Genetic Exam 1 - Bacterial Transcription
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
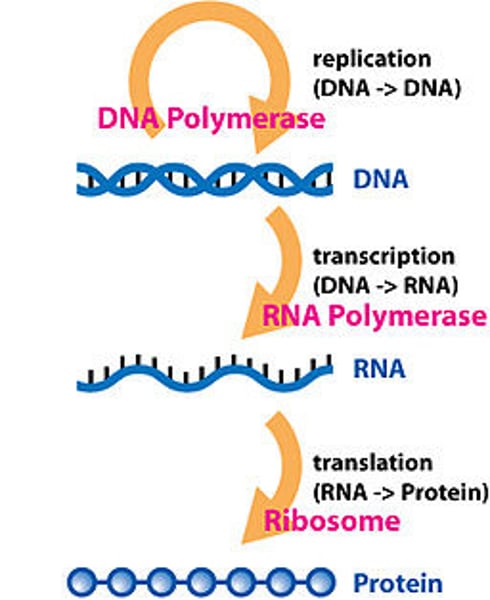
Central Dogma
DNA -> transcribed into RNA -> translated into protein
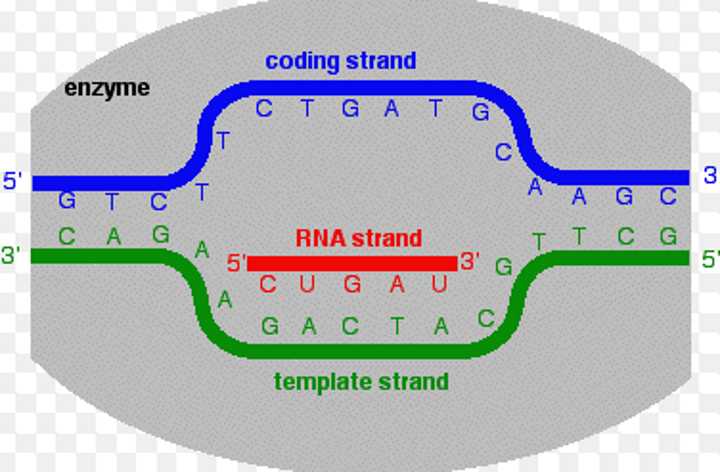
Template Strand/ non-coding
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an mRNA transcript.
3' - 5'
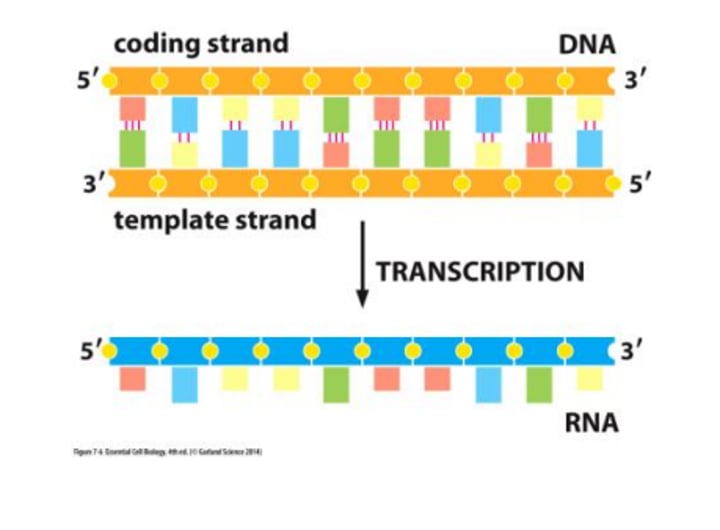
non-template strand (coding strand)
The strand of DNA that is not transcribed during synthesis of RNA. Its sequence corresponds to that of the mRNA produced from the other strand.
5' - 3'
3 stages of transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
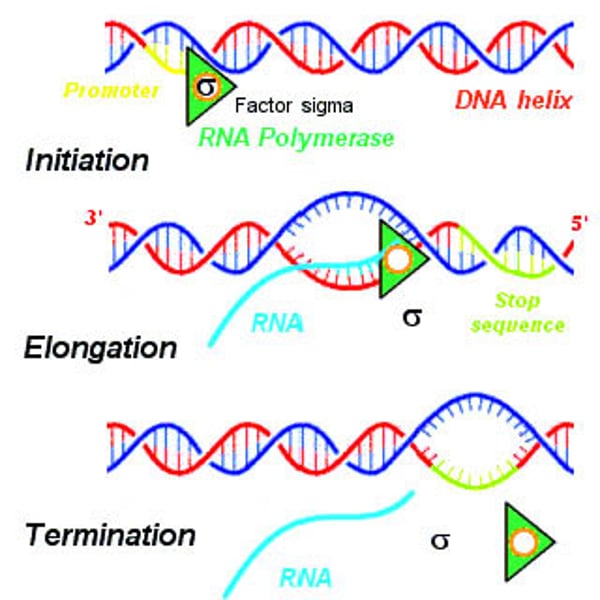
Initiation
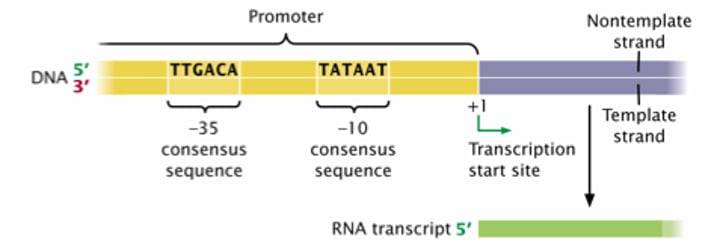
- occurs in the promoter region
- Consensus Sequences
- (-35 sequence) TTGACA
- (-10 sequence) TATAATA
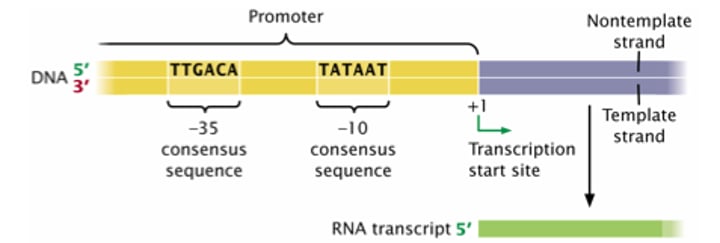
Transcriptional Start Site
+1
Transcription Factors
proteins that control the rate of transcription
Elongation
RNA nucleotides are added to the chain
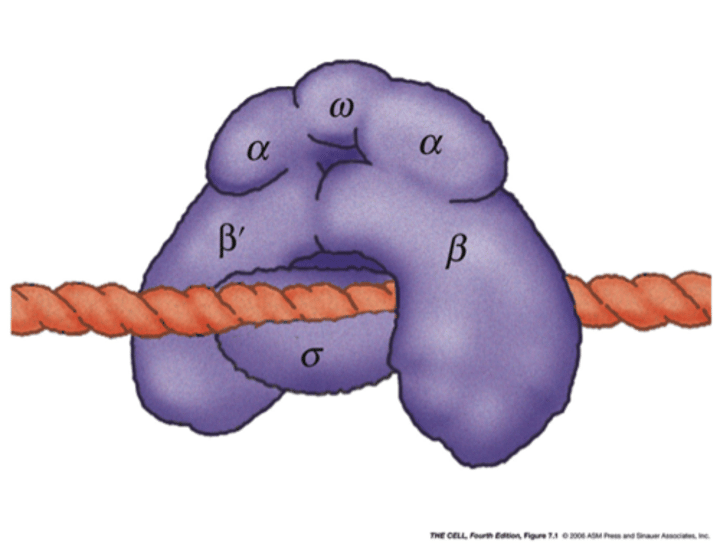
RNA Polymerase Structure
6 subunits, 4 unique
- alpha (2x): aid in assembly
- beta (2x): aid in binding and synthesis of RNA
- omega - aids in assembly of core
- sigma: recognizes promoter
Termination
2 types, RHO dependant and RHO independent
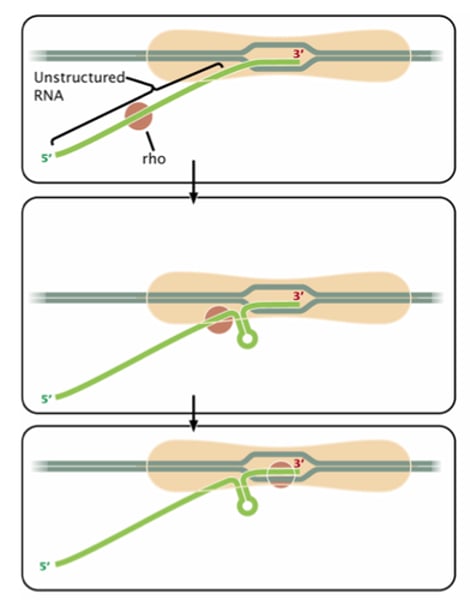
Rho Dependent Termination
- Rho utilization site (RUT): region before terminator sequence that signals the P protein
- P protein binds to rut site
- RNA polymerase stops due to hairpin and p protein shoots it off the DNA
Termination Sequence
GC rich region which ends up forming a hairpin structure to pause transcription
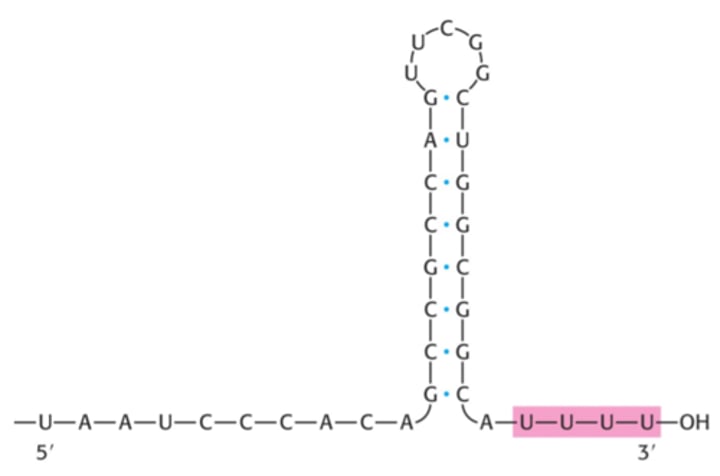
Rho Independent Termination
- GC rich region forms hairpin
- second T rich sequence results in a U rich sequence in RNA
- T - U bonds are weak and it dissociatess
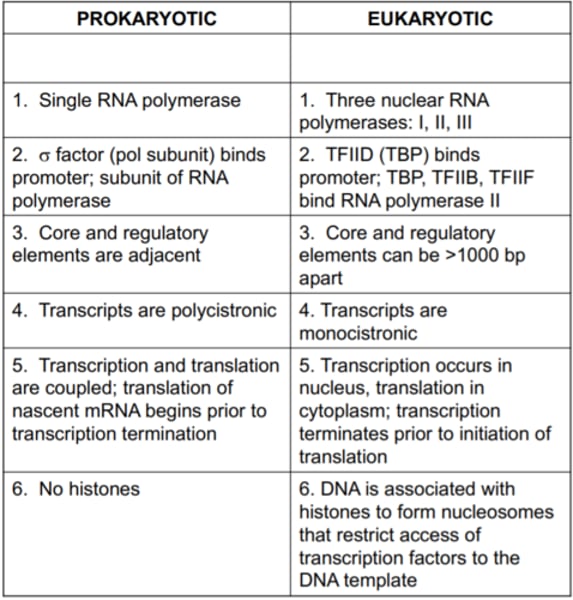
Prokaryotic Transcription vs Eukaryotic Transcription
Bacteria:
- RNA polymerase made of 6 subunits
- Promoter Region
- TTGACA -35 from +1
- TATAATA - 10 from +1
- Elongation
-