BIOLOGY UNIT 1 K2
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Structure and Replication of DNA
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What do nucleotides consist of ?
Phosphate
Deoxyribose sugar
base
What does DNA consist of ?
DNA consists of repeating units called nucleotides twisted into a double stranded helix
Where do the base and phosphate attach to a deoxyribose sugar in a nucleotide ?
Deoxyribose sugar in a nucleotide has a base attached to its first (1st) carbon and a phosphate attached to its fifth (5th) carbon
What does the base sequence of DNA form ?
The base sequence of DNA forms the genetic code
What are nucleotides joined by ?
Nucleotides are joined by their deoxyribose sugar and phosphates to form a stand with a sugar phosphate backbone
What are the base pairs ?
Adenine - Thymine
Cytosine - Guanine
What are base pairs of opposite strands held together by ?
Base pairs on opposite stands are held together by weak hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
What is the double stranded anti-parallel structure ?
The double stranded anti-parallel structure is the strands of DNA (2) whose backbones run in opposite directions and each strand has a deoxyribose sugar at 3’ end and a phosphate group at the 5’ end
What part of the nucleotide is at the 3’ end and what part is at the 5’ end ?
A deoxyribose sugar is at the 3’ end and. phosphate group is at the 5’ end
5’ ………………………………………… ………. ... 3’
3’ ………………………………………5’
What do the lines between the base pairs represent ?
Weak hydrogen bonds
What are primers ?
A primer is a short strand of nucleotides which bind to the 3’ end of the template DNA strand allowing DNA polymerase to add nucleotides
What is needed to start DNA replication and why ?
Primers are needed to start DNA replication as DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides in one direction - to the 3’ end of the new strand
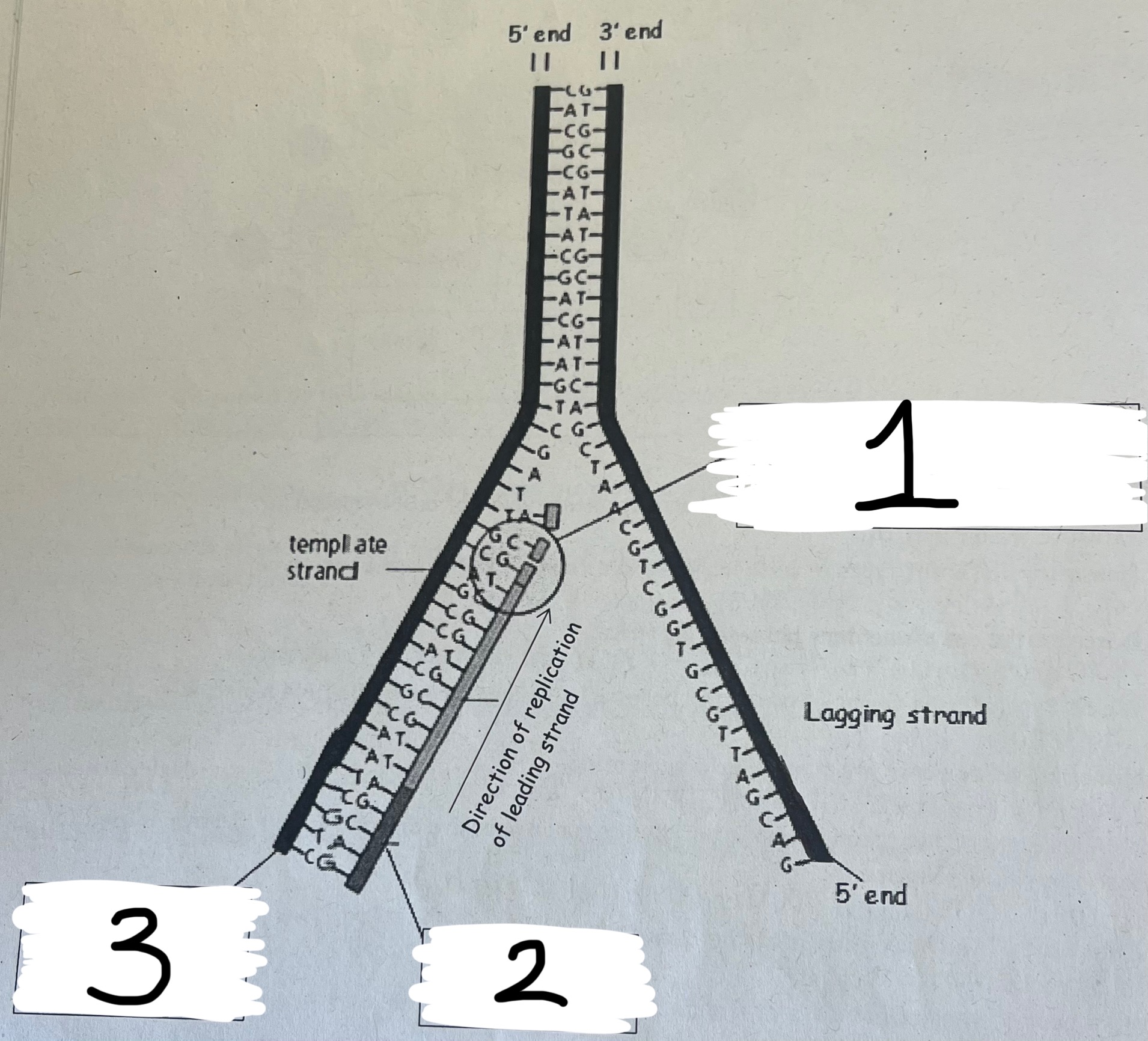
Name boxes 1 , 2 and 3
DNA polymerase adding nucleotides continuously
primer
3’ end of template strand
What are the requirements for DNA replication ?
DNA replication will take place if the nucleus contains
DNA template
Free DNA nucleotides
Primers
Enzymes (DNA polymerase and DNA ligase)
Supply of ATP
What are the stages of DNA replication ?
The DNA molecule unwinds
Hydrogen bonds between base pairs break to form two template strands
A primer binds to the 3’ end of the original template strand
DNA polymerase enzyme adds DNA nucleotides using complementary base pairing, to the 3’ end of the new DNA strand
This results in the leading strand replicating continuously
On the lagging strand, nucleotides are added by DNA polymerase to form DNA fragments
Ligase enzyme joins DNA fragments on the lagging strand to form a complete strand
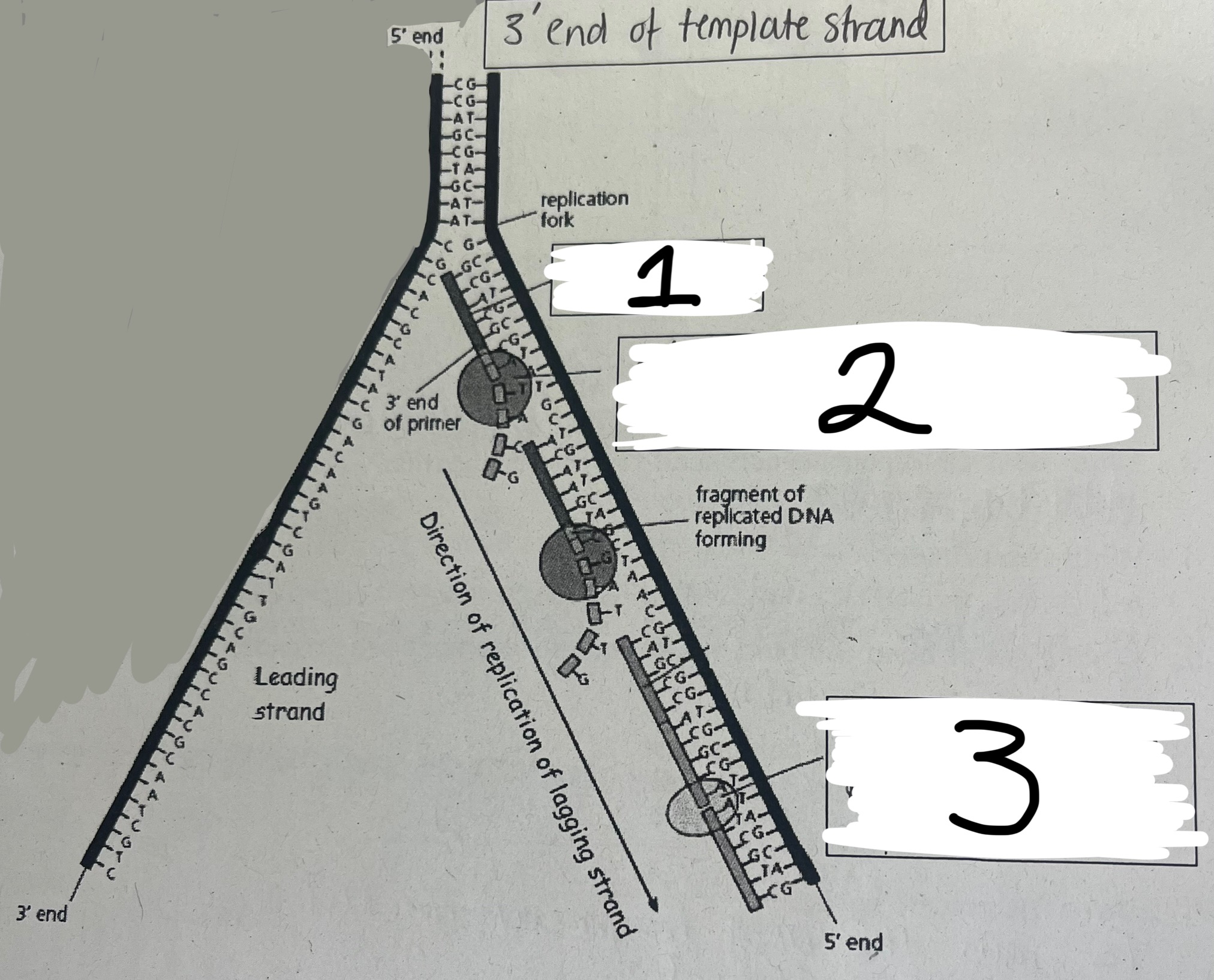
Name boxes 1, 2 and 3
primer
DNA polymerase adding nucleotides
ligase joining DNA fragements
Which strand replicates continuously and which strand replicates in fragments
The leading strand replicates continuously
The lagging strand replicates in fragments
What is the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)?
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a laboratory technique that amplifies specific target sequences of DNA
What does PCR use and why ?
PCR uses primers which are complementary to specific target sequences at the two ends of the region of DNA to be amplified
What are the stages of PCR ?
DNA is heated to between 92 and 98*C to separate the DNA strands ( breaking hydrogen bonds )
It is then cooled to between 50*C and 65*C to allow primers to bind to target sequences
It is then heated to between 70*C and 80*C for heat tolerant DNA polymerase to replicate the target region of DNA
Two identical copies of DNA after the first cycle . Repeated cycles of heating and cooling amplify the target region of DNA and allow billions of copies of the target sequence to be produced
What can PCR amplify DNA to help?
solve crimes
settle paternity suits
diagnose genetic disorders
How many molecules are there after one cycle of PCR ?
Thera would be two molecules as the number continues to double with every cycle
