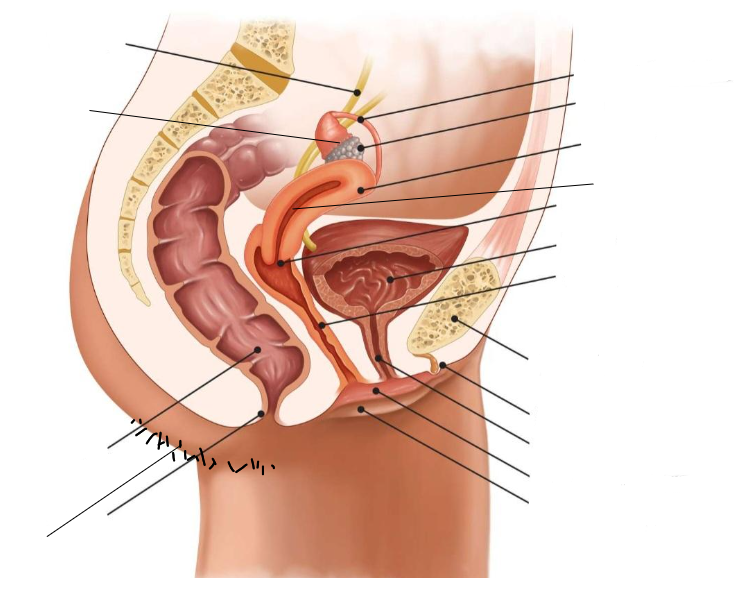
Label the female reproductive system. Include each structure’s functions.
***Refer to one of our diagrams, will input image soon
Label the male reproductive system. Include each structure’s functions.
***Will input image soon
What are the two parts of the menstrual cycle and what occurs in them?
First half: follicular phase
Group of follicles developing within ovary
Within each follicle is an egg
Endometrium (repairs first, then) thickens
Most developed follicle breaks open, releases egg into oviduct
Second half: luteal phase
Broken follicle develops into corpus luteum
Endometrium continues to develop, preparing for embryo implantation (in case of egg being fertilised)
No fertilisation leads breakdown of corpus luteum, shedding of the endometrium (menstruation)
What do FSH and LH do?
***Protein hormones produced by the pituitary gland that bind to FSH and LH receptors in the membranes of follicle cells.
Outline the steps of the menstrual cycle
FSH rises to a peak towards the end of the menstrual cycle, stimulates follicle growth
Also stimulates estrogen secretion by follicle wall
Estrogen rises to a peak towards the end of the follicular phase
Stimulates thickening endometrium after menstruation
↑ FSH receptors to make follicles more receptive to FSH ; LEADS TO ↑ estrogen (POSITIVE FEEDBACK); LEADS TO inhibiting FSH (NEGATIVE FEEDBACK); stimulates LH secretion
LH reaches a peak at the end of follicular phase, stimulates completion of meiosis in oocyte and partial digestion of follicle wall allowing it to burst at ovulation
LH promotes follicle growing into corpus luteum, which secretes estrogen (POSITIVE FEEDBACK) and progesterone
↑ Progesterone at start of luteal phase, reaches peak and then ↓ again at the end of phase
Progesterone promotes thickening/maintenance of endometrium
Inhibits FSH and LH (NEGATIVE FEEDBACK)