CA 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Name the drugs that work on the transporters of the presynaptic cleft
Methylphenidate
Fluoxetine
Cocaine
Amphetamine
MDMA
Name the drugs that work on the vesicles of the presynaptic cleft
Amphetamine
MDMA
How does THC affect the presynaptic cleft
It binds to the CB1 receptor & reduces the frequency of NTs being released into the synaptic cleft
Name the drugs that work on the postsynaptic cleft
Diazepam
Beta Blockers
Adrenaline
Name the drugs that work on the receptors of the postsynaptic cleft
Beta blockers
Adrenaline
Name a beta blocker
Propranolol
Name the drug that works on the ion channels of the postsynaptic cleft
Diazepam
Diazepam is a form of what type of drug
benzodiazepine
Name the receptors that are constitutively active (R*)
Cannabinoid
Benzodiazepine
Serotonin
(other receptors if diseased)
Difference between resistance, tolerance & desensitisation
Resistance = tumours/bacteria adapting to drug
Tolerance = slow adaptation
Desensitisation = fast adaptation
Name 2 phase 1 trials that were pulled & when were they pulled
TGN1412 (Theralizumab) - to treat B cell lymphoma - pulled in 2006
BIA 10-2474 - to treat Parkinson’s Disease - pulled in 2016
Opioid antidote
Nalaxone
Insulin antidote
Glucagon
Paracetamol antidote
N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
Benzodiazepines (e.g. midazolam) antidote
Flumazenil
Heparin antidote
Protamine
Anticholinesterases antidote
Pralidoxime
Novichok antidote
Atropine
Name 2 NSAIDs, give their function & mechanism
ibuprofen & aspirin (& paracetamol)
Reduce pain, fever & inflammation
Inhibit COX
Role of Statins
Reduce plasma cholesterol
Warfarin role
Anticoaggulant
Clozapine role
Treats treatment resistant schizophrenia
Role of Fluoxetine
(hydrochloride)(brand name = prozac): first successful serotonin reuptake inhibitor, used as an antidepressant
Beta-blockers (e.g. propranolol) role
Prevent β-adrenoceptor-mediated phosphorylation of calcium channels → reduced Ca²⁺ entry → decreased heart contractility.
Role of diazepam
greater hyperpolarisation. works on ion channels of post synaptic neurons (lowers chance of depolarisation)
Role of Glucocorticoids & mechanism
inhibit transcription of COX-2 (cyclo-oxygenase-2), → anti-inflammatory effect.
Name 6 opioids. Of the 6 pick out 2 full opioid agonists & 1 partial
Morphine - full opioid agonist
Heroin - full opioid agonist
Buprenorphine - partial opioid agonist
Codeine - opioid agonist
Fentanyl - opioid agonist
Methadone - opioid agonist
Name a statin & its role & mechanism
Atorvastatin - reduce plasma cholesterol - HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
Current use of Thalidomide
treatment of leprosy and multiple myeloma
Give 3 examples of Type B drug harm
Anaphylaxis to penicillin
Aplastic anaemia from chloramphenicol
Agranulocytosis from clozapine
ADR with Statins
Muscle pain
ADR with antiepileptic drugs
Teratogenic effect
ADR with Isotretinoin
Teratogenic effect
ADR with Thalidomide
Teratogenic effect - phocomelia (deletion of long bones)
ADR with Sodium valproate
In pregnancy - FVS (foetal valproate syndrome)
ADR with Clozapine
agranulocytosis
ADR with Aspirin
Long term use → gastrointestinal haemorrhage
Why was Cerustatin (Baycol) withdrawn
Why was Thiorazedine withdrawn
Why was Rimonabant withdrawn
4 signs of drug hypersensitivity
Pruritus - itch
Erythematous eruptions - rash
Urticaria - hives
Anaphylactic shock
What is Anaphylactic shock treated with
Adrenaline, chlorpheniramine, corticosteroid
4 signs of inflammation
Calor (warmth), Rubor (red), Dolor (pain), Tumor (swelling)
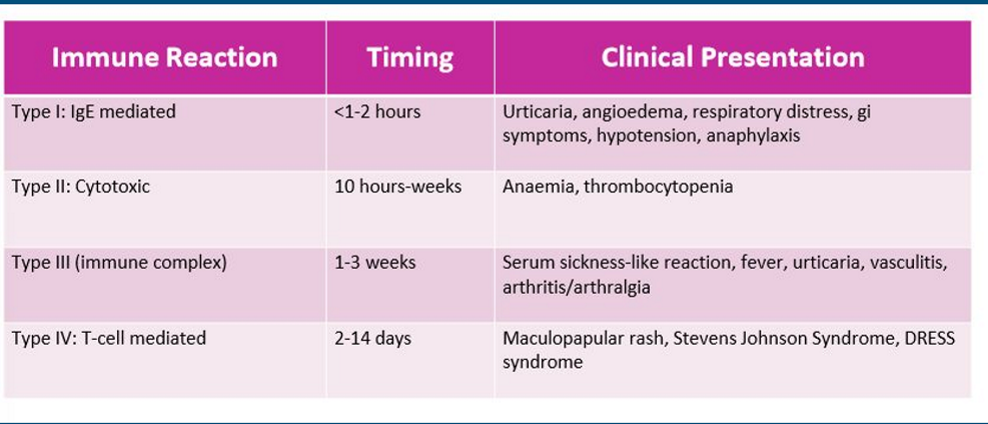
What are the 4 types of hypersensitivity, their timing & clinical presentation
What parameters can be derived from a drug/occupancy graph
Bmax
Affinity
Kd
What parameters can be derived from a conc./response graph
Potency
Efficiency
Emax
EC50
What parameters can be derived from a therapeutic/toxic dose graph
TD50
ED50
TI
Origin/Source of morphine
Opium Poppy
Origin/source of codeine
Opium Poppy
Origin/source of THC
Cannabis plant
Origin/source of penicillin
Penicillium mould
When & why was thioridazine withdrawn from the market
Withdrawn in 2005 due to QT prolongation → ventricular arrhythmias
What was the function of rimonabant (Accomplia) and when & why was it withdrawn from the market
Withdrawn in 2008. Was a treatment for obesity but doubled the risk of psychiatric disorder
Why was Cerustatin withdrawn from the market
It is a statin. Withdrawn due to rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of skeletal muscle) & death