3.1.4 - proteins
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.1.4.1 (general properties of proteins) - 3.1.4.2 (many proteins are enzymes)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
what monomers are polypeptides made from
what do polypeptides combine to form
amino acids
proteins (note: amino acids are still the MONOMERS proteins are made from!)
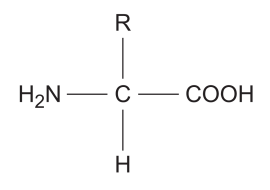
diagram of general structure of amino acids
more visual diagram of general structure of amino acids
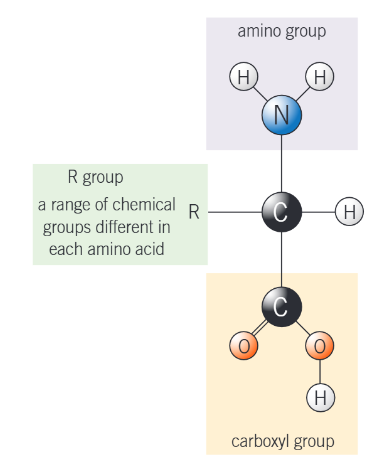
what does each part in the diagram represent?
NH2 - an amine group, the AMINO part of amino acid
COOH - a carboxyl group. an acidic group, the ACID part of amino acid
H atom
R - a side chain
the R group can be a v_______ of different groups
variety
how many amino acids are common in all organisms?
20
what is the only way in which they differ?
in their R (side) group
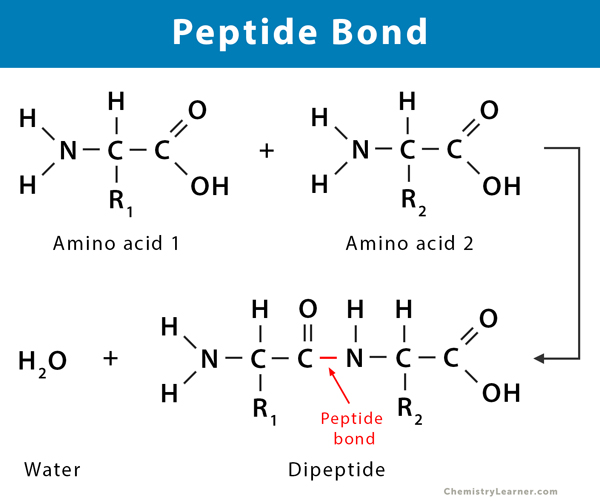
how is a peptide bond formed between 2 amino acids
by a condensation reaction (and hence the removal of a water molecule)
what are dipeptides formed by?
the condensation of 2 amino acids
how is the water molecule made
by combining an —OH from the carboxyl group of one amino acid
and a —H from the amino group of another amino acid
what is the resulting peptide bond between (like what atoms is it between)
the C atom of one amino acid
and the N atom of the other
what can the peptide bond of a dipeptide be broken by (to give 2 amino acids)
hydrolysis (the same way a glycosidic bond of a disaccharide can be broken by the addition of water)
diagram of formation of a peptide bond
what are polypeptides formed by?
the condensation of many (hundreds of!) amino acids
what forms the primary structure of a protein
the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
what is this sequence determined by
DNA
why is there an almost limitless number of possible combinations (and therefore types) of protein structures
polypeptides have many of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids
and these are joined in different sequences
what does the primary structure of a protein determine
shape
function
what can lead to a change in the shape of the protein
what may this stop the protein from doing
a change of just a single amino acid in the primary sequence
carrying out its function
hence, a protein’s shape is v___ s________ to its function. change its shape and it will function l___ w____, or differently.
hence, a protein’s shape is very specific to its function. change its shape and it will function less well, or differently.
how many polypeptides does a functional protein contain?
a simple protein may consist of 1.
more commonly, a protein is made up of more / lots of polypeptides
on either side of every peptide bond, what 2 groups are there?
—NH group and —C==O groups
the H of the —NH group has an o________ p_________ c_______ while the O of the —C==O group has an o_________ n__________ c_______
the H of the —NH group has an overall positive charge while the O of the —C==O group has an overall negative charge
therefore, what do these 2 groups readily form
weak bonds (hydrogen bonds)
what does this cause the long polypeptide chain to twist into
a 3D shape
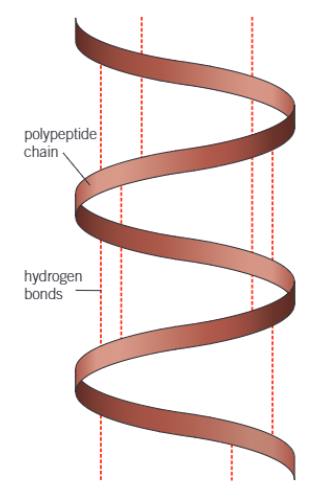
hence, what is the secondary structure of a protein
the shape which the polypeptide chain forms as a result of hydrogen bonding
give 2 examples of the secondary structure of proteins
alpha helix (α-helix), which is a coil
beta-pleated sheet
diagram of the structure of the α-helix
what can the α-helices (plural of helix) of the secondary protein structure be twisted + folded even more into
what is this known as
the complex (and often specific) structure of each protein
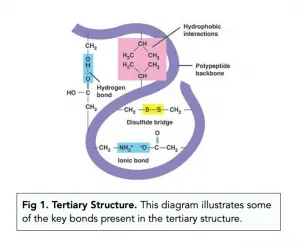
the tertiary structure
what is the tertiary structure maintained by
different bonds
where the bonds occur depends on…
the primary structure of the protein
what 3 bonds do these include
disulfide bridges
ionic bonds
hydrogen bonds
describe strength of disulfide bridges
are they easily broken?
fairly strong
no
what are the ionic bonds formed between
describe their strength compared to disulfide bonds
what are the ionic bonds easily broken by?
any carboxyl and amino groups that are not involved in forming peptide bonds
weaker than disulfide bonds
changes in pH
in summary, what is the tertiary structure of proteins
the bending and twisting of the polypeptide helix into a compact structure
all 3 types of bond (hydrogen, ionic and disulfide) contribute to the maintenance of this structure
diagram of tertiary structure of proteins
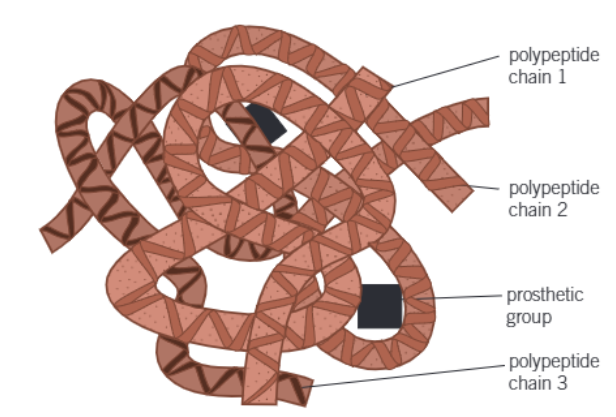
what is the quatenary structure of proteins
when large proteins form complex molecules
containing a no. of individual polypeptide chains
that are linked in various ways
what may also be associated with the molecules
give an example of these
non-protein (prosthetic) groups
the iron-containing haem group in haemoglobin
diagram of the quaternary structure
relationship between primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure, and protein function
basically, the 3D shape of the protein (determined by primary, secondary, tertiary and quatenary structure) is essential for the protein’s function
3D shape of the protein allows it to be distinctive, to recognise and be recognised by other molecules so it can interact with them in a v. specific way (this is the protein’s function)
what is the test for proteins
what exactly does it detect
biuret test
peptide bonds
how to carry out a biuret test
place sample in a test tube
add an equal vol. of NaOH at room temp.
add a few drops of v. dilute copper (II) sulfate solution
(or check if you can just say add biuret’s reagent)
mix gently
what indicates peptide bonds (and hence proteins) are present
what means proteins aren’t present
if solution turns purple
if solution stays blue
what are fibrous proteins
what are their functions
long, insoluble strands of polypeptide chains
structural functions, e.g. to provide strength, to support tissues like skin, bone, hair
describe the structure of a fibrous protein in more detail
long, rope-like shape
repetitive, stable amino acid sequences
many H bonds between polypeptide chains —→ these provide strong cross-linkages (remember, even though the H bonds are weak on their own, altogether, they are strong)
why are fibrous proteins insoluble
have a large proportion of hydrophobic R groups
give 2 examples of fibrous proteins
collagen —→ forms connective tissues
keratin —→ found in hair and nails
what are globular proteins
what is their function
compact, spherical macromolecules
to perform vital biological functions
describe the structure of globular proteins in more detail
have hydrophobic amino acid side chains clustered in the center
have hydrophilic amino acids on the surface
what does this structure allow to happen (i.e. how is it suited to its function)
H2O molecules can surround the protein
so the protein is soluble in water
this = essential for their transport and involvement in metabolic processes / transport
extra: why are globular proteins considered more unstable than fibrous proteins
they can undergo denaturation from environmental changes, whereas fibrous proteins have strong cross-linkages (from the H bonds)
give four examples of globular proteins, and the aforementioned vital biological functions they carry out
enzymes —→ catalyzing reactions
haemoglobin —→ transports molecules (O2)
hormones
antibodies
what do catalysts do
alter the rate of a chemical reaction
w/o undergoing permanent changes themselves
spec points to make flashcards on
3.1.4.2, all the bullet points and everything after that, and the RQ1
how many times can catalysts be used
so they are therefore effective in…
repeatedly
small amounts
what is activation energy
minimum amnt. of energy req. for a chemical reaction to occur
what does an enzyme do in the reaction it catalyses
lowers the activation energy
so reactions can take place at a l_______ t_________________ than normal
lower temperature
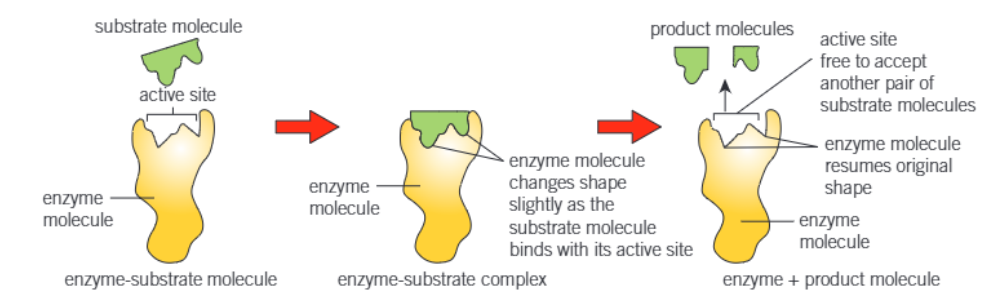
what is formed when a substrate binds to an active site
enzyme-substrate complex
KIND OF EXTRA: how is the substrate molecule held within the active site
by bonds
that temporarily form between certain amino acids of the active site
and groups on the substrate molecule
what does the induced fit model of enzyme action propose
that the active site forms as the enzyme and substrate interact
the enzyme has a certain general shape, but it is flexible and can alter in the presence of the substrate by molding itself around the substrate
what does the enzyme do to the substrate molecule when it changes shape
puts a strain on it
what does this strain do
distorts a particular bond / bonds in the substrate
consequently = lowers the activation energy required to break the bond
any change in the enzymes’s e______________ is likely to change its s_______
environment, shape
the very act of colliding with its substrate is a change in its environment
and so its shape changes —→ induced fit
say substrate is COMPLEMENTARY to active site
diagram of all the mechanism of enzyme action
what do almost all the factors that affect the rate of enzyme-controlled reactions affect?
the substrate
the active site
what are these factors
enzyme conc
substrate conc
conc of competitive + non -competitive inhibitors
pH
temperature
to investigate how enzymes are affected by various factors, we need to be able to measure the rate of the reactions they catalyse. we do this by…
measuring its time-course (how long it takes for a particular event to run its course). this includes:
the formation of the products of the reaction
the disappearance of the substrate
graph for formation of the product
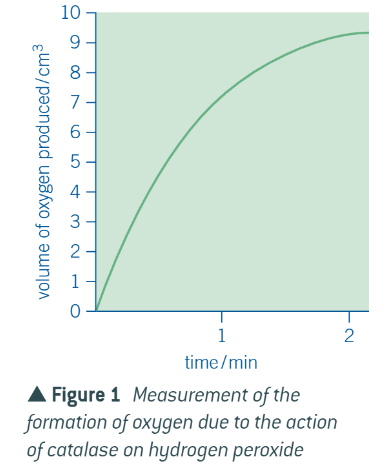
graph for disappearance of the substrate
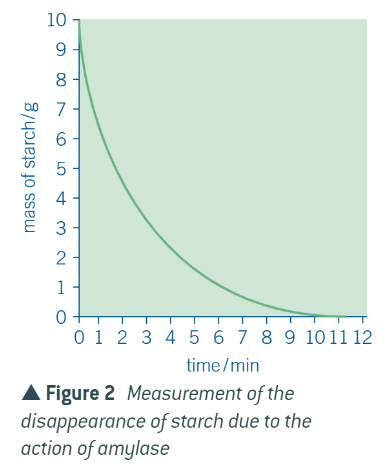
explanation of these graphs is the same:
at first = a lot of substrate and not product
easy for substrates to come into contact w empty active sites
all active sites = filled, and substrate is broken down into products
as reaction proceeds = less substrate, more product
becomes more difficult for substrates to come into contact w/ active sites BECAUSE there are fewer substrates + product molecules may get in the way of substrates reaching the active sites
so, takes longer for substrate molecules to be broken down by the enzyme, so rate of disappearance slows, and consequently, rate of formation of product also slows
when graphs flatten out = all substrate has been used up, so no new product can be produced
how to measure rate of change in a a reaction at a certain point on a curved graph
draw a tangent to graph at the point (make sure the tangent doesn’t cut THROUGH the graph)
find the gradient of this (change in y / change in x)
rate is always expressed…
per unit time (NOT hertz 💔)
when investigating the effect of a named variable on the rate of an enzyme reaction…
all other variables must be kept constant
EFFECT OF TEMP:
a rise in temp. increases the k_______ e______ of molecules
what happens as a result
kinetic energy
molecules move around more rapidly + collide w/ each other more often
more enzyme-substrate complexes are formed
so RoR = increases.
graph of effect of temp. on an enzyme controlled reaction
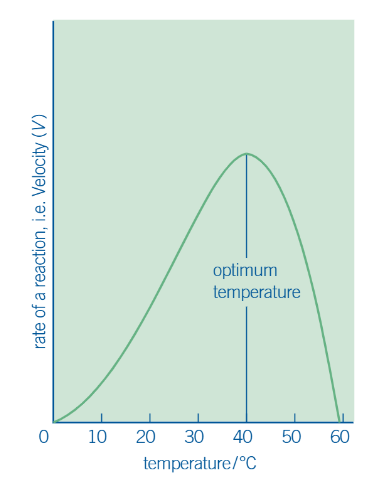
description of graph
gives a rising curve
curve peaks at optimum temp, where enzyme works most efficiently.
but increasing temp = causes H bonds + other bonds in molecule to break
so enzyme starts to change shape —→ substrate fits less easily into changed active site —→ slowed rate of reaction. curve starts to fall.
at some point (usually around 60 degrees) = enzyme denatures. (permanent change, enzyme does not function again)
how to calculate pH of a solution
press log button on calc
in the bracket, enter the H ion conc (given)
press equals. should give you the answer
example: H ion conc = 1 × 10-9. so do log (1 × 10-9) which gives pH = 9.
effect of pH on enzyme action
each enzyme has a optimum pH. an increase / decrease in optimum pH
if change in pH = extreme, then beyond a certain pH, enzyme denatures.
what does a change in pH do to the active site
alters the charges on the amino acids that make up the active site
so substrate can no longer attach to it
and enzyme-substrate complex can no longer be formed
may also cause bonds maintaining enzyme’s tertiary structure to break —→ active site therefore changes shape
kinda extra: why is the bonding in the active site changed
arrangement of active site = partially determined by H bonds and ionic bonds between —NH2 and —COOH groups of the polypeptides that make up the enzyme
change in H+ ions affects this bonding (so active site changes shape)
graph of effect of pH on the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction
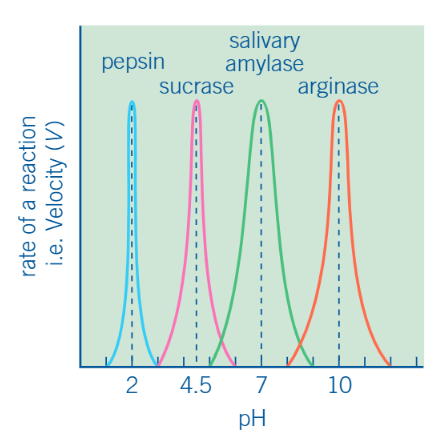
description of graph
increasing pH (towards optimum): activity rises as environment becomes more favorable
decreasing pH (away from optimum): activity drops as H+ interfere with enzyme-substrate binding
extreme pH: at very low / high pH, enzyme denatures —→ reaction rate falls to zero
effect of enzyme conc. on rate of reaction
as long as there is an excess of substrate, an increase in the amount of enzyme leads to a __________ in the rate of reaction
(proportionate) increase
on a graph of rate of reaction against enzyme conc…
RoR = low. enzyme conc is limiting —→ more substrates than enzyme’s AS can deal w
then RoR = increase as enzyme conc. = increases. bc excess substrate can be acted upon