Unit 1: The Living World (Ecosystems) 1.1-1.4
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Environment
The sum of all the conditions surrounding us that influence life
Environmental science vs Environmentalism
-Interactions among human systems and those found in nature
vs
-Social movement that seeks to protect the environment through lobbying, activism, and education
APES - Four "Big Ideas"
-Energy Transfer
-Interactions Between Earth's Systems
-Interactions Between Different Species and the Environment
-Sustainability
Energy Transfer
-Conversion and transfer of energy among different components of systems (whether natural or manmade)
Interactions Between Earth's Systems
-Humans and natural factors influence Earth's systems.
Interactions Between Different Species and the Environment
-Life on Earth present for 4.5 by, but human life only past 2.5 my.
-Human tech has a profound impact on the nat'l environ
Sustainability
-Using Earth's resources in a way that doesn't jeopardize future generations
Dependent and Independent variables
-Dependent variables: factors which are being measured
-Independent variables: factors which are not being measured.
Accuracy vs Precision
-Accuracy: how close to true value
-Precision: How close repeated measurements are to eachother
Uncertainty
-Estimate of how much a value differs from the true value
Community Ecology
-The study of interactions among species.
-Consumption, competition, symbiosis.
Ecosystem
-A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
-Ecosystem boundaries are determined by abiotic and biotic factors, such as temperature, salinity, soil, etc --> can vary in size
Gause's Law (Competitive Exclusion Principle)
-Two species competing for the same resource cannot reasonably coexist.
-Negative Negative
-^leads too the extinction of the weaker competitor, or evolutionary/behavioral shift toward a different ecological niche
Resource partitioning
-Two species evolve to divide a resource through behavior or morphology in order to avoid competition.
Predation
-One animal kills and consumes another animal, in order to consume their energy. (Wolf hunting moose)
-Positive Negative
Parasitism
-One organism lives on or in another organism, consuming a small fraction of the host in order to keep it alive.
-^Sometimes consumes their prey by laying eggs inside the host organism, which then hatch and slowly consume it from the inside
-Positive Negative
Pathogens
-NOT PARASITES!
-Organisms that cause disease (viruses, bacteria, fungi, protists, and helminths worm-like parasites)
Herbivory
-Animals that only eat plants.
-An increase in herbivores can lead to collapse of ecosystems, so predation can sometimes keep them under control
-Positive Negative
Morphological defenses
-Camouflage, sharp spines, chemical defenses, mimicry
Mutualism
-A relationship between two species in which both species benefit
-Positive Positive
-EX: bees and flowers
Commensalism.
-A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
-Positive Zero
-EX: bird and tree
Invasive Species
-Species that spread quickly and cause harm to native ecosystems
Exotic/non-native/cultivated species
-Those that are out of their historical range and can have an impact on those native species.
"Biome"
-A region of the world where particular plants and animals can be found.
Terrestrial biomes
-Defined by the dominant plant growth forms as well as annual temperature and precipitation
-Tundra and taiga biomes
-Temperate biomes
-Tropical biomes
Habitat
-Where a particular species lives in nature, not characterized by plants.
-Different from biome (smaller vs bigger)
Tundra
-A cold and treeless biome with low-growing vegetation defined by permafrost, a frozen layer of soil that prevents drainage.
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-100
-Average Temp (C): -20-10
-Arctic fox, snowy owl
-Only in north bc no land in southern hemisphere
Taiga/coniferous/boreal
-A forest biome made of primarily coniferous evergreen trees that tolerate cold winters and short growing seasons, sometimes referred to as a boreal forest.
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-100
-Average Temp: -20-20
-Spruce, evergreen
-Only in north bc no land in southern hemisphere
Temperate Rainforest
-A coastal biome typified by moderate temperatures and high precipitation
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-200
-Average Temp: 0-20
Temperate Seasonal/ Deciduous Forest
-A biome with warm summers and cold winders with over 1 meter (39 inches) of annual precipitation.
-New Jersey!!!!
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-100
-Average Temp: 0-20
Shrubland/Woodland
-Characterized by hot, dry summers, and mild, rainy winters
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-100
-Average Temp: 10-20
Temperate grassland/cold desert
-Sometimes referred to as a cold
desert, typically has cold, harsh
winters and hot, dry summers
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-100
-Average Temp: 0-25
Tropical Rainforest
-Warm and wet biome found between 20° N and 20° S of the equator, with little seasonal temperature variation, and high precipitation, soils are typically poor (heat + water = weathering and erosion)
-Average Precipitation (mm): 200-400
-Average Temp: 20-30
Savana
-Also known as tropical seasonal forest, is known for warm temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0-200
-Average Temp: 10-25
Hot Desert
-Located at roughly 30° N and 30° S with hot temperatures, extremely dry conditions, and sparse vegetation
-Average Precipitation (mm): 0
-Average Temp: 10-20
Aquatic Biomes
-Characterized by different means, such as salinity, depth, and water flow
-Freshwater
-^Streams, rivers, lakes, and wetlands
-Marine (Seawater)
-^Estuaries (where freshwater rivers meet ocean water), coral reefs, and open ocean
Freshwater biomes: Rivers and Streams
-Low salinity and are categorized as streams, rivers, lakes, ponds, and freshwater wetlands.
-MUST have flowing freshwater.
-Fast-moving streams tend to combine, forming rivers, which then slow down.
-Streams tend to have few plants and algae
-^When combined into a slower moving river, more sediments and organic material settle so plant growth
Freshwater biomes : Lakes/ponds - zones
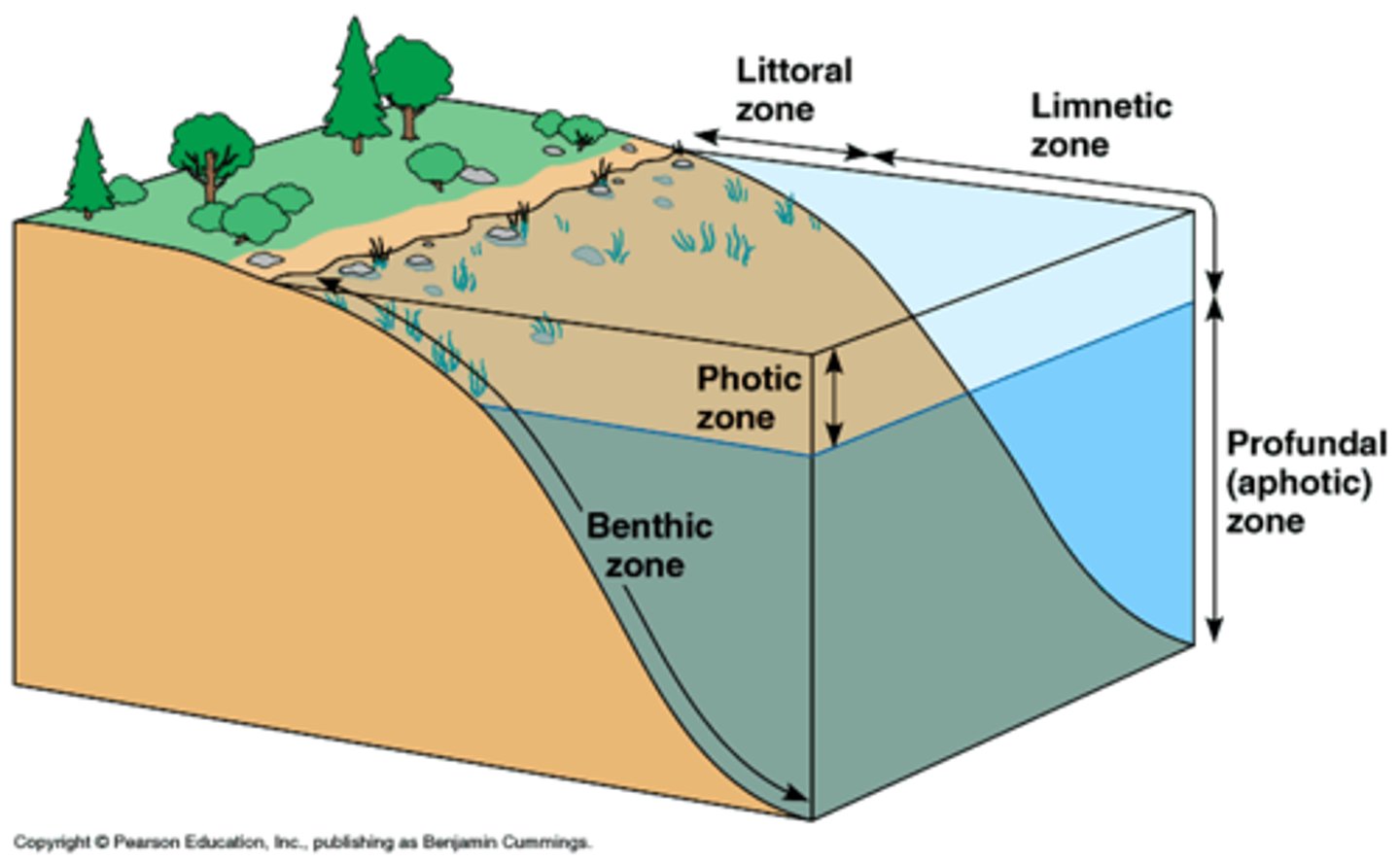
-Lakes and ponds tend to have standing water, and may be too deep to support vegetation except near the shorelines, or the littoral zone (shallow down-sloping shelf).
-Limnetic zone: layer that receives
sufficient sunlight, allowing for photosynthesis. AKA “photic zone”. Photosynthetic algae!
-Profundal zone: Areas WITHOUT sunlight
-Benthic zone: BOTTOM of lake, pond, or ocean.
Classification of lakes through nutrients
-Oligotrophic lake = LOW amount of nutrients
-Mesotrophic lake = MODERATE amount of nutrients
-Eutrophic lake = HIGH amount of nutrients
-^Eutrophic lakes can have high concentrations of algae which block light → underwater plants can not perform photosynthesis!
Freshwater biomes : Freshwater wetlands
-Land that is saturated by water for at least part of the year, but shallow enough to support vegetation.
-Many bird species depend on wetlands during migration and breeding seasons.
-Much of these areas have been drained for agriculture and development.
-Marshes, swamps, bogs, fens, etc.
Marine biomes
-Characterized by salt water
-Estuaries/salt marshes
-Mangrove swamps
-Intertidal zones
-Open ocean
Marine biomes : Estuaries
-Near coast lines where rivers of freshwater and saltwater from the ocean combine --> Mark transition zone from land to sea.
-Tend to carry nutrients from rivers; estuaries then become very productive areas, and can help filter contaminants.
-Lack of biodiversity
-brackish water
Marine biomes: Salt Marshes
-Coastal wetlands that are defined by the areas flooded with saltwater and subsequently drained (often based on tide cycles)
-The safety provided by both estuaries and salt marshes mean that they tend to be nurseries for fish and other organisms.
Marine biomes: Mangrove Swamps
-Occur near tropical and subtropical coasts, and are characterized by mangroves with roots that rise above water to survive high salt content.
Marine biomes: Intertidal zones
-Narrow bands of coastline that exist between high and low tide.
-Many species must adapt to extreme temperatures and desiccation (loss of moisture)
Marine biomes: Coral Reefs
-Earth's most diverse marine biome, found in warm shallow waters beyond the shoreline in tropical regions.
-They are characterized by symbiotic coral species that are prone to coral bleaching.
Flowing water: Freshwater (low salinity) vs Marine (high salinity)
-Streams and Rivers
-Estuaries/salt marshes, mangrove swamps
Standing water, Deep water: Freshwater (low salinity) vs Marine (high salinity)
-Ponds and lakes
-Open Ocean
Standing water, Shallow water: Freshwater (low salinity) vs Marine (high salinity)
-Freshwater wetlands
-Coral reefs
Fluctuating water depths: Freshwater (low salinity) vs Marine (high salinity)
-N/A
-Intertidal zones