CH. 11 Alkanes Flashcards
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM 8.1 Flashcards about Alkanes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Alkane
A hydrocarbon that contains only carbon-carbon single bonds.
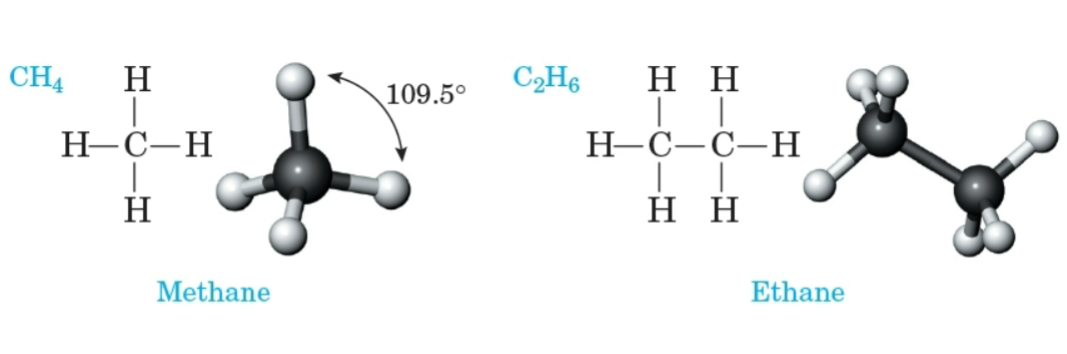
Hydrocarbon
A compound composed only of carbon and hydrogen.
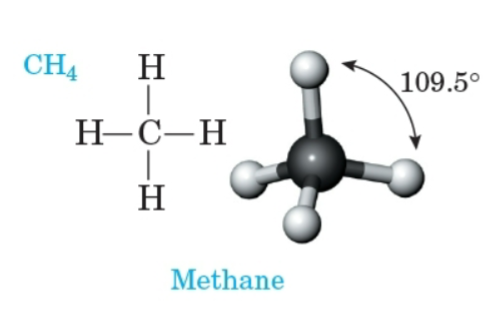
Methane
The simplest alkane, with the molecular formula CH4.
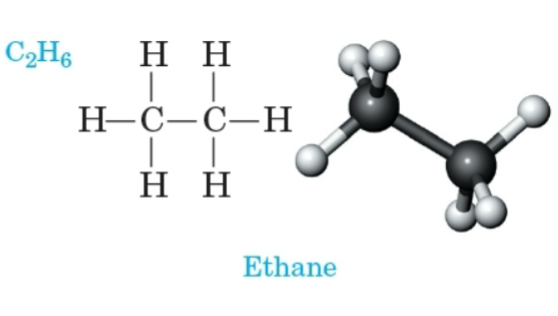
Ethane
An alkane with the molecular formula C2H6.
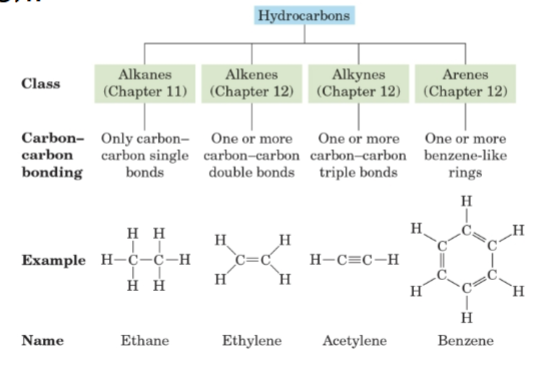
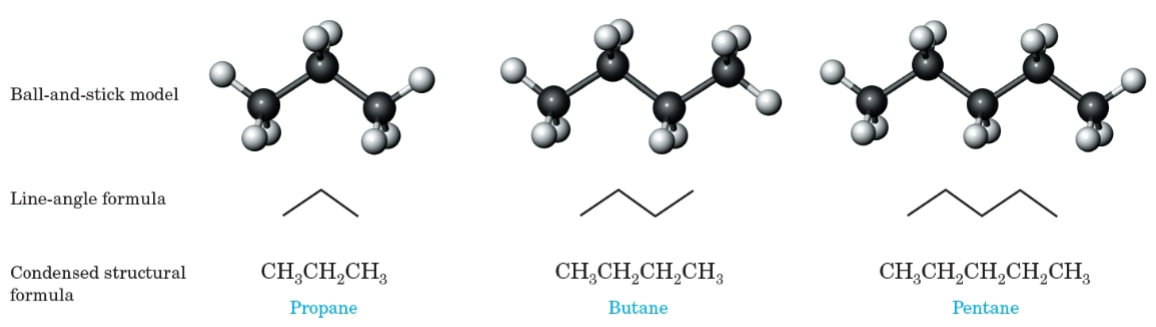
Line-angle formula
A shorthand way to draw organic structures where lines represent carbon-carbon bonds, vertices and line termini represent carbon atoms, and hydrogen atoms are not shown.
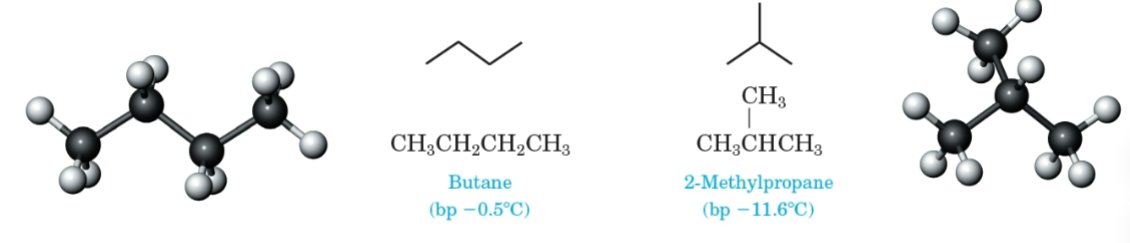
Constitutional isomers
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
IUPAC name
A systematic way to name organic compounds.
Parent name
The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in a molecule.
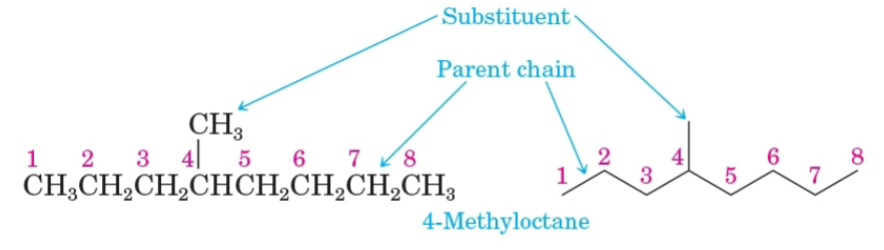
Substituent
A group bonded to the parent chain.
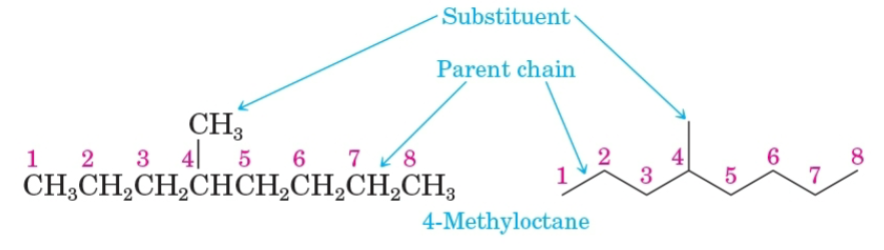
Alkyl group
A substituent group derived from an alkane by removing a hydrogen atom.
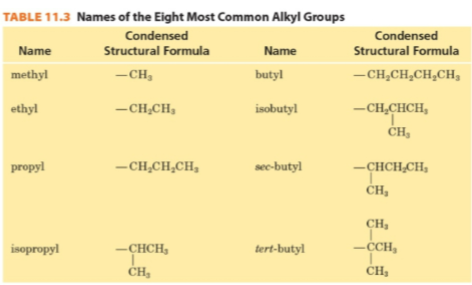
Common names
An older system for naming organic molecules.
Natural gas
A naturally occurring mixture of gaseous alkanes, mostly methane.
Petroleum
A thick, viscous liquid mixture of hydrocarbons.
Cycloalkane
A cyclic hydrocarbon in which all carbons of the ring are saturated.
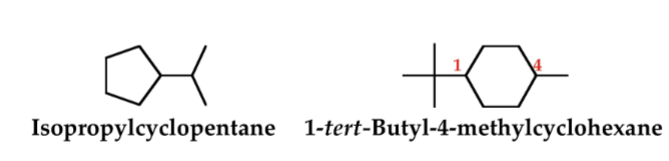
Cyclic hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon that contains carbon atoms joined to form a ring.
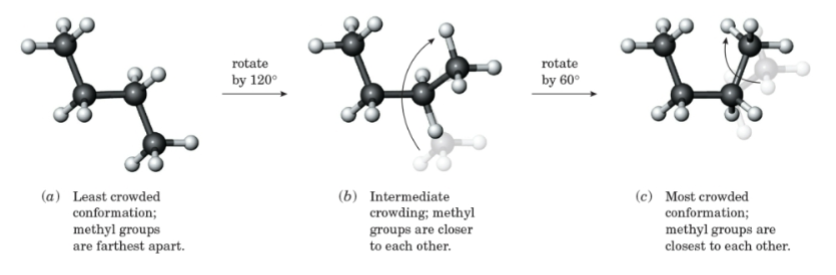
Conformation
Any three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule that results by rotation about a single bond.
Chair conformation
The most stable conformation of a cyclohexane ring.
Axial
A position on a cyclohexane ring that is perpendicular to the average plane of the ring.
Equatorial
A position on a cyclohexane ring that is approximately in the plane of the ring.
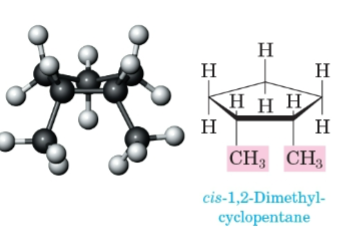
Cis
On the same side of the ring.
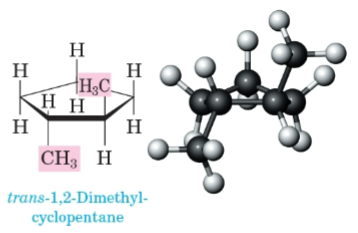
Trans
On the opposite side of the ring.
Stereoisomers
Isomers that differ in the orientation of their atoms in space, but not in their connectivity.
London dispersion forces
Weak intermolecular forces that occur between nonpolar molecules.
Oxidation
A reaction in which a substance combines with oxygen.
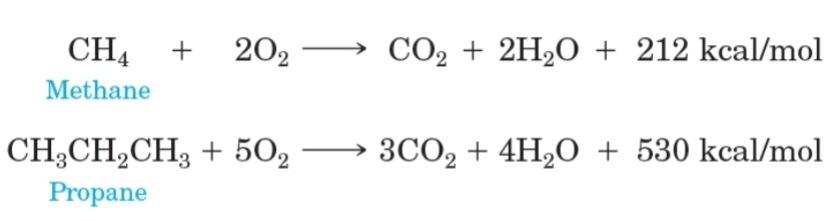
Combustion
A rapid reaction between a substance with an oxidant, usually oxygen, to produce heat and light.
Halogenation
The reaction of an alkane with a halogen.
Substitution reaction
A reaction in which one atom or group is replaced by another atom or group.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Organic compounds that contain only carbon, chlorine, and fluorine.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
Organic compounds that contain only carbon, hydrogen, and fluorine.
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs)
Organic compounds that contain carbon, hydrogen, chlorine, and fluorine.
Global Warming Potential (GWP)
A measure of how much energy the emissions of 1 ton of a gas will absorb over a given period of time, relative to the emissions of 1 ton of carbon dioxide.
Alkane
A saturated hydrocarbon.
Alkene
A hydrocarbon containing one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
Alkyne
A hydrocarbon containing one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds.
Arene
A hydrocarbon containing one or more benzene-like rings.
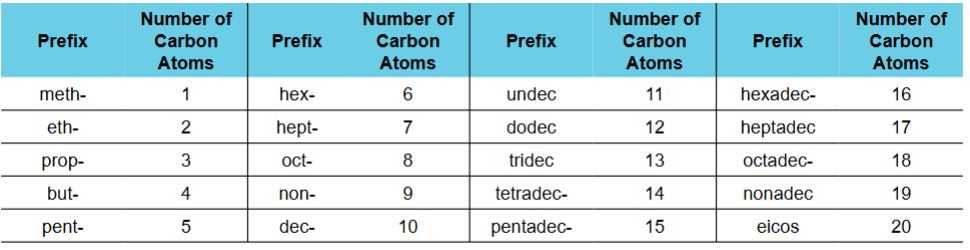
Prefix 'meth-'
Indicates the presence of one carbon atom.
Prefix 'eth-'
Indicates the presence of two carbon atoms.
Prefix 'prop-'
Indicates the presence of three carbon atoms.
Prefix 'but-'
Indicates the presence of four carbon atoms.
Prefix 'pent-'
Indicates the presence of five carbon atoms.
Prefix 'hex-'
Indicates the presence of six carbon atoms.
Prefix 'hept-'
Indicates the presence of seven carbon atoms.
Prefix 'oct-'
Indicates the presence of eight carbon atoms.
Prefix 'non-'
Indicates the presence of nine carbon atoms.
Prefix 'dec-'
Indicates the presence of ten carbon atoms.
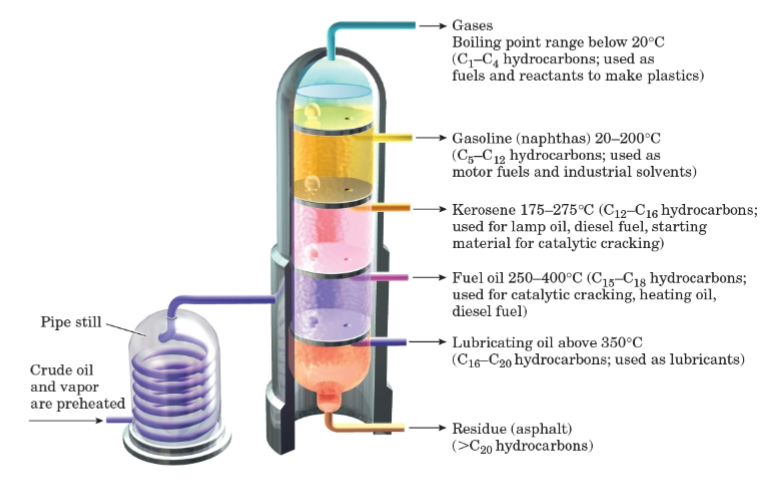
Fractional distillation
A process of separating the components of a liquid mixture based on their boiling points.
Naphthas
A volatile fraction of petroleum used as motor fuels and industrial solvents.
Kerosene
A petroleum fraction used for lamp oil and diesel fuel.
Fuel oil
A heavier petroleum fraction used for heating oil and diesel fuel.
Lubricating oil
A viscous petroleum fraction used as lubricants.
Residue (asphalt)
The heaviest petroleum fraction consisting of hydrocarbons with more than 20 carbon atoms.
Envelope conformation
The most stable conformation of a cyclopentane ring.
Boiling point trend in alkanes
Boiling points increase with increasing molecular weight.
Solubility of alkanes
Alkanes are not soluble in water but are soluble in nonpolar organic compounds.
Density of alkanes
Liquid and solid Alkanes are less dense than water.
Iso-
Shows that one end of an otherwise unbranched chain terminates in (CH3)2CH-
Prefixes in Alphabetizing
Do not include the prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, and so on or the hyphenated prefixes sec- and tert- in alphabetizing
Refrigerant gases
HFCs and HCFCs
Prefix 'eicos-'
Indicates the presence of twenty carbon atoms.
Prefix 'undec-'
Indicates the presence of eleven carbon atoms.
Prefix 'dodec-'
Indicates the presence of twelve carbon atoms.
Prefix 'tridec-'
Indicates the presence of thirteen carbon atoms.
Prefix 'tetradec-'
Indicates the presence of fourteen carbon atoms.
Prefix 'Pentadec-'
Indicates the presence of fifteen carbon atoms.