Week 8- Chronic Alterations in Hematology and Endocrinology
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
283 Terms
Iron deficiency anemia (IDA)
decreased hemoglobin and iron
IDA is caused by inadequate ____ and chronic ____
dietary intake of iron, blood loss
Common causes of IDA blood loss in females
pregnancy and menorrhagia
Common causes of IDA blood loss in males
ulcers, hiatial hernia, esophageal varacies, cirrhosis, hemorrhoids, ulcerative colitis, and cancer
IDA is a what type of anemia?
microcytic hypochromic (small cells, low hemoglobin)
Most common cause of IDA in children is
inadequate intake
IDA is the most common nutritional deficiency in
children
If IDA is untreated in children, it can cause irreversible effects on
development
Children are at risk for IDA due to _____ and ____
rapid growth, poor eating habits
Cows milk can cause an
increased risk of developing IDA
What aged children are most at risk for IDA?
6 months to 2 yrs
IDA in children can cause ____ deficiency
intelectual/behavioural
Chronic IDA 3 main causes
parasitic infection, hemorrhagic disease, or PUD
IDA is also associated with the
SEDOHs (poverty/developing countries)
4 main causes of IDA (diet and blood loss related) include
dietary deficiencies, impaired absorption, increased metabolic requirements, and chronic blood loss
Most common dietary deficiency that causes IDA is
inadequate protein intake
Other dietary deficiencies that cause IDA include
vegetarian diet and PICA
PICA
an abnormal craving for nonfood substances, such as dirt, paint, or clay
Impaired absorption causing IDA includes ______, ______, and _____
partial/total gastrectomy, chronic diarrhea, and malabsorption syndrome
Increased metabolic requirements causing IDA includes _____ and _____
pregnancy, lactation
Chronic blood loss causing IDA includes ______ and _____
GI bleed, menstrual loss
Common cause of GI bleeds are ____ and ____
ulcers, chronic NSAID use
A surgical procedure that could cause IDA (blood loss ) is a
gastric bypass
Impaired absorption causes of IDA in children
celiac disease, chronic diarrhea, and malabsorption syndrome
Increased requirement cause of IDA in children is due to
growth spurts
Other causes of IDA in children are ____, ____, and ____
GI lesions, parasitic infections, hemorrhagic disease
Stage 1 IDA
low iron, normal RBC, and normal hemoglobin
Stage 2 IDA
low iron, abnormal RBC production
Stage 3 IDA
hemoglobin-deficient RBC enter the circulation, clinical manifestations appear
Iron deficiency anemia early clinical manifestations
fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, increased HR, and pale earlobes/palms/conjunctiva
IDA clinical manifestations (neuro)
irritability, decreased activity tolerance/weakness, headaches, and confusion/memory loss in older adults
IDA clinical manifestations (resp)
dyspnea
IDA clinical manifestations (GI)
PICA, smooth/sore/red/beefy tongue, glossitis, dysphagia, gastritis
Dysphagia in IGA commonly occurs due to
web of mucus and inflammatory cells forming at the base of the esophagus
IDA clinical manifestations (integ)
angular stomatitis and spoon shaped nails
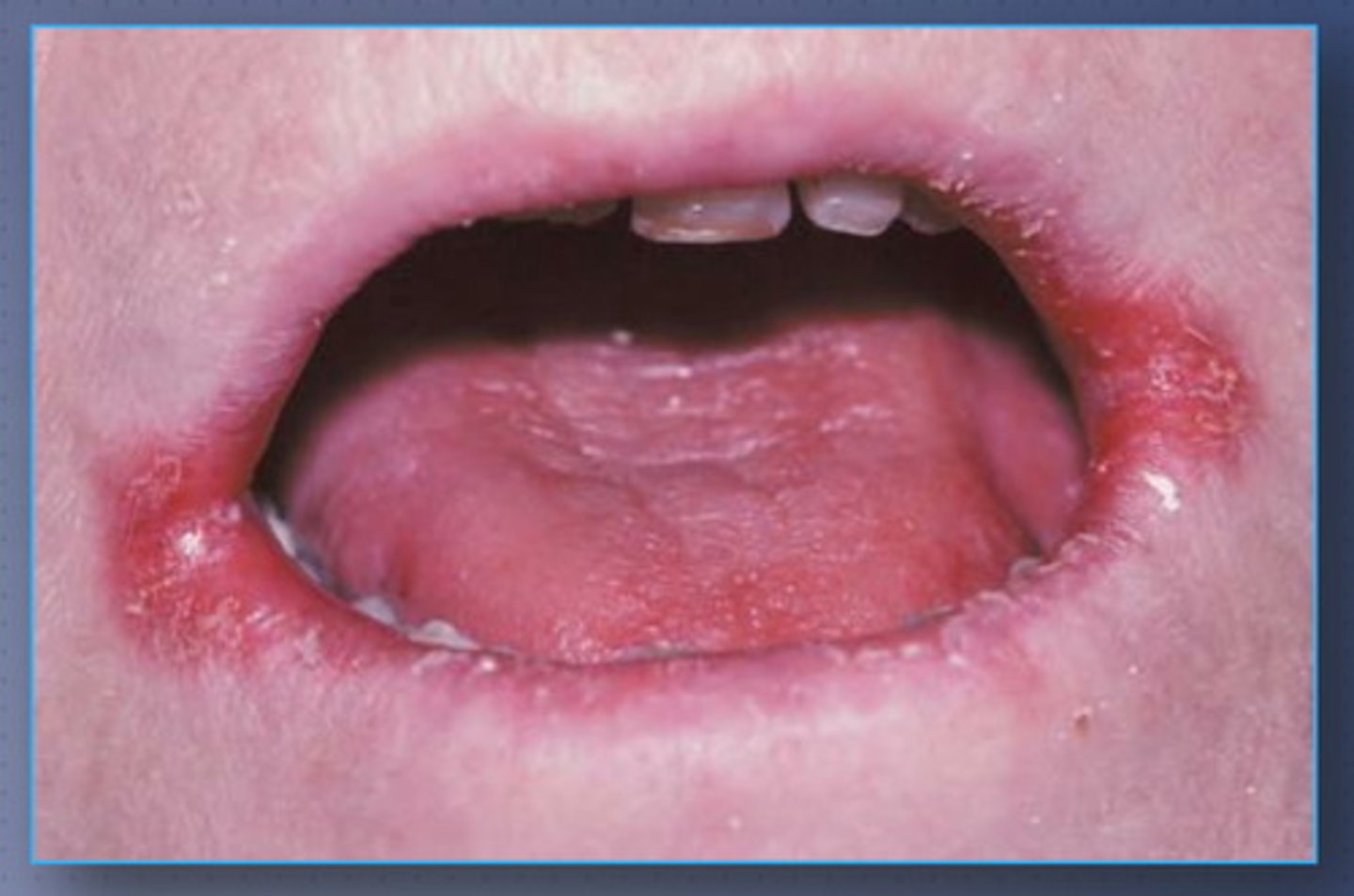
Angular stomatitis
cracks in the corners of the mouth
Mild IDA clinical manifestations in children
lethargy, listlessness, irritability, decreased activity tolerance, weakness, and lack of interest in play (anhedonia)
Mild IDA hemoglobin levels
70-100 (can usually be treated with diet)
Severe IDA clinical manifestations in children
pallor, tachycardia, systolic murmurs, splenomegaly, widened scull sutures, developmental delays, decreased physical growth, PICA, cognitive impairment
Severe IDA hemoglobin levels
<70 (or symptomatic)
What is not an indicator of IDA in children?
weight
Hemoglobin levels for packed RBC transfusion usually occurs when hemoglobin drops <_____ or patient is _____
70, symptomatic
Diagnostic tests for IDA include
CBC, serum iron, red cell distribution width (RDW), and rarely bone marrow biopsy (other tests are also performed, all have to do with iron or cell count)
Primary hemochromatosis is a hereditary
autosomal recessive disorder
Primary hemochromatosis is characterized by increased
GU iron absorption and tissue iron deposition (too much iron)
Where is excess iron first deposited?
liver and pancreas
Following the liver and pancreas, where is the excess iron stored?
heart, joints, and endocrine glands
Secondary causes of hemochromatosis include
anemias with inefficient erythropoiesis (siderblastic anemia, aplastic anemia), dietary iron overload, or conditions that require repeated blood transfusions
Hemochromatosis iron accumulation in the body occurs due to deficiency of
hepcidin
Hepcidins job is to
decrease plasma iron levels
Iron overload in hemochromatosis results in
liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, diabetes, hypothyroidism, arthritis, cardiomyopathies, and skin hyperpigmentation
Major goal of hereditary hemochromatosis screening and treatment is to prevent
cirrhosis
Hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (neuro)
fatigue and malaise
Hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (CV)
cardiomegaly (usually restrictive), ascites, and low albumin
Hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (GI/GU)
abdominal pain, impotence, hepatomegaly, abnormal liver enzymes, and diabetes
Hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (Integ/MSK)
arthralgias and bronzed skin
Juvenile hemochromatosis usually presents before the age of
30
Juvenile hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (female)
fail to start menstrual cycle at proper age or absent and erratic periods/stops once it begins
Juvenile hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (male)
hypogonadism
Juvenile hemochromatosis clinical manifestations (other)
cardiomyopathy, a-fib, jaundice or odd colour skin (ashen grey/green/reddish), RUQ pain (liver), gallbladder/pancreas/liver problems, joint pain, rapid weight loss, irregular heartbeat, and elevated blood sugars
Due to liver involvement in hemochromatosis we should always monitor
LFTs
When assessing our patient for hemochromatosis we want to ask about their
diet
Diet to improve hemochromatosis includes
reduce consumption of red meat, avoid foods high in animal fat, limit vitamin C intake, decrease alcoholic beverages, avoid sugary foods/beverages, consume fruits/veggies, eat grains/nuts/rice/beans, avoid raw shellfish, and have meals with tea or coffee (reduces iron absorption)
Foods that contain ___ will decrease iron absorption
tannins
Sickle cell disorders are a hereditary condition where there is a replacement of normal hemoglobin with
abnormal hemoglobin
Chronic hemolytic anemia has no
cure (life long)
Sickle cell trait (most common)
1 normal hemoglobin gene and 1 sickle cell hemoglobin gene, child is a carrier of sickle cell anemia and rarely has symptoms (heterozygous)
Sickle cell anemia
2 sickle hemoglobin genes, child is subject to sickle cell crisis
Children under 5 with sickle cell disease are at increased risk for
infection, sepsis, and death
Most people with sickle cell anemia live into their
5th decade
During episodes of sickling, RBCs become ___ shaped
cresent
What three factors can increase the rate of sickling?
oxygenation, pH, and hydration (dehydration)
Decreased oxygenation causes
increased sickled cells
Lowered pH causes
increased sickled cells
Dehydration causes
increased sickled cells
Repeated sickling/unsickling weaken the RBC membranes and they are then
hemolyzed and removed
Sickle cells can regenerate (after persistent hypoxemia) when they are adequately
hydrated and oxygenated
Sickle cell disease decreases the _____ and increases the demand for ____
lifespan of RBCs, RBC production
When sickled cells occlude a blood vessel it can cause ___ and ____
ischemia, organ damage
Sickle cell diseases have an increased risk for ischemia/clots causing
strokes, PE, blockages of capillaries in kidneys, etc.
Sickle cell disease labs
CBC (hemoglobin/platelets/WBC) and creatinine/BUN
Individuals with sickle cell disease have severe ___ anemia
hemolytic (breakdown faster than replaced despite erythropoiesis)
Certain populations have an increased
risk for sickle cell diseases
Other precipitating factors for sickling include
low environmental/body temperature (altitude), excessive exercise, dehydration, infections, fever, and pregnancy
Sickle cell anemia diagnostics (newborns/children)
cord blood test (newborns), genetic testing, sickle turbidity test, and hemoglobin electrophoresis
Sickle turbidity test
tests hemoglobin in children >6 months once the fetal hemoglobin levels fall
Sickle cell anemia may be triggered by ____ and _____
fever, emotional stress
Sickle cell anemia can increase patient risk for
acute chest syndrome, stroke, infection, and priapism
Acute chest syndrome
sickle cells get trapped in the lungs
Acute chest syndrome symptoms include
fever, chest pain, progressive respiratory distress, increased WBC count, and pulmonary infiltrates
Priapism
persistent and painful erection
Sickle cell anemia HBSS acronym (clinical manifestations)
H- hemolysis
B- bone marrow hyperplasia/infarction
S- stroke
S- skin ulcers
Sickle cell anemia PAIN acronym (clinical manifestations)
P- pain/psychosocial problems/priapism
A- anemia/aplastic crisis/avascular necrosis
I- Infections
N- nocturia (frequent urination)
Sickle cell anemia CRISIS acronym (clinical manifestations)
C- chest syndrome/cardiomegaly/HF
R- retinopathy/renal failure
I- Infarction
S- sequestration crisis
I- increased fetal loss during pregnancy
S- sepsis
Sickle cell crisis occurs when the % of sickled hemoglobin ____ resulting in the appearance of symptoms usually marked by _____
increases, acute pain from ischemia
Acute ischemic pain usually occurs in
joints, heart, or kidneys
3 types of sickle cell crisis
vaso-occlusive, splenic sequestration, aplastic
Most common sickle cell crisis is
vaso-occlusive crisis (can occur over days/weeks)
Vaso-occlusive crisis occurs when stasis of blood causes sickle cells to _____, causing ____
clump in vasculature, ischemia/infarction
What may occur to local tissue if the vaso-occlusive crisis is not reversed?
thrombosis and infarction causing renal failure, AMI, strokes, etc.