Plant Physiology Ch. 15: Signal Transduction | Quizlet
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What does the signal transduction in plants usually involve?
"repressing a repressor"
- ON to begin with and a negative regulator is removed
What is the first plant hormone to be discovered?
auxin
An environmental input that initiates one or more plant responses is referred to as a..
signal
The physical component that biochemically responds to that signal is designated a..
receptor
Once receptors sense their specific signal, they must __________ the signal in order to amplify the signal and trigger the cellular response
transduce
Receptors trigger the cellular response by employing intracellular signaling molecules called..
second messengers
All signal transduction pathways typically involve the following chain of events:
Signal --> receptor --> signal transduction --> response
In a ______________ to an environmental signal, both signal reception and response occur in the same cell
cell autonomous response
A _____________ is one in which signal reception occurs in one and the response occurs in distal cells, tissues, or organs.
non-cell autonomous response
What is the general scheme for signal transduction?
- environmental or developmental signals are perceived by specialized receptors.
- a signaling cascade is then activated that involves second messengers and leads to a response by the plant cell.
- when an optimal response has been achieved, feedback mechanisms attenuate the signal
Where are receptors located?
plasma membrane
cytosol
endomembrane system
nucleus
__________ is the most ubiquitous second messenger in plants and other eukaryotes
Ca^2+
What is the difference between animal cascades and plant cascades?
- animal signal transduction cascades are a series of positive steps
- plant signal transduction cascade usually involves "repressing a repressor" or inactivate a repressor
What do secondary messengers do?
amplify the signal
What can secondary messengers include?
Ca^2+
pH changes
modified lipids
reactive oxygen species
What are secondary messengers?
small molecules and ions produced or mobilized in relatively high levels after signal perception, and act in the signal cascade between the receptor and response
What are the four ways that plants can increase the pool of active hormones?
1. biosynthesis
2. activation
3. release from internal stores
4. uptake
What are four ways that plants can decrease the pool of active hormones?
1. degradation
2. inactivation or conjugation
3. sequestration
4. efflux
What does the chemical structure of auxin look like?
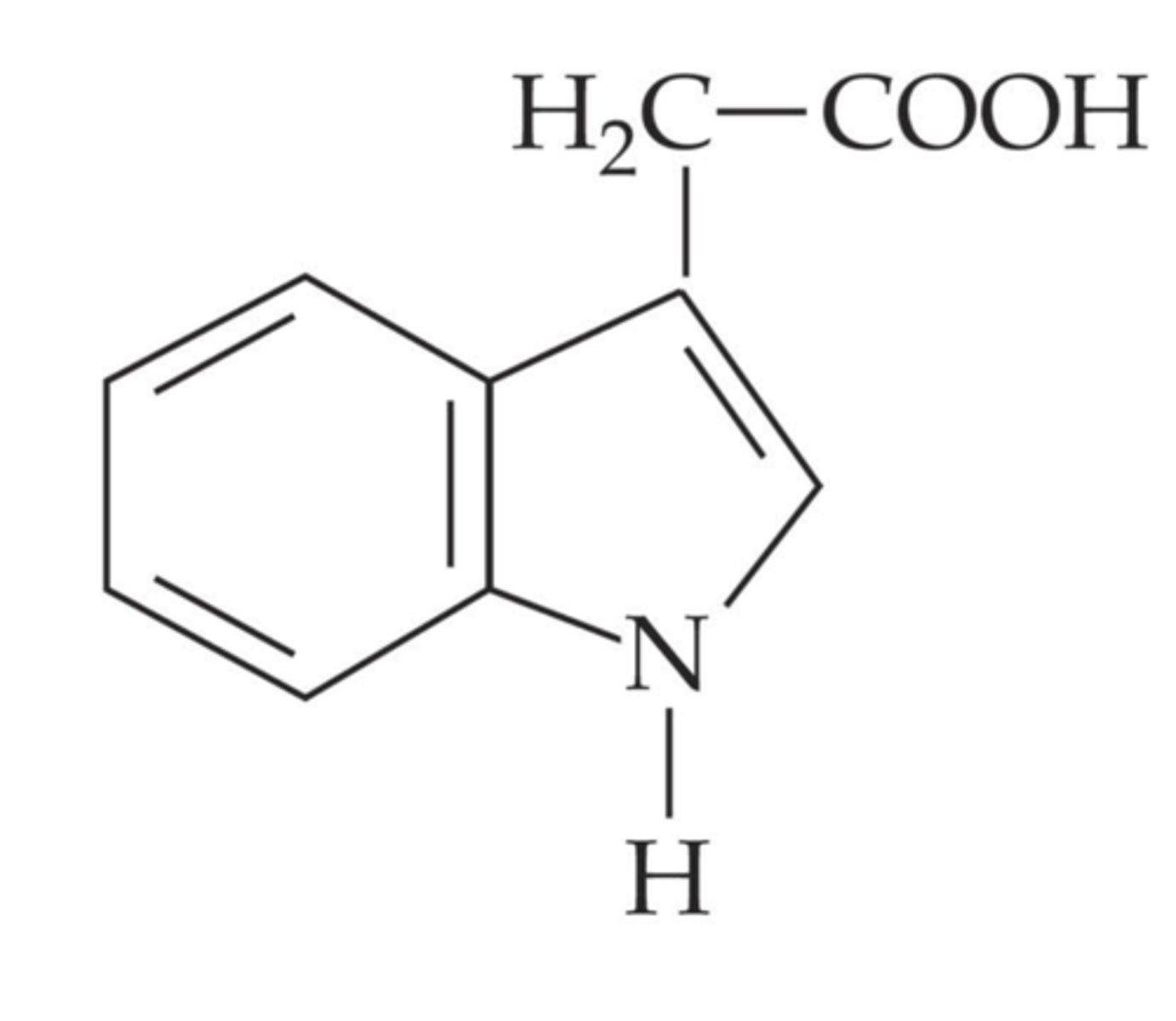
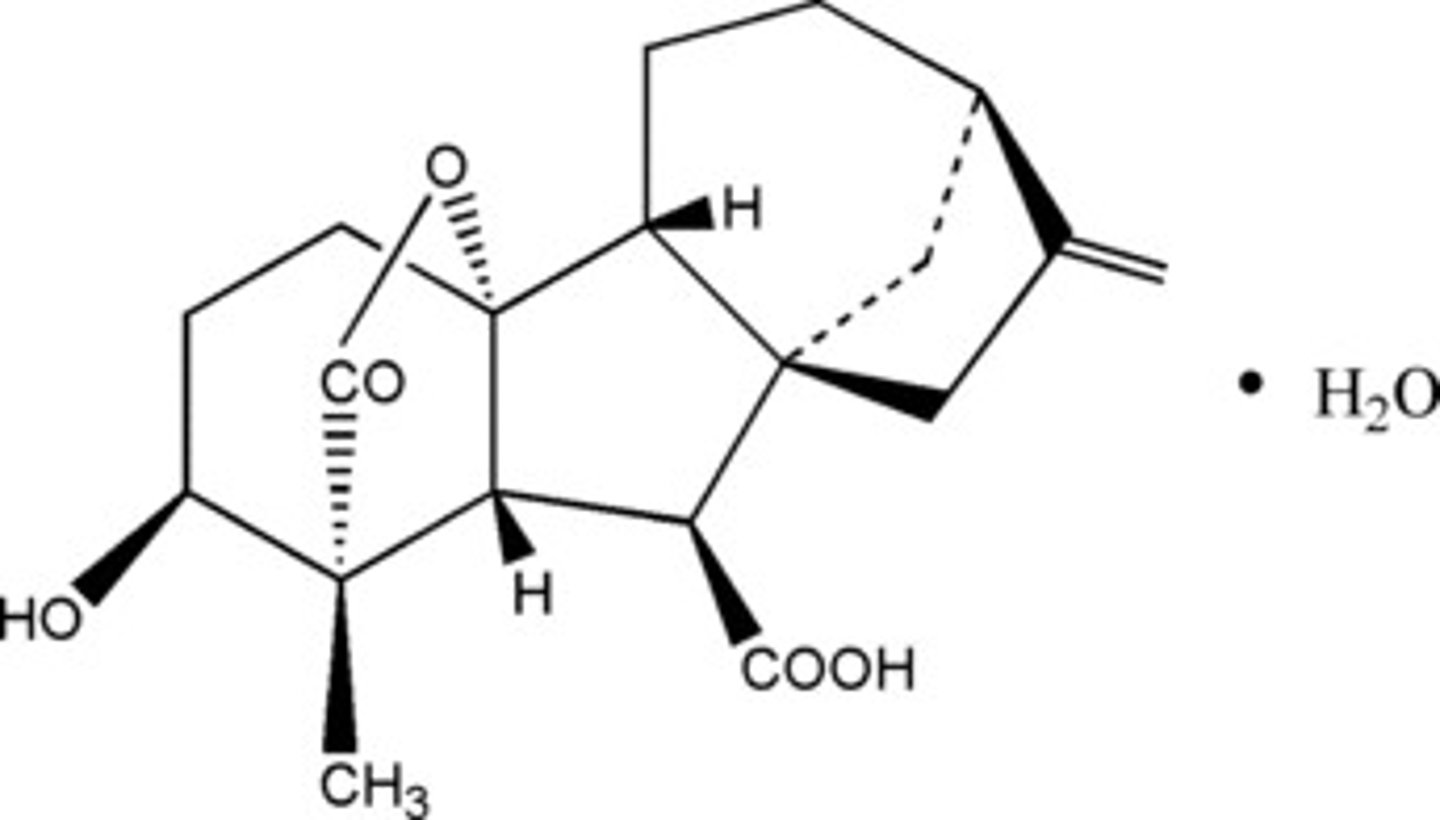
What does the chemical structure of a gibberellin look like?
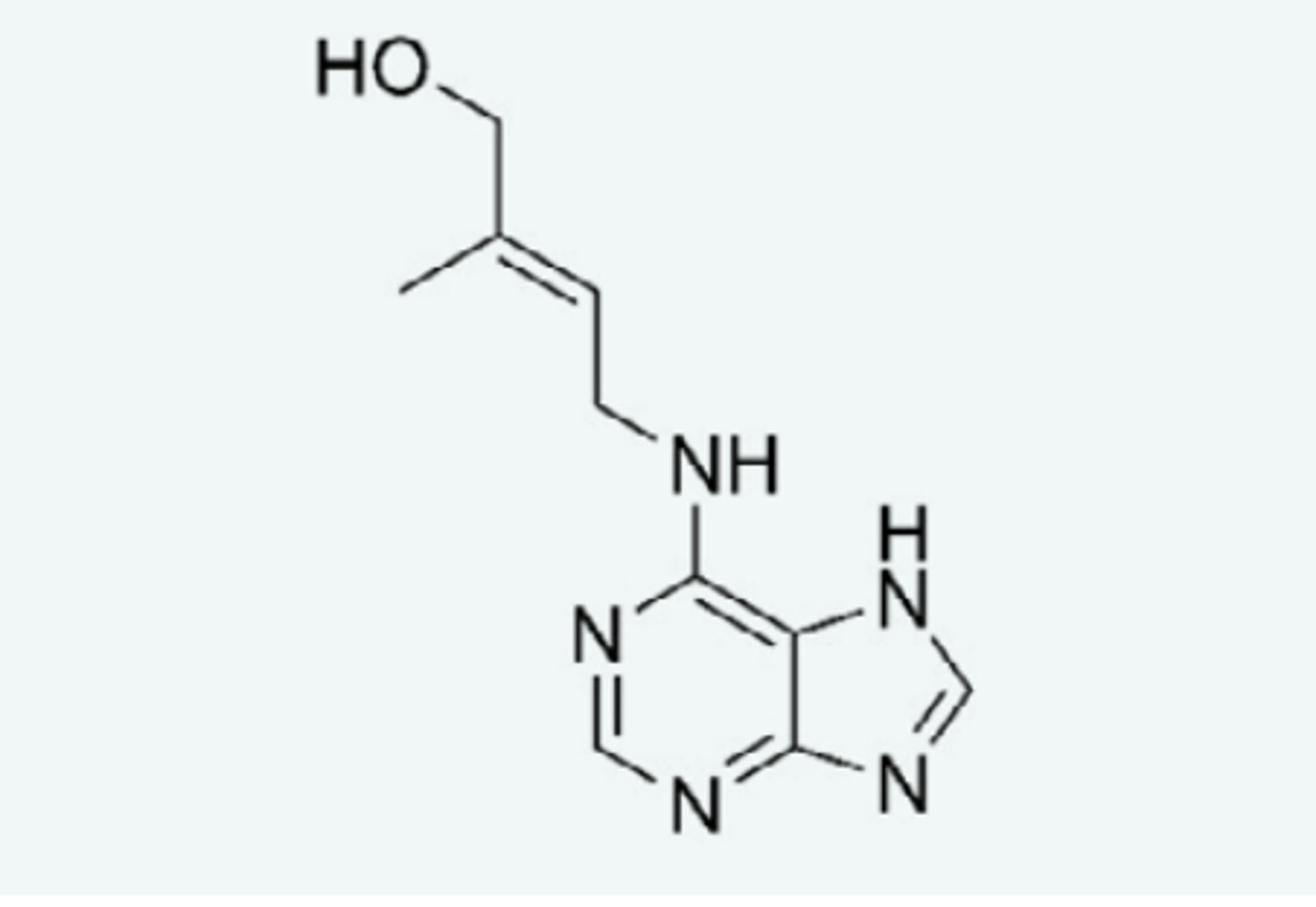
What does the chemical structure of cytokinin look like?
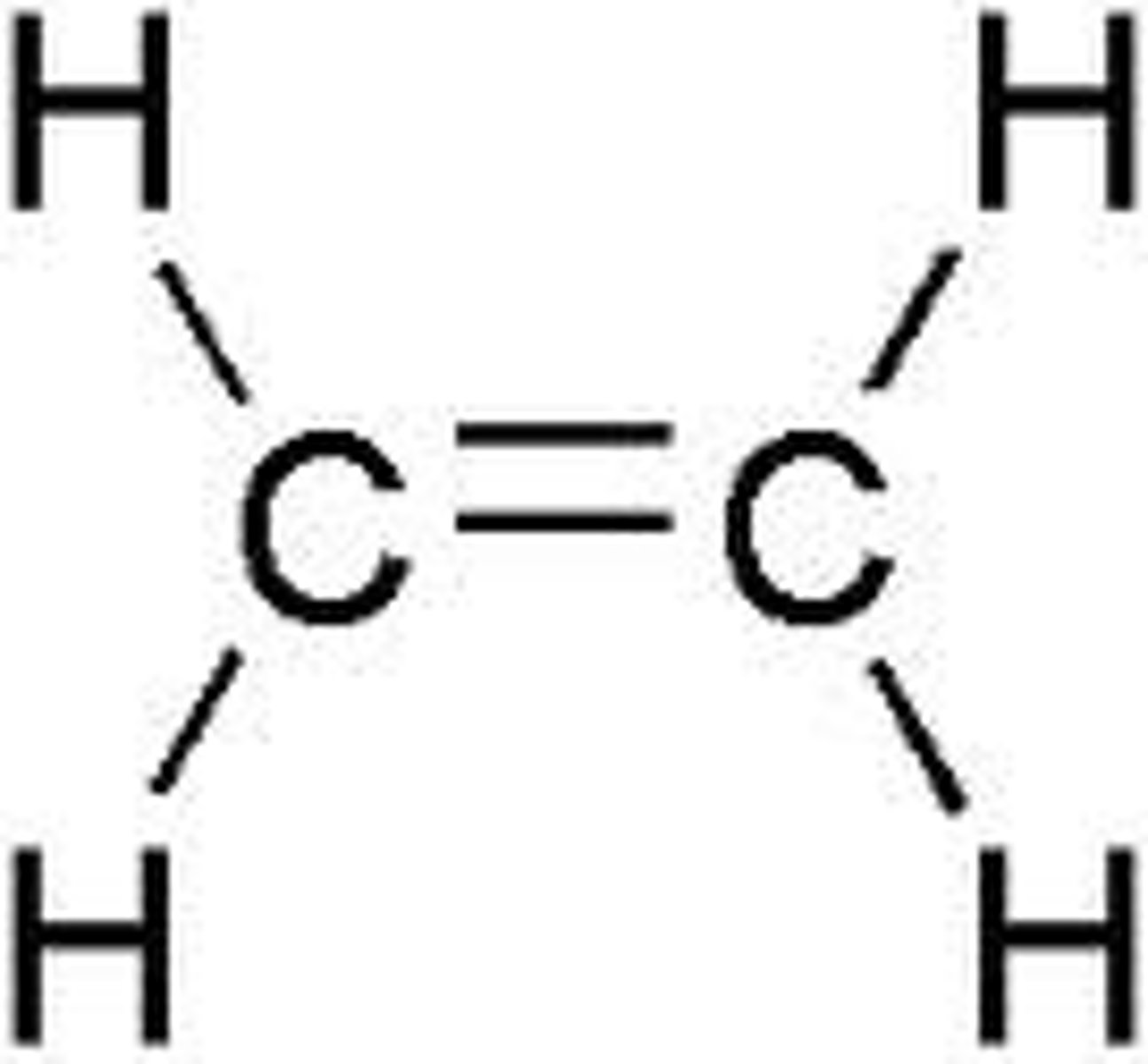
What does the chemical structure of ethylene look like?
What does the chemical structure of abscisic acid (ABA) look like?
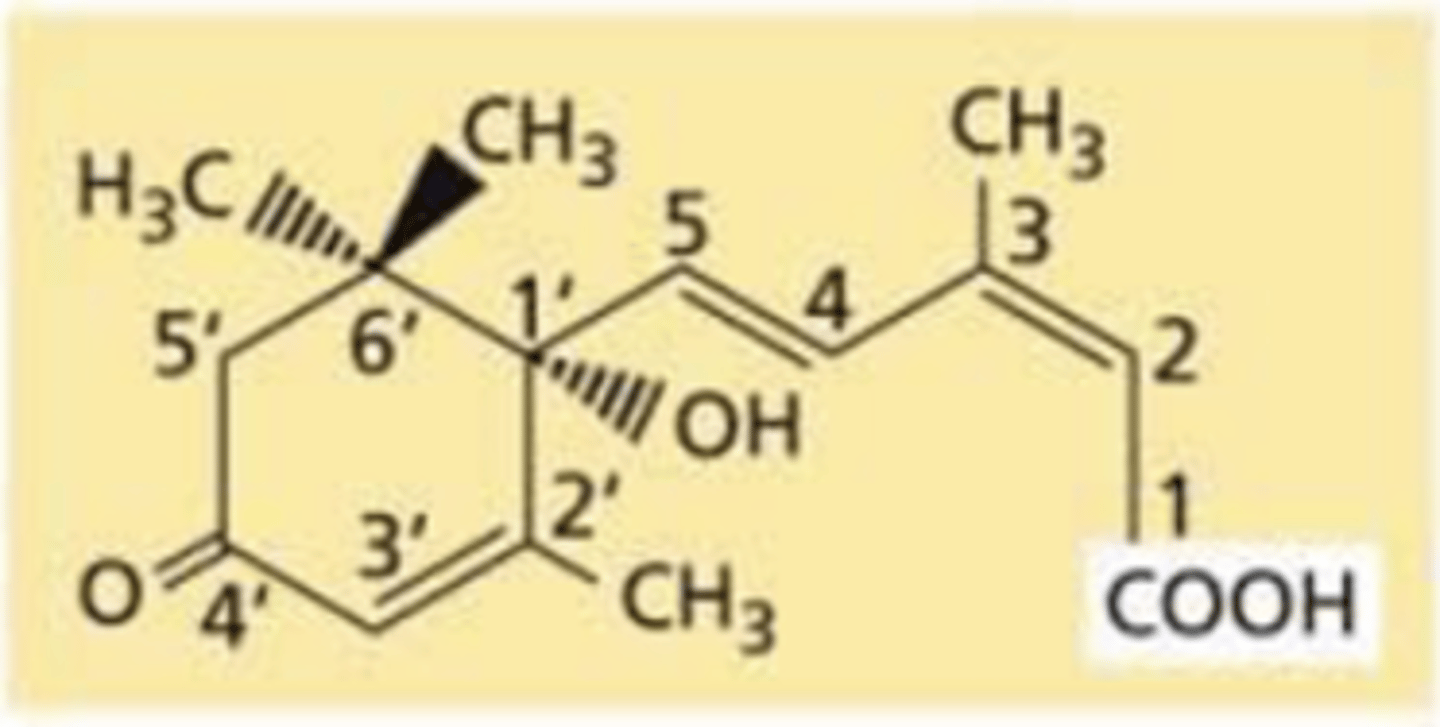
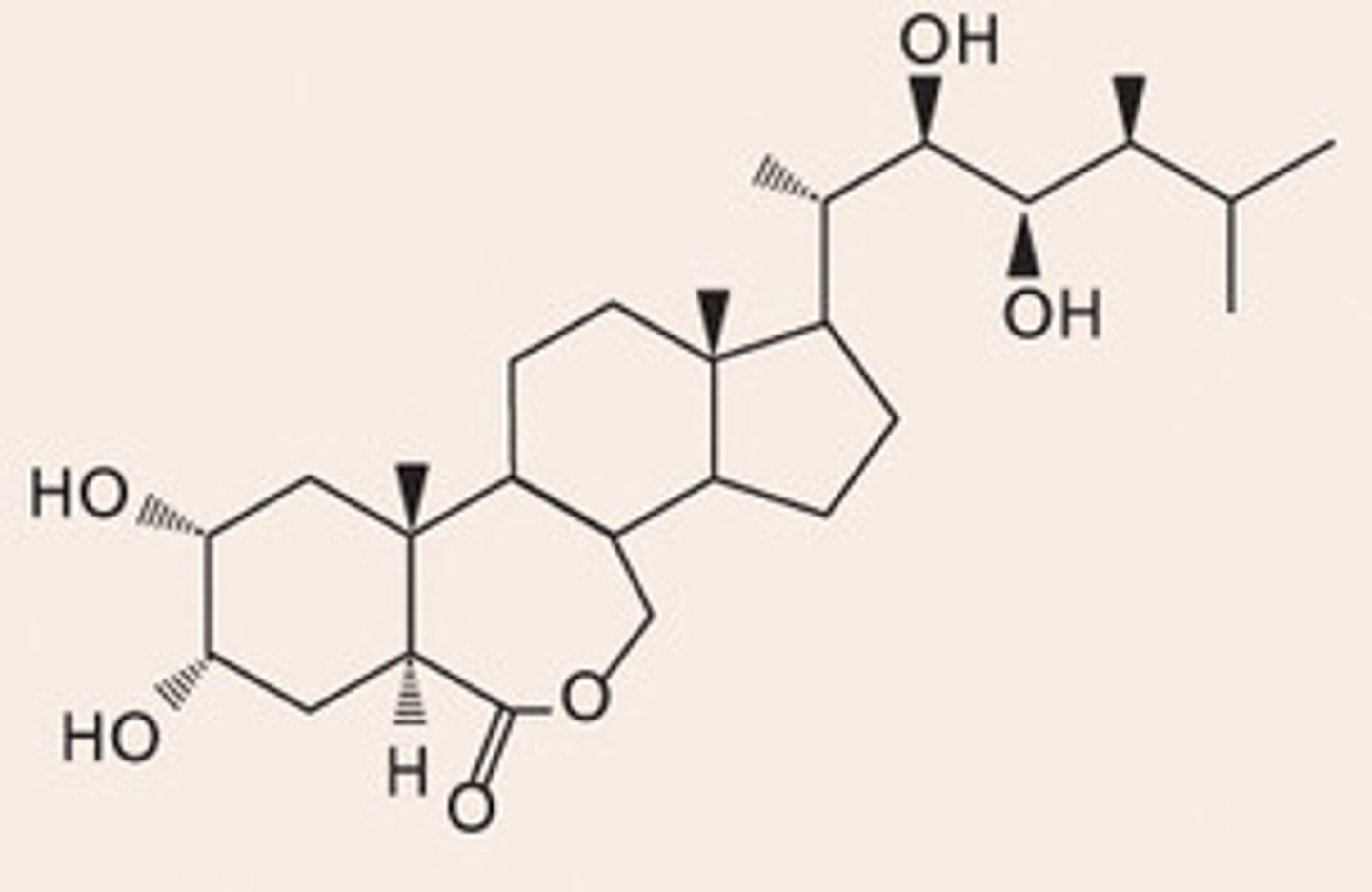
What does the chemical structure of brassinosteroids look like?
Which statement is the most FALSE regarding signal transduction cascades in plants?
Plant cascades are usually a positive activation step
A secondary messenger in a signal transduction cascade..
transmits the signal from the receptor to the site of the response
What are the 5 "classic hormones"
- auxin
- gibberellin
- cytokinin
- abscisic acid
- ethylene
What was the first growth hormone to be studied?
auxin
Who discovered the existence of auxin?
Charles and Francis Darwin
How did the Darwins discover auxin?
They studied the bending of seedling sheath leaves (coleoptiles) of canary grass and seedling hypocotyls of other species in response to undirectional light, and concluded that a signal produced at the apex travels downward and causes lower cells on the shaded side to grow faster than on the illuminated side. The signal was a chemical that could diffuse through gelatin blocks and was subsequently named auxin.
Where is auxin produced?
in the apical meristem and young organs
Auxin promotes...
cell elongation and tissue expansion
______________ are used widely in agriculture and horticulture to promote flowering and fruiting and control weeds (2,4-D)
synthetic auxins
__________ work together with auxin to control cell division and differentiation
cytokinin
What hormone are regulators of cell division in plants?
cytokinin
__________ slow aging of some organs by inhibiting protein breakdown, stimulating RNA and protein synthesis, and mobilizing nutrients from surrounding tissues
cytokinin
ex: lettuce is genetically engineered to make more cytokinin so it stays fresher longer
What is the function of gibberellins?
regulators of plant height, seed germination, and flowering
ex: think of grapes
What are some effects of gibberellin?
stem elongation, fruit growth, and seed germination
- commercially used to promote growth in grapes, and grain germination for malting to stimulate breakdown of starch in endosperm
What hormones slows growth?
abscisic acid (ABA)
What are the effects of abscisic acid?
- promotes seed dormancy and prevents premature germination
- promotes drought tolerance
In drought, ___________ causes rapid efflux of K+ and H2O from guard cells causing stomata to close and prevent water loss
abscisic acid (ABA)
An example of hormones having antagonistic functions would be __________________ promoting seed maturation and dormancy and _______________, which promotes seed germination
abscisic acid; gibberellin
When Agrobacterium tumefaciens infects a plant to form a crown gall, it transfers to the plant genes that promote the synthesis of the hormones ______________ and ______________.
auxin; cytokinin
When auxin promotes cell wall expansion, it does so by:
Enhancing activity ATPase to pump protons into the extracellular space
Which of the following statements is true of receptors in a signal transduction cascade
The receptor can be anywhere in the cell that the signal can reach
The fundamental chain of events in a signal transduction cascade is
Signal → Receptor → Signal Transduction → Response
__________ promotes seed maturation and dormancy, and antagonizes GA, which promotes germination
ABA
In response to drought, _________ promotes stomatal closure and favors root growth
ABA
What is the gaseous hormone involved in ripening?
ethylene
A burst of __________ in a fruit triggers the ripening process
ethylene
Plants produce ethylene in response to what kind of stresses?
drought, flooding, mechanical pressure, injury, and infection
What is senescence?
the programmed aging and death of plant cells, organs, or whole plants and is associated with a burst of ethylene
A change in the balance of ________________ controls leaf abscission (the process that occurs in autumn when a leaf falls)
auxin and ethylene
In a plant phosphor-relay system, which are thought to be derived from bacterial two-component signaling cascades,
A phosphate is passed from a sensor histidine kinase to a histdine phosphotransfer protein (Hpt) and then to a response regulator (ARR)
Ethylene response includes...
senescence, leaf abscission, and fruit ripening
What do brassinosteroids regulate?
photomorphogenesis, germination, and other developmental processes
- cell devision, cell elongation, germination, etc
What do strigolaactones do?
they suppress branching and promote rhizosphere interactions
- suppress shoot branching and stimulate cambial activity and secondary growth
What is IAA biosynthesis associated with?
rapidly dividing and growing tissues, especially in shoots
What are the primary sites for auxin synthesis?
shoot apical meristems, young leaves, and young fruits
Why are synthetic auxins more effective than natural auxins?
the synthetic auxins are much less subject to homeostatic control -- degradation, conjugation, transport, and sequestration -- than natural auxins are
Gibberellins are synthesized by oxidation of the ..
diterpene ent-kaurene
Ethylene is synthesized from..
methionine via the intermediate ACC
Abscisic acid is synthesized from..
a carotenoid intermediate
An example of hormones having antagonistic functions would be __________ promoting seed maturation and dormancy and _________ which promotes seed germination
ABA; gibberellin
An example of hormones having cooperative functions would be ___________ promoting differentiation into roots, and ____________ promoting differentiation into shoots
cytokinin; auxin
What are phosphorelay systems?
a series of phosphate regulated intermediates
- ancient and found in bacteria
- two-component relay system
- signal activates Histidine kinase
- Kinase causes phosphorylation of the response regulator
- histidine phosphotransfer protein (HPT) is going to shuttle between the cytoplasm and the nucleus
- it is going to take that phosphate and transfer it
- ARR --> Arabidopsis response regulator
- Type B --> transcription factors
- Type A --> phosphorylate some other protein/enzyme to activate or repress a response
True or False: Hormones can signal cells within, nearby, or far way from their site of synthesis
true
Cytokinin and ethylene pathways use derived ______________, which involve membrane bound sensor proteins and soluble response regulator proteins
two component regulatory systems
Brassinosteroids and certain auxin pathways use _______________ to phosphorylate serine or threonine regions of target proteins
transmembrane receptor-like kinases (RLKs)
Abscisic acid pathways use ______________ as well as kinases
phosphatases